Bibliographic Analysis of Scientific Research on Downy Mildew (Pseudoperonospora humuli) in Hop (Humulus lupulus L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
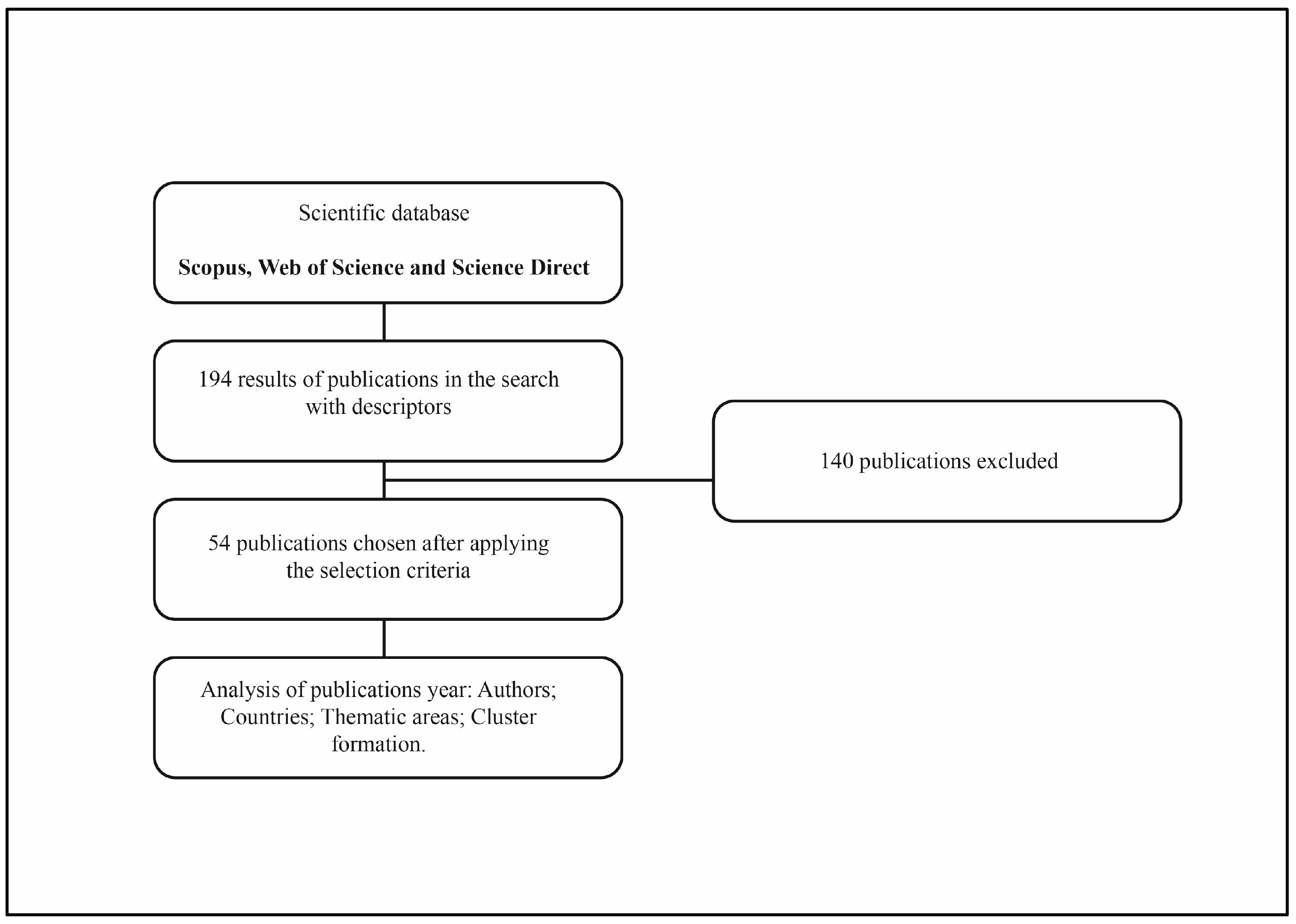
2. Material and Methods
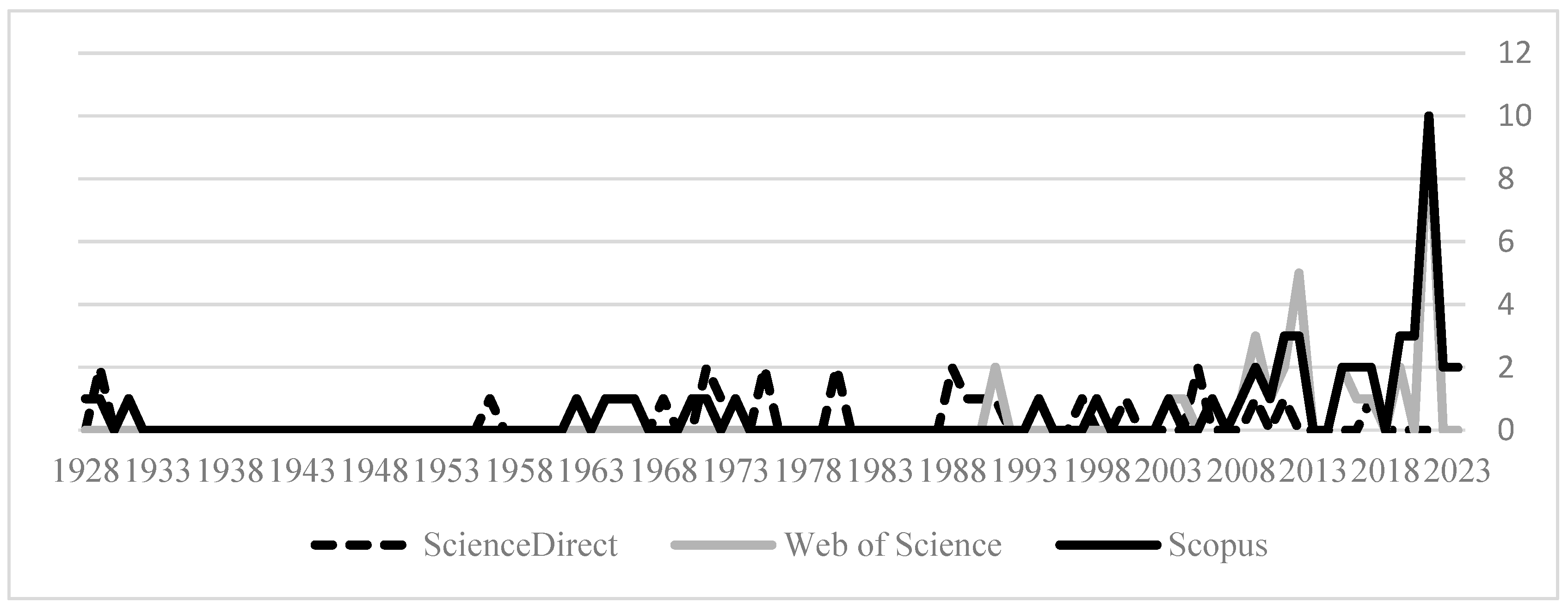
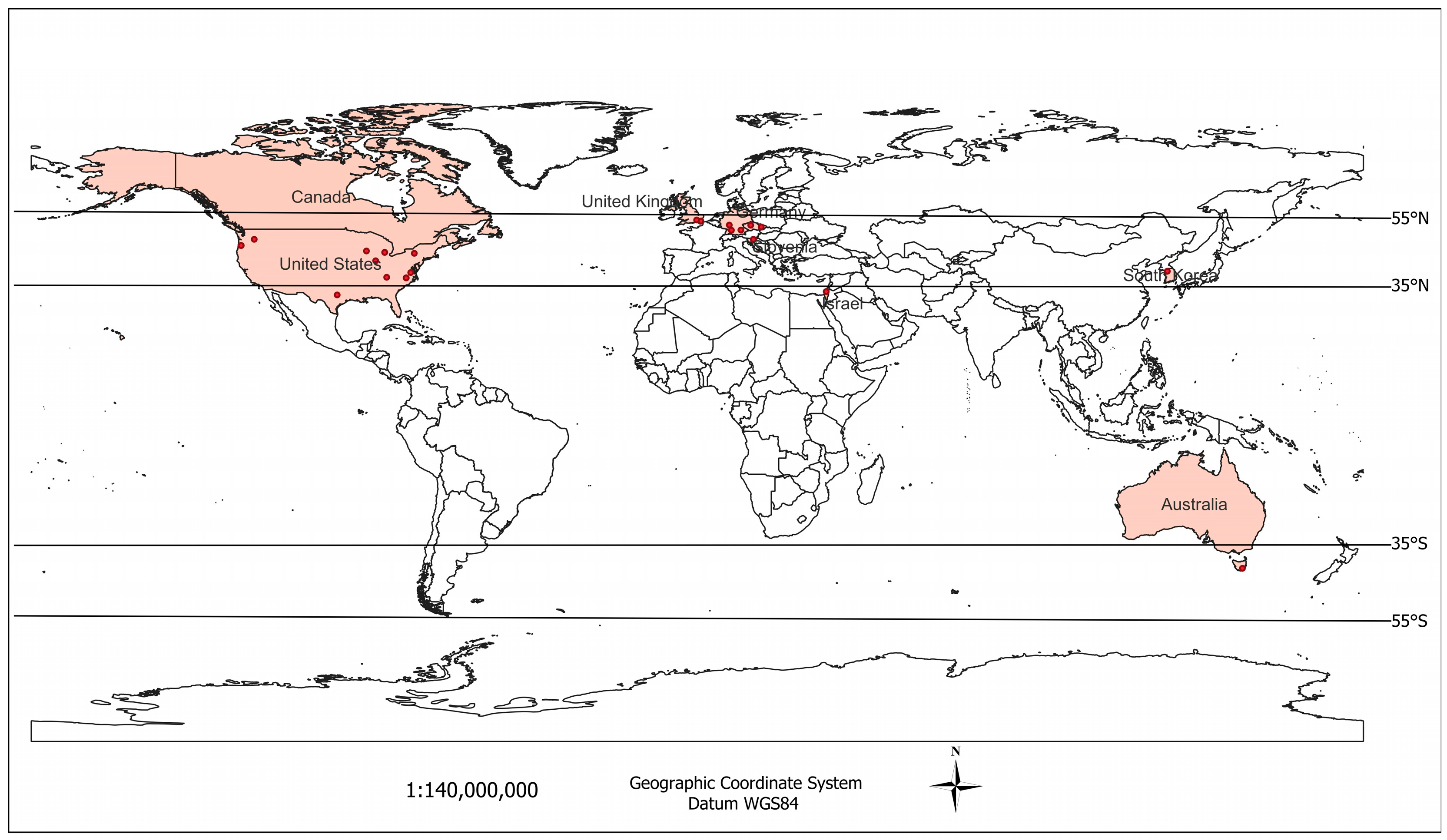
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Graphic Analysis of Keywords Using VOSviewer Software
3.2. Graphic Analysis of Keywords Using IRAMUTEQ Software
4. Final Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rossini, F.; Virga, G.; Loreti, P.; Iacuzzi, N.; Ruggeri, R.; Provenzano, M.E. Hops (Humulus lupulus L.) as a Novel Multipurpose Crop for the Mediterranean Region of Europe: Challenges and Opportunities of Their Cultivation. Agriculture 2021, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrombek, J.M.; Faguerazzi, M.M.; de Cássio Pierezan, H.; Rufato, L.; Sato, A.J.; da Silva Ricce, W.; Marques, V.V.; Leles, N.R.; Roberto, S.R. Hop: An Emerging Crop in Subtropical Areas in Brazil. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpanga, I.; Schalau, J.; Mpanga, I.K. Hop Production in Northern Arizona: Opportunity and Challenges for Small-scale Growers? Fertilization Strategies to Improve the Plant Growth-Promoting Potential of Microbial BE’s View Project Needs Assessment for Commercial Horticulture and Small Acreage Agriculture in Northern Arizona View 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341031002 (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Purayannur, S.; Miles, T.D.; Gent, D.H.; Pigg, S.; Quesada-Ocampo, L.M. Hop downy mildew caused by Pseudoperonospora humuli: A diagnostic guide. Plant Health Prog. 2020, 21, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizotte, E.; Sirrine, R.; Miles, T.; Chaudhari, S. Michigan Hop Management Guide 2022 [Internet]. 2022. Available online: www.hops.msu.edu (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Wyenandt, C.A.; Simon, J.E.; Pyne, R.M.; Homa, K.; McGrath, M.T.; Zhang, S.; Raid, R.N.; Ma, L.J.; Wick, R.; Guo, L.; et al. Basil Downy Mildew (Peronospora belbahrii): Discoveries and Challenges Relative to Its Control. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purayannur, S.; Gent, D.H.; Miles, T.D.; Radišek, S.; Quesada-Ocampo, L.M. The hop downy mildew pathogen Pseudoperonospora humuli. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, N.; Lee, J. Changing landscape of emergency management research: A systematic review with bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 49, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlou, S. L’analyse lexicale. Variances 1994, 3, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2018. Available online: https://www.Rproject.org (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Camargo, B.V.; Justo, A.M. IRAMUTEQ: Um software gratuito para análise de dados textuais. Temas Psicol. 2013, 21, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, P.; Ratinaud, P. Les primaires socialistes pour l’élection présidentielle française. In L’analyse de Similitude Appliquée Aux Corpus Textuels; LASLA-SESLA: Liège, Belgium, 2012; pp. 687–699. [Google Scholar]
- Runge, F.; Thines, M.; Wolfgang, J. Reevaluation of host specificity of the closely related species Pseudoperonospora humuli and P. cubensis. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, S.G.; Ramon, M.L.; Burkhardt, A.K.; Bello Rodriguez, J.C.; Adair, N.; Gent, D.H.; Hausbeck, M.K.; Quesada-Ocampo, L.M.; Martin, F.N. A Multiplex taqman qPCR assay for detection and quantification of clade 1 and clade2 isolates of Pseudoperonospora cubensis and Pseudoperonospora humuli. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 3154–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, J.C.; Sakalidis, M.L.; Perla, D.E.; Hausbeck, M.K. Detection of airborne sporangia of Pseudoperonospora cubensis and P. humuli in Michigan using burkard spore traps coupled to quantitative PCR. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, Y.; Eyal, H. Effects of light during infection on the incidence of downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora cubensis) on cucumbers. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1980, 17, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Salmon, E.S.; Ware, W.M. Inoculation experiments with the downy mildews of the hop and nettle (Pseudoperonospora humuli) (Miy. et Taka.) Wils. and P. urticae (lib.) Salmon et Ware. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1928, 15, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, W.M. Experiments on the Production of Diseased Shoots by the Hop Downy Mildew, Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. et Takah.), Wils. Ann. Bot. 1929, 43, 683–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, E.S.; Ware, W.M. The downy mildew of the hop in 1930. J. Inst. Brew. 1930, 37, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley-Smith, J.R. Overwintering of hop downy mildew Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. and Tak.) Wilson. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1962, 50, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley-Smith, J.R. Persistence and identification of downy mildew Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. and Tak.) Wilson in hop rootstocks. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1964, 53, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley-Smith, J.R. Infection of hop rootstocks by downy mildew Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. & Tak.) Wilson and its control by early-season dusts. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1965, 56, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Coley-Smith, J.R. Early-season control of hop downy mildew, Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. and Tak.) Wilson, with streptomycin and protectant fungicides in severely infected plantings. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1966, 57, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, D.J. Infection periods in relation to the natural development of hop downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora humuli). Ann. Appl. Biol. 1970, 66, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, D.J.; Thomas, G. The influence of stomatal opening on the infection of hop leaves by Pseudoperonospora humuli. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1971, 1, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, D.J. Quantitative relationships between infection by the hop downy mildew pathogen, Pseudoperonospora humuli, and weather and inoculum factors. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1973, 73, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, D.J.; Thomas, G.G. Factors affecting zoospore responses towards stomata in hop downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora humuli) including some comparisons with grapevine downy mildew (Plasmopara viticola). Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1973, 3, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinar, M.; Žolnir, M. Epidemic related decision model for control of downy mildew in hop (Pseudoperonospora humuli Miy. et Tak.), based on critical amount of spores. Bodenkultur 1994, 45, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Pares, R.; Greenwood, A. Ultrastructure of the Host-Parasite Relationships of Pseudoperonospora humuli on Hops. Aust. J. Bot. 1977, 25, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, D.; Kac, M.; Dolinar, M.; Zolnir, M.; Kralj, S. Marker-assisted hop (Humulus lupulus L.) breeding. Monatsschrift Brauwiss. 1998, 51, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Pethybridge, S.J.; Nelson, M.E.; Wilson, C.R. Forecasting climate suitability of Australian hop-growing regions for establishment of hop powdery and downy mildews. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2003, 32, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Hong, S.B.; Shin, H.D. A re-consideration of Pseudoperonospora cubensis and P. humuli based on molecular and morphological data. Mycol. Res. 2005, 109, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwekendiek, A.; Horlemann, C.; Spring, O.; Stanke, M.; Höhnle, M.; Weber, G. Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Transformation with Stilbene Synthase for Increasing Resistance against Fungal Pathogens. Acta Hortic 2005, 668, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chee, H.Y.; Nelson, M.E.; Grove, G.G.; Eastwell, K.C.; Kenny, S.T.; Klein, R.E. Population biology of Pseudoperonospora humuli in Oregon and Washington. Plant Dis. 2006, 90, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, D.H.; Nelson, M.E.; Grove, G.G. Persistence of phenylamide insensitivity in Pseudoperonospora humuli. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gent, D.H.; Ocamb, C.M. Predicting Infection Risk of Hop by Pseudoperonspora humuli. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gent, D.H.; Nelson, M.E.; Farnsworth, J.L.; Grove, G.G. PCR detection of Pseudoperonospora humuli in air samples from hop yards. Plant Pathol. 2009, 58, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, D.H.; Ocamb, C.M.; Farnsworth, J.L. Forecasting and management of hop downy mildew. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.N.; Ocamb, C.M.; Grünwald, N.J.; Mancino, L.E.; Gent, D.H. Genetic and pathogenic relatedness of Pseudoperonospora cubensis and P. humuli. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čerenak, A.; Radišek, S.; Luskar, M.O.; Košir, I.J. Registration of ‘Dana’-A Bittering Hop Cultivar with a Pleasant Hoppy Aroma. J. Plant Regist. 2012, 6, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, D.H.; Farnsworth, J.L.; Johnson, D.A. Spatial analysis and incidence-density relationships for downy mildew on hop. Plant Pathol. 2012, 61, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, D.H.; Nelson, M.E.; Grove, G.G.; Mahaffee, W.F.; Turechek, W.W.; Woods, J.L. Association of Spring Pruning Practices with Severity of Powdery Mildew and Downy mildew on Hop. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Gent, D.H.; Twomey, M.C.; Wolfenbarger, S.N.; Woods, J.L. Pre- and postinfection activity of fungicides in control of hop downy mildew. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, J.A.; Gent, D.H.; Twomey, M.C.; Townsend, M.S.; Pitra, N.J.; Matthews, P.D. Precision QTL mapping of downy mildew resistance in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Euphytica 2015, 202, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, C.F.; Adair, N.L.; Gent, D.H.; McGrath, M.T.; Smart, C.D. Pseudoperonospora cubensis and P. humuli detection using species-specific probes and high definition melt curve analysis. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2015, 37, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, J.A.; Gent, D.H.; Twomey, M.C.; Townsend, M.S.; Pitra, N.J.; Matthews, P.D. Genotyping-by-sequencing of a bi-parental mapping population segregating for downy mildew resistance in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Euphytica 2016, 208, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.L.; Gent, D.H. Susceptibility of hop cultivars to downy mildew: Associations with chemical characteristics and region of origin. Plant Health Prog. 2016, 17, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, D.H.; Cohen, Y.; Runge, F. Homothallism in Pseudoperonospora humuli. Plant Pathol. 2017, 66, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, D.H.; Adair, N.; Knaus, B.J.; Grünwald, N.J. Genotyping-by-Sequencing Reveals Fine-Scale Differentiation in Populations of Pseudoperonospora humuli. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, M.E.; Gevens, A.J. Investigating phenylamide insensitivity in Wisconsin populations of Pseudoperonospora humuli. Plant Health Prog. 2019, 20, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Góngora-Castillo, E.; Bowman, M.J.; Childs, K.L.; Gent, D.H.; Martin, F.N.; Quesada-Ocampo, L.M. Genome sequencing and transcriptome analysis of the hop downy mildew pathogen Pseudoperonospora humuli reveal species-specific genes for molecular detection. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dušek, M.; Vostřel, J.; Jandovská, V.; Mikyška, A. Post-harvest recognition of various fungicide treatments for downy mildew of hops using comprehensive pesticide residue monitoring. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 2020, 69, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, D.H.; Block, M.; Claassen, B.J. High levels of insensitivity to phosphonate fungicides in Pseudoperonospora humuli. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purayannur, S.; Cano, L.M.; Bowman, M.J.; Childs, K.L.; Gent, D.H.; Quesada-Ocampo, L.M. The Effector Repertoire of the Hop Downy Mildew Pathogen Pseudoperonospora humuli. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 538988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feiner, A.; Pitra, N.; Matthews, P.; Pillen, K.; Wessjohann, L.A.; Riewe, D. Downy mildew resistance is genetically mediated by prophylactic production of phenylpropanoids in hop. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, D.S.; Hausbeck, M.K. Susceptibility of hop cultivars and rootstock to downy mildew caused by Pseudoperonospora humuli. HortScience 2021, 56, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitner, M.; Runge, F.; Lebeda, A.; Vaculná, L.; Sedláková, B.; Thines, M. Pseudoperonospora humuli might be an introduced species in Central Europe with low genetic diversity but high distribution potential. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 159, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, M.; Hadziabdic, D.; Trigiano, R.N.; Boggess, S.L.; Kanetis, L.; Wadl, P.A.; Ojiambo, P.S.; Cubeta, M.A.; Spring, O.; Thines, M.; et al. ‘Jumping Jack’: Genomic Microsatellites Underscore the Distinctiveness of Closely Related Pseudoperonospora cubensis and Pseudoperonospora humuli and Provide New Insights Into Their Evolutionary Past. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 686759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutto, L.K.; Xu, Y.; Ren, S.; Scoggins, H.; Davis, J. Results from hop cultivar trials in mid-atlantic United States. Horttechnology 2021, 31, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, D.S.; Miles, T.D.; Hausbeck, M.K. Fungicide efficacy against Pseudoperonospora humuli and point mutations linked to carboxylic acid amide resistance in Michigan. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, D.S.; Miles, T.D.; Byrne, J.M.; Hausbeck, M.K. Optimizing Molecular Detection for the Hop Downy Mildew Pathogen Pseudoperonospora humuli in Plant Tissue. Phytopathology 2022, 112, 2426–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procházka, P.; Řehoř, J.; Vostřel, J.; Fraňková, A. Use of botanicals to protect early stage growth of hop plants against Pseudoperonospora humuli. Crop Prot. 2022, 157, 105978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatoye, M.O.; Wiseman, M.; Gent, D.H.; Henning, J.A.; Altendorf, K.R. Genetic characterization of downy mildew resistance from the hop (Humulus lupulus L.) line USDA 64035M. Crop Sci. 2023, 63, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, M.; Somalraju, A.; Ghose, K.; McCallum, J.; Mills, A.; Fillmore, S.; Fofana, B. Diversity in genetic and downy mildew resistance among wild and mutagenized hops as revealed by single nucleotide polymorphisms and disease rating. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2023, 103, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagherazzi, M.M.; Rufato, L. Produzir lúpulo no Brasil, utopia ou realidade? Rev. Agron. Bras. 2018, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsaga, R.F. Desenvolvimento de híbridos de lúpulo adaptados às condições tropicais. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- de Jesus Guimarães, J.; de Sousa, F.G.G.; Román, R.M.S.; Dal Pai, A.; Rodrigues, S.A.; Sarnighausen, V.C.R. “Effect of irrigation water pH on the agronomic development of hops in protected cultivation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 253, 106924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Database | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Scopus | (TITLE-ABS-KEY (hop) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (downy AND mildew) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (Pseudoperonospora AND humuli) AND PUBYEAR < 2023 AND PUBYEAR < 2023) |
| Web of Science | hop (Topic) and downy mildew (Topic) and Pseudoperonospora humuli (Topic) |
| ScienceDirect | hop AND downy AND mildew AND Pseudoperonospora humuli |
| Author | Title of the Article | Journal | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Web of Science | |||
| 1 | [14] | Reevaluation of Host Specificity of the Closely Related Species Pseudoperonospora humuli and P. cubensis | Plant disease |
| 2 | [15] | A Multiplex TaqMan qPCR Assay for Detection and Quantification of Clade 1 and Clade 2 Isolates of Pseudoperonospora cubensis and Pseudoperonospora humuli | |
| 3 | [16] | Detection of Airborne Sporangia of Pseudoperonospora cubensis and P. humuli in Michigan Using Burkard Spore Traps Coupled to Quantitative PCR | |
| ScienceDirect | |||
| 1 | [17] | Effects of light during infection on the incidence of downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora cubensis) on cucumbers | Physiological Plant Pathology |
| Scopus | |||
| 1 | [18] | Inoculation experiments with the downy mildews of the Hop and Nettle (Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. et Taka.) Wils. and P. Urticare (Lib.) Salmon et Ware) | Annals of Botany |
| 2 | [19] | Experiments on the Production of Diseased Shoots by the Hop Downy Mildew, Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. et Takah.), Wils. | |
| 3 | [20] | The downy mildew of the hop in 1930. | |
| 4 | [21] | Overwintering of hop downy mildew Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. and Tak.) Wilson | Annals of Applied Biology |
| 5 | [22] | Persistence and identification of downy mildew Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. and Tak.) Wilson in hop rootstocks | |
| 6 | [23] | Infection of hop rootstocks by downy mildew Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. & Tak.) Wilson and its control by early-season dusts | |
| 7 | [24] | Early -season control of hop downy mildew, Pseudoperonospora humuli (Miy. and Tak.) Wilson, with streptomycin and protectant fungicides in severely infected plantings | |
| 8 | [25] | Infection periods in relation to the natural development of hop downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora humuli) | |
| 9 | [26] | The influence of stomatal opening on the infection of hop leaves by Pseudoperonospora humuli | Physiological Plant Pathology |
| 10 | [27] | Quantitative relationships between infection by the hop downy mildew pathogen, Pseudoperonospora humuli, and weather and inoculum factors | Annals of Applied Biology |
| 11 | [28] | Factors affecting zoospore responses towards stomata in hop downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora humuli) including some comparisons with grapevine downy mildew (Plasmopara viticola) | Physiological Plant Pathology |
| 12 | [29] | Epidemic related decision model for control of downy mildew in hop (Pseudoperonospora humuli Miy. et Tak.), based on critical amount of spores | Invasive Species Compendium |
| 13 | [30] | Ultrastructure of the Host-Parasite Relationships of Pseudoperonospora humuli on Hops | Australian Journal of botany |
| 14 | [31] | Marker-assisted hop (Humulus lupulus L.) breeding | Monatsschrift fur Brauwissenschaft |
| 15 | [32] | Forecasting climate suitability of Australian hop-growing regions for establishment of hop powdery and downy mildews | Australasian Plant Pathology |
| 16 | [33] | A re-consideration of Pseudoperonospora cubensis and P. humuli based on molecular and morphological data | The British Mycological Society |
| 17 | [34] | Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Transformation with Stilbene Synthase for Increasing Resistance against Fungal Pathogens | Acta Horticulturae |
| 18 | [35] | Population Biology of Pseudoperonospora humuli in Oregon and Washington | The American Phytopathological Society |
| 19 | [36] | Persistence of Phenylamide Insensitivity in Pseudoperonospora humuli | Plant Disease |
| 20 | [37] | Predicting Infection Risk of Hop by Pseudoperonspora humuli | The American Phytopathological Society |
| 21 | [38] | PCR detection of Pseudoperonospora humuli in air samples from hop yards | Plant Pathology |
| 22 | [39] | Forecasting and Management of Hop Downy Mildew | Plant Disease |
| 23 | [40] | Genetic and Pathogenic Relatedness of Pseudoperonospora cubensis and P. humuli | The American Phytopathological Society |
| 24 | [41] | Registration of ‘Dana’—A Bittering Hop Cultivar with a Pleasant Hoppy Aroma | Journal of Plant Registrations |
| 25 | [42] | Spatial analysis and incidence–density relationships for downy mildew on hop | Plant Pathology |
| 26 | [43] | Association of Spring Pruning Practices with Severity of Powdery Mildew and Downy Mildew on Hop | The American Phytopathological Society |
| 27 | [44] | Pre-and postinfection activity of fungicides in control of hop downy mildew | Plant Disease |
| 28 | [45] | Precision QTL mapping of downy mildew resistance in hop (Humulus lupulus L.) | Euphytica |
| 29 | [46] | Pseudoperonospora cubensis and P. humuli detection using species-specific probes and high-definition melt curve analysis | Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology |
| 30 | [47] | Genotyping-by-sequencing of a bi-parental mapping population segregating for downy mildew resistance in hop (Humulus lupulus L.) | Euphytica |
| 31 | [48] | Susceptibility of Hop Cultivars to Downy Mildew: Associations with Chemical Characteristics and Region of Origin | Plant Health Progress |
| 32 | [49] | Homothallism in Pseudoperonospora humuli | Plant Pathology |
| 33 | [50] | Genotyping-by-Sequencing Reveals Fine-Scale Differentiation in Populations of Pseudoperonospora humuli | Phytopathology |
| 34 | [51] | Investigating Phenylamide Insensitivity in Wisconsin Populations of Pseudoperonospora humuli | Plant Health Progress |
| 35 | [52] | Genome sequencing and transcriptome analysis of the hop downy mildew pathogen Pseudoperonospora humuli reveal species-specific genes for molecular detection | Phytopathology |
| 36 | [53] | Post-harvest recognition of various fungicide treatments for downy mildew of hops using comprehensive pesticide residue monitoring | International Journal of Pest Management |
| 37 | [54] | High Levels of Insensitivity to Phosphonate Fungicides in Pseudoperonospora humuli | Plant Disease |
| 38 | [55] | The Effector Repertoire of the Hop Downy Mildew Pathogen Pseudoperonospora humuli | Frontiers Genetic |
| 39 | [4] | Hop Downy Mildew Caused by Pseudoperonospora humuli: A Diagnostic Guide | Plant Health Progress |
| 40 | [56] | Downy mildew resistance is genetically mediated by prophylactic production of phenylpropanoids in hop | Plant, Cell & Environment |
| 41 | [57] | Susceptibility of Hop Cultivars and Rootstock to Downy Mildew Caused by Pseudoperonospora humuli | HortScience |
| 42 | [58] | Pseudoperonospora humuli might be an introduced species in Central Europe with low genetic diversity but high distribution potential | Jornal Plant Pathology |
| 43 | [59] | “Jumping Jack”: Genomic Microsatellites Underscore the Distinctiveness of Closely Related Pseudoperonospora cubensis and Pseudoperonospora humuli and provide new insights into their evolutionary past | Frontiers Microbiology |
| 44 | [7] | The hop downy mildew pathogen Pseudoperonospora humuli | Wiley Molecular Plant Pathology |
| 45 | [60] | Results from Hop Cultivar Trials in Mid-Atlantic United States | HortTechnology |
| 46 | [61] | Fungicide efficacy against Pseudoperonospora humuli and point-mutations linked to carboxylic acid amide (CAA) resistance in Michigan | Plant Disease |
| 47 | [62] | Optimizing Molecular Detection for the Hop Downy Mildew Pathogen Pseudoperonospora humuli in Plant Tissue | Phytopathology |
| 48 | [63] | Use of botanicals to protect early stage growth of hop plants against Pseudoperonospora humuli | Crop Protection |
| 49 | [64] | Genetic characterization of downy mildew resistance from the hop (Humulus lupulus L.) line USDA 64035M | Crop Science |
| 50 | [65] | Diversity in genetic and downy mildew resistance among wild and mutagenized hops as revealed by single nucleotide polymorphisms and disease rating | Canadian Journal of Plant Science |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Arruda, M.M.; Soares, F.d.S.; Lima, M.T.; Doracenzi, E.L.; Costa, P.B.; Oliveira, D.N.; Fonsêca, T.K.d.S.; de Jesus Junior, W.C.; Santos, A.R.d. Bibliographic Analysis of Scientific Research on Downy Mildew (Pseudoperonospora humuli) in Hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Agriculture 2024, 14, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050714
de Arruda MM, Soares FdS, Lima MT, Doracenzi EL, Costa PB, Oliveira DN, Fonsêca TKdS, de Jesus Junior WC, Santos ARd. Bibliographic Analysis of Scientific Research on Downy Mildew (Pseudoperonospora humuli) in Hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Agriculture. 2024; 14(5):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050714
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Arruda, Marcia Magalhães, Fabiana da Silva Soares, Marcelle Teodoro Lima, Eduardo Lopes Doracenzi, Pedro Bartholo Costa, Duane Nascimento Oliveira, Thayse Karollyne dos Santos Fonsêca, Waldir Cintra de Jesus Junior, and Alexandre Rosa dos Santos. 2024. "Bibliographic Analysis of Scientific Research on Downy Mildew (Pseudoperonospora humuli) in Hop (Humulus lupulus L.)" Agriculture 14, no. 5: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050714
APA Stylede Arruda, M. M., Soares, F. d. S., Lima, M. T., Doracenzi, E. L., Costa, P. B., Oliveira, D. N., Fonsêca, T. K. d. S., de Jesus Junior, W. C., & Santos, A. R. d. (2024). Bibliographic Analysis of Scientific Research on Downy Mildew (Pseudoperonospora humuli) in Hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Agriculture, 14(5), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050714







