Abstract
The observations of atmospheric, oceanic, and sea ice data from the Multidisciplinary drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate (MOSAiC) expedition were used to analyze the influence of snow redistribution and melt-pond processes on the evolution of sea ice thickness (SIT) in 2019 and 2020. To mitigate the effect of missing atmospheric observations from the time of the expedition, we used ERA5 atmospheric reanalysis along the MOSAiC drift trajectory to force the single-column sea ice model Icepack. SIT simulations from six combinations of two melt-pond schemes and three snow-redistribution configurations of Icepack were compared with observations and analyzed to investigate the sources of model–observation discrepancies. The three snow-redistribution configurations are the bulk scheme, the snwITDrdg scheme, and one simulation conducted without snow redistribution. The bulk scheme describes snow loss from level ice to leads and open water, and snwITDrdg describes wind-driven snow redistribution and compaction. The two melt-pond schemes are the TOPO scheme and the LVL scheme, which differ in the distribution of melt water. The results show that Icepack without snow redistribution simulates excessive snow–ice formation, resulting in an SIT thicker than that observed in spring. Applying snow-redistribution schemes in Icepack reduces snow–ice formation while enhancing the congelation rate. The bulk snow-redistribution scheme improves the SIT simulation for winter and spring, while the bias is large in simulations using the snwITDrdg scheme. During the summer, Icepack underestimates the sea ice surface albedo, resulting in an underestimation of SIT at the end of simulation. The simulations using the TOPO scheme are characterized by a more realistic melt-pond evolution compared to those using the LVL scheme, resulting in a smaller bias in SIT simulation.
1. Introduction
The arctic plays an essential role in the Earth’s climate and weather. It has warmed faster than the global mean with climate change in a phenomenon called Arctic amplification [1]. Melting sea ice exposes more low-albedo ocean, which in turn absorbs more heat and causes more ice to melt. This positive ice–albedo feedback causes Arctic amplification. The amount of Arctic sea ice has been rapidly declining over the past 40 years. According to the passive microwave remote-sensing data from 1979 to 2021, the extent of the Arctic sea ice in September has declined by about 12.7% per decade [2]. Sea ice thickness (SIT) is another important indicator that, in combination with sea ice extent, can be used to study changes in sea ice volume. Meier and Stroeve [2] analyzed 1979–2021 SIT data records from submarine sonar, radar. and laser altimeters and noted that although measurements of SIT have been made over a relatively short period of time and are subject to large uncertainty, the trend of SIT decline over the last 10 years has been very pronounced. The decline of Arctic sea ice will cause changes in the Arctic atmospheric circulation, which will affect the global climate. Therefore, paying attention to and studying the physical processes in Arctic sea ice is key to the understanding of a range of issues related to climate change in the Arctic.
The Multidisciplinary drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate (MOSAiC) [3] across the central Arctic, from September 2019 to October 2020, centered around the German icebreaker Polarstern. The main goal of the MOSAiC expedition is to improve the understanding of Arctic climate change and of its complex interactions and feedbacks within the atmosphere–ice–ocean–biogeochemistry–ecosystem system. During the drift, researchers conducted coordinated observations of the atmosphere [3], ocean [4] and sea ice [5]. Making full use of data from the MOSAiC expedition will advance research on Arctic sea ice.
The Los Alamos Community Ice CodE (CICE) [6] is a widely used model that simulates the growth, melting, and movement of sea ice. It represents the sea ice cover as sea-categories of ice thickness, defined as ice thickness distribution (ITD) [7]. CICE has the submodule Icepack, which simulates vertical processes, which are mainly thermodynamic in nature, in CICE. Most Earth system models in CMIP6 (Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6) use CICE as their sea ice component [8]. The current CMIP6 models are able to simulate sea ice extent and the long-term trends in sea ice relatively well, but there are still biases in SIT and significant differences in simulations of future trends in Arctic sea ice [8]. Underestimation of summer SIT is a common issue in the current CMIP6 models [9]. The main reason for this bias may be related to the representation of physical processes of sea ice in these models, which can be attributed in part to the lack of sea ice observations.
The albedo is an important factor controlling the heat balance on the sea ice surface. Accurate simulation of the albedo is the basis for accurately simulating surface heat budget and the growth and melt rates of sea ice. However, there are some problems with albedo parameterization schemes in current sea ice models. On the one hand, the current albedo parameterization does not fully consider physical processes. On the other hand, albedo observation in the Arctic region is difficult and there are few data points available, with the result that albedo parameterization schemes are constrained by the availability of observational data [10]. The development of albedo parameterization schemes commonly involves a semi-empirical approach, which causes parametric uncertainty and reduces the accuracy and reliability of sea ice models.
Snow cover on sea ice has significant influence on the ice mass and surface heat balance [11], as the most incoming solar radiation is reflected rather than absorbed by the high-albedo snowpack. Snow is also an excellent thermal insulator, which reduces the rate of conductive heat loss from the ocean and ice and causes slower ice growth [12]. There is a snow formulation in Icepack describing the essential effects of snow on sea ice, such as its albedo, vertical conduction, and growth/melt processes [13]. Snow redistribution is an important process in sea ice models [14]. The wind-blown snow from level ice can be lost in leads or accumulate on ridges. The redistribution of snow changes the amount and distribution of snow on the sea ice, as well as snow properties and melt-pond formation. Icepack [13] run without snow compaction and redistribution overestimates SIT and snow depth in the winter and spring seasons [15,16]. Two snow-redistribution schemes have already been implemented in Icepack v1.4.1 [17], and these can be used to understand the effect of snow redistribution on the results of sea ice models.
Due to the difficulty of conducting in situ observations in the Arctic, there are few datasets that include atmospheric, oceanic, and sea ice observations. There is now a new opportunity to create an improved sea ice model using the observations from the MOSAiC expedition. Icepack, which is commonly used for single-column simulations suitable for understanding thermodynamic processes [18], has already been applied to simulate SIT during the MOSAiC expedition. For example, Gu et al. [19] investigated the impact of freezing-temperature parameterization in Icepack during the MOSAiC expedition and generated improved SIT simulations with a modified parameterization scheme. Raphael et al. [20] used Icepack to explore factors contributing to sea ice growth and melt during the MOSAiC expedition. These studies suggest the feasibility of single-column simulation with Icepack using data collected during the MOSAiC expedition.
Two periods (from early May to late June and from late July to August) lack atmosphere observations from the time of the expedition. Lu et al. [16] simulated SIT evolution during MOSAiC for two periods to avoid gaps in the forcing fields. In order to get more appropriate simulation results, we used complete atmospheric forcing from ERA5 (ECMWF Reanalysis v5) to run Icepack v1.4.1. The simulation of sea ice thickness was validated against the MOSAiC observations, and sources of bias in the research were analyzed. Improvements to Icepack can be generalized to CICE and improve the simulation of SIT in current climate models. Our research is organized as follows. The MOSAiC expedition and atmospheric forcing are introduced in Section 2.1. The relevant model physics for our research and the setup of the simulation experiment are discussed in Section 2.2. The analysis of Icepack simulations is presented in Section 3. Section 4 compares the present research with the results from some earlier works and discusses future research directions. Conclusions are summarized in Section 5.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MOSAiC Expedition and Observations
The MOSAiC expedition drift started Drift 1 with the departure of the German research icebreaker Polarstern on 20 September 2019. An ice camp named Central Observatory (CO) was established on the floe around Polarstern. A distributed network (DN) of autonomous buoys was deployed around the CO. The drift was divided into five legs. The first Central Observatory (CO1) was established during the initial phases of Leg 1, moving along with Polarstern in the winter (Leg 2 to Leg 3). On 16 May 2020, Drift 1 ended and Polarstern left the floe for logistical operations and personnel exchange. Afterwards, Polarstern returned to the floe of CO1 to start Drift 2 (Leg 4) with CO1 on 19 June 2020. CO2 and DN1 were deployed in the floe. Drift 2 ended when Polarstern moved near the ice edge in Fram Strait, and CO2 broke up on 31 July 2020. The ship transited to a higher latitude in the Central Arctic for Leg 5 (Drift 3) with the establishment of CO3 and DN2 at a new ice floe on 21 August 2020. On 20 September 2020, Polarstern left the ice floe and returned to Bremerhaven, Germany, concluding Drift 3 of the MOSAiC expedition. The remaining autonomous buoys from DN2 that had been deployed during Leg 5 continued to collect data through early 2021. The atmospheric forcing in the position of CO1 and CO2 was used in our simulation experiments (Figure 1).
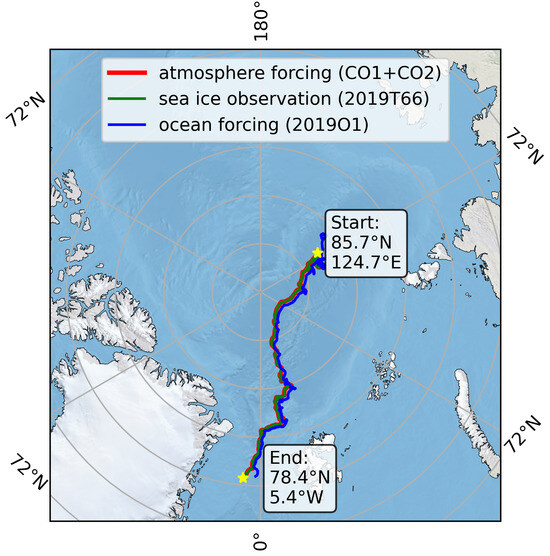
Figure 1.
The drift tracks of the MOSAiC expedition, where atmospheric, oceanic and sea ice observations used in the present research were taken. The atmospheric forcing data are in red, sea ice observations in green, and ocean forcing data in blue. The red line is overlapped by the green line.
SIMBA buoys (SAMS Ice Mass Balance Buoy) [21], developed by Scottish Association for Marine Science (SAMS), were used to measure SIT and snow depth during the MOSAiC expedition. The length of the SIMBA thermistor chains is 5.12 m, and the chains include 241 thermistors with a spacing of 2 cm. Temperature is measured through the thermistors to find the ice–ocean and ice–snow/air interfaces. We used the sea ice-thickness observations from the buoy 2019T66 [22], which was the one closest to Polarstern (Figure 1). The observation period for SIT and snow depth was from 30 October 2019 to 4 August 2020, including Drift 1 and Drift 2, with a temporal resolution of 1 day and an accuracy of 0.02 m. The time period of the simulation was based on the observation period of buoy 2019T66 to facilitate comparison.
MOSAiC atmosphere observation data include hourly 10 m u and v components of wind, 2 m temperature, specific humidity, precipitation, and downward shortwave and longwave radiation, which were averaged from higher-frequency observations. The atmospheric observation is missing from early May to late June and from late July to late August 2020 due to logistical operations. Rinke et al. [23] compared meteorological conditions during the MOSAiC expedition and ERA5 reanalysis and concluded that the cyclones were stronger and more frequent than normal in the period from late winter to spring and weaker in the summer. In summer, the conditions were warmer and wetter than usual near Polarstern. The temperature in July and August 2020 was especially anomalous, representing the warmest values in the 1979–2020 period [23].
The Conductivity–Temperature–Depth instrument (CTD) of buoy 2019O1 in the MOSAiC DN, built by Sea-Bird Scientific, Bellevue, WA, USA, performed well throughout the entire operation period, observing ocean temperature and salinity at different depths [24]. Five SBE37IMP CTDs were mounted in a 100 m long inductive modem cable at depths of 10, 20, 50, 75 and 100 m. For this study, we selected CTD data at a depth of 10 m, this depth being the closest to the bottom of the sea ice, to obtain the daily averaged temperature and salinity of seawater as the ocean forcing data for Icepack.
Observations of the melt-pond depth during the spring-to-summer melt season (from late June to late July) were conducted at the position of CO2 [25]. Melt-pond depth was measured using the magnaprobe, an automated snow-depth probe equipped with a GPS logger. Measurements were collected every 1–2 steps, which equated to 1–3 m sampling along repeat transect routes. Four weekly measurements were taken from 29 June through 26 July, for a total of 18 complete measurements, while low visibility and polar bear activity prevented complete measurements from being taken on 16, 23, 24, and 27 July. The melt-pond fraction (MPF) was extracted by Niehaus et al. [26] from Sentinel-2 satellite imagery, which starts from 21 June 2020. Earlier observations of melt ponds are not available, as the latitudes reached during MOSAiC exceeded the observational coverage of the satellite mission. The data on melt-pond fraction and melt-pond depth were compared with model outputs.
ERA5 is a reanalysis product for global climate that was released by the European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) and is widely used for studying changes in the Arctic and forcing sea ice models (e.g., [27]). Compared with other reanalysis datasets, ERA5 uses more advanced 4D-Var assimilation methods and has significantly improved data quality near the Arctic [28]. Wang et al. [29] showed that ERA5 has better performance for surface shortwave radiation in the Arctic. Data at the single level with 0.25° × 0.25° horizontal spatial resolution and hourly temporal resolution were used in this study. Due to the missing observations, we could not force Icepack directly with the MOSAiC atmospheric forcing. Bilinear interpolation was performed to obtain the complete atmospheric forcing from ERA5 along the drift trajectories of CO1 and CO2. The specific humidity data needed for Icepack forcing were computed from the 2 m air temperature and 2 m dew-point temperature of ERA5.
2.2. Icepack Model
2.2.1. Thermodynamic Processes
A thermodynamic component was used to compute changes in the ice/snow thickness and vertical temperature profile resulting from radiative, turbulent, and conductive heat fluxes in Icepack. Melt and growth of ice/snow were computed by updating the ice and snow temperatures. Snow depth increased with snowfall and decreased due to melt, sublimation, or snow redistribution. Shortwave radiation was treated as an important heat source for changes in sea ice thickness. Icepack uses Delta–Eddington parameterization [30] to compute surface albedo and shortwave fluxes. The albedo was altered by the presence of melt ponds.
Icepack includes two thermodynamics options, the Bitz and Lipscomb scheme [31], which assumes a fixed salinity profile, and a Mushy scheme [32], which takes salinity change into consideration. In the Mushy scheme, sea ice is assumed to be a mixed-phase layer composed of both fresh ice and liquid brine pockets. The changes in SIT are calculated by the enthalpy and absorbed heat flux within the ice. Both these thermodynamic schemes include at least one snow layer and multiple ice layers, with a default setting of one snow layer and seven ice layers. In our simulations, only the Mushy scheme was used.
2.2.2. Delta–Eddington Radiation Parameterization
The Delta–Eddington parameterization scheme is the algorithm used for computing albedo and shortwave fluxes in Icepack and is based on a multiple-scattering radiative-transfer approach. It computes apparent optical properties (AOPs) through inherent optical properties (IOPs). The AOPs include the albedo, internal absorption, and transmission of radiation in the snow and sea ice, while the IOPs include single-scattering albedo, extinction coefficient, and asymmetry coefficient. The surfaces of the sea ice are divided into three types: bare ice, snow, and melt pond. The albedo of snow is the highest, and the albedo of a melt pond is the lowest. The growth of melt ponds is the main reason for the albedo decrease observed in summer. In the Delta–Eddington scheme, the albedo and radiation flux of snow, ice, and melt ponds are calculated separately. Grid-averaged albedo and radiation fluxes are computed by weighting the results by the fractional coverage of the surface types. The Delta–Eddington scheme also accounts for the dependence of surface albedo on the solar zenith angle (computed from the local latitude and longitude), with albedo increasing at larger solar zenith angles.
2.2.3. Snow-Redistribution Scheme
Two snow-redistribution parameterization schemes can be implemented in Icepack v1.4.1 to calculate snow depth by considering the redistribution of snow by winds over a snow-covered area within a grid cell. Redistribution processes between grid cells are neglected, and snow can be lost into leads and open water. The remaining snow on the sea ice contributes to the mass balance of the sea ice. The snow-redistribution processes also influence the snow-grain radius and radiation balance in the Delta–Eddington scheme.
The first snow-redistribution scheme is a bulk snow-redistribution scheme and is based on observations collected during the Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic (SHEBA), which revealed that snow near ridged ice is deeper than snow on undeformed ice [11]. In the bulk scheme, the deposition of snow from level ice areas into leads reduces the amount of snow. The snowfall rate is adjusted based on the average level ice area fraction to account for snow loss to the ocean and leads, as follows:
where is the original snowfall rate, is the modified snowfall rate, is the average level-ice fraction tracer value, and p is a parameter that determines the ratio of snow on ridges to that on level ice. The default value of p is 0.3.
The second snow-redistribution scheme [33], labeled in Icepack as an option called snwITDrdg, allows for wind-driven snow compaction, erosion, and redeposition of snow across different categories of sea ice thickness. The snow volume and energy-state variables are updated in two steps, first for erosion of snow into suspension, then for snow redeposition. This scheme redeploys suspended snow back onto other thickness categories, calculating snow energy proportionally among affected types of sea ice. There are two processes, snow lost into leads and wind-driven snow compaction, that affect the snow depth in this scheme. The compacted snow becomes denser and limits snow erosion.
Icepack v1.4.1 also provides a model configuration option, “none”, that does not use either of the above two schemes. When this selection is made, no snow-redistribution scheme is used and the snow depth is the same across all sea ice categories. In our numerical experiments, we tested two snow-redistribution schemes and used the no-snow-redistribution case for comparison.
2.2.4. Melt-Pond Scheme
Two melt-pond parameterization schemes were used in conjunction with a Delta–Eddington scheme to simulate the effect of melt ponds on albedo. Both schemes allocate melt water based on sea ice topography, and the difference between these two schemes is the method by which sea ice topography is determined. The first melt-pond scheme is TOPO (topographic) [34], which is based on the concept that melt water begins to collect on the lowest parts of the ice. Since Icepack does not explicitly model ice topography, the ITD is split into a surface height and basal depth distribution relative to sea level. Melt water collects on the ice of the lowest surface height and fills higher parts later. The second scheme is LVL (level-ice) [35], which accounts for gravity effects, but in an innovative way; melt ponds can form only on the level (undeformed) ice areas of each ice category. If ice deforms into ice ridges, the melted water above the ridges will flow into the ocean. The LVL scheme also considers the pond aspect ratio in melt-pond evolution. This parameter is defined as the ratio of pond depth to pond area.
2.3. Experiment Design
The SIT simulation is a one-point simulation using Icepack v1.4.1, in which a snow-redistribution scheme was implemented. The time range of our simulations was based on the time frame of SIT observations from buoy 2019T66, spanning from 1 November 2019 to 4 August 2020 for one complete period. To fill in the missing MOSAiC observations from May to June, we used the hourly atmospheric forcing from ERA5 and the ocean forcing from buoy 2019O1. Here, we chose the Mushy scheme as the thermodynamic scheme, as it is a comprehensive thermodynamic scheme in Icepack that considers changes in temperature and salinity along the vertical profile of sea ice over time. Two melt-pond schemes (TOPO and LVL) were combined with three snow-redistribution configurations: no snow redistribution (nosnwredist), the bulk scheme, and the snwITDrdg scheme. In the following discussion, we use “melt-pond scheme + snow-redistribution configuration” to represent the six combinations. Initial SIT, snow depth, melt-pond fraction and melt-pond depth are from MOSAiC observations made on 1 November 2019. In Icepack, the maximum snow depth on the first step on sea ice is limited by 0.2 times SIT (0.44 m), regardless of its initial value. In our simulations, the initial snow thickness was limited to 0.088 m, although the observed snow thickness at the initial time was 0.12 m. The increase in simulated snow depth was entirely caused by snowfall in the atmospheric forcing, and the initial snow depth has limited impact on snow depth at the end of spring. The geographic location of observation station varies during the MOSAiC drifting, while the original Icepack code can simulate only for a fixed location. We modified the Icepack code to run a model with changing latitude and longitude. However, for the MOSAiC expedition location, varying location did not influence the simulation significantly. The setup of Icepack is detailed in Table 1. Other configurations not listed are the default settings in Icepack.

Table 1.
The details of the Icepack v1.4.1 configuration used in numerical experiments. The initial conditions were taken from the MOSAiC observation on 1 November 2019. Two melt-pond schemes (TOPO and LVL) and three snow-redistribution configurations (none, bulk, and snwITDrdg) were used.
3. Results
3.1. MOSAiC and ERA5 Comparison
The time series of the near-surface meteorological variables during the MOSAiC expedition and ERA5 reanalysis are shown in Figure 2. The root mean square errors (RMSEs) and correlation coefficients for each atmospheric variable are presented in Table 2. ERA5 reproduced wind, humidity, and radiation well during the MOSAiC expedition. There was no significant seasonal variation in observed wind speed during the MOSAiC drift, with maximum monthly wind speeds of 10 to 14 m . A positive phase of the Arctic Oscillation (AO) occurred in the Arctic during January–March 2020; this resulted in stronger-than-normal cyclone activity [36], which caused dramatic changes in wind patterns. The RMSE of wind between ERA5 reanalysis and MOSAiC observations is 1.47 m and 1.43 m for the u and v components (Table 2), respectively. The RMSE of total wind speed is 1.62 m . The winter temperature remained below −20 °C, with an increase in temperature starting in mid-April and the temperature reaching around 0 °C in summer. ERA5 reproduced the 2 m temperature well in the summer melt season, but the simulated temperature in the winter and spring was slightly higher than the observed values, since ERA5 might not successfully represent the turbulent heat fluxes that occur on the surface of the Arctic sea ice in winter [28]. The humidity is lower in winter and spring, and increases in summer. ERA5-modeled snowfall events showed good agreement in terms of timing, but the amount of snowfall (in terms of snow–water equivalent) tended to be higher than the amounts from the MOSAiC observations (accumulated snowfall of 138 mm in ERA5 compared with the MOSAiC observation of 108 mm from 1 November 2019 to 7 May 2020) due to the lack of representation in ERA5 snowfall/precipitation. Hence, observed snowfall from 1 November 2019 to 7 May 2020 was used in atmospheric forcing to account for snowfall bias. Correlation coefficients are above 0.9 for most atmospheric variables, but not for precipitation. The comparison between ERA5 and MOSAiC observations indicates that ERA5 can reproduce the atmospheric conditions from the MOSAiC expedition reasonably well. Therefore, using ERA5 reanalysis to obtain complete atmospheric forcing and run Icepack simulations is feasible.
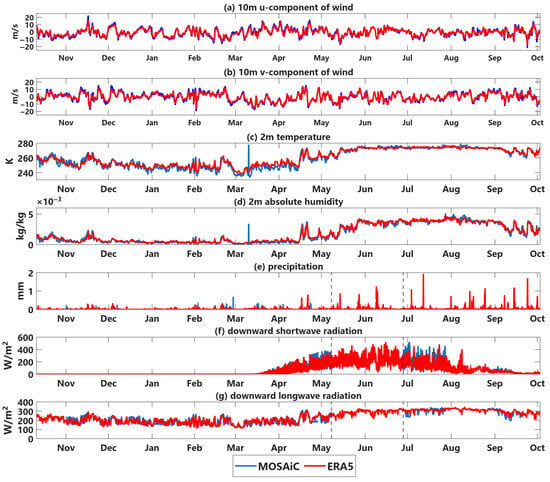
Figure 2.
Comparison between hourly MOSAiC atmospheric observations and ERA5 reanalysis. The blue lines are MOSAiC observations, and red lines are meteorological variables from ERA5 reanalysis. From top to bottom are the 10 m u and v components of wind, 2 m temperature, 2 m humidity, precipitation, downward shortwave radiation, and downward longwave radiation. MOSAiC observation is missing from early May to late June and from late July to late August 2020. The snowfall/precipitation and radiation observation is missing from 8 May to 26 June (between two vertical black dashed lines). ERA5 reanalysis can reproduce atmospheric conditions during MOSAiC expedition reasonably well.

Table 2.
The root mean square error (RMSE) and correlation coefficient between MOSAiC observations and ERA5 reanalysis. All the RMSEs and correlation coefficients were computed for hourly data. The correlation coefficients are significant at the 95% level except for snowfall/precipitation.
3.2. Sea Ice Thickness Simulations
The comparison between SIT observed during the MOSAiC expedition and data simulated using Icepack v1.4.1 is shown in Figure 3. The observed SIT increased from October 2019 to June 2020 and gradually decreased after June. Melt ponds do not form in winter and spring; hence, only snow-redistribution configurations influenced the SIT simulations. For the winter and spring seasons (November 2019 to May 2020), Icepack could reproduce the trend of SIT growth. Simulations without a snow-redistribution scheme tended to overestimate SIT during specific periods, such as December 2019, late February, mid-March, late April, and from May to June 2020. The springtime SIT simulations exhibited improved performance with a small bias when the bulk scheme is applied. Conversely, simulations using the snwITDrdg scheme showed higher bias compared to simulations without snow redistribution. With complete melt of snow after June, the melt-pond processes played a major role in SIT simulations in summer. Both the TOPO and LVL melt-pond schemes underestimated SIT in the summer melt season (July–August 2020), resulting in a significant underestimation compared to observations. The bias of SIT simulations in the TOPO scheme is lower than that in the LVL scheme in summer.
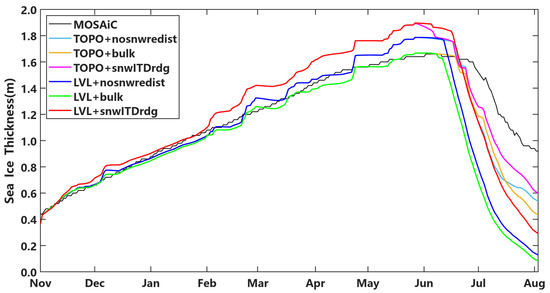
Figure 3.
The sea ice thickness (SIT) simulations using Icepack v1.4.1 for six combinations of three snow-redistribution configurations and two melt-pond schemes, compared with observations (black line). The lines are labeled with the format “melt-pond scheme + snow-redistribution configuration”. The TOPO without a snow-redistribution scheme (nosnwredist) is in cyan; TOPO with the bulk scheme in brown; TOPO with the snwITDrdg scheme in magenta; LVL without a snow-redistribution scheme in blue; LVL with the bulk scheme in green; and LVL with the snwITDrdg scheme in red. The lines of the TOPO scheme (cyan; brown and magenta) are overlapped by the lines of the LVL scheme (blue, green and red) from November 2019 to May 2020. Icepack could reproduce the trend of SIT growth in the winter and spring seasons but underestimated SIT in the summer melt season. Before snow melted in June, the bulk snow-redistribution scheme reproduced SIT better than other configurations. After snow melted in June, the TOPO melt-pond scheme simulations showed better performance for SIT than did the LVL scheme.
The significance of various simulated growth and reduction processes of SIT is depicted in Figure 4. During the winter and spring seasons, SIT growth is primarily driven by congelation and snow–ice formation, as also detailed in Table 3. Notably, snow–ice formation represented the dominant contribution to SIT growth between March and May 2020. There was still a small amount of bottom melt below m in December 2019 and March 2020, but this has no great influence on the change in SIT. Periods of significant snow–ice formation are concentrated in December 2019, February–March 2020, and late April 2020, aligning closely with snowfall events. In the Icepack model, substantial snow accumulation on the sea ice surface causes the ice to submerge, transforming the submerged snow into sea ice. This process contributed to the results showing thicker simulated sea ice in December 2019, late February, mid-March, late April, and May 2020 in the simulations without snow redistribution.
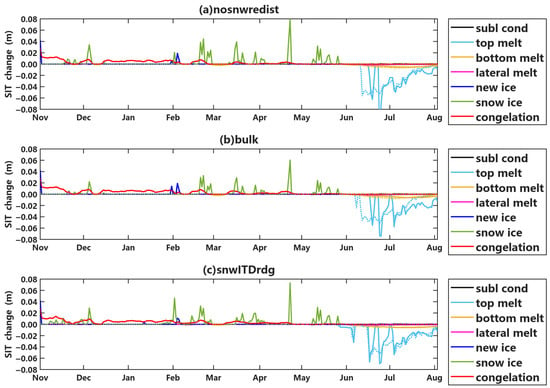
Figure 4.
Daily changes in sea ice thickness (SIT) for numerical experiments on six combinations of three snow-redistribution configurations and two melt-pond schemes. In the processes reducing SIT, top melt is in cyan; bottom melt is in brown; and lateral melt is in magenta. For the processes contributing to SIT growth, new ice formation is in blue; snow–ice formation is in green; and congelation is in red. The “subl cond” in black represents sublimation or condensation, negative values of which indicate SIT loss due to sublimation and positive values of which indicate SIT gain from condensation. Solid lines represent simulations with the TOPO scheme, while dotted lines correspond to the LVL scheme. Growth of sea ice is primarily driven by congelation and snow–ice formation during winter and spring, whereas reduction in sea ice is primarily driven by top melt during the summer melt season.

Table 3.
Accumulated changes in the thickness (SIT) (m) and RMSE of SIT throughout the time period of simulations for six combinations of two melt-pond schemes (column 1) and three snow-redistribution configurations (column 2). Columns 3 to 9 represent different processes of SIT change. Column 3 represents sublimation or condensation. Column 4 represents new ice formation. Column 5 represents snow–ice formation. Column 6 represents congelation. Columns 7 to 9 represent top melt, bottom melt, and lateral melt. Positive values indicate SIT growth, whereas negative values indicate SIT reduction. Column 10 is the RMSE for SIT between observation and simulations for the entire period.
Snow-ice formation occurs when snow base lies below sea level [37]. In the Mushy scheme, it is assumed that the porosity of the snow layer is filled with seawater and that the snow below the sea surface is converted to sea ice with the same thickness, so that the bottom of the snow reaches the sea level. This process contributed to the larger SIT in simulations without snow redistribution. The result indicates that neglecting snow redistribution in Icepack leads to excessive snow–ice formation in the period of sea-ice growth. In contrast, both the bulk and snwITDrdg schemes reduced the amount of snow on sea ice through snow loss into ocean and leads. The thinner snow cover and redistribution on the sea ice cause less snow to be submerged into ocean and the reduction of snow–ice formation. The higher congelation rate is seen in simulations with snow redistribution (Table 3), and this value is reflected in the sea ice growing thicker in the simulations using the snwITDrdg scheme. Overall, the bulk scheme performs the best for the winter and spring simulations.
The dominant melt process in summer is top melt, which exceeds bottom melt. Observations of daily accumulated top and bottom melt are derived from the SIMBA buoy 2019T66. Compared to an observed top melt of 0.44 m (Figure 3), the overestimation of top melt contributed to an underestimation of SIT during summer in the simulations. This difference in simulated top melt for six combinations might be primarily attributed to the melt-pond schemes. The simulated bottom melt in all configurations was close to the observed bottom melt (0.24 m). Simulations across all configurations overestimated the top melt in summer, leading to the underestimation of SIT. The LVL scheme simulated earlier and more top melt than the TOPO scheme, which caused a larger bias in SIT simulations in summer.
3.3. Snow-Depth Simulations
The snow-depth simulations and observations are depicted in Figure 5. Overall, the observed snow depth varied between 0.1 to 0.2 m from November 2019 to April 2020, gradually decreasing from early May, and the snow completely melted after 27 June, while simulated snow depths show an increasing trend over time, resulting in a notable overestimation. In early June, the snow depth decreased as the snow melted and the surface temperature rose to 0 ℃ (Figure 2). The snow in the simulations melted in June, earlier than the observed snow. The early melting of snow in the simulations may be related to the excessive solar radiation, as shown in Section 3.4.
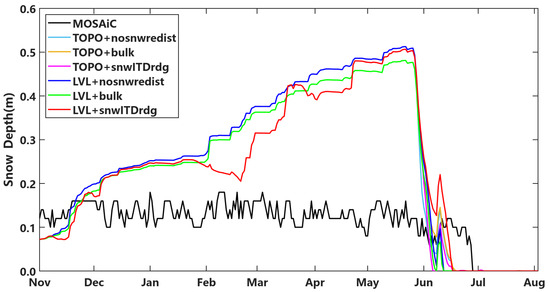
Figure 5.
The results of the snow-depth simulations run using Icepack for six combinations of three snow-redistribution configurations and two melt-pond schemes, compared with the snow-depth observations (black line). The lines are labeled with the format “melt-pond scheme + snow-redistribution configuration”. TOPO without a snow-redistribution scheme (nosnwredist) is in cyan; TOPO with the bulk scheme is in brown; TOPO with the snwITDrdg scheme is in magenta; LVL without a snow-redistribution scheme is in blue; LVL with the bulk scheme is in green; and LVL with the snwITDrdg scheme is in red. The lines of the TOPO scheme (cyan; brown; and magenta) are overlapped by the lines of the LVL scheme (blue, green, and red) from November 2019 to May 2020. Icepack simulated an trend of increasing snow depth over time, with a notable overestimation, while the redistribution scheme reduced the snow depth in simulations.
During winter and spring, the snow-redistribution schemes reduced the snow depth in simulations. The difference between the two snow-redistribution schemes in simulating SIT and snow depth arose from differences in the main processes contributing to reduction in snow depth. In the bulkscheme simulations, snow loss into the ocean and leads was the main process (Figure 6) reducing the amount of snow on the sea ice. The reduction in the amount of snow led to decreased snow–ice formation and enhanced congelation. Consequently, the bulk scheme exhibited better performance in SIT simulations corresponding to the time frame of the MOSAiC expedition. In contrast, the snwITDrdg simulations primarily attributed reductions in snow depth to wind-driven compaction during February–March and April–May. The compacted snow enhances the congelation rate, as mentioned by Clemens-Sewall et al. [14]. However, simulated snow loss into the ocean and leads was minimal, resulting in only a slight decrease in accumulated snow–ice formation (Table 3). In late February, the simulations showed a reduction in snow depth, which is consistent with in situ observations [38]. Snow erosion and compaction driven by high wind speed occurred in the observation and led to a significant reduction in snow depth. Since the snow density was not observed during the MOSAiC expedition, we were unable to calculate the simulation bias of snow density and the amount of snow in the experiment.
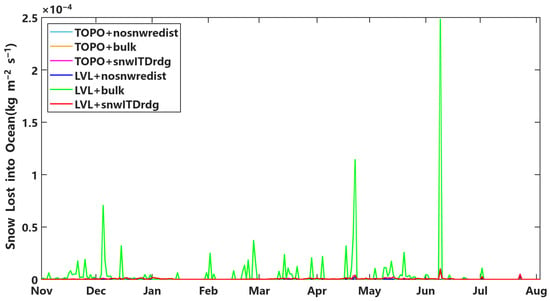
Figure 6.
The amount of snow lost into ocean and leads, as calculated using Icepack for six combinations of three snow-redistribution configurations and two melt-pond schemes. The lines are labeled with the format “melt-pond scheme + snow-redistribution configuration”. TOPO without a snow-redistribution scheme (nosnwredist) is in cyan; TOPO with the bulk scheme is in brown; TOPO with the snwITDrdg scheme is in magenta, LVL without a snow-redistribution scheme is in blue; LVL with the bulk scheme is in green, LVL with the snwITDrdg scheme is in red. The lines of the TOPO scheme (cyan; brown and magenta) are overlapped by the lines of the LVL scheme (blue, green, red) from November 2019 to July 2020, so that only three lines are visible. The bulk scheme simulates more snow loss into ocean and leads than other configurations.
3.4. Radiation Flux and Albedo
Figure 7 presents the daily averaged simulated and observed net radiation fluxes at the sea ice surface, defined as positive downward. The simulated net longwave radiation is close to the observation values from the winter and spring seasons. Starting in mid-March 2020, the shortwave radiation flux increased, coinciding with the seasonal rise in solar radiation. The springtime net shortwave radiation flux in simulations using the bulk scheme and no snow redistribution is slightly lower than the observed values. The simulated net shortwave radiation flux found with the snwITDrdg scheme was closer to observations than the values found with other configurations. At the beginning of July, the simulated net shortwave radiation flux exceeded the observation, resulting in increased heat absorption by the sea ice and enhanced top melt. It is a significant factor contributing to the underestimation of SIT in summer. The overestimation of net shortwave radiation may occur earlier than July. However, it is hard to be certain because the observation before July is missing. From November 2019 to July 2020, the simulated net longwave radiation was consistent with observations, which indicates that Icepack could reproduce the sea ice surface temperature well for the period of the MOSAiC expedition.
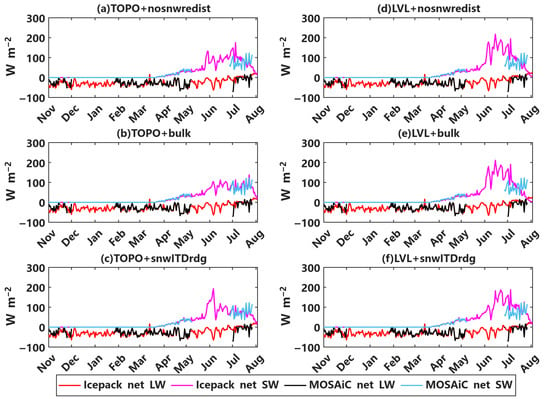
Figure 7.
Daily averaged net radiation flux for six combinations using three snow-redistribution configurations and two melt-pond schemes compared with MOSAiC observations, defined as positive downward. Simulated net longwave radiation is shown in red, simulated net shortwave radiation in magenta, observed net longwave radiation in black, and observed net shortwave radiation in cyan. The outgoing longwave radiation flux is the sum of the values from the ice and ocean. Icepack simulations using no snow redistribution and the bulk scheme slightly underestimated the net shortwave radiation flux in the winter and spring seasons, and all combinations overestimated the net shortwave radiation flux at the beginning of the summer melt season.
The albedo is calculated as the ratio of upward shortwave radiation flux to downward shortwave radiation flux, as shown in Figure 8. From the beginning of early April, the observed sea ice albedo exhibited temporal variability, ranging between 0.7 and 0.95, whereas the albedo in bulk and no-snow-redistribution simulations remained nearly constant, at approximately 0.86. The albedo using no snow redistribution and the bulk scheme was slightly higher than the value of the observation from March to May, a difference linked to the underestimation of net shortwave flux. The albedo values in snwITDrdg simulations were closer to observed values than were those from other two snow-redistribution configurations. During spring, the sea ice surface is mainly snow-covered, with snow playing a major role in determining surface albedo. The snow albedo is influenced by the snow status, the incident solar spectrum, and the solar zenith angle, while the snow status is determined by snow-grain radius. The presence of snow grains with larger radii allows photons to travel a longer path in the snow, increasing the absorption of incoming solar radiation and reducing the albedo [39]. The temperature has a notable impact on the snow-grain radius. As the temperature increases before snow reaches the melting temperature, the snow-grain radius will increase and the snow albedo will decrease. The relationship between snow-grain radius and surface temperatures is as follows:
where is the snow albedo tuning parameter, which adjusts the albedo by changing the snow-grain radius, is the temperature at which snow-grain radius changes, which is −1.5 °C, and = 1500 m is the maximum melting snow-grain radius. The simulated surface temperature rose to −8.2 °C in early May, remaining below both the temperature for snow-grain change and the snow melting point (Figure 2). Consequently, the snow-grain radius in Icepack remained unchanged and no melting occurred, resulting in minimal changes in the simulated sea ice surface albedo. The snow-redistribution processes in the snwITDrdg scheme changed the snow status and its albedo in April, which caused the albedo value to be closer to the observed value. It indicates that the snow albedo parameters in Icepack need to be further adjusted.
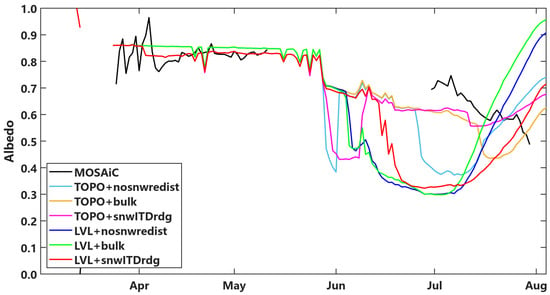
Figure 8.
Simulated daily averaged albedo for six combinations using three snow-redistribution configurations and two melt-pond schemes, compared with MOSAiC observations (black line). The lines are labeled with the format “melt-pond scheme + snow-redistribution configuration”. TOPO without a snow-redistribution scheme (nosnwredist) is in cyan; TOPO with the bulk scheme is in brown; TOPO with the snwITDrdg scheme is in magenta; LVL without a snow-redistribution scheme is in blue; LVL with the bulk scheme is in green; and LVL with the snwITDrdg scheme is in red. From April to June, the lines in cyan; brown and blue are overlapped by the green line, and the line in magenta is overlapped by the red line. The bulk and nosnwredist simulations slightly overestimated albedo in spring, while the albedo in snwITDrdg simulations was closer to observed values. Albedo was underestimated from early July to mid July for all combinations.
With the formation of melt ponds in late May, the simulated albedo decreased, though a temporary increase occurred in mid-June following a snowfall event. However, albedo observations are missing from late May to June, so it is not possible to make a comparison for this period. In late June, complete snow melt and formation of melt pond led to a decrease in albedo, increasing the absorption of shortwave radiation by the sea ice. This process might have contributed to top-melt overestimation and the underestimation of SIT in our simulations. Until July, the simulated albedo was still lower than the observed value. However, the situation changed after mid-July. The observed albedo decreased over time, while the simulated albedo increased with the increase of the solar zenith angle from the mid-July to August.
3.5. Melt Pond
Figure 9 compares the melt-pond simulations for six combinations with observational data. Webster et al. [25] described the evolution of melt pondd during the MOSAiC expedition and found that following the onset of above-freezing temperatures and rainfall on 25 May, melt ponds were first observed on 28 May. However, the depths of those melt pond were negligible. Subsequent freezing conditions and fresh snowfall temporarily covered the surface, delaying further pond development until mid-June. In our Icepack simulations, above-freezing temperatures occurred on 25 May, and melt ponds formed by 27 May in both the TOPO and LVL simulations, aligning closely with observations. However, Icepack significantly overestimated melt-pond growth, with pond area and depth increasing rapidly after pond formation. There are substantial differences between the melt-pond simulations and observation.
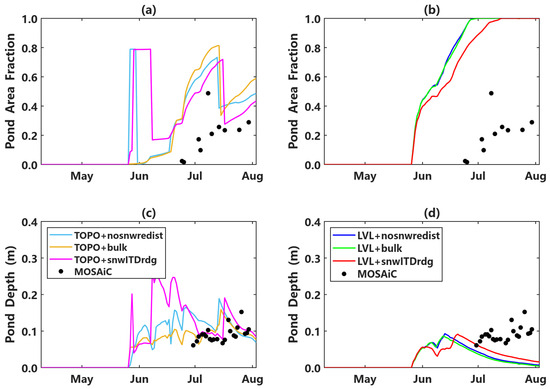
Figure 9.
The comparison of melt-pond fraction and depth from numerical simulations and observations: (a) pond area and (c) pond depth for simulations with the TOPO melt-pond scheme. (b) pond area and (d) pond depth for simulations with the LVL melt-pond scheme. The lines are labeled with the format “melt-pond scheme + snow-redistribution configuration”. MOSAiC observations are shown in black; TOPO without a snow-redistribution scheme (nosnwredist) is in cyan; TOPO with the bulk scheme is in brown; TOPO with the snwITDrdg scheme is in magenta; LVL without a snow-redistribution scheme is in blue; LVL with the bulk scheme is in green; and LVL with the snwITDrdg scheme is in red. The TOPO scheme simulates more realistic melt-pond evolution than the LVL scheme, and thus the bias associated with SIT values is lower in TOPO simulations than in LVL simulations.
The TOPO scheme had better performance in simulating melt-pond fraction and depth, but rapid fluctuations in pond area and depth occurred in the simulations, since the redistribution of melt water occurred when the volume of melt-pond was larger than the space provided by the lowest sea ice category available [34]. The melt-pond observations from late June indicate a more gradual increase in pond depth, without abrupt fluctuations. The large size of the simulated pond area in LVL might be due to the fact that there is only level ice, since sea ice dynamics that involve forming ridges are not represented in Icepack [40]; a result is that the melt water spreads over a rather large area, creating a relatively shallow pond. The excessive simulated pond area in Icepack contributes to lower albedo, which in turn causes increased top melt and thinner SIT during the summer melt season. The TOPO scheme simulates melt-pond evolution more realistically than the LVL scheme; thus, the bias in SIT values in TOPO simulations is lower than that in LVL simulations.
Both TOPO and LVL schemes overestimate the melt-pond fraction. This issue possibly indicates the deficiency of representation of melt-pond drainage [41], which affects the melt-pond fraction and depth significantly. Vertical drainage events of large melt ponds occurred in the windy and rainy conditions on 11–13 July during the MOSAiC expedition, after which pond area fraction significantly decreased [25]. Modifying parameters controlling melt-pond drainage (e.g., the fraction of the melt water added to the pond) might improve the SIT simulations in summer, but complete observation of these processes during the MOSAiC expedition are needed to justify changing the parameters. The sub-grid scale processes of melt-pond evolution are essential for understanding the simulation bias in summer. Webster et al. [25] analyzed the simulations of melt-pond and sea ice properties for five categories of ice thickness and noticed that a large amount of melt water was retained on the thin sea ice, causing positive bias in the measurement of melt-pond fraction. Studying the evolution of melt ponds on different sea ice categories might help us to understand the bias, but currently such work is limited to using the publicly available and complete melt-pond observations.
4. Discussion
Many studies have investigated SIT simulation using Icepack but have concentrated on different processes. Using Icepack, the influence of a change in the thermodynamic scheme from the Bitz and Lipcomb scheme (BL99) [31] to the Mushy layer scheme [32] was assessed using ice mass balance buoy observations for landfast ice [15]. It was demonstrated that with a modified version of the Mushy scheme, the SIT simulation was improved, a difference mainly attributed to the improvement in snow–ice formation and congelation processes. In our investigation, the Mushy scheme was used. The SIT measurements from MOSAiC were compared with measurements from an earlier field campaign. The initial snow depth and SIT can influence SIT growth during sea ice growth season, and Icepack simulation was used to verify this finding [20]. In our simulation, our initial conditions of snow depth and SIT are taken directly from observations.
The atmospheric forcing during the MOSAiC expedition was used to force Icepack with a focus on the freezing temperature parametrization in Icepack [19]. However, in this study, the snow depth was specified; snow–ice formation was excluded; and different freezing temperature parameterization schemes were compared. It was previously demonstrated that the SIT simulation error can be reduced with a modified version of the freezing temperature parameterization scheme. Both that study and the present study demonstrate the potential applications of MOSAiC expedition observations for evaluating and improving the sub-grid-scale process-parameterization schemes in sea ice simulations.
In this study, we focus on the impact of different snow-redistribution and melt-pond schemes on SIT simulation. We found that SIT simulation can be improved by using the bulk scheme during the winter season and that the bias in summer can be caused by melt-pond processes. There is still some room for improvement in our research. The ERA5 reanalysis, which has its own uncertainty, is used to force Icepack and will cause uncertainty in the simulations. Since our comparison is mainly among combinations of different snow-redistribution configurations and melt-pond schemes, with the forcing field unchanged, the uncertainty in the forcing may not influence our conclusion regarding the effect of these schemes. The uncertainty in the forcing may be addressed by running ensemble integrations in future studies. Ridging is an important process for the formation of leads that would increase loss of snow. Icepack is a single-column thermodynamic model, and sea ice dynamic processes, such as ridge formation, are not represented in the model. Considering dynamic processes might improve the SIT simulations. Sub-grid-scale processes are essential for a more comprehensive understanding of the melt-pond evolution. In this study, we analyze the grid-level melt-pond fraction and depth simulations. The evolution of ice, snow and melt-pond on different sea categories of ice thickness should be compared to observations in future.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the Icepack model was used to reproduce the SIT evolution from the time of the MOSAiC expedition. Due to the missing observation from the time of the expedition, ERA5 atmosphere reanalysis, along the MOSAiC drift trajectory, after its validation, was used to force Icepack. The simulation time range extended from 1 November 2019 to 4 August 2020, in accordance with the time period of SIT and snow-depth observations. We compared SIT simulations against MOSAiC observations to understand the reasons of SIT simulation misfits for different combinations of two melt-pond schemes and three snow-redistribution configurations. The three snow-redistribution configurations were the bulk scheme, the snwITDrdg scheme, and one simulation selection without snow redistribution, and the two melt-pond schemes were the TOPO scheme and the LVL scheme. The bulk scheme describes snow on ridged ice as thicker than undeformed ice and snow on level ice as potentially lost to leads and open water. The snwITDrdg scheme includes snow redistribution between different sea ice categories and wind-driven snow compaction and erosion. The TOPO and LVL melt-pond scheme describe the process of melt water distribution differently. In TOPO scheme, melt water begins to be collected on the lowest parts of the ice, and fills higher parts later. In LVL scheme, ponds can only form on the level ice areas in each ice category, and distribution of melt water is determined by pond aspect ratio.
Our simulations show that Icepack can reproduce sea ice growth in the winter and spring periods of MOSAiC expedition. However, simulations without a snow-redistribution scheme tend to overestimate SIT. The primary reason for this overestimation is suggested to be inaccurate simulations of snow–ice formation and its contribution to sea ice mass balance. The excess snow submerges into seawater and is converted into sea ice, leading to SIT overestimation. Applying snow redistribution in Icepack reduces snow–ice formation while enhancing congelation. The bulk snow-redistribution scheme improves the SIT simulation in winter and spring, while the bias is larger in simulations using the snwITDrdg scheme. Additionally, albedo in no-snow-redistribution and bulk scheme simulations during spring is higher than the observed value, resulting in underestimated net shortwave radiation, while the albedo in snwITDrdg simulations is closer to observation. The observed albedo varies over time, while simulated albedo is almost constant in winter and spring, as the snow properties remain unchanged in these periods. These findings highlight the need for further parameter estimation in the Delta–Eddington scheme.
In the summer melt season, Icepack underestimates the SIT, as the simulated top melt is larger than the observed value. The larger simulated top melt may be attributed to the lower albedo and larger melt-pond area than the observed value in summer, which enhances the absorption of shortwave radiation by the sea ice. The TOPO scheme simulates melt-pond evolution more closely to observation than the LVL scheme, resulting in a smaller bias in SIT simulations. The overestimation of melt-pond fraction might be related to the process of melt-pond drainage, but more observations are needed for adjusting the parameters of drainage processes. It suggests that sensitivity analysis and parameter estimation of the Delta–Eddington scheme and melt-pond schemes should be used in the future to improve the SIT simulations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W.; Data curation, J.Z., Y.L. and H.Z.; Formal analysis, J.Z.; Funding acquisition, X.W.; Investigation, J.Z.; Methodology, J.Z., Y.L., H.Z. and X.W.; Project administration, X.W.; Resources, X.W.; Supervision, X.W.; Validation, J.Z., Y.L. and X.W.; Writing—original draft, J.Z.; Writing—review & editing, X.W. and J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42376200).
Data Availability Statement
The Icepack version 1.4.1 releases are available on https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.11223808 [17] accessed on 9 June 2025. The ERA5 reanalysis datasets are availiable on https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-era5-single-levels accessed on 9 June 2025. MOSAiC atmosphere observation are avaliable on https://adc.arm.gov/discovery/#/results/iopShortName::amf2019mosaic accessed on 9 June 2025. The MOSAiC buoy datasets are avaliable at https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.938134 [22] accessed on 9 June 2025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sweeney, A.J.; Fu, Q.; Po-Chedley, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, M. Internal Variability Increased Arctic Amplification During 1980–2022. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL106060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, W.N.; Stroeve, J. An Updated Assessment of the Changing Arctic Sea Ice Cover. Oceanography 2022, 35, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shupe, M.D.; Rex, M.; Blomquist, B.; Persson, P.O.G.; Schmale, J.; Uttal, T.; Althausen, D.; Angot, H.; Archer, S.; Bariteau, L.; et al. Overview of the MOSAiC expedition: Atmosphere. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2022, 10, 00060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, B.; Heuzé, C.; Regnery, J.; Aksenov, Y.; Allerholt, J.; Athanase, M.; Bai, Y.; Basque, C.; Bauch, D.; Baumann, T.M.; et al. Overview of the MOSAiC expedition: Physical oceanography. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2022, 10, 00062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaus, M.; Perovich, D.K.; Spreen, G.; Granskog, M.A.; von Albedyll, L.; Angelopoulos, M.; Anhaus, P.; Arndt, S.; Belter, H.J.; Bessonov, V.; et al. Overview of the MOSAiC expedition: Snow and sea ice. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2022, 10, 000046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunke, E.; Lipscomb, W. CICE: The Los Alamos Sea Ice Model Documentation and Software User’s Manual Version 4.0 LA-CC-06-012; Tech. Rep. LA-CC-06-012; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thorndike, A.S.; Rothrock, D.A.; Maykut, G.A.; Colony, R. The thickness distribution of sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. (1896–1977) 1975, 80, 4501–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Zhang, L.; Hu, S.; Qian, S. Multi-Aspect Assessment of CMIP6 Models for Arctic Sea Ice Simulation. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Jin, J.; Cao, J.; He, J.; Yu, Y.; Gao, X.; Song, M.; et al. Influence of New Parameterization Schemes on Arctic Sea Ice Simulation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L. Review of Sea Ice Albedo Parameterizations. Adv. Earth Sci. 2010, 25, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sturm, M.; Holmgren, J.; Perovich, D.K. Winter snow cover on the sea ice of the Arctic Ocean at the Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean (SHEBA): Temporal evolution and spatial variability. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2002, 107, SHE 23-1–SHE 23-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maykut, G.A.; Untersteiner, N. Some results from a time-dependent thermodynamic model of sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. (1896–1977) 1971, 76, 1550–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunke, E.; Allard, R.; Bailey, D.; Blain, P.; Craig, T.; Damsgaard, A.; Dupont, F.; DuVivier, A.; Grumbine, R.; Holland, M.; et al. CICE Consortium/Icepack Version 1.1.0; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens-Sewall, D.; Smith, M.M.; Holland, M.M.; Polashenski, C.; Perovich, D. Snow redistribution onto young sea ice: Observations and implications for climate models. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2022, 10, 00115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plante, M.; Lemieux, J.F.; Tremblay, L.B.; Tivy, A.; Angnatok, J.; Roy, F.; Smith, G.; Dupont, F. Using Icepack to reproduce Ice Mass Balance buoy observations in landfast ice: Improvements from the mushy layer thermodynamics. Cryosphere 2024, 18, 1708–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Lei, R.; Yu, X. Simulation error diagnosis of the seasonal evolution of sea ice thickness during MOSAiC in-situ observation. Haiyang Xuebao 2024, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunke, E.; Allard, R.; Bailey, D.A.; Blain, P.; Craig, A.; Dupont, F.; DuVivier, A.; Grumbine, R.; Hebert, D.; Holland, M.; et al. CICE-Consortium/Icepack: Icepack Version 1.4.1; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Vihma, T.; Johansson, M.; Bian, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, H. Model experiments on snow and ice thermodynamics in the Arctic Ocean with CHINARE 2003 data. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, C09020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Kauker, F.; Yang, Q.; Han, B.; Fang, Y.; Liu, C. Effects of Freezing Temperature Parameterization on Simulated Sea-Ice Thickness Validated by MOSAiC Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL108281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, I.A.; Perovich, D.K.; Polashenski, C.M.; Clemens-Sewall, D.; Itkin, P.; Lei, R.; Nicolaus, M.; Regnery, J.; Smith, M.M.; Webster, M.; et al. Sea ice mass balance during the MOSAiC drift experiment: Results from manual ice and snow thickness gauges. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2024, 12, 00040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.; Wilkinson, J.; Maksym, T.; Meldrum, D.; Beckers, J.; Haas, C.; Mackenzie, D. A Novel and Low-Cost Sea Ice Mass Balance Buoy. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 2676–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Cheng, B.; Hoppmann, M.; Zuo, G. Snow Depth and Sea Ice Thickness Derived from the Measurements of SIMBA Buoys Deployed in the Arctic Ocean During the Legs 1a, 1, and 3 of the MOSAiC Campaign in 2019–2020. PANGAEA 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinke, A.; Cassano, J.J.; Cassano, E.N.; Jaiser, R.; Handorf, D. Meteorological conditions during the MOSAiC expedition: Normal or anomalous? Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2021, 9, 00023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppmann, M.; Kuznetsov, I.; Fang, Y.C.; Rabe, B. Mesoscale observations of temperature and salinity in the Arctic Transpolar Drift: A high-resolution dataset from the MOSAiC Distributed Network. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4901–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, M.A.; Holland, M.; Wright, N.C.; Hendricks, S.; Hutter, N.; Itkin, P.; Light, B.; Linhardt, F.; Perovich, D.K.; Raphael, I.A.; et al. Spatiotemporal evolution of melt ponds on Arctic sea ice: MOSAiC observations and model results. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2022, 10, 000072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehaus, H.; Spreen, G.; Birnbaum, G.; Istomina, L.; Jäkel, E.; Linhardt, F.; Neckel, N.; Fuchs, N.; Nicolaus, M.; Sperzel, T.; et al. Sea Ice Melt Pond Fraction Derived From Sentinel-2 Data: Along the MOSAiC Drift and Arctic-Wide. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2022GL102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Ahuir, E.G.; Wang, Z. Optimized sea ice simulation in MITgcm-ECCO2 forced by ERA5. Ocean Model. 2023, 183, 102183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.M.; Cohen, L.; Ritzhaupt, N.; Segger, B.; Graversen, R.G.; Rinke, A.; Walden, V.P.; Granskog, M.A.; Hudson, S.R. Evaluation of Six Atmospheric Reanalyses over Arctic Sea Ice from Winter to Early Summer. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 4121–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Graham, R.M.; Wang, K.; Gerland, S.; Granskog, M.A. Comparison of ERA5 and ERA-Interim near-surface air temperature, snowfall and precipitation over Arctic sea ice: Effects on sea ice thermodynamics and evolution. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 1661–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briegleb, B.P.; Light, B. A Delta-Eddington Mutiple Scattering Parameterization for Solar Radiation in the Sea Ice Component of the Community Climate System Model; Technical Report; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bitz, C.M.; Lipscomb, W.H. An energy-conserving thermodynamic model of sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1999, 104, 15669–15677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltham, D.L.; Untersteiner, N.; Wettlaufer, J.S.; Worster, M.G. Sea ice is a mushy layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L14501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, O.; Fichefet, T.; Flocco, D.; Schroeder, D.; Vancoppenolle, M. Interactions between wind-blown snow redistribution and melt ponds in a coupled ocean–sea ice model. Ocean Model. 2015, 87, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flocco, D.; Feltham, D.L. A continuum model of melt pond evolution on Arctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2007, 112, C08016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunke, E.C.; Hebert, D.A.; Lecomte, O. Level-ice melt ponds in the Los Alamos sea ice model, CICE. Arct. Ocean 2013, 71, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, Z.D.; Perlwitz, J.; Butler, A.H.; Manney, G.L.; Newman, P.A.; Lee, S.H.; Nash, E.R. The Remarkably Strong Arctic Stratospheric Polar Vortex of Winter 2020: Links to Record-Breaking Arctic Oscillation and Ozone Loss. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Yang, Q.; Kauker, F.; Liu, C.; Hao, G.; Yang, C.Y.; Liu, J.; Heil, P.; Li, X.; Han, B. The sensitivity of landfast sea ice to atmospheric forcing in single-column model simulations: A case study at Zhongshan Station, Antarctica. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.N.; Shupe, M.D.; Cox, C.; Persson, O.G.; Uttal, T.; Frey, M.M.; Kirchgaessner, A.; Schneebeli, M.; Jaggi, M.; Macfarlane, A.R.; et al. Snowfall and snow accumulation during the MOSAiC winter and spring seasons. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 2373–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeit, M.; Ganopolski, A. The importance of snow albedo for ice sheet evolution over the last glacial cycle. Clim. Past 2018, 14, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofsteenge, M. Evaluation of 1D and 3D Simulations with CICE: Sea Ice thermodynamics and Dynamics During the SHEBA Expedition; Zenodo: Genève, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polashenski, C.; Perovich, D.; Courville, Z. The mechanisms of sea ice melt pond formation and evolution. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117, C01001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).