Effects of River Input on the Inorganic Nitrogen Components in Estuary–Bay Waters: Zhanjiang Bay, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
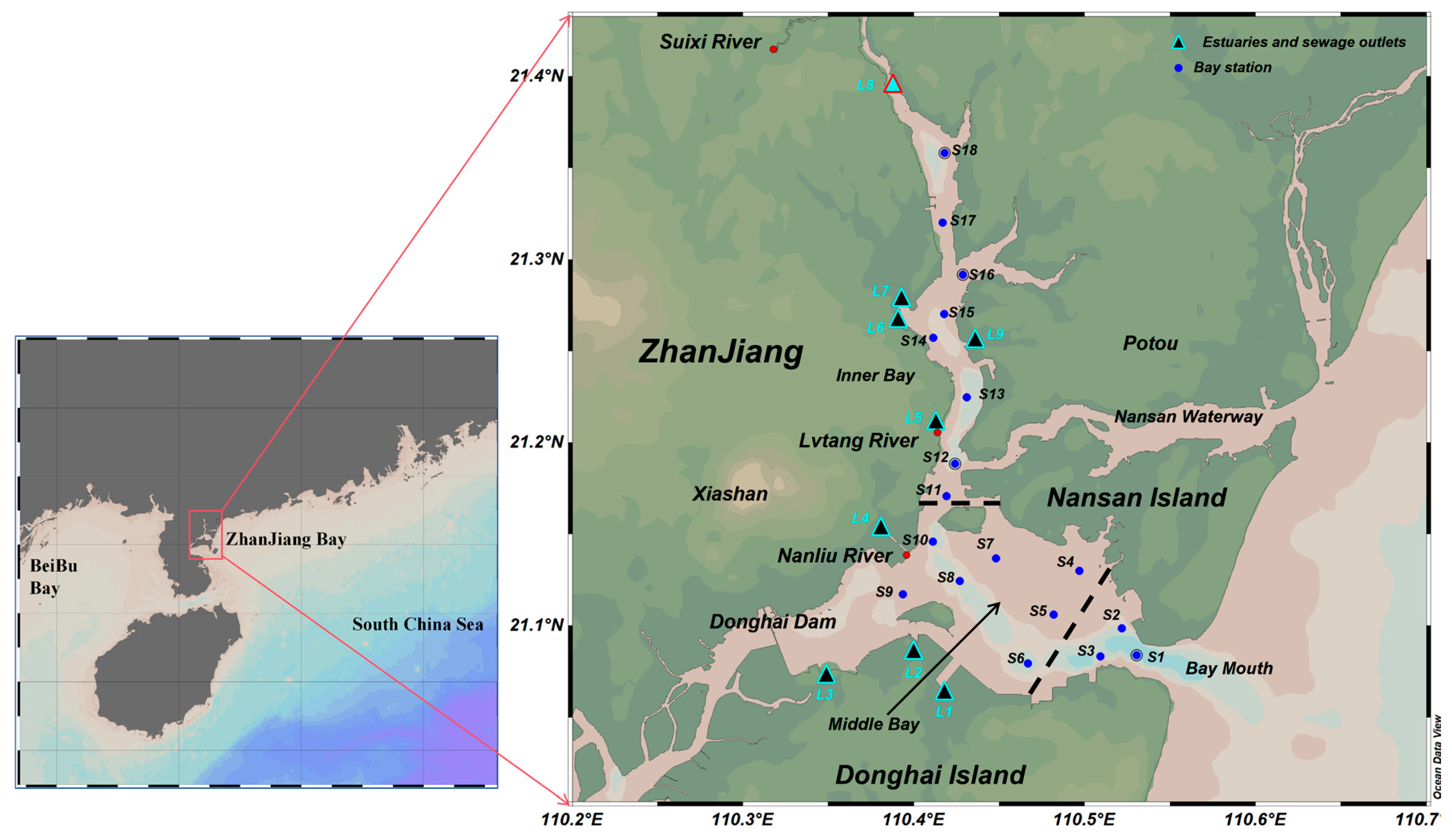
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Sampling and Measurement
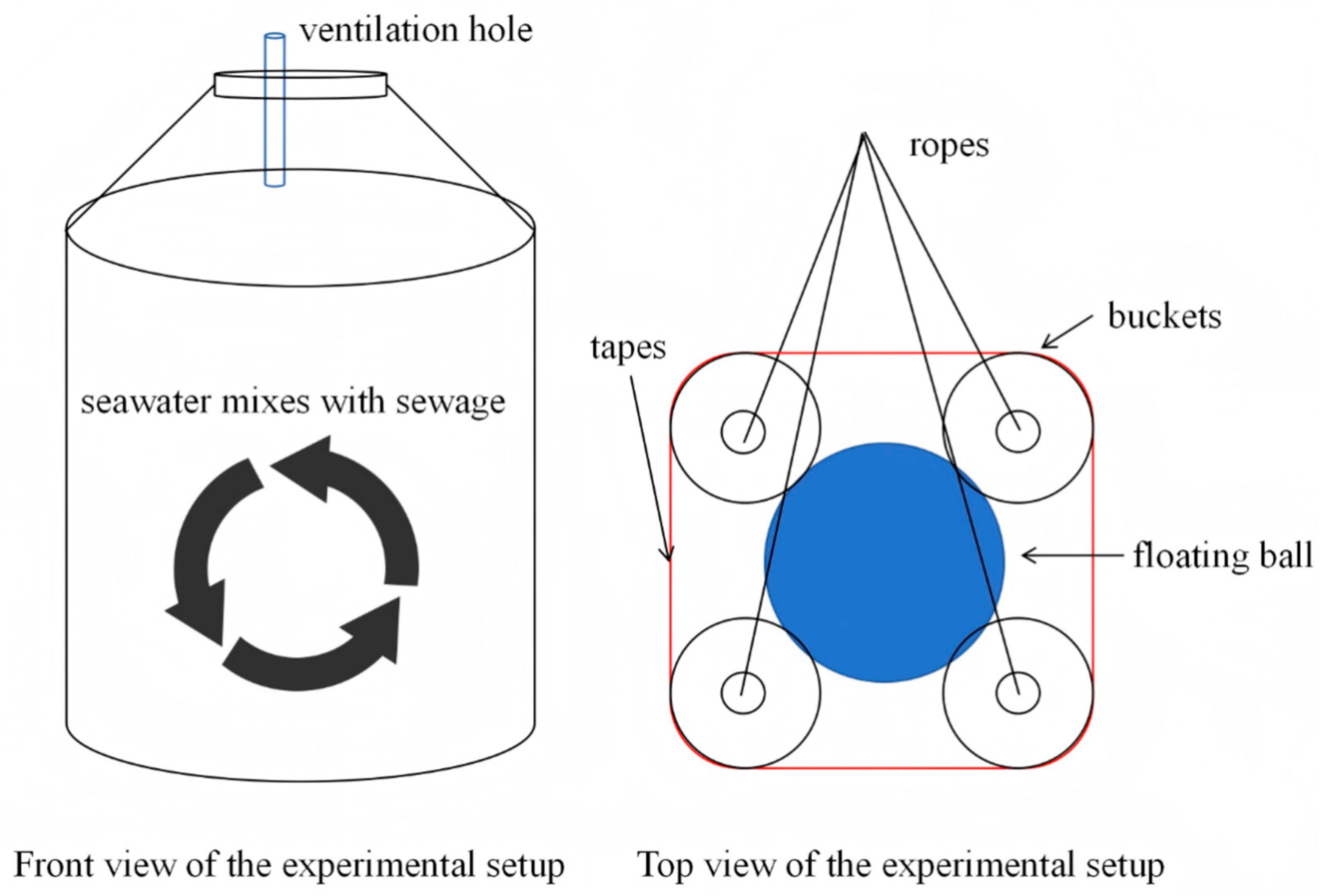
2.3. Experiment of Nutrient Transport and Change Under Different Salinities
2.4. Research Data Processing Methods
2.4.1. The Calculation Method for the Flux of Nitrogen Input from Land to the Ocean
2.4.2. Data Statistics and Analysis Methods
3. Results
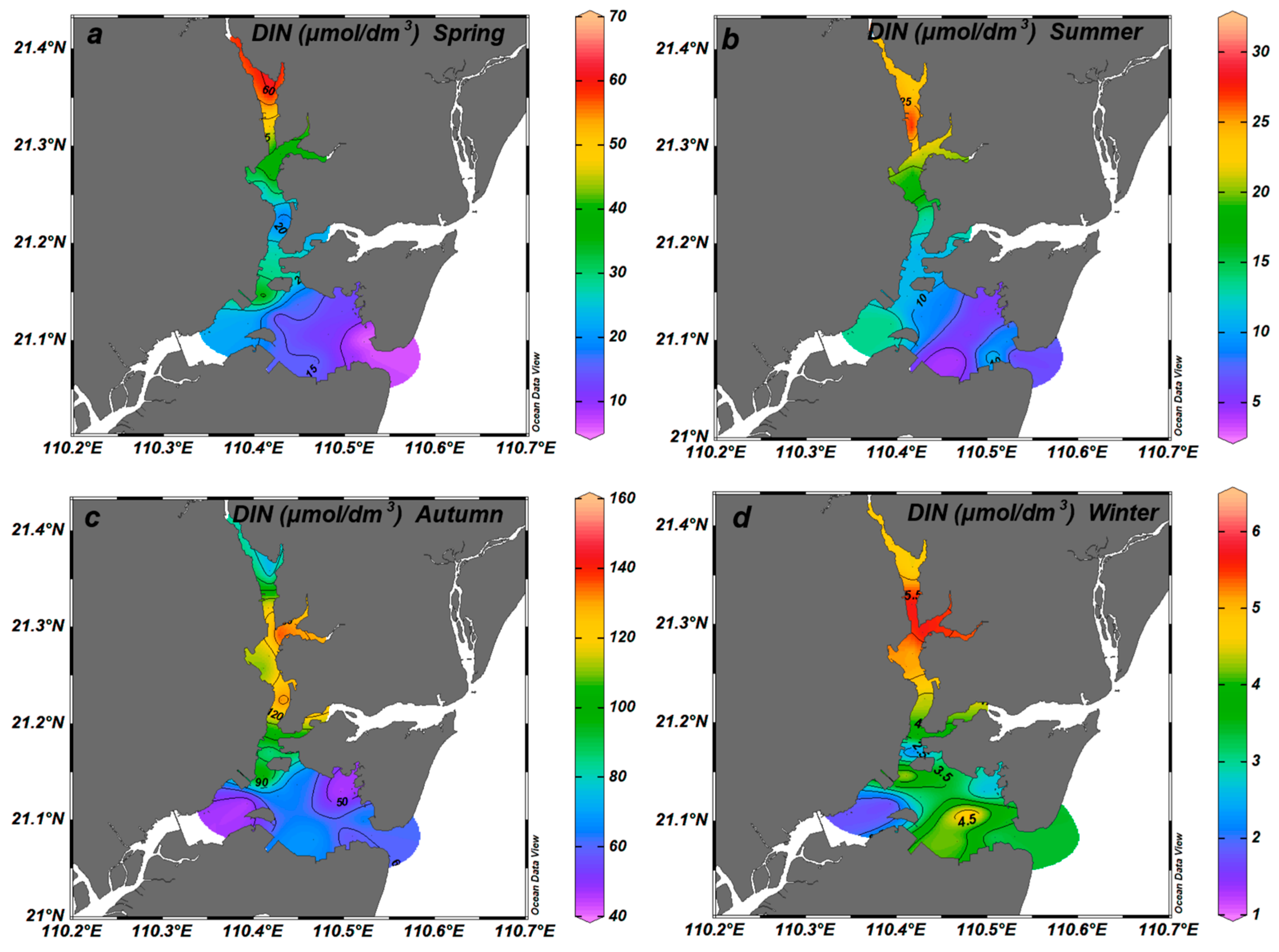
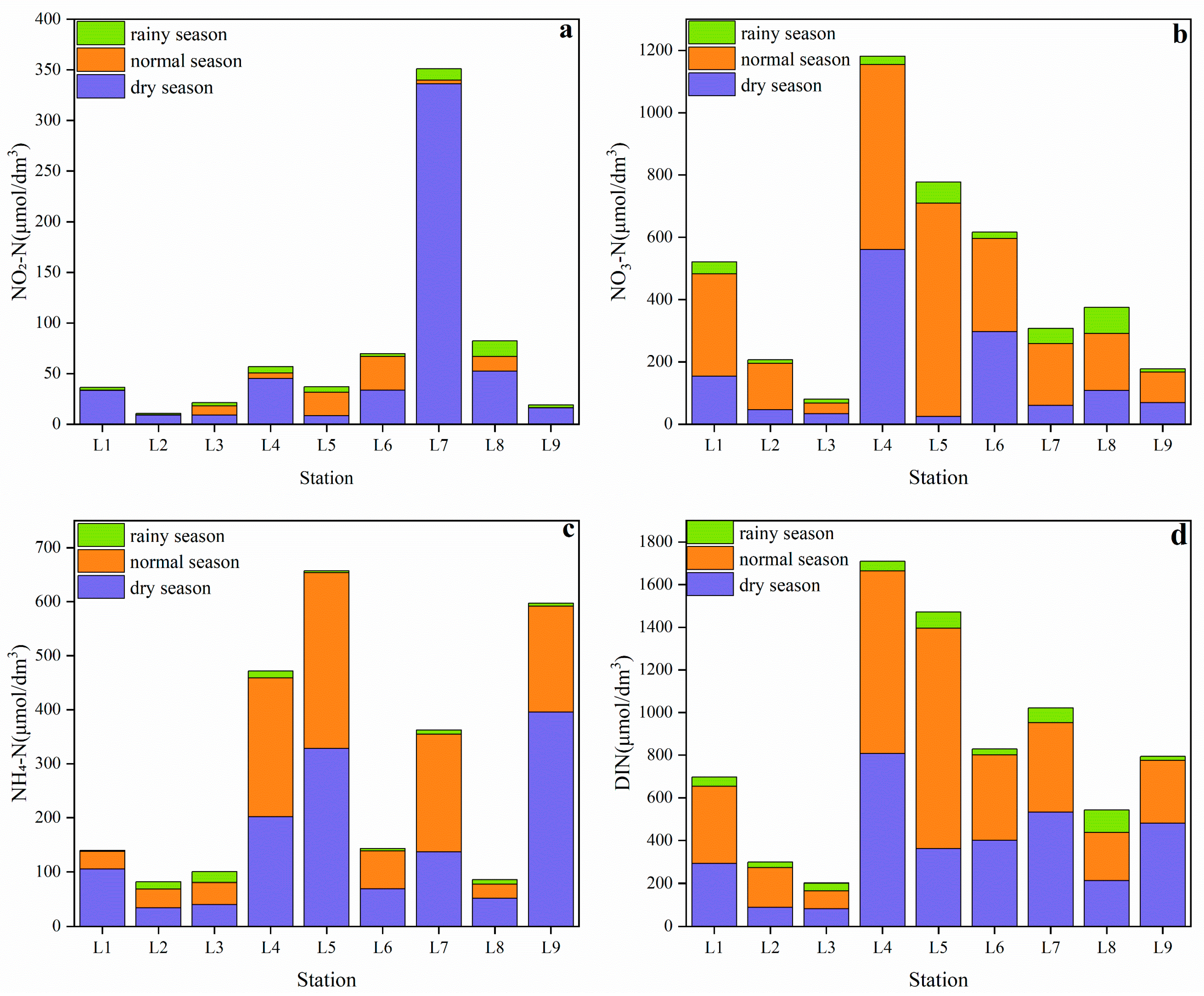
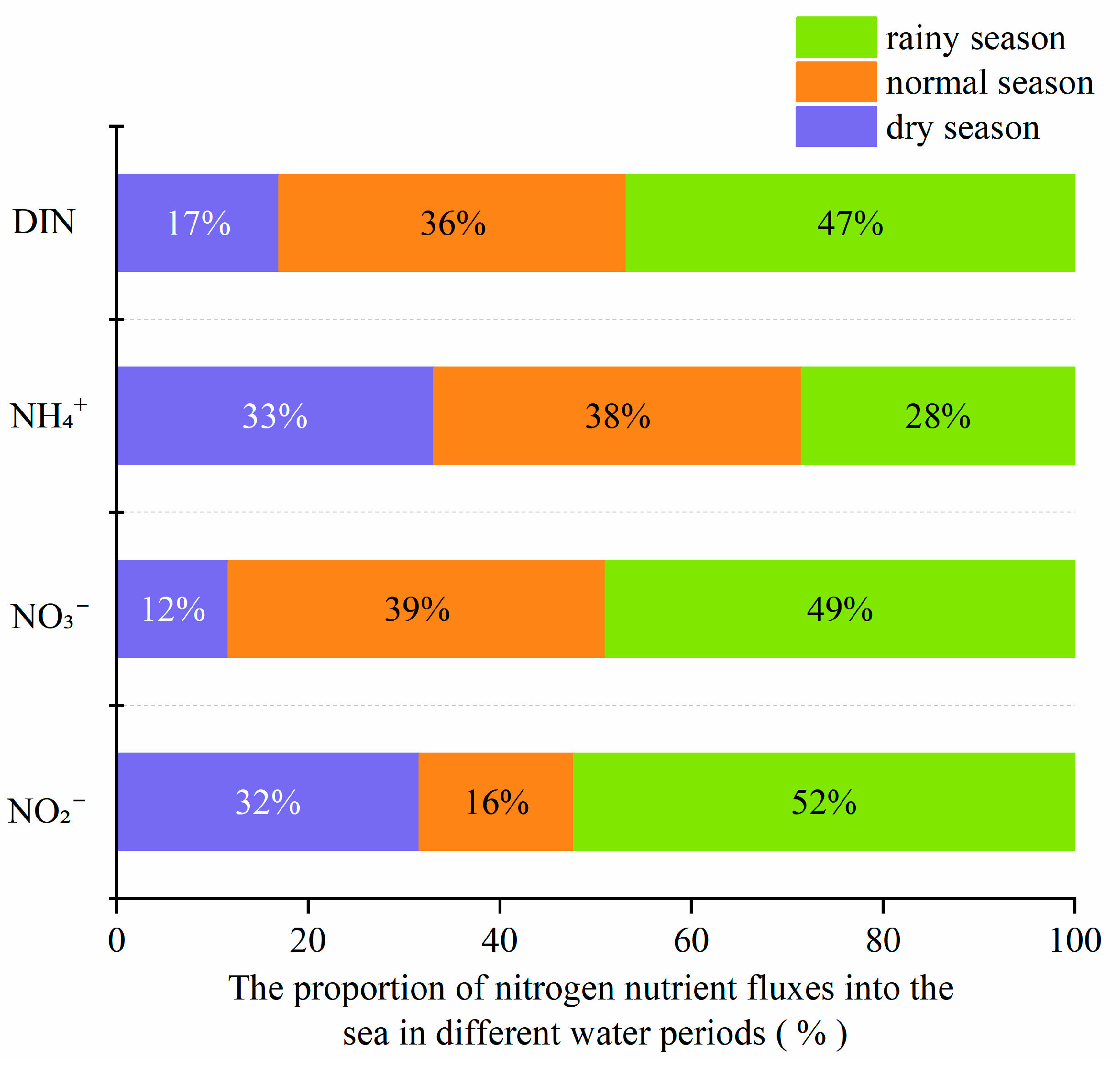
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Inorganic Nitrogen Components
3.2. The Variation in DIN Contents Under Different Salinity Conditions
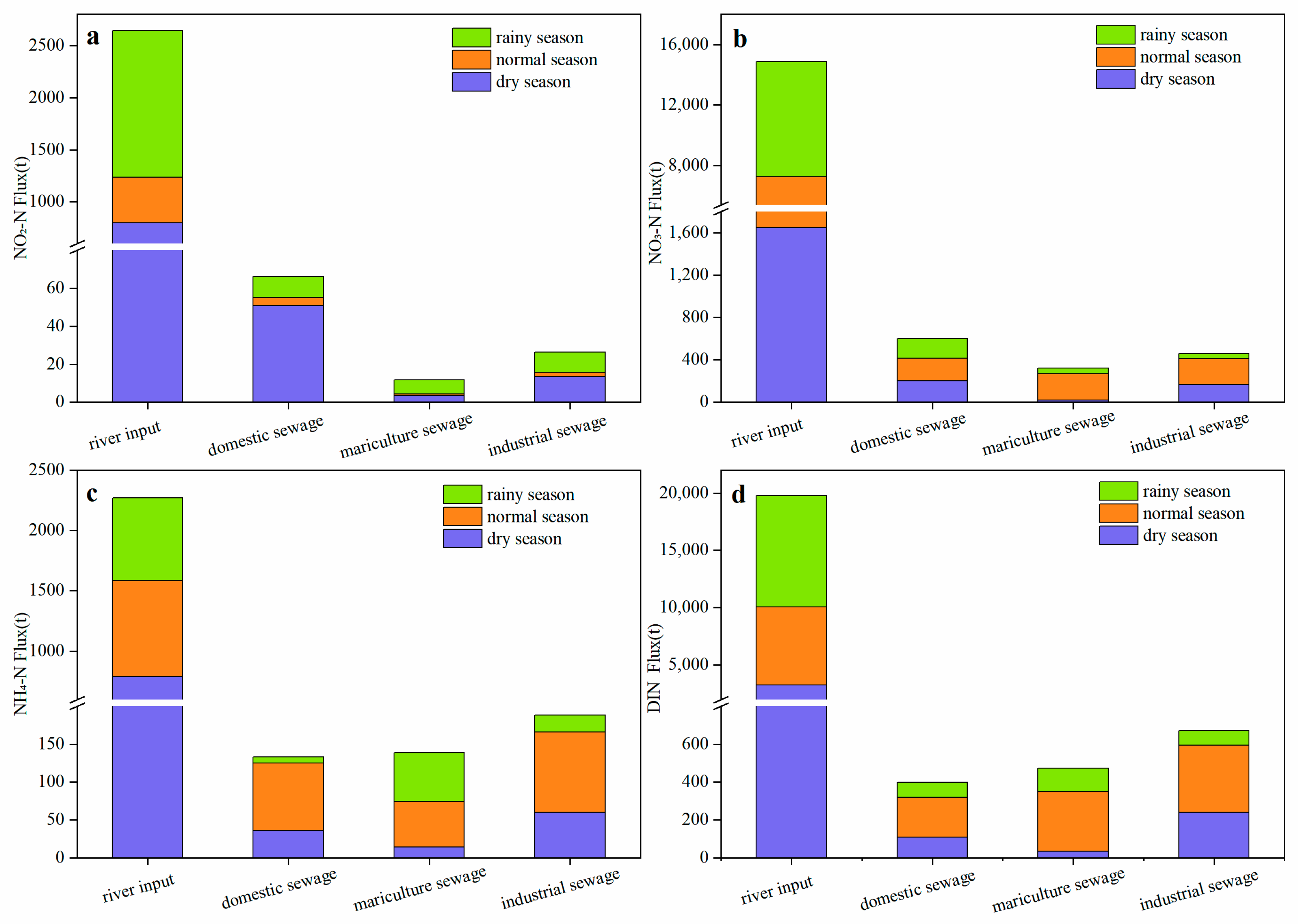
3.3. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Terrestrial Nitrogen Input
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonal Dynamics of DIN and Its Comparison with Other Coastal Waters, Both Domestically and Internationally
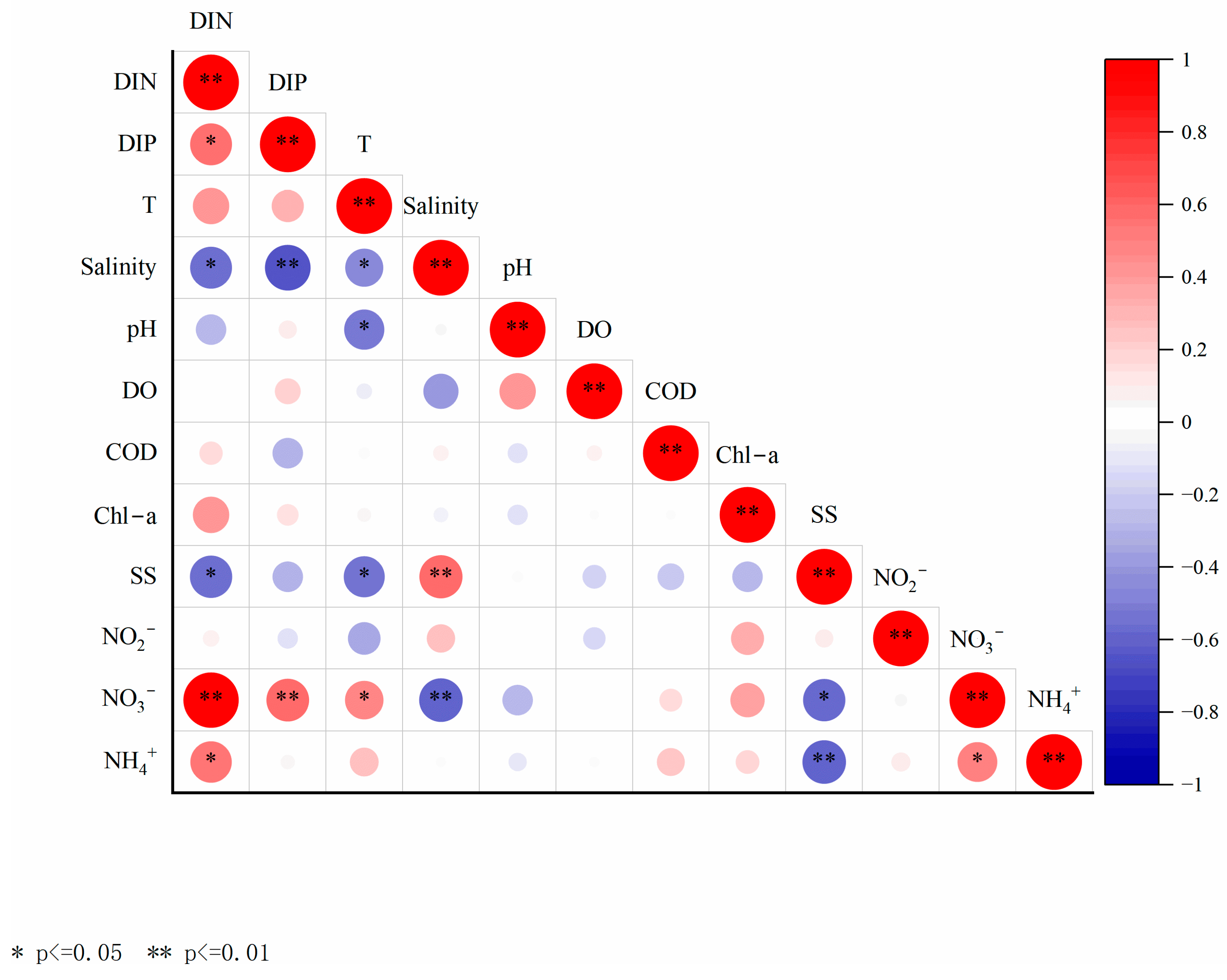
4.2. Migration, Change, and Influencing Factors of Nitrogen in Estuary–Bay Systems
4.3. Multi-Process Analysis of Nitrogen Migration and Transformation in Zhanjiang Bay
4.4. Recommendations for Environmental Governance of the Bay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, Z.; Feng, T.; Meng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Shao, S.; Sun, W. Impacts of Coastal Nutrient Increases on the Marine Ecosystem in the East China Sea During 1982–2012: A Coupled Hydrodynamic-Ecological Modeling Study. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2025, 130, e2024JC021553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, D.A.; Capone, D.G. The marine nitrogen cycle: New developments and global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, S.; Hu, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y. In-field nutrient enrichment experiments in Sanggou Bay kelp farming. Oceanol. Limnol. 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Deng, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Long, C.; Lu, C.; Wang, D.; et al. Unveiling the eutrophication crisis: 20 years of nutrient development in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1373716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lai, J.; Peng, D.; Ke, S.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal variation, composition, and implications for transport flux of nitrogen in Leizhou Peninsula coastal water, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2024, 275, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, F.; Chen, M.; Chen, N.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, D.; Gan, J.; Guan, D.; Hong, Y.; et al. Persistent eutrophication and hypoxia in the coastal ocean. Camb. Prism. Coast. Futures 2023, 1, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yao, Q.; Mi, T.; Wei, Q.; Chen, H.; Yu, Z. Change of the Long-Term Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Changjiang (Yangtze) River Estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 885311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czapla, K.M.; Owens, M.S.; Cornwell, J.C.; Senn, D.B.; Francis, C.A.; Chelsky, A. Microbial Nitrogen Removal in South San Francisco Bay: Does It Play a Role in Eutrophication Resistance? Estuaries Coasts 2025, 48, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Dong, Y.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, W.D.; Lu, S.H.; Ou, L.J. From human-driven eutrophication to effective management: Controlling brown tides in the coastal waters of Qinhuangdao, China. Harmful Algae. 2025, 150, 102997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, P.; Yang, F. Assessing the atmospheric deposition of inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus over the Yellow Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2025, 89, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, P.; Elliott, E.; Gilbertson, L.M. Estimating Daily Nitrate Loads in Iowa Streams Using a Partial Least Squares Regression Framework. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2025, 61, e70036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Feng, P.; Cong, P.; Tao, G.; Liu, H.; Duan, W. Spatial-temporal distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients and potential eutrophication assessment in Bohai Bay, China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2025, 267, 107741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Song, J.; Dai, J.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Yuan, H.; Duan, L.; Wang, Q. Nutrient characteristics driven by multiple factors in large estuaries during summer: A case study of the Yangtze River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Ma, Y.; Long, G.; He, H.; Li, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wan, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, B. Evaluation of water quality pollution and analysis of vertical distribution characteristics of typical Rivers in the Pearl River Delta, South China. J. Sea Res. 2023, 193, 102380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, C.; Sheng, Y. Fluxes of chemical oxygen demand and nutrients in coastal rivers and their influence on water quality evolution in the Bohai Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 52, 102322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ruan, H.; Dai, P.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal river flux and composition of nutrients affecting adjacent coastal water quality in Hainan Island, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.; Erler, D.V.; Rosentreter, J.; Wells, N.S.; Eyre, B.D. Seasonal and spatial controls on N2O concentrations and emissions in low-nitrogen estuaries: Evidence from three tropical systems. Mar. Chem. 2020, 221, 103779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lei, X.; Yuehua, G.; Zhou, Y.; Han, J.C.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.; Mao, X.Z.; Tang, Z. A novel method of identifying estuary high-nutrient zones for water quality management. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, D.; Yu, Y.; Yan, R.; Li, Y.; Gong, W.; Xiao, K.; Li, S.; Chen, N. Drought reduces nitrogen supply and N2O emission in coastal bays. Water Res. 2024, 266, 122362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Lao, Q.; Chen, F. Changes in fronts regulate nitrate cycling in Zhanjiang Bay: A comparative study during the normal wet season, rainstorm, and typhoon periods. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang-ying, Y.; Wen-bo, Z.; Jin-tao, L.; Jun-yi, T. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution in Zhanjiang Bay, Guangdong Province. Environ. Ecol. 2024, 6, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lao, Q.; Wu, J.; Chen, F.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Q.; Deng, Z.; Li, J. Increasing intrusion of high salinity water alters the mariculture activities in Zhanjiang Bay during the past two decades identified by dual water isotopes. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Lao, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, F. The impact of algal blooms on promoting in-situ N2O emissions: A case in Zhanjiang bay, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 358, 120935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, T.C.; Newton, A. The Globalization of Cultural Eutrophication in the Coastal Ocean: Causes and Consequences. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Olofsson, M.; Boyer, G.L.; Marcarelli, A.M. Salinity adaption and toxicity of harmful algal blooms in three bays of Great Salt Lake (USA). Harmful Algae. 2025, 150, 102959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Whalen, J.K.; Cai, C.; Shan, K.; Zhou, H. Harmful cyanobacteria-diatom/dinoflagellate blooms and their cyanotoxins in freshwaters: A nonnegligible chronic health and ecological hazard. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P. Seasonal variation, spatial distribution, and sources of PAHs in surface seawater from Zhanjiang bay influenced by land-based inputs. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 188, 106028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonghao, S.; Liangwen, J.; Heng, Z.; Yitong, L. Environmental capacity calculation and sewage treatment in Inner Zhanjiang Bay. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2021, 40, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, F.; Song, Z. Changes in net anthropogenic nitrogen input in the watershed region of Zhanjiang Bay in south China from 1978 to 2018. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 17201–17219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, F.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X. Analysis of Dissolved Oxygen and Nutrients in Zhanjiang Bay and the Adjacent Sea Area in Spring. Sustainability 2020, 12, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 50179-93; River Flow Test Gauge. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2005.
- GB/T 12764.4-2-7; Specifications for Oceanographic Surey-Part 4: Survey of Chemical Parameters in Sea Water. AQSIQ: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Shi, Y.; Jia, L.; Zhang, H. Analysis of the water residence time and influencing factors in Zhanjiang Bay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Pan, G.; Zhao, H.; Tian, K. Regulation of winter river input on the nutrient structure of typical tropical bays around Leizhou Peninsula, South China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 256, 107272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Liu, X.; Van Dingenen, R.; Dentener, F.; Yao, Q.; Xu, B.; Ran, X.; Yu, Z.; Bouwman, A.F. Spatially Explicit Inventory of Sources of Nitrogen Inputs to the Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and South China Sea for the Period 1970–2010. Earth’s Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, W.; Luo, L.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Kao, S.J.; Zheng, N.; Li, Q.; et al. Decadal nutrient dynamics in a tropical bay: Spatiotemporal variations and drivers in Haikou Bay and adjacent coastal waters (2010–2021). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 221, 118499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Peng, C.; Dai, P.; Lai, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal variation, composition of DIN and its contribution to eutrophication in coastal waters adjacent to Hainan Island, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 37, 101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; He, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Q.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Linking water quality with the total pollutant load control management for nitrogen in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzburg, M.; Scholten, J.; Hsu, F.-H.; Liebetrau, V.; Sültenfuß, J.; Rapaglia, J.; Schlüter, M. Submarine Groundwater Discharge-Derived Nutrient Fluxes in Eckernförde Bay (Western Baltic Sea). Estuaries Coasts 2023, 46, 1190–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Shi, X.; Han, X.; Tang, H. Spatial-temporal variation of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) and impacts of water mass on the reserves estimation of the total DIN content in the Yellow Sea. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 1642–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Xiao, W.; Zhou, P.; Tian, C.; Zhang, C.; Du, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, B. Coastal eutrophication in China: Trend, sources, and ecological effects. Harmful Algae. 2021, 107, 102058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, S.; Ren, Y.; Yang, J.; Song, X.; Huang, X.; He, D. Terrestrial and Biological Activities Shaped the Fate of Dissolved Organic Nitrogen in a Subtropical River-Dominated Estuary and Adjacent Coastal Area. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2023, 128, e2023JC019911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, W.; Felix Dan, S.; Yang, B.; Kang, Z.; Yu, K. Sources and long-term variation characteristics of dissolved nutrients in Maowei Sea, Beibu Gulf, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 615, 128576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, S.; Mizuno, K. Long-term trends in eutrophication in the inner part of Tokyo Bay, Japan, from 1998 to 2023. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2025, 85, 104153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damar, A.; Colijn, F.; Hesse, K.-J.; Adrianto, L.; Yonvitner, Y.; Fahrudin, A.; Kurniawan, F.; Prismayanti, A.D.; Rahayu, S.M.; Rudianto, B.Y.; et al. Phytoplankton Biomass Dynamics in Tropical Coastal Waters of Jakarta Bay, Indonesia in the Period between 2001 and 2019. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormaza-González, F.I.; Campi-Alvarez, P.A.; Cárdenas-Condoy, J.W.; Caiza-Quinga, R.J.; Statham, P.J. Further evidence for increasing global near-shore eutrophication from the Estero Salado, Guayaquil, Ecuador. Cont. Shelf Res. 2024, 278, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgulet, D.; Lopez, C.V.; Douglas, A.R.; Eissa, M.; Das, K. Nitrogen and carbon cycling and relationships to radium behavior in porewater and surface water: Insight from a dry year sampling in a hypersaline estuary. Mar. Chem. 2024, 258, 104351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Cheng, T.; Song, J.; Zhou, J.; Hung, C.-C.; Cai, Z. Internal nutrient loading is a potential source of eutrophication in Shenzhen Bay, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.R.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Yue, W.; Wu, M.; Wang, Y. Developing a salinity-based approach for the evaluation of DIN removal rate in estuarine ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Niu, L.; Dong, Y.; Fu, T.; Lou, Q. Nutrient Pollution and Its Dynamic Source-Sink Pattern in the Pearl River Estuary (South China). Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 713907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, S.; Yao, Q.; Yin, C. Influence of Salinity on Microbial Community in Activated Sludge and Its Application in Simulated Dye Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 2972–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yu, C.; Han, Y.; Tang, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Hu, L. Research progress in microbial treatment of high-salinity industrial organic wastewater. Microbiol. China 2023, 50, 1720–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Ding, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Cui, Z.; Sun, J.; Wei, Y. River inflow and seawater intrusion shape distinct phytoplankton communities in jinghai bay, a coastal bay of the Yellow Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 210, 107309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H. Spatial distribution of the summer chlorophyll a and nutrients in the Pearl River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 220, 118479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, P.; He, J.; Jia, G. Progress in the study of marine stable nitrogen isotopic changes and its geological records. Adv. Earth Sci. 2020, 35, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhou, P.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Feng, Y. Research progress on nitrogen biogeochemical processes in coastal groundwater. Environ. Chem. 2024, 43, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G. Novel nitrogen cycles in terrestrial and freshwater ecosystems. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2020, 60, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Zhao, L. Tracing external sources of nutrients in the East China Sea and evaluating their contributions to primary production. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 176, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Dong, H.; Chen, F.; Hou, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Z.; Ling, W. Abundance, Diversity, and Distribution of Denitrifier and Anammox Bacteria in Zhanjiang Bay Sediments. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2020, 51, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Hu, N.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Sheng, Y. Estuarine fine particles enhance nitrogen elevation and nutritional imbalance in coastal and offshore waters. J. Hydrol. 2025, 659, 133179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Pu, L.; Wang, S.; Vogt, R.D.; Lu, X. Riverine fluxes of dissolved inorganic nitrogen may be underestimated in gated estuaries: Influence of suspended sediments. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; van Prooijen, B.C.; Zhu, C.; Guo, L.; He, Q.; Wang, Z.B.; Yang, Q. Deepening and narrowing impacts on circulation, stratification, and sediment transport in the Changjiang Estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1598417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, M.; Zheng, C.; Li, H. Submarine groundwater discharge and associated nutrient fluxes in the Greater Bay Area, China revealed by radium and stable isotopes. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Peng, D.; Shi, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J. Seasonal Total Nitrogen and Phosphorus Variation, Speciation, and Composition in the Maowei Sea Affected by Riverine Flux Input, South China Sea. Water 2022, 14, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangdong Province Marine Functional Zoning (2011–2020); Guangdong Provincial People’s Government: Guangzhou, China, 2013.
- GB 3097-1997; Sea Water Quality Standard. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 1998.
- Department of Ecological Environment in Guangdong Province. 14th Five-Year Plan for Marine Ecological Environment Protection in Guangdong Province; Department of Ecological Environment in Guangdong Province: Guangzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Su, Y.; Liang, S.-k.; Li, K.-q.; Li, Y.-b.; Wang, X.-l. Assessment of long-term water quality variation affected by high-intensity land-based inputs and land reclamation in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Lan, W.; Li, T.; Hong, M.; Peng, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.; Jiang, H. Control of phytoplankton by oysters and the consequent impact on nitrogen cycling in a Subtropical Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 149007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

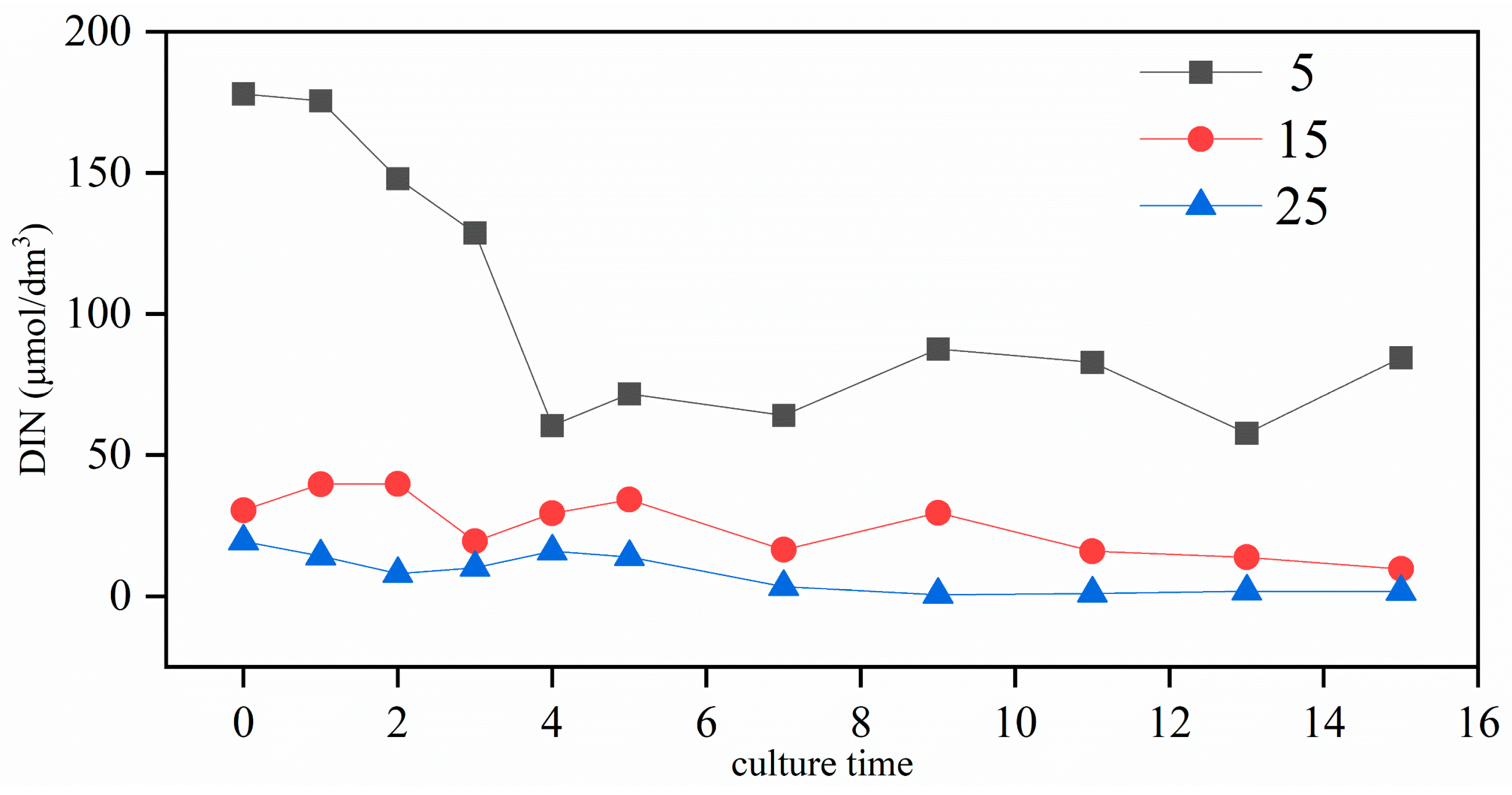

| 5 | 15 | 25 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIN | −16.3 ± 8.22 | −2.00 ± 4.33 | −2.29 ± 1.89 |
| NO2-N | −0.774 ± 0.997 | −0.095 ± 0.122 | −0.076 ± 0.062 |
| NO3-N | −13.4 ± 7.49 | −1.48 ± 0.826 | −2.12 ± 1.73 |
| NH4-N | −2.11 ± 2.43 | −0.428 ± 0.493 | −0.112 ± 0.092 |
| Study Area | Sampling Time | DIN | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (μmol/dm3) | Mean (μmol/dm3) | |||
| Changjiang River Estuary | 1984–2016 | 0.714–84.2 | 43.7 | [7] |
| Hainan Island | 2016 | 0.571–27.5 | 8.14 ± 6.21 | [37] |
| Jiaozhou Bay | 2001 | 31.8 ± 18.9 | [38] | |
| 2007 | 48.4 ± 27.4 | [38] | ||
| 2009–2015 | 22.1 ± 2.29 | [38] | ||
| Eckernförde Bay | 2012 | 1.57–496 | 92.9 ± 135 | [39] |
| Yellow Sea | 2013–2016 | 0.214–18.0 | 4.50~7.43 | [40] |
| Bohai Sea | 2019 summer | 0.214–71.6 | 9.00 ± 10.9 | [41] |
| 2019 winter | 1.07–96.7 | 13.9 ± 13.7 | [41] | |
| Pearl River Estuary | 2019–2020 | 0.643–220.7 | 80.0 ± 39.3 | [42] |
| Maowei Sea | 2011–2017 | 26.0 ± 11.4 | [43] | |
| Qinzhou Port | 2011–2017 | 20.1 ± 17.2 | [43] | |
| Tokyo Bay | 1998–2023 | 27.9–275 | 107 ± 2.14 | [44] |
| Jakarta Bay | 2019 | 89.3 ± 32.0 | [45] | |
| Gulf of Guayaquil | 2016–2022 | 39.5–2616 | >300 | [46] |
| Baffin Bay | 2016 | 9.70 ± 9.30 | [47] | |
| Shenzhen Bay | 2018–2019 | >35.7 | [48] | |
| Zhanjiang Bay | 2021 | 1.50–151 | 26.9 ± 36.4 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, F.; Chen, Z.-L.; Zeng, Y.-Y.; Yang, G.-H.; Zhang, J.-B.; Zhang, P.; Fu, M.-J. Effects of River Input on the Inorganic Nitrogen Components in Estuary–Bay Waters: Zhanjiang Bay, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122312
Yue F, Chen Z-L, Zeng Y-Y, Yang G-H, Zhang J-B, Zhang P, Fu M-J. Effects of River Input on the Inorganic Nitrogen Components in Estuary–Bay Waters: Zhanjiang Bay, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(12):2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122312
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Fei, Zi-Liang Chen, Ying-Ying Zeng, Guo-Huan Yang, Ji-Biao Zhang, Peng Zhang, and Miao-Jian Fu. 2025. "Effects of River Input on the Inorganic Nitrogen Components in Estuary–Bay Waters: Zhanjiang Bay, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 12: 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122312
APA StyleYue, F., Chen, Z.-L., Zeng, Y.-Y., Yang, G.-H., Zhang, J.-B., Zhang, P., & Fu, M.-J. (2025). Effects of River Input on the Inorganic Nitrogen Components in Estuary–Bay Waters: Zhanjiang Bay, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(12), 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122312





