Essential and Non-Essential Elemental Composition and Health Risks in Pacific Sardine in the Northwest Pacific Ocean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Pre-Treatment and Instrumental Measurement
2.3. Quality Control and Assurance
2.4. Age and Fatness
2.4.1. Assessment of Biological Age
2.4.2. Degree of Fish Fatness
2.5. Health Risk Evaluation
2.5.1. Estimated Daily Intake
2.5.2. Target Hazard Quotient
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Elements in S. sagax
3.2. Correlation between Elements
3.3. Influence of Biosignatures on Elemental Fate
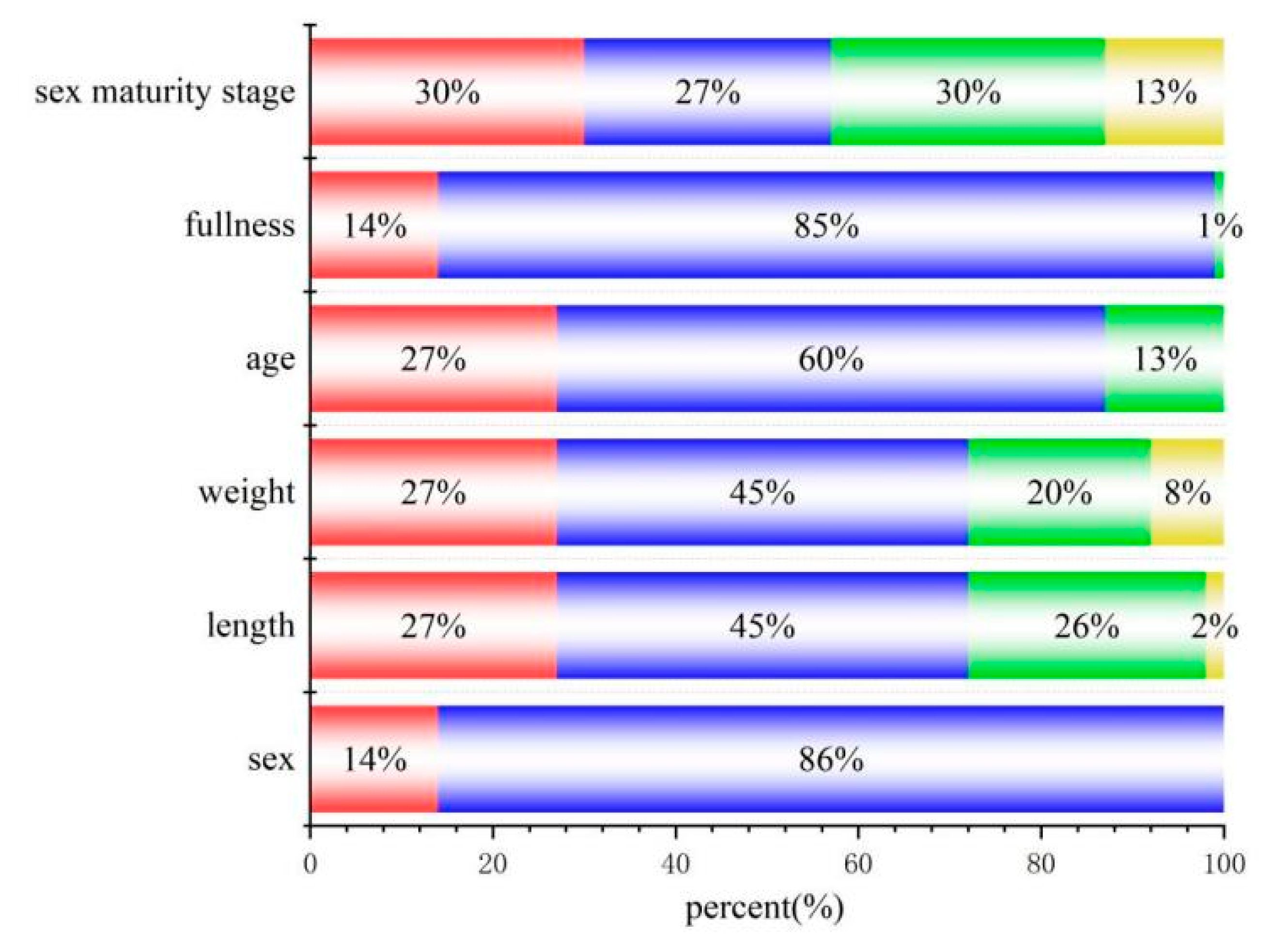
3.3.1. Biological Properties of S. sagax
3.3.2. Relationship between Biological Factors and Elements
3.4. Health Risk Assessment for Consumption
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowe, C.E.; Figueira, W.; Raubenheimer, D.; Solon-Biet, S.M.; Machovsky-Capuska, G.E. Effects of temperature on macronutrient selection, metabolic and swimming performance of the Indo-Pacific Damselfish (Abudefduf vaigiensis). Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, R.; Benbi, D.K.; Reichl, F.X.; Nieder, R.; Benbi, D.K.; Reichl, F.X. Macro-and secondary elements and their role in human health. In Soil Components and Human Health; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 257–315. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-024-1222-2_6 (accessed on 9 February 2024).
- Annasawmy, P.; Bustamante, P.; Point, D.; Churlaud, C.; Romanov, E.V.; Bodin, N. Trace elements and δ15N values in micronekton of the south-western Indian Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, S.; Yoo, J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, J.W.; Jung, J. Effect of salinity on acute copper and zinc toxicity to Tigriopus japonicus: The difference between metal ions and nanoparticles. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Bilbao, E.; Jurado-Ruzafa, A.; Lozano, G.; Jiménez, S.; Hardisson, A.; Rubio, C.; Weller, D.; Paz, S.; Gutiérrez, A. Development stage and season influence in the metal content of small pelagic fish in the North-West Africa. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, G.; Manzoor, F.; Javid, A.; Azmat, H.; Arshad, M.; Fatima, S. Evaluation of fish health status and histopathology in gills and liver due to metal contaminated sediments exposure. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 100, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.C.; O’Neill, B.; Sigge, G.O.; Kerwath, S.E.; Hoffman, L.C. Heavy metals in marine fish meat and consumer health: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissar, S.; Bakhtiyar, Y.; Arafat, M.Y.; Andrabi, S.; Bhat, A.A.; Yousuf, T. A review of the ecosystem services provided by the marine forage fish. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 2871–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, N.; Lesperance, D.; Albert, R.; Hollanda, S.; Michaud, P.; Degroote, M.; Churlaud, C.; Bustamante, P. Trace elements in oceanic pelagic communities in the western Indian Ocean. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afandi, I.; Talba, S.; Benhra, A.; Benbrahim, S.; Chfiri, R.; Labonne, M.; Masski, H.; Laë, R.; Morais, L.T.D.; Bekkali, M.; et al. Trace metal distribution in pelagic fish species from the north-west African coast (Morocco). Int. Aquat. Res. 2018, 10, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, B.; Çelik, M. Essential elements and contaminants in tissues of commercial pelagic fish from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalini, R.; Jeyasekaran, G.; Shakila, R.J.; Arisekar, U. Trace element concentrations in the organs of fish along the southeast coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 162, 111817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.A.M. Trace element levels in some commercially valuable fish species from coastal waters of Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 73, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughan, D.; Di, D.F.; Hata, H. Sardinops sagax (errata version published in 2019). In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources: Gland, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Kang, B.; Fan, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, S.; Cui, X.; Dai, Y. Spatio-Temporal Variations in the Potential Habitat Distribution of Pacific Sardine (Sardinops sagax) in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Fishes 2023, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, Y.; Tadokoro, K.; Furuichi, S.; Yukami, R. Stronger density-dependent growth of Japanese sardine with lower food availability: Comparison of growth and zooplankton biomass between a historical and current stock-increase period in the western North Pacific. Fish. Res. 2022, 255, 106461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB5009.268-2016; Standard Nazionale per la Determinazione della Sicurezza Alimentare dei Multielementi Negli Alimenti. Ministero dell’Agricoltura della Repubblica Popolare Cinese, Casa Editrice Agricola: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Zhan, B.Y. Fisheries Resource Assessment. Fish. Resour. Assess. 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pauly, D. Gill Size and Temperature as Governing Factors in Fish Growth: A Generalization of Von Bertalanffy’s Growth Formula. 1979. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:97233525 (accessed on 9 February 2024).
- Yang, C.; Zhao, G.Q.; Han, H.B.; Zhang, H.; Shang, C.; Shu, B.; Liu, S.Y.; Jiang, P.W.; Xiang, D.L.; Luo, M.B. Analysis of biological characteristics of Sardinops sagax in the high seas of the northwest Pacific Ocean. Mar. Fish. 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.T.; Amenyogbe, E.; Chen, G.; Huang, J.S. Effects of feed fat level on growth performance, body composition and serum biochemical indices of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus× Epinephelus polyphekadion). Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, O.; Devesa, V.; Suñer, M.A.; Velez, D.; Montoro, R.; Uriera, I.; Macho, M.L.; Jalon, M. Total and inorganic arsenic in fresh and processed fish products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4369–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics: Global Capture Production 1950–2021 (FishStatJ); Food and Agriculture Organization: Québec City, QC, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Traina, A.; Bono, G.; Bonsignore, M.; Falco, F.; Giuga, M.; Quinci, E.M.; Vitale, S.; Sprovieri, M. Heavy metals concentrations in some commercially key species from Sicilian coasts (Mediterranean Sea): Potential human health risk estimation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); Interim Final; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Copat, C.; Arena, G.; Fiore, M.; Ledda, C.; Fallico, R.; Sciacca, S.; Ferrante, M. Heavy metals concentrations in fish and shellfish from eastern Mediterranean Sea: Consumption advisories. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Zaman, M.R. Evaluation of possible health risks of heavy metals by consumption of foodstuffs available in the central market of Rajshahi City, Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 3867–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment); EPA/540/R/99/005; USA Office of Emerage and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, M.J.; Franco, F.; Martinho, F.; Carvalho, L.; Pereira, M.E.; Coelho, J.P.; Pardal, M.A. Essential mineral content variations in commercial marine species induced by ecological and taxonomical attributes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 103, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, J.P.; Machado, J.F.; Pereira, E.; Bustamante, P.; Carvalho, L.; Soares, E.; Stevens, D.W.; Xavier, J.C. Antarctic toothfish Dissostichus mawsoni as a bioindicator of trace and rare earth elements in the Southern Ocean. Chemosphere 2023, 321, 138134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Qin, D.; Mou, Z.; Zhao, J.; Tang, S.; Wu, S.; Gao, L. Trace elements in farmed fish (Cyprinus carpio, Ctenopharyngodon idella and Oncorhynchus mykiss) from Beijing: Implication from feed. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2016, 9, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. Biotransformation of inorganic arsenic in a marine herbivorous fish Siganus fuscescens after dietborne exposure. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maage, A.; Lygren, B.; El-Mowafi, A.F.A. Manganese requirement of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fry. Fish. Sci. 2000, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, T.T.; Xie, J.Q.; Liu, B.L. Progress on trace elements occurrence of marine pelagic fish. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 18, 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.H. The Cooperation and Antagonism between Trace Elements and Nutrients. J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2005, 27, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, J.W.; Hodson, P.V. Effects of diet composition on selenium metabolism in rainbow trout. J. Nutr. 1983, 113, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenawy, N.S.; EL-Hak, H.N.G.; Ghobashy, M.A.; Mansour, F.A.; Soliman, M.F. Using antioxidant changes in liver and gonads of Oreochromis niloticus as biomarkers for the assessment of heavy metals pollution at Sharkia province, Egypt. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 46, 101863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, R.T. Joint Toxicity of Arsenic, Copper and Phenol to Carpsicyprinus carpio Linn. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2001, 7, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.H. Studies on the Speciation of Mercury and Seleniumin the Soft Tissues of Bay Scallops and the Antagonism of Selenium Species to Mercury Species. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2014; pp. 92–93. [Google Scholar]
- Jomova, K.; Makova, M.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Essential metals in health and disease. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 367, 110173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Wu, W.J.; Lin, L.L. Acute toxicity and co-toxicity of heavy metals Cd, Zn to clams (Clamectes edulis). Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2014, 42, 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, K.; Sahrul, M.; Hidaka, H.; Tatsukawa, R. Organ and tissue distribution of heavy metals, and their growth-related changes in Antarctic fish, Pagothenia borchgrevinki. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1983, 47, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, G.; Storelli, A.; Mallamaci, R.; Storelli, M.M. Comparative study on trace metal accumulation in liver of Mediterranean deep-sea fish and their selenium/mercury molar ratios. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2017, 228, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemoto, T.; Kunito, T.; Watanabe, I.; Genta Yasunaga, G.; Baba, N.; Miyazaki, N.; Petrove, E.A.; Tanabe, S. Comparison of trace element accumulation in Baikal seals (Pusa sibirica), Caspian seals (Pusa caspica) and northern fur seals (Callorhinus ursinus). Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lall, S.P.; Kaushik, S.J. Nutrition and metabolism of minerals in fish. Animals 2021, 11, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Erian, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Salem, S.M.; Mohammady, E.Y.; El-Haroun, E.R.; Hassaan, M.S. Evaluation of different copper sources in Nile tilapia diets: Growth, body indices, hematological assay, plasma metabolites, immune, anti-oxidative ability, and intestinal morphometric measurements. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 4900–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, W.J.; Spence, S.K. Biological factors involved in metal concentrations observed in aquatic organisms. Met. Metal. Speciat. Bioavailab. Aquat. Syst. 1995, 3, 407–478. [Google Scholar]
- Khezri, P.H.; Takhsha, M.; Jamshid, K.A.; Haghshenas, A. Assessment level of heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Hg) in four fish species of Persian Gulf (Bushehr-Iran). Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Res. 2014, 4, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Sci. Opin. Arsen. Food Arsen. Food 2009, 7, 1351. [CrossRef]
- Kruglyakova, U.S.; Bagryantseva, O.V.; Evstratova, A.D.; Malinkin, A.D.; Gmoshinskii, I.V.; Khotimchenko, S.A. Separate quontitative determination of organic and non-organic arsenic in sea products. Health Risk Anal. 2018, 2, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgec, A.S.; Kljaković-Gašpić, Z.; Orct, T.; Tičina, V.; Sekovanić, A.; Jurasović, J.; Piasek, M. Mercury and selenium in fish from the eastern part of the Adriatic Sea: A risk-benefit assessment in vulnerable population groups. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Class | Elements | Mean ± SD | Max | Min | Detection Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macroelement | K | 3110 ± 1350 | 10,500 | 1120 | 100% |
| Na | 1240 ± 738 | 5890 | 470 | 100% | |
| Mg | 361 ± 196 | 1530 | 54 | 100% | |
| Ca | 2220 ± 2090 | 10,300 | 155 | 100% | |
| Essential trace elements | B | 0.4 ± 1.0 | 9.86 | ND | 26% |
| Zn | 25.6 ± 14.6 | 85.3 | 6.02 | 100% | |
| Cu | 2.00 ± 1.43 | 9.46 | ND | 98% | |
| Se | 0.62 ± 0.33 | 2.51 | 0.08 | 100% | |
| Cr | 0.35 ± 1.10 | 9.67 | ND | 53% | |
| Mn | 1.0 ± 1.0 | 6.81 | ND | 87% | |
| Fe | 48 ± 53 | 488 | 1.58 | 100% | |
| Co | 0.018 ± 0.017 | 0.142 | ND | 72% | |
| Mo | 0.08 ± 0.67 | 11.0 | ND | 83% | |
| Non-essential trace elements | Al | 20.4 ± 48.7 | 448 | ND | 87% |
| Ni | 0.6 ± 1.4 | 13.1 | ND | 57% | |
| As | 2.22 ± 1.03 | 8.58 | 0.57 | 100% | |
| Ti | 0.11 ± 0.13 | 0.92 | 0.01 | 64% | |
| Sr | 3.5 ± 5.6 | 46.0 | 0.1 | 91% | |
| V | 0.165 ± 0.346 | 3.27 | ND | 86% | |
| Cd | 0.172 ± 0.205 | 1.37 | ND | 91% | |
| Sn | 0.01 ± 0.03 | 0.33 | ND | 28% | |
| Sb | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.319 | ND | 31% | |
| Ba | 0.19 ± 0.40 | 5.47 | ND | 74% | |
| Tl | 0.0119 ± 0.0189 | 0.266 | ND | 60% | |
| Pb | 0.09 ± 0.39 | 4.82 | ND | 61% |
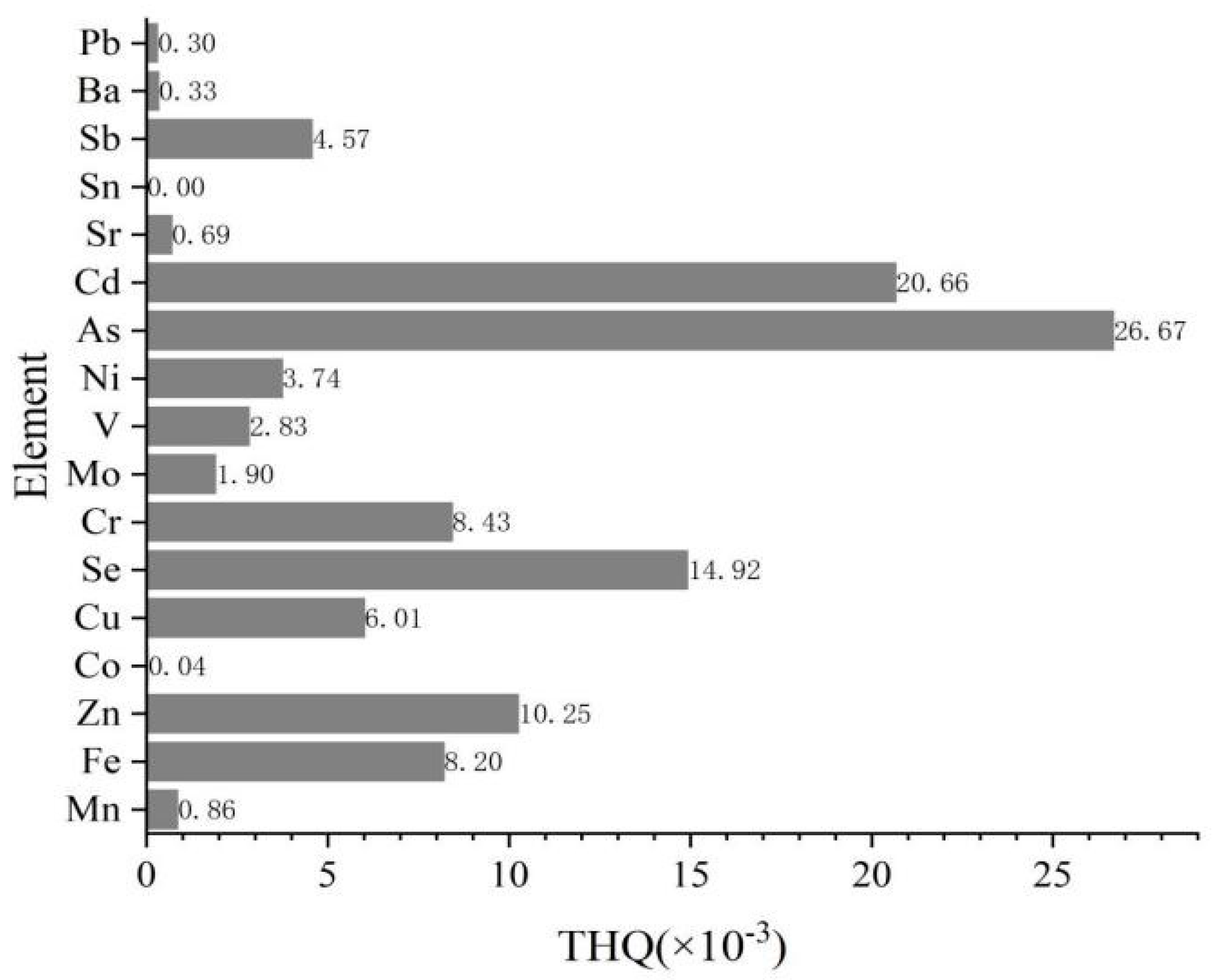
| Class | Elements | RfD (mg kg−1 d−1) | PTDI (g d−1) | Ci (mg kg−1) | EDI (×10−3 mg·kg−1·d−1) | THQ (×10−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Essential trace elements | Mn | 0.14 | 9.8 | 0.998 | 0.120 | 0.856 |
| Fe | 0.7 | 49 | 47.8 | 5.743 | 8.204 | |
| Zn | 0.3 | 21 | 25.6 | 3.076 | 10.252 | |
| Co | 0.06 | 4.2 | 0.0178 | 0.002 | 0.036 | |
| Cu | 0.04 | 2.8 | 2 | 0.240 | 6.007 | |
| Se | 0.005 | 0.35 | 0.621 | 0.075 | 14.922 | |
| Cr | 0.005 | 0.35 | 0.351 | 0.042 | 8.434 | |
| Mo | 0.005 | 0.35 | 0.0792 | 0.010 | 1.903 | |
| Non-essential trace elements | V | 0.007 | 0.49 | 0.165 | 0.020 | 2.832 |
| Ni | 0.02 | 1.4 | 0.623 | 0.075 | 3.742 | |
| As | 0.0003 | 0.021 | 0.0666 | 0.008 | 26.672 | |
| Cd | 0.001 | 0.07 | 0.172 | 0.021 | 20.665 | |
| Sr | 0.6 | 42 | 3.45 | 0.414 | 0.691 | |
| Sn | 0.6 | 42 | 0.0129 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| Sb | 0.0004 | 0.028 | 0.0152 | 0.002 | 4.565 | |
| Ba | 0.07 | 4.9 | 0.192 | 0.023 | 0.330 | |
| Pb | 0.036 | 2.52 | 0.0894 | 0.011 | 0.298 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leng, T.; Liu, B.; Xie, J.; Zou, L.; Lu, D. Essential and Non-Essential Elemental Composition and Health Risks in Pacific Sardine in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030368
Leng T, Liu B, Xie J, Zou L, Lu D. Essential and Non-Essential Elemental Composition and Health Risks in Pacific Sardine in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(3):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030368
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeng, Tiantian, Bilin Liu, Jingqian Xie, Leilei Zou, and Dongqi Lu. 2024. "Essential and Non-Essential Elemental Composition and Health Risks in Pacific Sardine in the Northwest Pacific Ocean" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 3: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030368
APA StyleLeng, T., Liu, B., Xie, J., Zou, L., & Lu, D. (2024). Essential and Non-Essential Elemental Composition and Health Risks in Pacific Sardine in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(3), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12030368






