Measurement of Diurnal Body Tilt Angle Distributions of Threeline Grunt Parapristipoma trilineatum Using Micro-Acceleration Data Loggers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
3. Results

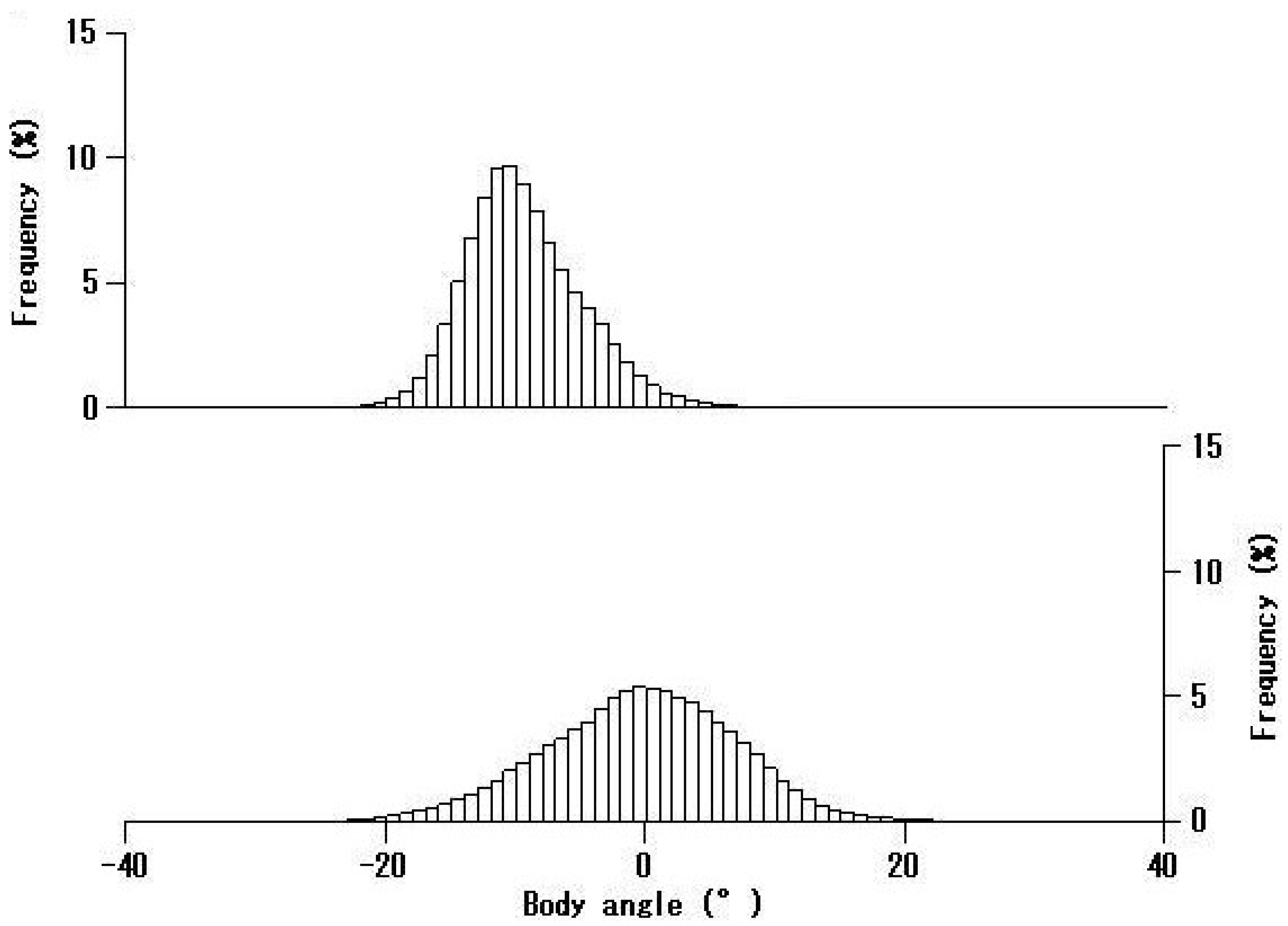
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Johanneson, K.A.; Mitson, R.B. A practical manual for aquatic biomass estimation. FAO Fish. Tech. Pap. 1983, 240, 1–249. [Google Scholar]
- Nakken, O.; Olsen, K. Target-strength measurements of fish. Rapp. P.-v. Réun. Cons. Int. Explor. Mer. 1977, 170, 53–69. [Google Scholar]
- Foote, K.G. Linearity of fisheries acoustics, with addition theorems. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1983, 73, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, K.G.; Ona, E. Tilt angles of schooling penned saithe. ICES Counc. Meet. Pap. 1985, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hazen, E.L.; Horne, J.K. Comparing the modelled and measured target-strength variability of walleye pollock, Theragra chalcogramma. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2004, 61, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooyman, G.L. Genesis and Evolution of Bio-logging Devices: 1963–2002. In Bio-Logging Science; Naito, Y., Ed.; National Institute of Polar Research Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2004; Volume 58, pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Takagi, Y.; Naito, Y. Swimming speeds and buoyancy compensation of migrating adult chum salmon Oncorhynchus keta revealed by speed/depth/acceleration data logger. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 3895–3904. [Google Scholar]
- Alabsi, N.M.; Tanoue, H.; Komatsu, T.; Charef, A.; Mitani, I.; Kato, M.; Horii, T.; Aoki, I.; Miyazaki, N. Measurement of the Swimming behavior of a deep-water fish, the splendid alfonsino (beryx splendens), in captivity using micro data loggers. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 6, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanoue, H.; Komatsu, T.; Tsujino, T.; Suzuki, I.; Watanabe, M.; Goto, H.; Miyazaki, N. Feeding events of Japanese lates Lates japonicus detected by a high-speed video camera and three-axis micro-acceleration data-logger. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 533–538. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Takagi, T.; Hiraishi, T. Video analysis of fish schooling behavior in finite space using a mathematical model. Fish. Res. 2003, 60, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, T.; Tanoue, H.; Mohamad, N.; Watariguchi, K.; Osswald, T.; Hill, D.; Miyazaki, N. Relation Between Body Tilt Angle and Tail Beat Acceleration of a Small Fish, Parapristipoma trilineatum (Threeline Grunt), During Mobile and Immobile Periods Measured with a Micro Data Logger. In Global Change: Mankind-Marine Environment Interactions; Ceccaldi, H.-J., Dekeyser, I., Giraut, M., Stora, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Weihs, D. Hydromechanics of fish schooling. Nature 1973, 241, 290–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.J.W.; Krause, J. Body length assortative shoaling in the European minnow, Phoxinus phoxinus. Anim Behav. 2001, 62, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallepp, G.W.; Magnuson, J.J. Effects of negative buoyancy on the behavior of the bluegill, Lepomis macrochirus Rafinesque. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 1972, 101, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, S.; Steven, B.J.; Cooke, W.; Gary, A.; Scott, R.M. Evidence to challenge the “2% rule” for biotelemetry. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1999, 19, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropert-Coudert, Y.; Kato, A.; Wilson, R.P.; Cannell, B. Foraging strategies and prey encounter rate of free-ranging Little Penguins. Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridger, C.J.; Booth, R.K. The effects of biotelemetry transmitter presence and attachment procedures on fish physiology and behavior. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2003, 11, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumiya, Y.; Takahashi, K. Feeding habit of grunt, Parapristipoma trilineatum in Shijiki Bay, Hirado Island. Bull. Seikai Reg. Fish. Res. Lab. 1983, 59, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kawano, M. Study of the management of Threeline Grunt (Parapristipoma trilineatum) in coastal waters off Yamaguchi Prefecture. Bull. Yamaguchi Prefect. Gaikai Fish. Exp. Stn. 1997, 26, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanoue, H.; Komatsu, T.; Natheer, A.; Mitani, I.; Watanabe, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Hamano, A.; Miyazaki, N. Measurement of Diurnal Body Tilt Angle Distributions of Threeline Grunt Parapristipoma trilineatum Using Micro-Acceleration Data Loggers. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2013, 1, 3-9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse1010003
Tanoue H, Komatsu T, Natheer A, Mitani I, Watanabe S, Watanabe Y, Hamano A, Miyazaki N. Measurement of Diurnal Body Tilt Angle Distributions of Threeline Grunt Parapristipoma trilineatum Using Micro-Acceleration Data Loggers. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2013; 1(1):3-9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse1010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanoue, Hideaki, Teruhisa Komatsu, Alabsi Natheer, Isamu Mitani, Shinichi Watanabe, Yuuki Watanabe, Akira Hamano, and Nobuyuki Miyazaki. 2013. "Measurement of Diurnal Body Tilt Angle Distributions of Threeline Grunt Parapristipoma trilineatum Using Micro-Acceleration Data Loggers" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 1, no. 1: 3-9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse1010003
APA StyleTanoue, H., Komatsu, T., Natheer, A., Mitani, I., Watanabe, S., Watanabe, Y., Hamano, A., & Miyazaki, N. (2013). Measurement of Diurnal Body Tilt Angle Distributions of Threeline Grunt Parapristipoma trilineatum Using Micro-Acceleration Data Loggers. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 1(1), 3-9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse1010003




