A Comparison of Methods of Visual Census and Cryptobenthic Fish Collecting, an Integrative Approach to the Qualitative and Quantitative Composition of the Mediterranean Temperate Reef Fish Assemblages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
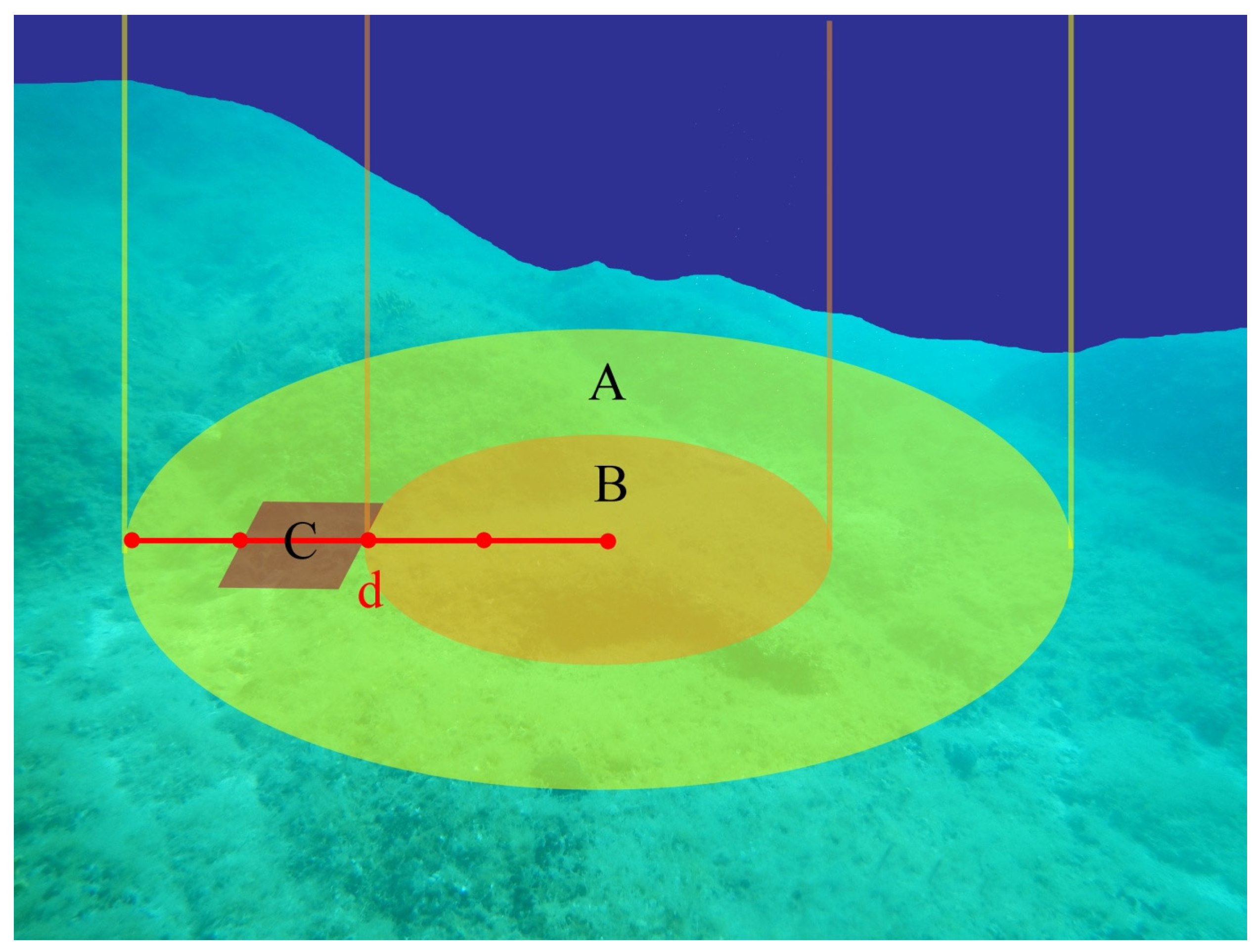
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Design
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
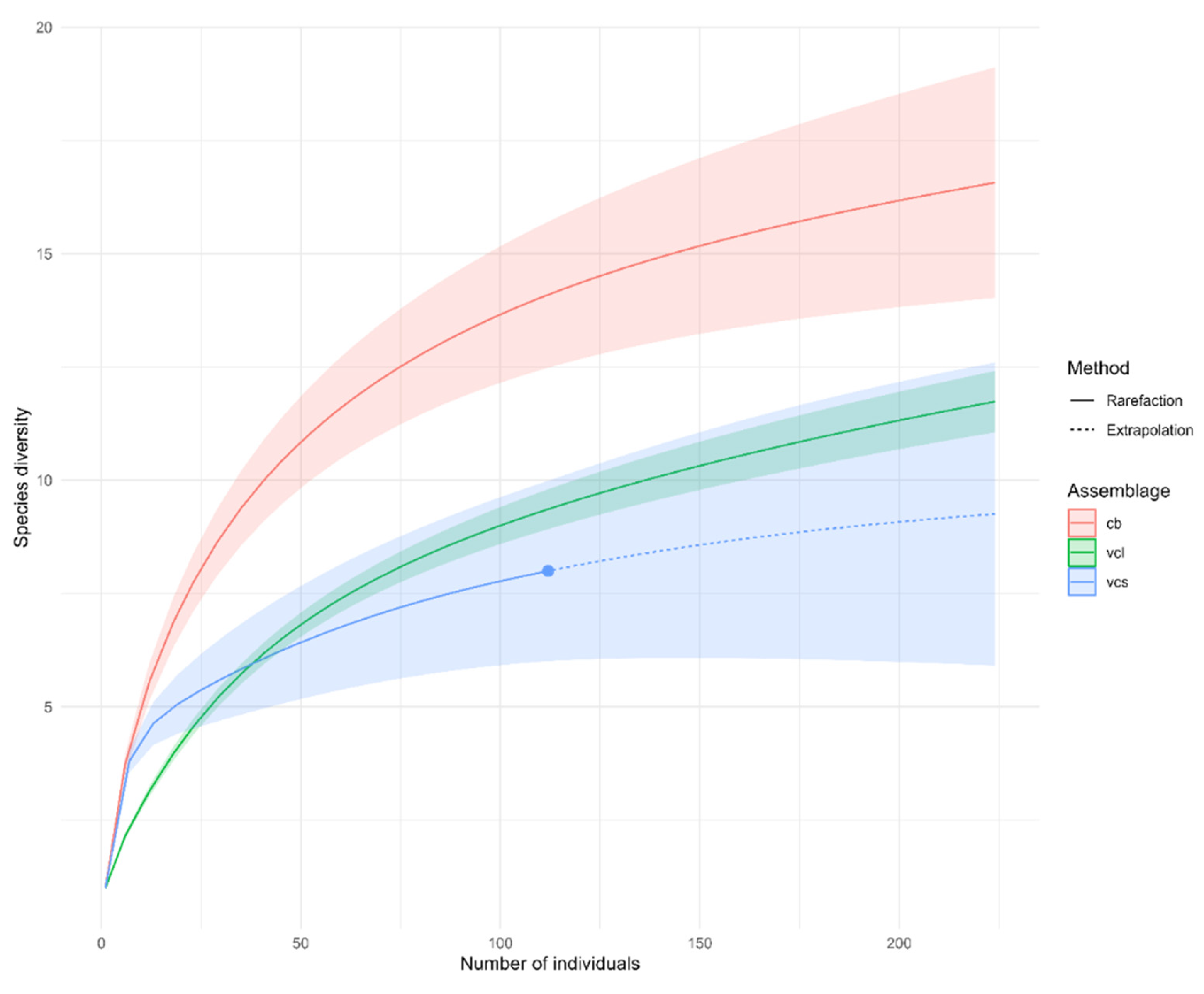
3.1. Diversity of Fish Species
3.2. Total Fish Abundance
3.3. Fish Assemblage Structure and Fish Species Abundance and Frequency
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watson, D.L.; Harvey, E.S.; Anderson, M.J.; Kendrick, G.A. A comparison of temperate reef fish assemblages recorded by three underwater stereo-video techniques. Mar. Biol. 2005, 148, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, V.E. A preliminary report on a method of estimating reef fish populations. J. Wildl. Manag. 1954, 18, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmelin-Vivien, M.L.; Harmelin, J.G. Présentation d’une méthode d’évaluation in situ de la faune ichtyologique. Parc Natl. Port-Cros Trav. Sci. Port-Cros 1975, 1, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Harmelin-Vivien, M.L.; Harmelin, J.G.; Chauvet, C.; Duval, C.; Galzin, R.; Lejeune, P.; Barnabe, G.; Blanc, F.; Chevalier, R.; Duclerc, J.; et al. Evaluation visuelle des peuplements et populations de poissons méthodes et problèmes. Rev. Écol. (Terre Vie) 1985, 40, 467–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, R.E. A critique of the visual census method for assessing coral reef fish populations. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1982, 32, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman, J.L.; Bellwood, D.R. Reef fish assemblages: A reevaluation using enclosed rotenone stations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 206, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, T. Visual census methods underestimate density and diversity of cryptic reef fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 1408–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Vaniz, W.F.; Jelks, H.L.; Rocha, L.A. Relevance of cryptic fishes in the biodiversity assessments: A case study at Buck Island Reef National Monument, St. Croix. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2006, 79, 17–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačić, M.; Patzner, R.A.; Schliewen, U.K. A first quantitative assessment of the ecology of cryptobenthic fishes in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 2731–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzate, A.; Zapata, F.A.; Giraldo, A. A comparison of visual and collection-based methods for assessing community structure of coral reef fishes in the Tropical Eastern Pacific. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2014, 62 (Suppl. S1), 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beldade, R.; Goncalves, E.J. An interference visual census technique applied to cryptobenthic fish assemblages. Vie Milieu 2007, 57, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoldi, C.; De Girolamo, M. Littoral fish community of the Island Lampedusa (Italy): A visual census approach. Ital. J. Zool. 1998, 65 (Suppl. S1), 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldo, A.; Glavičić, I.; Kovačić, M. Combining Methods to Better Estimate Total Fish Richness on Temperate Reefs: The Case of a Mediterranean Coralligenous Cliff. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minte-Vera, C.V.; de Moura, R.L.; Francini-Filho, R.B. Nested sampling: An improved visual-census technique for studying reef fish assemblages. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 367, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnsack, J.A.; Bannerot, S.P. A Stationary Visual Census Technique for Quantitatively Assessing Community Structure of Coral Reef Fishes; NOAA Technical Report NMFS; U.S. Department of Commerce, National Technical Information Service: Springfield, VA, USA, 1986; Volume 41, pp. 1–15.
- Tiralongo, F. Blennies of the Mediterranean Sea: Biology and identification of Blenniidae, Clinidae, Tripterygiidae; Amazon Fulfillment Poland Sp. z o.o.: Wroclaw, Poland, 2020; p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačić, M.; Renoult, J.P.; Pillon, R.; Svensen, R.; Bogorodsky, S.V.; Engin, S.; Louisy, P. Identification of Mediterranean marine gobies (Actinopterygii: Gobiidae) of the continental shelf from photographs of in situ individuals. Zootaxa 2022, 5144, 1–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Ma, K.H.; Chao, A. iNEXT: An R package for rarefaction and extrapolation of species diversity (Hill numbers). Methods Ecol. Evol. 1987, 7, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez Arbizu, P. pairwiseAdonis: Pairwise multilevel comparison using adonis. R Package Version 001. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/pmartinezarbizu/pairwiseAdonis (accessed on 1 December 2017).
- Field, J.G.; Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. A practical strategy for analysing multispecies distribution pattern. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1982, 8, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, E.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M. The trouble with stress: A flexible method for the evaluation of nonmetric multidimensional scaling. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2018, 16, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Càceres, M.; Legendre, P. Associations between species and groups of sites: Indices and statistical inference. Ecology 2009, 90, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufrene, M.; Legendre, P. Species Assemblages and Indicator Species: The Need for a Flexible Asymmetrical Approach. Ecol. Monogr. 1997, 67, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O‘Hara, R.G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package Version 2.5-7. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Glavičić, I.; Paliska, D.; Soldo, A.; Kovačić, M. A quantitative assessment of the cryptobenthic fish assemblage at deep littoral cliffs in the Mediterranean. Sci. Mar. 2016, 80, 329–337. [Google Scholar]
- Glavičić, I.; Kovačić, M.; Soldo, A.; Schliewen, U. A quantitative assessment of the diel influence on the cryptobenthic fish assemblage of the shallow Mediterranean infralittoral zone. Sci. Mar. 2020, 84, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačić, M.; Glavičić, I.; Paliska, D.; Valić, Z. A first qualitative and quantitative study of marine cave fish assemblages of intracave cavities. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 263, 107624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmelin, J.-G. Structure et variabilite de l‘ichtyofaune d‘une zone rocheuse protegee en Mediterranee (Pare national de Port-Cros, France). Mar. Ecol. 1987, 8, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francour, P.; Harmelin-Vivien, M.; Harmelin, J.G.; Duclerc, J. Impact of Caulerpa taxifolia colonization on the littoral ichthyofauna of North-Western Mediterranean Sea: Preliminary results. Hydrobiologia 1995, 300–301, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, P. Differences among Fish Assemblages Associated with Nearshore Posidonia oceanica Seagrass Beds, Rocky–algal Reefs and Unvegetated Sand Habitats in the Adriatic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 50, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Charton, J.A.; Pérez-Ruzafa, Á. Spatial pattern and the habitat structure of a Mediterranean rocky reef fish local assemblage. Mar. Biol. 2001, 138, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Pais, A.; Consoli, P.; Andaloro, F. Evaluating day–night changes in shallow Mediterranean rocky reef fish assemblages by visual census. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, M.; Mazzoldi, C. The application of visual census on Mediterranean rocky habitats. Mar. Environ. Res. 2001, 51, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.D. Effects of Depth and Marine Reserve Fishing Restrictions on the Structure of a Rocky Reef Fish Assemblage in the North-Western Mediterranean Sea. J. Appl. Ecol. 1983, 20, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ResearchGate. ResearchGate GmbH. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Orlando-Bonaca, M.; Lipej, L. Factors affecting habitat occupancy of fish assemblage in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Mar. Ecol. 2005, 26, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordines, F.; Moranta, J.; Palmer, M.; Lerycke, A.; Suau, A.; Morales-Nin, B.; Grau, A.M. Variations in a shallow rocky reef fish community at different spatial scales in the western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 304, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Giakoumi, S.; Kokkoeis, G.D. Effects of habitat and substrate complexity on shallow sublittoral fish assemblages in the Cyclades Archipelago, North-eastern Mediterranean sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2013, 14, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species | Number of Individuals | Abundance (Individuals/m2) | Frequency of Occurrence (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recorded species from the VCL method | |||
| Boops boops (Linnaeus, 1758) | 96 | 0.0382 | 8% |
| Chromis chromis (Linnaeus, 1758) | 2960 | 1.1783 | 94% |
| Coris julis (Linnaeus, 1758) | 179 | 0.0713 | 98% |
| Diplodus annularis (Walbaum, 1792) | 143 | 0.0569 | 26% |
| Diplodus puntazzo (Walbaum, 1792) | 9 | 0.0036 | 14% |
| Diplodus sargus (Valenciennes, 1830) | 4 | 0.0016 | 10% |
| Diplodus vulgaris (Geoffroy St. Hilaire, 1817) | 110 | 0.0438 | 80% |
| Mullus surmuletus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 3 | 0.0012 | 6% |
| Oblada melanura (Linnaeus, 1758) | 17 | 0.0068 | 8% |
| Sarpa salpa (Linnaeus, 1758) | 5 | 0.0020 | 6% |
| Scorpaena porcus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 2 | 0.0008 | 6% |
| Seriola dumerili (Risso, 1810) | 1 | 0.0004 | 4% |
| Serranus cabrilla (Linnaeus, 1758) | 7 | 0.0028 | 14% |
| Serranus scriba (Linnaeus, 1758) | 20 | 0.0080 | 30% |
| Sparus aurata (Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | 0.0004 | 4% |
| Spicara maena (Linnaeus, 1758) | 45 | 0.0179 | 16% |
| Spicara smaris (Linnaeus, 1758) | 96 | 0.0382 | 6% |
| Spondyliosoma cantharus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 9 | 0.0036 | 12% |
| Symphodus cinereus (Bonnaterre, 1788) | 1 | 0.0004 | 4% |
| Symphodus mediterraneus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 9 | 0.0036 | 16% |
| Symphodus melanocercus (Risso, 1810) | 1 | 0.0004 | 4% |
| Symphodus ocellatus (Forsskål, 1775) | 16 | 0.0064 | 18% |
| Symphodus tinca (Linnaeus, 1758) | 3 | 0.0012 | 8% |
| Recorded species from the VCS method | |||
| Gobius auratus (Risso, 1810) | 30 | 0.0478 | 24% |
| Gobius fallax (Sarato, 1889) | 19 | 0.0303 | 20% |
| Gobius geniporus (Valenciennes, 1837) | 3 | 0.0048 | 8% |
| Gobius incognitus (Kovačić & Šanda, 2016) | 1 | 0.0016 | 4% |
| Gobius roulei (de Buen, 1928) | 2 | 0.0032 | 6% |
| Gobius vittatus (Vinciguerra, 1883) | 31 | 0.0494 | 38% |
| Parablennius rouxi (Cocco, 1833) | 25 | 0.0398 | 32% |
| Tripterygion delaisi (Cadenat & Blache, 1970) | 1 | 0.0016 | 4% |
| Recorded species from the CB method | |||
| Chromis chromis (Linnaeus, 1758) | 6 | 0.12 | 10% |
| Chromogobius zebratus (Kolombatović, 1891) | 6 | 0.12 | 12% |
| Corcyrogobius liechtensteini (Kolombatović, 1891) | 18 | 0.36 | 18% |
| Marcelogobius splechtnai (Ahnelt & Patzner, 1995) | 3 | 0.06 | 6% |
| Gaidropsarus mediterraneus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | 0.02 | 4% |
| Gobius auratus (Risso, 1810) | 7 | 0.14 | 12% |
| Gobius fallax (Sarato, 1889) | 15 | 0.3 | 22% |
| Gobius vittatus (Vinciguerra, 1883) | 26 | 0.52 | 36% |
| Grammonus ater (Risso, 1810) | 1 | 0.02 | 4% |
| Lepadogaster candolii (Risso, 1810) | 6 | 0.12 | 12% |
| Millerigobius macrocephalus (Kolombatović, 1891) | 19 | 0.38 | 26% |
| Odondebuenia balearica (Pellegrin and Fage, 1907) | 135 | 2.7 | 80% |
| Parablennius rouxi (Cocco, 1833) | 7 | 0.14 | 14% |
| Scorpaena notata (Rafinesque, 1810) | 2 | 0.04 | 6% |
| Symphodus ocellatus (Forsskål, 1775) | 1 | 0.02 | 4% |
| Thorogobius macrolepis (Kolombatović, 1891) | 1 | 0.02 | 4% |
| Tripterygion delaisi (Cadenat & Blache, 1970) | 4 | 0.08 | 8% |
| Zebrus zebrus (Risso, 1827) | 72 | 1.44 | 68% |
| Method | m | SC | qD | qD.LCL | qD.UCL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCL | 224 | 0.923 | 11.7 | 11.0 | 12.4 |
| VCS | 224 | 0.994 | 9.26 | 5.5 | 13.1 |
| CB | 224 | 0.924 | 16.6 | 14.2 | 12.9 |
| Source of Variation | Df | MS | Pseudo-F | p (Perm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | ||||
| Locality | 2 | 0.251 | 2.825 | 0.0317 * |
| Method | 2 | 7.137 | 80.236 | 0.0001 *** |
| Season | 1 | 0.226 | 3.034 | 0.0508 |
| (b) | ||||
| Locality | 2 | 0.513 | 2.313 | 1 × 10−4 *** |
| Locality: Method | 6 | 2.467 | 27.71 | 1 × 10−4 *** |
| (c) | ||||
| Locality: Method, CB vs. VCS | 5 | 2.706 | 42.965 | 1 × 10−4 *** |
| Locality: Method, CB vs. VCL | 5 | 0.842 | 9.0415 | 1 × 10−4 *** |
| Locality: Method, VCS vs. VCL | 5 | 1.241 | 11.265 | 1 × 10−4 *** |
| Source of Variation | Df | MS | Pseudo-F | p (Perm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | ||||
| Depth | 1 | 0.011 | 3.105 | 0.010 ** |
| Inclination | 1 | 0.006 | 1.773 | 0.105 |
| Sand | 1 | 0.004 | 1.113 | 0.343 |
| Gravel | 1 | 0.004 | 1.271 | 0.249 |
| Cobbles | 1 | 0.004 | 1.137 | 0.334 |
| Boulders | 1 | 0.005 | 1.439 | 0.192 |
| Bedrock | 1 | 0.009 | 2.582 | 0.025 * |
| Bottom layers | 1 | 0.005 | 1.243 | 0.279 |
| Short thallus algae | 1 | 0.002 | 0.513 | 0.827 |
| Calcareous algae | 1 | 0.099 | 1.288 | 0.222 |
| Zoocover | 1 | 0.006 | 1.774 | 0.091 |
| No biocover | 1 | 0.005 | 1.627 | 0.131 |
| (b) | ||||
| Locality | 2 | 0.039 | 5.437 | 0.001 *** |
| Method | 2 | 0.471 | 65.695 | 0.001 *** |
| Season | 1 | 0.005 | 1.450 | 0.173 |
| (c) | ||||
| Locality | 2 | 0.041 | 5.981 | 0.001 *** |
| Locality: Method | 6 | 0.516 | 25.028 | 0.001 *** |
| (d) ZL | ||||
| Locality: Method, CB vs. VCS | 1 | 0.266 | 11.576 | 0.001 *** |
| Locality: Method, CB vs. VCL | 1 | 0.559 | 43.133 | 0.001 *** |
| (e) TA | ||||
| Locality: Method, CB vs. VCS | 1 | 0.294 | 12.914 | 0.001 *** |
| Locality: Method, CB vs. VCL | 1 | 0.618 | 54.996 | 0.001 *** |
| (f) GO | ||||
| Locality: Method, CB vs. VCS | 1 | 0.372 | 11.271 | 0.001 *** |
| Locality: Method, CB vs. VCL | 1 | 0.640 | 46.405 | 0.001 *** |
| R Value | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Locality: Method | 0.780 | 1 × 10−4 *** |
| Locality: Method, CB vs. VCS | 0.546 | 1 × 10−4 *** |
| Locality: Method, CB vs. VCL | 0.921 | 1 × 10−4 *** |
| CB vs. VCS | CB vs. VCL | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Species | % | Species | % |
| Odondebuenia balearica | 24.2 | Chromis chromis | 30.1 |
| Zebrus zebrus | 15.5 | Coris julis | 14.0 |
| Gobius vittatus | 11.0 | Odondebuenia balearica | 10.5 |
| Parablennius rouxi | 8.8 | Diplodus vulgaris | 8.7 |
| Gobius auratus | 7.7 | Zebrus zebrus | 6.8 |
| Gobius fallax | 6.7 | Gobius vittatus | 2.8 |
| Millerigobius macrocephalus | 4.2 | Diplodus annularis | 2.5 |
| Corcyrogobius liechtensteini | 3.0 | Millerigobius macrocephalus | 2.0 |
| Chromogobius zebratus | 1.6 | Serranus scriba | 1.9 |
| Lepadogaster candolii | 1.5 | Spicara maena | 1.8 |
| Species | Indicator Value | p |
|---|---|---|
| VCL | ||
| Coris julis | 0.900 | 0.0001 *** |
| Chromis chromis | 0.848 | 0.0001 *** |
| Diplodus vulgaris | 0.725 | 0.0001 *** |
| Serranus scriba | 0.382 | 0.0001 *** |
| Symphodus mediterraneus | 0.267 | 0.0114 * |
| Diplodus annularis | 0.253 | 0.0004 *** |
| Serranus cabrilla | 0.248 | 0.0270 * |
| Symphodus ocellatus | 0.247 | 0.0200 * |
| Diplodus puntazzo | 0.233 | 0.0257 * |
| Spicara maena | 0.227 | 0.0137 * |
| CB (vs. VCL) | ||
| Odondebuenia balearica | 0.732 | 0.0001 *** |
| Zebrus zebrus | 0.651 | 0.0001 *** |
| Gobius vittatus | 0.423 | 0.0001 *** |
| Millerigobius macrocephalus | 0.352 | 0.0003 *** |
| Gobius fallax | 0.320 | 0.0019 ** |
| Corcyrogobius liechtensteini | 0.270 | 0.0054 ** |
| Parablennius rouxi | 0.248 | 0.0286 * |
| VCS | ||
| Parablennius rouxi | 0.335 | 0.0018 ** |
| Gobius auratus | 0.260 | 0.0110 * |
| CB (vs. VCS) | ||
| Odondebuenia balearica | 0.732 | 0.0001 *** |
| Zebrus zebrus | 0.651 | 0.0001 *** |
| Millerigobius macrocephalus | 0.352 | 0.0009 *** |
| Corcyrogobius liechtensteini | 0.270 | 0.0098 ** |
| Reference | Number of Identified Cryptobenthic Species | Number of Identified Small (≤10 cm) Epibenthic Species | Both Categories Sum as the Percentage of the Total Recorded Species Richness * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual census studies | |||
| Bell [36] | 0 | 2 | 5.7% |
| Harmelin [30] | 0 | 7 | 14.9% |
| Francour et al. [31] | 0 | 5 | 15.2% |
| Guidetti [32] | 0 | 4 | 11.8% |
| De Girolamo & Mazzoldi [35] | 0 | 6 | 25.0% |
| Ordines et al. [39] | 0 | 0 | 0.0% |
| García-Charton & Pérez-Ruzafa [33] | 0 | 0 | 0.0% |
| Orlando-Bonaca & Lipej [38] | 0 | 11 | 29.7% |
| Azzurro et al. [34] | 0 | 6 | 14.3% |
| Giakoumi & Kokkoeis [40] | 0 | 0 | 0.0% |
| Studies with qualitatively combined data | |||
| Mazzoldi and De Girolamo [12] | 6 | 14 | 26.0% |
| Soldo et al. [13] | 22 | 13 | 39.4% |
| Present research | 18 | 8 | 45.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovačić, M.; Glavičić, I.; Paliska, D.; Soldo, A.; Valić, Z. A Comparison of Methods of Visual Census and Cryptobenthic Fish Collecting, an Integrative Approach to the Qualitative and Quantitative Composition of the Mediterranean Temperate Reef Fish Assemblages. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12040644
Kovačić M, Glavičić I, Paliska D, Soldo A, Valić Z. A Comparison of Methods of Visual Census and Cryptobenthic Fish Collecting, an Integrative Approach to the Qualitative and Quantitative Composition of the Mediterranean Temperate Reef Fish Assemblages. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(4):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12040644
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovačić, Marcelo, Igor Glavičić, Dejan Paliska, Alen Soldo, and Zoran Valić. 2024. "A Comparison of Methods of Visual Census and Cryptobenthic Fish Collecting, an Integrative Approach to the Qualitative and Quantitative Composition of the Mediterranean Temperate Reef Fish Assemblages" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 4: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12040644
APA StyleKovačić, M., Glavičić, I., Paliska, D., Soldo, A., & Valić, Z. (2024). A Comparison of Methods of Visual Census and Cryptobenthic Fish Collecting, an Integrative Approach to the Qualitative and Quantitative Composition of the Mediterranean Temperate Reef Fish Assemblages. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(4), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12040644







