Abstract
Nitrogen (N) plays a decisive role in the growth and yield of crops. Hence, a high maize grain yield depends upon substantial N inputs. In the present study, morphological traits and yield components, grain yield, rain use efficiency (RUE), and N partial factor productivity (NPFP) were analyzed in two maize hybrids (ZP666 and NS6030) for 2 yr using four N rates (0 (N0), 60 (N60), 120 (N120), and 180 (N180) kg N ha−1). In a climatically more favorable year (2022), the studied traits and NPFP were higher, while RUE was lower. Hybrid ZP666 had higher values of morphological traits and yield component traits, except 1000-grain weight, grain yield, RUE, and NPFP, than hybrid NS6030. The highest values for morphological traits, yield components, grain yield (9383 and 9456 kg ha−1), and RUE (27.1 and 27.2 kg ha−1 mm−1) were obtained at 120 and 180 kg N ha−1. The NPFP decreased significantly with increasing N input, from 137.6 (control) to 52.5 kg grain per kg fertilizer N (180 kg N ha−1). A suitable hybrid selection and the application of a moderate N fertilizer rate of 120 kg N ha−1 could contribute to high yields and lower nitrogen losses to the environment and promote sustainable agriculture.
1. Introduction
Maize (Zea mays L.) is one of the world’s most important sources of food for humans and animal feed. It is also used for various industrial purposes where different parts of a plant are used. It is adaptable to different environments and is cultivated between 58° north latitude and 40° south latitude. In 2023, global maize grain production was about 1.24 billion tons on an area of 208 million hectares with an average yield of 5.9 t ha−1 [1]. The United States, China, and Brazil were the largest producers of maize, accounting for 48.8% of the area under cultivation [1]. In the same year, maize was grown on 922,980 ha (27.2% of the total cultivated area) in Serbia, with an average yield of 7.2 t ha−1 and a production of 6.6 million tons [1]. Average maize yields have increased over time. The factors that have contributed to the achievement of high maize yields are based on the improvement of agronomic traits and adaptation to different agroclimatic and ecological conditions [2,3,4], including soil and crop management [5,6]. A recent study reported that improvements in climate, agronomy, and genetics increased maize grain yield by 48, 39, and 13%, respectively [7]. These findings highlight the predominant role of environmental and management factors over genetic gains in recent decades. Therefore, understanding the interaction between nitrogen input and genotype performance remains a key priority for sustainable yield improvements. The dominant strategy in maize breeding is to develop genotypes with wide adaptation to agroecological conditions and high and stable yields [8]. According to Egli [9], new genotypes were developed through breeding that quadrupled maize yields in terms of agronomic traits between 1930 and 2014. Apart from breeding, the maize production is based mainly on mineral N fertilizers, considering that N is a key factor determining crop yield and quality. Therefore, selecting the appropriate N fertilizer is one of the most important aspects needed to maximize maize yield [10] and prevent N losses in the environment through denitrification, leaching, and volatilization [11,12]. Many researchers showed that N fertilization increases morphological and productive traits of maize. Galindo et al. [10] observed that increasing N levels from 50 to 200 kg ha−1 led to increased soil N availability, plant height, ear diameter, the number of grains per ear, 100-grain weight, and grain yield of maize. Grain yield and its attributing traits of maize hybrids increased with the increasing N rate from 160 to 220 kg ha−1 [13]. Authors have indicated that this increase was particularly pronounced in the 10V10 genotype compared to Rajkumar F1 and NMH-731. According to Delibaltova [14], Marković et al. [15], and Gheith et al. [16], yield components and grain yield increased significantly with increasing N fertilization up to 240 kg ha−1, 200 kg ha−1, and 336 kg ha−1, respectively. The authors also suggested that hybrids of maize respond differently to N rates under the same environmental conditions, emphasizing that the choice of hybrid and appropriate N rate are key factors for maximizing maize yield.
The aims of this study were to determine differences in maize agronomic traits and grain yields as a function of N fertilization and the choice of hybrids with greater efficiency in order to indicate an effective field strategy for improving grain yields. N fertilization represents an important agronomic input for improving quantitative traits in maize hybrids, particularly during variable meteorological conditions for growth.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment
A field experiment was conducted under dryland conditions at an experimental station of the Institute for Animal Husbandry, Belgrade-Zemun (latitude: 44° 85′ N, longitude: 20° 29′ E, altitude: 88 m), in 2021 and 2022. The two dent maize hybrids NS6030 and ZP666 (FAO600 maturity group) were tested. These hybrids widespread cultivated in the region and are very popular with Serbian farmers due to their high genetic yield potential, remarkable phenotypic plasticity, and good adaptation to the environment. They are suitable for both grain and forage production. They are also drought tolerant due to their delayed leaf senescence (stay-green trait). Four N rates were examined: 0 (control), 60, 120, and 180 kg N ha−1, denoted as N0, N60, N120, and N180, respectively. The preceding crop was winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Planting was performed on 12 April 2021 and 8 April 2022. The maize was planted in 4 rows, 6 m long, with an inter-row distance of 0.7 m (64,900 plants ha−1). A standard cultivation practice was uniformly applied in all experimental plots. Basic fertilization with NPK fertilizer (10-30-20) was applied each autumn at a rate of 200 kg ha−1. The N fertilizer CAN (calcium ammonium nitrate with 27% of N and 8% of Ca; HIP—Azotara Pančevo, Serbia) was applied in both years in May at the V3 to V5 stage in quantities of 0, 222.2, 444.4, and 666.6 kg ha−1, respectively. Accordingly, the N treatments were 0, 60, 120, and 180 kg N ha−1. The harvest was performed on 3 October 2021 and 1 October 2022.
2.2. Meteorological Conditions
For the long-term reference period of 1981–2010, the total rainfall amount and average annual temperature were 391.9 mm and 19.3 °C; for 2021, 272.4 mm and 19.8 °C; and for 2022, 447.0 mm and 20.4 °C (Figure 1). Therefore, the total seasonal rainfall of 447 mm for 2022 was 14.1% above the long-term period average of 391.9 mm and 64.1% above the 2021 average of 272.4 mm. In contrast, the total seasonal rainfall of 272.4 mm in 2021 was 31% lower than in the long-term reference period. In 2021, there were dry periods in June (intensive stem growth), August, and September (dough stage (R4) and physiological maturity (R6)). In 2022, the meteorological conditions were favorable for maize growth.
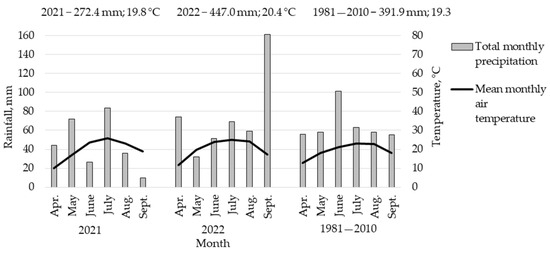
Figure 1.
Meteorological conditions during the maize growing seasons and the long-term average period 1981—2010.
2.3. Soil Properties
The CaCO3 content, organic matter, total N, and available P and K were determined using the Scheibler calcimeter [17], Kotzmann [18], Kjeldahl [19], and Egner–Riehm Al [20] methods, respectively. The pH of the soil was determined in a 1:2.5 suspension (soil:1 mol dm−3 KCl) using a digital pH meter (Hanna Instruments HI 83141, Italy). The results showed that the topsoil layer of 0—30 cm contained 0—30 cm contains 4.24% CaCO3, 5.1% organic matter, 0.27% total N, 13.6 mg P2O5 100 g soil−1, and 17.8 mg K2O 100 g soil−1. The pH in KCl was 7.24.
2.4. Data Collection
Immediately after July silking in both years, ten plants in the central rows of each subplot were taken for measuring plant height, ear height, and the number of leaves per plant. At full maturity, on 6 October 2021 and 10 October 2022, the trial was manually harvested. Grain yield was determined using the two central rows of each plot to avoid edge effects, adjusted to 14% moisture content, and converted on a per-hectare basis. Ten ears from the bulk were taken to measure ear length, the number of rows per ear, the number of grains per ear, grain weight per ear, and 1000-grain weight. Rain use efficiency (RUE, kg ha−1 mm−1) was calculated by the following formula: grain yield/total seasonal rainfall. N partial factor productivity (NPFP, kg grain kg fertilizer N−1) was calculated according to Cheng et al. [21] using the formula grain yield/N input. The experiment was carried out in four replications.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
A field experiment was analyzed using a three-factor random block system design with four replications. STATISTICA version 20 (StatSoft, Tulsa, OK, USA) was used for data analysis. The Tukey test at p ≤ 0.05 was used to detect the difference between the means of the parameter, whereas the p-value (p ≤ 0.05 and p ≤ 0.01) was used to determine the significance level. Pearson correlation coefficients (p ≤ 0.05 and p ≤ 0.01) were used for the interdependence between studied parameters. In addition, the principal component analysis (PCA) of investigated traits and parameters based on different N rates was applied using RStudio version 2024.12.1, Build 563. Determination of stability in the observed agronomic traits was carried out using AMMI analysis. Evaluation of genotype x environment interactions and determination of stability in the observed agronomic traits were carried out using AMMI (Additive Main Effects and Multiplicative Interaction) analysis. AMMI analysis combines analysis of variance for the additive main effects (genotypes and environments) with principal component analysis for the multiplicative interaction effects [22]. The combination of nitrogen doses and the years in which the experiments were conducted (N0, N60, N120, and N180 × 2 observed years) was considered as the environment. The analysis was performed using free RStudio software, version 2024.12.1, Build 563. In order to rank the observed characteristics in terms of stability, the AMMI stability value (ASV) was calculated [23].
SS = sum of squares; PC1 = first principal component; PC2 = second principal component.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Variations in Parameters
Descriptive statistics and variations for the investigated parameters are shown in Table 1. Plant height varied little, ranging from 220.0 cm to 285.0 cm, with an average of 244.7 cm. Ear height followed a similar trend, spanning from 60.5 cm to 118.8 cm (mean 97.1 cm), while the number of leaves per plant ranged between 11.0 and 14.5, averaging 12.8. Ear length showed medium variability and ranged from 16.4 cm to 27.1 cm (mean 20.3 cm), with the number of rows per ear ranging from 12.0 to 16.7 (mean 14.1). The number of grains per ear varied from 407.1 to 816.1, with a mean of 581.9 grains. Grain weight per ear ranged from 118.5 g to 245.1 g, with a mean of 184.5 g, while 1000-grain weight ranged from 197.5 g to 396.0 g (mean 278.3 g). Grain yield exhibited a wide range, from 4315.5 to 12561.5 kg ha−1, averaging 8634.7 kg ha−1. RUE varied between 15.8 and 46.1 kg ha−1 mm−1 (mean 24.8 kg ha−1 mm−1), and NPFP ranged from 39.0 to 161.2 kg grain per kg fertilizer N−1, with a mean of 89.4 kg grain per kg fertilizer N−1. The coefficient of variation for the traits ranged from 5.2% (plant height) to 20.1% (grain yield); for RUE and NPFP, it was 22.6% and 43.2% respectively.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of morphological traits, yield component traits, grain yield, RUE, and NPFP of maize hybrids at different N rates.
3.2. Morphological Plant Traits
We have analyzed morphological traits of the two maize hybrids under different weather conditions and N rates. Under favorable weather conditions, present in the second year, plant height was greater by 2.7%, ear height by 25.2%, and the number of leaves by 15.1% than in the first year (241.5 cm, 86.2 cm, and 11.9, respectively), as shown in Table 2. Further analysis indicated that, averaged across years and N rates, the hybrid ZP666 had a higher value of plant height by 5.6% than hybrid NS6030 (238.0 cm). The average values of investigated traits across two years and two hybrids increased with increasing N rate. Compared to the control, significantly higher plant height and the number of leaves per plant were observed at 120 and 180 kg N ha−1, while a significantly greater ear height was recorded at 180 kg N ha−1. Interactions among factors were not significant for these morphological traits.

Table 2.
Effects of year, hybrid, and N rate on morphological traits of maize.
3.3. Grain Yield and Yield Component Traits
According to the variance analyses, the effects of year, hybrid, and N rate have a significant influence on the characteristics of the yield components and grain yield, as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Effects of year, hybrid, and N rate on yield components traits, grain yield, RUE, and NPFP of maize.
As for the two hybrids and four N rates, the values of the investigated parameters were higher in 2022 than in 2021 on average. The ear length was higher by 15.4%, the number of rows per ear by 8.9%, the number of grains per ear by 24.7%, grain weight per ear by 19.8%, 1000-grain weight by 32.7%, and grain yield by 26.3% than in 2021 (18.8 cm, 13.5, 518.0, 168.8 g, 239.2 g, and 7631 kg ha−1, respectively). Averaged over years and N rates, the hybrid ZP666 had a higher value of investigated traits, except for 1000-grain weight, compared to the hybrid NS6030. Higher N inputs (120 and 180 kg ha−1) significantly increased the yield component traits and grain yield compared to the control. The lowest N rate of 60 kg ha−1 significantly increased the number of grains per ear by 10.7% and 1000-grain weight by 13.3% compared to the control (529.0 and 247.4 g). The interaction of year × hybrid was not significant for ear length only; the interaction of year × N rate was not significant for grain weight per ear and grain yield, while the interaction of hybrid × N rate was not significant for the number of rows per ear, grain weight per ear, and grain yield. The interaction of year × hybrid × N rate was significant for ear length (p ≤ 0.05) and the number of rows per ear (p ≤ 0.05).
3.4. Rain Use Efficiency (RUE) and N Partial Factor Productivity (NPFP)
As expected, the RUE (21.6 kg ha−1 mm−1) was lower while NPFP (97.8 kg grain kg fertilizer N−1) was higher in 2022, the year with a favorable growing season (Table 2). The hybrid ZP666 had higher RUE (25.9 kg ha−1 mm−1) and NPFP (93.2 kg grain kg fertilizer N−1) than the hybrid NS6030 (23.7 kg ha−1 mm−1 and 85.7 kg grain kg fertilizer N−1, respectively). The N rates of 120 and 180 kg ha−1 significantly increased the RUE compared to the control. On the contrary, NPFP decreased significantly with increasing N rates, and the lowest NPFP (52.5 kg grain kg fertilizer N−1) was recorded at 180 kg N ha−1. The interaction of year × hybrid was significant for RUE (p ≤ 0.05) and NPFP (p ≤ 0.05), and the interaction of year × N rate was significant for RUE (p ≤ 0.05).
3.5. Principal Component Analysis and AMMI Analysis for Measured and Calculated Parameters
Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that the first (PC1) and second (PC2) components contributed 97.1%, 92.48%, and 95.14% of the total variation for two hybrids (general, ZP666, and NS6030), respectively (Figure 2). All observed variables are positively correlated with the first principal component. The length of the vector of the observed traits differs between the two observed hybrids, and therefore their variance. The highest variability was found for NPFP in both observed hybrids. In the hybrid ZP666, a greater variability of traits was observed compared to NS6030.
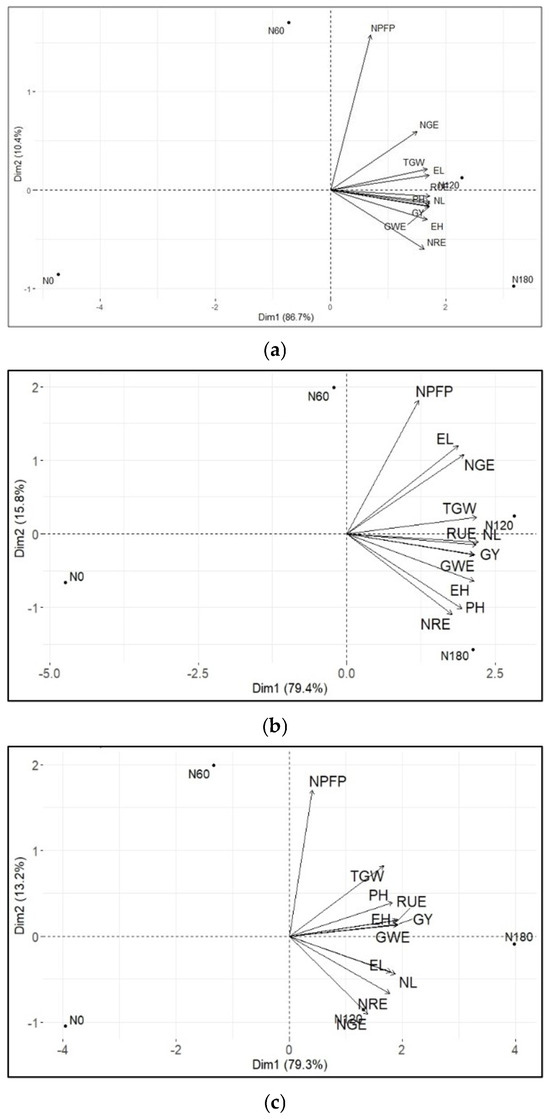
Figure 2.
(a) Principal component analysis (PCA) of morphological and yield components traits, yield, RUE, and NPFP based on different N rates; PH—plant height; EH—ear height; NL—number of leaves per plant; EL—ear length; NRE—number of rows per ear; NGE—number of grains per ear; GWE—grain weight per ear; TGW—1000-grain weight; GY—grain yield; RUE—rain use efficiency; NPFP—N partial factor productivity; N0—0 kg N ha−1; N60—60 kg N ha−1; N120—120 kg N ha−1; N180—180 kg N ha−1; (b) vector plot of variables for ZP666, (c) vector plot of variables for NS6030.
Among the parameters tested for ZP666, RUE, grain yield, number of leaves per plant, number of grains per ear, and ear length are significantly correlated with each other, but the first three parameters are negatively correlated with PC2. Among the parameters tested for NS6030, RUE, ear height, grain yield, and grain weight per ear are significantly correlated with each other and positively correlated with the second axis (PC2). In both hybrids, NPFP is positively correlated with TGW.
In addition, it was established that an N rate of 120 kg ha−1 contributed most to the variability in the seven observed parameters (ear length, 1000-grain weight, RUE, plant height, number of leaves per plant, grain yield, and grain weight per ear). When different hybrids are observed, for ZP666, 120 kg ha−1 N rate in the greatest degree contributed to the variability in grain yield, 1000-grain weight, RUE, grain weight per ear, and the number of leaves per plant, while, for NS6030, 180 kg ha−1 N rate contributed to the variability in the grain weight per ear, grain yield, ear height, and RUE. The 60 kg ha−1 N rates slightly induced variability in NPFP in both genotypes.
According to the AMMI analysis, the stability of the agronomic traits differs in relation to the nitrogen dose used, which maize hybrid was used, and the growing conditions (Tables S1–S12, Figures S1–S11). NS6030 gave more stable and better results in both observed years, compared to ZP666. Regarding the plant height trait, ZP666 had more stable results in conditions with less rainfall during the season, while NS6030 was more stable in more optimal corn growing conditions. Rain use efficiency was more stable in drier conditions, and better results were recorded with ZP666. The hybrid NS6030 had stable results for most of the observed traits at lower doses of nitrogen (control and 60 kg ha−1) and at the highest applied dose (180 kg ha−1). ZP666 gave the best (most stable) results with the application of a nitrogen dose of 120 kg ha−1. All traits varied less during the second experimental year. Based on AMMI stability values (ASV), the highest variability (highest values of the stability coefficient) was determined for the traits the number of grain per ear, and grain yield, while the most stable traits (lowest variability) were plant height, number of leaves per plant, ear length, number of rows per ear, and RUE (Table 4).

Table 4.
AMMI stability values (ASV) for eleven parameters of two maize hybrids across two growing seasons and four N rates.
3.6. Correlation Among Parameters
The simple correlation coefficients showed that grain yield had a significant and strongly positively correlation with the number of leaves per plant (r = 0.66 **), grain weight per ear (r = 0.91 **), and 1000—grain weight (r = 0.67 **); a significant and moderately positive correlation with plant height (r = 0.42 **), ear height (r = 0.52 **), ear length (r = 0.55 **), number of rows per ear (r = 0.58 **), and number of grains per ear (r = 0.59 **); and a significant and weakly positive correlation with RUE (r = 0.31 *) and NPFP (r = 0.30 *), Table 5.

Table 5.
Correlation matrix (Pearson) between studied parameters.
The number of leaves per plant showed a strong positive correlation with ear height (r = 0.85 **) and a high correlation with 1000-grain weight (r = 0.74 **). Similarly, ear length showed a high positive correlation with the number of grains per ear (r = 0.77 **). The NPFP showed a weak, significant positive correlation with the number of grains per ear (r = 0.33 **), the grain weight per ear (r = 0.29 *), and the 1000-grain weight (r = 0.29 **).
4. Discussion
4.1. Year Impact on Morphological and Yield Component Traits, Yield, Rain Use Efficiency, and N Partial Factor Productivity
Our results showed a low CV for plant height, number of leaves per plant, and number of rows per ear; a medium CV for ear height, ear length, number of grains per ear, grain weight per ear, and 1000-grain weight and a high CV for grain yield, rain use efficiency (RUE), and N partial factor productivity (NPFP), as indicated by Pimentel–Gomes [24]. A reasonable coefficient of variation for morphological traits, ear-related traits, and grain yield suggests the experiment’s high level of precision.
It is estimated that 80% of the maize of worldwide arable land is grown under rainfed conditions [25]. Its productivity is influenced by numerous factors such as genetics; temperature; rainfall; physical, chemical, and biological soil properties; and agronomic practices. Maize cultivation in Serbia and neighboring countries depends primarily on rainfall, which is often irregular or unevenly distributed. The present study revealed a significant influence of two contrasting years regarding climatic parameters on morphological and yield component traits, yield, RUE, and NPFP. The two years differed in the amount and distribution of monthly rainfall and temperatures during the maize growing season. Specifically, total seasonal rainfall was 1.6 times higher in the second year than in the first year, resulting in higher values of all parameters except RUE. In the first year, the main cause of yield losses was long-term drought stress during the stem elongation (June) and grain filling (August–September) stages. In the stem elongation phase (second half of June), high temperatures combined with water deficiency reduced stem cell elongation, resulting in shorter internode lengths and reduced plant height. Further, prolonged water stress in August and September negatively affected several yield-related traits, including the number of grains per ear, grain weight per ear, and 1000-grain weight, which ultimately led to lower grain yield. These traits are crucial for grain yield potential and exhibit a high correlation with final grain yield. In August of the same year, water stress during the grain filling stage shortened this stage and reduced grain weight. Drought stress at this stage leads to daily yield losses of 3–5.8%, while extreme drought stress leads to losses of 20–30% [26]. The lower grain weight after flowering can be attributed to a reduced transfer of photosynthetic assimilates to the grains. Similarly, Sah et al. [27] indicated that water deficit stress in the pre-flowering and grain-filling stages decreased morphological traits, ear length, ear width, number of ears per plant, number of grains per row, number of grain rows per ear, and grain yield. In our findings, RUE was higher, while NPFP was lower under unfavorable climatic conditions, aligning with results observed in previous research [28,29]. In drier climates, RUE tends to increase while NPFP decreases, indicating larger rainfall efficiency but lower nitrogen productivity.
4.2. Hybrid Impact on Morphological and Yield Components Traits, Yield, Rain Use Efficiency, and N Partial Factor Productivity
The choice of a proper maize hybrid is an important factor for high grain production and should be adapted to the respective cultivation area together with the application of adequate agricultural practices. Today, hybrids have a high genetic yield potential. Due to their remarkable phenotypic plasticity, the hybrids from the FAO600 group are the most productive and adapted to the production conditions, suitable for grain and forage production [30,31]. The two divergent late-maturing hybrids (NS 6030 and ZP 666) used in the present study are highly adaptive to the climate and soil conditions of southeastern Europe and are grown in lowland regions and river valleys at altitudes of up to 300 m above sea level [32]. The hybrids have delayed leaf senescence, stay-green traits, and are tolerant to drought. For the tested maize hybrids, most of the studied parameters displayed differences. The hybrid ZP 666 had significantly higher plant height, ear length, number of rows per ear, number of grains per ear, grain weight per ear, grain yield, RUE, and NPFP than the hybrid NS 6030. It indicated the existence of inter-varietal differences that can be attributed to genetic divergence, i.e., background [33]. On the other hand, ear height, number of leaves, and 1000-grain weight showed no significant differences between hybrids. In both hybrids, the ears were at approximately the same height within the crop. Regarding NPFP, it is necessary for hybrids to have a higher value, as it is associated with a greater photosynthetic capacity, which contributes to a higher accumulation of dry biomass and a higher grain yield [34]. In addition, genotypes with high NPFP achieve higher yields with low soil N content and lower N fertilizer application [35,36]. Both hybrids exhibit a higher NPFP compared to the average NPFP in China (35 kg grain kg fertilizer N−1) and in agriculturally developed countries for maize production (58 kg grain kg fertilizer N−1), as reported by Wang and Mi [37]. Moreover, the selection of hybrids with high NPFP is one of the ways to reduce the production costs of many crops [38].
4.3. N Rate Impact on Morphological and Yield Components Traits, Yield, Rain Use Efficiency, and N Partial Factor Productivity
An optimal nitrogen (N) fertilization rate maximizes crop production while conserving natural resources [39]. Consequently, it is essential to apply N at a rate that aligns with plant requirements, taking into account various factors that influence N utilization, such as soil properties, climatic conditions, and management practices. Our results showed that all investigated traits, except NPFP, increased with increasing N applications. However, the rate of 180 kg N ha−1 did not significantly increase the observed traits compared to 120 kg N ha−1. Hence, this study recommends applying 120 kg N ha−1 for optimal grain yield. The increase in N rates resulted in enhanced values of morphological traits because N positively influences photosynthesis, cell division, and cell expansion, as established by Castro et al. [40] and Safari et al. [41]. The increase in the number of nodes and the length of internodes is associated with higher leaf production [42]. The yield components also increased with enhanced N rates, thereby causing yield improvement. Yield reduction was primarily driven by N reduction due to decreased yield components and NPFP. Interestingly, 1000-grain weight reached higher values at a rate of 60 kg N ha−1 than in the control, suggesting that lower N rates may promote efficient transfer of assimilates from leaves to grains, although this did not translate into higher overall yield compared to higher N rates. The response of maize to the lowest N rate confirms the conclusion that 1000-grain weight is affected by climatic conditions and nutrient availability between the onset of flowering and the beginning of grain formation [43]. In addition, hybrids with delayed leaf senescence show a higher post-silking N accumulation in the grain, which is reflected in higher yields [44]. The present study indicates that increased N application can significantly increase the value of RUE, so the highest RUE was recorded at N rates of 120 and 180 kg ha−1. Conversely, the lowest NPFP was recorded at 180 kg N ha−1. Du et al. [45] and Rawal et al. [46] also found that NPFP declined with increasing N rates due to lower nitrogen utilization by maize. Furthermore, Galindo et al. [47] and Davies et al. [48] showed that the grain yield of maize increased with increasing N rates up to the optimum, supporting the results noticed in this study, while further N increase expressed no effect or was suppressive. This could be related to the increased N availability and accelerated photosynthetic rate leading to higher production of carbohydrates, resulting in better ear performance and consequently to the grain yield [49]. Additionally, several studies have indicated that the N rate is the most important factor affecting yield components and grain yield of maize. In particular, the studies by Imran et al. [50], Biswas and Ma [51], and Karki et al. [52] showed that application of nitrogen at rates of 210, 150–200, and 120 kg N ha−1, respectively, resulted in maximum grain yield and yield components.
4.4. Interaction of Factors Affected Studied Parameters
The interactions of year × hybrid and year × N rate resulted in significant variation in yield component traits. This is of particular importance considering that stress periods occurring at later growth stages of maize can significantly affect these traits. Drought stress impairs the mineralization of N in the soil, the transport of N from the roots to the shoots, and the N metabolism in the plants, which impairs the uptake and utilization of N in the plants [53]. In our case, reduced soil water availability in August and September 2021, which coincided with the grain filling and maturity stages, hindered N mobility in the grains, contributing to lower grain yield, including NPFP, similar to Sinclair and Rufty [54]. In the wet year (2022), the availability of soil moisture promoted better mineralization and mobility of N, resulting in increased N uptake by plants and higher grain yields. Furthermore, the maize hybrids exhibited distinct responses to varying N rates for ear length, number of grains per ear, and 1000-grain weight. Consistent with our findings, Bello et al. [55] reported that the interaction between year and N rate significantly affected grain yield, while the interactions between hybrid and N rate particularly affected plant height, number of grains per ear, 1000-grain weight, and grain yield. Amanullah et al. [56] found a significant interaction between N rates and maize genotypes for the number of grains per ear. The three-way interaction between year, hybrid, and N rate was significant for ear length, number of rows per ear, and NPFP. These findings suggest that optimal N fertilization has the potential to enhance some quantitative traits, even under extreme climatic conditions such as drought. Dragičević et al. [57] also found that high N fertilization led to yield stability of maize under drought stress in a 20-year long-term experiment.
The maize hybrids differed in their drought tolerance depending on the N rate applied. In the dry year 2021, the hybrid ZP666 achieved the highest yield (9550.7 kg ha−1) and RUE (35.1 kg ha−1 mm−1) at 120 kg N ha−1. In contrast, the hybrid NS6030 exhibited greater yield stability at low (0 and 60 kg N ha−1) and extreme N rates (180 kg N ha−1), suggesting its potential suitability for both low-input and high-input of N. These findings suggest that certain hybrids, such as ZP666, can achieve higher yields under drought stress when provided with adequate nitrogen, emphasizing the importance of appropriate hybrid selection and N management under water-limited conditions, consistent with the observations of Zhang et al. [58]. In the wet year 2022, the hybrid ZP666 again achieved the highest yield (11,053.9 kg ha−1) and RUE (24.7 kg ha−1 mm−1) at 120 kg N ha−1, while the hybrid NS6030 (10,551.4 kg ha−1) achieved the highest RUE (23.6 kg ha−1 mm−1) at the highest N rate. Overall, these results underline the importance of tailored hybrid choice and N management strategies to optimize maize productivity in different environmental scenarios.
4.5. PCA and Correlation Among Parameters
PCA may allow for greater flexibility in determining the N rates that are optimal for achieving high grain yield and, accordingly, the component traits that primarily contribute to higher yield potential. Correspondingly, the application of 120 kg N ha−1 could significantly affect key maize traits, including the number of rows per ear, grain weight per ear, 1000-grain weight, and grain yield.
The correlation between the agronomic traits of maize showed a significant positive relationship between grain yield and yield-related traits. Grain weight per ear and 1000-grain weight had the greatest influence on grain yield compared to other yield components, which emphasizes the importance of sufficient grain filling and is consistent with the results of Ali et al. [59]. Therefore, the improvement of yield component traits is crucial for maximizing grain yield. In addition, morphological traits showed moderate correlation with grain yield, which is consistent with the observations of Mousavi and Nagy [60], suggesting that plant height is not a major determinant of productivity, as modern hybrids tend to have a shorter stature.
5. Conclusions
To enhance crop productivity, it is essential to implement effective soil and crop management practices. Genetic, environmental, and agronomic factors determine crop yield formation. So, maize production is significantly impacted by climatic conditions, particularly rainfall during the growing season, the selection of suitable hybrids, and the application of N fertilizer. Our results indicated that applying 120 kg N per hectare is optimal for enhancing maize yield in semi-arid regions. This nitrogen input improves key yield components, resulting in a notable increase in yield. However, NS6030 showed greater yield stability at low and high N inputs. This indicates a trade-off between the performance and adaptability of the hybrid. In general, the data show that the combination of an optimal N rate and the choice of a hybrid that is more efficient in N utilization can be useful tools to improve the agronomic parameters of maize grain yield while ensuring N savings and protection of the environment from N pollution. Therefore, recommendations should consider both the average performance and yield stability of maize hybrids, depending on the specific production context, including agroecological conditions, resource availability, technological level of the cropping system, and overall production objectives.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture15131387/s1: Table S1: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—plant height; Table S2: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—ear height; Table S3: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—number of leaves per plant; Table S4: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—ear length; Table S5: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—number of rows per ear; Table S6: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—number of grains per ear; Table S7: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—grain weight per ear; Table S8: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—1000-grain weight; Table S9: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—grain yield; Table S10: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—rain use efficiency (RUE); Table S11: Analysis of variance for the AMMI model—N partial factor productivity (NPFP); Table S12: Coordinates for variables (11 observed parameters) and individuals (four N rates)—PC1 and PC2 values used to create 3 biplots (Figure 2a–c); Figure S1: The stability of plant height based on AMMI—biplot analysis; Figure S2: The stability of ear height based on AMMI—biplot analysis; Figure S3: The stability of number of leaves per plant based on AMMI—biplot analysis; Figure S4: The stability of ear length based on AMMI—biplot analysis; Figure S5: The stability of number of rows per ear based on AMMI—biplot analysis; Figure S6: The stability of number of grains per ear based on AMMI—biplot analysis; Figure S7: The stability of grain weight per ear based on AMMI—biplot analysis; Figure S8: The stability of 1000-grain weight based on AMMI—biplot analysis; Figure S9: The stability of grain yield based on AMMI—biplot analysis; Figure S10: The stability of rain use efficiency (RUE) based on AMMI—biplot analysis; Figure S11: The stability of N partial factor productivity (NPFP) based on AMMI—biplot analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.M.; methodology, V.M.; investigation, V.K., Z.G., M.B., N.M., M.M. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, V.M.; writing—review and editing, M.B.; supervision, A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia, based on the Agreement on the realization and financing of scientific research work of SRO in 2025 No. 451-03-136/2025-03/200022.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAO. FAO Statistical Yearbook; Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Conant, R.T.; Berdanier, A.B.; Grace, P.R. Patterns and trends in nitrogen use and nitrogen recovery efficiency in world agriculture. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2013, 27, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatlidis, I.S. Adapting maize crop to climate change. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Grant, B.; Qi, Z.; He, W.; Qian, B.; Jing, Q.; VanderZaag, A.; Drury, C.F.; St. Luce, M.; Wagner-Riddle, C. Towards an improved methodology for modelling climate change impacts on cropping systems in cool climates. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, I.; Han, Q. Nitrogen fertilization affects maize grain yield through regulating nitrogen uptake, radiation and water use efficiency, photosynthesis and root distribution. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Qadri, S.A.A.; Dubbey, V.; Sofi, I.B.; Huang, N. Impact of crop management practices on maize yield: Insights from farming in tropical regions and predictive modeling using machine learning. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Monzon, J.P.; Tenorio, F.A.; Howard, R.; Cassman, K.G.; Grassini, P. Climate and agronomy, not genetics, underpin recent maize yield gains in favorable environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113629119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocianowski, J.; Nowosad, K.; Rejek, D. Genotype-environment interaction for grain yield in maize (Zea mays L.) using the additive main effects and multiplicative interaction (AMMI) model. J. Appl. Genet. 2024, 65, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, D.B. Is there a role for sink size in understanding maize population-yield relationships? Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, F.S.; Teixeira Filho, M.C.M.; Buzetti, S.; Pagliari, P.H.; Santini, J.M.K.; Alves, C.J.; Megda, M.M.; Nogueira, T.A.R.; Andreotti, M.; Arf, O. Maize yield response to nitrogen rates and sources associated with Azospirillum brasilense. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodley, A.L.; Drury, C.F.; Yang, X.Y.; Phillips, L.A.; Reynolds, D.W.; Calder, W.; Oloya, T.O. Ammonia volatilization, nitrous oxide emissions, and corn yields as influenced by nitrogen placement and enhanced efficiency fertilizers. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, K.; Dawar, A.; Tariq, M.; Mian, I.A.; Muhammad, A.; Farid, L.; Khan, S.; Khan, K.; Fahad, S.; Danish, S.; et al. Enhancing nitrogen use efficiency and yield of maize (Zea mays L.) through ammonia volatilization mitigation and nitrogen management approaches. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, K.; Bhandari, S.; Aryal, K.; Mahato, M.; Shrestha, J. Effect of different levels of nitrogen on growth and yield of hybrid maize (Zea mays L.) varieties. J. Agric. Res. Nat. Res. 2021, 4, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delibaltova, V. Response of maize hybrids to different nitrogen applications under climatic conditions of Plovdiv region. Int. J. Farming Allied Sci. 2014, 3, 408–412. [Google Scholar]
- Marković, M.; Josipović, M.; Šoštarić, J.; Jambrović, A.; Brkić, A. Response of maize (Zea mays L.) grain yield and yield components to irrigation and nitrogen fertilization. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2017, 18, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gheith, E.M.S.; El-Badry, O.Z.; Lamlom, S.F.; Ali, H.M.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Ghareeb, R.Y.; El-Sheikh, M.H.; Jebril, J.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Kandil, E.E. Maize (Zea mays L.) productivity and nitrogen use efficiency in response to nitrogen application levels and time. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 941343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacar, B. Toprak Analizleri; Nobel Akademik Yayıncılık Eğitim Danışmanlık Tic. Ltd. Şti.: Ankara, Turkey, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jakovljević, M.; Pantović, M.; Blagojević, S. Laboratory Manual of Soil and Water Chemistry; Faculty of Agriculture, University of Belgrade: Belgrade, Serbia, 1995. (In Serbian) [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Determination of nitrogen in soil by the Kjeldahl method. J. Agric. Sci. 1960, 55, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ure, A.M. Heavy Metals in Soils, 2nd ed.; Alloway, B.J., Ed.; Blackie Academic and Professional: Glasgow, UK, 1995; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.X.; Huo, Z.J.; Liu, P.; Dong, S.T.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhao, B. Modified fertilization management of summer maize (Zea mays L.) in northern China improves grain yield and efficiency of nitrogen use. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1644–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauch, H.G. Statistical Analysis of Regional Yield Trials: AMMI Analysis of Factorial Designs; Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 1–278. [Google Scholar]
- Purchase, J.L.; Hatting, H. Genotype × environment interaction of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in South Africa: II. Stability analysis of yield performance. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2000, 17, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Gomes, F. Curso de Estatística Experimental, 15th ed.; FEALQ: Piracicaba, Brazil, 2009; p. 451. [Google Scholar]
- Aakash; Thakur, N.S.; Singh, M.K.; Bhayal, L.; Meena, K.; Choudhary, S.K.; Kumawat, N.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, U.P.; Singh, S.K.; et al. Sustainability in rainfed maize (Zea mays L.) production using choice of corn variety and nitrogen scheduling. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Lee, B.-M. Effects of climate change and drought tolerance on maize growth. Plants 2023, 12, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.P.; Chakraborty, M.; Prasad, K.; Pandit, M.; Tudu, V.K.; Chakravarty, M.K.; Narayan, S.C.; Rana, M.; Moharana, D. Impact of water deficit stress in maize: Phenology and yield components. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandić, V.; Bijelić, Z.; Krnjaja, V.; Simić, A.; Simić, M.; Brankov, M.; Đorđević, S. Sowing and fertilization strategies to improve maize productivity. Maydica 2017, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fu, W.; Guo, W.; Ren, N.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, Y. Efficient physiological and nutrient use efficiency responses of maize leaves to drought stress under different field nitrogen conditions. Agronomy 2020, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madić, M.; Bokan, N.; Živić, M.; Đurović, D.; Paunović, A.; Tomić, D. Grain yield of maize hybrids at different plant densities. Acta Agric. Serbica 2017, 22, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhiniček, I.; Kaučić, D.; Kozić, Z.; Jukić, M.; Gunjača, J.; Šarčević, H.; Stepinac, D.; Šimić, D. Trends in maize grain yields across five maturity groups in a long-term experiment with changing genotypes. Agriculture 2021, 11, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, M.; Jovanović, Ž.; Tolimir, M. New ZP hybrid selection trends. In Proceedings of the XX Conference on Biotechnology, Čačak, Serbia, 13–14 March 2015; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, J.; Cai, H.; Ren, J.; Liang, Y.; Hou, W.; Chen, G. Accumulation and partition of dry mass and nitrogen in three maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids grown under five planting densities. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 5683–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakelaitis, A.; Silva, A.A.; Ferreira, L.R. Efeitos do nitrogênio sobre o milho cultivado em consórcio com Brachiaria brizantha. Acta Sci. Agron. 2005, 27, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeoluwa, O.O.; Mutengwa, C.S.; Chiduza, C.; Tandzi, N.L. Nitrogen use efficiency of quality protein maize (Zea mays L.) Genotypes. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzawla, W.; Setsoafia, E.D.; Amoabeng-Nimako, S.; Atakora, W.K.; Camara, O.; Jemo, M.; Bindraban, P.S. Fertilizer use efficiency and economic viability in maize production in the savannah and transitional zones of Ghana. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1340927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Mi, G.H. Fertilizer application in maize production in northern China: Current status and fertilization optimal potential. J. Maize Sci. 2021, 29, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerowicz, N.; Pereira, J.M.S.; Medici, L.O.; Bison, O.; Pereira, M.B.; Santos, J.U.M. Estudo da eficiência de uso do nitrogênio em variedades locais e melhoradas de milho. Rev. Bras. Bot. 2002, 25, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.F.; Li, C.; Fritschi, F.B. Diurnal dynamics of maize leaf photosynthesis and carbohydrate concentrations in response to differential N availability. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 99, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.R.C.; Kluge, R.A.; Sestari, I. Manual of Plant Physiology: Crop Physiology; Agronômica Ceres: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008; p. 864. [Google Scholar]
- Safari, A.R.; Hemayati, S.S.; Salighedar, F.; Barimavandi, A.R. Yield and quality of forage corn (Zea mays L.) cultivar Single Cross 704 in response to nitrogen fertilization and plant density. Int. J. Biosci. 2014, 4, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.E.H. Effect of different nitrogen sources on growth, yield and quality of fodder maize (Zea mays L.). J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2011, 10, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, T.Y.; Buzetti, S.; Teixeira Filho, M.C.M.; Galindo, F.S.; Nogueira, L.M. Residual effects of nitrogen fertilizer with polymer-coated urea in a maize crop. Rev. Caatinga 2017, 30, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.; Banerjee, H.; Dutta, S.; Sarkar, S.; Murrell, T.S.; Singh, V.K.; Majumdar, K. Macronutrient management effects on nutrient accumulation, partitioning, remobilization, and yield of hybrid maize cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, Z.; Lei, W.; Kong, L. Increased planting density combined with reduced nitrogen rate to achieve high yield in maize. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, N.; Vista, S.P.; Khadka, D.; Paneru, P. Grain yield, nitrogen accumulation, and its use efficiency of maize (Zea mays L.) as influenced by varying nitrogen rates. Int. J. Agron. 2024, 2024, 4104123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, F.S.; Teixeira Filho, M.C.M.; Buzetti, S.; Santini, J.M.K.; Alves, C.J.; Nogueira, L.M.; Ludkiewicz, M.G.Z.; Andreotti, M.; Bellotte, J.L.M. Maize yield and foliar diagnosis affected by nitrogen fertilization and inoculation with Azospirillum brasilense. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2016, 40, e015036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.; Coulter, J.A.; Pagliari, P.H. Timing and rate of nitrogen fertilization influence maize yield and nitrogen use efficiency. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, A.; Derebe, B.; Bitew, Y.; Chakelie, G.; Andualem, M. Response of maize (Zea mays L.) to nitrogen and planting density in Jabitahinan district, Western Amhara region. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1770405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, S.; Arif, M.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.A.; Shah, W.; Latif, A. Effect of nitrogen levels and plant population on yield and yield components of maize. Adv. Crop Sci. Technol. 2015, 3, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, D.K.; Ma, B.L. Effect of nitrogen rate and fertilizer nitrogen source on physiology, yield, grain quality, and nitrogen use efficiency in corn. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2016, 96, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, M.; Panth, B.P.; Subedi, P.; Aarty, G.C.; Regmi, R. Effect of Different Doses of Nitrogen on Production of Spring Maize (Zea mays) in Gulmi, Nepal. Sustain. Food Agric. 2020, 1, 01–05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, T.C.; Comas, L.H.; Schneekloth, J.; Schipanski, M. Nitrogen and water availability affect soil nitrogen mineralization and maize nitrogen uptake dynamics. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2025, 130, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, T.R.; Rufty, T.W. Nitrogen and water resources commonly limit crop yield increases, not necessarily plant genetics. Global Food Sec. 2012, 1, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.B.; Olawuyi, O.J.; Lawal, M.; Ige, S.A.; Mahamood, J.; Afolabi, M.S.; Azeez, M.A.; Abdulmaliq, S.Y. Genetic gains in three breeding eras of maize hybrids under low and optimum nitrogen fertilization. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 59, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanullah; Iqbal, A.; Ali, A.; Fahad, S.; Parmar, B. Nitrogen source and rate management improve maize productivity of smallholders under semiarid climates. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragičević, V.; Kresović, B.; Videnović, Z.; Spasojević, I.; Simić, M. Fitting cropping technology in a changing climate. Agric. Forestry 2015, 61, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, Z.; Wu, X.; Gan, Y.; Chen, X.; Xia, H.; Kamran, M.; Jia, Z.; Han, Q.; Shayakhmetova, A.; et al. Matching fertilization with water availability enhances maize productivity and water use efficiency in a semi-arid area: Mechanisms and solutions. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 214, 105164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Ahsan, M.; Ali, Q.; Kanwal, N. Phenotypic stability of Zea mays grain yield and its attributing traits under drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.N.; Nagy, J. Evaluation of plant characteristics related to grain yield of FAO410 and FAO340 hybrids using regression models. Cereal Res. Commun. 2021, 49, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).