Analysis of Soil Nutrient and Yield Differences in Korla Fragrant Pear Orchards Between the Core and Expansion Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
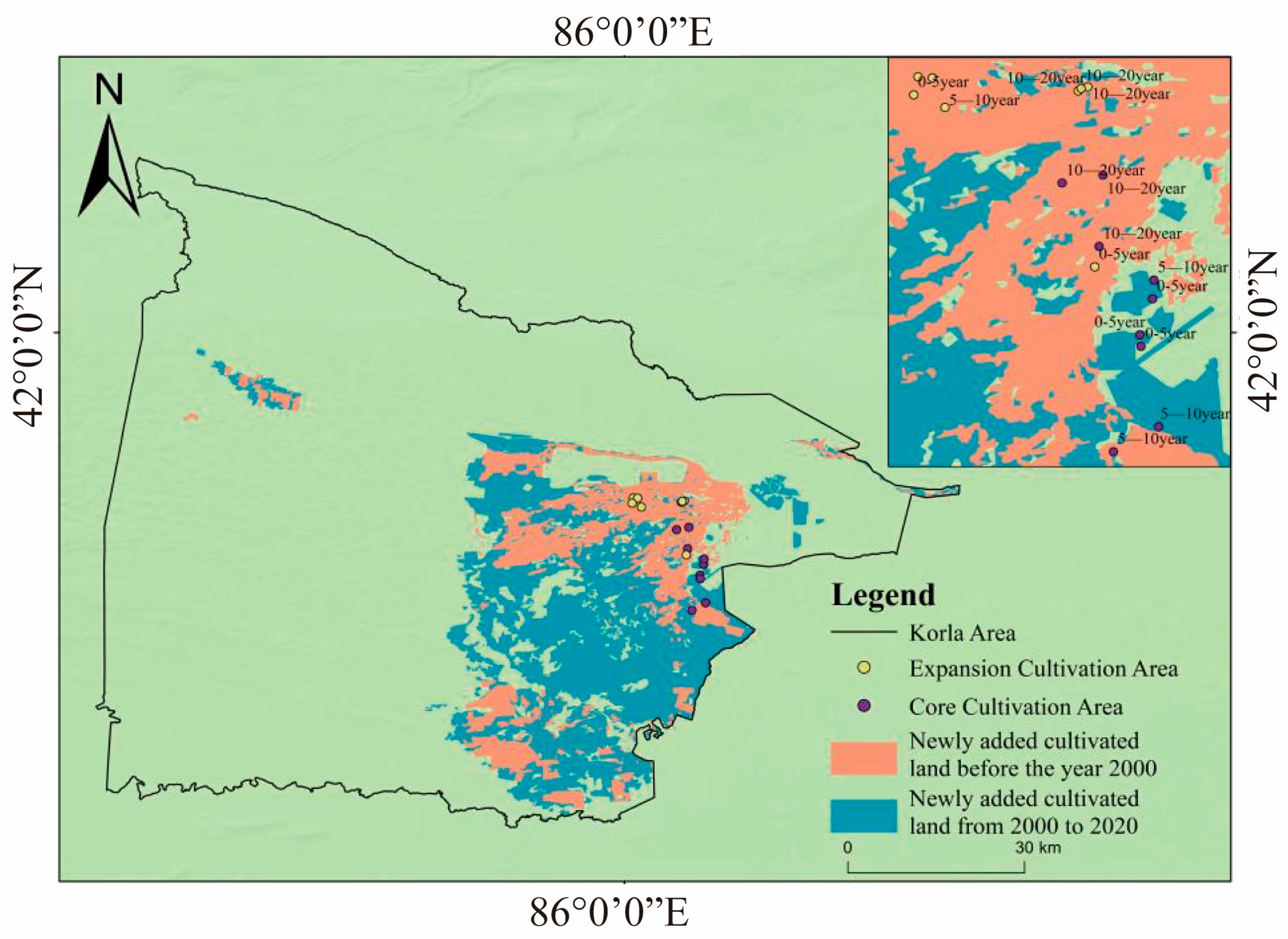
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Collection and Determination of Samples
2.3.1. Sample Collection
2.3.2. Measurement and Calculation
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Soil Nutrient Characteristics of Korla Fragrant Pear in Different Regions
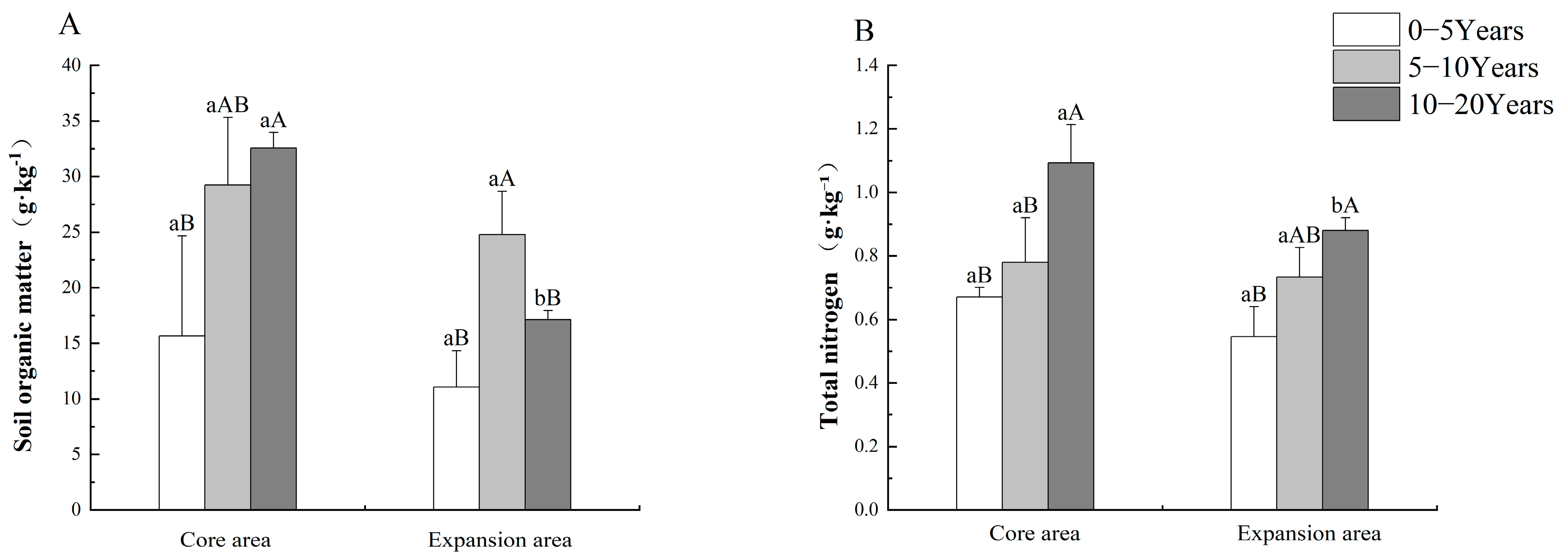
3.1.1. Characteristics of Soil Organic Matter and Total Nitrogen in Korla Fragrant Pear Orchards of Different Cultivation Areas and Tree Ages
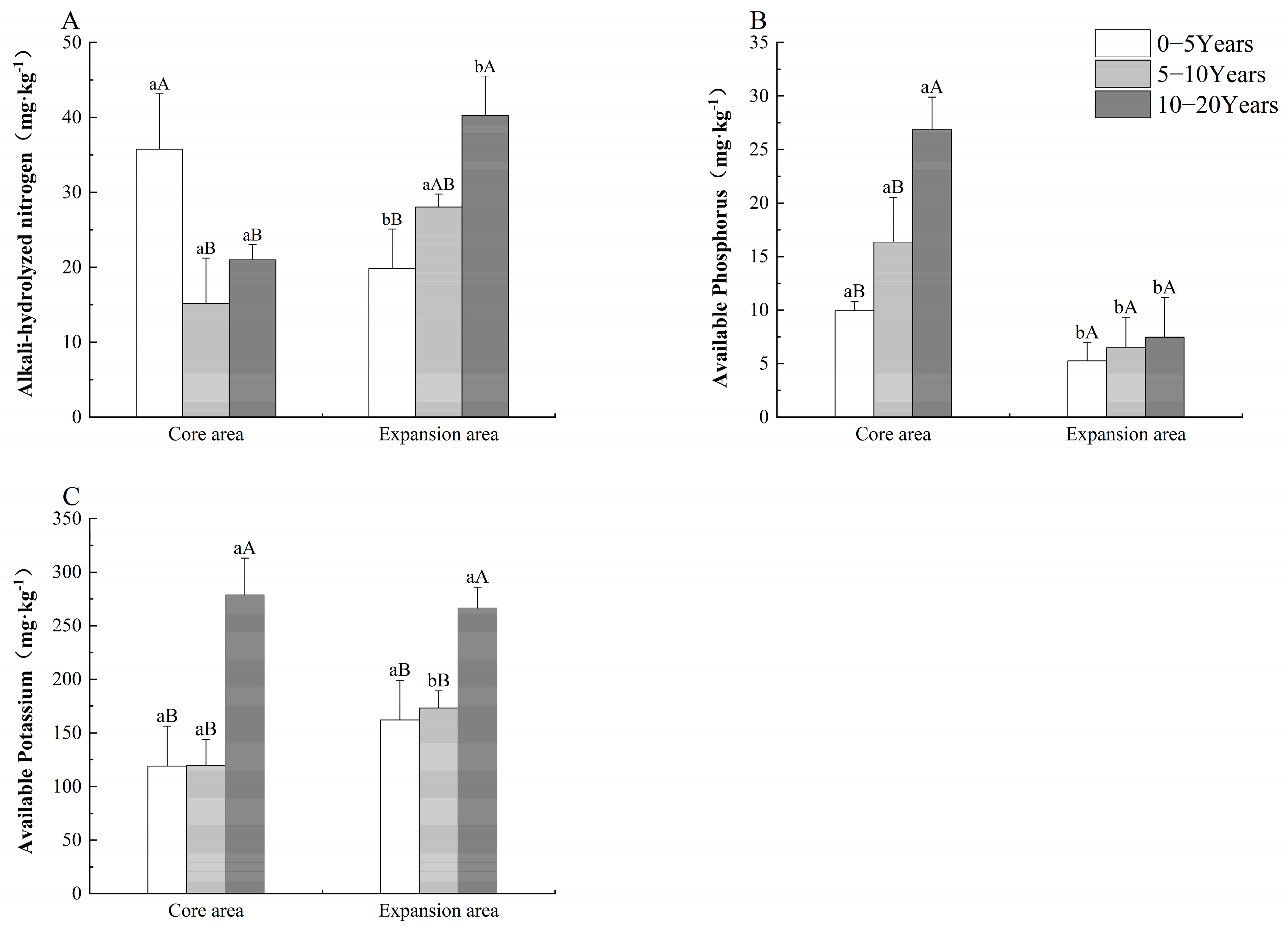
3.1.2. Characteristics of Available Nutrients in Korla Fragrant Pear Orchards of Different Cultivation Areas and Tree Ages
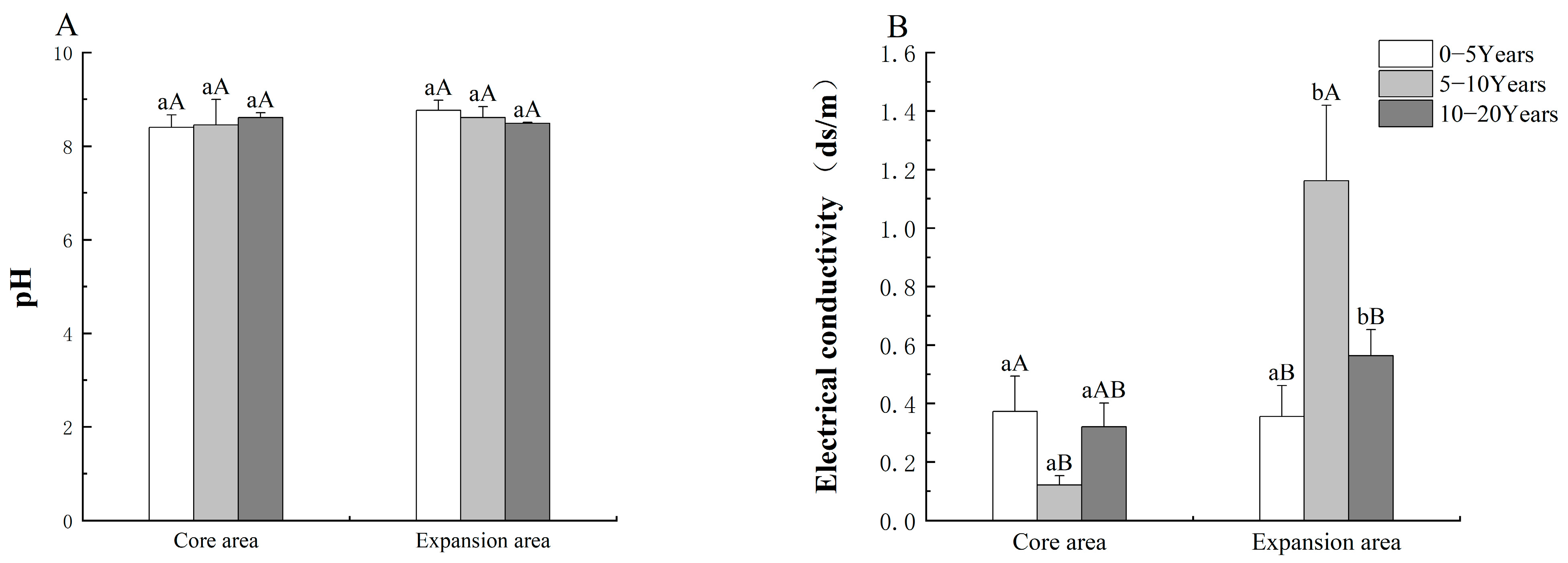
3.1.3. Characteristics of pH and Electrical Conductivity in Korla Fragrant Pear Orchards of Different Cultivation Areas and Tree Ages
3.1.4. Characteristics of Trace Elements in the Soil of Korla Fragrant Pear of Different Cultivation Areas and Tree Ages
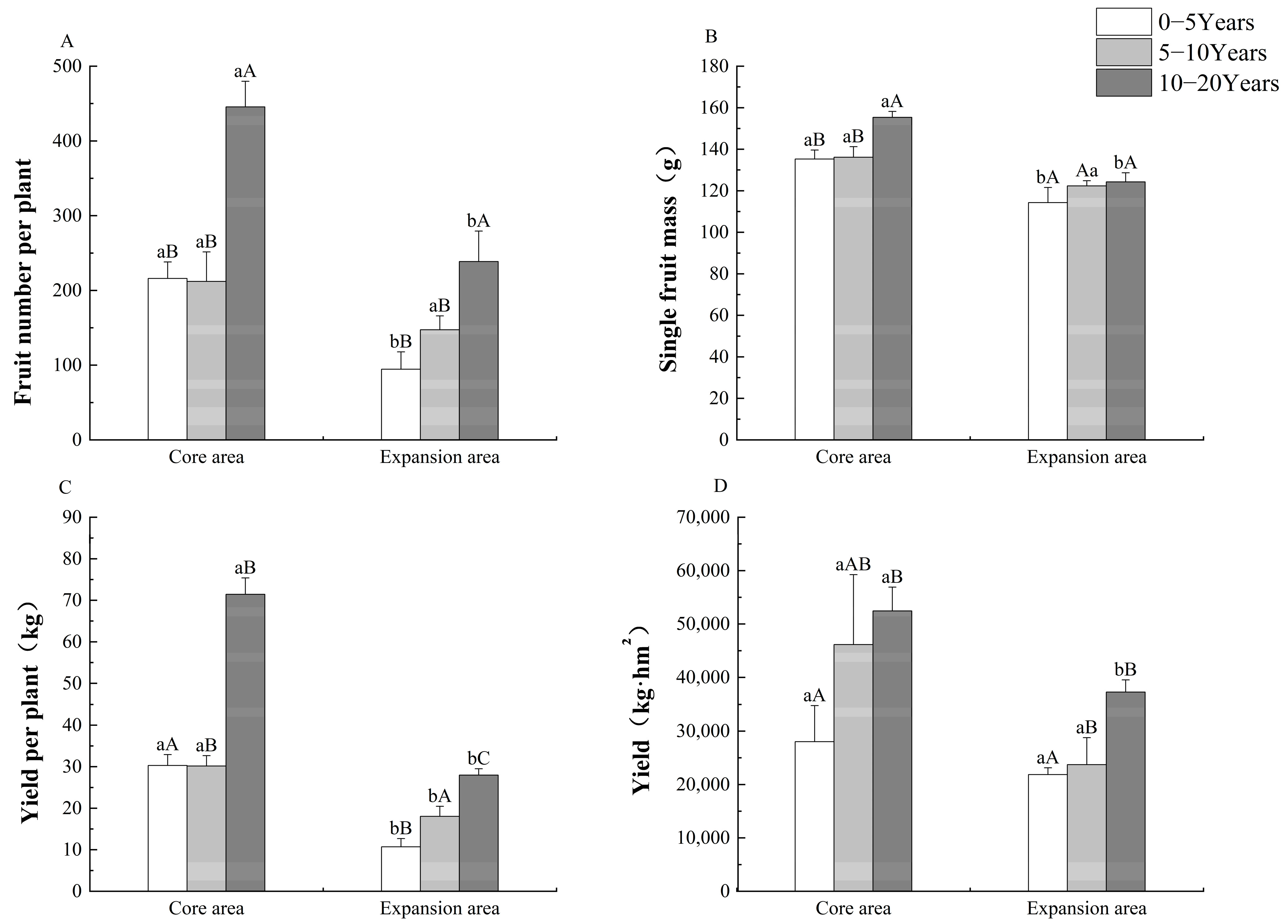
3.2. Yield Characteristics of Korla Fragrant Pear Orchards in Different Cultivation Areas and of Different Tree Ages
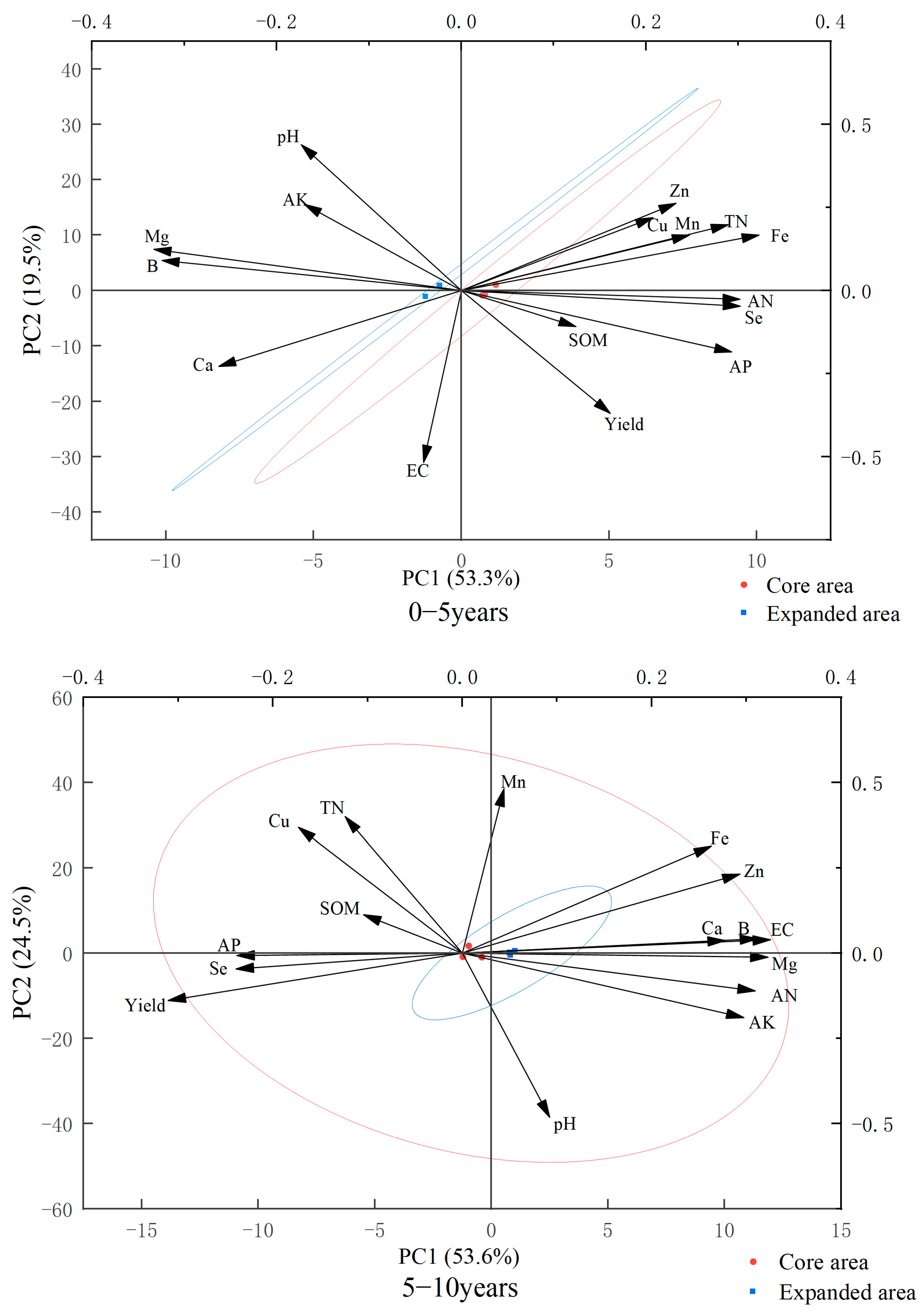
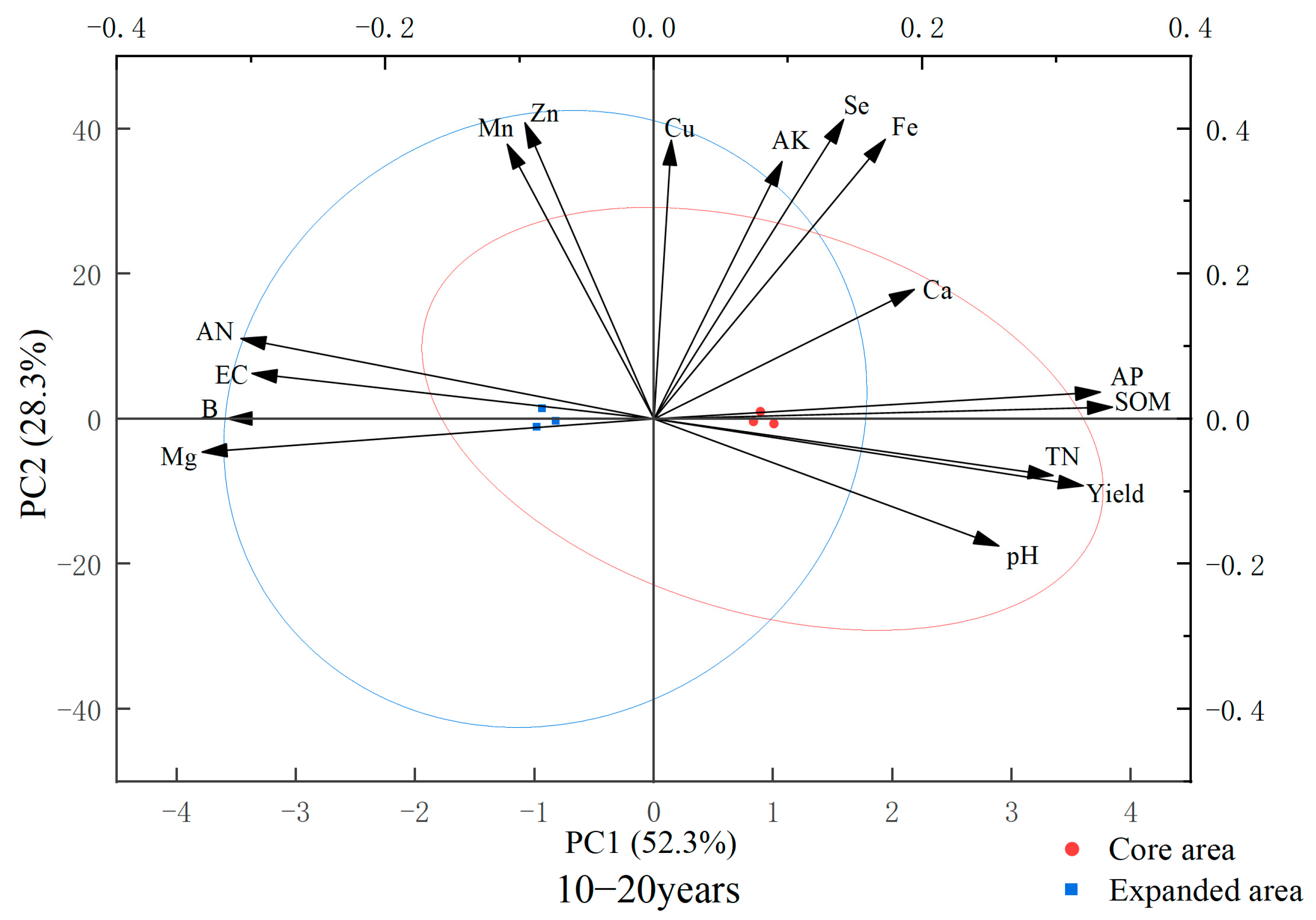
3.3. Analysis of Yield and Main Components of Soil Nutrients of Korla Fragrant Pear in Different Regions
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Nutrient Characteristics in Different Cultivation Areas
4.2. Yield Characteristics of Different Cultivation Areas
4.3. Correlation Between Yield and Soil Nutrients in Different Cultivation Areas
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- You, S.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Yu, X.; Tu, K.; Lan, W.; Pan, L. Evaluating the microstructure and physicochemical properties of ‘Korla’ fragrant pear disease caused by Alternaria alternata: Vis-NIR hyperspectral microscope imaging coupled with convolutional neural network. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 212, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Zhao, S.; Nasir, M.; Dong, S.; Zhang, S.; Liao, K. Genetic relationship between the ‘Korla fragrant pear’ and local pear varieties in Xinjiang based on floral organ characteristics. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 257, 108621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Yang, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Cheng, S.; Chen, G. Phenylpropanoid pathway mediated the defense response of ‘Korla’ fragrant pear against Alternaria alternata infection. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 220, 113318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, W.; Cui, R.; Du, B.; Song, L. Effect of different pretreatment methods on soluble dietary fiber macromolecules extracted from Korla fragrant pear (Pyrus sinkiangensis Yü): Structure, physicochemical properties, and biological activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 302, 140901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Bai, B.; Du, H.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Mao, J.; Zhu, C.; Yan, M.; Qin, H.; et al. Co-expression of metabolites and sensory attributes through weighted correlation network analysis to explore flavor-contributing factors in various Pyrus spp. Cultivars. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Ge, Y. Carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolisms are involved in delaying senescence of ‘Zaosu’ pear fruit following caffeic acid treatment. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 212, 112877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, H. Non-destructive quality assessment method for Korla fragrant pears based on electrical properties and adaptive neural-fuzzy inference system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, X.; Bao, J. Effects of Different Foliar Fertilizer Treatments on Fruit Quality of the Korla Fragrant Pear. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Noah, I.; Nitsan, I.; Cohen, B.; Kaplan, G.; Friedman, S.P. Soil aeration using air injection in a citrus orchard with shallow groundwater. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Du, R.; Liu, J.; Yu, F.; Liu, S. Soil, leaf and fruit nutrient data for pear orchards located in the Circum-Bohai Bay and Loess Plateau regions. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, B.L. Characteristics of soil nutrients in ‘Kuerle Xiangli’ (Pear) orchards of different tree ages. J. Pome Fruit Sci. 2016, 33, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Li, S.; Makar, R.S.; Li, H.; Feng, C.; Luo, D.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Fang, L. Proximal Soil Sensing of Low Salinity in Southern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.P.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, B.L. Nutritional diagnosis of Korla fragrant pear leaves. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2014, 32, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; Chinese Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Xue, D.; Feng, W.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Lv, M.; Han, Y.; Lv, Y.; Hu, A.; et al. Long-term organic fertilization alters soil microbial community structure and its influence on faba bean production in a six-crop rotation system. Plant Soil 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamuru, S.T.; Morash, J.; Lea-Cox, J.D.; Ristvey, A.G.; Davis, A.P.; Aydilek, A.H. Nutrient transport, shear strength and hydraulic characteristics of topsoils amended with mulch, compost and biosolids. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Pang, Y.; Xing, T.; Peng, X.; Li, L. Digestate-based organic amendment substitution improves the red soil quality and pakchoi yield. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 125005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S.; Gai, X.; Chen, G. Bone biochar and humic acid improved soil quality and promoted Olea europaea growth in coastal saline soil by enhancing the stoichiometric homeostasis of nutrient elements. Biochar 2025, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Farqani, A.; Fazio, G.; Cheng, L.; Robinson, T.L. Effects of soil pH on growth, early fruiting and mineral nutrient profile of ‘Honeycrisp’ apple trees grafted on eight rootstocks. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 342, 114029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Flores, J.L.; Ramos Rodríguez, M.; González Jiménez, A.; Farzamian, M.; Herencia Galán, J.F.; Salvatierra Bellido, B.; Cermeño Sacristan, P.; Vanderlinden, K. Depth-Specific Soil Electrical Conductivity and NDVI Elucidate Salinity Effects on Crop Development in Reclaimed Marsh Soils. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Chen, L.; Xiang, W.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, H.; Lei, P.; Xiao, W.; Li, S.; Zeng, L.; Kuzyakov, Y. Increase of soil nitrogen availability and recycling with stand age of Chinese-fir plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 480, 118643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Rengel, Z.; Li, H. Differential root nutrient-acquisition strategies underlie biogeochemical niche separation between grasses and forbs across grassland biomes. Funct. Ecol. 2024, 38, 2286–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, N.K.; Asrey, R. Tree Age Affects Postharvest Attributes and Mineral Content in Amrapali Mango (Mangifera indica) Fruits. Hortic. Plant J. 2018, 4, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Q.; Dai, L.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ci, L. Functional carbon nanodots improve soil quality and tomato tolerance in saline-alkali soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ran, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Song, Y. Effects of fertilization on soil ecological stoichiometry and fruit quality in Karst pitaya orchard. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Ma, L.; Wei, A.; Shi, Q. Regional quality differences in Zanthoxylum bungeanum using sensor-based analysis and climate factors. Food Chem. 2025, 490, 145135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z.; Wang, G.G.; Smith, W.K.; Wu, T. Does stoichiometric homeostasis differ among tree organs and with tree age? For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 453, 117637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zuohereguli, K.; Zhang, L.; Kang, Y.; Shi, L.; Xu, H.; Ruan, Y.; Wen, T.; Mei, X.; Dong, C.; et al. Soil Microbial Mechanisms to Improve Pear Seedling Growth by Applying Bacillus and Trichoderma-Amended Biofertilizers. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 48, 3968–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmo, M.; Lozano, A.M.; Barrón, V.; Villar, R. Spatial heterogeneity of soil biochar content affects soil quality and wheat growth and yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gong, P.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Irrigation Method and Volume for Korla Fragrant Pear: Impact on Soil Water and Salinity, Yield, and Fruit Quality. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Bai, R.; Yu, Q.; Bao, Y.; Yang, W. The Effect of Nitrogen Reduction and Applying Bio-Organic Fertilisers on Soil Nutrients and Apple Fruit Quality and Yield. Agronomy 2024, 14, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, F.; Chan, N.W.; Shi, J.; Tan, M.L.; Kung, H.T.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, Q. Interactions of climate, topography, and soil factors can enhance the effect of a single factor on spring phenology in the arid/semi-arid grasslands of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 473, 143556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Grading Standard | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Name | Rich | Flat | Lack | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| SOM (g·kg−1) | ≥40 | 30–40 | 20–30 | 10–20 | 6–10 | <6 |
| TN (g·kg−1) | ≥2.0 | 1.5–2.0 | 1.0–1.5 | 0.5–1.0 | 0.3–0.5 | <0.3 |
| AN (mg·kg−1) | ≥150 | 120–150 | 90–120 | 60–90 | 30–60 | <30 |
| AP (mg·kg−1) | ≥40 | 20–40 | 10–20 | 5–10 | 3–5 | <3 |
| AK (mg·kg−1) | ≥200 | 150–200 | 100–150 | 50–100 | 30–50 | <30 |
| pH | ≥8.5 | 8.0–8.5 | 7.5–8.0 | 7.0–7.5 | 6.5–7.0 | <6.5 |
| EC (dS/m) | ≥4.0 | 3.0–4.0 | 2.0–3.0 | 1.0–2.0 | 0.5–1.0 | <0.5 |
| Tree Age/(years) | High-Yield Orchard/(kg·hm2) | Low-Yield Orchard/(kg·hm2) |
|---|---|---|
| 0–5 | ≥15,000 | <7500 |
| 5–10 | ≥18,000 | <9000 |
| 10–20 | ≥27,000 | <12,000 |
| Soil Elements/ Different Regions | Core Area | Expansion Area | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–5 Years | 5–10 Years | 10–20 Years | 0–5 Years | 5–10 Years | 10–20 Years | |
| Ca (mg/g) | 83.96 ± 14.66 aB | 98.27 ± 6.89 aAB | 115.81 ± 9.08 aA | 98.91 ± 3.48 aB | 105.18 ± 2.81 aAB | 107.84 ± 1.73 aA |
| Fe (mg/g) | 34.05 ± 3.93 aA | 21.28 ± 2.50 aB | 25.92 ± 1.54 aB | 24.61 ± 3.34 bA | 24.61 ± 1.01 aA | 24.38 ± 1.59 aA |
| Mg (mg/g) | 22.59 ± 0.52 bB | 19.63 ± 2.41 bB | 31.54 ± 0.53 bA | 44.72 ± 1.38 aA | 42.26 ± 5.69 aA | 45.40 ± 3.40 aA |
| Zn (mg/g) | 0.09 ± 0.02 aA | 0.06 ± 0.01 bA | 0.08 ± 0.01 aA | 0.07 ± 0.01 aA | 0.07 ± 0.004 aA | 0.09 ± 0.01 aA |
| Mn (μg/g) | 0.67 ± 0.05 aA | 0.55 ± 0.18 aA | 0.7 ± 0.08 aA | 0.57 ± 0.09 aA | 0.58 ± 0.06 aA | 0.78 ± 0.20 aA |
| Cu (μg/g) | 17.57 ± 2.05 aA | 16.40 ± 1.83 aA | 18.59 ± 0.36 aA | 14.86 ± 3.47 aA | 15.56 ± 0.35 aA | 18.49 ± 3.28 aA |
| B (μg/g) | 31.94 ± 3.10 bA | 27.45 ± 4.36 bA | 36.89 ± 4.75 bA | 49.43 ± 3.42 aA | 46.94 ± 6.89 aA | 53.02 ± 5.44 aA |
| Se (μg/g) | 1.63 ± 0.18 aA | 1.35 ± 0.08 aA | 1.43 ± 0.08 aA | 1.15 ± 0.12 bA | 1.20 ± 0.02 bA | 1.31 ± 0.21 aA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Ke, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xue, Y.; Shen, X.; Chai, Z. Analysis of Soil Nutrient and Yield Differences in Korla Fragrant Pear Orchards Between the Core and Expansion Areas. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171873
Liu X, Wang Y, Zhao K, Ke Y, Guo Y, Xue Y, Shen X, Chai Z. Analysis of Soil Nutrient and Yield Differences in Korla Fragrant Pear Orchards Between the Core and Expansion Areas. Agriculture. 2025; 15(17):1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171873
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiuxiu, Yiru Wang, Kexin Zhao, Yixin Ke, Yanke Guo, Yingnan Xue, Xing Shen, and Zhongping Chai. 2025. "Analysis of Soil Nutrient and Yield Differences in Korla Fragrant Pear Orchards Between the Core and Expansion Areas" Agriculture 15, no. 17: 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171873
APA StyleLiu, X., Wang, Y., Zhao, K., Ke, Y., Guo, Y., Xue, Y., Shen, X., & Chai, Z. (2025). Analysis of Soil Nutrient and Yield Differences in Korla Fragrant Pear Orchards Between the Core and Expansion Areas. Agriculture, 15(17), 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171873







