Effects of Soluble Organic Fertilizer Combined with Inorganic Fertilizer on Greenhouse Tomatoes with Different Irrigation Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
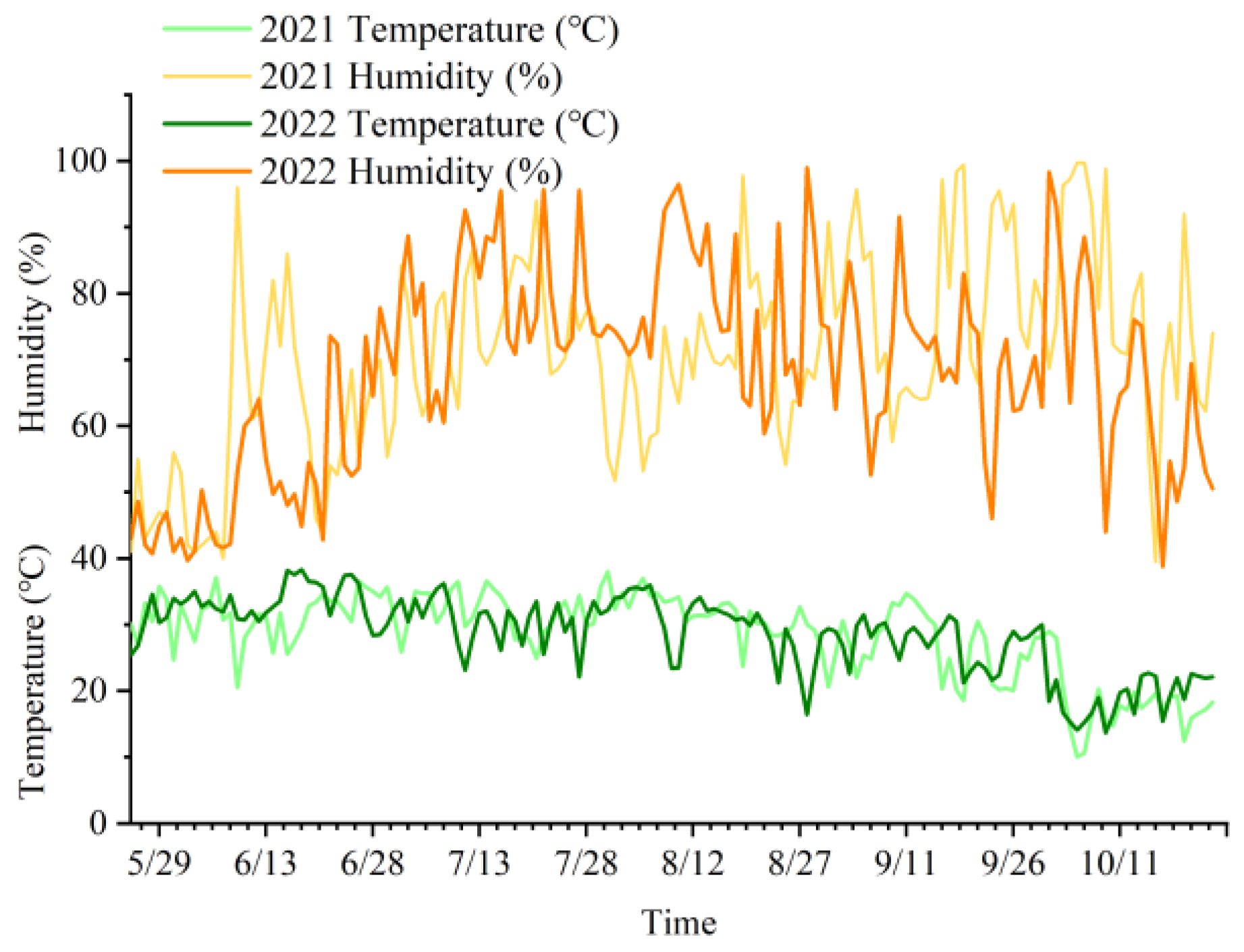
2.1. Experimental Location and Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement Indicators and Methods
2.3.1. Growth Indicators
2.3.2. Quality Indicators
2.3.3. Production Indicators
2.3.4. Water and Fertilizer Use Efficiency
2.4. TOPSIS Comprehensive Evaluation Model of the Entropy-Weight Method
2.4.1. The Entropy-Weight Method Determines the Weight of Each Index
- (1)
- Initial matrix
- (2)
- The processing of indicator data was standardized. In order to avoid the influence of the inconsistency of different index dimensions, the range method was used to standardize the data of each index. The normalization of positive and negative indicators is shown by the following formula:
- (3)
- Initial matrix R normalization
- (4)
- The entropy value and utility value of index information were calculated.
- (5)
- The weight of the ith indicator was calculated.
2.4.2. TOPSIS Model
- (1)
- Isonomialization of all indicators. When Gij is a high-performance indicator, G’ij = Gij; when Gij is a low-performance indicator, G’ij = 1/Gij.
- (2)
- A normalized initial matrix is constructed.
- (3)
- The positive and negative ideal solutions are determined. Based on the normalized matrix Z, the cosine method is used to find the positive ideal solution and the negative ideal solution. The positive ideal solution Z+ is composed of the maximum value of each column element, and the negative ideal solution Z− is composed of the minimum value of each column element, as follows:
- (4)
- The Euclidean distance between each evaluation object is calculated along with the positive and negative ideal solutions.
- (5)
- The proximity of each evaluation object is calculated.
2.5. Data Analysis Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Result of the Growth of Tomato Plants
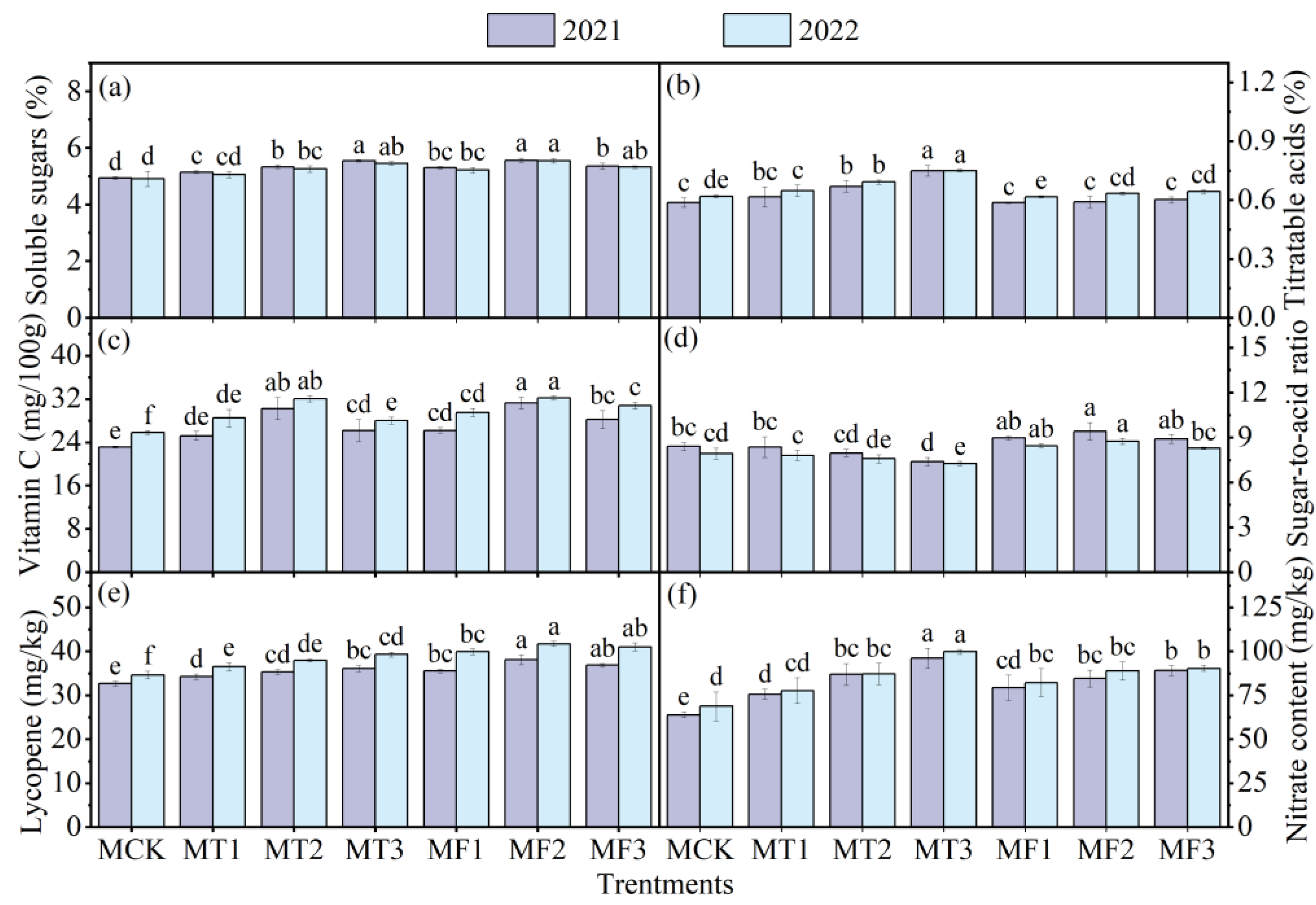
3.2. Results of Tomato Fruit Quality
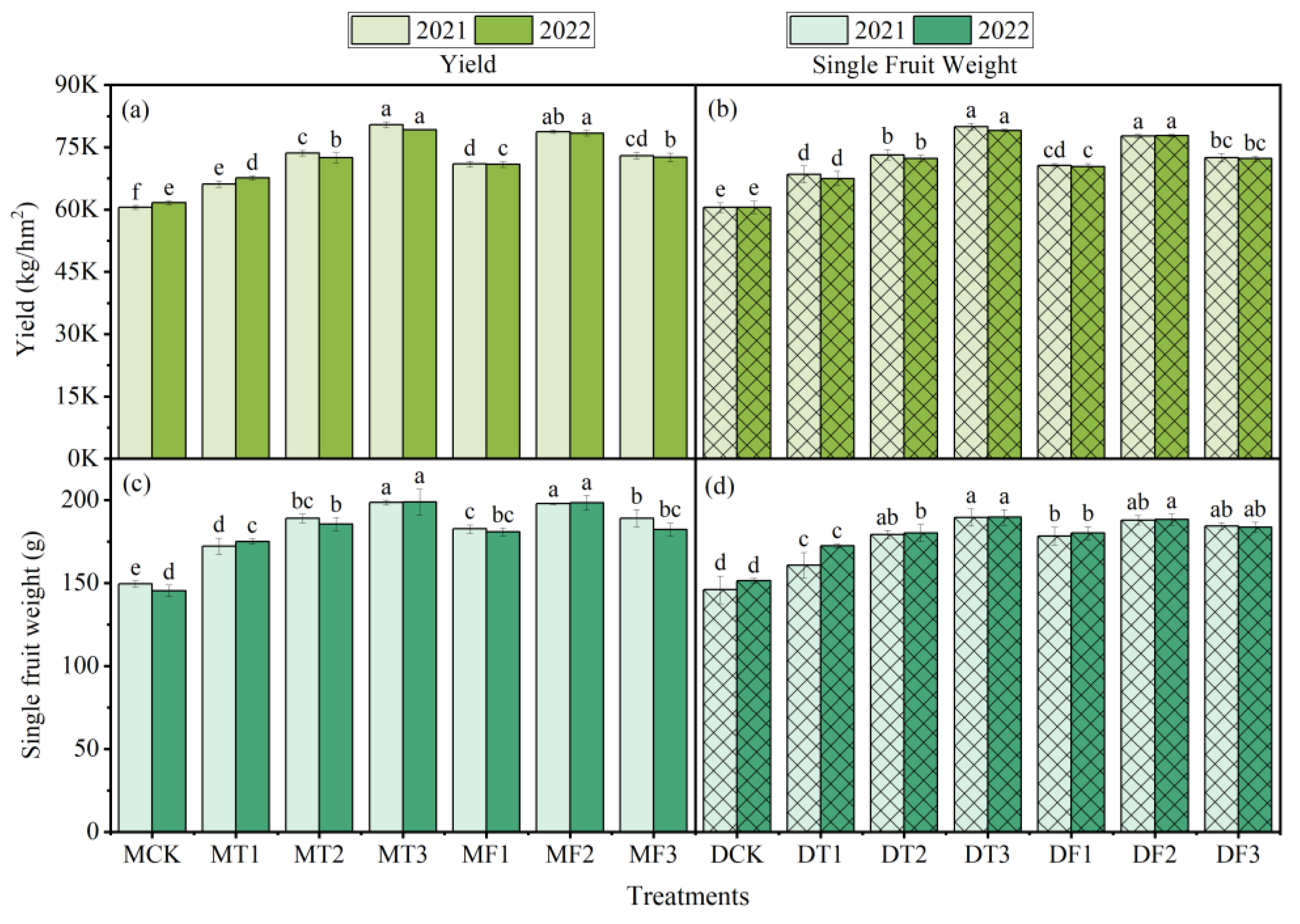
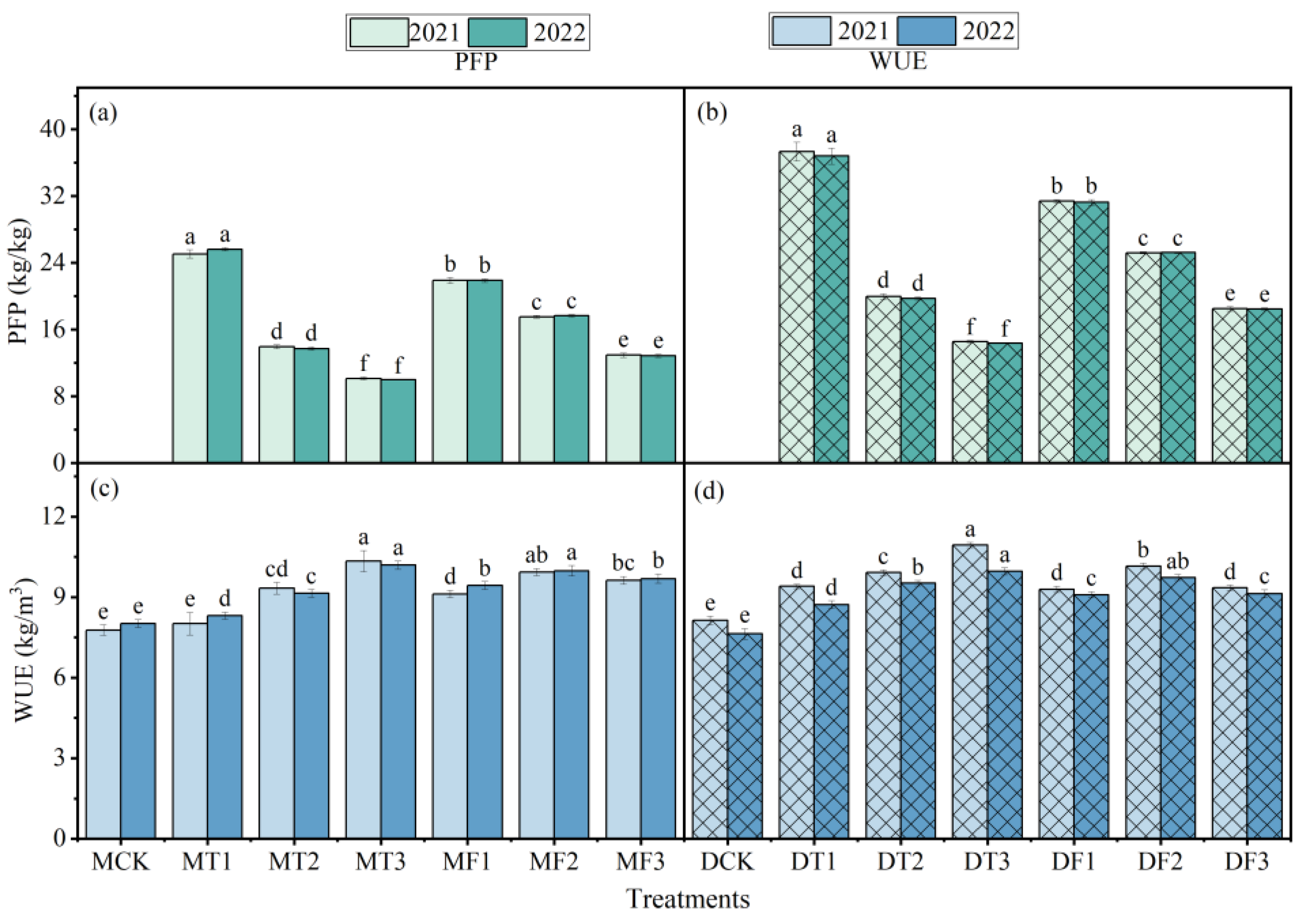
3.3. Results of Tomato Yield and Water and Fertilizer Efficiency
3.4. Comprehensive Evaluation of Tomatoes Based on the Entropy-Weight TOPSIS Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Treatments on Tomato Fruit Quality
4.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Tomato Growth, Yield, and Efficiency
4.3. A Comprehensive Evaluation Model of Tomatoes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tudor-Radu, M.; Vijan, L.E.; Tudor-Radu, C.M.; Tita, I.; Sima, R.; Mitrea, R. Assessment of Ascorbic Acid, Polyphenols, Flavonoids, Anthocyanins and Carotenoids Content in Tomato Fruits. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2016, 44, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmann, E. The influence of organic and conventional cultivation systems on the nutritional value and content of bioactive compounds in selected tomato types. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2840–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanambell, H.; Bishop, K.S.; Quek, S.Y. Tangerine tomatoes: Origin, biochemistry, potential health benefits and future prospects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2237–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harutyunyan, N.; Kushugulova, A.; Hovhannisyan, N.; Pepoyan, A. One Health Probiotics as Biocontrol Agents: One Health Tomato Probiotics. Plants 2022, 11, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xing, Y. Evaluation of the effects of irrigation and fertilization on tomato fruit yield and quality: A principal component analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.P.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhu, P.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, C.J.; Wu, L.; Tian, Y.F.; Xu, M.G.; Gunina, A.N. Stoichiometric imbalance of soil carbon and nutrients drives microbial community structure under long-term fertilization. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 168, 104119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Chen, Z.; Peng, T.; Chen, H.; Li, W. Comparative studi es on fertilizing effects of fen manure and fertilizer on chinese cabbage and cauliflower. Chin. J. Ecol. 2004, 23, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O.; Dahunsi, S.O.; Ayeni, J.F.; Aremu, C.; Aboyeji, C.M.; Okunlola, F.; Oyelami, A.E. Organic and in-organic fertilizers effects on the performance of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and cucumber (Cucumis sativus) grown on soilless medium. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Yao, H.; Shen, H.; Liang, S.; Jia, X. Effects of Different Kinds of Fertilizer on Wheat Yield and Soil Fertility. J. Hebei Agric. Sci. 2016, 20, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, B. Crop Yield and Soil Fertility Response to Commercial Organic Fertilizer Substituting Chemical Fertilizer. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 2136–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Ma, C.; Huang, J.; Liu, K.; Xue, Y.; Li, D.; LIU, l.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Variation in Rice Yield Response to Fertilization in China: Meta-analysis. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2019, 52, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yin, N.; Zheng, M.; Huang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chen, S.; Cai, K.; Wang, J. Effects of Reduction of Chemical Fertilizer and Organic Manure Supplement on Vegetables Yield and Quality. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2012, 28, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Tang, L.H.; Peng, Y.K.; Ni, J.Y.; Chang, Y.N. Effects of Composite Inorganic, Organic Fertilizer and Foliar Spray of Multi-nutrients on Growth, Yield and Quality of Cherry Tomato. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 17, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.C.; Zhang, S.X.; Wang, Y.Q. What could promote farmers to replace chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers? J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Yaguang, Z.; Jifeng, Z.; Fenghua, Z. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction combined with organic liquid fertilizer on processed tomato growth and soil enzyme activity. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2021, 2, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yan, S.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, J.; Guo, J.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, L. Combined effects of irrigation level and fertilization practice on yield, economic benefit and water-nitrogen use efficiency of drip-irrigated greenhouse tomato. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 262, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Wei, D.; Jin, L.; Li, Y.; Ding, J.; Han, B. Effects of Organic and Inorganic Combined Application on Soil Nutrients, Tomato Yield and Quality. North. Hortic. 2022, 6, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, E.K.; Senzanje, A.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Mubanga, S.C. Nutritional yield and nutritional water productivity of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp) under varying irrigation water regimes. Water SA 2020, 46, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirwai, T.L.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Kanda, E.K.; Senzanje, A. Moistube irrigation technology development, adoption and future prospects: A systematic scoping review. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wei, H. Establishment and verification of the prediction model of soil wetting pattern size in vertical moistube irrigation. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2020, 21, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, E.K.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Senzanje, A. Hydraulic and clogging characteristics of Moistube irrigation as influenced by water quality. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2018, 67, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, X.; Ma, J.; Shi, X.; Guo, X. Effects of Different Water Treatments under Film Drip Irrigation on Root Activity and Water Use Efficiency of Greenhouse Tomato. Water Sav. Irrig. 2019, 12, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.M.; Shen, L.X.; Zhang, G.X. An Experimental Study on the Dynamic Growth of Onion with Moistube-irrigation Technology in Greenhouse. Water Sav. Irrig. 2017, 2, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yue, X.; Liang, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Li, N. Micro-moistening irrigation combined with bio-organic fertilizer: An adaptive irrigation and fertilization strategy to improve soil environment, edible Rose yield, and nutritional quality. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 196, 116487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, C. Effects of Regulated Deficit Irrigation On Yield and Quality of Isatis Indigotica in a Cold and Arid Environment. Water 2021, 14, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D. Effects of Different Aerobic Drip Irrigation Methods on Yield, Quality, and Photosynthesis of Cherry Tomato in Greenhouse. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 36, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jin, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, J. Suitable Sowing Time for Processing Tomato Variety Liger 87-5 in Shihhotze Regions of Xinjiang Autonomous Region. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2009, 30, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Bai, J. Study on Extraction and Antibacterial Activity of Iycopene. China Feed 2022, 24, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, K.; Niu, X.; Hu, T. Construction of comprehensive nutritional quality index for tomato and its response to water and fertilizer supply. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wu, H.; Dong, C.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C. Effects of Different Precooling Temperature on the Storage Quality of Postharvest Tomato. Food Res. Dev. 2018, 39, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cui, J.; Xie, H.; Pei, H.; Gao, J. Effects of Different Organic Fertilizers on Growth Development, Quality and Yield of Sand-culture Tomato. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2017, 45, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Guo, X.; Su, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Lei, T. Study on Suitable Technical Parameters of Green Pepper Moistube-irrigation Based on Entropy—TOPSIS—Gray Correlation Mode. Water Sav. Irrig. 2023, 2, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, R.; He, D. Water and Fertilizer Irrigation Decision of Melon Based on Grey Relation Analysis and TOPSIS Coupling Model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zou, G.; Song, D.; Xu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Liu, B. Influence of Compost and Chemical Fertilizers on Tomato Yield and Quality. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 40, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Cai, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W.; Chen, J. Influence of organic and chemical fertilizers on tomato yield, quality, and the content of available heavy metals in soil. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 1, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fracchiolla, M.; Renna, M.; Durante, M.; Mita, G.; Serio, F.; Cazzato, E. Cover Crops and Manure Combined with Commercial Fertilizers Differently Affect Yield and Quality of Processing Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Organically Grown in Puglia. Agriculture 2021, 11, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Born, M.L.; Niu, W.; Liu, F. Biochar amendment improves shoot biomass of tomato seedlings and sustains water relations and leaf gas exchange rates under different irrigation and nitrogen regimes. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Determination of optimal amount of irrigation and fertilizer under drip fertigated system based on tomato yield, quality, water and fertilizer use efficiency. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31 (Suppl. S1), 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of Water and Fertilizer Coupling on Activity and Water and Fertilizer Utilization in Greenhouse Tomato Leaves. Water Sav. Irrig. 2023, 12, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pan, T.; Wang, L.; Du, Q.; Liu, Y. Effects of water-fertilizer coupling on tomato photosynthesis, yield and water use efficiency. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Effect of Different Organic Fertilizer and Amount on Growth Characteristics of Facility and Substrate Groove Cultivated Tomato. North. Hortic. 2018, 4, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jiang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L. Effects of partial chemical fertilizer substitution by organic fertilizer on the yield, quality and soil properties of facility tomato. China Cucurbits Veg. 2021, 34, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi, H.; Delshad, M. The effects of cluster pruning and the K:N ratio on greenhouse tomato yield and quality. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2021, 62, 691–700. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Z.H.; Cai, H.J.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.N.; Wang, X.Y. Effect of Water-Fertilizer-Gas Coupling on Soil N2O Emission and Yield in Greenhouse Tomato. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 2924–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Z.; Xiao, N.; Li, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.X. Growth and Fruit Yields of Greenhouse Tomato under the Integrated Water and Fertilizer by Moistube Irrigation. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, B.; Yao, M.; Niu, D.; Gao, M.; Mao, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, J. Optimising water and nitrogen management for greenhouse tomatoes in Northeast China using EWM−TOPSIS−AISM model. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 290, 108579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhu, C.; Qi, X.; Wei, J.; Yang, S.; Sun, Q. The Effecs of Irrigation with Diluted Biogas Slurry on Growth, Yield and Fruit Quality of Tomato. J. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 41, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, M.; Xing, Y.; Dang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Optimization of Fertilizer and Drip Irrigation Levels for Efficient Potato Production Based on Entropy Weight Method and TOPSIS. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2023, 29, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soil Physicochemical Properties | Data |
|---|---|
| Soil type | Sandy loam |
| Soil pH | 7.2 |
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 1.54 |
| Field capacity (%) | 26.71 |
| Soil nitrogen content (mg/kg) | 12.30 |
| Available phosphorus content (mg/kg) | 19.23 |
| Available potassium content (mg/kg) | 116.60 |
| Organic matter content (g/kg) | 11.23 |
| Treatments | N (kg/hm2) | P2O5 (kg/hm2) | K2O (kg/hm2) | Organic Fertilizer (kg/hm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moistube Irrigation | Drip Irrigation | ||||
| MCK | DCK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MT1 | DT1 | 150 | 60 | 120 | 0 |
| MT2 | DT2 | 300 | 120 | 240 | 0 |
| MT3 | DT3 | 450 | 180 | 360 | 0 |
| MF1 | DF1 | 150 | 60 | 120 | 75 |
| MF2 | DF2 | 150 | 60 | 120 | 225 |
| MF3 | DF3 | 150 | 60 | 120 | 375 |
| Irrigation Method | Year | Number of Days during the Whole Growth Period (d) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seeding Stage | Flowering Stage | Fruiting Stage | ||
| Moistube irrigation | 2021 | 39 | 21 | 75 |
| 2022 | 38 | 22 | 73 | |
| Drip irrigation | 2021 | 40 | 26 | 76 |
| 2022 | 39 | 25 | 74 | |
| Number | Quality Indicator | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total Soluble Sugars (TSU) | Handheld refractometer |
| 2 | Nitrate Content (NC) | Ultraviolet spectrophotometer |
| 3 | Titratable Acids (TA) | Neutralization titration |
| 4 | Vitamin C Content (VC) | Titration method |
| 5 | Lycopene Content (LYC) | Ultraviolet spectrophotometer |
| 6 | Sugar/Acid Ratio (SAR) | Sugar divided by acid |
| Index | 2021 | 2022 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ei | di | Weight | ei | di | Weight | |
| C1 | 0.937 | 0.063 | 6.999 | 0.938 | 0.062 | 6.552 |
| C2 | 0.950 | 0.050 | 5.539 | 0.932 | 0.068 | 7.187 |
| C3 | 0.926 | 0.074 | 8.213 | 0.915 | 0.085 | 8.925 |
| C4 | 0.942 | 0.058 | 6.368 | 0.934 | 0.066 | 6.992 |
| C5 | 0.926 | 0.074 | 8.205 | 0.935 | 0.065 | 6.839 |
| C6 | 0.938 | 0.062 | 6.825 | 0.931 | 0.069 | 7.261 |
| C7 | 0.913 | 0.087 | 9.547 | 0.914 | 0.086 | 9.073 |
| C8 | 0.943 | 0.057 | 6.289 | 0.938 | 0.062 | 6.478 |
| C9 | 0.923 | 0.077 | 8.507 | 0.913 | 0.087 | 9.200 |
| C10 | 0.921 | 0.079 | 8.668 | 0.904 | 0.096 | 10.089 |
| C11 | 0.937 | 0.063 | 6.985 | 0.948 | 0.052 | 5.430 |
| C12 | 0.913 | 0.087 | 9.639 | 0.908 | 0.092 | 9.718 |
| C13 | 0.926 | 0.074 | 8.215 | 0.941 | 0.059 | 6.256 |
| Treatment | 2021 | 2022 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive Ideal Solution | Negative Ideal Solution | Positive Ideal Solution | Negative Ideal Solution | |
| MCK | 0.748 | 0.437 | 0.793 | 0.400 |
| MT1 | 0.550 | 0.506 | 0.588 | 0.458 |
| MT2 | 0.456 | 0.646 | 0.504 | 0.576 |
| MT3 | 0.558 | 0.733 | 0.571 | 0.750 |
| MF1 | 0.403 | 0.633 | 0.455 | 0.603 |
| MF2 | 0.283 | 0.839 | 0.289 | 0.867 |
| MF3 | 0.390 | 0.686 | 0.435 | 0.643 |
| DCK | 0.857 | 0.452 | 0.848 | 0.452 |
| DT1 | 0.669 | 0.454 | 0.653 | 0.469 |
| DT2 | 0.565 | 0.498 | 0.548 | 0.490 |
| DT3 | 0.590 | 0.657 | 0.586 | 0.628 |
| DF1 | 0.503 | 0.541 | 0.520 | 0.553 |
| DF2 | 0.350 | 0.697 | 0.327 | 0.721 |
| DF3 | 0.472 | 0.557 | 0.485 | 0.550 |
| Treatment | 2021 | 2022 | Ranking Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score | Rank | Score | Rank | ||
| MCK | 0.369 | 13 | 0.335 | 14 | ↓ |
| MT1 | 0.479 | 10 | 0.438 | 11 | ↓ |
| MT2 | 0.586 | 5 | 0.533 | 6 | ↓ |
| MT3 | 0.568 | 6 | 0.568 | 5 | ↑ |
| MF1 | 0.611 | 4 | 0.570 | 4 | – |
| MF2 | 0.758 | 1 | 0.750 | 1 | – |
| MF3 | 0.637 | 3 | 0.597 | 3 | – |
| DCK | 0.345 | 14 | 0.348 | 13 | ↑ |
| DT1 | 0.404 | 12 | 0.418 | 12 | – |
| DT2 | 0.468 | 11 | 0.472 | 10 | ↑ |
| DT3 | 0.523 | 8 | 0.517 | 8 | – |
| DF1 | 0.518 | 9 | 0.516 | 9 | – |
| DF2 | 0.666 | 2 | 0.688 | 2 | – |
| DF3 | 0.541 | 7 | 0.532 | 7 | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Shen, L. Effects of Soluble Organic Fertilizer Combined with Inorganic Fertilizer on Greenhouse Tomatoes with Different Irrigation Techniques. Agriculture 2024, 14, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14020313
Li B, Shen L. Effects of Soluble Organic Fertilizer Combined with Inorganic Fertilizer on Greenhouse Tomatoes with Different Irrigation Techniques. Agriculture. 2024; 14(2):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14020313
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Binnan, and Lixia Shen. 2024. "Effects of Soluble Organic Fertilizer Combined with Inorganic Fertilizer on Greenhouse Tomatoes with Different Irrigation Techniques" Agriculture 14, no. 2: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14020313
APA StyleLi, B., & Shen, L. (2024). Effects of Soluble Organic Fertilizer Combined with Inorganic Fertilizer on Greenhouse Tomatoes with Different Irrigation Techniques. Agriculture, 14(2), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14020313





