Abstract
This study analyses the impact of agricultural greenwashing on financial performance via green innovation. To this end, it employs data from Chinese A-share agribusinesses from 2012 to 2022. The study indicates the following results: (1) the practice of greenwashing (ESG disclosure–performance gap, GW) has a significant negative impact on ROA, particularly in non-state firms; (2) green innovation (patents, GI) partially mediates this relationship, with a percentage of 9.09%, as GW diverts research and development resources toward image management. Robustness checks are employed to confirm the results obtained using ROE and lagged models. Property rights moderate the effects: non-state firms are more adversely affected by innovation dependency, while state firms are protected by policies. The “double-edged” mechanism elucidates GW’s short-term legitimacy gains in contrast to long-term innovation suppression and financial decline. The report calls for the establishment of standardised ESG metrics (for example, the disclosure of pesticide residue) and targeted green incentives (for example, SME R&D subsidies) to be aligned with UN SDGs 9.4 (green tech) and 12.6 (responsible production). The present study offers insights into the governance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) matters within the context of agriculture in China.
1. Introduction
Since the global environmental pollution situation has continued to deteriorate, a significant number of companies worldwide have come to regard environmental issues as being of critical importance in terms of their strategic considerations. In the Chinese context, environmental challenges such as haze and water pollution are becoming increasingly severe [1], and the scope and depth of their impacts are expanding. In this context, the frequent occurrence of environmental problems and the awakening of public awareness of environmental protection have formed a dual drive, prompting multiple stakeholders, such as investors, end consumers, policymakers, and enterprise-level customers [2,3], concurrently, and subject to mounting regulatory constraints, the oversight of environmental protection non-governmental organisations (NGOs) and other pressure groups, and the influence of shareholder activism [3], to give increasingly more attention to the practice of corporate environmental responsibility, and to put forward a higher demand for transparency in environmental performance disclosure and the ability to supply environmentally friendly products. For instance, in recent years, China has implemented a series of policies and regulations with the aim of strengthening environmental governance and information disclosure. These include the “Green Bond Support Project Catalogue (2021 Edition)” in 2021, the regular operation of the national carbon market, and the “Measures for the Administration of Enterprises’ Environmental Information Disclosure in Accordance with the Law”. These measures have had a considerable impact on the compliance costs and risks of greenwashing, as well as engendering a more transparent supervisory environment. As demonstrated in the empirical study by Vollero and other scholars [4], companies in the energy industry are experiencing mounting external pressure from stakeholders to expedite the process of sustainable product development and optimise clean energy production systems. The fundamental cause of this phenomenon is the heightened environmental awareness within society [5,6]. The consumer group has emerged as a pivotal driving force, shaping a substantial market orientation that prioritises environmentally conscious consumption. The demand for green products and the inclination to purchase have been steadily increasing [7]. In this context, enterprises must recognise the imperative to integrate their business operations with social responsibility and environmental protection. This necessitates the establishment of a sustainable development paradigm and a social responsibility governance system [5]. In the context of mounting environmental regulations and market pressures, some enterprises have been observed to adopt a green marketing strategy, characterised by selective disclosure of environmental performance, with the objective of projecting a corporate citizen image to stakeholders [8]. Nevertheless, such strategic behaviours may evolve into distorted information disclosure, such as greenwashing or brownwashing. This is evidenced by the strategic disclosure of information aimed at cultivating a green image (e.g., the exaggeration of emission reduction achievements), leading to the formation of greenwashing behaviour [9]. Alternatively, there is the systematic underreporting of environmental performance (e.g., the concealment of pollution data) due to the avoidance of regulatory or public opinion risks, resulting in the formation of brownwashing behaviour [2]. Following the revelation of the emergent tendency of the green market by Delmas and Burbano [9], the field has undergone exponential expansion. The green consumer market, green capital market, environmental product spectrum, sustainable service supply, and corporate green practice system all demonstrate dynamic evolution characteristics. However, in the process of rapid market expansion, greenwashing behaviour has attracted widespread attention as a concomitant phenomenon.
The concept of greenwashing was first systematically constructed in 1986 by Jay Westerveld, a pioneer in the environmental movement. In his critical study of environmental behaviour, Westerveld introduced the term to deconstruct the falsity of business environmental narratives. At the time, he used the hotel industry’s towel reuse programme as a prime example to reveal the nature of the symbolic manipulation of companies’ packaging cost-cutting strategies as “environmental rescue operations”. The industry established a green business ethic that was not consistent with the lack of environmental governance mechanisms and ineffective policies that were in place at the time [10]. A decade later, the concept formally entered the academic research paradigm, and Greer and Bruno (1996) [11] in their seminal work Greenwash: The reality behind corporate environmentalism. The present study systematically deconstructed the manner in which businesses manipulate environmental issues. This was achieved by means of critical discourse analysis, which was utilised to examine the manner in which multinational corporations constructed the illusion of environmental responsibility through marketing rhetoric. According to KPMG (2023), the definition is as follows: a company or investment fund may make misleading or unverified third-party claims about the environmental impacts, social benefits, and governance efficacy of its products or operations in the dimension of sustainability performance through strategic disclosure, selective factual presentation, and conceptual discursive packaging [12]. In the early stages of research on greenwashing, the focus was on the nexus of marketing and corporate social responsibility (CSR). The prevailing theoretical framework underwent an evolution, developing along two primary strands: symbolic rhetoric [13] and institutional arbitrage [14]. In recent years, this topic has gained traction within the field of accounting, establishing a novel dimension in the study of the credibility of environmental information disclosure. However, empirical studies present a ”performance paradox”—whilst the majority of studies have identified a negative correlation between greenwashing behaviour and corporate financial performance [15,16], some studies have not found a significant impact or have demonstrated a weak positive correlation [17]. Furthermore, research on the generating causes of greenwashing remains in its infancy [18]. However, extant research on greenwashing primarily concentrates on the manufacturing and energy industries, and there is a paucity of systematic analysis in the agricultural sector [18].
The following reasons underpin the necessity for further theoretical development in this area: On the one hand, agriculture holds a unique and crucial position in global sustainable development. China is the world’s largest producer of agricultural products and carbon emitter, accounting for 17% of agricultural greenhouse gas emissions [19], while facing serious environmental challenges such as soil degradation and excessive use of chemical fertilisers [20]. On the other hand, the hidden nature and specificity of agricultural greenwashing, in contrast to the characteristics of industrial pollution, agricultural surface pollution is distinguished by its dispersal, randomness, and high monitoring difficulty [21]. Enterprises are able to engage in greenwashing more readily through selective disclosure (e.g., reporting water-saving technology whilst concealing pesticide misuse) [9]. Furthermore, the composition of Chinese agribusinesses is distinctly diverse and institutionally complex, comprising three main categories: state-owned agribusinesses (e.g., COFCO), private agribusinesses (which account for more than 60% of listed entities), and agricultural cooperatives [22,23], whose operations are subject to the dual influence of policy support and market pressure. For instance, state-owned agribusinesses may prioritise policy patronage over environmental responsibility, while private firms tend to adopt short-term greenwashing strategies due to financing constraints [24]. Therefore, this study innovatively introduces the theory of greenwashing into the paradigm of agricultural economic analysis, revealing its dual mechanism of action: (1) Resource crowding-out effect: enterprises’ greenwashing behaviour leads to the erosion of long-term competitiveness through the strategic allocation of resources (e.g., transferring funds and talents that should have been used for green technological innovations to the packaging of environmental symbols) [25]. (2) The trap of legitimacy arbitrage: When there is a systemic mismatch between the intensity of environmental regulations and market pressure for environmental protection, enterprises may obtain short-term legitimacy through greenwashing, but this will lead to the depletion of reputation capital and systemic financial risks [26]. Based on the empirical findings of this study, we can provide critical and constructive Chinese experiences for the global agricultural green transformation, and promote a paradigm shift from the ”greenwashing trap” to substantive innovation.
Drawing upon the aforementioned background, this study investigates Chinese agricultural enterprises as its object. It develops a theoretical framework delineating “greenwashing behaviour–green innovation–financial performance”. Utilising A-share data of Chinese agricultural enterprises from 2012 to 2022, the study employs a two-way fixed effect model and a mediation effect analysis method to empirically assess the inhibitory effect of greenwashing (as measured by the discrepancy in ESG disclosure) on financial performance (ROA) and the mediating mechanism of green innovation (patent application). Research findings indicate that the negative effects of greenwashing are more pronounced in non-state-owned enterprises, with green innovation accounting for 9.09% of the intermediary proportion. The robustness of the tests provides support for the reliability of the conclusion. The conclusion of the study proposes the establishment of ESG standards, the introduction of incentives for technological innovation, and the implementation of diversified governance pathways based on property rights. These proposals directly align with UN SDG 9.4 (green technology) and 12.6 (responsible production). The study provides a theoretical and practical foundation for the low-carbon transformation of agriculture. The structure of this article is organised as follows: The initial section, entitled Introduction, methodically expounds upon the research background and theoretical lacuna pertinent to the phenomenon of agricultural greenwashing. The subsequent section, the Literature Review, methodically categorises the extant research according to three distinct aspects: greenwashing behaviour, green innovation, and financial performance. The third part of the study constructs a theoretical framework and proposes research hypotheses. The fourth part of the thesis provides a detailed exposition of the research design, encompassing the data sources, variable definitions, and model settings. The fifth part of the study presents the empirical results (i.e., the benchmark regression, the mediating effect, the robustness test, and the heterogeneity analysis). The sixth part of the study summarises the research conclusions and puts forward policy suggestions.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Greenwashing Behaviour and Green Innovation
Green innovation is defined as the innovation that occurs in the context of sustainable development through the development or improvement of technologies, processes, products, services, or management, with the objective of reducing negative impacts on the environment and enhancing resource utilisation efficiency [27], and it possesses dual value attributes [28]. Enterprise green innovation is regarded as a key factor in promoting high-quality economic growth [29,30].
In the context of the relationship between greenwashing and green innovation, greenwashing behaviour has been demonstrated to have a significant suppressive effect on the level of green innovation in enterprises, by distorting resource allocation and market signals [31]. The first issue is that of resource misallocation. The practice of greenwashing results in the biased allocation of resources toward the achievement of short-term profit goals, while environmental and social responsibilities are placed in a secondary position [32,33]. Enterprises reallocate resources that are supposed to be dedicated to innovation and research and development to uphold a superficial corporate image, aiming to address environmental supervision and public opinion pressure.This disproportionate distribution of resources has been shown to impede the formulation of long-term innovation strategies and the accumulation of innovation resources by enterprises, consequently hindering the enhancement of innovation levels [34]. For instance, Hu et al. (2023) found through empirical analysis of Chinese manufacturing and agricultural enterprises that greenwashing behaviour in ISO 14001 certification led to a 12.7% reduction in green R&D investment, and this effect was more pronounced in regions with lax policy enforcement [35]. Secondly, market signals are distorted. Enterprises have been found to distort the authenticity and transparency of market information through false or dishonest environmental disclosures, making it difficult for investors to accurately assess the risks and value of enterprises. This may result in a decline in investors’ confidence in and propensity to invest in enterprises, consequently impeding the capacity of enterprises to secure funds for innovation activities [36]. Huang (2025) [37] conducted research on Chinese-listed companies, the results of which indicate that the cost of financing through green bonds for enterprises that engage in greenwashing is 1.8 percentage points higher than that of enterprises that are honest. This has a direct effect on the acquisition of innovative capital. From the perspective of economic agents pursuing profit, unethical managers utilise greenwashing as a strategy to expedite market capture and resource acquisition, leveraging the benefits of low-cost investment and high-income generation [38,39]. The practice of greenwashing has been demonstrated to exert a substitution effect on innovation, thereby suppressing the willingness of enterprises to achieve economic growth through innovation [35]. Testa et al. proposed the “greenwashing-innovation substitution” theoretical framework, which posits that enterprises divert resources from innovation to environmental image management. For every 10% increase in the degree of greenwashing, there is a 3.2% decrease in R&D investment [15]. This distorted and untrustworthy behaviour on the part of enterprises poses a serious threat to their innovation and development [30].
It is important to note that the relationship between greenwashing and innovation is subject to institutional background and industry heterogeneity. On the one hand, there is the regulatory role of policy. Mandatory ESG disclosure systems (for example, the EU’s Non-Financial Reporting Directive) have been shown to reduce the negative impact of greenwashing on innovation by up to 42% [9]. On the other hand, the agricultural sector is distinguished by its unique characteristics. It is evident that the complexity inherent in the monitoring of non-point source pollution has the potential to result in the occurrence of greenwashing, a phenomenon that is characterised by selective disclosure, for instance the concealment of excessive pesticide usage. This, in turn, has the effect of diverting resources from the areas of technological research and development [21].
2.2. Green Innovation and Corporate Financial Performance
In addressing the correlation between green innovation and corporate financial performance, the prevailing academic consensus suggests a predominantly positive influence of green innovation on corporate financial performance. A number of studies have indicated a negative correlation [40,41], a U-shaped relationship [42], an inverted U-shaped relationship [43], or even no relationship [44] between the two. However, the majority of the most recent empirical studies grounded in the Chinese context lend support to the “Porter Hypothesis”, which posits that green innovation has a positive effect on corporate financial performance [45]. The overarching objective of green innovation is to reduce pollution, enhance energy productivity, minimise waste, substitute finite resources with sustainable ones, and promote recycling [46]. In the context of green innovation, the allocation of resources and the strategic orientation of such initiatives are frequently prioritised toward financial performance and value creation. These elements are fundamental to the company’s strategy, aimed at ensuring competitiveness and profitability [47,48]. Zhang et al. (2019) conducted a panel data analysis of listed manufacturing and agricultural companies in China from 2012 to 2017, the results of which indicated that for every 1% increase in green patents, the return on assets (ROA) of enterprises increased by 0.12% [43]. Guo et al. (2021) demonstrated in a study of provincial agricultural enterprises in China that, under the policy background of the “Zero Growth of Chemical Fertilizer Action” (implemented in 2015), enterprises adopting water-saving irrigation technologies saw their ROA increase by an average of 2.3 percentage points [45]. As posited by Huang et al. (2025) [49], a “time-lag effect” is present in the domain of agricultural green innovation. The financial returns of technologies such as biopesticides manifest after a period of 3 to 5 years, yet the long-term ROA growth rate can attain 1.8 times the industry average. Green innovation has been identified as a potentially effective mechanism for addressing environmental issues [50] and enhancing corporate sustainability [51]. This has led to an increased focus on the topic from policymakers and scholars in relevant fields. In the context of mounting ESG regulatory strictures within China (illustrated by the introduction of the “Measures for the Administration of the Law-based Disclosure of Environmental Information by Enterprises” in 2022), enterprises have started to pay greater attention to the environmental impact of their decision-making and management behaviours, and to promote green innovation [52,53]. Consequently, green innovation has been demonstrated to assist enterprises in balancing environmental expenditures by enhancing resource productivity, which has a positive financial influence [49,54]. Furthermore, enterprises have the potential to expand into new domains and increase market share by introducing environmental innovations [45]. According to Chen [55], the “first-mover advantage” is a concept that pertains to the benefits that green innovators are likely to accrue. The “first-mover advantage” is defined by a number of factors, including higher commodity prices, a stronger corporate image, expanding market opportunities, and competitive superiority. In the context of the Chinese agricultural market, this phenomenon is characterised by a technology premium, evidenced by price premiums ranging from 15% to 30% for organically certified agricultural products. Additionally, policy subsidies, notably those allocated to green technology, account for between 20% and 40% of research and development investment.
2.3. Greenwashing Behaviour, Green Innovation, and Corporate Financial Performance
In accordance with the legitimacy theory, the objectives of environmental information disclosure by enterprises encompass the following: fulfilment of environmental legitimacy management, communication of their environmental performance to stakeholders, enhancement of corporate image, and acquisition of favourable government resource allocation In instances where agricultural enterprises find themselves confronted with the implementation of emission reduction policies, yet their technical capabilities are found to be inadequate, there is a tendency for these enterprises to engage in practices of greenwashing, thereby seeking to attain short-term legitimacy [56]. However, this has been shown to result in a “dynamic trap”: under stricter supervision, the probability of greenwashing being detected increases, leading to the cost of maintaining legitimacy growing faster than innovation investment [57]. In accordance with the signalling theory, the disclosure of positive environmental information is advantageous for enterprises in the financial market. Enterprises demonstrating commendable environmental performance are more predisposed to voluntarily disclose their environmental information, seeking to distinguish themselves from those with less robust environmental performance. In the context of the green financial market, enterprises engaging in greenwashing—the practice of misrepresenting environmental credentials—release false signals pertaining to their environmental performance. This can take the form of exaggerating the progress made in achieving carbon neutrality, among other methods. Such practices trigger adverse selection by investors, resulting in a 15% decline in the subscription rate of green bonds [33]. In contrast, enterprises that are genuinely innovative in their environmental practices release credible signals through green patents and obtain an “ESG premium” [43].
The extant literature on the impact of greenwashing on corporate financial performance is still evolving, and there is no consensus. There are two primary reasons for this phenomenon. The first of these is the divergence in concept measurement, given the extensive coverage of the concept of greenwashing, scholars have not reached a consensus on a consistent method to classify companies as complete greenwashers [58]. The most recent research (2020–2024) has enhanced the accuracy of identification through text analysis, specifically the environmental performance deviation method (Text–Performance Deviation, TPD). For instance, Zhou et al. (2024) [31] developed a greenwashing index for China’s manufacturing sector, combining the density of environmental keywords in annual reports with the deviation of actual pollutant emissions data. The accuracy rate was shown to have improved by 27% in comparison with traditional methods. Secondly, the existing body of research is both contradictory and limited in scope. The concept of greenwashing has been the subject of scholarly discourse, with various studies offering divergent perspectives on its nature and implications. Some authors interpret greenwashing as a form of selective positive disclosure, which, while potentially misleading, is not necessarily false [59]. In contrast, others condemn greenwashing as a deliberate and unethical practice [60], deeming it hypocritical and deceptive [61]. Furthermore, the policy context is subject to constant evolution. The intensity of ESG regulation in China has increased considerably since the establishment of the “dual carbon” goals in 2020, rendering previous conclusions (e.g., Du’s discovery of the greenwashing premium effect [60]) invalid under the current stringent disclosure regime. Following the implementation of the “Measures for the Administration of the Law-based Disclosure of Environmental Information by Enterprises” in 2022, the probability of regulatory penalties for enterprises engaging in greenwashing has increased by 40%, directly raising compliance costs [62].
Existing literature calls for further expansion in the relationship between greenwashing and corporate financial performance [18]. The hypothesis that greenwashing exerts a significant impact on corporate financial performance is one that has been contested by some scholars [17]. The prevailing scholarly consensus posits a negative correlation between greenwashing and corporate financial performance [63]. In the context of the capital market, the phenomenon of greenwashing has been demonstrated to be associated with elevated rates of employee turnover [64], impairment to corporate reputation [65], diminution of corporate legitimacy, escalation in the probability of stock mispricing, and deleterious effects on corporate value [31]. Empirical findings from non-Chinese samples predominantly show a negative correlation between greenwashing and performance. Testa et al. (2018) conducted a study in which they tracked EU enterprises and found that greenwashing behaviour reduced long-term stock returns by 12.3% during the period from 2008 to 2017 [15]. Akturan (2018) used experimental design to confirm that consumer purchase intention dropped by 35% and brand equity was damaged by 24% after greenwashing exposure [66]. Berrone et al. (2017) verified that greenwashing reduced R&D investment by 19% through the “resource crowding-out effect”, creating a vicious cycle of “compliance illusion–innovation stagnation” [67]. The EU’s Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD, 2018) has been shown to mitigate the adverse impact of greenwashing on financial performance by 42% through the implementation of mandatory third-party audits [9]. The core conclusion drawn from a comprehensive study of Chinese samples (2018–2024) indicates that greenwashing is associated with direct financial penalties, including increased financing costs and market value depreciation. Zhang (2023) demonstrated that enterprises engaging in greenwashing activities within Chinese-listed companies exhibit a credit spread on their green bonds that is 1.8 percentage points higher than that of honest enterprises, thereby directly restricting the acquisition of innovative capital [33]. Zhou et al. (2024) found that the Tobin’s Q value of greenwashing enterprises decreased by 0.21 (covering the period from 2015 to 2022), and this effect was magnified by 1.7 times following the implementation of the “dual-carbon” policy [31].
Green innovation has been shown to play a complex mediating role between greenwashing behaviour and corporate financial performance. The intensity of this transmission path is regulated by both the property rights attributes of enterprises and the institutional environment. Empirical test of the mediating effect: the analysis of agricultural enterprises using the structural equation model (SEM) [36] demonstrates that greenwashing behaviour indirectly reduces the return on assets by weakening the input of green innovation resources, with a mediating effect accounting for 21.7%. The joint contribution of direct and indirect effects constitutes a negative driving mechanism for financial performance. Regulatory effect of property rights heterogeneity: it is evident that non-state-owned agricultural enterprises are more reliant on market reputation capital due to the restricted financing channels available to them. The inhibitory intensity of greenwashing on green innovation in non-state-owned enterprises is 37% higher than that in state-owned enterprises [68]. Quantitative analysis demonstrates that for each one standard deviation increase in the degree of greenwashing in private enterprises, the number of green patent applications decreases by 0.24, while in state-owned enterprises, it only drops by 0.15 [69,70]. The regulatory effect of policy regulations has shown that mandatory ESG information disclosure systems (for example, the EU’s Non-Financial Reporting Directive) weaken the negative transmission effect of greenwashing on green innovation by 42% through enhancing the transparency of environmental information and increasing the cost of greenwashing operations [9]. On the one hand, greenwashing behaviour may enhance a company’s image in the short term; however, if the company fails to engage in substantive green innovation, it may have a negative impact on the company’s financial performance in the long run. Specifically, greenwashing behaviour may cause enterprises to reallocate resources originally intended for innovation and R&D to maintaining their image, thereby weakening the formulation of long-term innovation strategies and the accumulation of innovation resources, and thus posing an obstacle to the improvement in innovation levels [70]. Moreover, enterprises’ false or dishonest environmental disclosures distort the authenticity and transparency of market information, making it difficult for investors to accurately assess the risks and value of the enterprise. This may result in a decline in investor confidence and a decrease in their propensity to invest in the enterprise, consequently constraining the enterprise’s capacity to acquire funds for innovation endeavours and ultimately leading to deterioration in its financial performance [71].
3. Theoretical Analysis, Research Hypotheses, and Conceptual Model
3.1. Definition of Key Concepts
This study establishes a theoretical framework predicated upon the following operational definitions: Greenwashing behaviour refers to the actions of enterprises to construct a false image of environmental responsibility in the ESG performance dimension through strategic information disclosure (for example, exaggerating emission reduction achievements, selectively disclosing environmental data) or symbolic rhetoric means [12]. Green innovation focuses on the development of green technology; it signifies substantial advancements in environmental technology, as evidenced by patent applications (inventions and utility models). Achievements in this field are expected to foster long-term competitiveness by reducing resource consumption and pollution emissions [36]. Financial performance utilises return on assets (ROA) as the pivotal metric; it offers a comprehensive evaluation of the immediate financial performance of enterprises, encompassing the efficacy with which resources are employed and the degree of profitability [32].
3.2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
3.2.1. Impact of Greenwashing Behaviour on Financial Performance of Agribusinesses
In accordance with the tenets of the legitimacy theory framework [72], corporate greenwashing strategies frequently entail the fabrication or exaggeration of environmental commitments, thereby engendering a specious appearance of legitimacy in the short term. This is undertaken in response to external regulatory pressure and stakeholder expectations. However, from a dynamic development perspective, such greenwashing practices will ultimately result in severe reputation crises and regulatory penalties [15]. In the context of China, Du (2015) discovered that the capital market exerts a substantial negative valuation effect on enterprises engaging in greenwashing [60]. Recent studies on Chinese enterprises [31] and agricultural conglomerates [73] also support the view that greenwashing behaviour damages financial performance. Within the agricultural sector, the inherent challenges of identifying, dispersing, and tracing the sources of non-point source pollution provide a natural “cover” for greenwashing behaviour, thereby encouraging enterprises to adopt selective environmental information disclosure strategies, including the deliberate concealment of key negative information, such as excessive pesticide use and over-application of fertilisers. This information distortion and misrepresentation will directly lead to the erosion of stakeholders’ trust in the enterprise [74]. Empirical research provides robust support for this perspective. In their study of greenwashing enterprises in the Canadian pollution industry, Walker and Wan [16] found that greenwashing is detrimental to corporate financial performance. A subsequent analysis discloses that, in comparison with state-owned enterprises, non-state-owned enterprises, due to facing more severe financing constraints and having a lower dependence on policy resource support, are more sensitive to market reputation and investor confidence in their business decisions. Consequently, the adverse economic repercussions of greenwashing are more evident in non-state-owned enterprises [56].
Based on the above analysis, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H1:
Greenwashing behaviour is negatively correlated with the financial performance of agricultural enterprises.
3.2.2. Mediating Effect of Green Innovation on Greenwashing Behaviour and Corporate Financial Performance
In accordance with the fundamental logic of the resource substitution theory [75], the practice of corporate greenwashing can be regarded as a detrimental cycle of resource misallocation. This behavioural pattern involves enterprises reallocating strategic resources that had been earmarked for green technology research and development and innovation, instead utilising them for short-term image-building and public relations maintenance activities. This strategic shift has a direct impact on the scale and sustainability of green innovation investment [36]. Empirical research provides quantitative evidence for this mechanism: Shan et al. [57] conducted a modelling analysis using agricultural enterprises as samples and found that for every 10% increase in the degree of corporate greenwashing, the output of green patents would decrease by 0.3. It is noteworthy that this negative effect is more pronounced in technology-intensive industries (where the negative impact coefficient is twice as high as that in traditional industries). This indicates that areas with high technological barriers and strong reliance on R&D are more vulnerable to the “resource siphoning” impact of greenwashing behaviour.
From the perspective of dynamic competition, the weakening of green innovation capabilities will undermine a firm’s long-term competitiveness through multi-dimensional transmission mechanisms. Water-intensive agriculture, for instance, is a sector that is particularly vulnerable to the consequences of climate change. The absence of green innovation achievements, such as water-saving irrigation technologies and wastewater recycling systems, will directly lead to the pressure of rising production costs for enterprises [19]. This cost disadvantage is attributable not only to inadequate resource utilisation efficiency but also to the escalation in environmental compliance costs resulting from more stringent regulations. Furthermore, green innovation is identified as a pivotal factor in enabling enterprises to establish sustainable competitive advantages through a series of interconnected processes, including the establishment of technological barriers, the acquisition of first-mover advantages, the consolidation of market share, and the enhancement of pricing power [55]. When greenwashing behaviour causes this innovation engine to “stall”, enterprises will fall into a double predicament of shrinking market share and declining product premium capacity, ultimately dragging down financial performance through paths such as slower revenue growth and compressed profit margins. However, an “innovation applicability paradox” exists within the agricultural sector [20,43]; that is, the cycle from the research and development of green technologies to their commercial application and significant financial returns is relatively protracted (“time-lag trap”), and due to factors such as the imperfect patent value assessment system [55], their short-term financial conversion efficiency may be lower than that in the industrial sector. However, this does not negate the long-term significance of green innovation as a pivotal mediating mechanism. This mechanism elucidates the comprehensive chain of consequences engendered by greenwashing behaviour, encompassing resource misallocation, innovation suppression, and the deterioration of financial performance.
Based on the above analysis, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H2:
Green innovation plays a partial mediating role between greenwashing behaviour and financial performance. Greenwashing indirectly exacerbates performance decline by suppressing green innovation.
3.3. Conceptual Model Construction
Based on theoretical analysis and hypotheses, this study constructs a chain mediation model of “greenwashing behaviour–green innovation–financial performance”. As demonstrated in Figure 1, the legitimacy theory [72] is employed to propose the direct impact of greenwashing behaviour on financial performance (H1). The resource substitution theory [75] is then utilised to construct the mediating path of ”greenwashing → green innovation → financial performance” (H2). The mechanism of the effect of green innovation on financial performance is derived from the discussion in the dynamic capability theory [55,76] regarding the construction of competitive advantages through technological accumulation.
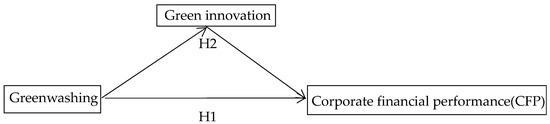
Figure 1.
Conceptual framework and research hypotheses.
4. Research Design
4.1. Data Sources
The present document refers to the “Guidelines for the Classification of Listed Companies by Industry (Revised in 2012)” issued by the China Securities Regulatory Commission. The subjects of the research are selected from enterprises in the “Agriculture, Forestry, Animal Husbandry and Fishery” industry, and those in the “Processing of Agricultural and Forestry Products”, “Food Manufacturing”, “Beverage and Tea Manufacturing”, “Textile Industry”, “Leather, Fur, Feather and Down Products and Footwear Manufacturing”, and “Wood Processing and Wood, Bamboo, Rattan, Palm and Grass Products” sectors within the manufacturing industry. The sample enterprises for this study are A-share-listed agricultural (related) enterprises from 2012 to 2022. To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data, the data processing in this paper follows the practices of existing literature: companies with ST, *ST, and delisted status are excluded, and samples with missing data are deleted. In conclusion, 97 A-share-listed agricultural enterprises were obtained, with a total of 754 sample observations.
The ESG disclosure score data for agricultural enterprises are sourced from the Bloomberg database; the Huazheng ESG rating data are derived from the Wind database; the green patent data of enterprises are from the National Intellectual Property Administration, and all other financial data are from the CSMAR database. To circumvent any potential errors that may be present in the sample data of the selected agricultural enterprises, this study employed a linear interpolation method to process the missing values of the relevant indicators that were not disclosed by individual agricultural-listed enterprises. To circumvent the impact of extreme values, this study employed a winsorisation procedure on all continuous variables at the 1% and 99% quantiles. The present study employed Stata 17.0 statistical software for the analysis of data.
4.2. Definition of Variables
4.2.1. Explained Variable: Corporate Financial Performance
There are various ways to measure the financial performance of enterprises, mainly single-dimension indicators and multidimension indicators. Commonly used unidimensional indicators are return on assets (ROA), return on equity (ROE), etc. Multidimensional indicators include factor analysis and principal component analysis. For this study, ROA was chosen as the explanatory variable, i.e., it is measured by ROA (the ratio of net profit to total assets). Furthermore, return on equity (ROE) was chosen to replace ROA for the robustness test.
4.2.2. Main Explanatory Variables: Agribusiness Greenwashing Behaviour (GW)
In the context of sustainable operation, enterprises that adopt greenwashing information disclosure strategies often engage in the selective disclosure of high-visibility ESG issues (e.g., carbon neutrality commitments and data on charitable donations), with the objective of obscuring their fundamental environmental performance deficiencies and substantial ESG management inadequacies. The ESG integration analysis framework demonstrates that there are significant synergy effects and transmission mechanisms among the three dimensions of environment (E), social responsibility (S), and corporate governance (G). It is evident that environmental behaviour is not only the core carrier of environmental dimension performance, but also reflects the quality of enterprises’ responses to government regulations, ESG rating requirements of financial institutions, consumers’ green preferences, and community environmental rights through quantitative indicators such as resource utilisation efficiency and pollution emission control. This constitutes the substantive evaluation benchmark of the social responsibility dimension [77]. Therefore, this study, referring to the research conducted by Yu [78] and Zhang [62], utilises a methodological approach that calculates the discrepancy between the ESG disclosure score (standardised by peers) and the actual ESG performance score (also standardised by peers) for agricultural enterprises, with the objective of measuring the extent of greenwashing behaviour exhibited by these enterprises.
The specific calculation formula is as follows.
where ESGdis is the ESG disclosure score of agribusiness, expressed by Bloomberg ESG score, and dis is the mean of ESG disclosure score of peer firms; σdis is the standard deviation of ESG disclosure score of peer firms; ESGper is the actual ESG performance of the firms, expressed by CSI ESG ratings, and per is the mean of ESG true performance of peer firms; and σper is the standard deviation of peer firms’ ESG performance. The larger the positive value of greenwashing, the more serious the behaviour of greenwashing.
4.2.3. Mediating Variable: Corporate Green Innovation (GI)
This study employs the number of green patent applications as a metric for the quantity of green innovation (GI) of enterprises, as previously defined in existing research [57,76]. Specifically, the number of green invention patent applications and the number of green utility model applications are first summed. Subsequently, the logarithm of the total number of green patent applications plus one is employed to address the right-skewed distribution problem in green patent application data.
4.2.4. Control Variables
This study employs a multifaceted theoretical framework, drawing upon the practices of analogous literature in the field. It selects enterprise scale, financial leverage, growth capacity, equity structure, capital intensity, and property-rights nature as the control variables. It is evident that variables such as enterprise scale (SIZE) and financial leverage (Lev) are indicative of the general framework of agricultural-enterprise financial performance research [30], which is instrumental in controlling the influence of economies of scale and capital structure. Furthermore, the incorporation of annual dummy variables in this study serves to regulate the impact of the year and enterprise financial performance (Table 1).

Table 1.
List of variable definitions.
4.3. Model Design
4.3.1. Baseline Model
Based on the research hypotheses, this study examines the impact of greenwashing behaviour on the financial performance of agribusinesses using the following model.
where the explained variable ROAi,t denotes the corporate financial performance of firm i in year t, and GWi,t is the corporate greenwashing behaviour, which denotes the degree of greenwashing of firm i in year t. Controli,t represents the set of control variables, including enterprise size, financial leverage, growth capacity, equity structure, capital intensity, the nature of property rights, and the percentage of independent directors. δi is the year fixed effect, μi is the industry fixed effect, and εi,t represents the random error term.
ROAi,t = α0 + α1GWi,t + ∑ αi Controli,t + μi + δi + εi,t
4.3.2. Modelling of Mediating Effects
To test hypothesis H2, whether greenwashing behaviour will have an impact on corporate financial performance through green innovation, this analysis constructs the following mediation effect model on the basis of model 1.
where GI stands for the mediating variable green innovation.
GIi,t = β0 + β1GWi,t + ∑ βi Controli,t + μi + δi + εi,t
ROAi,t = α0 + α1GWi,t + GIi,t + ∑ αi Controli,t + μi + δi + εi,t
5. Analysis of Empirical Results
5.1. Descriptive Statistical Analysis of Variables
In this study, reference is made to the standards provided in the Guidelines for Industry Classification of Listed Companies (2012 Revision), issued by the China Securities Regulatory Commission. A sample of 97 A-share-listed agricultural enterprises was selected, totalling 754 observations. The descriptive statistics of the relevant variables are as follows: as illustrated in the table, the maximum value of the explanatory variable (corporate financial performance [ROA]) is 0.258, the minimum value is −0.188, the standard deviation is 0.067, and the mean value is 0.061. This suggests that, despite the negative rate of return on total assets resulting from some operating fluctuations of agricultural enterprises, the overall profitability is concentrated in the positive range and the industry’s financial performance is relatively stable. From the perspective of the greenwashing score (GW) for the explanatory variable, its mean is −0.035, with a standard deviation of 0.616. The range between the maximum value of 2.268 and the minimum value of −1.878 is substantial. This finding is indicative of the comparatively limited transparency exhibited by certain enterprises within China’s agricultural sector with regard to environmental disclosure. There is a clear necessity for enhancement in the current level of transparency. In instances where GW is less than zero, it is indicative of an ESG performance that exceeds the disclosed level of the enterprise. This phenomenon, termed “greenwashing” or “brownwashing”, may be driven by strategic considerations of the enterprise, including the avoidance of excessive regulatory scrutiny, the mitigation of public expectations for future performance, the prevention of competitor imitation of successful practices, or the avoidance of perceived “hypocrisy” [15,79]. Despite the findings reported in the existing literature [15] indicating a negative correlation between “greenwashing” behaviour and financial performance, further exploration is required to elucidate the driving mechanisms and economic consequences of this behaviour in specific industries, such as agriculture. The negative GW value phenomenon proffers preliminary evidence for comprehending the “brownwashing” behaviour of agricultural enterprises and its potential impacts. The mean of the mediating variable green innovation (GI) is 0.481, with a maximum value of 3.219, a minimum value of 0, and a standard deviation of 0.742. This finding suggests that the overall level of green technological innovation in agricultural enterprises is not high, and that significant differences exist among enterprises. It is evident that a number of enterprises possess robust R&D capabilities; however, the majority have yet to amass effective technologies. From the perspective of control variables, the growth ability (Growth) of sample enterprises shows significant polarisation, and the equity concentration (Top1) and capital intensity (CAPI) have prominent differences, indicating that there is a significant imbalance in the competitive landscape and asset allocation model within the industry. In contrast, the distribution of enterprise scale (SIZE), debt level (Lev), and the proportion of independent directors (Lndep) is relatively concentrated. The proportion of state-owned enterprises in terms of property rights nature (State) is 40.9%, a figure that is highly consistent with the characteristics of the agricultural industry, such as heavy asset operation, the need to diversify business risks, and the requirements for corporate governance compliance (Table 2).

Table 2.
Results of descriptive statistics of variables.
5.2. Correlation Analysis
The results of the correlation analysis of the main variables are shown in the table below. Without controlling other variables, the correlation coefficient between greenwashing score (GW) and financial performance (ROA) of agribusinesses is −0.323 (p < 0.1), which is a significant negative correlation, indicating that the higher the degree of untruthfulness of environmental information disclosure of the enterprise, the more serious the impairment of its profitability, which directly supports the core hypothesis of ”greenwashing behaviour impairs financial performance”. Green innovation (GI) is positively correlated with ROA (0.238, p < 0.1), which implies that technology research and development has a limited effect on short-term performance enhancement, and its transmission path needs to be further verified through the mechanism test. Using the variance inflation factor for the test, it is concluded that all variables satisfy VIF < 5, and the mean value of VIF is 1.16, so there is no serious problem of multicollinearity, and the subsequent research and analysis can be carried out (Table 3).

Table 3.
Variable correlation analysis.
5.3. Regression Analysis
This study empirically analyses using a two-way fixed effects model to mitigate omitted variable bias by controlling for year and industry effects. The results in Table 4 show that there is a significant inhibitory effect of greenwashing behaviour (GW) on corporate financial performance (ROA). After controlling for year and industry effects, the coefficient of GW is −0.016 (p < 0.01); after adding the variables of firm size and financial leverage, its negative effect is still significant (coefficient −0.011, p < 0.01), and Hypothesis H1 is proved. Additionally, enterprise size expansion (SIZE) and capital intensity (CAPI) improvement significantly promote profitability, while high debt (Lev) exacerbates financial risk. The results suggest that the negative effects of agribusinesses’ greenwashing behaviour are robust and partially transmitted through economies of scale and resource allocation paths. The GW of agricultural enterprises is not invariably positive. In instances where GW > 0, the ESG disclosure score of the enterprise exceeds its actual performance, thereby indicating severe greenwashing behaviour. In instances where GW < 0, the ESG disclosure score of the enterprise is lower than its actual performance, this phenomenon may be indicative of a strategic behaviour on the part of enterprises. That is to say, despite possessing robust environmental management capabilities, enterprises may engage in selective underreporting of their performance, a practice often referred to as ”brownwashing”. This behaviour can be attributed to a desire to circumvent potential scrutiny, the prospect of heightened compliance requirements in the future, or the risk of being accused of ”hypocrisy”. The following two situations are encompassed within the scope of this study: 1. Conservative disclosure—the enterprise underreports its environmental performance to avoid the risk of overcommitment (such as failing to meet future targets). 2. Excellent actual performance—the enterprise has strong environmental management capabilities but does not fully disclose to reduce public expectation pressure.

Table 4.
Base model regression.
5.4. Tests for Mediating Effects
The present study employs the three-step method of mediation effect to examine the mediating mechanism of green innovation (GI) between greenwashing behaviour (GW) and financial performance (ROA). The regression results of the mediation effect given in Table 5 demonstrate that greenwashing behaviour (GW) exerts a significantly negative direct impact on the financial performance of enterprises (ROA) (coefficient −0.011, p < 0.01) and significantly inhibits green innovation (GI) (coefficient −0.091, p < 0.05) (Model 2). Following the incorporation of the green innovation (GI) variable (Model 3), the negative impact of GW is observed to diminish, though it maintains a substantial level of significance (coefficient −0.010, p < 0.01). Concurrently, the positive effect of GI on ROA successfully surpasses the 5% significance threshold (coefficient 0.007, p < 0.05). The mediating effect of GI is 9.09%, indicating that greenwashing primarily exerts an indirect influence on performance by suppressing innovation. However, the direct effect (e.g., reputation loss) remains predominant. This finding is consistent with the conclusions of Testa et al. [15], that the financial penalties of greenwashing have both direct and indirect paths. This finding suggests that greenwashing behaviour has a detrimental effect on financial performance, both directly and indirectly. The latter effect is characterised by the suppression of green innovation, which in turn exacerbates the aforementioned negative impact on performance. The second hypothesis, termed H2, which postulated the mediating effect of green innovation, was corroborated. This finding lends further credence to the hypothesis that agricultural enterprises are subject to considerable environmental regulation pressure, as evidenced by the implementation of policies aimed at reducing fertiliser use. However, the clandestine management of non-point source pollution has been demonstrated to heighten the likelihood of greenwashing through selective disclosure. This can be illustrated by the tendency to exaggerate water-saving achievements and conceal excessive pesticide use [9]. Greenwashing behaviour leads enterprises to shift resources from green innovation (such as water-saving technology research and development) to short-term image maintenance (such as false environmental protection publicity), forming a “resource crowding-out effect” [36]. This misallocation of resources has been demonstrated to impede the capacity for technological accumulation, consequently diminishing production efficiency and market competitiveness. Furthermore, the low coefficient of GI (0.007) serves to emphasise the distinctiveness of the agricultural industry. 1. Long-cycle characteristics of agricultural innovation: green technology is a long-term investment, with a protracted period between research and development and the subsequent commercialisation of the technology; this is due to the fact that the financial returns on such investments are limited in the short term [57]. 2. Heterogeneity of patent quality: the economic value of green utility model patents (with a high proportion) is lower than that of invention patents, which in turn reduces the overall financial effect of GI [49]. Zhang et al. [43] found that the elasticity coefficient of Chinese agricultural green patents on ROA is 0.005–0.01, which is highly consistent with the 0.007 found in this study.

Table 5.
Results of the analysis of the mediating effects of corporate green innovation.
5.5. Robustness Tests
This analysis employs a two-way fixed effects model in order to control for unobservable factors of time and industry. Furthermore, it employs a one-period lag test in order to alleviate the reverse causality problem. To ensure the measurement accuracy of the explanatory variable (ROA) and avoid potential errors, this study adopts a variable substitution strategy in order to perform robustness tests. Specifically, return on equity (ROE) is used as a proxy for the explanatory variables, aiming to explore more deeply the specific impact of the greenwashing behaviour of listed companies in the agricultural industry on their financial performance. The results are shown in Table 6. It can be seen that GW and ROE are significantly negatively correlated at the 1% level, and the regression results of other variables are basically unchanged, indicating that the ”greenwashing” behaviour of enterprises has a negative impact on their financial performance. Moreover, due to the influence of greenwashing behaviour of the listed agricultural companies on financial performance, there is a certain lag effect, so this analysis lags one period of the explanatory variable ROA. The results are shown in the second column of Table 6: GW and ROA are significantly negatively correlated at the level of 1%. In summary, the negative correlation between greenwash behaviour and the financial performance of agribusiness passed the robustness test.

Table 6.
Robustness tests.
5.6. Analysis of the Heterogeneity of Corporate Property Rights
According to the regression results of property rights heterogeneity shown in Table 7, greenwashing behaviour (GW) has a significant inhibitory effect on financial performance (ROA) in non-SOEs (coefficient −0.014, p < 0.01), while the effect on SOEs is insignificant (coefficient 0.000). Green innovation (GI) shows a marginal positive effect on financial performance in non-SOEs (coefficient 0.008 *, p < 0.10), but fails the significance test in SOEs, suggesting that the path of non-SOEs to mitigate the negative effects of greenwash through green innovation is more obvious. The results validate the heterogeneity of the nature of property rights on the effect of greenwashing, which mainly stems from the fact that non-SOEs are under high competitive pressure and need to rely on green innovation to enhance their credibility and buffer the risk of greenwashing, whereas SOEs may be affected by policy support or resource buffers, and the transmission of greenwashing behaviour on their financial performance is weaker.

Table 7.
Analysis of property rights heterogeneity.
6. Research Findings and Recommendations
6.1. Conclusions of the Study
This study employs a logical framework of “theoretical construction–empirical testing–countermeasure application” and is divided into six parts: The introduction meticulously delineates the research background and theoretical lacuna pertinent to agricultural greenwashing, thereby substantiating the imperative for the present study. The literature review methodically categorises the contentious issues from three distinct perspectives: greenwashing behaviour, its correlation with financial performance, and the mediating effect of green innovation. It is noteworthy that extant research exhibits a paucity of attention to the agricultural sector. The theoretical analysis and hypothesis proffer two major hypotheses: The present study aims to explore the relationship between ”greenwashing” and financial performance, with a particular focus on the mediating role of ”green innovation”. To this end, a theoretical framework is proposed, encompassing the concepts of resource substitution and institutional legitimacy. The research design is based on the panel data of A-share agricultural-listed companies from 2012 to 2022, using the two-way fixed effect model and the three-step method of mediating effect to quantify the degree of greenwashing (ESG disclosure difference), green innovation (patent application), and financial performance (ROA). The empirical analysis verifies the hypotheses and reveals findings such as a higher sensitivity for non-state-owned enterprises and a 9.09% mediating proportion of green innovation. The robustness of the model is ensured through the implementation of variable replacement and lag tests, which empirically assess the impact of greenwashing behaviour on corporate financial performance and the mediating role of corporate green innovation. The primary conclusions that can be drawn from this analysis are as follows:
First, there is a negative relationship between greenwashing behaviour and corporate financial performance. The regression coefficient of greenwashing behaviour is significantly negative, indicating that the more serious the enterprise’s greenwash behaviour, the worse its financial performance. This result reveals the inhibitory effect of greenwashing behaviour on the economic performance of enterprises in agribusiness. It indicates that the false environmental protection propaganda of agribusinesses not only fails to enhance market trust, but also leads to the deterioration in financial performance. Heterogeneity analysis further reveals that the negative impact of greenwashing behaviour is particularly prominent in non-state-owned enterprises due to high competitive pressure and weak policy support, while the effect is insignificant in state-owned enterprises due to resource buffering.
Second, the mediation-effect test shows that greenwashing behaviour indirectly reduces financial performance by inhibiting green innovation. Specifically, greenwashing behaviour significantly reduces enterprises’ green innovation inputs, while insufficient green innovation further weakens financial performance. This suggests that green innovation is a key transmission path for greenwashing behaviour to affect financial performance. Although the short-term effect of green innovation on ROA is weak, its long-term value-creation ability cannot be ignored (Table 8).

Table 8.
The results of the research hypothesis testing.
6.2. Discussion
This study verified the mechanism through which the greenwashing behaviour of agricultural enterprises indirectly harms financial performance by suppressing green innovation. This finding is in alignment with the research on the greenwashing effect in the manufacturing industry (e.g., Testa et al. [15]; Walker & Wan [16]), at the behavioural logic level. However, due to the characteristics of the agricultural industry, it exhibits significant contextual differences.
6.2.1. The Amplification Effect of Environmental Information Asymmetry in Agriculture
The spatio-temporal heterogeneity of agricultural non-point source pollution, in conjunction with the technical challenges inherent in monitoring [21], facilitates the creation of a “green illusion” through strategic information disclosure. This phenomenon is characterised by an overestimation of the benefits of ecological water-saving technologies in environmental performance accounting, alongside an avoidance of disclosure concerning long-term environmental liabilities such as pesticide residues and soil degradation. Concerning technology adoption, a predilection for short-term visible investments in water-saving irrigation equipment is evident, accompanied by a diminution of systematic green technological innovations such as biological control. This particular information production mechanism has been demonstrated to have a detrimental effect on the allocation of agricultural capital, both to traditional production factors and to green technologies. Furthermore, it has been shown to have a negative effect on the carrying capacity of regional ecosystems, by virtue of the transfer of pollution externalities.
6.2.2. Differentiation of Innovation Incentives Under Heterogeneous Property Rights
The findings of the present study, when analysed using the framework of resource dependence theory, indicate that the property rights attribute significantly moderates the innovation inhibitory effect of greenwashing behaviour through the transmission paths of policy perception and market pressure. Non-state-owned agricultural enterprises, devoid of policy resource protection, are compelled to rely more heavily on green technology certification to gain market access [69]. The practice of greenwashing can be seen as a deliberate strategy that limits innovation resources, creating a cycle of “false compliance–innovation stagnation”. In contrast, although state-owned agricultural enterprises are subject to weaker policy constraints [56], their excessive reliance on fiscal subsidies leads to path dependence in technology adoption, manifested as an aversion to high-risk green technologies. This innovation differentiation under the property rights divide essentially reflects the tension between market-oriented reform and policy intervention in the agricultural sector.
6.2.3. The Paradox of the Applicability of Green Innovation in Agriculture
Empirical evidence indicates the presence of a substantial “time-lag trap” in the financial performance transformation of agricultural green innovation [43]. This phenomenon can be attributed to the dual constraints of agricultural technology commercialisation. Firstly, the objective laws of crop growth cycles and the time it takes for ecological effects to manifest lead to a significantly longer payback period for green technology investments compared to the industrial sector. Secondly, the imperfect agricultural patent value assessment system (such as the difficulty in obtaining evidence of infringement in breeding technology and the lack of monetisation standards for ecological benefits) results in a reduction in the market value of innovation achievements. This finding engages in a theoretical dialogue with Chen’s [55] assertion about the “non-neutrality” of green technology standards, revealing a unique “innovation paradox” in the agricultural sector. That is to say, although the adoption of green technologies can enhance environmental performance, it is difficult to convert this into a competitive advantage for enterprises due to deficiencies in the institutional environment.
6.3. Theoretical Significance and Practical Enlightenment
6.3.1. Theoretical Implications
- (1)
- Construct a three-dimensional transmission model of “greenwashing behaviour–green innovation–financial performance”
This study challenges the conventional binary analysis framework of “compliance greenwashing” and “substantive innovation” in the domain of environmental governance research. Notably, it is the first study to integrate the resource substitution theory [75] into the context of agricultural enterprises, proposing a novel “greenwashing–innovation–performance” chain transmission model. The model demonstrates that agricultural enterprises attain short-term regulatory legitimacy through strategic environmental information disclosure (e.g., selectively presenting the benefits of water-saving technologies and avoiding soil pollution data). However, this ultimately results in the diversion of resources from green technology research and development (e.g., biological control technologies and ecological cycle system development), consequently weakening the enterprise’s long-term competitiveness. This finding serves to further elaborate the theoretical explanation of the “greenwashing paradox” in the agricultural sector, that is, the negative correlation mechanism between environmental compliance improvement and green technology adoption.
- (2)
- The Dynamic Trap Effect of Deconstructing Institutional Legitimacy
Drawing upon Suchman’s [72] legitimacy theory, this study identifies the dynamic trap of “short-term legitimacy gains–long-term innovation costs” in agricultural greenwashing behaviour. Specifically, agricultural enterprises can temporarily alleviate regulatory pressure through false environmental commitments (such as exaggerating the coverage of organic certification), but this strategic behaviour will lead to: ① technological cognition solidification—the management forms a path dependence of “low-cost compliance is superior to high-risk innovation”; ② innovation resource siphoning—the budget for environmental information disclosure squeezes the investment in green technology research and development; and ③ market signal distortion—consumers’ trust in “green labels” declines, triggering adverse selection. This finding provides a new theoretical perspective for understanding the “unintended consequences” of institutional legitimacy in the agricultural sector.
6.3.2. Practical Insights
- (1)
- Micro-subjects: Capacity Building and Consciousness Reconstruction
At the employee level: build a “cognition–skill–behaviour” trinity green literacy cultivation system; through immersive training such as simulating pesticide pollution scenarios with virtual reality (VR) technology and conducting field ecological cycle experiments, enhance the embodied cognition of grassroots employees regarding agricultural non-point source pollution [53]. At the management level: establish a “dual-track” decision-making and evaluation mechanism, and incorporate green innovation investment into the core agenda of the strategic investment committee; by introducing “greenwashing behaviour identification indices” (such as the coefficient of environmental information disclosure authenticity and the lag index of green technology adoption), dynamically balance short-term image projects and long-term innovation layouts [25].
- (2)
- Organisational Mechanism: Technological Empowerment and Institutional Guarantee
ESG governance upgrade: build an “on-chain–off-chain” collaborative governance platform based on blockchain to achieve full lifecycle traceability of environmental data; automatically trigger environmental violation warnings through smart contracts and use zero-knowledge-proof technology to ensure the compatibility of business secrets and data transparency [77]. Innovative incentive restructuring: design a “green innovation risk compensation fund” to provide R&D subsidies and priority market access to enterprises adopting cutting-edge green technologies (such as gene-edited drought-resistant crops and microbial nitrogen fixation technology), alleviating the “valley of death” dilemma in the commercialisation of agricultural technologies.
- (3)
- Industry Ecosystem: Technology Diffusion and Cost Sharing
Platform-based collaboration: led by industry associations, build a “cloud platform for sharing green agricultural technologies”, integrating patent resources from universities, research institutes, and leading enterprises, and lowering the technology adoption threshold for small- and medium-sized enterprises through “modular technology packages + scenario-based solutions” [73]. Cluster-based transformation: pilot “green technology incubation alliances” in major grain-producing areas, and build an “R&D–pilot testing–promotion” collaborative innovation network through models such as technology licensing, cross-licensing of patents, and joint research and development.
- (4)
- Environmental Governance: Technology Integration and Participatory Monitoring
Upgrading the monitoring system: establish a three-dimensional “satellite remote sensing–unmanned aerial vehicle inspection–farmer self-reporting” environmental monitoring network, use multispectral images to identify hotspots of agricultural non-point source pollution, and store farmers’ environmental protection behaviour data through blockchain technology [74]. Incentive compatibility mechanism: implement a “green credit bank” system, quantify farmers’ participation in ecological compensation (such as returning straw to the field, soil testing and formula fertilisation) as tradable environmental credits, and connect them to the carbon-sink trading market to form an economic incentive loop.
6.4. Policy Recommendations
6.4.1. Building a Global Synergistic Governance System for Greenwashing
The issue of greenwashing in agriculture has become a significant impediment to global sustainable development, underscoring the need for the urgent establishment of an international collaborative regulatory mechanism. It is recommended that the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), in collaboration with the World Bank and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), assume the role of leading the formulation of the “International Guidelines for ESG Disclosure of Agricultural Enterprises”. These guidelines would serve to provide clear definitions of greenwashing behaviours, such as “false carbon neutrality claims” and “selective data disclosure”. Additionally, they would mandate the disclosure of core indicators, including carbon emission intensity and pesticide residue rate. The integration of blockchain technology is imperative to ensure the verification of data and the execution of third-party audits. The implementation of the EU’s Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) demonstrates that enhancing environmental data transparency can lead to a 23% reduction in greenwashing [9]. Furthermore, it is recommended that a “greenwashing blacklist” be established within the framework of the World Trade Organization (WTO), with the aim of imposing export restrictions and revoking certification qualifications for non-compliant enterprises, thereby establishing a cross-border joint punishment mechanism.
6.4.2. Optimise the Capital Allocation Mechanism for Green Technologies
The core driving force to break the deadlock of agricultural greenwashing is green technological innovation. It is recommended that the World Bank and the Green Climate Fund (GCF) collaborate to establish a “Special Fund for Agricultural Green Technologies”, with the objective of providing financial support for the development and adoption of low-carbon technologies, such as drip irrigation systems and microbial nitrogen-fixing fertilisers. The fund should be expected to offer interest-free loans or subsidies of up to 30% to enterprises that demonstrate a substantial investment in research and development, with a minimum ratio of 5% for such investments. At the policy level, a coordinated incentive mechanism of "taxation-carbon trading" should be established: value-added tax should be reduced or exempted for enterprises adopting green technologies, and carbon sink benefits should be included in financial statements; drawing on Brazil’s "Amazon Carbon Credit Program", enterprises should be allowed to obtain carbon quotas through rainforest protection projects. In terms of cooperation among industry, academia and research, multinational enterprises and universities should jointly build "green technology incubators". These incubators have the potential to reduce the commercialisation cycle of technologies by more than 30%.
6.4.3. Implement a Classified Guidance Strategy for Enterprise Governance
It is imperative that agricultural enterprises formulate governance plans that are tailored to the specific differences in property rights and scale. The following recommendations are intended for the benefit of non-state-owned enterprises. It is recommended that the ISO 14001 certification system be promoted, and that a “green reputation index” be established for the purpose of guiding investor decisions. The “organic certification” programme administered by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has been demonstrated to engender an increase in product premiums ranging from 15% to 30%, whilst concomitantly effectuating a 35% diminution in greenwashing behaviour among certified enterprises [15]. The following recommendations are intended for the benefit of state-owned enterprises. The integration of ESG indicators into the framework of executive compensation, alongside the establishment of “green innovation KPIs” (such as the annual completion rate of emission reduction targets), is imperative for effective environmental stewardship. Following the implementation of pilot projects in China’s central enterprises, which associated environmental performance with promotions, there was a 24% increase in green technology investment [31]. The following text is intended for the attention of proprietors of small- and medium-sized enterprises. It is recommended that financing thresholds be reduced through the implementation of “green microloans”, a concept based on the Grameen Bank model in Bangladesh. Furthermore, the establishment of regional technology promotion centres is advised, with the provision of complimentary training and equipment rental.
6.4.4. Improve the Public-Participation, Supervision, and Feedback System
The implementation of public supervision has been identified as a key mechanism in addressing the issue of greenwashing, serving as a social deterrent to prevent the dissemination of misleading information. The promotion of a unified “green agricultural product certification” label by international consumer organisations is recommended. The EU’s “Eco-label” initiative has demonstrated its capacity to augment the market share of compliant products by up to 12% [66]. Social media platforms have the potential to initiate a “Zero Greenwashing Challenge”, leveraging user-generated content to exert pressure and enhance the response speed of enterprises to rectification by 40% [64]. It is imperative that policymaking processes incorporate small-farm representatives. The “Farmers’ Environmental Parliament” in India has been instrumental in reducing pesticide use by 30% through democratic consultation [30]. Concurrently, the implementation of a “Farmer Green Skills Training Programme” is advocated, utilising field schools, virtual-reality simulations, and analogous methodologies to enhance ecological awareness.
Author Contributions
Both authors contributed to the study conception and design. Z.W. and X.T. designed this study. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Z.W. and X.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the project of Science and Technology Innovation Plan of Beijing Forestry University in 2021. Research on Behavioural Motivation and Guiding Mechanism of Forest Farmers under the Objective of High Quality Development of Forest Economy (grant no. 2021SRY10).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request. The data are not available to the public due to privacy protection.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank their schools and colleagues as well as those who funded the project. All support and assistance are sincerely appreciated.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Guo, R.; Tao, L.; Gao, P. The research on greenwashing brands’ rebuilding strategies and mechanism of brand trust after biochemical and other pollutions. Biotechnology 2014, 10, 3270–3279. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.H.; Lyon, T.P. Greenwash vs. brownwash: Exaggeration and undue modesty in corporate sustainability disclosure. Organ. Sci. 2015, 26, 705–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, C.; Toffel, M.W.; Zhou, Y. Scrutiny, norms, and selective disclosure: A global study of greenwashing. Organ. Sci. 2016, 27, 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollero, A.; Palazzo, M.; Siano, A.; Elving, W.J. Avoiding the greenwashing trap: Between CSR communication and stakeholder engagement. Int. J. Innov. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 10, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, D.; Santos, A.; Hurtado, A. The communication of the LCA: The need for guidelines to avoid greenwashing. Espacios 2015, 36, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wolniak, R.; Hąbek, P. Reporting process of corporate social responsibility and greenwashing. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConf. SGEM 2015, 5, 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.H.; Chen, Y.S. Managing green brand equity: The perspective of perceived risk theory. Qual. Quant. 2014, 48, 1753–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Cao, C.; Huang, S. The influence of greenwashing perception on green purchasing intentions: The mediating role of green word-of-mouth and moderating role of green concern. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, M.A.; Burbano, V.C. The drivers of greenwashing. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2011, 54, 64–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J. Are we doing the right thing? Leadership and prioritisation for public benefit. J. Corp. Citizsh. 2010, 37, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Greer, J.; Kenny, B. Greenwash: The Reality Behind Corporate Environmentalism; Apex Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- KPMG. Avoiding the Greenwash Peril: Best Practices for the Asset Management Sector. 2023. Available online: https://assets.kpmg.com/content/dam/kpmg/ie/pdf/2023/01/ie-getting-ahead-of-greenwashing.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Alves, I.M. Green Spin Everywhere: How Greenwashing Reveals the Limits of the CSR Paradigm. J. Glob. Change Gov. 2009, 2, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, F.; Aragon-Correa, J.A. Greenwashing in corporate environmentalism research and practice: The importance of what we say and do. Organ. Environ. 2014, 27, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, F.; Boiral, O.; Iraldo, F. Internalization of environmental practices and institutional complexity: Can stakeholders pressures encourage greenwashing? J. Bus. Ethics 2018, 147, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.; Wan, F. The harm of symbolic actions and green-washing: Corporate actions and communications on environmental performance and their financial implications. J. Bus. Ethics 2012, 109, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, F.; Iraldo, F.; Vaccari, A.; Ferrari, E. Why eco-labels can be effective marketing tools: Evidence from a study on Italian consumers. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2015, 24, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, T.P.; Montgomery, A.W. The means and end of greenwash. Organ. Environ. 2015, 28, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jin, X.; Zhao, R.; Han, B.; Zhou, Y.; Tittonell, P. Assessing uncertainties and discrepancies in agricultural greenhouse gas emissions estimation in China: A comprehensive review. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Bai, W.; Deng, X. Factors analysis for the decoupling of grain production and carbon emissions from crop planting in China: A discussion on the regulating effects of planting scale and technological progress. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 103, 107249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, A.; Wang, D. Evaluation of agricultural and rural pollution under environmental measures in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yin, G.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Gao, L. Structural Changes to China’s Agricultural Business Entities System Under the Perspective of Competitive Evolution. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Huang, J.; Xu, Z.; Rozelle, S. Policy support and emerging farmer professional cooperatives in rural China. China Econ. Rev. 2010, 21, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Anderson, H.; Chi, J.; Liao, J. Going Green or Greenwashing? Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment of Chinese Air Quality Monitoring Network. 2024. Available online: https://acfr.aut.ac.nz/__data/assets/pdf_file/0008/926009/Going-green-or-greenwashing-Evidence-from-a-quasi-natural-experiment-of-Chinese-Air-Quality-Monitoring-Network.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Hojnik, J.; Ruzzier, M. The driving forces of process eco-innovation and its impact on performance: Insights from Slovenia. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, J. Influence of Greenwashing Strategy on Pricing: A Game-Theoretical Model for Quality Heterogeneous Enterprises. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Green Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 336–343. [Google Scholar]
- Hojnik, J.; Ruzzier, M. What drives eco-innovation? A review of an emerging literature. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2016, 19, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunila, M. Understanding innovation performance measurement in SMEs. Meas. Bus. Excell. 2017, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Bai, D.; Chen, X. Can crude oil futures market volatility motivate peer firms in competing ESG performance? An exploration of Shanghai International Energy Exchange. Energy Econ. 2024, 129, 107240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Kong, Q. Green energy transition and sustainable development of energy firms: An assessment of renewable energy policy. Energy Econ. 2022, 111, 106060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W. “Environmental disclosure greenwashing” and corporate value: The premium effect and premium devalue of environmental information. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2024, 31, 2424–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fu, Q.; Chang, C.P. What are the shocks of climate change on clean energy investment: A diversified exploration. Energy Econ. 2021, 95, 105136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D. Does green finance really inhibit extreme hypocritical ESG risk? A greenwashing perspective exploration. Energy Econ. 2023, 121, 106688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ma, Y.; Feng, G.F.; Chang, C.P. Does environmental governance mitigate the detriment of greenwashing on innovation in China? Pac.-Basin Financ. J. 2024, 86, 102450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, M.; Wu, M.; Wang, A. Voluntary environmental regulations, greenwashing and green innovation: Empirical study of China’s ISO14001 certification. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 102, 107224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. From green-washing to innovation-washing: Environmental information intangibility and corporate green innovation in China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 93, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tang, C.; Liu, Y.; Ge, P. Greening or greenwashing? Corporate green bonds and stock pricing efficiency in China. Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 2025, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liang, M.; Dabić, M.; Lin, W. “Chasing Grade” or “Driving Innovation”? Social Responsibility Grades of Heavily Polluting Enterprises and Exploratory Innovation. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 11166–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuck, D.; Matthes, J.; Naderer, B. Misleading consumers with green advertising? An affect–reason–involvement account of greenwashing effects in environmental advertising. J. Advert. 2018, 472, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baah, C.; Opoku-Agyeman, D.; Acquah, I.S.K.; Agyabeng-Mensah, Y.; Afum, E.; Faibil, D.; Abdoulaye, F.A.M. Examining the correlations between stakeholder pressures, green production practices, firm reputation, environmental and financial performance: Evidence from manufacturing SMEs. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przychodzen, W.; Gómez-Bezares, F.; Przychodzen, J. Green information technologies practices and financial performance–the empirical evidence from German publicly traded companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, L. Promoting or inhibiting? The impact of environmental regulation on corporate financial performance—An empirical analysis based on China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Rong, Z.; Ji, Q. Green innovation and firm performance: Evidence from listed companies in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 144, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyabeng-Mensah, Y.; Afum, E.; Ahenkorah, E. Exploring financial performance and green logistics management practices: Examining the mediating influences of market, environmental and social performances. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ali, S.; Shahzad, U.; Cui, L. Exploring the role of green innovation and investment in energy for environmental quality: An empirical appraisal from provincial data of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harel, R.; Schwartz, D.; Kaufmann, D. Organizational culture processes for promoting innovation in small businesses. EuroMed J. Bus. 2021, 16, 218–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Ceballos, J.; Aragón-Correa, J.A.; Ortiz-de-Mandojana, N.; Rueda-Manzanares, A. The effect of internal barriers on the connection between stakeholder integration and proactive environmental strategies. J. Bus. Ethics 2012, 107, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelino, F.; Caputo, M.; Cammarano, A.; Lamberti, E. Inbound and outbound open innovation: Organization and performances. J. Technol. Manag. Innov. 2014, 9, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Fu, W.; Guo, P.; Zhang, Z.; Khan, F. Unpacking greenwashing: The impact of environmental attitude, proactive strategies, and network embeddedness on corporate environmental performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivimaa, P. Integrating environment for innovation: Experiences from product development in paper and packaging. Organ. Environ. 2008, 21, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, T.J.; Nordberg, P. The evolution of organizations and natural environment discourse: Some critical remarks. Organ. Environ. 2006, 19, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.J.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhu, T.; Cui, J.J.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhu, T.; Gong, W.J.; Zhou, H.H.; Liu, Z.Q.; Yin, J.Y. Gene-gene and gene-environment interactions influence platinum-based chemotherapy response and toxicity in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, A.; Salehzadeh, R.; Panahi, R.; Abolghasemian, S. Multiple pathways linking environmental knowledge and awareness to employees’ green behavior. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2018, 18, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Burgos-Jiménez, J.; Vázquez-Brust, D.; Plaza-Úbeda, J.A.; Dijkshoorn, J. Environmental protection and financial performance: An empirical analysis in Wales. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2013, 33, 981–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S. The positive effect of green intellectual capital on competitive advantages of firms. J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 77, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chang, B. The Impact and Mechanisms of State-Owned Shareholding on Greenwashing Behaviors in Chinese A-Share Private Enterprises. Sustainability 2025, 17, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Shao, S. Impact of green innovation on carbon reduction in China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seele, P.; Gatti, L. Greenwashing revisited: In search of a typology and accusation—Based definition incorporating legitimacy strategies. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2017, 26, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shu, X.; Liao, G. Does corporate greenwashing affect investors’ decisions? Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 67, 105877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X. How the market values greenwashing? Evidence from China. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 128, 547–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.; O’sullivan, P. Corporate social responsibility: Internet social and environmental reporting by banks. Meditari Account. Res. 2017, 25, 414–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, K.; Ji, F. The effect of digitalization transformation on greenwashing of Chinese listed companies: An analysis from the dual perspectives of resource-based view and legitimacy. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1179419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.T.; Suh, I. Understanding the effects of Environment, Social, and Governance conduct on financial performance: Arguments for a process and integrated modelling approach. Sustain. Technol. Entrep. 2022, 11, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.L.; Montgomery, A.W.; Ozbilir, T. Employees’ response to corporate greenwashing. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 32, 4015–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, Y.; Mazloomi, H.; Berrone, P. Understanding the impact of symbolic and substantive environmental actions on organizational reputation. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2021, 92, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akturan, U. How does greenwashing affect green branding equity and purchase intention? An empirical research. Mark. Intell. Plan. 2018, 36, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrone, P.; Fosfuri, A.; Gelabert, L. Does greenwashing pay off? Understanding the relationship between environmental actions and environmental legitimacy. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 144, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, B.; Khalil, K.; Ahmad, S.; Ahmed, F.; Ullah, M.; Usama, H.A. Impact of Corporate Governance on Green Innovation: Evidence from Pakistan. Russ. Law J. 2023, 11, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, S. The effects of corporate governance uncertainty on state-owned enterprises’ green innovation in China: Perspective from the participation of non-state-owned shareholders. Energy Econ. 2022, 115, 106402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Luo, F.; Bu, Y. Green innovation and corporate financial performance: Insights from operating risks. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 456, 142353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, J.; Shinwari, R.; Bouri, E. Do green finance and green innovation affect corporate credit rating performance? Evidence from machine learning approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 360, 121212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchman, M.C. Managing legitimacy: Strategic and institutional approaches. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1995, 20, 571–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daroshka, V.; Aleksandrov, I.; Fedorova, M.; Chekhovskikh, I.; Ol, E.; Trushkin, V. Agriculture and ESG transformation: Domestic and foreign experience of green agribusiness finance. Int. Sci. Conf. Agric. Mach. Ind. Interagromash 2022, 575, 2357–2368. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, G.; Shen, Y.; Dong, C. The Impact of Green Finance on Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution: Analysis of the Role of Environmental Regulation and Rural Land Transfer. Land 2024, 13, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechezleprêtre, A.; Sato, M. The impacts of environmental regulations on competitiveness. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y. Can companies get more government subsidies through improving their ESG performance? Empirical evidence from China. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.P.; van Luu, B.; Chen, C.H. Greenwashing in environmental, social and governance disclosures. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2020, 52, 101192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Francoeur, C.; Brammer, S. What drives and curbs brownwashing? Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 31, 2518–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).