Differences in Thermo-Rheological Structure between Qiongdongnan Basin and Pearl River Mouth Basin: Implications for the Extension Model in the Northwestern Margin of the South China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
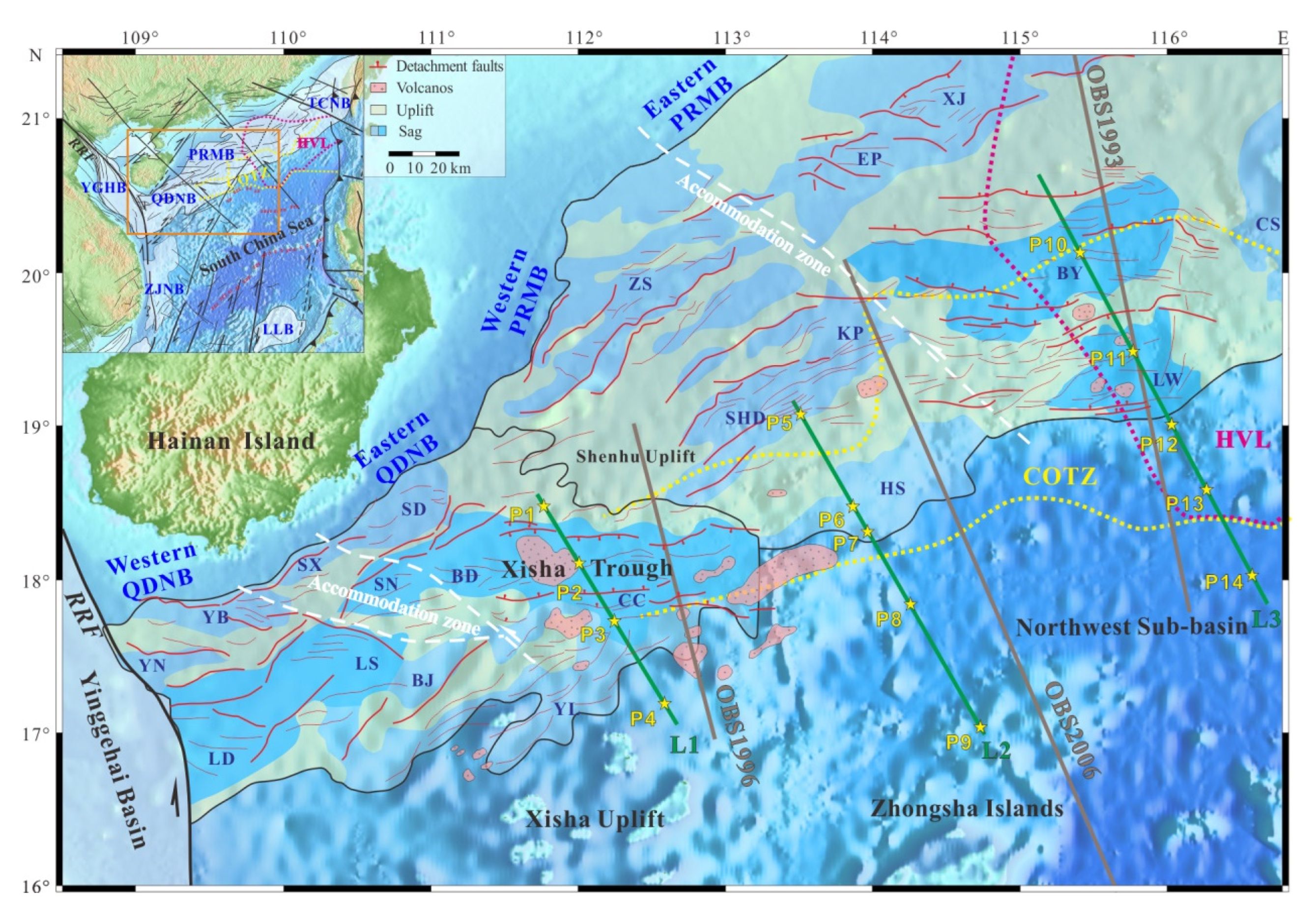
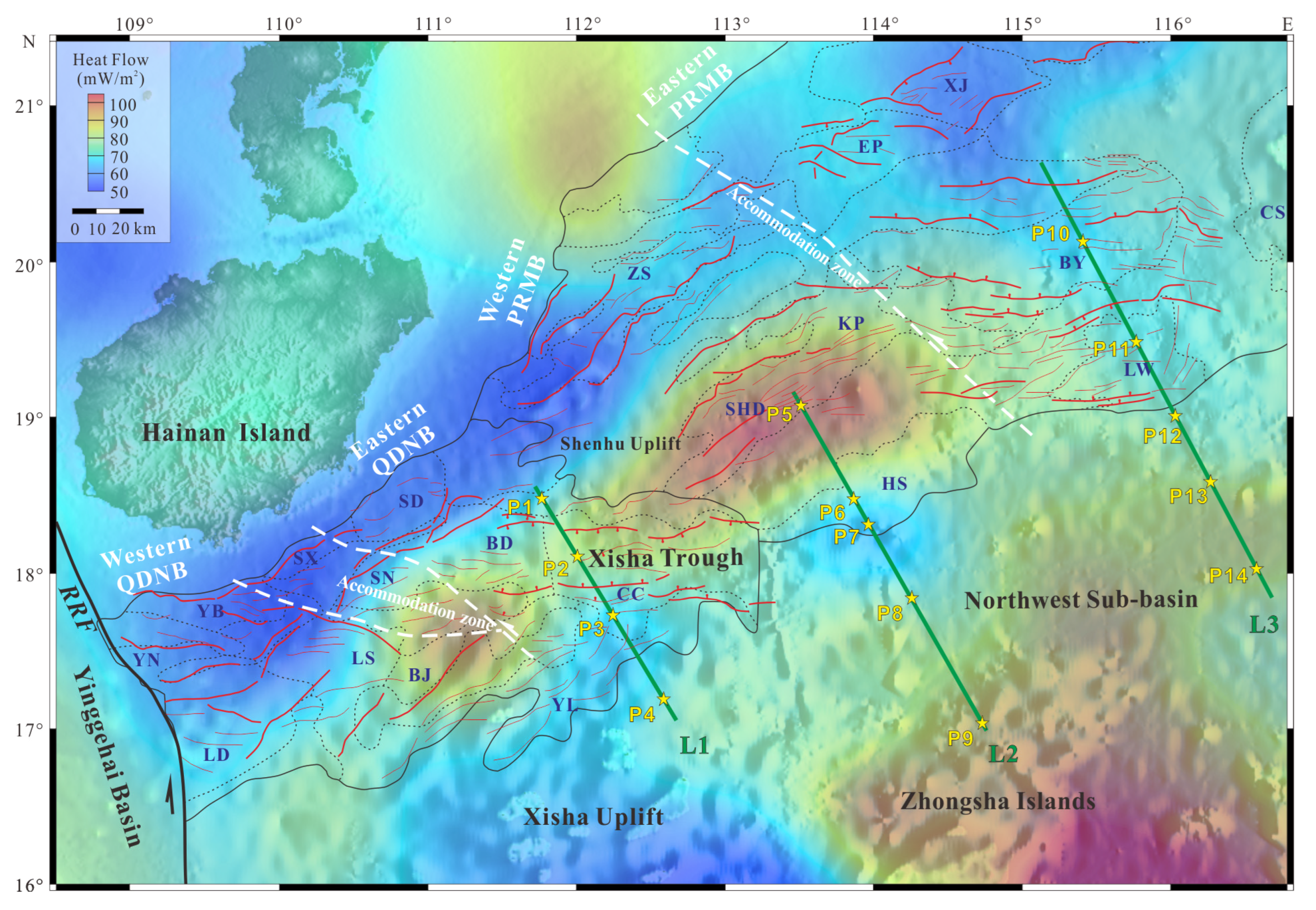
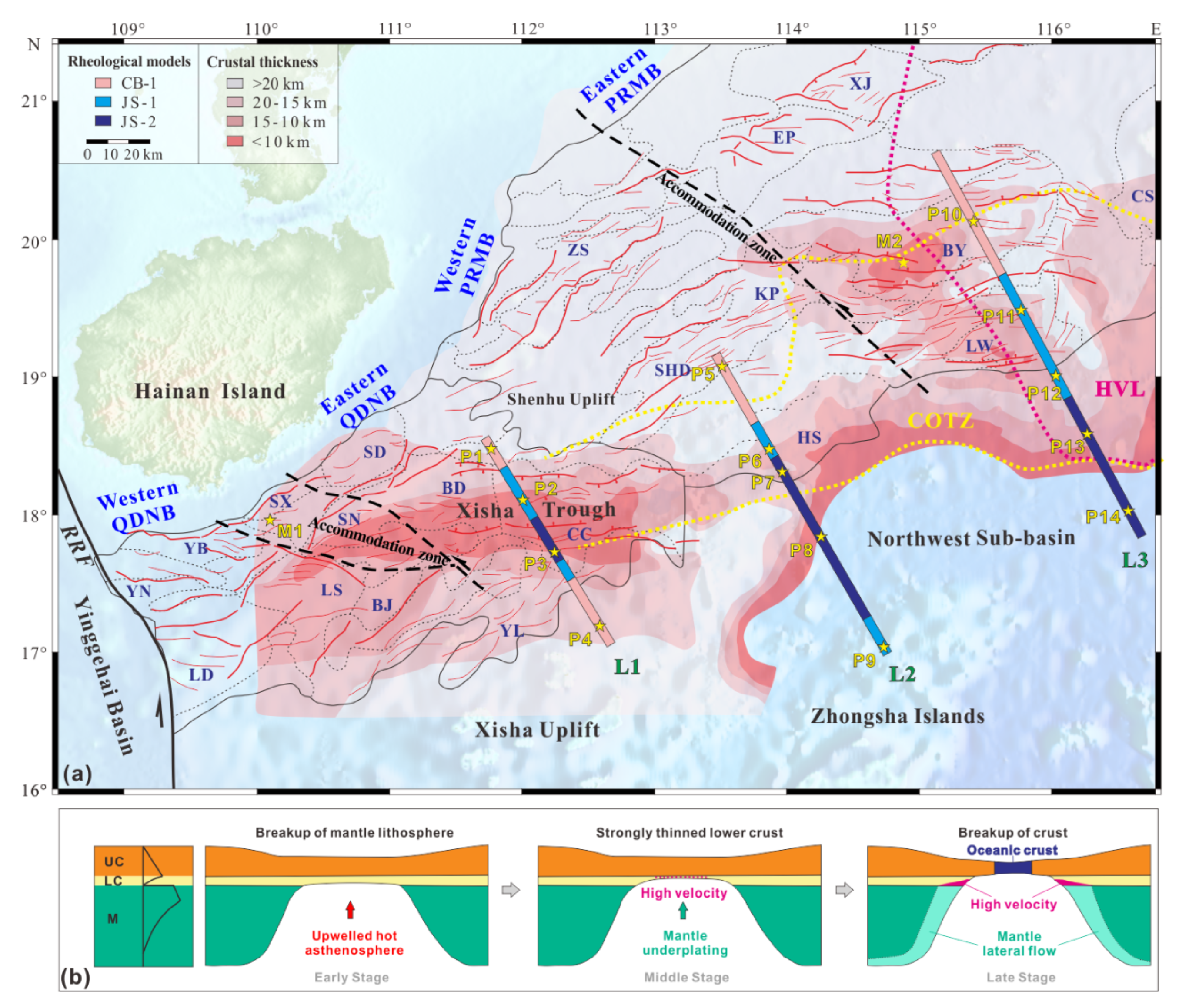
2. Geological Setting
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Thermal Model
3.3. Rheological Structure
4. Results
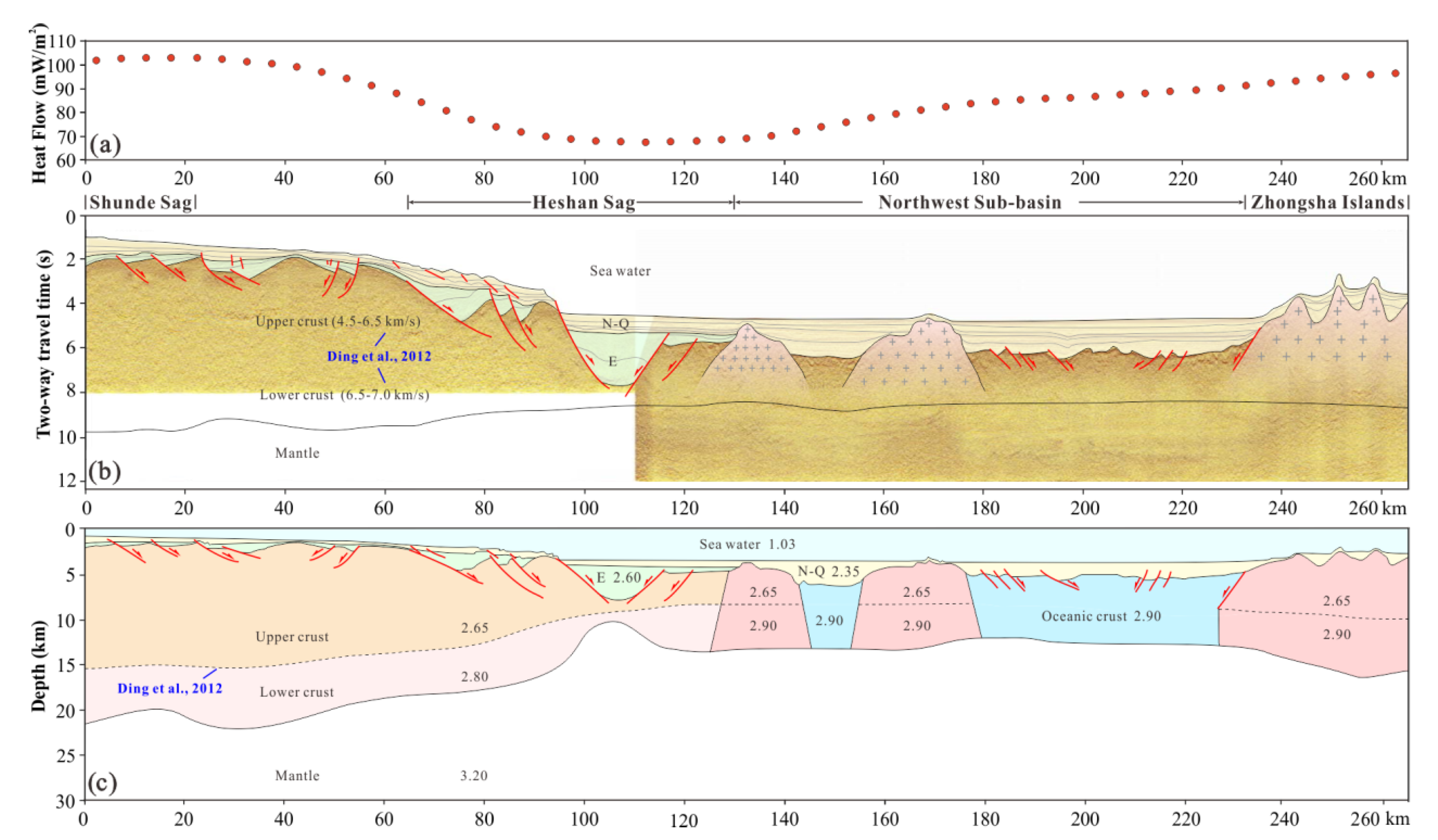
4.1. Temperature Distribution
4.2. Rheological Structure
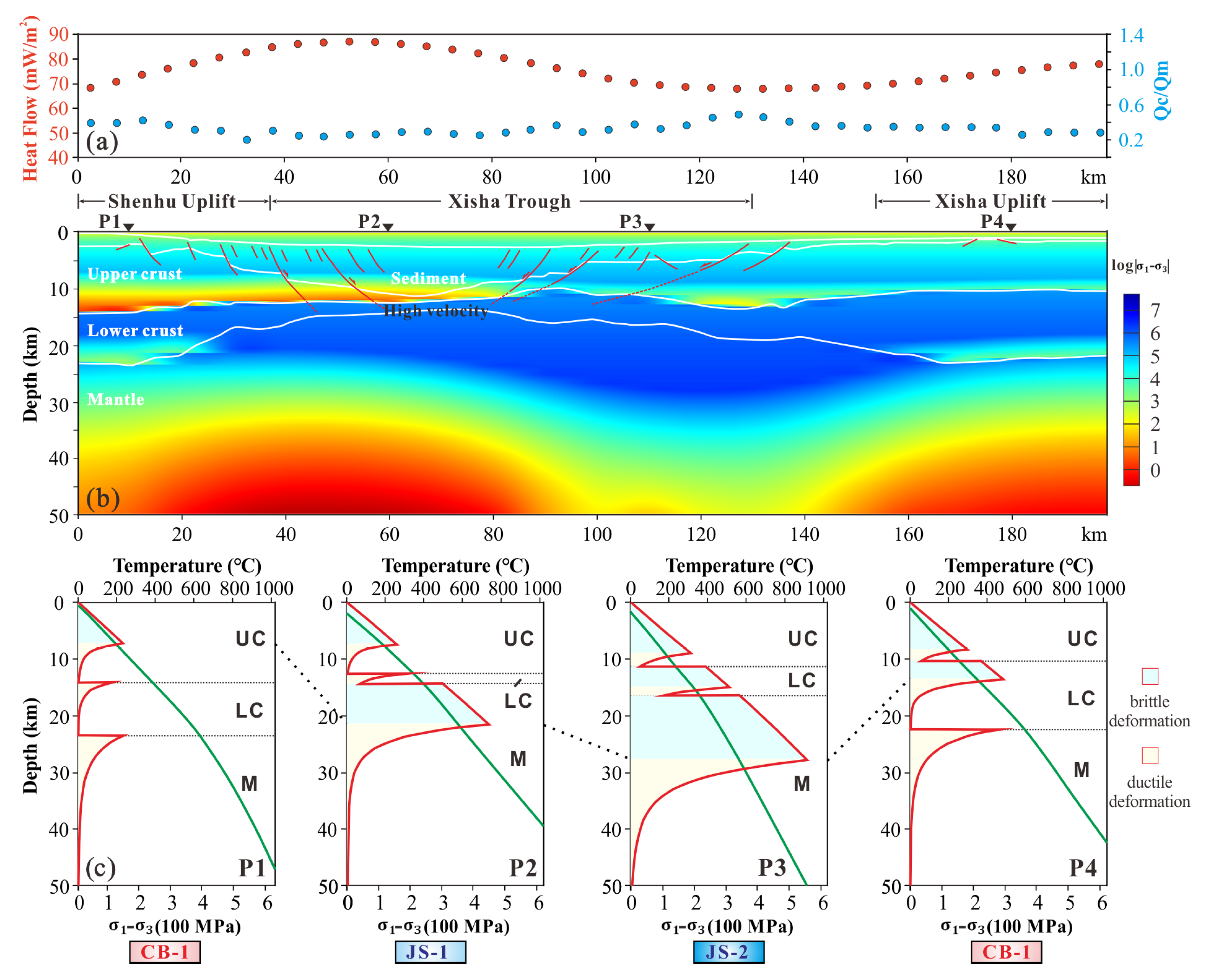
5. Discussion
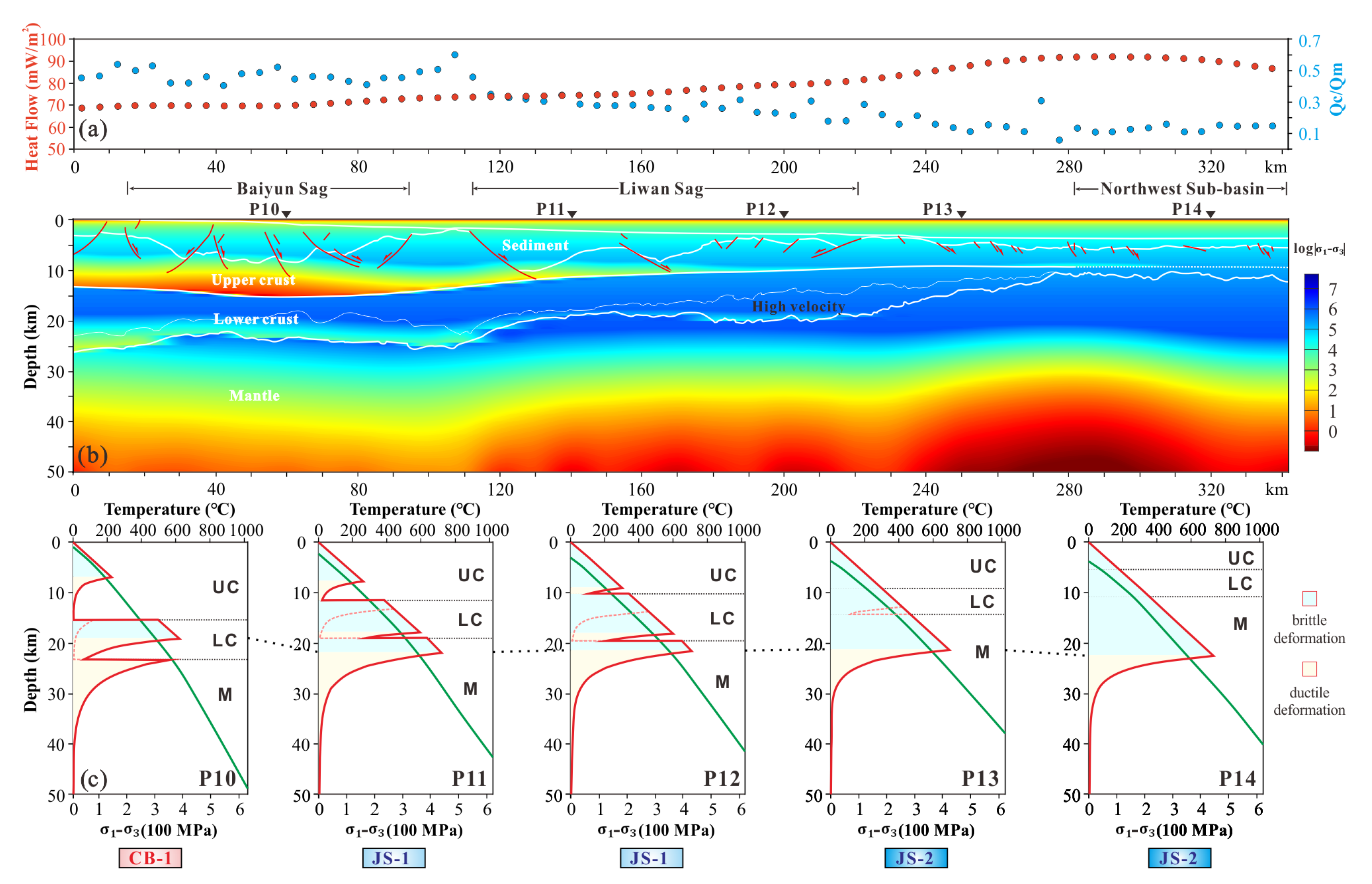
5.1. Differences in Thermo-Rheological Structure between QDNB and PRMB
5.2. Variation of Rifting Stage in the Northwestern SCS
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The east–west variation of thermo-rheological structures has been presented along the northwestern SCS. The PRMB exhibits a seaward-increasing trend in lithospheric rheological strength, from the CB-1 regime at the continental shelf to the JS-2 regime at the NSB. The central Xisha Trough falls is a JS-2 regime caused by the cooling of the heavily thinned lower crust in the middle continental margin rifting stage.
- (2)
- The lower crustal HVLs beneath the eastern PRMB increase the lower crustal strength, which forms at the late stage of continental rifting due to the mantle lateral flow, facilitated by the tectonic activities of the surrounding blocks.
- (3)
- The absence of HVLs in the western PRMB may indicate the limited impact of mantle lateral flow. This area exhibits a characteristically transitional thermo-rheological structure from the Xisha Trough to the eastern PRMB.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, L.; Shi, Y.; Ma, R. On the formation and evolution of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic active continental margin and island arc tectonic of the western Pacific Ocean. Acta Geol. Sin. 1983, 1, 11–21, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hall, R. Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: Computer-based reconstructions, model and animations. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2002, 20, 353–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Suo, Y.; Liu, X.; Dai, L.; Yu, S.; Zhao, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, S.; Xu, Y. Basic Structural Pattern and Tectonic Models of the South China Sea: Problems, Advances and Controversies. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2012, 32, 35–53, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, S.; Suo, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, G.; Hui, G.; Santosh, M.; Somerville, I.D.; Cao, X.; Li, Y. Plate tectonic control on the formation and tectonic migration of Cenozoic basins in northern margin of the South China Sea. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.; Hayes, D.; Buhl, P.; Diebold, J. Deep penetration seismic soundings across the northern margin of the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 1995, 100, 22407–22433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wu, F.; Zhang, G.; Ren, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, K.; Zhong, K.; Liu, S. Discrepancy tectonic evolution and petroleum exploration in China offshore Cenozoic basins. Earth Sci. Front. 2015, 22, 88–101, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, J.; Wu, J. Cenozoic Faults Systems and its Geodynamics of the Continental Margin Basins in the Northern of South China Sea. J. China Univ. Geosci. (Chin. Ed.) 2019, 44, 603–625, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dean, S.M.; Minshull, T.A.; Whitmarsh, R.B.; Louden, K.E. Deep structure of the ocean-continent transition in the southern Iberia Abyssal Plain from seismic refraction profiles: The IAM-9 transect at 40°20′N. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2000, 105, 5859–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkinson, L.; Beard, J.S.; Boulter, C.A. The hydrothermal plumbing of a serpentinite-hosted detachment: Evidence from the West Iberia non-volcanic rifted continental margin. Mar. Geol. 2004, 204, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gussinyé, M.; Morgan, J.P.; Reston, T.J.; Ranero, C.R. The rift to drift transition at non-volcanic margins: Insights from numerical modeling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 244, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhou, D.; Qiu, X. Tectonic Setting of the Northern Margin of South China Sea. Geol. J. China Univ. 2001, 7, 419–426, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Schnabel, M.; Franke, D.; Ruan, A.; Wu, Z. Crustal Structure across the Northwestern Margin of South China Sea: Evidence for Magma-poor Rifting from a Wide-angle Seismic Profile. Acta Geol. Sin. 2012, 86, 854–866. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, D. Rifting, lithosphere breakup and volcanism: Comparison of magma-poor and volcanic rifted margins. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 43, 63–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, S.; Mcintosh, K.; Mi, L.; Yao, B.; Zhen, Z.; Jia, L. The continent–ocean transition at the mid-northern margin of the South China Sea. Tectonophysics 2015, 654, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Pang, X.; Lei, C.; Yuan, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, L. Ocean and continent transition in passive continental margins and analysis of lithospheric extension and breakup process: Implication for research of the deepwater basins in the continental margins of South China Sea. Earth Sci. Front. 2015, 22, 102–114, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, D.; Guo, X.; Shi, X.; Wu, X.; Pang, X. Cenozoic crustal thinning in the northern margin of the South China Sea and its dynamical significance. Sci. China Ser. D 2007, 37, 1609–1616. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Teng, J.; Giuliano, P. Seismic structure and rheology of the crust under mainland China. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 1455–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Zhou, D.; Liu, Z. A crustal structure profile across the northern continental margin of the South China Sea. Tectonophysics 2001, 338, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Clift, P.; Sun, Z. The sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the Yinggehai-Song Hong basin and the southern Hainan margin, South China Sea: Implications for Tibetan uplift and monsoon intensification. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2006, 111, B06405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fan, W.; Chen, L. The depth-dependence of crustal extension beneath Qiongdongnan basin area and its tectonic implications. Chin. J. Geophys. 2010, 53, 57–66, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Ren, J. Hyper-extended rift systems in the Xisha Trough, northwestern South China Sea: Implications for extreme crustal thinning ahead of a propagating ocean. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 846–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, M.; Lee, C.; Xia, K. Seismic imaging of the transitional crust across the northeastern margin of the South China Sea. Tectonophysics 2006, 412, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Qiu, X.; Kopp, H.; Xu, H.; Sun, Z.; Ruan, A.; Sun, J.; Wei, X. Shallow anatomy of a continent–ocean transition zone in the northern South China Sea from multichannel seismic data. Tectonophysics 2012, 554, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Fan, W. Crustal P-wave velocity structure and layering beneath Zhujiangkou-Qiongdongnan basins, the northern continental margin of South China Sea. Chin. J. Geophys. 2009, 52, 2461–2471, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, D. Geophysical investigations of crust-scale structural model of the Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern South China Sea. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2013, 34, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, S.; Mcintosh, K.; Mi, L.; Liu, Z.; Spence, G. Crustal structure and extension mode in the northwestern margin of the South China Sea. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2016, 17, 2143–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J. Dynamics of the continental margin of South China Sea: Scientific experiments and research progresses. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 2993–3003, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Xiong, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Dong, S. Tectono-thermal modeling of the Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. Sci. China Ser. D 2001, 44, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shi, X.; Wang, L.; Gao, S.; Hu, X.; Feng, C. Recent advances in studies on the formation mechanism of the South China Sea and thermo-rheological structure of lithosphere in its northern margin: An overview. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2006, 26, 117–124, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Peron-Pinvidic, G.; Manatschal, G. Rifted Margins: State of the Art and Future Challenges. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huismans, R.; Beaumont, C. Depth-dependent extension, two-stage breakup and cratonic underplating at rifted margins. Nature 2011, 473, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, J.L.; Buiter, S.J.H. The influence of extension rate and crustal rheology on the evolution of passive margins from rifting to break-up. Tectonophysics 2018, 746, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Deep geothermal characteristics in the northern continental margin of the South China Sea. Scientia 2000, 45, 1095–1100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Yu, C.; Chen, M.; Yang, X.; Zhao, J. Analyses of variation features and influential factors of heat flow in the northern margin of the South China Sea. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 56–64, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, G.; Yang, S.; Hu, S. Lithospheric thermal structure of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea. Chin. J. Geophys. 2018, 61, 3749–3759, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Jiang, X.; Gong, W. Thermo-rheological structure and passive continental margin rifting in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea, China. J. Ocean Univ. China 2022, 21, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Ye, S.; Wu, S.; Shi, X.; Zhou, D.; Xia, K.; Flueh, E.R. Crustal structure across the Xisha Trough, northwestern South China Sea. Tectonophysics 2001, 341, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Lei, C. Tectonic stratigraphic framework of Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basins and its implication for tectonic province division in South China Sea. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 3303–3314, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, F.; Luo, Y. South China Sea basin opening: Lithospheric rifting and interaction with surrounding subduction zones. Sci. Tech. Rev. 2020, 38, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yao, Y.; Shen, B.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Wei, C.; Chen, J. On Linkage of Western Boundary Faults of the South China Sea. J. China Univ. Geosci. (Chin. Ed.) 2015, 40, 615–632, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Ren, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Lei, C. Difference of tectonic evolution of continental marginal basins of South China Sea and relationship with SCS spreading. Earth Sci. Front. 2015, 22, 77–87, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Lin, J.; Qiu, N.; Jian, Z.; Wang, P.; Pang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, B. The role of magmatism in the thinning and breakup of the South China Sea continental margin. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Keep, M.; Zhou, D.; Cai, D.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Jiang, J. 3D analogue modeling of the South China Sea: A discussion on breakup pattern. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 34, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Asia: A preliminary synthesis. Tectonophysics 2010, 488, 293–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doust, H.; Sumner, H.S. Petroleum systems in rift basins—A collective approach in Southeast Asian basins. Pet. Geosci. 2007, 13, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briais, A.; Patriat, P.; Tapponnier, P. Updated Interpretation of Magnetic Anomalies and Seafloor Spreading Stages in the South China Sea Implications for the Tertiary Tectonics of Southeast Asia. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 1993, 98, 6299–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braitenberg, C.; Wienecke, S.; Wang, Y. Basement structures from satellite-derived gravity field: South China Sea ridge. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2006, 111, B05407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barckhausen, U.; Engels, M.; Franke, D.; Ladage, S.; Pubellier, M. Evolution of the South China Sea: Revised ages for breakup and seafloor spreading. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 58, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Li, C.; Jiang, X. Connection between uplifting of the Tibetan Plateau and opening of the South China Sea (SCS): The basin-mountain coupling in the northwestern margin of the SCS. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 268–283, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, D.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Yuan, S. Cenozoic tectonic and sedimentary evolution of deepwater area, Pearl River Mouth Basin. J. China Univ. Pet. 2009, 53, 17–29, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Ren, J.; Pei, X.; Lin, H.; Yin, X.; Tong, D. Tectonic Framework and Multiple Episode Tectonic Evolution in Deepwater Area of Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern Continental Margin of South China Sea. J. China Univ. Geosci. (Chin. Ed.) 2011, 36, 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Morley, C.K. Major Unconformities/termination of Extension Events and Associated Surfaces in the South China Seas: Review and Implications for Tectonic Development. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 120, 62–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Fan, C.; Wang, D.; Cao, J.; Zhao, F. Hyperextended crustal structure of the Qiongdongnan Basin and subsequent magmatic influence from the Hainan mantle plume. Sci. China Ser. D 2022, 65, 845–862, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Qiu, N.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z. Crustal structure of Changchang sag in the deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin. Mar. Geol. Front. 2013, 29, 7–17, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yao, B.; Wan, L.; Wu, N. Cenozoic tectonic evolution and the 3D structure of the lithosphere of the South China Sea. Geol. Bull. China 2005, 24, 1–8, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Zhou, D. Lithospheric thermal-rheological structure of the northern continental margin of the South China Sea. Scientia 2000, 45, 1660–1665. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Ren, J.; Lei, C.; Yang, H.; Yin, X. Lithosphere Stretching Model of Deep Water in Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern Continental Margin of South China Sea, and Controlling of the Post-Rift Subsidence. J. China Univ. Geosci. (Chin. Ed.) 2009, 34, 963–974, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, S. Crustal density and composition models beneath Qiongdongnan basin. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 98–107, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lester, R.; Van Avendonk, H.J.; Mcintosh, K.; Lavier, L.; Liu, C.S.; Wang, T.K.; Wu, F. Rifting and magmatism in the northeastern South China Sea from wide-angle tomography and seismic reflection imaging. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2014, 119, 2305–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Petrology and chemical composition models of the lower crust of the Xisha Trough, northern continental margin of the South China Sea. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2007, 26, 29–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Tian, Y.; Long, Z.; Hu, D.; Hu, S. Thermo-rheological structure of the northern margin of the South China Sea: Structural and geodynamic implications. Tectonophysics 2020, 777, 228338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhou, D.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, Y. Thermal and rheological structures of the Xisha Trough, South China Sea. Tectonophysics 2002, 351, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, X.; Yang, J.; Huang, B.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Yu, C.; Yang, X. Analyses on the tectonic thermal evolution and influence factors in the deep-water Qiongdongnan Basin. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 33, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zhong, Z.; Qiu, X.; Zeng, Z. A study on basal controlling fault pattern of Ying-Qiong basin through analogue modeling. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2005, 24, 70–78, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lebedev, S.; Nolet, G. Upper mantle beneath Southeast Asia from S velocity tomography. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, Y. S-wave velocity structure of South China Sea and surrounding regions from surface wave tomography. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 3089–3097, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, S.; He, L.; Yang, S. Characteristics and genesis of geothermal field in deep-water area of the northern South China Sea. Acta Pet. Sin. 2009, 30, 27–32, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Shi, X. Seafloor in-situ heat flow measurements in the deep-water area of the northern slope, South China Sea. Chin. J. Geophys. 2010, 53, 2161–2170, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Xia, S.; Cao, J.; Zhao, F.; Sun, J.; Wan, K.; Xu, H. Lateral crustal variation and post-rift magmatism in the northeastern South China Sea determined by wide-angle seismic data. Mar. Geol. 2019, 410, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wan, J.; Chen, A.; Liu, T. Thermal structure of Nansha Trough Foreland Basin. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2012, 31, 155–161, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, M.; Wu, S.; Gao, L. Lithosphere thermal-rheological structure and geodynamic evolution model of the Nansha trough basin, South China Sea. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 27–40, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; He, L. The different lithospheric thermal structure of North China Craton and its implications. Chin. J. Geophys. 2016, 59, 3618–3626, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- He, L. Permian to Late Triassic evolution of the Longmen Shan Foreland Basin (Western Sichuan): Model results from both the lithospheric extension and flexure. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 93, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Z.; Sun, Z.; Yang, J.; Yu, C.; Yang, X. Vertical variations of geothermal parameters in rifted basins and heat flow distribution features of the Qiongdongnan Basin. Chin. J. Geophys. 2015, 58, 939–952, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, J.; Xiong, X.; Li, X.; Yin, H. Thermal Properties Characterization of the Rocks in the Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern Margin of the South China Sea. Geol. J. China Univ. 2019, 25, 538–547, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cermák, V. Crustal heat production and mantle heat flow in Central and Eastern Europe. Tectonophysics 1989, 159, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, X.; Li, D.; Xing, J.; Gong, W. Thermal-rheological property of lithosphere beneath Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Geotecton. Metallog. 2017, 41, 481–490, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, J. Faulting, Flow, and the Strength of the Continental Lithosphere. Int. Geol. Rev. 2002, 44, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burov, E.B.; Watts, A.B. The long-term strength of continental lithosphere: “Jelly sandwich” or “crème brûlée”? GSA Today 2006, 16, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Structural differences between the western and eastern Qiongdongnan Basin: Evidence of Indochina block extrusion and South China Sea seafloor spreading. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2013, 34, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranalli, G. Regional variations in lithosphere rheology from heat flow observations. In Terrestrial Heat Flow and the Lithosphere Structure; Cermak, V., Rybach, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Heat flow pattern and lateral variations of lithosphere strength in China mainland: Constraints on active deformation. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2001, 126, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, S.H. Rheology of the lithosphere. Rev. Geophys. 1983, 21, 1458–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.P.; Ruiz, J.; Rosenburg, M.A.; Aharonson, M.A.; Phillips, O.; Roger, J. Insolation driven variations of Mercury’s lithospheric strength. J. Geophys. Res-Planet. 2011, 116, E01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michel, G.W.; Yu, Y.Q.; Zhu, S.Y.; Reigber, C.; Becker, M.; Reinhartb, E.; Simons, W.; Ambrosius, B.; Vigny, C.; Chamot-Rooke, N. Crustal motion and block behavior in SE-Asia from GPS measurements. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 187, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zang, S.; Li, Y.; Wei, R. The Determination of Rheological Mechanics of Lithosphere and the Influencing Factors on the Rheological Strength of Lithosphere. Prog. Geophys. 2002, 17, 50–60, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Burov, E.B.; Diament, M. The effective elastic thickness (Te) of continental lithosphere: What does it really mean? J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 1995, 100, 3905–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, J.; McKenzie, D.; Priestley, K.; Emmerson, B. New views on the structure and rheology of the lithosphere. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2008, 165, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. The Cenozoic Crustal Thinning and Development of Hyper-Extended Rift System in the Northern South China Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2018. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Buck, W.R. The dynamics of continental breakup and extension. In Crustal and Lithosphere Dynamics; Watts, A.B., Ed.; Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 325–379. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H. Continental marginal rifting along the northern South China Sea: The crustal response to the lower lithospheric delamination. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2001, 21, 39–44, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
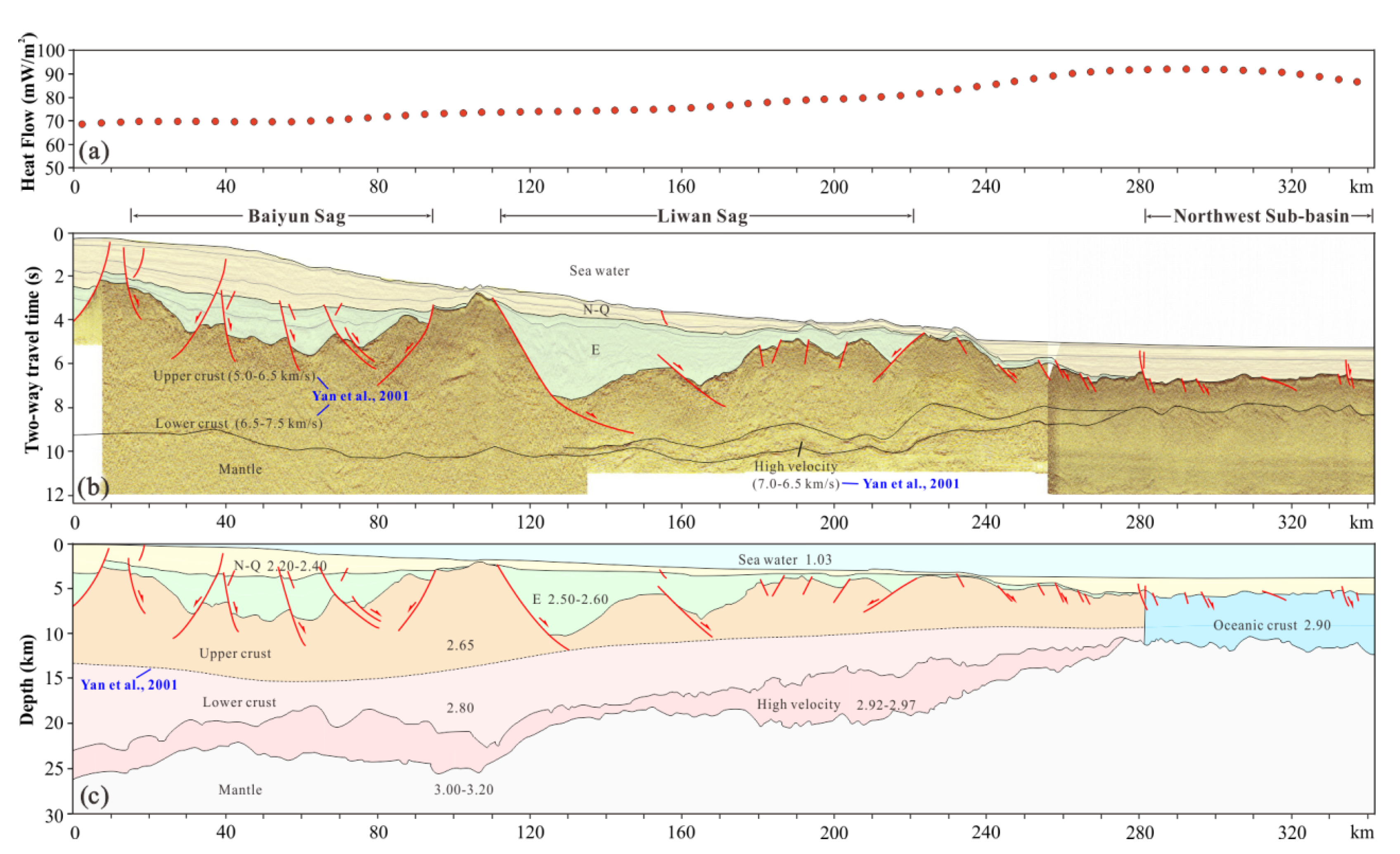
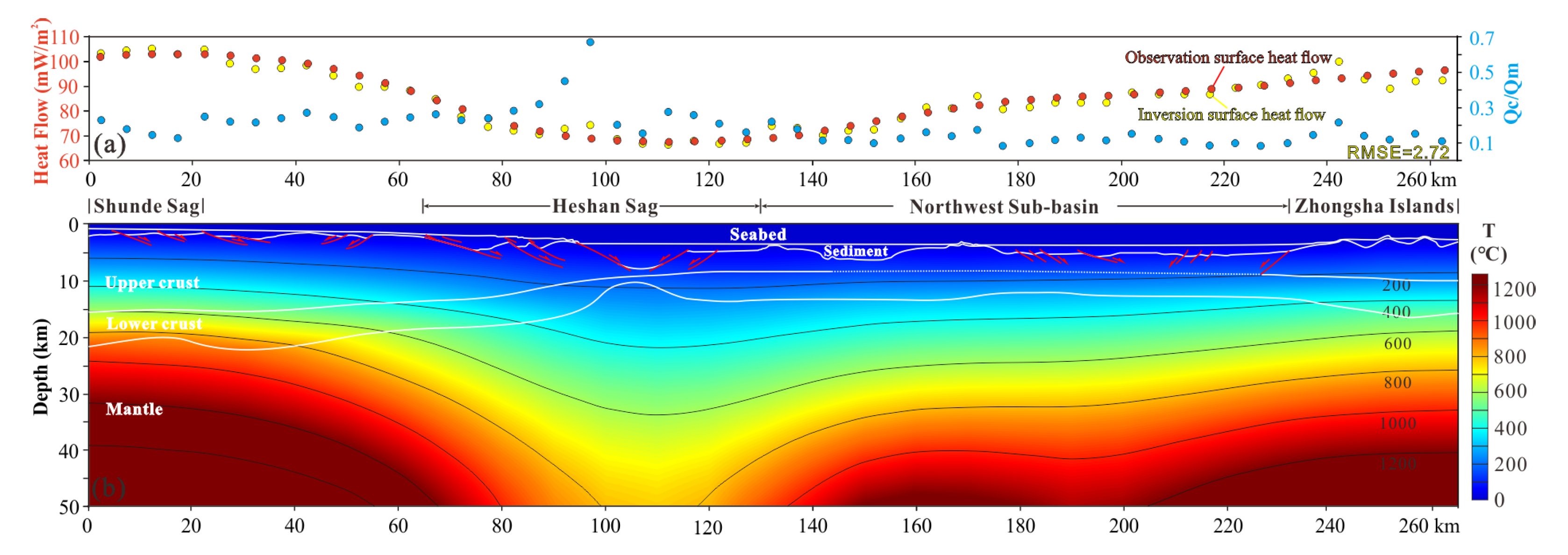
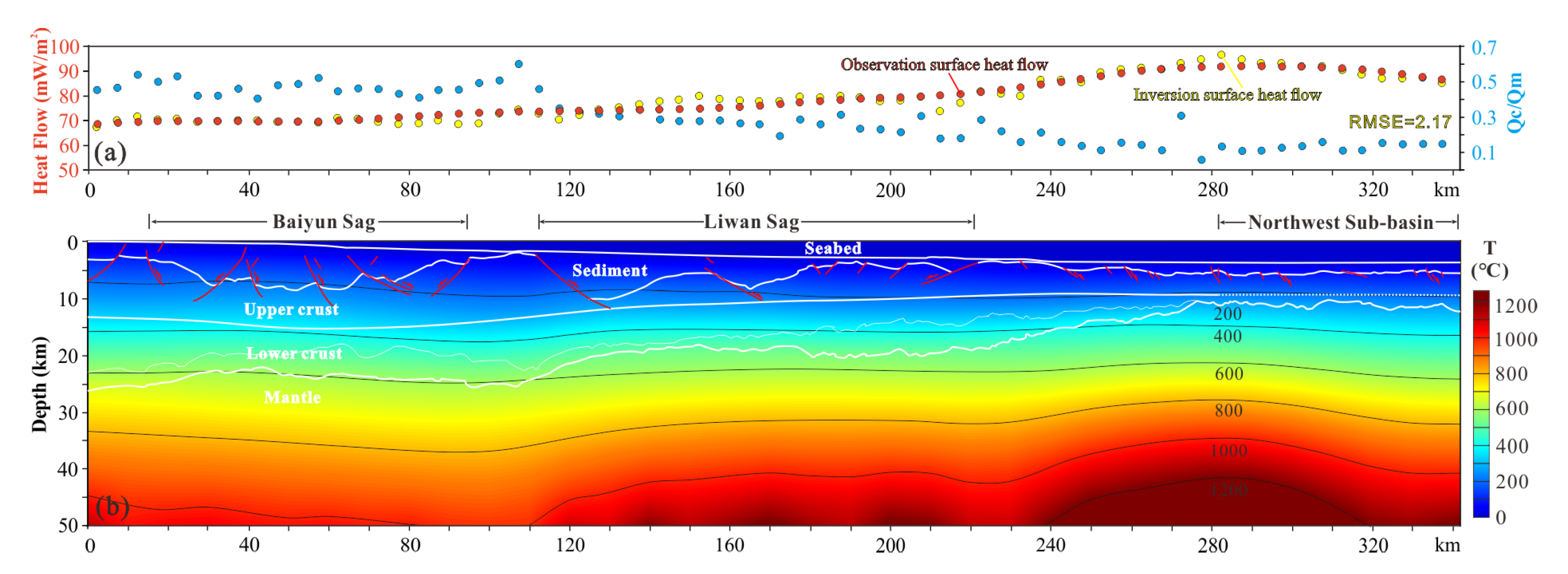
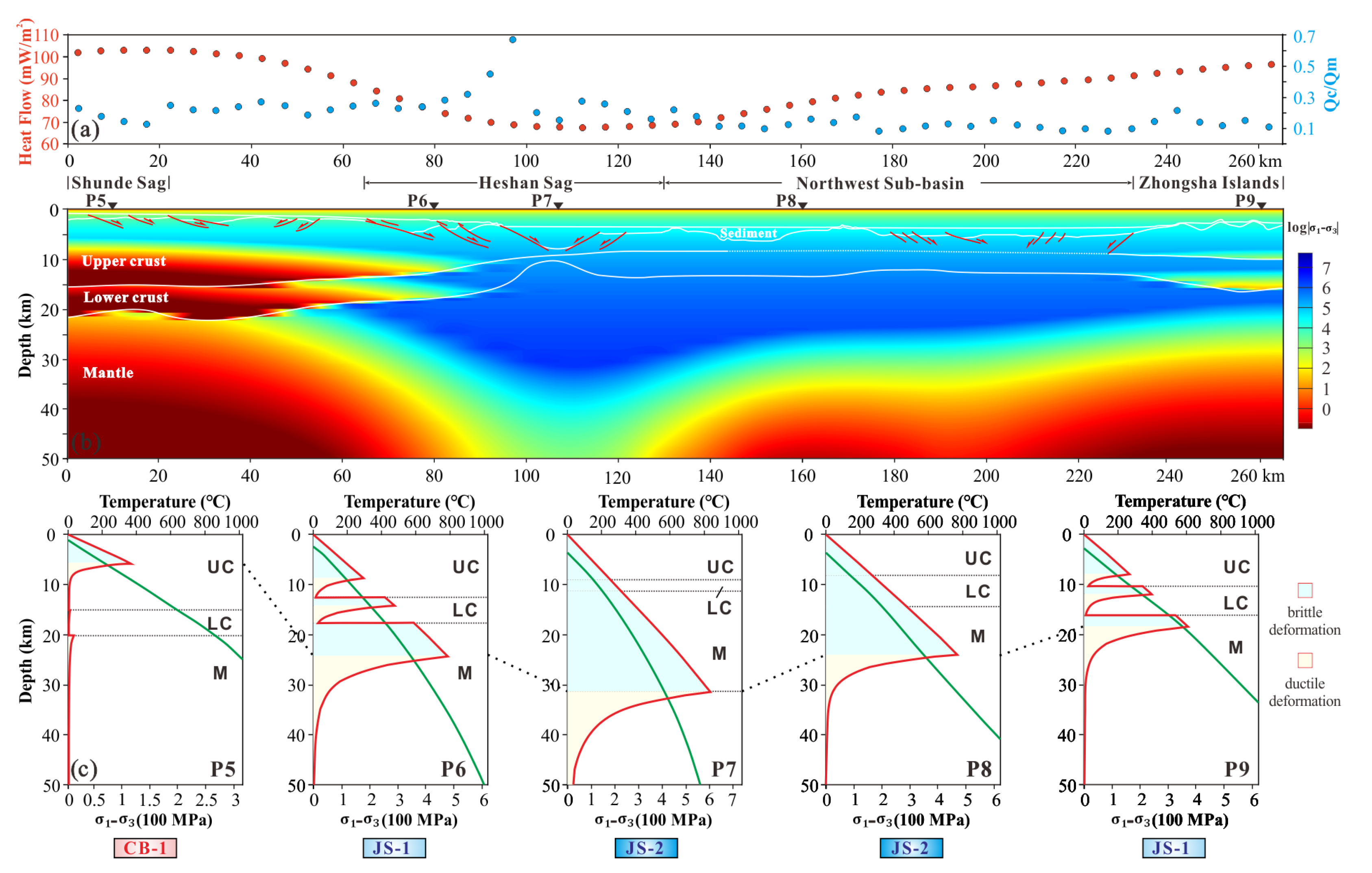
| Layers | Thermal Conductivity K (W/mK) | Heat Production A (μW/m3) | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediments | N-Q | 2.01 | 2.08 | Tang et al. [35] |
| E | 2.20 | 2.35 | Hu et al. [61] | |
| Upper crust | UTK | K = (0.33 + 0.33 × 10−3T)−1 | A = A0exp(−z/D) | Shi et al. [62] |
| other parts | lnA = 12.6–2.17Vp | |||
| Lower crust | K = (0.41 + 0.29 × 10−3T)−1 | lnA = 12.6–2.17Vp | Ma et al. [70] | |
| Upper mantle | K = (0.21 + 0.50 × 10−3T)−1 −0.52 + 2.3 × 10−3T | 0.003 | Cai et al. [75] | |
| Layers | Lithology | Pre-Exponential Constant A (MPa-n/s) | Powerlaw Exponent n | Powerlaw Activation Energy E (KJ/mol) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediments | Wet quartz | 3.20 × 10−6 | 2.3 | 154 | Hu et al. [61] |
| Upper crust | Wet quartz | 3.20 × 10−6 | 2.3 | 154 | Shi et al. [63] |
| Lower crust | Intermediate granulite (L1, L2 and L3) | 1.30 × 10−3 | 2.4 | 219 | Zhou et al. [77] |
| Mafic granulite (L3) | 1.24 × 104 | 4.2 | 445 | Wang [82] | |
| Upper mantle | Aheim dunite | 3.98 × 10−2 | 4.5 | 498 | Zang [86] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Zhi, P.; Ding, R.; Zhao, L.; Gong, W.; Li, Z.; Ge, J. Differences in Thermo-Rheological Structure between Qiongdongnan Basin and Pearl River Mouth Basin: Implications for the Extension Model in the Northwestern Margin of the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020443
Li C, Zhi P, Ding R, Zhao L, Gong W, Li Z, Ge J. Differences in Thermo-Rheological Structure between Qiongdongnan Basin and Pearl River Mouth Basin: Implications for the Extension Model in the Northwestern Margin of the South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(2):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020443
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chaoyang, Pengyao Zhi, Renwei Ding, Lihong Zhao, Wei Gong, Zhonghua Li, and Jiayu Ge. 2023. "Differences in Thermo-Rheological Structure between Qiongdongnan Basin and Pearl River Mouth Basin: Implications for the Extension Model in the Northwestern Margin of the South China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 2: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020443
APA StyleLi, C., Zhi, P., Ding, R., Zhao, L., Gong, W., Li, Z., & Ge, J. (2023). Differences in Thermo-Rheological Structure between Qiongdongnan Basin and Pearl River Mouth Basin: Implications for the Extension Model in the Northwestern Margin of the South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(2), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020443





