Intercropping Forage Mulberry Benefits Nodulation and Growth of Soybeans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Agriotechnical Methods in Experimental
2.3. Evaluation of Soybean Growth Performance and Yield
2.4. Gas Exchange Measurement
2.5. Measurement of Related Nitrogen Metabolism Activity
2.6. Transcriptome Analysis
2.7. Estimation of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
2.8. Statistical Processing of Data
3. Results
3.1. Growth Indices
3.2. The Yield Components of Soybean
3.3. Root Nodule Traits
3.4. Physical and Chemical Properties in Rhizosphere Soil
3.5. Photosythetic Parameters
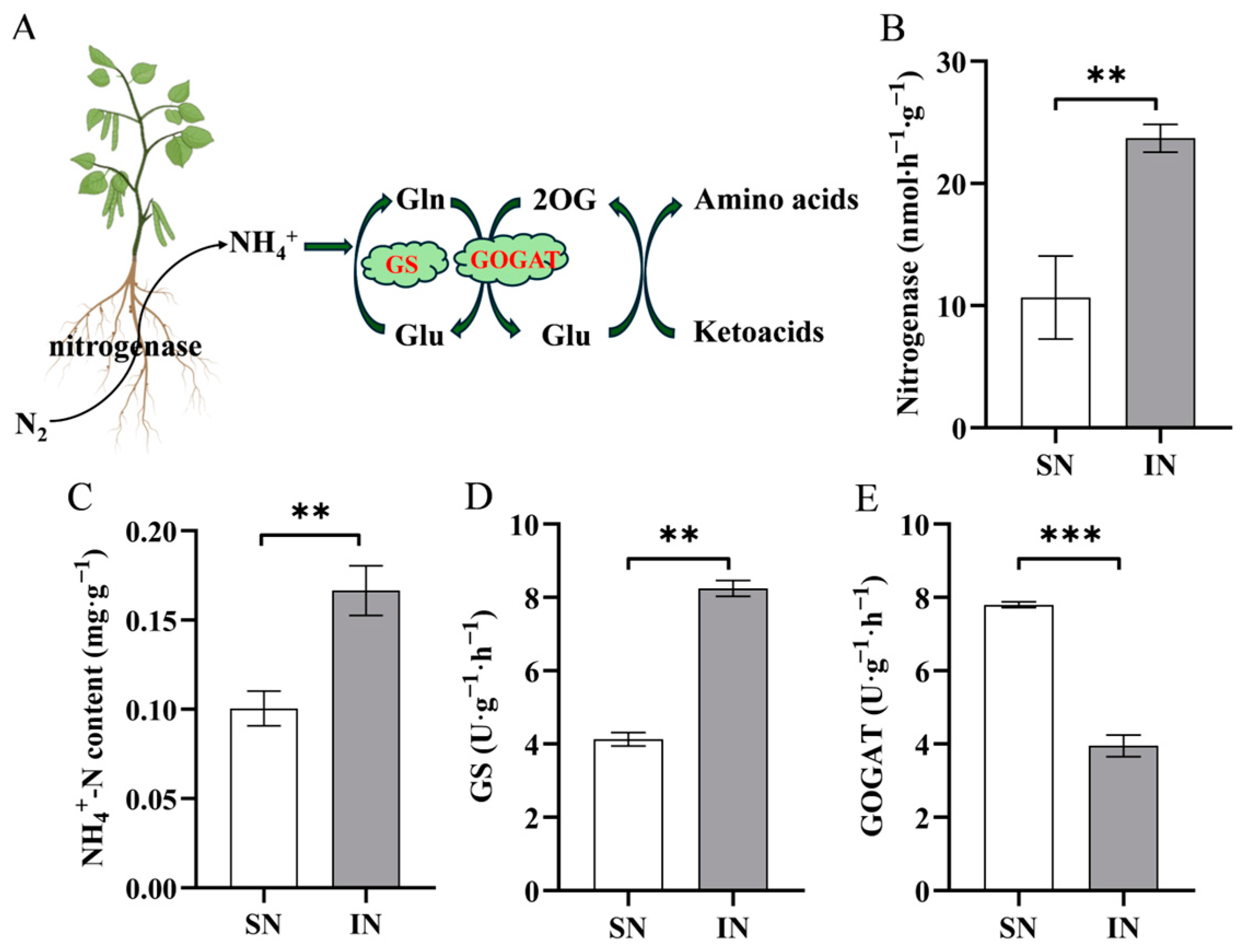
3.6. Nitrogen Metabolism Changes
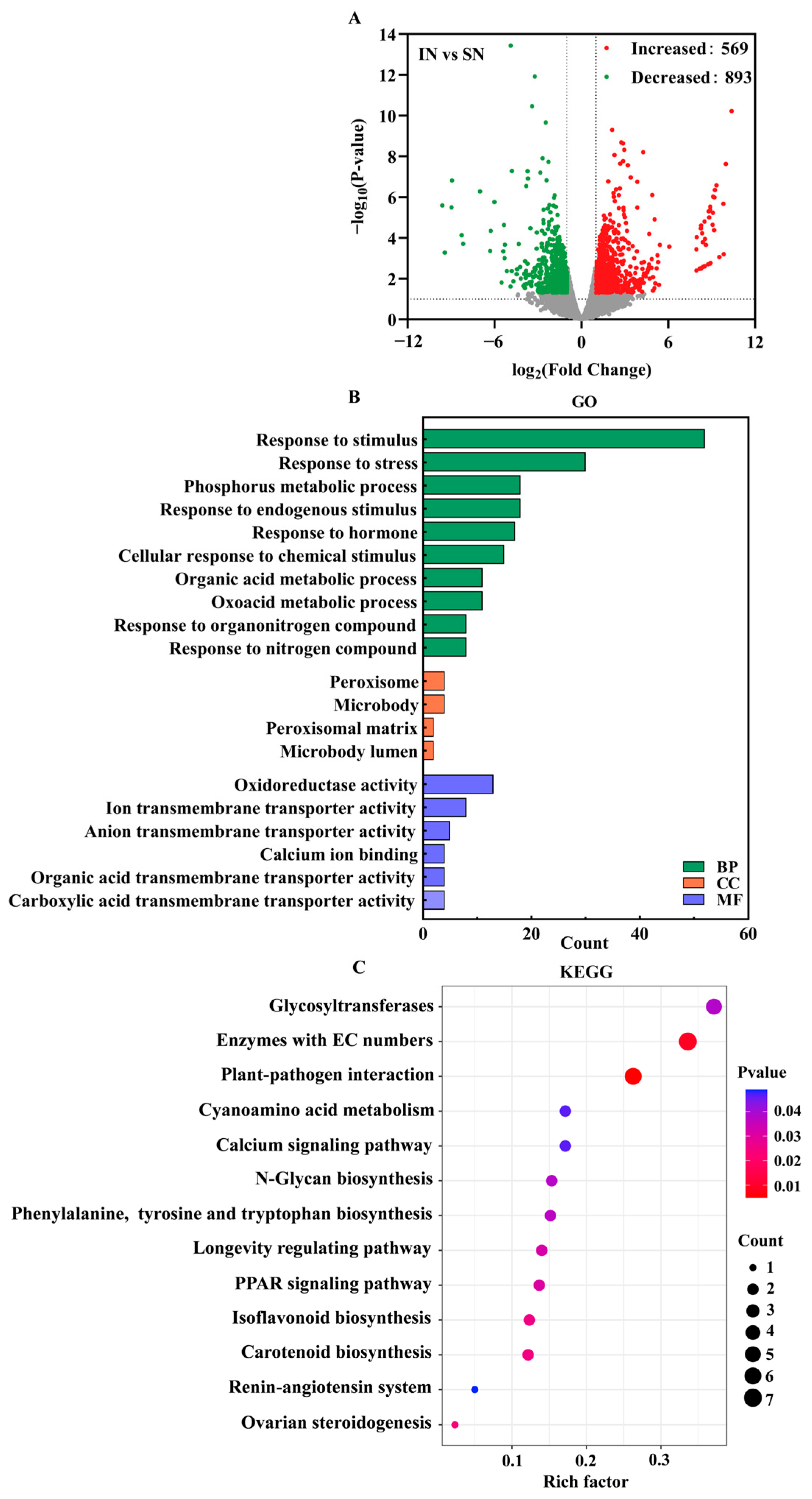
3.7. Transcriptome Analysis
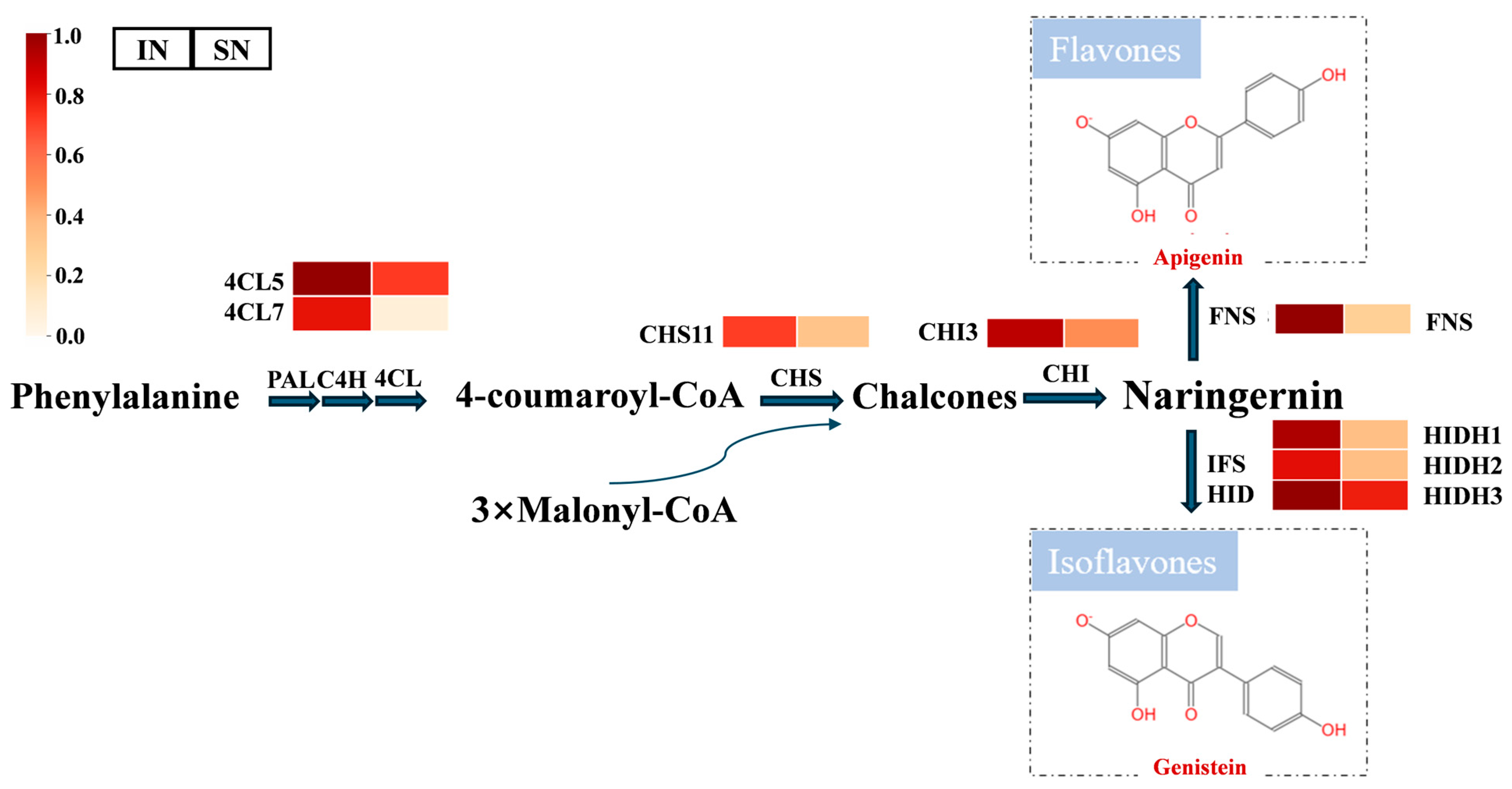
3.8. Isoflavone Biosynthesis
3.9. Redundancy Analysis
3.10. Structural Equation Modeling
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Intercropping of Forage Mulberry on Soybean Growth
4.2. Effects of Intercropping on Nodulation Related Indicators
4.3. Effects of Intercropping on NH4+-N Assimilation in Soybean Leaf
4.4. Relationships Between Plant Pattern and Parameters of Soybean
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, J.M.; Zhuang, Y.B.; Li, X.C.; Li, X.M.; Sun, C.C.; Ding, Z.J.; Xu, R.; Zhang, D.J. Time–series transcriptome comparison reveals the gene regulation network under salt stress in soybean (Glycine max L.) roots. BMC Plant. Biol. 2022, 22, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, A.O.; Zhao, M.H.; Zhu, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Mei, Y.C.; Li, C.H.; Yao, X.D.; Xie, F.T. Study on plant morphological traits and production characteristics of super high–yielding soybean. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 7, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.B.; Herbert, S.J. Fifteen years of research examining cultivation of continuous soybean in northeast China: A review. Field. Crops. Res. 2002, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.C.; Wang, L.; Li, M.X.; Sun, X.H.; Fei, S.P.; Xiao, S.F.; Yan, L.; Li, Y.H.; et al. Improving soybean yield prediction by integrating UAV nadir and cross–circling oblique imaging. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 155, 127134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.B.; Han, T.F.; Gai, J.Y.; Yong, T.W.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.C.; Yang, F.; Liu, J.; Shu, K.; Liu, W.G. Maize–soybean strip intercropping: Achieved a balance between high productivity and sustainability. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, S.; Hossain, A.; Brestic, M.; Skalicky, M.; Sairam, M. Intercropping system–A low input agricultural strategy for food and environmental security. Agronomy 2021, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.B.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.S. Effect of root contact on interspecific competition and N transfer between wheat and fababean using direct and indirect N–15 techniques. Plant Soil 2004, 262, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.S.; Li, L. Using competitive and facilitative interactions in intercropping systems enhances crop productivity and nutrient–use efficiency. Plant Soil 2003, 248, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.F.; Long, S.R. Rhizobium–plant signal exchange. Nature 1992, 357, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Yang, J.; Long, Y.P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D.P.; Zhang, X.W.; Dong, W.T.; Zhao, L.; Liu, C.W.; Zhai, J.X.; et al. Single–nucleus transcriptomes reveal spatiotemporal symbiotic perception and early response in Medicago. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 1734–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasto, M.K.; Alvarez–Clare, S.; Lekberg, Y.; Sullivan, B.W.; Townsend, A.R.; Cleveland, C.C.; Johnson, N. Interactions among nitrogen fixation and soil phosphorus acquisition strategies in lowland tropical rain forests. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 17, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, N.; Sun, G. Use of mulberry–soybean intercropping in salt–alkali soil impacts the diversity of the soil bacterial community. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Pang, T.; Iqbal, N.; Shafiq, I.; Yang, W.Y. Acclimation strategy and plasticity of different soybean genotypes in intercropping. Funct. Plant Biol. 2020, 47, 592–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.D.; Zhou, H.L.; Zhu, Q.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Wu, J.J.; Xie, F.T. Photosynthetic response of soybean leaf to wide light–fluctuation in maize–soybean intercropping system. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Shafiq, I.; Chattha, M.S.; Mumtaz, M.; Brestic, M.; Rastogi, A.S.; Chen, G.P.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Liu, W.G.; Yang, W.Y. Effect of Ti treatments on growth, photosynthesis, phosphorus uptake and yield of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] in maize–soybean relay strip intercropping. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 187, 104476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.F.; Chen, J.X.; Cheng, Y.J.; Raza, M.A.; Wu, X.L.; Wan, Z.L.; Liu, Q.L.; Wang, R.; Wan, X.C.; Yong, T.W.; et al. Effect of shading and light recovery on the growth, leaf structure, and photosynthetic performance of soybean in a maize–soybean relay–strip intercropping system. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Huang, S.; Gao, R.C.; Liu, W.G.; Yong, T.W.; Wang, X.C.; Wu, X.L.; Yang, W.Y. Growth of soybean seedlings in relay strip intercropping systems in relation to light quantity and red:far–red ratio. Field Crops Res. 2014, 155, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Liu, Q.L.; Cheng, Y.J.; Feng, L.Y.; Wu, X.L.; Fan, Y.F.; Raza, M.A.; Wang, X.C.; Yong, T.W.; Liu, W.G.; et al. Low red/far–red ratio as a signal promotes carbon assimilation of soybean seedlings by increasing the photosynthetic capacity. BMC. Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Liu, T.; Iqbal, N.; Brestic, M.; Pang, T.; Mumtaz, M.; Shafiq, I.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; et al. Effects of lignin, cellulose, hemicellulose, sucrose and monosaccharide carbohydrates on soybean physical stem strength and yield in intercropping. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2020, 19, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.G.; Deng, Y.C.; Hussain, S.; Zou, J.L.; Yuan, J.; Luo, L.; Yang, C.Y.; Yuan, X.Q.; Yang, W.Y. Relationship between cellulose accumulation and lodging resistance in the stem of relay intercropped soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. Field. Crops Res. 2016, 196, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.J.; Wang, W.B.; Yu, R.W.; Zhou, T.; Ahmad, I.; Raza, A.; Jiang, S.J.; Xu, M.; et al. Shade–tolerant soybean reduces yield loss by regulating its canopy structure and stem characteristics in the maize–soybean strip intercropping system. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 848893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.L.; Pan, X.F.; Lan, X.M.; Wang, Q.L.; Xiao, R. Rational maize–soybean strip intercropping planting system improves interspecific relationships and increases crop yield and income in the China Hexi Oasis Irrigation Area. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Wu, J.; Yan, X.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Su, S.; Liu, B.; Liu, J. Study on the Growth Dynamics and Harvesting Time of Forage Mulberry. Chin. J. Grassl. 2023, 45, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez–Garcia, E.; Martin Martin, G. Biomass yield and nutrient content of a tropical mulberry forage bank: Effects of season, harvest frequency and fertilization rate. Grass Forage Sci. 2017, 72, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Huang, R.; Wang, M.; Cao, H.; Li, Z. Phytoremediation potential of forage mulberry (Morus atropurpurea Roxb.) for cadmium contaminated paddy soils. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2022, 24, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.S. A Preliminary Survey of the Book Ch’I Min Yao Shu an Agricutural Encyclopaedia of the 6th Century; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Zhu, W.; Xu, N.; Sun, G. Effects of mulberry–soybean intercropping on growth of mulberry and soybean, and photosynthesis responsive to light intensity. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2013, 33, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, W.R. Stage of development descriptions for soybeans Glycine max (L.) Merrill. Crop Sci. 1971, 11, 775–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Soil and Agro–Chemistry Analytical Methods; Agricutural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.Y.; Raza, M.A.; Li, Z.C.; Chen, Y.K.; Khalid, M.H.B.; Du, J.B.; Liu, W.G.; Wu, X.L.; Song, C.; Yu, L. The Influence of Light Intensity and Leaf Movement on Photosynthesis Characteristics and Carbon Balance of Soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.S. Chemical tests for potentially available nitrogen in soil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1968, 19, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledgard, S.F.; Freney, J.R.; Simpson, J.R. Assessing nitrogen transfer from legumes to associated grasses. Soil. Boil. Biochem. 1985, 17, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhofer–Walzl, K.; Rasmussen, J.; Høgh–Jensen, H.; Eriksen, J.; Søegaard, K.; Rasmussen, J. Nitrogen transfer from forage legumes to nine neighbouring plants in a multi–species grassland. Plant Soil 2012, 350, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.S.; Yu, L.L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, W.T.; Li, Z.X.; Wang, J.W. Effects of reduced nitrogen input on productivity and N2O emissions in a sugarcane/soybean intercropping system. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 81, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.L.; Bennett, J.M.; Boote, K.J. Relationship of nitrogenase activity to plant water stress in field–grown soybeans. Field Crops Res. 1984, 8, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guo, J.; Peng, Y.Q.; Lyu, X.G.; Liu, B.; Sun, S.Y.; Wang, X.L. Light–induced mobile factors from shoots regulate rhizobium–triggered soybean root nodulation. Science 2021, 374, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Y.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Huang, P.H.; Fan, C.M.; Yu, G.L.; Chen, F.L.; Xu, K.; Chen, Q.S.; Miao, Y.C.; et al. Spatial divergence of PHR–PHT1 modules maintains phosphorus homeostasis in soybean nodules. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Wang, N.; Zhang, J.Y.; Hu, Y.B.; Cai, D.J.; Guo, J.H.; Wu, D.; Sun, G.Y. Soil physicochemical properties and the rhizosphere soil fungal community in a mulberry/alfalfa intercropping system. Forests 2019, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.N.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, K.N.; Yan, M.; Zhang, J.F.; Yu, M.; Tang, S.; Wang, L.Y.; Qu, H.Y.; Luo, L. Nitrogen mediates flowering time and nitrogen use efficiency via floral regulators in rice. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 671–683.e675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, X.; Xiao, J.; Tang, L.; Zheng, Y. Interactive influences of intercropping by nitrogen on flavonoid exudation and nodulation in faba bean. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Stacey, G.; Yu, O. Distinct, crucial roles of flavonoids during legume nodulation. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, S.M.; Sun, J.H.; Zhou, L.L.; Bao, X.G.; Zhang, H.G.; Zhang, F.S. Diversity enhances agricultural productivity via rhizosphere phosphorus facilitation on phosphorus–deficient soils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11192–11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranca, C.; Varennes, A.D.; Rolston, D. Biological nitrogen fixation by fababean, pea and chickpea, under field conditions, estimated by the 15N isotope dilution technique. Eur. J. Agron. 1999, 10, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, T.T.; Wei, W.; Zhang, S.; Keyhani, A.B.; Li, L.; Zhang, W. Border row effects on the distribution of root and soil resources in maize–soybean strip intercropping systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 233, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.L.; Zhao, Q.; He, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Ao, X.; Yao, X.D.; Xie, F.T. Rapid effect of enriched nitrogen on soybean nitrogen uptake, distribution, and assimilation during early flowering stage. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2022, 22, 3798–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.S.; Chung, Y.H.; Ming, H.H. Glutamate: A multifunctional amino acid in plants. Plant Sci. 2022, 318, 111238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, B.G.; Lea, P.J. Glutamate in plants: Metabolism, regulation, and signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2339–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.H.; Dong, Q.Q.; Han, Y.; Zhang, K.Z.; Shi, X.L.; Yang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, D.Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.G.; et al. Maize/peanut intercropping improves nutrient uptake of side–row maize and system microbial community diversity. BMC. Microbiol. 2022, 22, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Feng, Y.D.; Zhao, Z.H.; Bao, Y.B.; Cui, Z.G.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, Q.Z.; Cui, J.H. Macrogenomics–based analysis of the effects of intercropped soybean photosynthetic characteristics and nitrogen–assimilating enzyme activities on yield at different nitrogen levels. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.H.; Xia, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiao, N.Y.; Guo, S.; Lu, Y.W.; Li, J.X.; Wei, Z.M.; Gao, F.C.; et al. Interpreting variety–location–fertilizer interactions to enhance foxtail millet productivity in northern China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Treatment | Plant Height (cm) | Stem Diameter (mm) | Leaf Area (cm2) | Fw of Plant (g∙plant−1) | DW of Plant (g∙plant−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | |
| 2021 | 60.50 | 61.19 | 4.67 | 4.67 | 19.09 b | 20.08 a | 29.43 c | 31.14 a | 12.88 b | 13.42 a |
| 2022 | 60.56 | 60.99 | 4.68 | 4.67 | 19.13 b | 20.68 a | 29.75 b | 31.26 a | 12.88 b | 13.22 a |
| 2023 | 60.12 | 61.17 | 4.69 | 4.66 | 19.11 b | 20.22 a | 29.78 b | 31.16 a | 12.80 b | 13.29 a |
| Source of variation | F value from two-way ANOVA test | |||||||||
| Pattern | 1.445 ns | 3.808 ns | 50.075 ns | 255.289 * | 62.405 ns | |||||
| Year | 0.924 ns | 1.533 ns | 1.268 ns | 2.27 ns | 1.362 ns | |||||
| Pattern × Year | 0.326 ns | 0.186 ns | 0.776 ns | 0.639 ns | 1.03 ns | |||||
| Treatment | Number of Pods Plant−1 | Number of Seeds Plant−1 | Grain Yield (g∙plant−1) | 100-Seeds (g) | Yield (kg∙ha−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | |
| 2021 | 58.41 bc | 61.60 a | 150.4 c | 169.4 a | 10.58 b | 11.37 a | 29.43 c | 31.14 a | 2160 b | 2342 a |
| 2022 | 59.20 b | 61.80 a | 154.8 b | 172.4 a | 10.58 b | 11.25 a | 29.75 b | 31.26 a | 2180 b | 2347 a |
| 2023 | 58.20 b | 61.60 a | 155.8 bc | 169.6 a | 10.71 b | 11.55 a | 29.78 b | 31.16 a | 2131 b | 2363 a |
| Source of variation | F value from two-way ANOVA test | |||||||||
| Pattern | 162.769 ns | 90.249 ns | 227.532 * | 216.552 * | 97.859 ns | |||||
| Year | 2.385 ns | 1.556 ns | 6.558 ns | 4.69 ns | 0.254 ns | |||||
| Pattern × Year | 0.65 ns | 1.801 ns | 0.243 ns | 1.82 ns | 0.502 ns | |||||
| Treatment | Number of Nodules Plant−1 | FW of Nodules (g∙plant−1) | DW of Nodules (g∙plant−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | |
| 2021 | 39.20 b | 47.60 a | 0.46 b | 0.69 a | 0.12 b | 0.17 a |
| 2022 | 38.00 c | 47.20 a | 0.45 b | 0.71 a | 0.12 b | 0.17 a |
| 2023 | 38.00 c | 47.80 a | 0.46 b | 0.71 a | 0.11 b | 0.17 a |
| Source of variation | F value from two-way ANOVA test | |||||
| Pattern | 507.27 * | 1365.81 * | 294.646 * | |||
| Year | 1.324 ns | 0.877 ns | 0.212 ns | |||
| Pattern × Year | 1.51 ns | 5.91 ns | 2.717 ns | |||
| Treatment | Availabe Nitrogen (mg∙kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg∙kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg∙kg−1) | SWC (%) | pH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | Sole Crop | Intercrop | |
| 2021 | 138.1 a | 124.3 c | 257.6 b | 300.7 a | 286.7 b | 343.4 a | 18.26 b | 20.73 a | 6.45 a | 6.34 b |
| 2022 | 137.9 a | 127.6 bc | 256.9 b | 299.2 a | 287.3 b | 343.4 a | 18.41 b | 20.48 a | 6.48 a | 6.28 b |
| 2023 | 138.2 a | 125.8 ab | 258.7 b | 300.8 a | 286.2 b | 345.0 a | 18.13 b | 21.46 a | 6.46 a | 6.30 b |
| Source of variation | F value from two-way ANOVA test | |||||||||
| Pattern | 1025.242 * | 22,934.79 * | 46,878.507 * | 369.304 * | 32.58 * | |||||
| Year | 2.801 ns | 12.692 ns | 0.119 ns | 2.077 ns | 0.197 ns | |||||
| Pattern × Year | 1.247 ns | 0.048 ns | 1.637 ns | 0.151 ns | 1.511 ns | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Zhong, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H. Intercropping Forage Mulberry Benefits Nodulation and Growth of Soybeans. Agriculture 2025, 15, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080902
Feng X, Zhong M, Zhao X, Zhang X, Hu Y, Zhang H. Intercropping Forage Mulberry Benefits Nodulation and Growth of Soybeans. Agriculture. 2025; 15(8):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080902
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xinjie, Minghui Zhong, Xuexian Zhao, Xiuli Zhang, Yanbo Hu, and Huihui Zhang. 2025. "Intercropping Forage Mulberry Benefits Nodulation and Growth of Soybeans" Agriculture 15, no. 8: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080902
APA StyleFeng, X., Zhong, M., Zhao, X., Zhang, X., Hu, Y., & Zhang, H. (2025). Intercropping Forage Mulberry Benefits Nodulation and Growth of Soybeans. Agriculture, 15(8), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080902







