Paleoenvironmental Evolution and Organic Matter Accumulation in a Hydrocarbon-Bearing Depression in the East China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
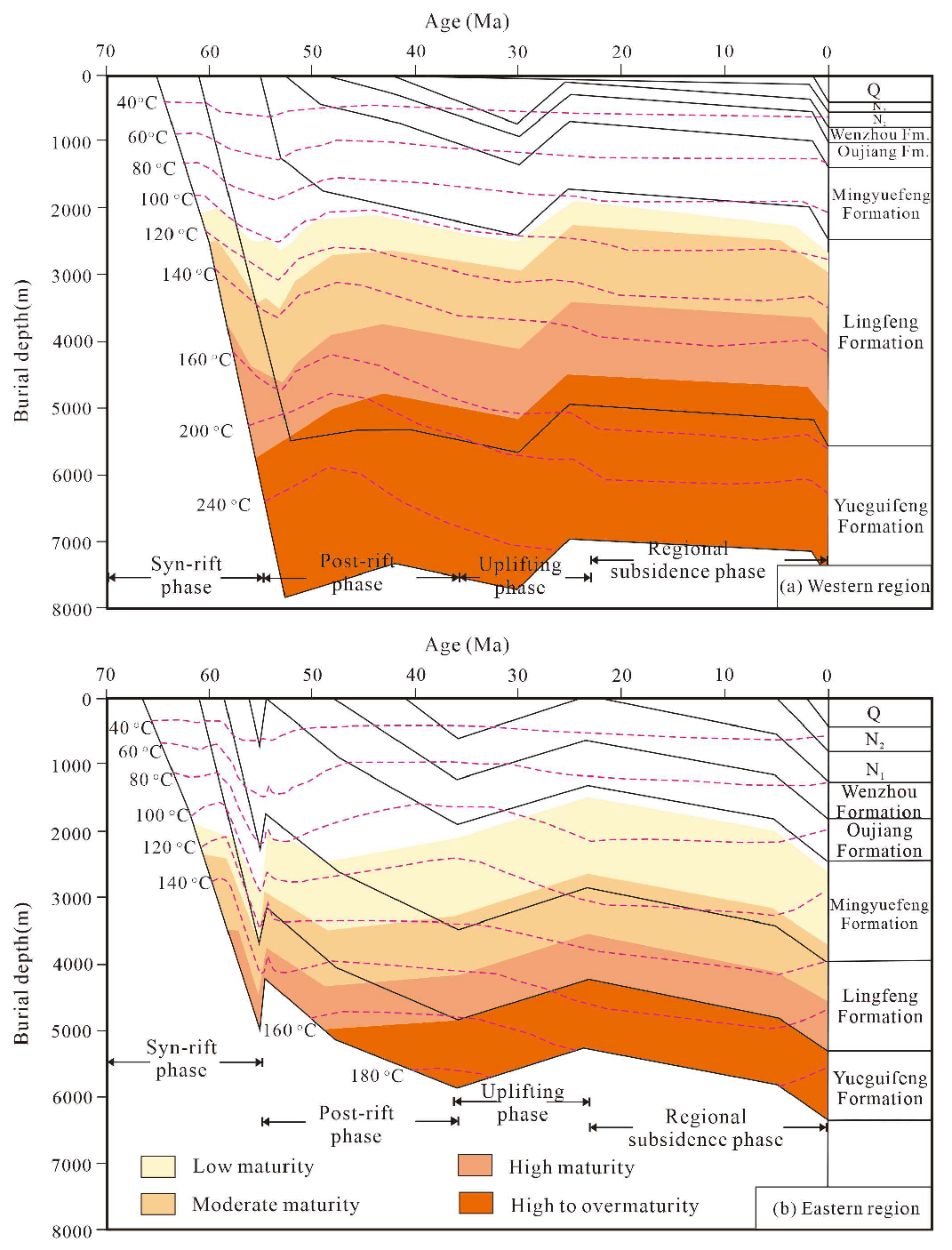
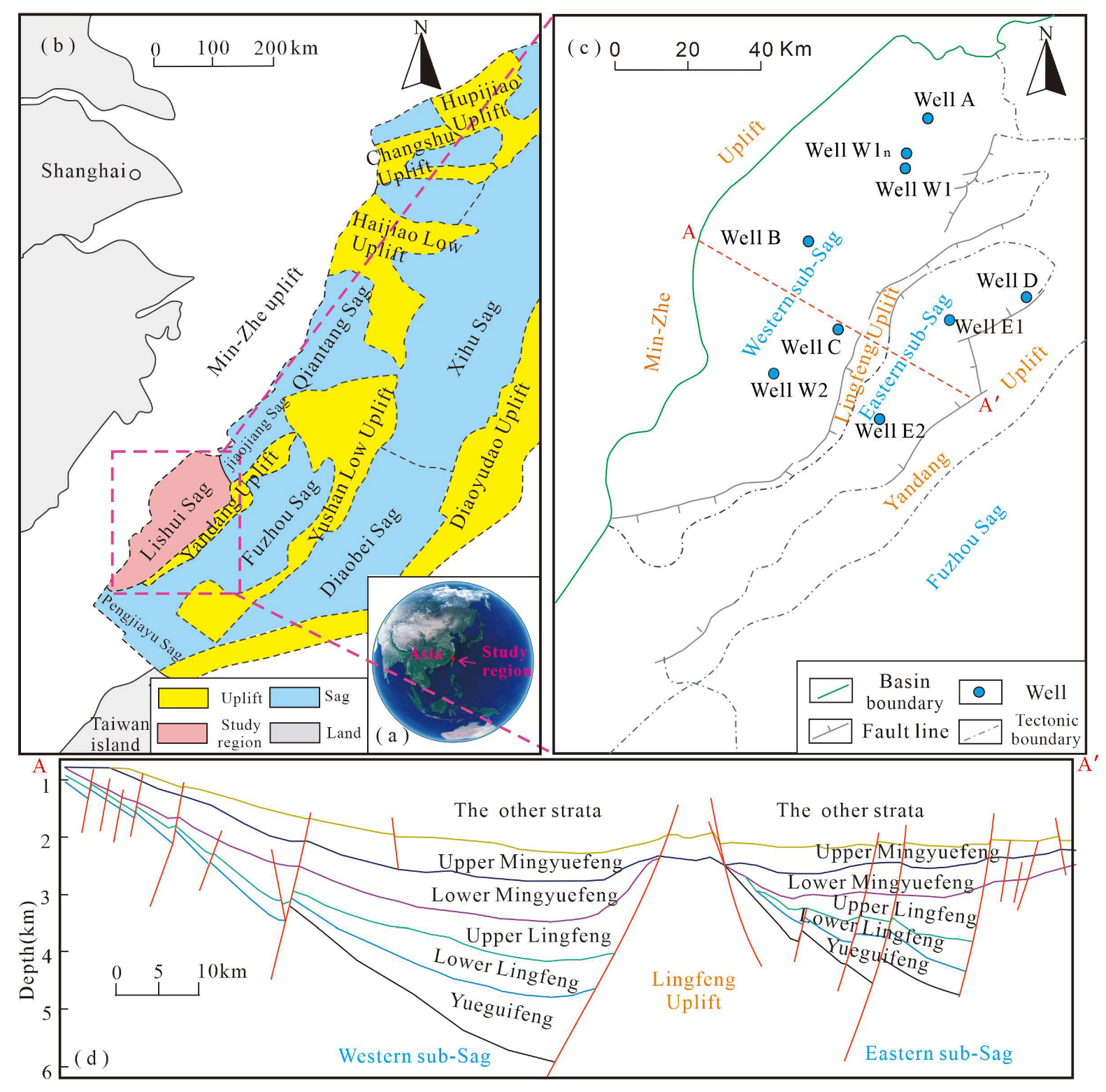
2. Geological Setting
3. Sample and Experimental Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. TOC and Rock-Eval Pyrolysis
3.3. Major and Trace Elements Analysis
3.4. GC and GC-MS Analysis
4. Results
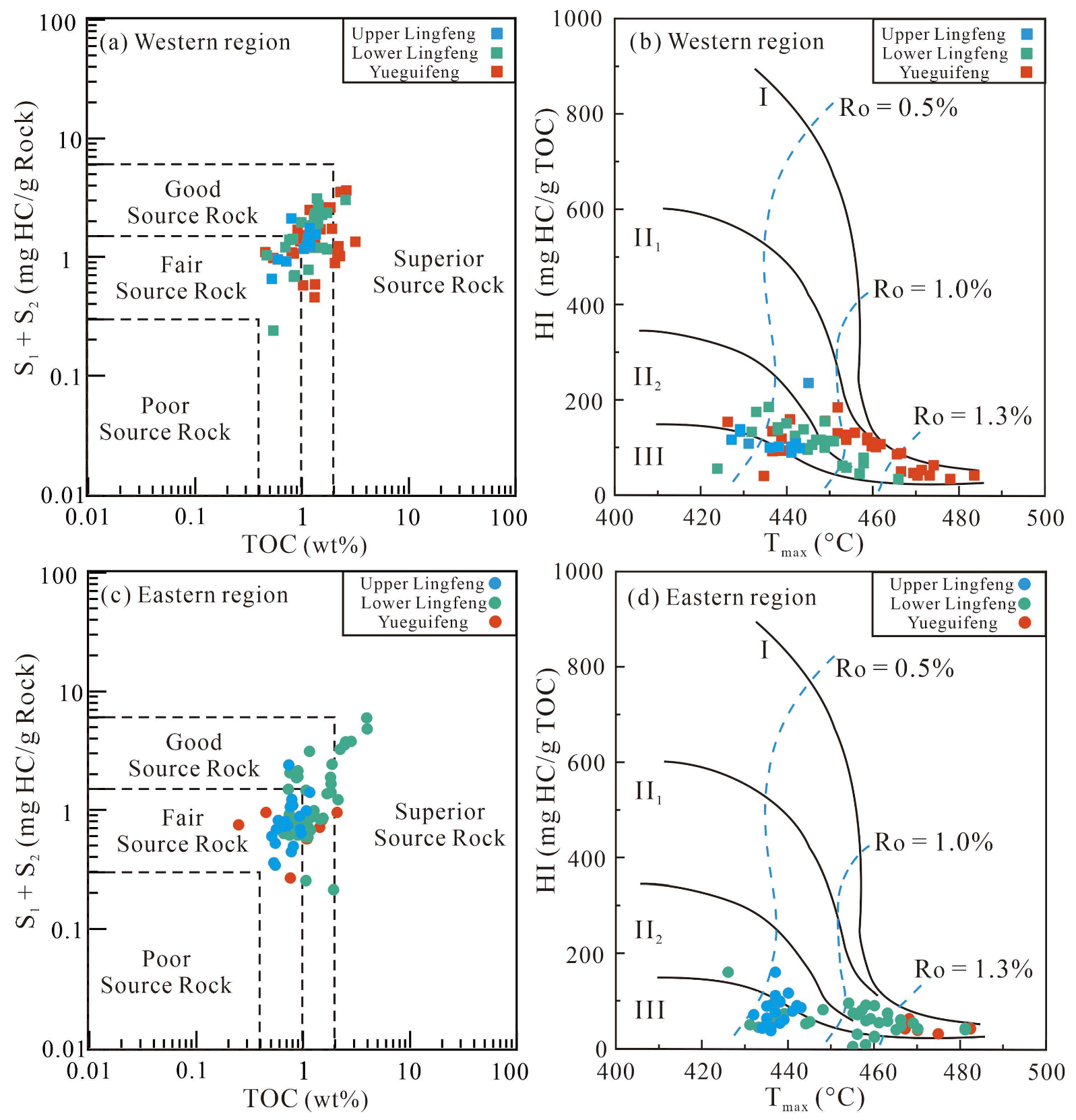
4.1. TOC and Rock-Eval Pyrolysis Data
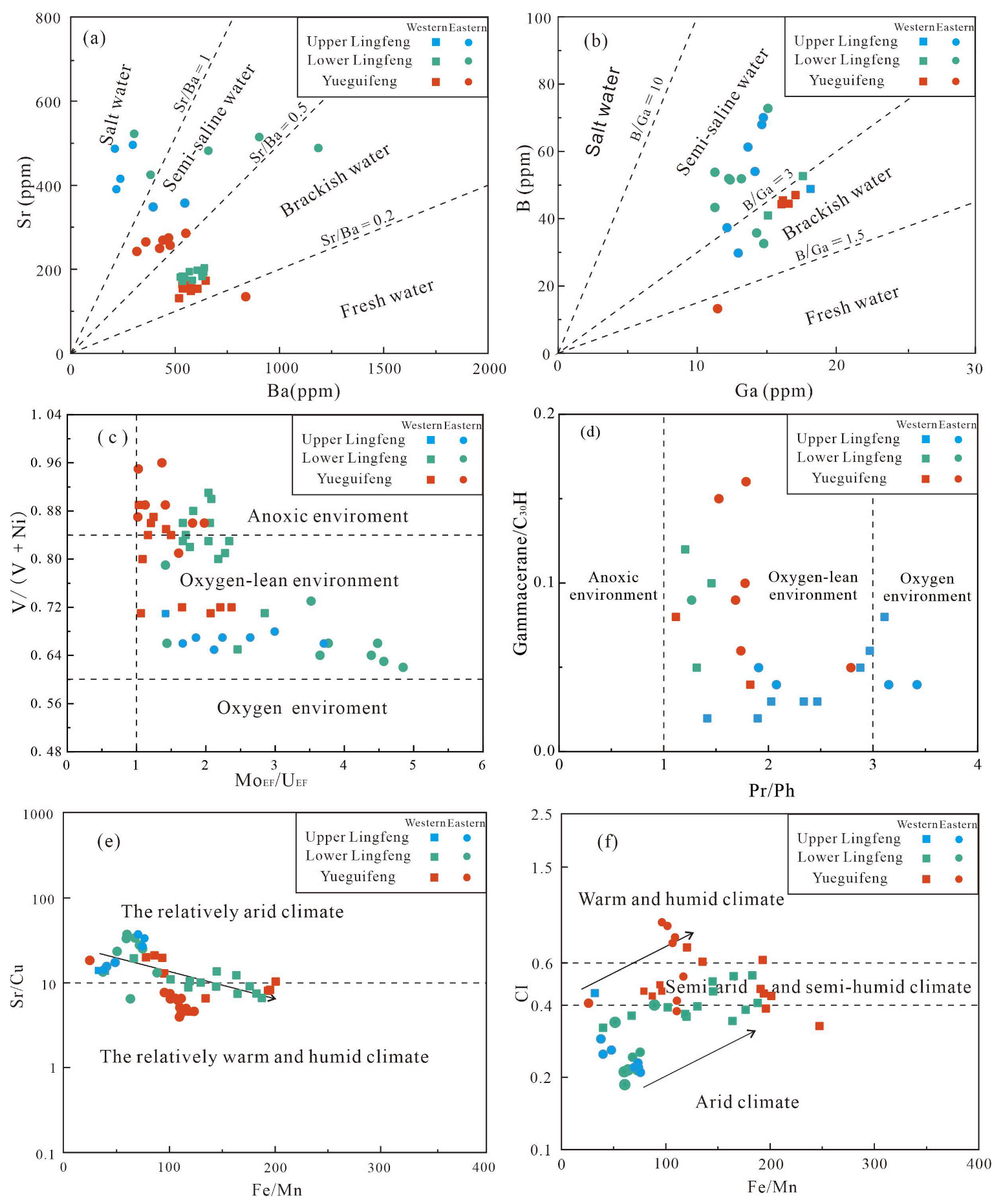
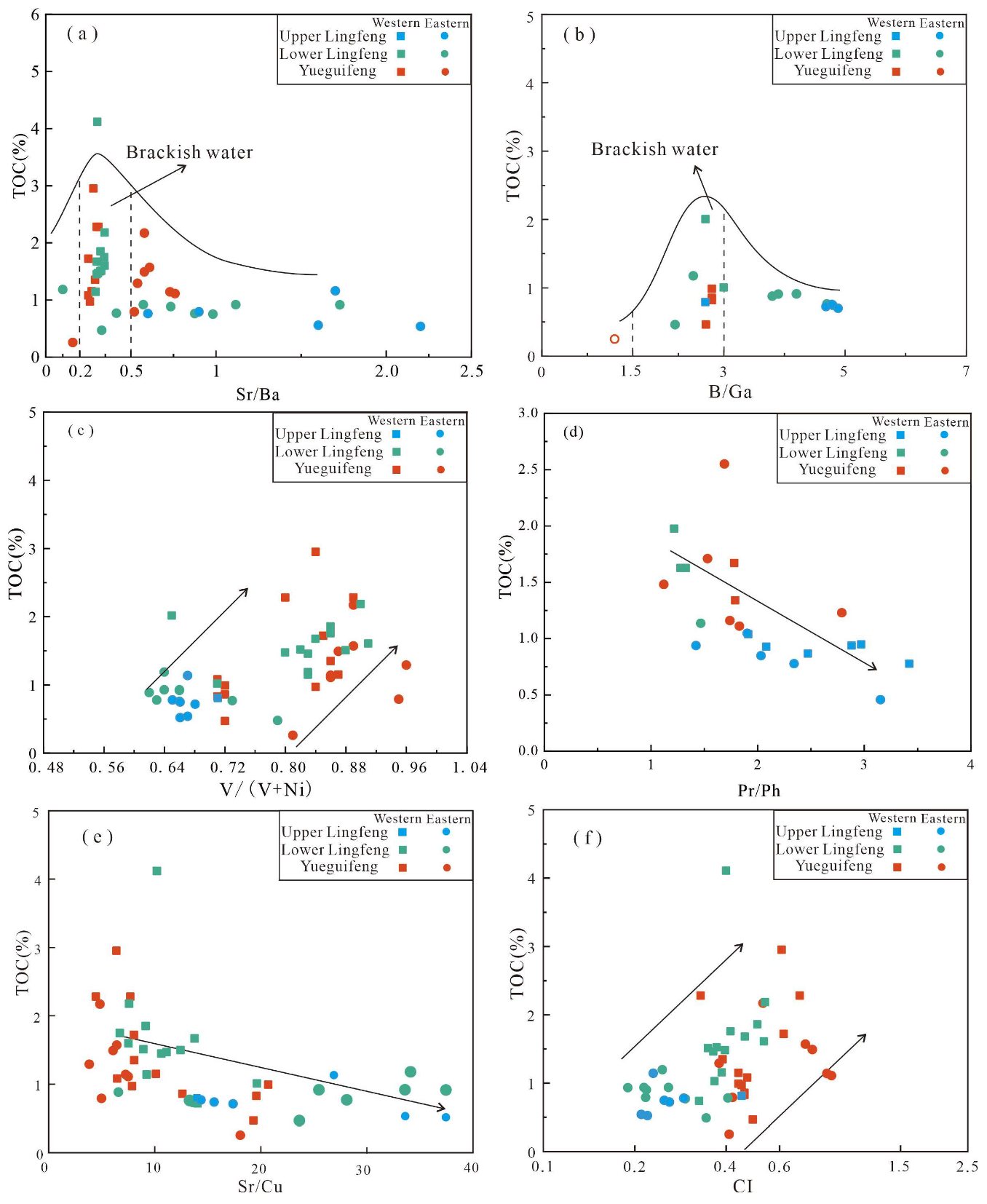
4.2. Major and Trace Elements Data
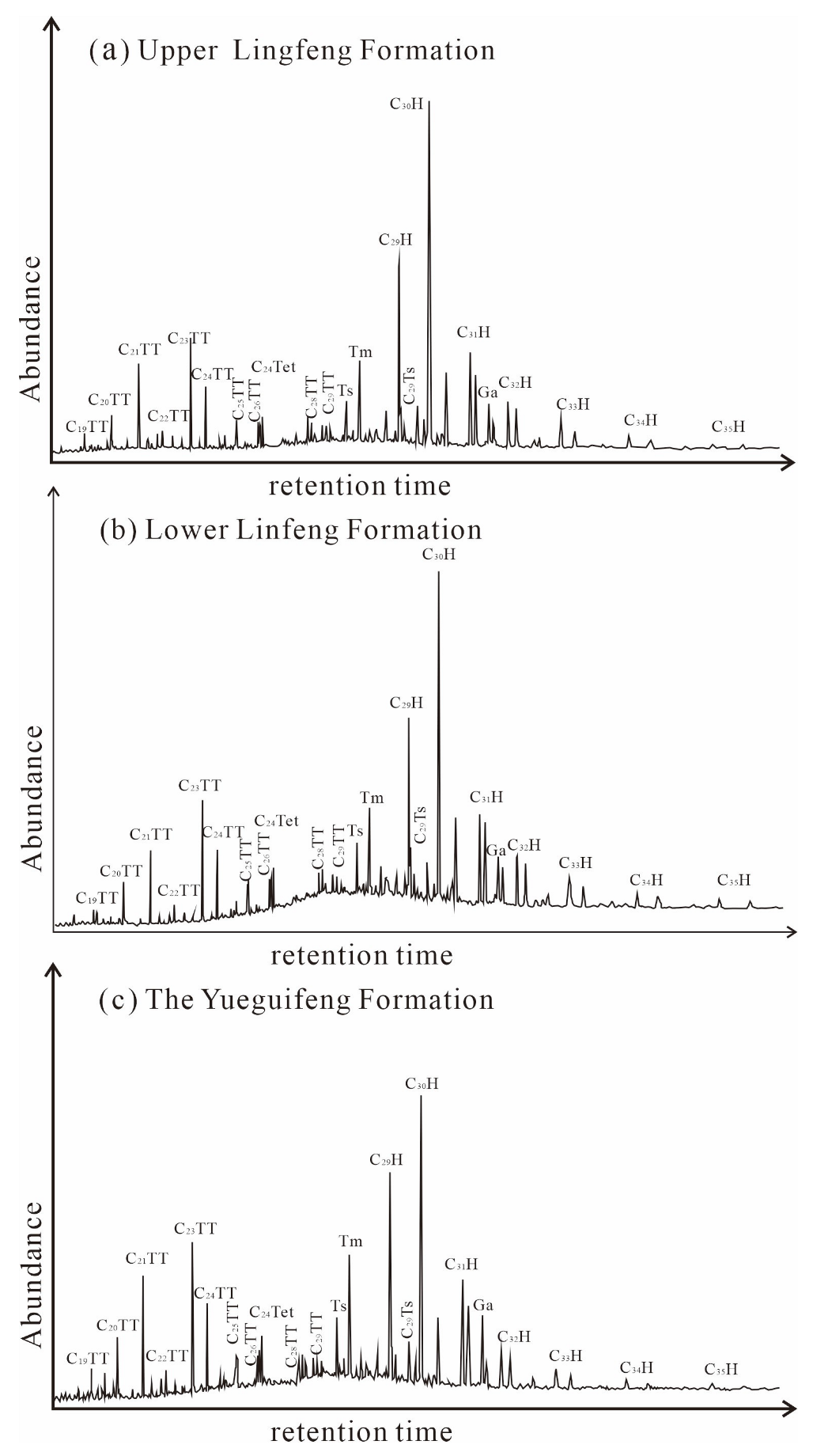
4.3. GC and GC-MS Analysis Results
5. Discussion
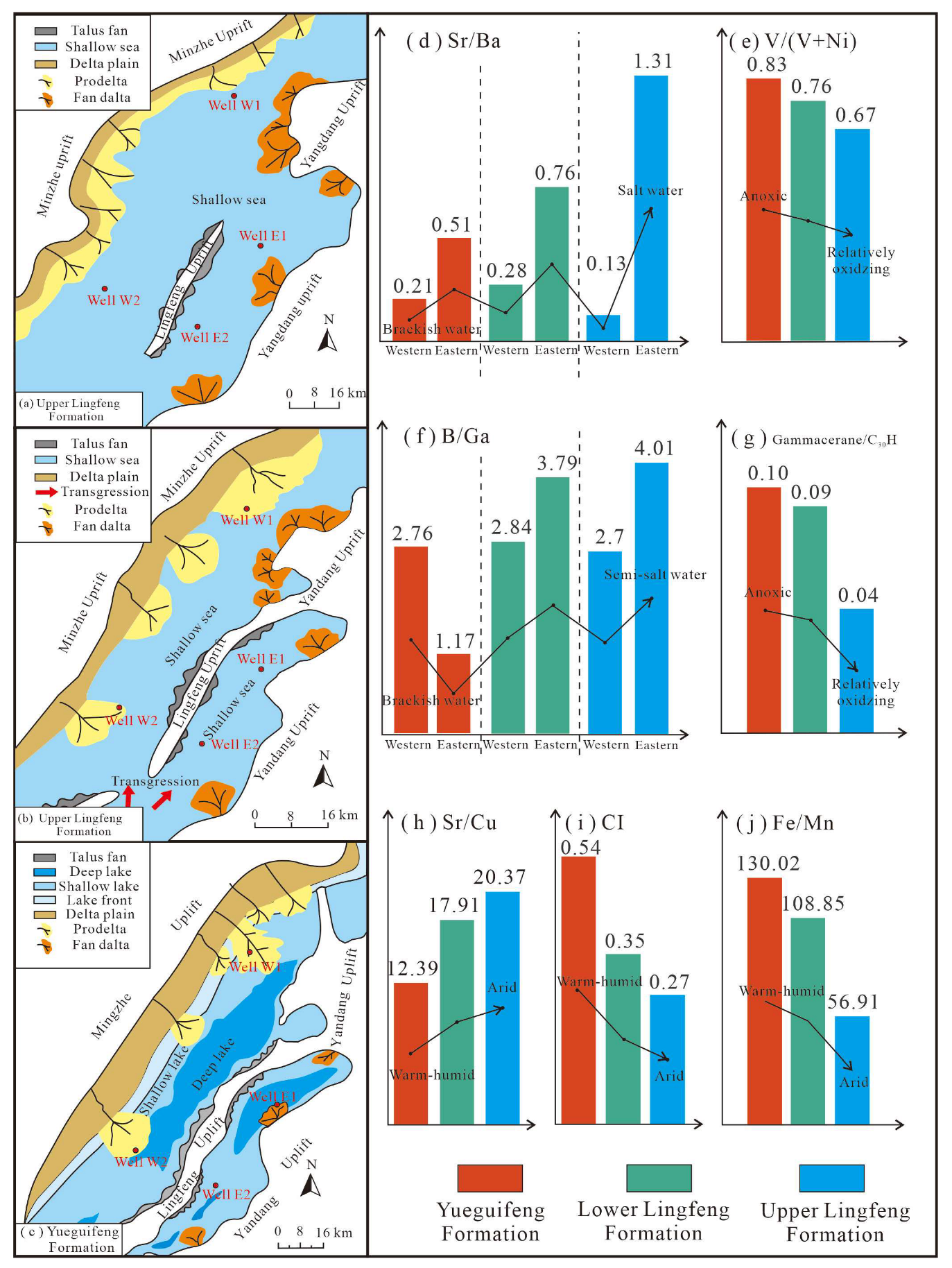
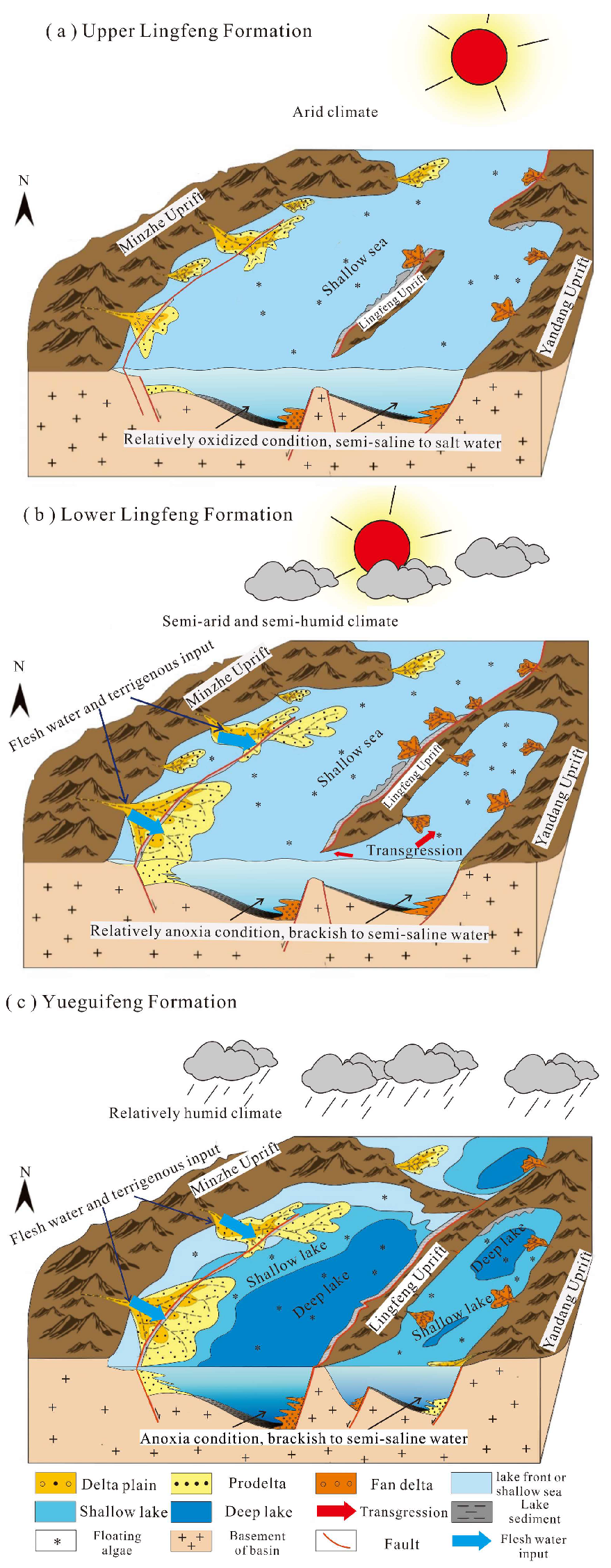
5.1. Paleoenvironmental Evolution in the Paleocene (66~59.2 Ma)
5.2. Accumulation Factors of Organic Matter in a Saline Condition Rift Basin
5.3. Implications for Hydrocarbon Exploration in the Lishui Depression
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- During the Paleocene, the Lishui Sag transformed from a closed lake to an open-marine environment, accompanied by a shift from warm-humid to arid climate conditions. Trace elements and biomarkers further support this transition, indicating a gradual oxidation process and an increase in salinity levels.
- (2)
- In the early Paleocene, lacustrine hydrocarbon source rocks in the Yueguifeng Formation formed in a warm-humid climate and brackish water environment, preserving a significant amount of mixed organic matter under anoxic conditions. In the late stage, marine hydrocarbon source rocks in the Lingfeng Formation developed under relatively arid and oxidizing conditions, with increased input of terrestrial organic matter and water salinity.
- (3)
- The source rocks in the Yueguifeng and lower member of Lingfeng formations are dominated by Type II kerogen, while Type Ⅲ kerogen is predominant in the upper member of Lingfeng Formation. The majority of source rocks have reached maturity and the threshold for hydrocarbon generation. Additionally, the thermal maturity of samples from the Yueguifeng Formation is higher compared to the samples from the Lingfeng Formation. Biomarker results reveal a transition from a blend of aquatic and terrestrial organic matter sources to a greater inflow of terrestrial organic matter in the source rocks.
- (4)
- The northeastern part of Lishui Sag is recommended as a significant target zone for future exploration. The source rocks in this region have reached the gas-generating threshold and further exploration should be advised to intensify efforts to search gas fields.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, D.W.; Zhou, C.M.; Zhang, Z.J.; Yuan, X.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Chen, X.Y. Paleo-environment reconstruction of the middle Permian Lucaogou Formation, southeastern Junggar Basin, NW China: Implications for the mechanism of organic matter enrichment in an ancient lake. J. Earth Sci. 2022, 33, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, R.V. Sedimentary Organic Matter: Organic Facies and Palynofacies; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cirilli, S.; Simonetta, N.; Gugliotti, L.; Frixa, A. Palynostratigraphy and palynofacies of the Upper Triassic Streppenosa Formation (SE Sicily, Italy) and inference on the main controlling factors in the organic rich shale deposition. Rev. Palaeobot. 2015, 218, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playford, G.; Hashemi, H.; Wicander, R. The palynostratigraphy of the Lower Carboniferous (middle Tournaisian–upper Viséan) Shishtu Formation from the Howz-e-Dorah section, southeast Tabas, central Iranian Basin. Palynology 2017, 40, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.Y.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, S.C.; Dai, J.X.; Wang, G.M.; Zhang, L.H.; Li, J. Characteristics and origin of deep lake oil shale of the Shahejie Formation of Paleogene in Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression. Palaeogeography 2005, 7, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gallego-Torres, D.; Martínez-Ruiz, F.; Paytan, A.; Jiménez-Espejo, F.J.; Ortega-Huertas, M. Pliocene-Holocene evolution of depositional conditions in the eastern Mediterranean: Role of anoxia vs. productivity at time of sapropel deposition. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2007, 246, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Liu, Z.J.; Bechtel, A.; Meng, Q.T.; Sun, P.C.; Jia, J.L.; Cheng, L.J.; Song, Y. Basin evolution and oil shale deposition during Upper Cretaceous in the Songliao Basin (NE China): Implications from sequence stratigraphy and geochemistry. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 149, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, T.F.; Calvert, S.E. Anoxia vs. productivity: What controls the formation of organic-carbon-rich sediments and sedimentary rocks?: Reply (1). AAPG Bull. 1991, 75, 500–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.C.; Zhang, B.M.; Bian, L.Z.; Jin, Z.J.; Wang, D.R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Gao, Z.Y.; Chen, J.F. Development constraints of marine source rocks in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2005, 12, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Demaison, G.J.; Moore, G.T. Anoxic environments and oil source bed genesis. Org. Geochem. 1980, 2, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, M.A.; Sageman, B.B. Marine black shales: Depositional mechanisms and environments of ancient deposits. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1994, 22, 499–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.G.; Bustin, R.M. Production and preservation of organic matter during deposition of the Bakken formation (Late Devonian and Early Mississippian), Williston Basin. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1998, 142, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, P.A.; Ishiwatari, R. Lacustrine organic geochemistry—An overview of indicators of organic matter sources and diagenesis in lake sediments. Org. Geochem. 1993, 20, 867–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Li, H.H.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, S.J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Z.Q.; Liu, J.; Tian, J.X.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X. Geochemical characteristics of the Paleogene and Neogene saline lacustrine source rocks in the western Qaidam Basin, northwestern China. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 4537–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Wu, X.S.; Wang, B.; Duan, Y.J.; Qu, Y.; Chen, D.F. Research progress of the enrichment mechanism of sedimentary organics in lacustrine basin. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2016, 34, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacka, K.; Mikulewicz, M. Biomarkers of trace element status. Recent Adv. Trace Elem. 2018, 457–467. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanova, M.; Kortenski, J.; Zdravkov, A.; Marinov, S. Paleoenvironmental settings of the Sofia lignite basin: Insights from coal petrography and molecular indicators. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 107, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summons, R.E.; Metzger, P.; Largeau, C.; Murray, A.P.; Hope, J.M. Polymethylsqualanes from Botryococcus braunii in lacustrine sediments and crude oils. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKirdy, D.M.; Cox, R.E.; Volkman, J.K.; Howell, V.J. Botryococcane in a new class of Australian non-marine crude oils. Nature 1986, 320, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Dutta, S. Higher plant biomarker signatures of Early Eocene sediments of North Eastern India. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 57, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, A.; Cirilli, S.; Sorci, A.; Schito, A.; Clayton, G.; Corrado, S.; Rettori, R. Assessing thermal maturity through a multi-proxy approach: A case study from the Permian Faraghan Formation (Zagros Basin, Southwest Iran). Sediment. Geol. 2021, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algeo, T.J.; Maynard, J.B. Trace-element behavior and redox facies in core shales of Upper Pennsylvanian Kansas-type cyclothems. Chem. Geol. 2004, 206, 289–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Jiang, L.; Liu, B.J.; Zhao, S.H.; Tang, S.H.; Tan, F.R. Investigation of Organic Matter Sources and Depositional Environment Changes for Terrestrial Shale Succession from the Yuka Depression: Implications from Organic Geochemistry and Petrological Analyses. J. Earth Sci. 2023, 34, 1577–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Horsfield, B. Critical review of the uncertainty of Tmax in revealing the thermal maturity of organic matter in sedimentary rocks. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2020, 22, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartkopf-Fröder, C.; Königshof, P.; Littke, R.; Schwarzbauer, J. Optical thermal maturity parameters and organic geochemical alteration at low grade diagenesis to anchimetamorphism: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 150, 74–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C Cirilli, S.; Panfili, G.; Buratti, N.; Frixa, A. Paleoenvironmental reconstruction by means of palynofacies and lithofacies analyses: An example from the Upper Triassic subsurface succession of the Hyblean Plateau Petroleum System (SE Sicily, Italy). Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2018, 253, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schito, A.; Corrado, S.; Trolese, M.; Aldega, L.; Caricchi, C.; Cirilli, S.; Grigo, D.; Guedes, A.; Romano, C.; Spina, A.; et al. Assessment of thermal evolution of Paleozoic successions of the Holy Cross Mountains (Poland). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 80, 112–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schito, A.; Spina, A.; Corrado, S.; Cirilli, S.; Romano, C. Comparing optical and Raman spectroscopic investigations of phytoclasts and sporomorphs for thermal maturity assessment: The case study of Hettangian continental facies in the Holy cross Mts.(central Poland). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 104, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Wang, T.-G.; Li, M.J.; Yang, F.L.; Cheng, B. Biomarker geochemistry of crude oils and Lower Paleozoic source rocks in the Tarim Basin, western China: An oil-source rock correlation study. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 96, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, S.J.; Su, Z.; Rong, H. Geochemical Characteristics and Origin of Crude Oil and Natural Gas in the Southern Slope Zone, Kuqa Foreland Basin, NW China. J. Earth Sci. 2022, 33, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, J.R.; Leventhal, J.S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, USA. Chem. Geol. 1992, 99, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, B.; Xu, Y. Charging of Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in the eastern Chepaizi uplift, junggar basin (northwestern China) constrained by oil geochemistry and fluid inclusion. AAPG Bull. 2019, 103, 1625–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, F.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Hou, G.; Zhang, P. Paleocene sequence stratigraphy and depositional systems in the Lishui Sag, East China Sea shelf Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 59, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.; Chen, H.H.; Cao, L.S.; Lei, M.Z.; Wang, C.W.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, P.J. Genesis, source and charging of oil and gas in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2014, 41, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.H.; Yu, S. Formation of the LS36-1 oil and gas structure in the Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2003, 30, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.Z.; Li, Y.J.; Du, H.L.; Zhang, Y.F. The Cenozoic structural evolution and its influences on gas accumulation in the Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 22, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Jiang, Y.M.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, S.; Li, N.; Liu, J.S.; Qiao, P.J.; Zhong, K.; Chen, S.H.; Goh, T.L. Early Cenozoic paleontological assemblages and provenance evolution of the Lishui Sag, East China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, J.L.; Shen, W.L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.S.; Wang, J.K.; Xie, J. Recovery of the erosion thickness and characterization of the paleogeomorphology in the southern Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf basin. J. Ocean Univ. China 2020, 19, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Li, S.L.; Li, S.L.; Xu, J.Y.; Huang, Y.Y. Genetic types of mudstone in a closed-lacustrine to open-marine transition and their organic matter accumulation patterns: A case study of the Paleocene source rocks in the East China Sea Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhu, W.L.; Yuan, L.C.; Cai, J.G. Influence of Provenance and the Sedimentary Environment on the Formation of High-Quality Source Rocks in the Paleocene Lishui Sag, China. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 5791–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Yin, S.Y.; Ye, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Gao, B. Characteristics and deposition models of the Paleocene source rocks in the Lishui Sag, East China Sea shelf Basin: Evidences from organic and inorganic geochemistry. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 200, 108342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.T.; Price, N.B. Departure curves for computing paleosalinity from boron in illites and shales. AAPG Bull. 1963, 47, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.D.; Haynes, J.R.; Walker, C.T. Boron in Holocene Illites of the Dovey Estuary, Wales, and its Relationship to Palaeosalinity in CYCLOTHEMS 1. Sedimentology 1965, 4, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makeen, Y.M.; Hakimi, M.H.; Abdullah, W.H. The origin, type and preservation of organic matter of the Barremian–Aptian organic-rich shales in the Muglad Basin, Southern Sudan, and their relation to paleoenvironmental and paleoclimate conditions. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 65, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Shen, W.L.; Chang, X.C.; Sun, Z.Q.; Xu, G.C. Organic geochemistry, distribution and hydrocarbon potential of source rocks in the Paleocene, Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 107, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.L.; Zhong, Z.; Fu, X.W.; Chen, C.F.; Zhang, M.Q.; Gao, S.L. The formation and evolution of the East China Sea Shelf Basin: A new view. Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 190, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zhao, J.M.; Zheng, Y.W. The hydrocarbon generation controlled by source rocks and heat in the offshore superimpose rift-subsidence basin: A case study from Lishui-jiaojiang Sag. J. Inner Mongolia Univ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 40, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Hu, B.Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Gu, Z.P.; Hong, Q. Geochemical Characteristics of Light Hydrocarbons in Crude Oil from Lishui 36-1 Oil and Gas Field. J. Chongqing Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 22, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Zhu, W.L.; Gao, S.L.; Fu, X.W. Key Geological Questions of the Formation and Evolution and Hydrocarbon Accumulation of the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Earth Sci. 2018, 43, 3485–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.G.; Kominz, M.A.; Browning, J.V.; Wright, J.D.; Mountain, G.S.; Katz, M.E.; Pekar, S. The Phanerozoic record of global sea-level change. Science 2005, 31, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Guan, S.W.; Wu, L.; Ren, R.; Xiong, L.Q. Geochemical characteristics and its paleo-environmental significance of the Lower Cambrian carbonate in the northwestern Tarim Basin: A case study of Well Shutan-1. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2021, 40, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclennan, S.M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks; influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Rev. Mineral Geochem. 1989, 21, 169–200. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J. Petroleum Geochemistry and Geology; Freeman Company: New York, NY, USA, 1996; 743p. [Google Scholar]
- Zachos, J.; Pagani, M.; Sloan, L.; Thomas, E.; Billups, K. Trends, Rhythms, and Aberrations in Global Climate 65 Ma to Present. Science 2001, 292, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Shen, W.L.; Li, Y.; Li, L.J. Sedimentological signatures and identification of Paleocene sedimentary facies in the Lishui sag, East China Sea Shelf basin. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2020, 57, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkman, J.K. A review of sterol markers for marine and terrigenous organic matter. Org. Geochem. 1986, 9, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.T.; Cheng, R.H.; Liu, C.L. Review of Paleosalinity Recovering Methods. World Geol. 2002, 21, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Algeo, T.J. Elemental proxies for paleosalinity analysis of ancient shales and mudrocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 287, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Ren, L.y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.D.; He, F.; Wang, Y.X. Characteristic of diagenesis saline lake environment and its effect on high-porosity zones. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2003, 30, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, F.L.; Tang, G.M.; Li, G.X.; Zeng, X.X.; Wu, Y.P. Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of source rocks of the Dongying Formation in southwest subsag of Bozhong Sag. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2023, 42, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, J.; Wendler, J.; Leider, A.; Kuss, H.J.; Hinrichs, K.U. Molecular isotopic evidence of environmental and ecological changes across the Cenomanian–Turonian boundary in the Levant platform of central Jordan. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Weng, H.X.; Su, A.G.; Liang, D.G.; Peng, D.H. Geochemical characteristics of Tertiary saline lacustrine oils in the Western Qaidam Basin, northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1875–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.Z. The element, clay mineral, and depositional environment in Herein Sand Land. J. Desert Res. 1992, 12, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Song, Y.; Pang, X.Q.; Jiang, Z.X.; Guo, Y.C.; Zhang, H.G.; Pan, Z.H.; Jiang, H. Effects of paleo sedimentary environment in saline lacustrine basin on organic matter accumulation and preservation: A case study from the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 185, 106669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Hu, K.; Bian, L.Z.; Wang, L.G.; Zhang, Y. Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of Jurassic mudstones in the northern Qaidam basin, northwest China. Geochemistry 2012, 72, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, M.H.; Abdullah, W.H.; Makeen, Y.M.; Saeed, S.A.; Al-Hakame, H.; Al-Moliki, T.; Al-Sharabi, K.Q.; Hatem, B.A. Geochemical characterization of the Jurassic Amran deposits from Sharab area (SW Yemen): Origin of organic matter, paleoenvironmental and paleoclimate conditions during deposition. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 129, 579–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Liang, C.; Qiu, L.; Kamran, M.I.R.Z.A.; Wang, Y.; Kashif, M.; Teng, J. Depositional Environment and Lithofacies Analyses of Eocene Lacustrine Shale in the Bohai Bay Basin: Insights from Mineralogy and Elemental Geochemistry. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, 9, 589–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Wu, Z.X.; Yu, S.; Jia, D.H. Paleocene trace element geochemistry and its geological significance in Lishui sag. China Offshore Oil and Gas 2005, 17, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.T.; Chen, S.; Yan, D.T.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Jing, Z.H.; Pan, S.Q. Detrital zircon geochronology and heavy mineral composition constraints on provenance evolution in the western Pearl River Mouth basin, northern south China sea: A source to sink approach. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2022, 145, 105884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.T.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.X.; Pan, S.Q.; Jing, Z.H.; Ma, Q.L.; Gan, H.J.; Zhao, J.X. Sedimentary architecture and provenance analysis of a sublacustrine fan system in a half-graben rift depression of the South China Sea. Sediment. Geol. 2020, 409, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.E.; Carroll, A.R. Introduction to the Green River Formation. Stratigraphy and Paleolimnology of the Green River Formation, Western USA; Springer: Cham, Swizterland, 2015; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Smith, M.E. Lacustrine Sedimentology, Stratigraphy and Stable Isotope Geochemistry of the Tipton Member of the Green River Formation. Stratigrzaphy and Paleolimnology of the Green River Formation, Western USA; Springer: Cham, Swizterland, 2015; pp. 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Bakun, A. Global climate change and intensification of coastal ocean upwelling. Science 1990, 247, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broecker, W.S. Abrupt climate change: Causal constraints provided by the paleoclimate record. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2000, 51, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorci, A.; Cirilli, S.; Spina, A.; Ghorbani, M.; Rettori, R. Facies analysis and depositional environment of a late Cambrian mixed carbonate-siliciclastic ramp from the Zard Kuh Mountain (Zagros Basin, south-western Iran). Sediment. Geol. 2023, 449, 106370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, H.R.; Franseen, E.K.; Joeckel, R.M.; Heckel, P.H. Impact of longer-term modest climate shifts on architecture of high-frequency sequences (cyclothems), Pennsylvanian of Midcontinent USA. J. Sediment. Res. 2005, 75, 350–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.F.; Jiang, F.J.; Ji, H.C.; Jiang, S.; Liu, X.H.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.Q.; Xiong, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Effects of paleosedimentary environment on organic matter enrichment in a saline lacustrine rift basin-A case study of Paleogene source rock in the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 195, 107658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.B.; Hao, F.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhao, D.J.; Tian, J.Q.; Wang, Z.F. Source rock deposition controlled by tectonic subsidence and climate in the western Pearl River Mouth Basin, China: Evidence from organic and inorganic geochemistry. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 79, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, D.L. Cretaceous shales from the western interior of North America: Sulfur/carbon ratios and sulfur-isotope composition. Geology 1986, 14, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.B. Fractured shale-gas systems. AAPG Bull. 2002, 86, 1921–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.Y.; Tamaki, K.; Li, S.T.; Junxia, Z. Late Mesozoic and Cenozoic rifting and its dynamic setting in Eastern China and adjacent areas. Tectonophysics 2002, 344, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ye, J.R.; Lei, C.; Yang, B.L.; Dan, C.; He, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.M. Development controlling factors and forming model for source rock of Yueguifeng Formation in Lishui-jiaojiang sag, the East China Sea Continental Shelf Basin. Earth Sci. 2016, 41, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymo, M.E.; Ruddiman, W.F.; Froelich, P.N. Influence of late Cenozoic mountain building on ocean geochemical cycles. Geology 1988, 16, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, B.B.; Isaksen, M.F.; Jannasch, H.W. Bacterial sulfate reduction above 100 C in deep-sea hydrothermal vent sediments. Science 1992, 258, 1756–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.T. Organic and isotope geochemistry of the Early Cretaceous rift sequence in the Camamu Basin, Brazil: Paleolimnological inferences and source rock models. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohacs, K.M.; Carroll, A.R.; Neal, J.E.; Mankiewicz, P.J. Lake-Basin Type, Source Potential, and Hydrocarbon Character: An Integrated Sequence-Stratigraphic-Geochemical Framework; Studies in Geology #46; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2000; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tissot, B.P. Recent advances in petroleum geochemistry applied to hydrocarbon exploration. AAPG Bull. 1984, 68, 546–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembicki, H., Jr. Three common source rock evaluation errors made by geologists during prospect or play appraisals. AAPG Bull. 2009, 93, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Ge, H.P.; Chen, X.D.; Deng, C.P.; Liang, D.G. Classification and origin of natural gases from Lishui Sag, the East China Sea Basin. Sci. China, Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Yin, S.Y.; Ye, J.R.; Wu, J.F. Geochemical characteristics and hydrocarbon generation history of the Paleogene source rocks in the Jiaojiang Sag, East China Sea Basin. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 3575–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, J.; Liu, E.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, P.; Jiao, Y. Paleoenvironmental Evolution and Organic Matter Accumulation in a Hydrocarbon-Bearing Depression in the East China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122341
Zhan J, Liu E, Chen S, Zhang Q, Chen Y, Zhong J, Zhou Y, Yang P, Jiao Y. Paleoenvironmental Evolution and Organic Matter Accumulation in a Hydrocarbon-Bearing Depression in the East China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(12):2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122341
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Junming, Entao Liu, Si Chen, Qiyang Zhang, Yuyue Chen, Jialin Zhong, Yongkun Zhou, Peifeng Yang, and Yangshuo Jiao. 2023. "Paleoenvironmental Evolution and Organic Matter Accumulation in a Hydrocarbon-Bearing Depression in the East China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 12: 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122341
APA StyleZhan, J., Liu, E., Chen, S., Zhang, Q., Chen, Y., Zhong, J., Zhou, Y., Yang, P., & Jiao, Y. (2023). Paleoenvironmental Evolution and Organic Matter Accumulation in a Hydrocarbon-Bearing Depression in the East China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(12), 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122341







