Combination Mechanism of Soil Dissolved Organic Matter and Cu2+ in Vegetable Fields, Forests and Dry Farmland in Lujiang County
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Extraction and Analysis of DOM
2.3. Complexometric Titration of DOM and Cu2+
2.4. Spectral Analysis
2.5. Characterisation Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. Two-Dimensional (2D-COS) Analysis
2.6.2. Complexation Parameter Fitting
2.6.3. Data Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DOM Spectral Characteristics and Source Analysis
3.1.1. UV-Visible Spectral Parameter Analysis
3.1.2. The Fluorescence Components and Source of DOM in Different Agricultural Soils
3.2. Combination Process of Soil DOM with Cu2+ in Different Agricultural Soils
3.2.1. Fluorescence Quenching Characteristics of DOM at Different Cu2+ Concentrations
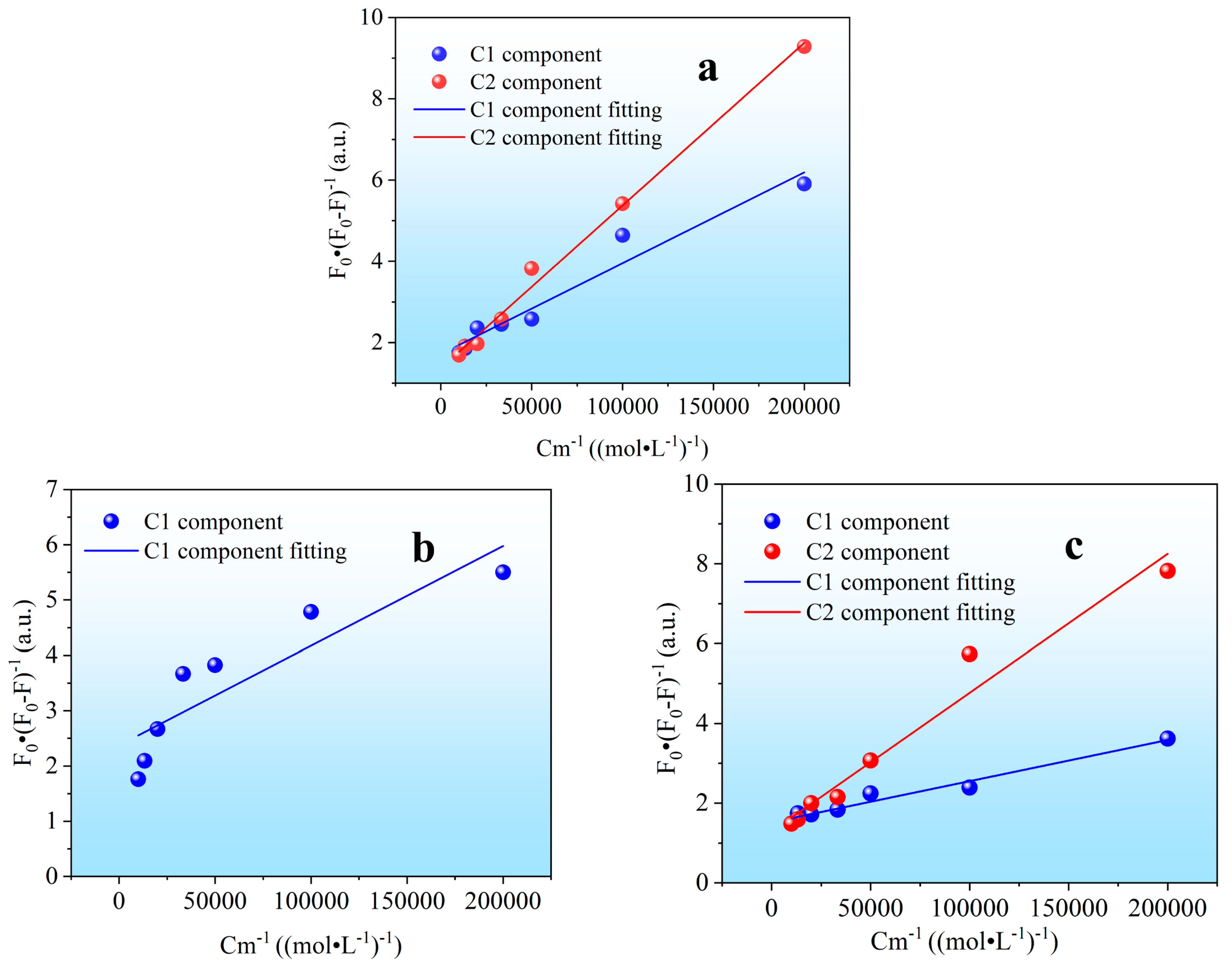
3.2.2. Kinetic fitting of DOM combines with Cu2+
3.3. The Combination Mechanism of DOM with Cu2+
3.3.1. Morphology and Structural Changes before and after Combining DOM with Cu2+
3.3.2. Effect of Surface Functional Groups on the Combination of DOM and Cu2+
3.3.3. Variations in Elemental Species after the Combination of DOM and Cu2+
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kríbek, B.; Sípková, A.; Ettler, V.; Mihaljevic, M.; Majer, V.; Knésl, I.; Mapani, B.; Penízek, V.; Vanek, A.; Sracek, O. Variability of the copper isotopic composition in soil and grass affected by mining and smelting in Tsumeb, Namibia. Chem. Geol. 2018, 493, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, M.X.; Wang, J.Z.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Duan, C.J.; Wang, X.X.; Zhao, S.L.; Bai, X.H.; Li, Z.J.; Li, Z.M.; et al. A global meta-analysis of heavy metal(loid)s pollution in soils near copper mines: Evaluation of pollution level and probabilistic health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, A.; Khan, M.S. Heavy metal induced oxidative damage and root morphology alterations of maize (Zea mays L.) plants and stress mitigation by metal tolerant nitrogen fixing Azotobacter chroococcum. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2018, 157, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoletano, P.; Guezgouz, N.; Benradia, I.; Benredjem, S.; Parisi, C.; Guerriero, G.; De Marco, A. Non-Lethal Assessment of Land Use Change Effects in Water and Soil of Algerian Riparian Areas along the Medjerda River through the Biosentinel Bufo spinosus Daudin. Water 2024, 16, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, G.; Mukhopadhyay, P.K.; Ayyappan, S. Biochemical composition of zooplankton community grown in freshwater earthen ponds: Nutritional implication in nursery rearing of fish larvae and early juveniles. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.T.; Lian, I.B.; Su, C.C.; Tsai, K.Y.; Lin, Y.P.; Chang, T.K. Spatiotemporal Trends in Oral Cancer Mortality and Potential Risks Associated with Heavy Metal Content in Taiwan Soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3916–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, C.; Foret, C.; Bazin, C.; Leduc, L.; Hammada, M.; Inácio, M.; Bedell, J.P. Bioavailability and bioaccumulation of heavy metals of several soils and sediments (from industrialized urban areas) for Eisenia fetida. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.R.; Ma, K.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Fang, F.M.; Lin, Y.S.; Yin, L.; Sun, L.; Zhang, C.H. Dissolved organic matter and Fe/Mn enhance the combination and transformation of As in Lake Chaohu Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.M.; Zhou, J.; Yang, R.P.; Jiang, S.H.; Yang, L.; Tang, B.P. Lower land use intensity promoted soil macrofaunal biodiversity on a reclaimed coast after land use conversion. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 306, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Shirani, H.; Besalatpour, A.A.; Esfandiarpour-Boroujeni, I.; Hajabbasi, M.A. High-energy moisture characteristics of various low organic matter sandy soils in different land uses. Geoderma 2021, 398, 115104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kong, W.D.; Shi, Q.; Wang, F.; He, C.; Wu, J.S.; Lin, Q.M.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhu, Y.G.; Liang, C.; et al. Patterns and drivers of the degradability of dissolved organic matter in dryland soils on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Guan, P.; Zhang, P.; Mo, X.H.; Yin, G.G.; Qu, B.; Xu, S.J.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; et al. Temperature Thresholds of Pyrogenic Dissolved Organic Matter in Heating Experiments Simulating Forest Fires. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 17291–17301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.C.; Cui, J.Y.; Wu, L.Z.; Liu, C.C.; Zhang, Q.F.; Zeng, Q.X.; Zhou, J.C.; Lin, K.M.; Wu, Y.; Lin, H.Y.; et al. Relationship between soil bacterial communities and dissolved organic matter in a subtropical Pinus taiwanensis forest after short-term nitrogen addition. Forest. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 512, 120165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Geng, J.; Cheng, S.L.; Fang, H.J.; Guo, Y.F.; Li, Y.A.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, F.Y.; Vancampenhout, K. Linking soil microbial community to the chemical composition of dissolved organic matter in a boreal forest during freeze-thaw cycles. Geoderma 2023, 431, 116359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.C.; Cui, J.Y.; Lin, K.M.; Liu, C.C.; Zhou, J.C.; Zhang, Q.F.; Zeng, Q.X.; Wu, L.Z.A.; Wu, Y.; Mei, K.C.; et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on the concentration and composition of soil-based dissolved organic matter in subtropical Pinus taiwanensis forests. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 1924–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.W.; Shi, L.L.; Liu, X.; Lei, H.J.; Yang, G.; Chen, H.R. Interactions Between Humic Acid and the Forms and Bioavailability of Copper in Water. Water Air Soil Poll. 2023, 234, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.J.; Dai, G.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; He, T.; Zhong, J.; Ma, Y.C.; Shu, Y.H. Field-scale fluorescence fingerprints of biochar-derived dissolved organic matter (DOM) provide an effective way to trace biochar migration and the downward co-migration of Pb, Cu and As in soil. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J.; Peng, Y.Y.; Li, N.X.; Tian, Y.Y.; Dai, L.C.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y. Effect of biochar-derived DOM on the interaction between Cu(II) and biochar prepared at different pyrolysis temperatures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.S.; Constantino, I.C.; Bento, L.R.; Tadini, A.M.; Bisinoti, M.C.; Boscolo, M.; Ferreira, O.P.; Mounier, S.; Piccolo, A.; Spaccini, R.; et al. Humic extracts from hydrochar and Amazonian Anthrosol: Molecular features and metal binding properties using EEM-PARAFAC and 2D FTIR correlation analyses. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yao, H.R.; Wu, Y.G. Effects of fresh and degraded dissolved organic matter derived from maize straw on copper sorption onto farmland loess. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, E.; Strawn, D.G.; Morra, M.; Moore, A.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Association between extracted copper and dissolved organic matter in dairy-manure amended soils. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.J.; He, X.S.; Li, C.W.; Li, N.X. The binding properties of copper and lead onto compost-derived DOM using Fourier-transform infrared, UV-vis and fluorescence spectra combined with two-dimensional correlation analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, E.; Meklesh, V.; Gentile, L.; Bhattacharya, A.; Stålbrand, H.; Tunlid, A.; Persson, P.; Olsson, U. Generation and properties of organic colloids extracted by water from the organic horizon of a boreal forest soil. Geoderma 2023, 432, 116386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Fernandez, I.J.; Hiradate, S.; Sherman, J.F. Effects of soil acidification and forest type on water soluble soil organic matter properties. Geoderma 2007, 140, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.Y.; Ma, F.Y.; Yao, X.; Shao, K.Q.; Yang, L.W. Multi-spectroscopic investigation on the spatial distribution and copper binding ability of sediment dissolved organic matter in Nansi Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; He, P.J.; Shao, L.M. Insight into the heavy metal binding potential of dissolved organic matter in MSW leachate using EEM quenching combined with PARAFAC analysis. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.P.; Gao, H.J.; Yu, H.B.; Song, Y.H. Applying EEM-PARAFAC combined with moving-window 2DCOS and structural equation modeling to characterize binding properties of Cu (II) with DOM from different sources in an urbanized river. Water Res. 2022, 227, 119317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.F.; Zhao, Y.F.; Yang, Z.W.; Lin, Z.M.; Tan, Z.Y.; Du, L.; Liu, C.L. Concentration and characterization of groundwater colloids from the northwest edge of Sichuan basin, China. Colloid. Surf. A 2018, 537, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, I.; Dowrey, A.E.; Marcott, C.; Story, G.M.; Ozaki, Y. Generalized two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 236A–248A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.J.; Ozaki, Y. Comparison of wavelets and smoothing for denoising spectra for two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2002, 56, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Q.; Jaffe, R. Interaction between Hg(II) and natural dissolved organic matter: A fluorescence spectroscopy based study. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.L.; Yeh, K.J.; Hsu, L.F.; Yu, W.C.; Lee, M.H.; Chen, T.C. Use of fluorescence quenching method to measure sorption constants of phenolic xenoestrogens onto humic fractions from sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 277, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miersch, T.; Czech, H.; Hartikainen, A.; Ihalainen, M.; Orasche, J.; Abbaszade, G.; Tissari, J.; Streibel, T.; Jokiniemi, J.; Sippula, O.; et al. Impact of photochemical ageing on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) and oxygenated PAH (Oxy-PAH/OH-PAH) in logwood stove emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selberg, A.; Viik, M.; Ehapalu, K.; Tenno, T. Content and composition of natural organic matter in water of Lake Pitkjarv and mire feeding Kuke River (Estonia). J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Srivastava, P.C.; Ghosh, D.; Zech, W. Characteristics of humic substances in cultivated and natural forest soils of Sikkim. Geoderma 1998, 84, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, L.L.; da Silva, W.T.L.; Milori, D.; Simoes, M.L.; Martin-Neto, L. Characterization of organic matter from composting of different residues by physicochemical and spectroscopic methods. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.C.; Wu, F.C.; Xing, B.S.; Meng, W.; Shi, G.L.; Ma, Y.; Giesy, J.P. Isolation and Characterization of Chinese Standard Fulvic Acid Sub-fractions Separated from Forest Soil by Stepwise Elution with Pyrophosphate Buffer. Sci. Rep.-UK 2015, 5, 8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artinger, R.; Buckau, G.; Geyer, S.; Fritz, P.; Wolf, M.; Kim, J.I. Characterization of groundwater humic substances: Influence of sedimentary organic carbon. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.V.M.; Hur, J. Tracing the sources of refractory dissolved organic matter in a large artificial lake using multiple analytical tools. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, C.C.; Li, J.Q.; Wang, P.; Ou, J.Q.; Cui, J.R. Interactions between copper(II) and DOM in the urban stormwater runoff: Modeling and characterizations. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiikkilä, O.; Smolander, A.; Kitunen, V. Degradability, molecular weight and adsorption properties of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen leached from different types of decomposing litter. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, Z.H.; Ren, D.J.; Zhang, S.Q. The spectral characteristics and cadmium complexation of soil dissolved organic matter in a wide range of forest lands. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Drosos, M.; Hu, H.L.; He, X.S.; Wang, G.X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.Y.; Xi, B.D. Organic amendments affect dissolved organic matter composition and mercury dissolution in pore waters of mercury-polluted paddy soil. Chemosphere 2019, 232, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korak, J.A.; Wert, E.C.; Rosario-Ortiz, F.L. Evaluating fluorescence spectroscopy as a tool to characterize cyanobacteria intracellular organic matter upon simulated release and oxidation in natural water. Water. Res. 2015, 68, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.L.; Zhao, W.H.; Miao, H. Studied on Colored Dissolved Organic Matter of Spring in North Yellow Sea with Three-Dimensional Fluorescence Spectroscopy Combined with Parallel Factor Analysis. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2016, 36, 2532–2537. [Google Scholar]
- De Mastro, F.; Cocozza, C.; Traversa, A.; Savy, D.; Abdelrahman, H.M.; Brunetti, G. Influence of crop rotation, tillage and fertilization on chemical and spectroscopic characteristics of humic acids. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, T.; Hess, N.J.; Qafoku, N.P. Current Understanding of the Use of Alkaline Extractions of Soils to Investigate Soil Organic Matter and Environmental Processes. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1561–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phungsai, P.; Kurisu, F.; Kasuga, I.; Furumai, H. Changes in dissolved organic matter during water treatment by sequential solid-phase extraction and unknown screening analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yao, Q.S.; Shao, L.M.; He, P.J. Toward understanding the role of individual fluorescent components in DOM-metal binding. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, C.; Brunetti, G.; Senesi, N.; Polo, A. Molecular and quantitative analysis of metal ion binding to humic acids from sewage sludge and sludge-amended soils by fluorescence spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Tu, C.; Yuan, G.D.; Liu, Y.; Bi, D.X.; Xiao, L.; Lu, J.; Theng, B.K.G.; Wang, H.L.; Zhang, L.J.; et al. Assessing the effect of pyrolysis temperature on the molecular properties and copper sorption capacity of a halophyte biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Habibul, N.; Liu, X.Y.; Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q. FTIR and Synchronous Fluorescence Heterospectral Two-Dimensional Correlation Analyses on the Binding Characteristics of Copper onto Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baken, S.; Degryse, F.; Verheyen, L.; Merckx, R.; Smolders, E. Metal Complexation Properties of Freshwater Dissolved Organic Matter Are Explained by Its Aromaticity and by Anthropogenic Ligands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2584–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, N.; Yang, W.; Gao, W.; Guo, P.; Zhao, C.; Chen, J. Characterization of ta-C film on micro arc oxidation coated titanium alloy in simulated seawater. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 117, 108483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetisov, A.V.; Kozhina, G.A.; Estemirova, S.K.; Fetisov, V.B.; Mitrofanov, V.Y.; Uporov, S.A.; Vedmid, L.B. XPS Study of Mechanically Activated YBa2Cu3O6+δ and NdBa2Cu3O6+δ. J. Spectrosc. 2013, 2013, 217268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Ding, J.F.; Gao, B.; Kan, E.; Hua, W.J. Accurate K-edge X-ray photoelectron and absorption spectra of g-C3N4 nanosheets by first-principles simulations and reinterpretations. Phys. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 22819–22830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.H.; Wu, M.J.; Wei, G.R.; Luo, Y.H.; Ran, W.; Wang, B.R.; Zhang, J.C.; Shen, Q.R. Binding of Organic Ligands with Al(III) in Dissolved Organic Matter from Soil: Implications for Soil Organic Carbon Storage. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6102–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.N.; Qian, T.T.; Dang, F.; Yin, Y.G.; Li, M.; Zhou, D.M. Significant contribution of metastable particulate organic matter to natural formation of silver nanoparticles in soils. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelker, B.M.; Morel, F.M.M.; Sulzberger, B. Iron redox cycling in surface waters: Effects of humic substances and light. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Land Use System | SUVA254 | SUVA260 | EET/EBz | E4/E6 | E2/E3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry farmland | 2.32 ± 0.03 a | 2.21 ± 0.03 a | 0.38 ± 0.01 a | 3.21 ± 0.87 a | 3.09 ± 0.08 a |
| Forest land | 9.12 ± 0.03 b | 8.75 ± 0.03 b | 0.74 ± 0.01 b | 4.04 ± 0.16 a | 2.69 ± 0.04 a |
| Vegetable fields | 2.22 ± 0.06 a | 2.05 ± 0.06 a | 0.15 ± 0.02 a | 3.22 ± 0.21 a | 3.90 ± 0.07 a |
| Type | Component | LgKM | f/% | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry farmland | C1 | 4.88 | 0.64 | 0.91 |
| C2 | 4.51 | 0.58 | 0.95 | |
| Forest land | C1 | 5.21 | 0.76 | 0.80 |
| Vegetable fields | C1 | 4.90 | 0.58 | 0.98 |
| C2 | 4.39 | 0.47 | 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, K.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, S. Combination Mechanism of Soil Dissolved Organic Matter and Cu2+ in Vegetable Fields, Forests and Dry Farmland in Lujiang County. Agriculture 2024, 14, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050684
Yao Y, Zhang J, Ma K, Li J, Hu X, Wang Y, Lin Y, Fang F, Li S. Combination Mechanism of Soil Dissolved Organic Matter and Cu2+ in Vegetable Fields, Forests and Dry Farmland in Lujiang County. Agriculture. 2024; 14(5):684. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050684
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Youru, Jingyi Zhang, Kang Ma, Jing Li, Xin Hu, Yusi Wang, Yuesheng Lin, Fengman Fang, and Shiyin Li. 2024. "Combination Mechanism of Soil Dissolved Organic Matter and Cu2+ in Vegetable Fields, Forests and Dry Farmland in Lujiang County" Agriculture 14, no. 5: 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050684
APA StyleYao, Y., Zhang, J., Ma, K., Li, J., Hu, X., Wang, Y., Lin, Y., Fang, F., & Li, S. (2024). Combination Mechanism of Soil Dissolved Organic Matter and Cu2+ in Vegetable Fields, Forests and Dry Farmland in Lujiang County. Agriculture, 14(5), 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14050684







