The Effect of Non-Breaking Wave Mixing on Ocean Modeling in the South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Overview and Experimental Design
2.1. Introduction to the WAVEWATCH III Model
2.1.1. Governing Equations
2.1.2. Source Function
2.1.3. WW3 Mode Configuration
2.2. Introduction to the LICOM Model
2.2.1. Momentum Equation
2.2.2. Turbulence Closure Model
2.2.3. Boundary Conditions
2.2.4. LICOM Model Configuration
2.3. Non-Breaking Wave Parameterization Scheme
2.3.1. Non-Breaking Wave Mixing Pw Scheme
2.3.2. Non-Breaking Wave Mixing Bv Scheme
2.4. Experimental Design
3. Validation of Simulation Results
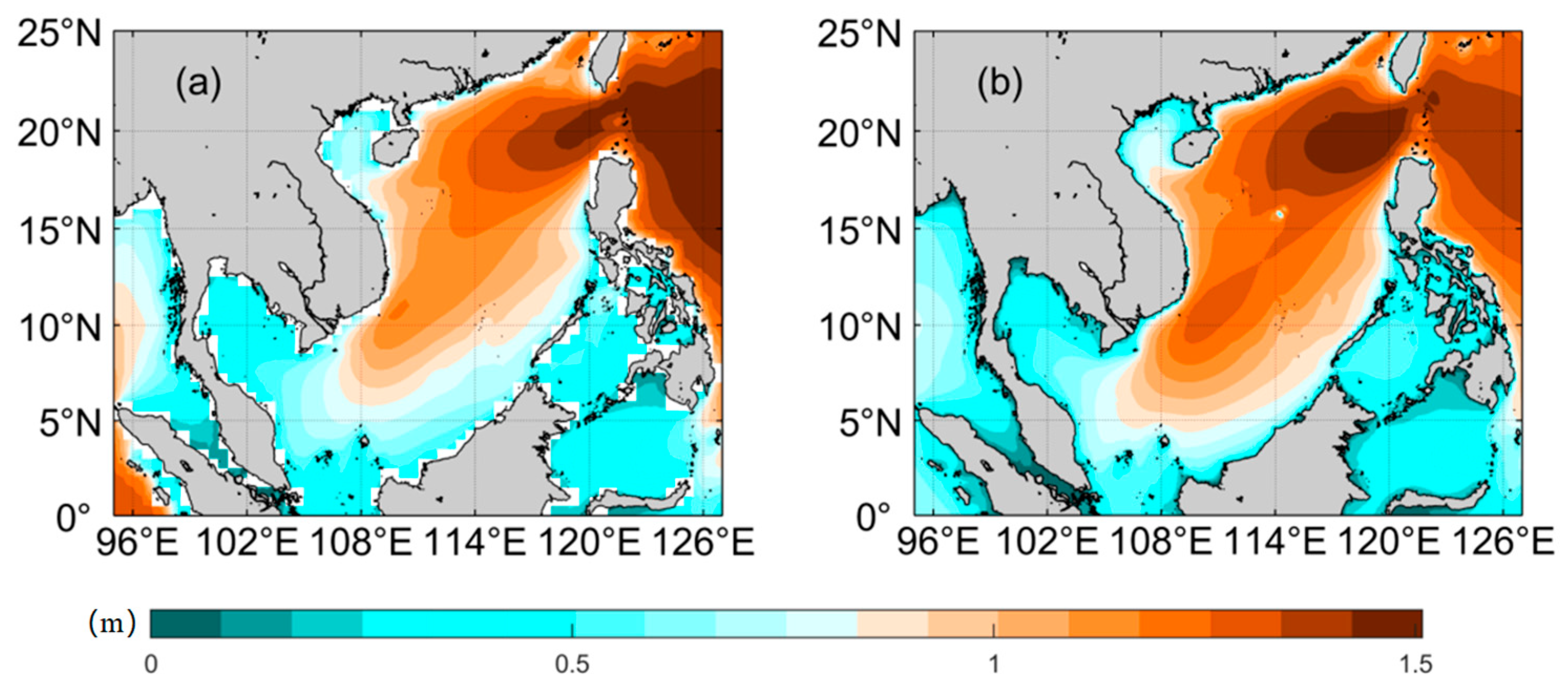
3.1. WW3 Model
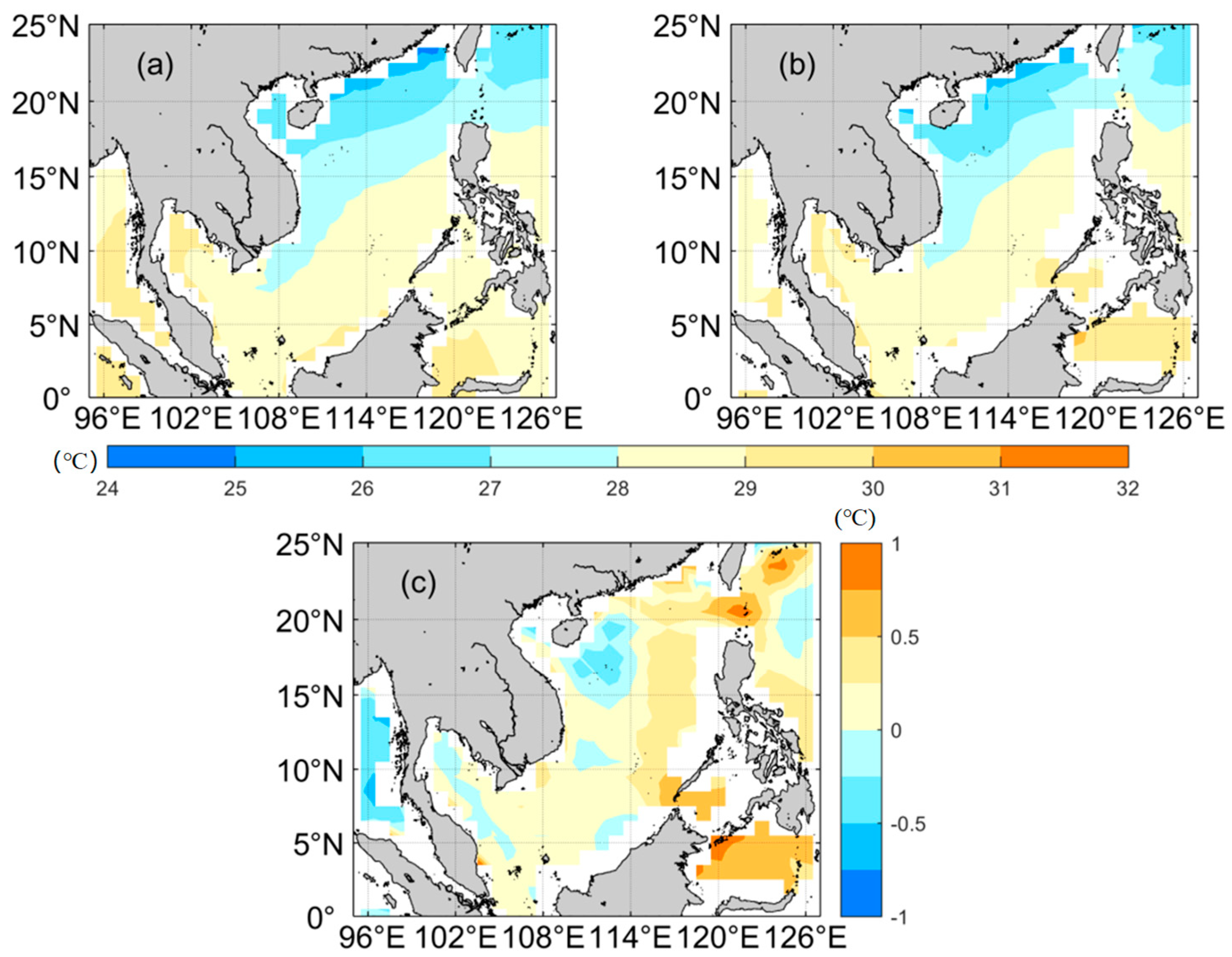
3.2. LICOM Model
4. Results Analysis
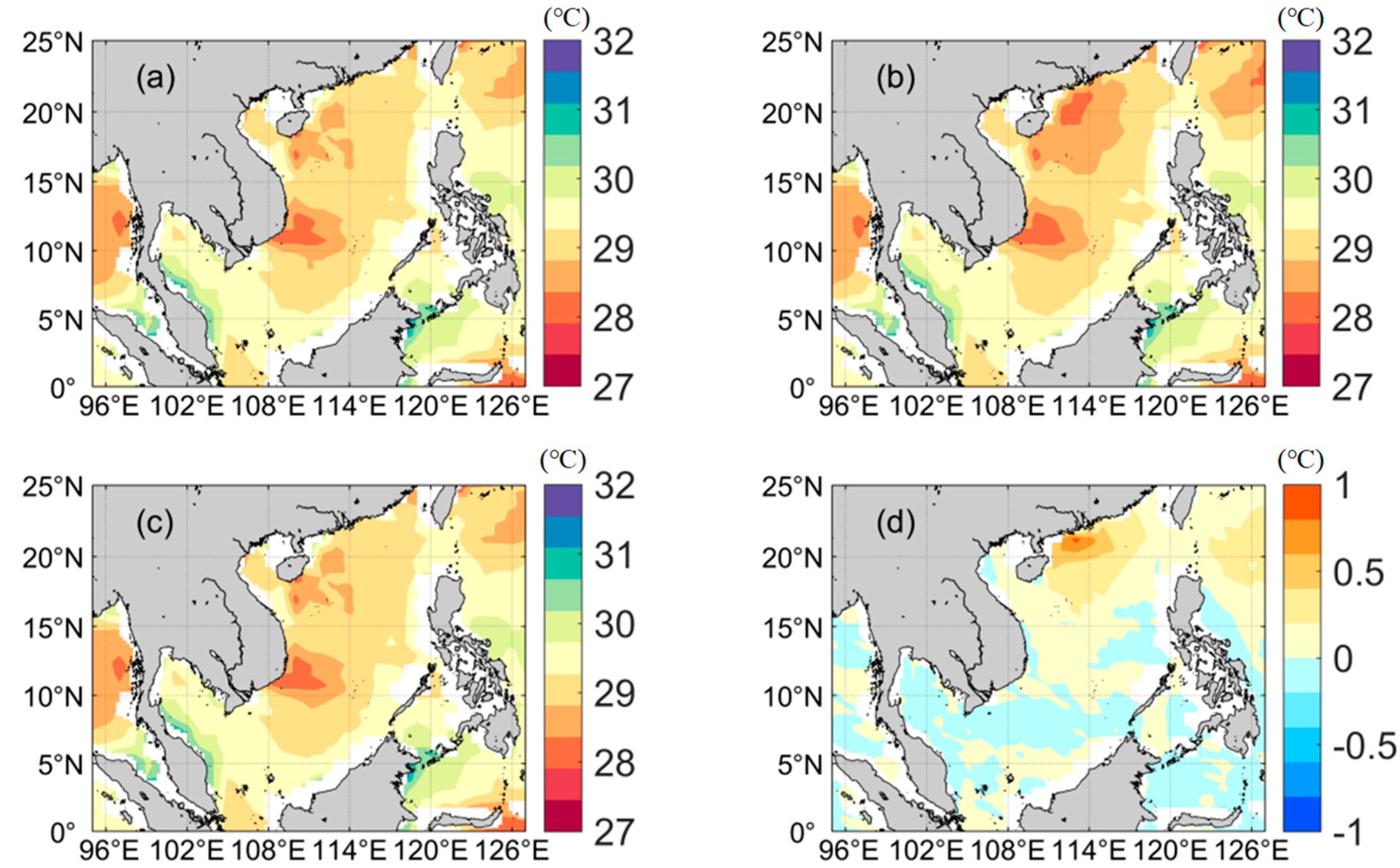
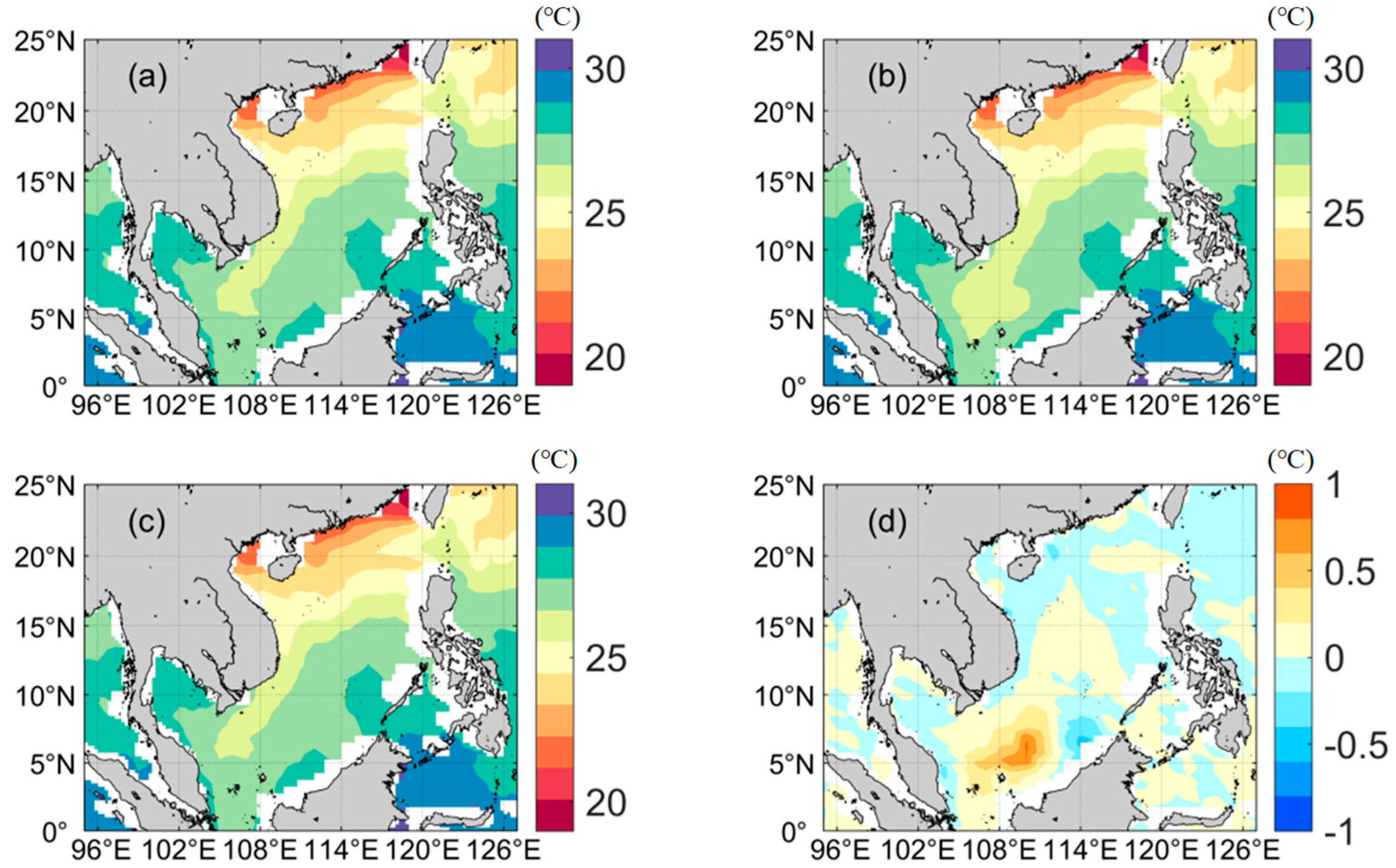
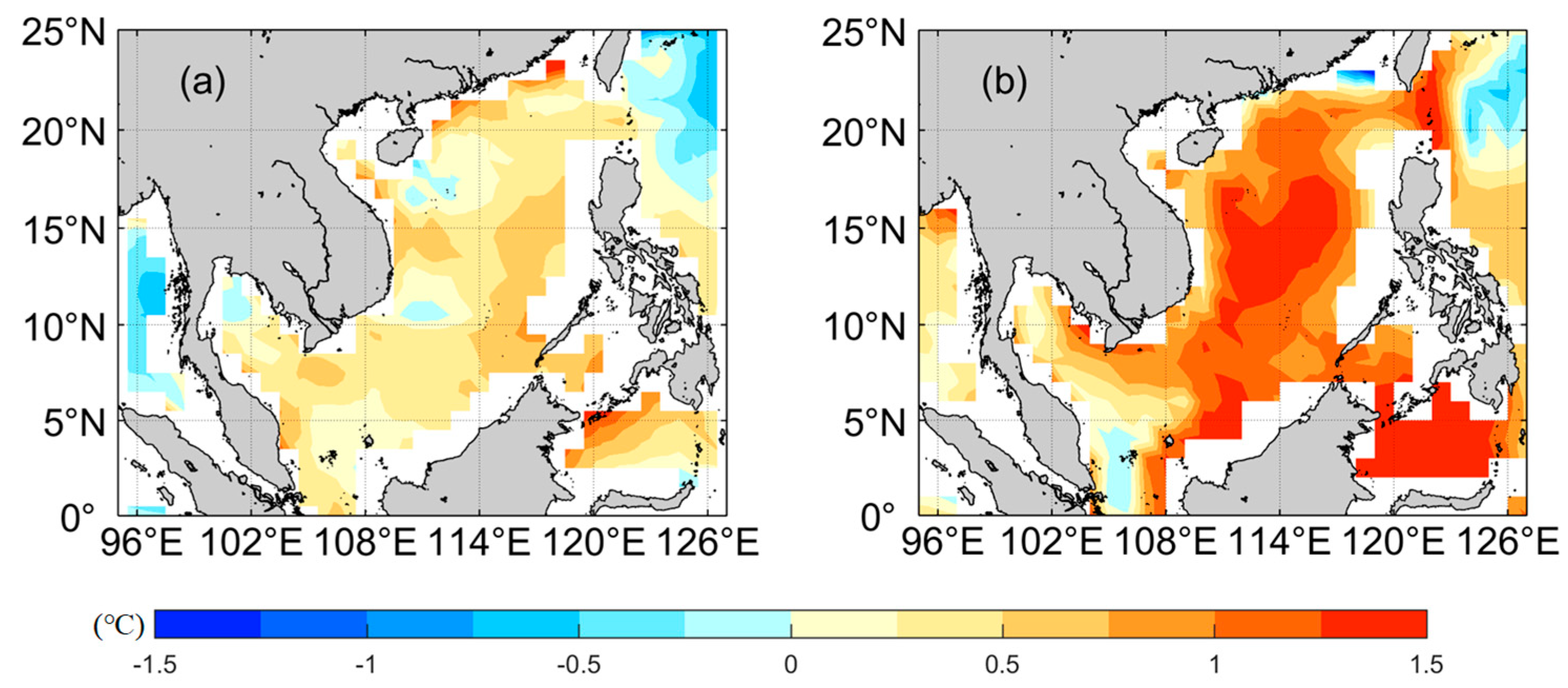
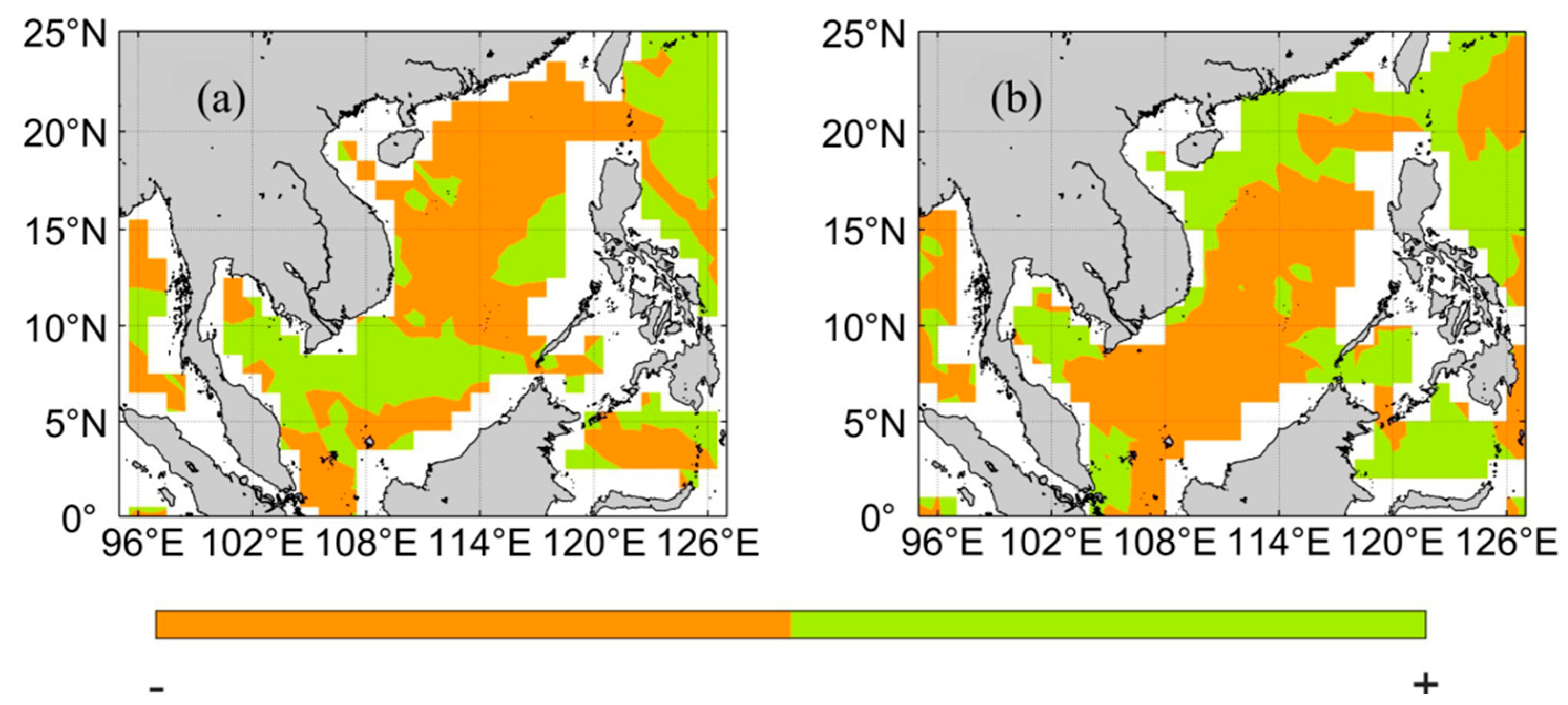
4.1. Effect of Wave Mixing on Temperature
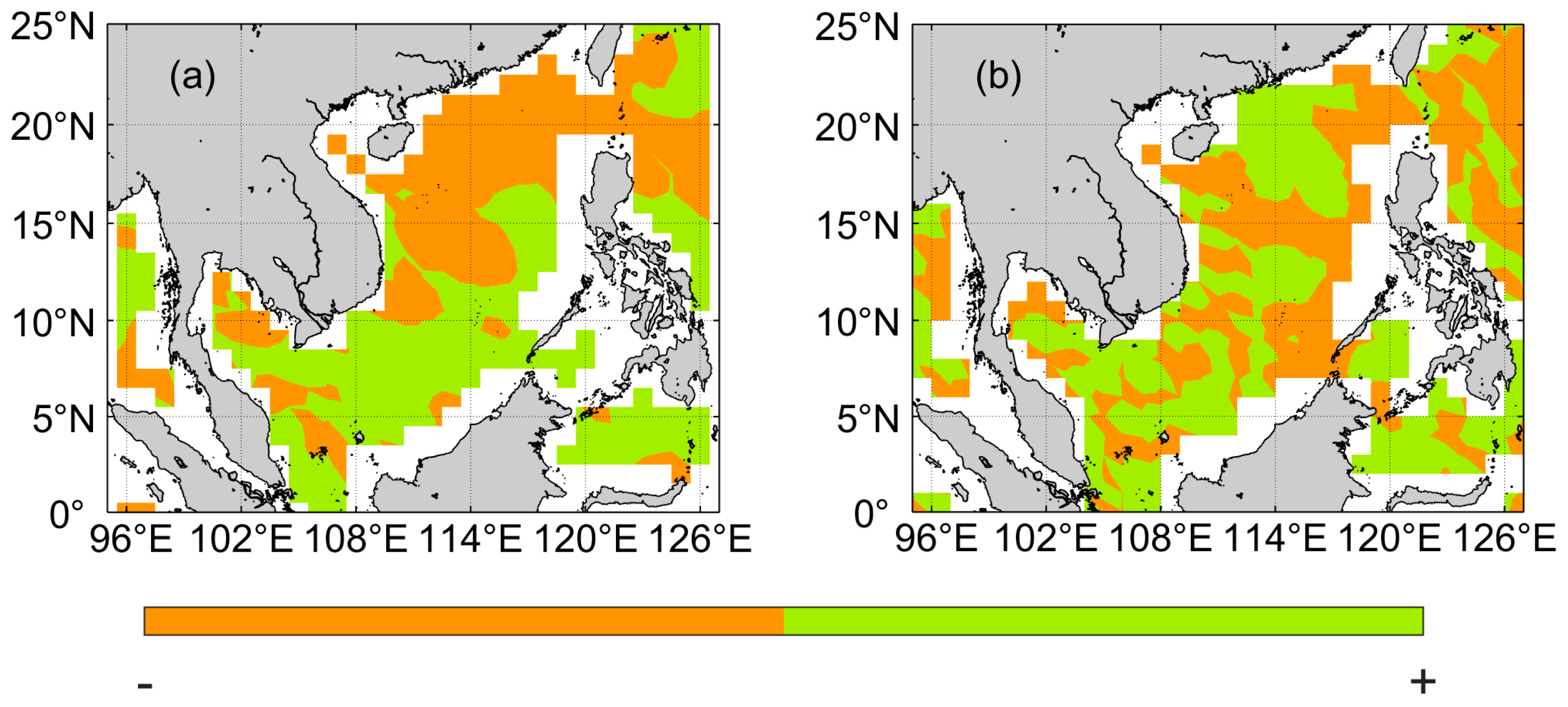
4.2. Effect of Waves on Vertical Mixing Coefficient
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rintoul, S.R.; England, M.H. Ekman transport dominates local air-sea fluxes in driving variability of Subantarctic Mode Water. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallée, J.B.; Wienders, N.; Speer, K.; Morrow, R. Formation of subantarctic mode water in the southeastern Indian Ocean. Ocean Dyn. 2006, 56, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Sprintall, J.; Gille, S.T.; Talley, L. Southern Ocean mixed-layer depth from Argo float profiles. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C06013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallée, J.B.; Shuckburgh, E.; Bruneau, N.; Meijers, A.J.S.; Bracegirdle, T.J.; Wang, Z. Assessment of Southern Ocean water mass circulation and characteristics in CMIP5 models: Historical bias and forcing response. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 1845–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoney, L.; Walsh, K.J.E.; Thomas, S.; Spence, P.; Babanin, A.V. Changes in ocean heat content caused by wave-induced mixing in a high-resolution ocean model. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2018, 48, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeberky, Y.; Battjes, J.A. Spectral modeling of wave breaking: Application to Boussinesq equations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1996, 101, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Voulgaris, G.; Warner, J.C.; Olabarrieta, M. Implementation of the vortex force formalism in the coupled ocean–atmosphere–wave–sediment transport (COAWST) modeling system for inner shelf and surf zone application. Ocean. Model. 2012, 47, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Xia, C.; Ma, J. Wave-induced mixing in the upper ocean: Distribution and application to a global ocean circulation model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulisz, W.; Paprota, M. On modeling of wave-induced vertical mixing. Ocean Eng. 2019, 194, 106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Babanin, A.V.; Walsh, K.J.E.; Stoney, L.; Heil, P. Effect of wave-induced mixing on Antarctic sea ice in a high-resolution ocean model. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.; Govekar, P.; Babanin, A.V.; Ghantous, M.; Spence, P.; Scoccimarro, E. The effect on simulated ocean climate of a parameterization of unbroken wave-induced mixing incorporated into the k-epsilon mixing scheme. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2017, 9, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanin, A. On wave-induced turbulence and a wave-mixed upper ocean layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L20605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffreys, H. On turbulence in the ocean. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1920, 39, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccino, M.; Daliri, M.; Buttarazzi, N.; Del Giudice, G.; Calabrese, M.; Somma, R. Arsenic contamination at the Bagnoli Bay seabed (South Italy) via particle tracking numerical modeling: Pollution patterns from stationary climatic forcings. Chemosphere 2022, 303 Pt 1, 134955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.J. Simulation of the mixed layer at OWS November and Papa with several models. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1985, 90, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, J. Modeling effects of tidal and wave mixing on circulation and thermohaline structures in the Bering Sea: Process studies. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115, C01006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aijaz, S.; Ghantous, M.; Babanin, A.; Ginis, I.; Thomas, B.; Wake, G. Nonbreaking wave-induced mixing in upper ocean during tropical cyclones using coupled hurricane-ocean-wave modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 3939–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.-L.; Song, J.-B.; Bai, Y.-F.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.-J.; Bi, F. Climate and extrema of ocean waves in the East China Sea. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 980–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, H.L. User Manual and System Documentation of WAVEWATCH III Version 3.14; NOAA/NWS/NCEP/MMAB Technical Note 276; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2009.
- Komen, G.J.; Cavaleri, L.; Donelan, M.; Hasselmann, K.; Hasselmann, S.; Janssen, P.A.E.M. Dynamics and Modelling of Ocean Waves; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardhuin, F.; Rogers, E.; Babanin, A.V.; Filipot, J.-F.; Magne, R.; Roland, A.; van der Westhuysen, A.; Queffeulou, P.; Lefevre, J.-M.; Aouf, L.; et al. Semi-empirical dissipation source functions for ocean waves. Part I: Definition, calibration and validation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 1917–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.; Hoffman, R.N.; Ardizzone, J.; Leidner, S.M.; Jusem, J.C.; Smith, D.K.; Gombos, D. A cross-calibrated, multi-platform (CCMP) ocean surface wind product for meteorological and oceanographic applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lin, P.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X. The baseline evaluation of LASG/IAP climate system ocean model (LICOM) version 2. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2012, 26, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lin, P.; Zheng, W.; Luan, Y.; Ma, J.; Ding, M.; Mo, H.; Wan, L.; Ling, T. A global eddy-resolving ocean forecast system in China—LICOM Forecast System (LFS). J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2021, 16, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuto, V.M.; Howard, A.; Cheng, Y.; Dubovikov, M.S. Ocean turbulence. Part I: One-point closure model-momentum and heat vertical diffusivities. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuto, V.M.; Dubovikov, M.S.; Howard, A.M.; Cheng, Y. Ocean turbulence. Part II: Vertical diffusivities of momentum, heat, salt, mass, and passive scalars. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 240–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanin, A. Breaking and Dissipation of Ocean Surface Waves; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Babanin, A.V.; Haus, B.K. On the existence of water turbulence induced by nonbreaking surface waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 2675–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghantous, M.; Babanin, A.V. One-dimensional modelling of upper ocean mixing by turbulence due to wave orbital motion. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2014, 21, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.; Babanin, A.V.; Zieger, S. The decay rate of ocean swell observed by altimeter. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 2322–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.L.; Yuan, Y.L.; Ezer, T.; Xia, C.S.; Ma, J. A three-dimensional surface wave–ocean circulation coupled model and its initial testing. Ocean. Dyn. 2010, 60, 1339–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiao, F.; Yin, X.; Shu, Q.; Ma, H. The improvement of the one-dimensional Mellor–Yamada and K-profile parameterization turbulence schemes with the non-breaking surface wave-induced vertical mixing. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2013, 32, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jing, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, R.; Yu, Z. The Effect of Non-Breaking Wave Mixing on Ocean Modeling in the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081548
Jing Y, Wu K, Li R, Yu Z. The Effect of Non-Breaking Wave Mixing on Ocean Modeling in the South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(8):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081548
Chicago/Turabian StyleJing, Yujie, Kejian Wu, Rui Li, and Zipeng Yu. 2025. "The Effect of Non-Breaking Wave Mixing on Ocean Modeling in the South China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 8: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081548
APA StyleJing, Y., Wu, K., Li, R., & Yu, Z. (2025). The Effect of Non-Breaking Wave Mixing on Ocean Modeling in the South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(8), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081548




