First Report of Pinnatoxins in Bivalve Molluscs from Inhaca Island (South of Mozambique)—South of the Indian Ocean
Abstract
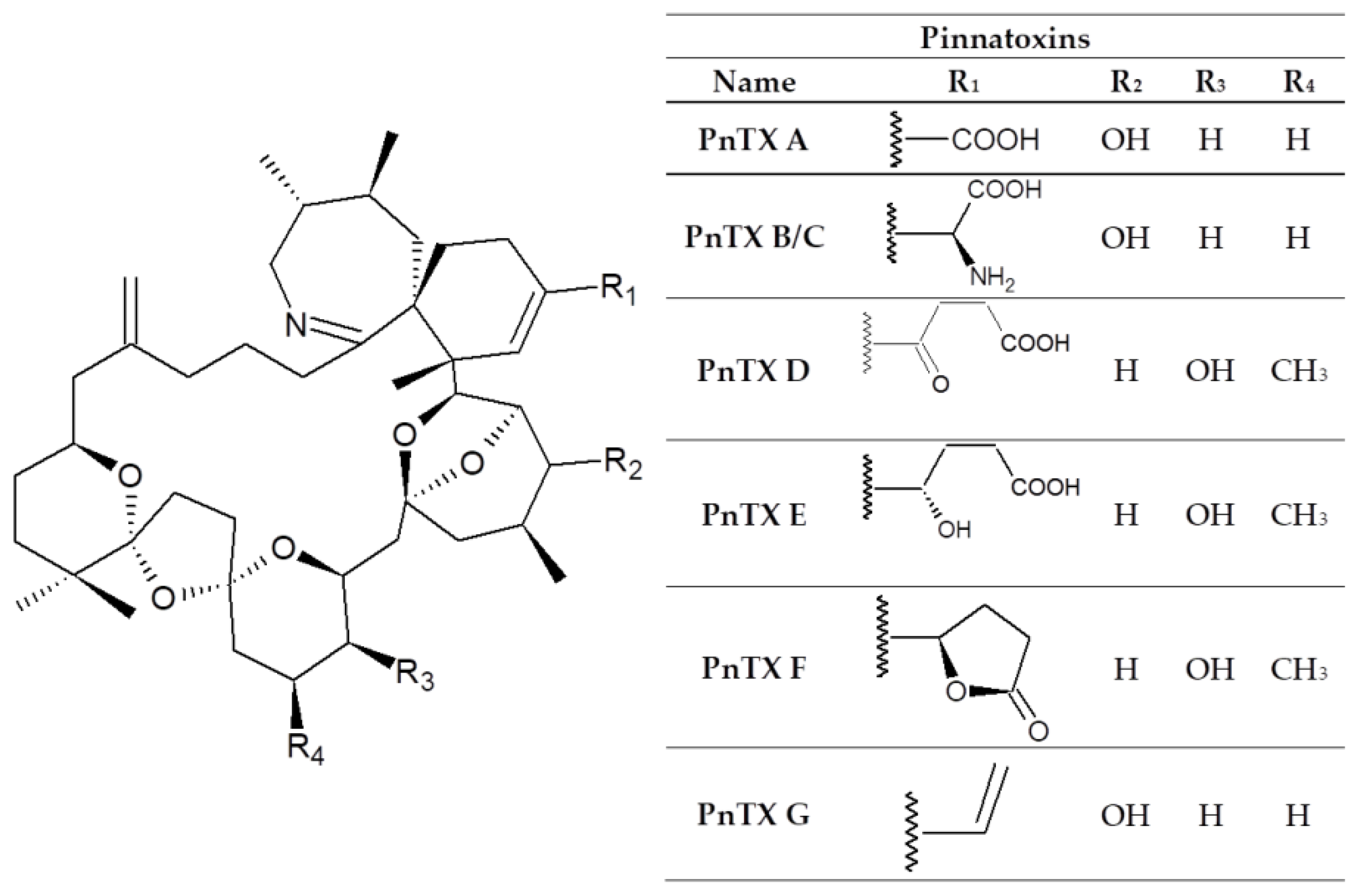
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
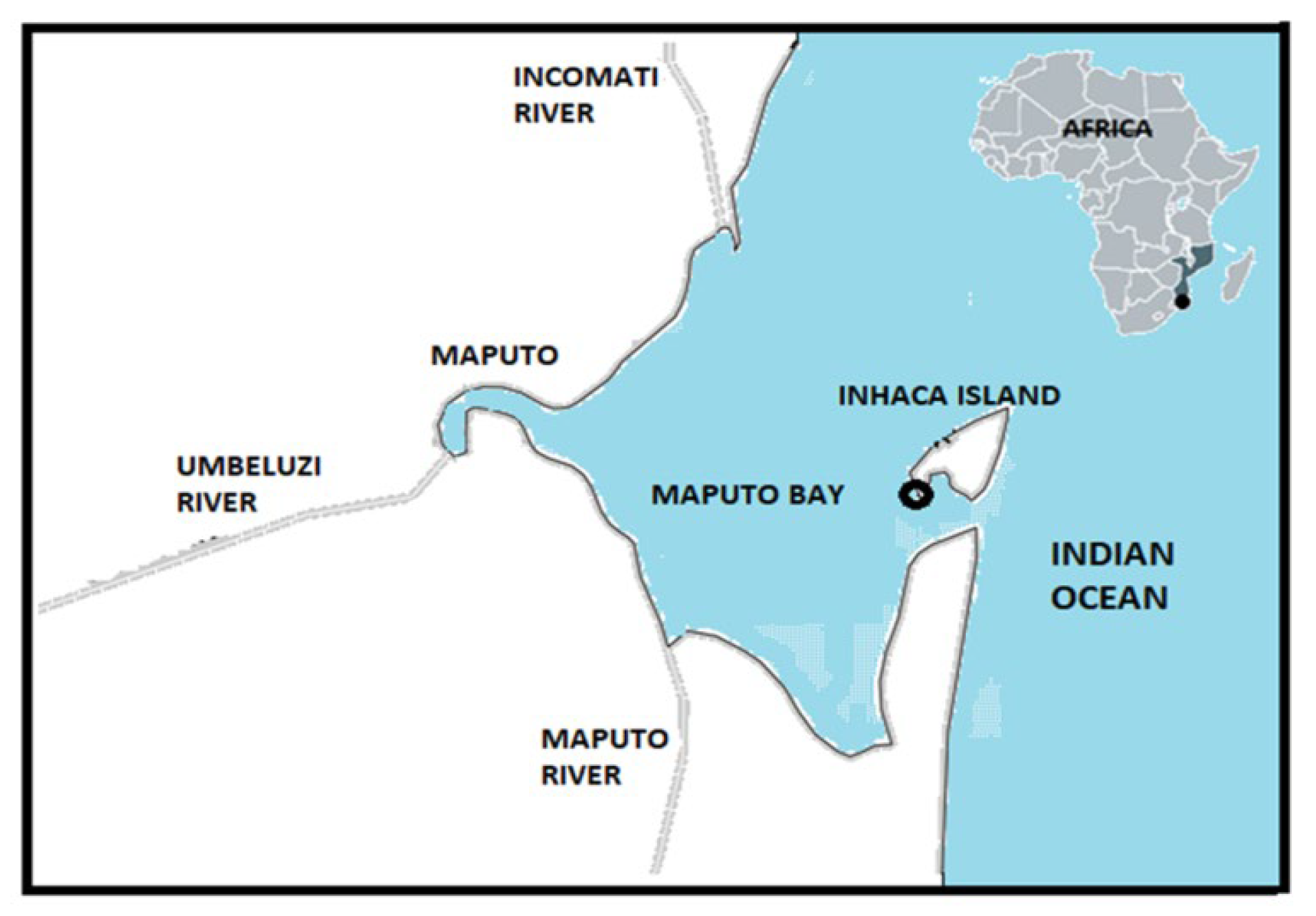
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Extraction of the Toxins
2.4. LC–MSMS Analysis
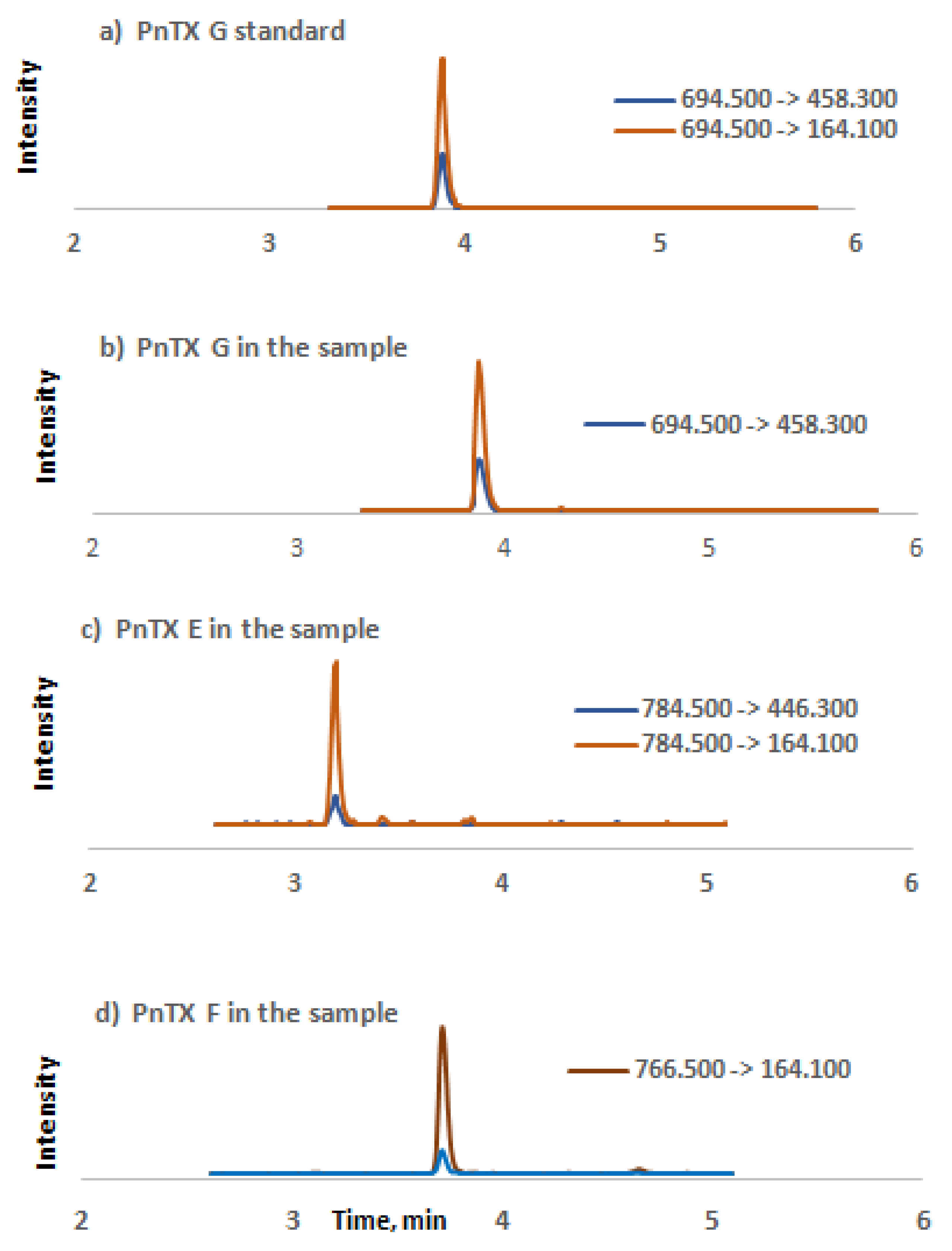
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tamele, I.J.; Silva, M.; Vasconcelos, V. The Incidence of Tetrodotoxin and Its Analogs in the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamele, I.J.; Silva, M.; Vasconcelos, V. The incidence of marine toxins and the associated seafood poisoning episodes in the African countries of the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea. Toxins 2019, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stivala, C.E.; Benoit, E.; Araoz, R.; Servent, D.; Novikov, A.; Molgó, J.; Zakarian, A. Synthesis and biology of cyclic imine toxins, an emerging class of potent, globally distributed marine toxins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 411–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, A.; Chapela, M.-J.; Atanassova, M.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. Cyclic imines: Chemistry and mechanism of action: A review. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish–Cyclic imines (spirolides, gymnodimines, pinnatoxins and pteriatoxins). EFSA 2010, 8, 1628. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Huang, F.; Chen, S.; Tan, X.; Zuo, J.; Peng, J.; Xie, R. The isolation and bioactivities of pinnatoxin. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs Zhongguo Haiyang Yaowu. Qingdao 1990, 9, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hellyer, S.D. Mechanism of Action of Pinnatoxins E, F and G; University of Otago: Dunedin, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Delcourt, N.; Lagrange, E.; Abadie, E.; Fessard, V.; Frémy, J.-M.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Peyrat, M.-B.; Maignien, T.; Arnich, N.; Molgó, J. Pinnatoxins’ deleterious effects on cholinergic networks: from experimental models to human health. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten-Hage, L.c.; Delaunay, N.; Pichon, V.; Couté, A.; Puiseux-Dao, S.; Turquet, J. Okadaic acid production from the marine benthic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum arenarium Faust (Dinophyceae) isolated from Europa Island coral reef ecosystem (SW Indian Ocean). Toxicon 2000, 38, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaıcha, N.; Chézeau, A.; Turquet, J.; Quod, J.-P.; Puiseux-Dao, S. Morphological and toxicological variability of Prorocentrum lima clones isolated from four locations in the south-west Indian Ocean. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermehl, G.G.; Krebs, H.C.; Rasoanaivo, P.; Ramialiharisoa, A. Severe ciguatera poisoning in Madagascar: A case report. Toxicon 1994, 32, 1539–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogène, J.; Reverté, L.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Del Río, V.; De La Iglesia, P.; Campàs, M.; Palacios, O.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Ralijaona, C. Identification of ciguatoxins in a shark involved in a fatal food poisoning in the Indian Ocean. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverté, L.; Soliño, L.; Carnicer, O.; Diogène, J.; Campàs, M. Alternative methods for the detection of emerging marine toxins: Biosensors, biochemical assays and cell-based assays. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5719–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molgó, J.; Marchot, P.; Aráoz, R.; Benoit, E.; Iorga, B.I.; Zakarian, A.; Taylor, P.; Bourne, Y.; Servent, D. Cyclic imine toxins from dinoflagellates: A growing family of potent antagonists of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EURLMB. EU-Harmonised Standard Operating Procedure for Determination of Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins in Molluscs by LC-MS/MS, Version 5; EURLMB: Vigo, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Selwood, A.I.; Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; van Ginkel, R.; Munday, R.; Rise, F.; McNabb, P. Isolation, structural determination and acute toxicity of pinnatoxins E, F and G. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6532–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Altares, M.; Casanova, A.; Bane, V.; Diogène, J.; Furey, A.; De la Iglesia, P. Confirmation of pinnatoxins and spirolides in shellfish and passive samplers from Catalonia (Spain) by liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole and high-resolution hybrid tandem mass spectrometry. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3706–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Vale, C.; Boente-Juncal, A.; Costas, C.; Louzao, M.C.; Botana, L.M. Detection of Cyclic Imine Toxins in Dietary Supplements of Green Lipped Mussels (Perna canaliculus) and in Shellfish Mytilus chilensis. Toxins 2020, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarron, P.; Rourke, W.A.; Hardstaff, W.; Pooley, B.; Quilliam, M.A. Identification of pinnatoxins and discovery of their fatty acid ester metabolites in mussels (Mytilus edulis) from eastern Canada. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundberget, T.; Aasen, J.A.B.; Selwood, A.I.; Miles, C.O. Pinnatoxins and spirolides in Norwegian blue mussels and seawater. Toxicon 2011, 58, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, P.; Abadie, E.; Hervé, F.; Berteaux, T.; Séchet, V.; Aráoz, R.; Molgó, J.; Zakarian, A.; Sibat, M.; Rundberget, T. Pinnatoxin G is responsible for atypical toxicity in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and clams (Venerupis decussata) from Ingril, a French Mediterranean lagoon. Toxicon 2013, 75, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNabb, P.; Rhodes, L.; Selwood, A. Results of analyses for brevetoxins and pinnatoxins in Rangaunu Harbour oysters, 1993–2008. Cawthron Rep. 2008, 1453, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Rambla-Alegre, M.; Miles, C.O.; de la Iglesia, P.; Fernandez-Tejedor, M.; Jacobs, S.; Sioen, I.; Verbeke, W.; Samdal, I.A.; Sandvik, M.; Barbosa, V. Occurrence of cyclic imines in European commercial seafood and consumers risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvrgić, K.; Lešić, T.; Aysal, A.I.; Džafić, N.; Pleadin, J. Cyclic imines in shellfish and ascidians in the northern Adriatic Sea. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2021, 14, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas, J.P.; Arévalo, F.; Moroño, Á.; Correa, J.; Muñíz, S.; Blanco, J. Detection and spatio-temporal distribution of pinnatoxins in shellfish from the Atlantic and Cantabrian coasts of Spain. Toxins 2019, 11, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, K.F.; Rhodes, L.L.; Suda, S.; Selwood, A.I. A dinoflagellate producer of pinnatoxin G, isolated from sub-tropical Japanese waters. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, A.; McNabb, P.; Van Ginkel, R.; Holland, P.; Munday, R. Production of pinnatoxins by a peridinoid dinoflagellate isolated from Northland, New Zealand. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, A.; McNabb, P.; Munday, R.; Suda, S.; Molenaar, S.; Hallegraeff, G. Dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum identified as the causative organism of pinnatoxins in Australia, New Zealand and Japan. Phycologia 2011, 50, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, A.; McNabb, P.; Molenaar, S.; Munday, R.; Wilkinson, C.; Hallegraeff, G. Production of pinnatoxins E, F and G by scrippsielloid dinoflagellates isolated from Franklin Harbour, South Australia. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 45, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.A. On the functional morphology of Pinna and Atrina larvae (Bivalvia: Pinnidae) from the Atlantic. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2011, 91, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, D.; Chou, T.; Haino, T.; Nagatsu, A.; Fukuzawa, S.; Zheng, S.-z.; Chen, H.-s. Pinnatoxin A: A toxic amphoteric macrocycle from the Okinawan bivalve Pinna muricata. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 1155–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.; Osamu, K.; Uemura, D. Relative stereochemistry of pinnatoxin A, a potent shellfish poison from Pinna muricata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 4023–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, N.; Umemura, N.; Suenaga, K.; Chou, T.; Nagatsu, A.; Haino, T.; Yamada, K.; Uemura, D. Pinnatoxins B and C, the most toxic components in the pinnatoxin series from the Okinawan bivalve Pinna muricata. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 3491–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.; Haino, T.; Kuramoto, M.; Uemura, D. Isolation and structure of pinnatoxin D, a new shellfish poison from the Okinawan bivalve Pinna muricata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 4027–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, N.; Umemura, N.; Suenaga, K.; Uemura, D. Structural determination of pteriatoxins A, B and C, extremely potent toxins from the bivalve Pteria penguin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 3495–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSES. Opinion of the French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety on the Assessment of the Health Risks Associated with Pinnatoxins in Shellfish; ANSES: Maisons-Alfort, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]

| Species | Individuals | Weigh (g) |
|---|---|---|
| Atrina vexillum | 5 | 17.2–43.1 |
| Pinctada imbricata | 28 | 30.9–51.4 |
| Anadara antiquata | 3 | 23.5–27.4 |
| Saccostrea cucculata | 40 | 34.4–63.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamele, I.J.; Timba, I.; Vasconcelos, V.; Costa, P.R. First Report of Pinnatoxins in Bivalve Molluscs from Inhaca Island (South of Mozambique)—South of the Indian Ocean. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091215
Tamele IJ, Timba I, Vasconcelos V, Costa PR. First Report of Pinnatoxins in Bivalve Molluscs from Inhaca Island (South of Mozambique)—South of the Indian Ocean. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(9):1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091215
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamele, Isidro José, Ilário Timba, Vitor Vasconcelos, and Pedro Reis Costa. 2022. "First Report of Pinnatoxins in Bivalve Molluscs from Inhaca Island (South of Mozambique)—South of the Indian Ocean" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 9: 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091215
APA StyleTamele, I. J., Timba, I., Vasconcelos, V., & Costa, P. R. (2022). First Report of Pinnatoxins in Bivalve Molluscs from Inhaca Island (South of Mozambique)—South of the Indian Ocean. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(9), 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091215








