Multi-Scale Geophysics and Chemistry-Based Investigation of Alteration Evolution Mechanisms in Buried Hills of the Northern South China Sea
Abstract
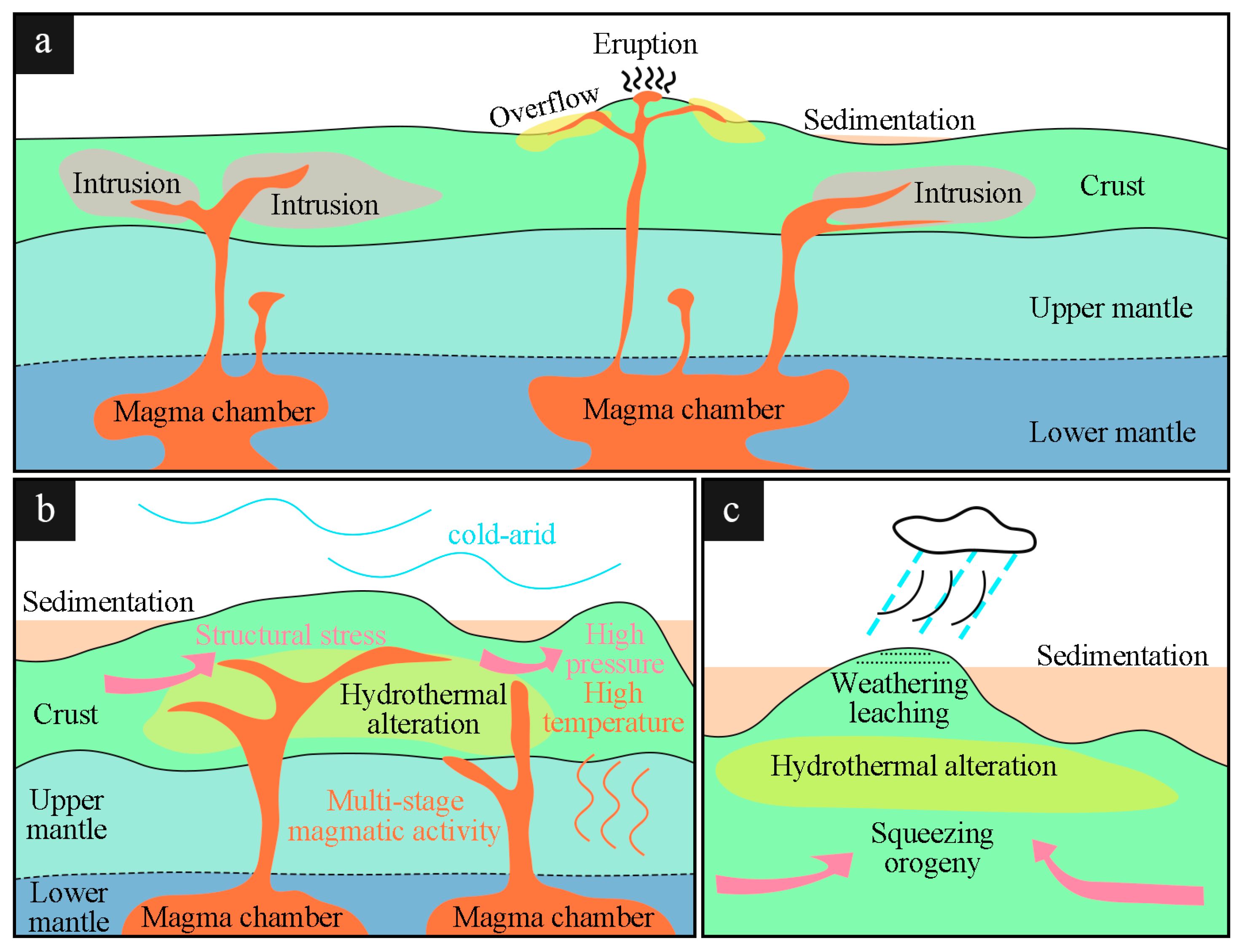
1. Introduction
2. Geology and Methods
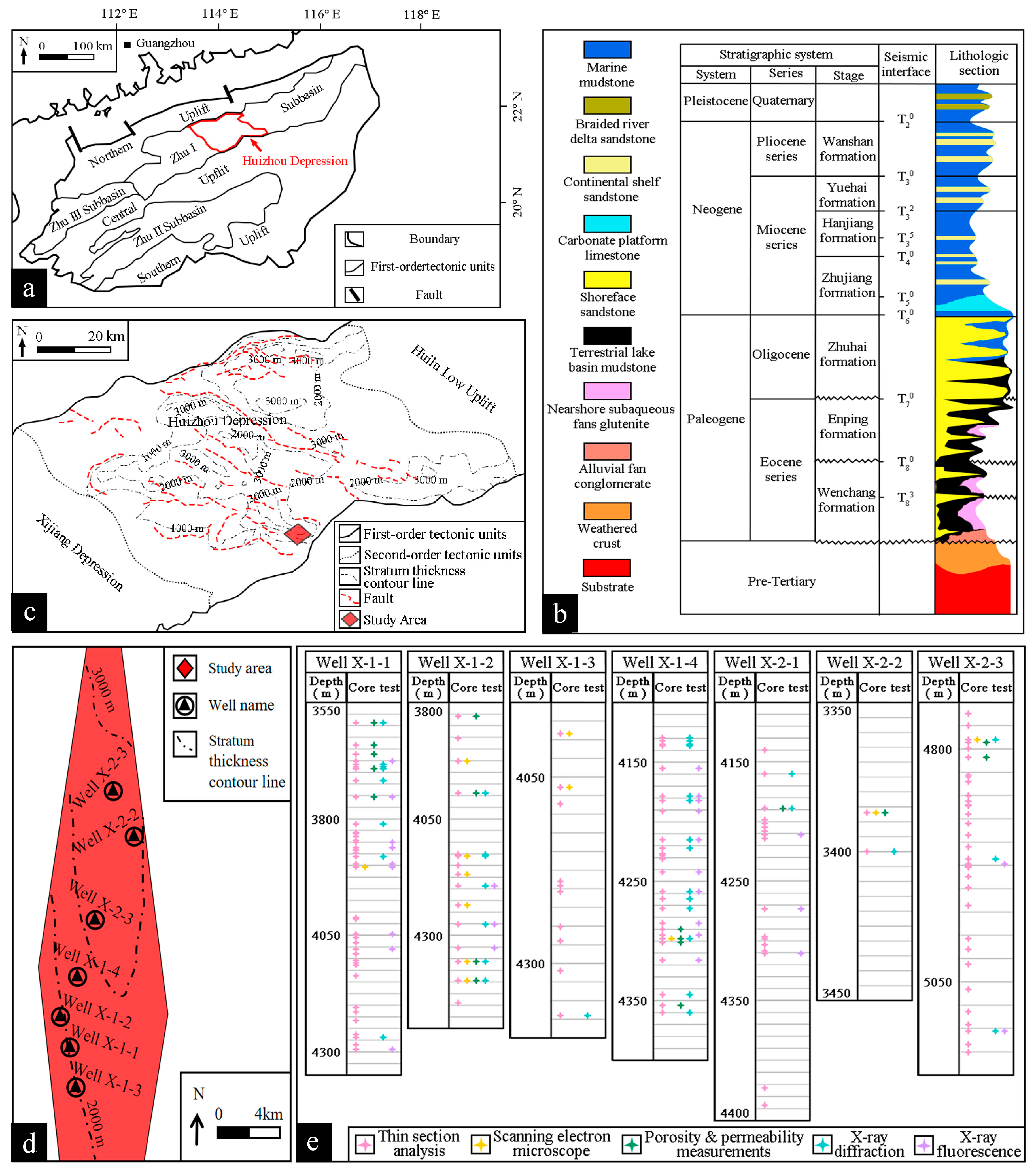
2.1. Geological Background
2.2. Methods and Experiment
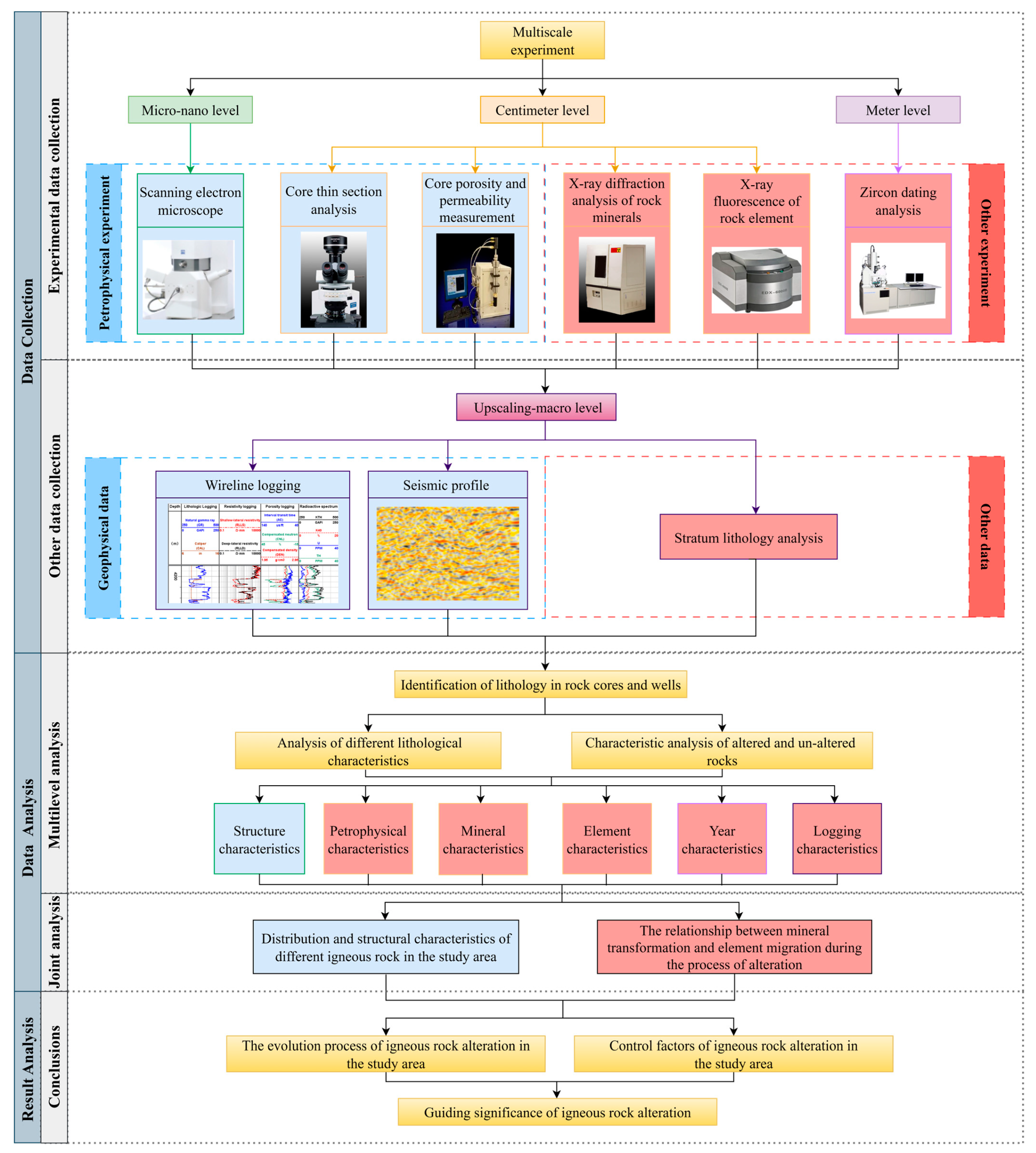
2.2.1. Multi-Scale Data Analysis Framework
2.2.2. Petrophysics Experiment
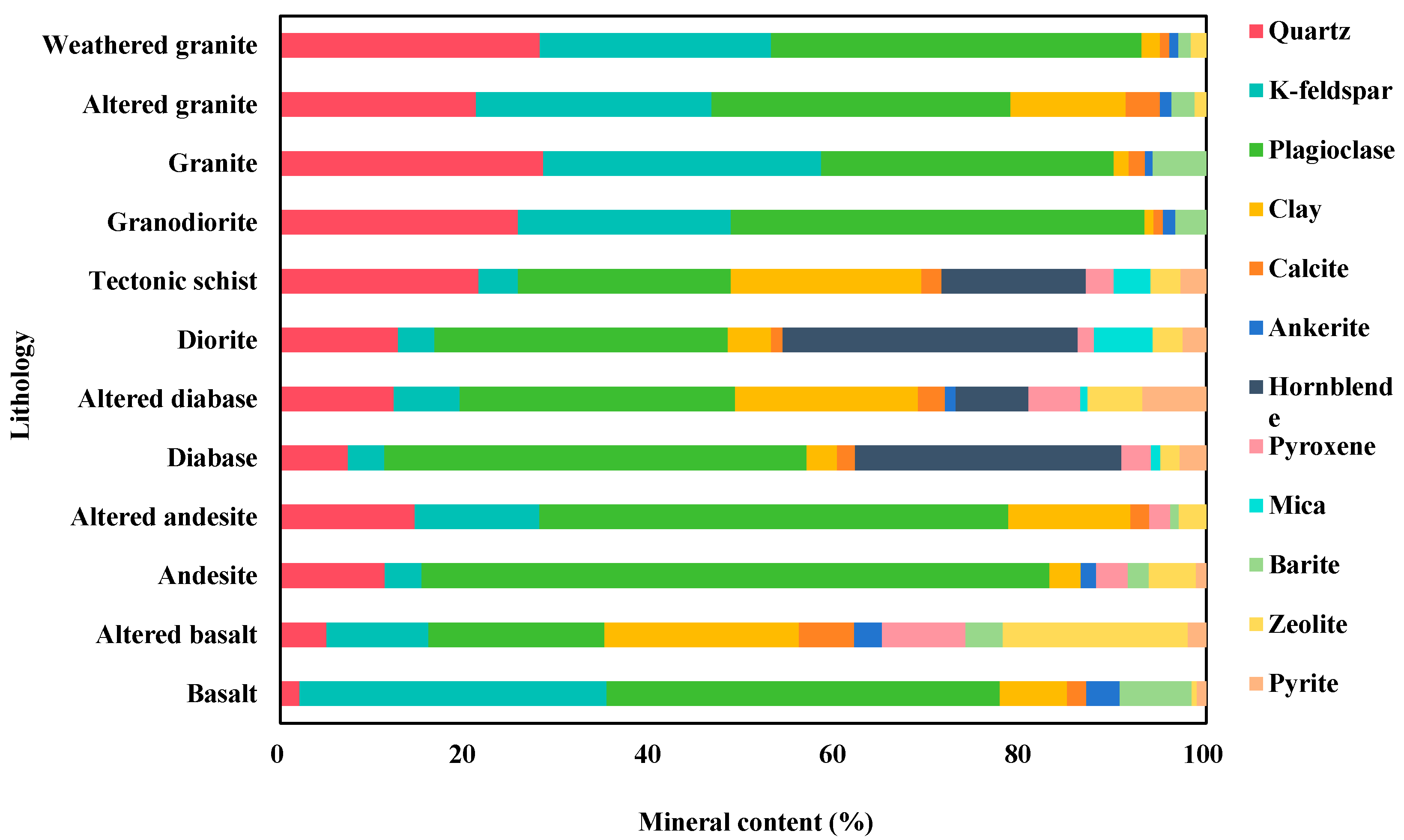
2.2.3. Rock Mineralogical Analysis
2.2.4. Elemental Analysis
2.2.5. Zircon Uranium Lead Dating Detection
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Results
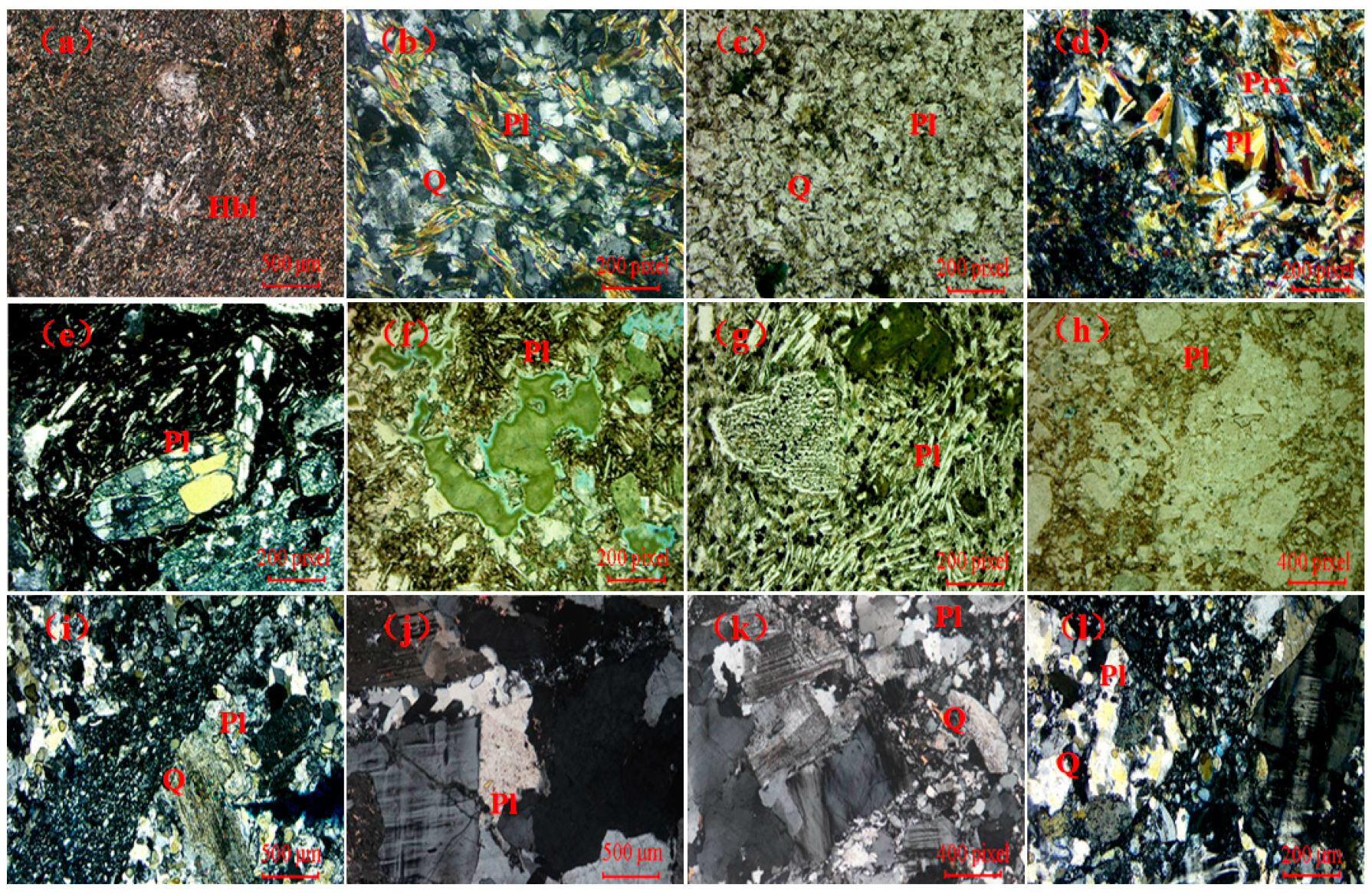
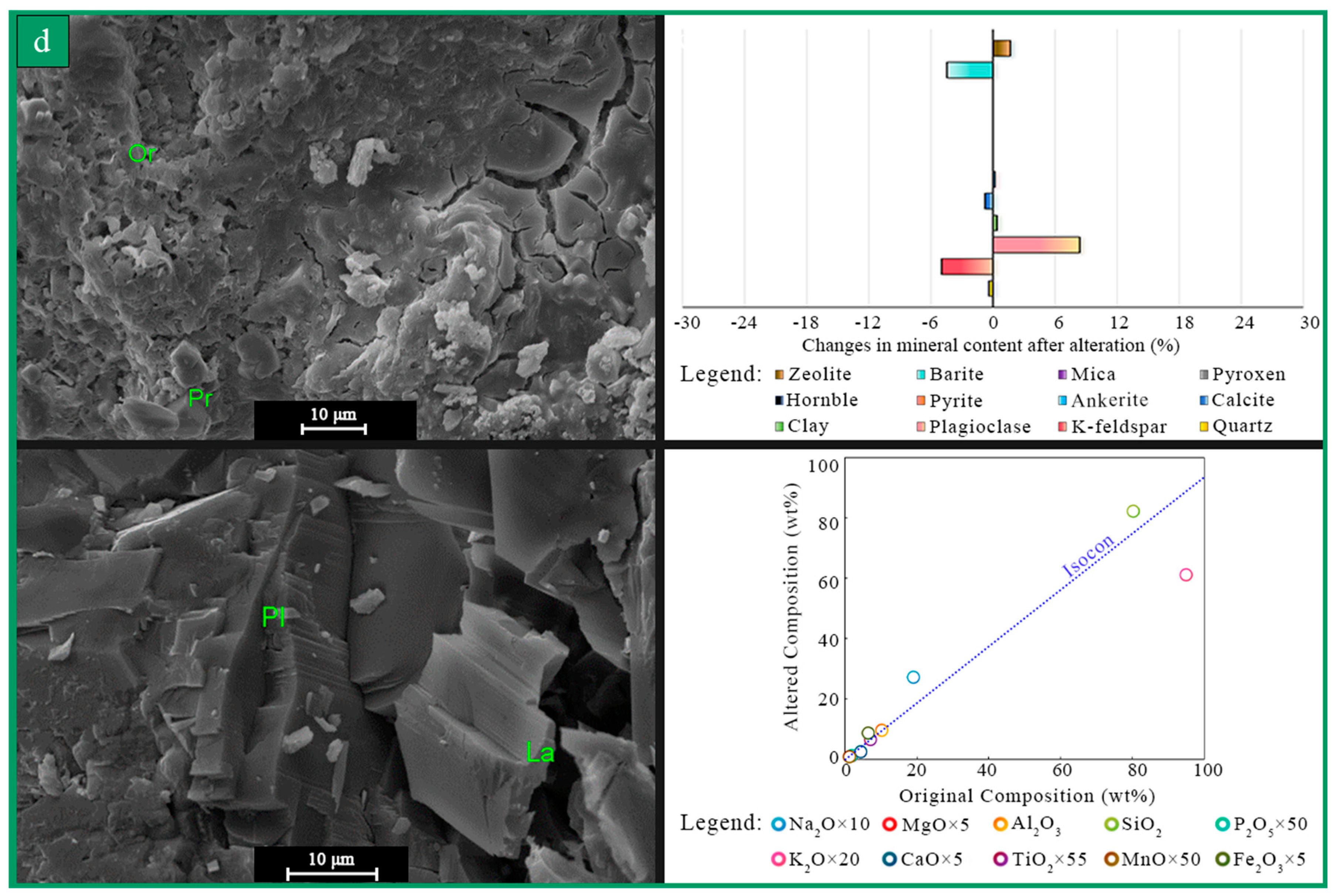
3.1.1. Petrography
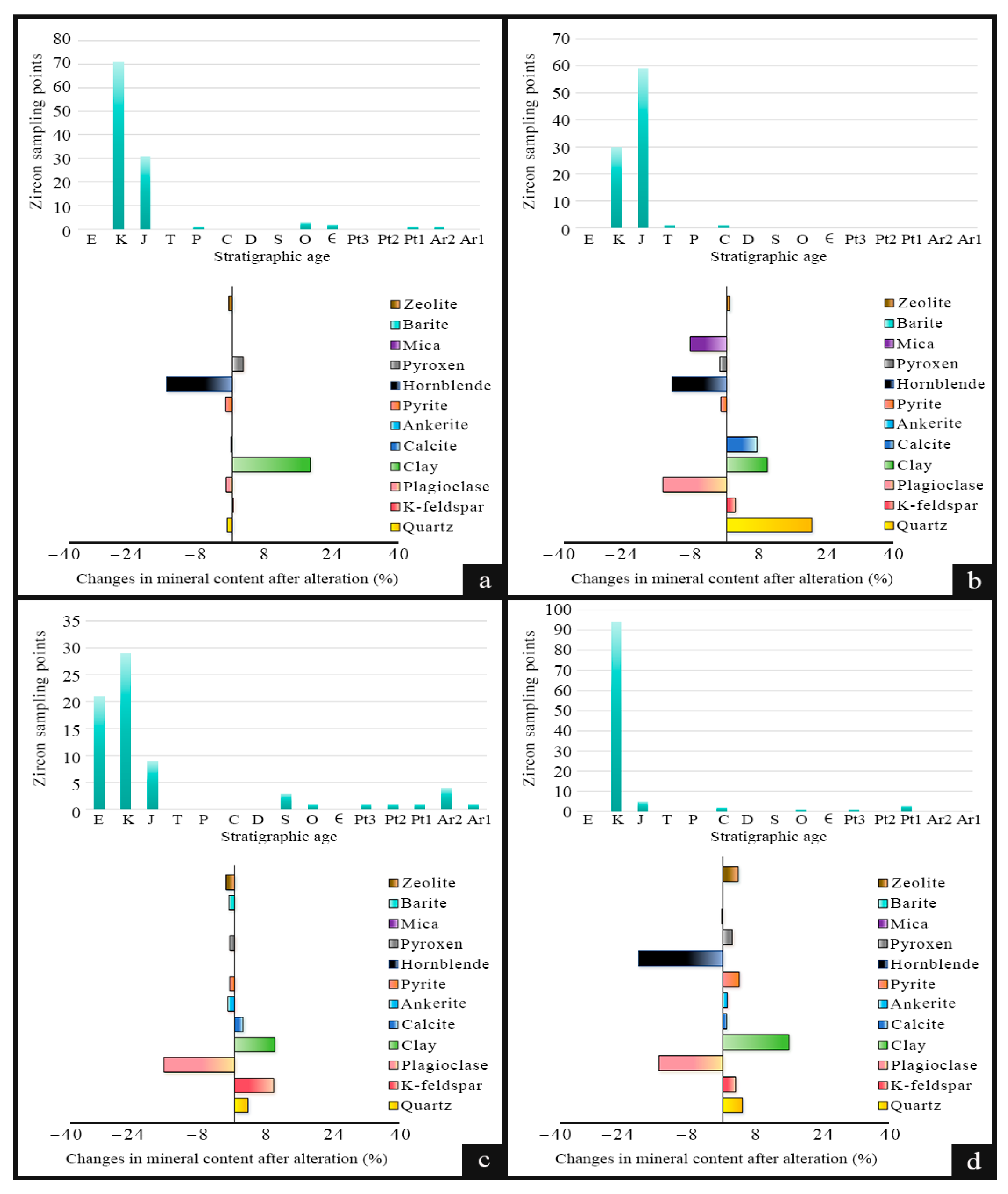
3.1.2. Geochronology
3.2. Drilling Data Processing
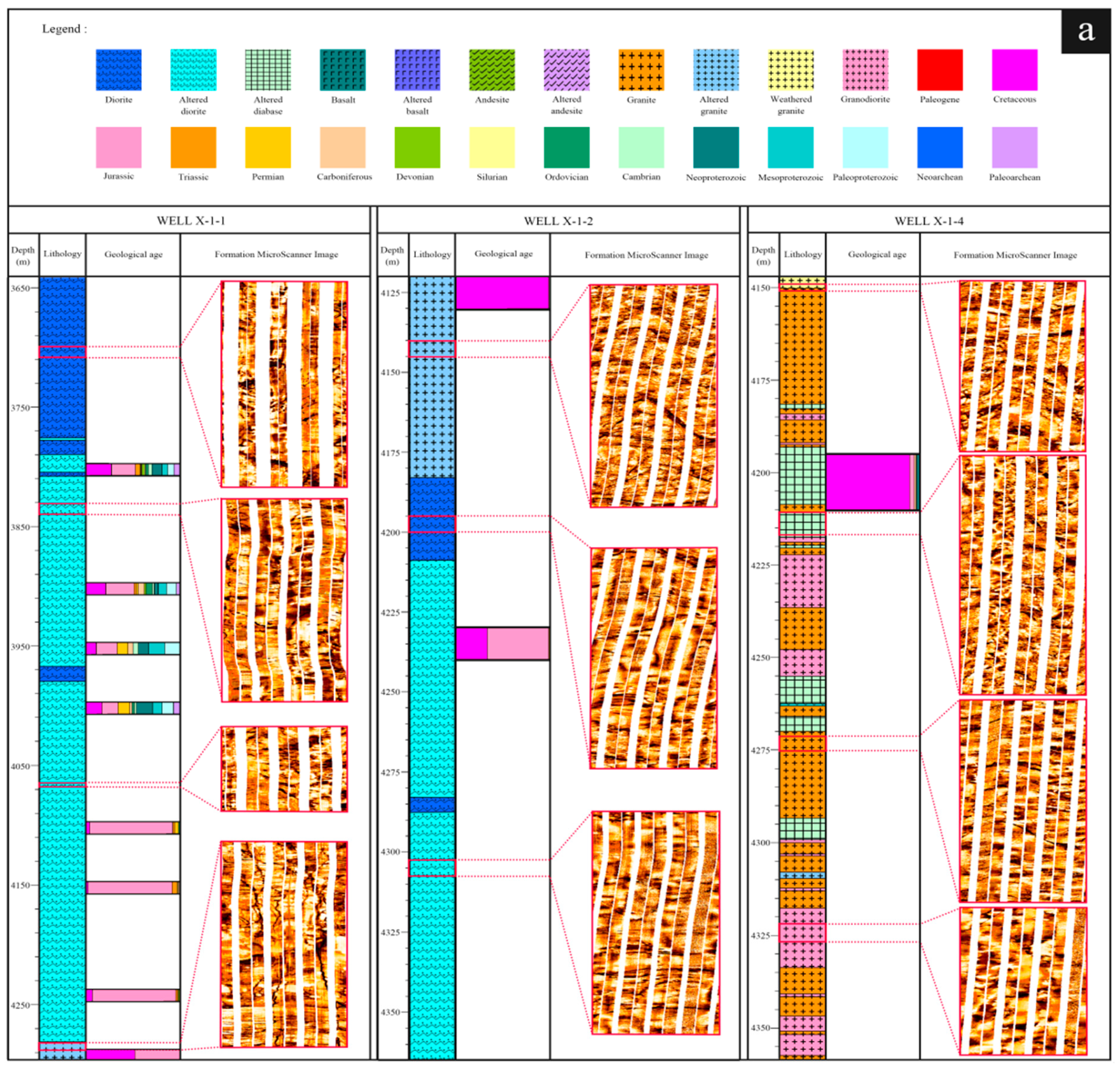
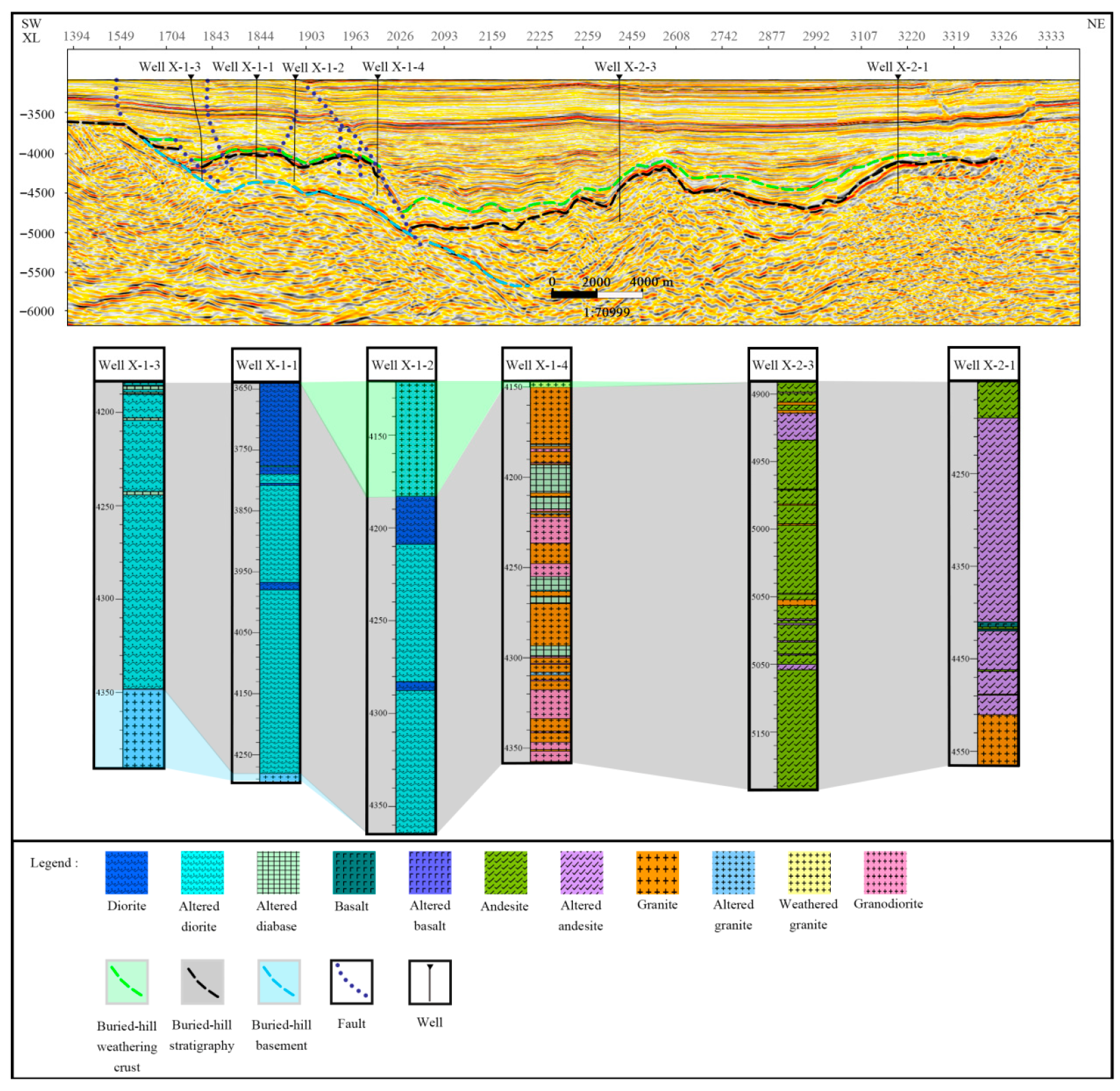
3.2.1. Lithology Identification in the Well
3.2.2. Formation MicroScanner Images
4. Discussion
4.1. Alteration Characteristics of Buried Hills
4.1.1. Core Alteration Characteristics
4.1.2. Alteration Characteristics in Well
4.1.3. Alteration Characteristics on Temporal Scale
4.2. The Alteration Cause of Buried Hills
5. Conclusion and Future Work
Abbreviation
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wood, D.A.; Hazra, B. Characterization of Organic-Rich Shales for Petroleum Exploration & Exploitation: A Review-Part 2: Geochemistry, Thermal Maturity, Isotopes and Biomarkers. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 28, 758–778. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhou, D.; Bai, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, M.; Li, Z.; Meng, Z.; Yang, Y.; et al. Fine-grained volcanic-hydrothermal sedimentary rocks in Permian Lucaogou Formation, Santanghu Basin, NW China: Implications on hydrocarbon source rocks and accumulation in lacustrine rift basins. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 114, 104201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, P. Olivine—The Alteration Rock Star. Elements 2023, 19, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Gao, J.; Eriksson, K.A.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Q.; Ping, X.; Zhang, Y. Diagenetic alterations in Eocene, deeply buried volcaniclastic sandstones with implications for reservoir quality in the Huizhou depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China. AAPG Bull. 2023, 107, 929–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L. Genesis mechanism of tuffaceous materials in Paleogene large-scale glutenite reservoirs and implications for hydrocarbon exploration in the Huizhou Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Earth Sci. 2022, 47, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, L.; Adebayo, A.; Mahmoud, M.; Sultan, A.; Patil, S. Thermal maturation, mineral catalysis, and gas generation kinetics of carbonate source rock. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 92, 104003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Sun, X.; Lu, B.; Ni, W. Cenozoic volcanic rocks in the Pearl River Mouth and Southeast Hainan Basins of South China Sea and their implications for petroleum geology. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Cui, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, X.; Tong, H.; Ma, L. Occurrence, composition, and origin of analcime in sedimentary rocks of non-marine petroliferous basins in China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 113, 104164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiu, B.; Huang, W.H.; Li, Y.; He, M. Influence of clay minerals and cementation on pore throat of tight sandstone gas reservoir in the eastern Ordos Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 87, 103762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowitt, S.; Jenkin, G.; Coogan, L.; Naden, J. Quantifying the release of base metals from source rocks for volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits: Effects of protolith composition and alteration mineralogy. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 118, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olavsdottir, J.; Andersen, M.S.; Boldreel, L.O. Reservoir quality of intrabasalt volcaniclastic units onshore Faroe Islands, North Atlantic Igneous Province, northeast Atlantic. AAPG Bull. 2015, 99, 467–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sætre, C.; Hellevang, H.; Dennehy, C.; Dypvik, H.; Clark, S. A diagenetic study of intrabasaltic siliciclastics sandstones from the Rosebank field. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Xi, K.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, G.; Kashif, M.; Song, M. Characteristics and origin of the major authigenic minerals and their impacts on reservoir quality in the Permian Wutonggou Formation of Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin, western China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 97, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lin, H.; Que, X.; He, Y.; Jia, L.; Xiao, Z.; Li, M. Paleogene geological framework and tectonic evolution of the central anticlinal zone in Lufeng 13 sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Pet. Res. 2019, 4, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Du, J.; Mei, L.; Zhang, X.; Hao, S.; Deng, P.; Zhang, Q. Huizhou Movement and its significance in Pearl River Mouth Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, A.; Cai, J.; He, L.; Hou, M.; Cao, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhong, L. Genesis of Mesozoic intermediate-basic volcanic reservoirs in Hui-Huizhou 26-6 buried hill, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. (Sci. Technol. Ed.) 2021, 48, 661–674. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, W.; Du, J.; Chen, W. Controlling effect of tectonic transformation in Paleogene Wenchang Formation on oil and gas accumulation in Zhu I Depression. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 1797–1813. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Shao, L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, W.; Qiao, P.; Zhang, X. A Mesozoic Andean-type active continental margin along coastal South China: New geological records from the basement of the northern South China Sea. Gondwana Res. 2021, 99, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, H.C.; Mohn, G.; Nirrengarten, M.; Sun, Z.; Stock, J.; Jian, Z.; Klaus, A.; Alvarez-Zarikian, C.A.; Boaga, J.; Bowden, S.A.; et al. Rapid transition from continental breakup to igneous oceanic crust in the South China Sea. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 782–789. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41561-018-0198-1 (accessed on 26 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Zahirovic, S.; Seton, M.; Müller, R.D. The Cretaceous and Cenozoic tectonic evolution of southeast Asia. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 227–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, C.K. Major unconformities/termination of extension events and associated surfaces in the South China Seas: Review and implications for tectonic development. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 120, 62–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Suppe, J. Proto-South China sea plate tectonics using subducted slab constraints from tomography. J. Earth Sci. China 2018, 29, 1304–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Suo, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Santosh, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, G.; Guo, L.; Yu, S.; Lan, H.; et al. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian ocean-continent connection zone to subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 192, 91–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L.; Yan, S.; Hu, L.; Ping, M.; Zhang, M. Cenozoic structure and tectonics of north subbasins in Beibu Gulf basin, northern South China Sea. Tectonophysics 2021, 812, 228912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zhu, X.; Pan, R.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S. A quantitative porosity evolution model of sandstone for Wenchang Formation in the Huizhou Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin: A case study from braided fluvial delta reservoir of HZ-A area. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2015, 33, 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, F.; Long, G.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y. Differential development characteristics and main controlling factors of the Paleogene high-quality reservoirs from the Zhu I Depression in the Pearl River Mouth Basin: A case on Wenchang Formation at Lufeng area and Huizhou area. Acta Petrol. Minera-Log. 2022, 41, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Robison, C.R.; Elord, L.W.; Bissada, K.K. Petroleum generation, migration, and entrapment in the Zhu 1 depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 37, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.; Shi, H.; Ding, L.; Du, J.; Yu, J.; Xie, J.; Wang, K. Constraints of three-dimensional geological modeling on reservoir connectivity: A case study of the Huizhou depression, Pearl River Mouth basin, South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 171, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Ding, L.; Li, X.; Fu, X. Differences of tuffaceous components dissolution and their impact on physical properties in sandstone reservoirs: A case study on Paleogene Wenchang Formation in Huizhou-Lufeng area, Zhu I Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Pang, X.; Peng, H.; Ma, X.; Shi, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xiao, S.; Zhu, J. Geochemistry, origin, and accumulation of petroleum in the Eocene Wenchang Formation reservoirs in Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea: A case study of HZ25-7 oil field. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 80, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Alves, T.M.; Xia, S.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Mi, L.; Wu, S.; Cao, J.; Fan, C. Along-strike segmentation of the South China Sea margin imposed by inherited prerift basement structures. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 530, 115862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, C. Mesozoic and early Cenozoic tectonic convergence-to-rifting transition prior to opening of the South China Sea. Int. Geol. Rev. 2012, 54, 1801–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Shi, X.; Zhao, C.; Yu, X. Summary and discussion on tuffaceous reservoir research progress. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2016, 23, 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Mei, L.; Shi, H.; Camanni, G.; Shu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, L.; Deng, P.; Li, G. The Late Cretaceous tectonic evolution of the South China Sea area: An overview, and new perspectives from 3D seismic reflection data. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 187, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Lao, M.; Feng, X. Tectonic evolution cycles and Cenozoic sedimentary environment changes in the Pearl River Mouth Basin. Earth Sci. 2022, 47, 2374–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, L.; Fan, T.; Fan, H.; Niu, T.; Gong, L.; Su, X.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, Y. Fracture development and controlling factors at metamorphic buried-hill reservoirs of Bozhong 19-6 gas field in Bohai Bay, East China. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1082439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Pang, X.; Chen, D.; Peng, H.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, X. Characteristics of source rock controlling hydrocarbon distribution in Huizhou depression of Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 171, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, X.; Li, M. Geomorphologic reconstruction of an uplift in a continental basin with a source-to-sink balance: An example from the Huizhou-Lufeng uplift, Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 128, 104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, X.; Yue, W.; Lian, E.; Yang, S. Tectonic and magmatic evolution of NE Cathaysia Block controls sediment geochemical heterogeneity of rivers in SE China. CATENA 2023, 223, 106910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X. Plagioclase-regulated hydrothermal alteration of basaltic rocks with implications for the South China Sea rifting. Chem. Geol. 2021, 585, 120569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, X.; Liao, J.; Ma, B.; Jones, B.G. Tectono-sedimentary signature of the second rift phase in multiphase rifts: A case study in the Lufeng Depression (38–33.9 Ma), Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 114, 104218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L. Sedimentary-reservoir characteristics under control of transfer model and implications for hydrocarbon exploration in Huizhou Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 4043–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, J.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, W. Structural characteristics and its significances on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Yunkai low uplift, Pearl River Mouth basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hao, F.; Zhu, J.Z.; Tian, J.Q.; Ji, Y.B. Origin and occurrence of crude oils in the Zhu1 sub-basin, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 97, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Jiang, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Qin, C.; Li, H.; Ran, H.; Wei, A.; Tian, H.; et al. Sequence architecture and depositional evolution of the northern continental slope of the South China Sea: Responses to tectonic processes and changes in sea level. Basin Res. 2017, 30, 568–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Snowdon, L.; Issler, D. Oil-source correlation in tertiary deltaic petroleum systems: A comparative study of the Beauforte-Mackenzie Basin in Canada and the Pearl River Mouth Basin in China. Org. Geochem. 2008, 39, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, F.; Qi, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Z. Igneous Rocks Lithology Identification with Deep Forest: Case Study from Eastern Sag, Liaohe Basin. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 208, 104892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; A, R.; Zhong, G. Multi-label prediction method for lithology, lithofacies and fluid classes based on data augmentation by cascade forest. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2023, 9, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwatani, T.; Yoshida, K.; Ueki, K.; Oyanagi, R.; Uno, M.; Akaho, S. Sparse isocon analysis: A data-driven approach for material transfer estimation. Chem. Geol. 2020, 532, 119345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yusuke, N.; Hisao, I.; Hu, W.; Wang, S. Prediction by fuzzy clustering and KNN on validation data with parallel ensemble of interpretable TSK fuzzy classifiers. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guan, Y. Multi-scale data joint inversion of minerals and porosity in altered igneous reservoirs—A case study in the South China Sea. Pet. Sci. 2023, 21, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricia, S.; Nora, R. Processes controlling porosity and permeability in volcanic reservoirs from the Austral and Neuquén basins, Argentina. AAPG Bull. 2007, 91, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.; Farrell, N.; Raeside, R.; Muirhead, D.; Healy, D.; Brasier, A.; Schofield, N. Observations of reservoir quality alteration in proximity to igneous intrusions for two distinct sandstones in Scotland. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 129, 10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ma, R.; Wang, Z. Natural fractures in a metamorphic buried hill reservoir, Bozhong 19-6 area, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 155, 106402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Du, X.; Fan, P.; Ma, S.; Liang, X.; Niu, T. Fault-Landform Double Controlled Archean Buried-Hill Reservoir Integrated Prediction for BZ26-6 Oil Field, Bohai Bay. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2023, 48, 429–438. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Heng, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, S. Lithofacies-controlled Fracture Modeling and Quality Control Methods for Complex Lithology Igneous Buried Hill Rrservior: Taking Igneous Buried Hill Rrservior of Huizhou 26-6 Oilfield as an Example. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 7671–7677. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, B.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ruhan, A.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y. Study on reservoir characteristics and evaluation methods of altered igneous reservoirs in Songliao Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 212, 110266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, S.; Wu, D.; Zhu, X. Authigenic minerals and diagenetic evolution in altered volcanic materials and their impacts on hydrocarbon reservoirs: Evidence from the lower Permian in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retallack, G.J. Pedogenic carbonate proxies for amount and seasonality of precipitation in paleosols. Geology 2005, 33, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craggs, H.J.; Valdes, P.J.; Widdowson, M. Climate model predictions for the latest Cretaceous: An evaluation using climatically sensitive sediments as proxy indicators. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2012, 315–316, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isozaki, Y.; Aoki, K.; Nakama, T.; Yanai, S. New insight into a subductionrelated orogen: A reappraisal of the geotectonic framework and evolution of the Japanese Islands. Gondwana Res. 2010, 18, 82–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.H.; Zhang, L.; Shi, H.S.; Brix, M.R.; Huhma, H.; Chen, L.H.; Zhang, M.Q.; Zhou, Z.Y. Tracing an early Jurassic magmatic arc from South to East China Seas. Tectonics 2017, 36, 466–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Lithology | Porosity | Permeability |
|---|---|---|
| % | mD | |
| Diorite | 1.7 | 0.002 |
| 2.7 | 0.006 | |
| Tectonic schist | 3.8 | 1.990 |
| 4.3 | 0.029 | |
| Diabase | 1.5 | 0.005 |
| Altered diabase | 10.4 | 8.850 |
| 4.2 | 0.005 | |
| Basalt | 6.9 | 0.004 |
| 7 | 0.005 | |
| Altered basalt | 14.8 | 0.002 |
| Andesite | 5.9 | 0.011 |
| Altered andesite | 6.7 | 0.007 |
| 4.9 | 0.030 | |
| Granite | 2.4 | 0.002 |
| Altered granite | 5.6 | 0.453 |
| Weathered granite | 4.4 | 0.014 |
| Granodiorite | 6.7 | 0.003 |
| Lithology | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | MnO | Fe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | |
| Diorite | 2.19 | 5.45 | 15.46 | 56.90 | 0.36 | 2.27 | 6.95 | 0.81 | 0.21 | 9.41 |
| Tectonic schist | 2.62 | 6.19 | 13.08 | 60.59 | 0.30 | 2.12 | 5.98 | 0.66 | 0.18 | 8.25 |
| Altered diabase | 2.57 | 5.29 | 12.78 | 68.39 | 0.09 | 2.47 | 2.84 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 4.97 |
| Basalt | 3.19 | 5.38 | 16.95 | 52.04 | 0.63 | 1.50 | 8.52 | 1.68 | 0.23 | 9.87 |
| Andesite | 1.82 | 2.33 | 19.30 | 59.53 | 0.20 | 2.42 | 6.84 | 0.71 | 0.12 | 6.73 |
| Altered andesite | 5.46 | 2.47 | 19.74 | 57.77 | 0.18 | 2.80 | 4.46 | 0.80 | 0.08 | 6.23 |
| Granite | 1.91 | 0.39 | 10.30 | 80.27 | 0.04 | 4.75 | 0.89 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 1.30 |
| Altered granite | 1.69 | 8.29 | 13.49 | 61.24 | 0.14 | 1.69 | 5.77 | 0.79 | 0.15 | 6.75 |
| Weathered granite | 2.72 | 0.24 | 9.62 | 82.20 | 0.02 | 3.05 | 0.50 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 1.50 |
| Well Name | Sample Number | Top Depth | Bottom Depth | Age Range | 206Pb/238Uaverage Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | m | Ma | Ma | ||
| X-1-1 | 1 | 3797 | 3807 | 108–126 | 116 |
| 137–167 | 153 | ||||
| 2 | 3897 | 3907 | 98–124 | 110.8 | |
| 146–164 | 154.3 | ||||
| 3 | 3947 | 3957 | 126–2374 | 105.3 | |
| 4 | 3997 | 4007 | 101–141 | 118 | |
| 251–263 | 254 | ||||
| 5 | 4097 | 4107 | 151–174 | 162.7 | |
| 6 | 4147 | 4157 | 147–189 | 163.8 | |
| 7 | 4237 | 4247 | 126–181 | 155.4 | |
| 8 | 4287 | 4297 | 112–157 | 133.8 | |
| X-1-2 | 1 | 4120 | 4130 | / | 110 |
| 2 | 4230 | 4240 | / | 144 | |
| X-1-4 | 1 | 4195 | 4210 | / | 116 |
| X-2-1 | 1 | 4290 | 4300 | 57–73 | 61.6 |
| 106–141 | 119.3 | ||||
| 2 | 4540 | 4550 | 106–135 | 116.5 | |
| X-2-2 | 1 | 3345 | 3354 | 100–120 | 112.4 |
| 2 | 3369 | 3378 | 100–120 | 111.4 | |
| 3 | 3390 | 3399 | 100–140 | 114.7 | |
| 248 | 248 | ||||
| 4 | 3399 | 3408 | 50–70 | 58.9 | |
| 100–130 | 113.4 | ||||
| 5 | 3411 | 3420 | 90–130 | 111.3 | |
| 6 | 3450 | 3459 | 100–130 | 114.2 | |
| X-2-3 | 1 | 4860 | 4880 | 46–70 | 55 |
| 151–160 | 155.3 | ||||
| 403–444 | 419 | ||||
| 893–895 | 894 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Pan, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, P. Multi-Scale Geophysics and Chemistry-Based Investigation of Alteration Evolution Mechanisms in Buried Hills of the Northern South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081549
Wang X, Pan B, Guo Y, Zhang J, Yu X, Zhang P. Multi-Scale Geophysics and Chemistry-Based Investigation of Alteration Evolution Mechanisms in Buried Hills of the Northern South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(8):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081549
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinru, Baozhi Pan, Yuhang Guo, Julin Zhang, Xun Yu, and Pengji Zhang. 2025. "Multi-Scale Geophysics and Chemistry-Based Investigation of Alteration Evolution Mechanisms in Buried Hills of the Northern South China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 8: 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081549
APA StyleWang, X., Pan, B., Guo, Y., Zhang, J., Yu, X., & Zhang, P. (2025). Multi-Scale Geophysics and Chemistry-Based Investigation of Alteration Evolution Mechanisms in Buried Hills of the Northern South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(8), 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081549






