Abstract
The long-term use of copper (Cu) fungicides in viticulture in Europe has led to Cu accumulation in vineyard top soils. However, less is known about the accumulation of Cu in grapevine grafts after the callusing process/before planting in the nursery. This paper presents the capacity of 5BB and SO4 rootstocks to accumulate Cu, as well as the patterns of translocation in the grafts. After heat forcing (callusing), the grapevine grafts of Sauvignon Blanc on 5BB and SO4 rootstocks were grown in pots for six months in a glasshouse and exposed to various Cu formulations (Cu-oxychloride, Cu-gluconate) and concentrations in peat (50, 150, 500, and 1000 mg Cu of dry weight (DW)). In addition to monitoring the shoot growth dynamics and analyzing the copper content in graft organs, bioaccumulation (BAFs) and translocation factors (TFs) of Cu were calculated. The mean Cu concentrations were ranked as follows: roots (15–164) > rootstock trunks (8–38) > canes (5–21) mg kg−1 DW. The Cu concentrations depended on the Cu formulation and concentration in the substrate. Higher Cu content was found in the roots of both rootstocks (5BB and SO4, 23–155 and 15–164 mg kg−1 DW, respectively) and the lowest in the canes (less than 10 mg kg−1 DW) of grafts grown in Cu-oxychloride-treated peat. Based on the BAFs and TFs, both rootstocks could be considered as Cu exclusive. A higher translocation rate was determined in systemic Cu-gluconate and SO4 rootstock. With shoot length measurements, the significant inhibitory effects of Cu on grapevine grafts growth could not be confirmed, despite the inhibitory effects that were clearly expressed in the first two months of growth. Soils containing more than 500 mg Cu/kg−1 are less suitable for growing vine grafts.
1. Introduction
In viticulture, decades of repeated use of Cu fungicides to control downy mildew [1] and a large number of Cu applications [2] have led to long-term accumulation of Cu in vineyard soils, even in deeper soil layers [3]. Therefore, in many grape growing areas the copper content in the vineyard soil exceeds 100 mg Cu kg−1 [4]. In French vineyard soils, in several cases, the content was 1500 mg of Cu kg−1 [1,5], and in southern Brazil, even 3200 mg kg−1 [6]. Conversely, Borkow and Gabby [7] reported that the long-term use of Cu fungicides cannot lead to excessive accumulation of Cu in the soil.
Copper ions are toxic to all plant cells and must, therefore, be used in specific, limited doses, or in relatively insoluble forms to avoid tissue damage in the exposed plants [8]. In the past, the annual Cu inputs into vineyards reached up to 30 kg ha−1. Nowadays, in European organic agriculture, a gradual reduction in Cu input levels from 8 kg ha−1 to 6 kg ha−1 (Commission Regulation EC No. 473/2002) is required. In certain countries, even lower annual rates are recommended. For example, the limit concentration of clearly detectable ecotoxic effects of Cu mentioned in environmental regulations in Republic of Slovenia is between 60 and 90 mg Cu kg−1 of soils (Official Gazette, Republic of Slovenia no. 84/05).
The elevated concentrations of Cu are toxic to soil organisms, e.g., earthworms [9], affect soil microbiota [10] and also grapevines [11]. Therefore, the management of contaminated soil has become very important [12]. The toxic effects of an excessive soil Cu depot are exerted through the disturbance of plant photosynthesis, lower enzyme activity, pigment and protein synthesis, and slower cell division [13,14,15]. It is observed that elevated levels of Cu in soil are reflected in higher Cu content in grapevine aboveground tissues [16,17]. Some studies have shown a very low correlation between soil Cu content and the amount of Cu extracted from plant tissues [18,19]. Soil and vines from organic vineyards had higher copper concentrations compared with those from conventional vineyards [20]. Certain plants have shown good potential for Cu hyper-accumulation in their tissues [21,22,23]. Cover crops growing between vine rows can reduce Cu concentrations in soils and grape plants [24].
Due to the elevated Cu concentrations in vineyard soils, it is necessary to know the effects of its bioaccumulation and phytotoxicity on the growth performance of grapevines. Considering the literature in general, Cu exposure effects have most often been studied in old plants in established vineyards. Information about the negative effects is also valuable for the grafts in the first year of growth when planted into soils with high Cu content. The toxicity of copper can postpone a vineyard entering into full yielding capacity. Because of this sensitivity, ecological relevance, and ease of assessment of their growth rate, young grapevine plants can also serve as suitable objects to determine the sub-lethal biological effects of copper on other plants. The roots of terrestrial plants are the first organs exposed to rhizosphere metals owing to their direct contact with the contaminated growth medium [16,25]. The inhibition of root elongation has generally been regarded as the primary and early effect of metal toxicity in plants [14,26,27,28,29]. Direct measurement of the metal concentration in the plant root tissue and observation of the inhibition of root elongation in field experiments are difficult. Some studies have focused on establishing the relationship between metal concentration in the aboveground parts, and the rhizotoxic effects in the plant’s root [30]. The proportion of the metal that is actually taken up by plant roots is extremely variable and depends on the plant species, the soil properties (soil pH, particle size, organic matter), and cation exchange capacity [5,31,32,33]. Some investigations to characterize Cu distribution and mobility in soils have been carried out in vineyards with fully established mature grapevines [1,26,34,35], but not in young grafts after planting in the nursery.
Information about the effects of high Cu concentration in soil on the development of young grapevines during the first season after grafting is not available in the literature. The effects of an elevated copper concentration on the development of grapevines directly after callusing are also important because young plants (grafts) can be grown in media where copper is added in high rates as a fungicide and bactericide to protect the grapevine against pathogens.
In comparison with field investigations, hydroponic experiments to investigate the bioaccumulation process of metals in plants are easy to conduct [36], but they can be regarded only as the first step in delineating the bioaccumulation and phytotoxicity of metals in plants since the metal availability pattern in the liquid solution cannot be fully compared with an extremely complex matrix of soil with many different particles having different biochemical natures. Also, interactions with other minerals and metals can occur. For example, it was shown that increased concentrations of calcium or magnesium can change the accumulation pattern of copper in grapevine roots [37]. Pot trials provide conditions more similar to natural conditions, but are still not completely comparable. In pot trials, a measurably significant reduction in root growth usually appears after the addition of 400 mg Cu kg−1 DW of soil [11,38].
To the authors’ knowledge, however, no study has attempted to assess the Cu bioaccumulation and phytotoxicity in grapevine grafts directly after heat forcing (callusing). Therefore, the purpose of this study was to conduct a pot experiment to determine the influence of substrate Cu concentration on bioaccumulation, the translocation of Cu in grafts organs, and the level of phytotoxicity in the first year of growth. The research contributes to knowledge on the effects of copper on the development of grapevine grafts in the early developmental stages. We recognize that the results of pot experiments cannot be directly extrapolated to the conditions of the development of grafts in the soil in the vineyard.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setting
Pot trials were carried out at the Faculty of Agriculture and Life Sciences in Maribor (Slovenia; 46°30′17.4″ N, 15°37′34.6″ E), during the vegetation period (from May to October 2011). The scions of Sauvignon Blanc grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) were bench-grafted (“omega” system) on 35 cm long cuttings of SO4 and 5BB (V. berlandieri Planc. × V. riparia Michx.) rootstocks. After heat forcing, only the grafts with completely overgrown callus were selected. They were uniform in thickness (9–10 mm) and weight (21.5 ± 0.39 g), so we tried to equalize the potential of reserve substances in the graft tissues at the beginning of the experiment [38]. The upper half of each graft was waxed (“Plastiffina top blu 7321”, Agrichem Barozzi, Revere, Italy). The grafts were randomly allocated to each treatment and then soaked in water for 24 h. The peat mixture Neuhaus Huminsubstrat N8 (pH 5.5–6.5, 210 mg N/L, 150 mg P2O5/L, 270 mg K2O/L, 100 mg MgO/L, 150 mg S/L) was used as the growing substrate, and 2.5 kg of substrate was placed in each of the 5 L pots. For each treatment, we had four pot replicates. Before filling the pots with the peat mixture, it was enriched with Cu. The content of the peat designed for filling each pot was placed in a clean polyethylene bag and soaked in 1 L of water solution in which the appropriate amount of Cu was added, based on the experimental design (50, 150, 500, and 1000 mg Cu++ kg−1 peat) and the peat’s initial Cu content (1.7 ± 0.03 mg Cu++ kg−1 of peat DW). Copper was added in two forms: as Cu-oxychloride (Cu2Cl(OH)3), (Cuprablau-Z 35 WP, Cinkarna Celje, Celje, Slovenia), a traditionally used fungicide; and as Cu-gluconate (C12H22CuO14), (Labicuper, Macasa, Spain). A systemic foliar fertilizer and the substrate in the bags were mixed thoroughly to ensure the uniform distribution of the copper solution. Two weeks after the planting in pots, only one shoot was left at each graft.
The pot experiment was conducted in a greenhouse (four plants per replicate) with a mean air temperature of 26 ± 1 °C, a relative humidity of 70 ± 2%, and with controlled drip irrigation. Protection against diseases was carried out only with Cu-free preparations. During the growth of grafts in a 6-month growing season (from the beginning of May till the end of October), the lateral shoots were regularly removed from the main shoots.
For the monitoring of shoot growth dynamics, every three weeks, the length of shoots was measured (from 7 June to 20 September). After six months (1 May to 31 October), the grafts were removed from the pots and sampled destructively by separating the plant organs (four plant per replicate). All plant samples of roots, the rootstock trunks and canes were washed thoroughly in deionized distilled water and were separately dried at 105 °C for 24 h till constant weight. This represented the total biomass of the graft. For statistical evaluation, the biomass is defined as the sum of the DWs of canes, roots, and the annual growth of the rootstock trunks (the difference between rootstock trunks weight at the start and the end of the trial).
The Cu contents (mg kg−1) of the dried root tissue, the rootstock trunk and the canes of all plants in each replicate (n = 4) were determined for homogenised samples obtained by acid digestion in microwave heating. The Cu content of each sample was determined using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Varian AA 240FS; Agilent Technologies, California, Santa Clara, CA, USA) performing absorbance readings at 324.8 nm, as described by Kurnik et al. [39]. All analyses of copper content were performed in duplicate. The analysis was performed by an internationally accredited laboratory. The metal recovery rate of the method is higher than 95%, and the limit of detection is above 0.035 mg L−1.
2.2. Growth Inhibition and Cu Accumulation Assessment
To analyze the effect of Cu on the growth of graft shoots, the relative growth rate of shoots (in %) was calculated. It is defined as the ratio between the length of shoots (in cm) of grafts developing in control pots without added copper (La) and the length of graft shoots developing in pots with added copper (Cu-gluconate or Cu-oxychloride) (Lb). The relative growth rate is calculated as (Lb/La) × 100. Values below 100% indicate growth inhibition, and values above 100% indicate growth acceleration.
In order to assess the rate of growth inhibition of grapevine grafts by copper, the dynamics of shoot growth were monitored. The model of Lai et al. [40] was used to describe the Cu uptake rate from the soil into the grapevine grafts in our experiment. By definition [17], the bioaccumulation factor (BAF) is the ratio between the Cu concentrations in the substrate and grapevine grafts organs as follows:
where BAFi is the bioaccumulation factor for the grapevine graft organ i, Cgi is the Cu concentration in graft organ i (mg kg−1), and Csu is the Cu concentration in the substrate (mg kg−1).
BAFi = Cgi/Csu
The translocation factors (TFs) are the ratios between the Cu concentrations in the roots and other organs of grapevine grafts. Thus, the TFs of Cu from the graft roots to rootstock trunk and canes were approximated by Chopin et al., [26] and Busuioc et al. [41]:
where Ci is the Cu concentration in the plant organ i (mg kg−1), Croot is the Cu concentration in the roots, and TFi is the translocation factor through the root to the plant organ i.
TFi = Ci/Croot
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were carried out for all presented parameters analysed in the graft samples. Differences between treatments were detected using an independent samples T-test and One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), followed by the Duncan multiple comparison procedures. Statistical evaluation of the data was performed using the SPSS 25.0 programme. Statistical significance was evaluated at p ≤ 0.05. For the evaluation of correlations, the Pearson coefficient was used.
3. Results
3.1. Shoot Growth Inhibition
The shoot growth rates do not confirm our expectation that the increase in Cu concentration in the growth substrate has a good correlation with the retarding effects on the shoot growth of grafts, as established by Toselli et al. [11]. After two months of graft growth in pots (28 June), the trends in inhibitory effects were observed (Figure 1; lower lines), and the highest shoot length was in the control. This first period was the time of adventitious roots formation on the grafts, and young roots were not yet able to mitigate the inhibitory effects of Cu on the growth of the grafts. We conclude that at this time, the highest concentration of Cu-gluconate in the SO4 rootstock had a toxic effect on the grafts as they all failed in this plot after one month of growth (Figure 1; right lower box). Generally, the lowest impact on relative shoot length was identified in the 5BB rootstock with Cu-oxychloride in the substrate (Figure 1; compare left upper box with right lower box). However, at this time, the minimum relative shoot length was at the highest concentration in the Cu gluconate, and differences between the Cu formulations were also confirmed by the t-test (p = 0.009).
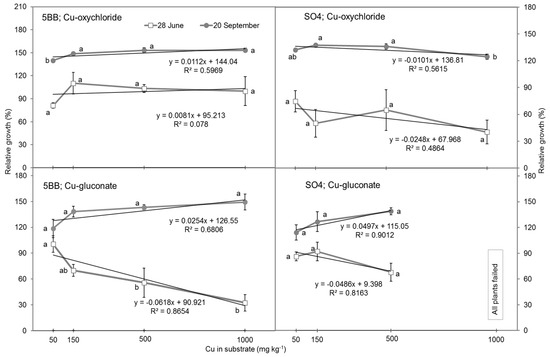
Figure 1.
Relative growth rate of grafts of Sauvignon Blanc grafted on 5BB and SO4 rootstocks in response to various Cu concentrations in the substrate after 58 d (20 June) and 143 d (20 September) of growth in pots. Values reported separately for rootstocks, Cu-formulation and measurement period, followed by the same letters are not significantly different according to the LSD test (p ≤ 0.05). Values represent mean ± SE, n = 4.
At the last shoot length measurement (20 September) (Figure 1; lines with circles), the increasing trend in the relative shoot length with the increase in Cu concentration in the substrate was confirmed, except for the SO4 rootstock (Cu-oxychloride), which was declining (Figure 1; right upper box). For the Cu-gluconate treatments, the differences between Cu concentrations were not significant (Figure 1; all data on lines marked with the same letter). The shoot length of the control plants without added Cu in the substrate were the lowest at the end of experiment.
These relations were confirmed by the daily shoot growth observations. During the last month of the experiment, the growth of shoots per day in the control plants was less than 0.2 cm per d, whereas in all other treatments, depending on the rootstock and Cu formulations, the growth rate ranged from 1.3 to 3 cm per d (p ≤ 0.031 for gluconate and p ≤ 0.0001 for oxychloride).
However, there were no significant differences in shoot growth per day between the first and second shoot length measurements, except for rootstock 5BB in Cu-gluconate (p = 0.007). The shoot growth rate was the highest in the control at more than 3 cm compared with 0.92 cm per d at the highest concentration (1000 mg Cu kg−1 of substrate). In both rootstocks and Cu-formulations, the average shoot length was the lowest in all treatments with the highest copper concentrations in the substrate. In this period, in the pots with SO4 rootstock and Cu-gluconate, all the grafts failed.
The DW values of roots, rootstock trunks, and canes are listed in Table 1. The general finding was that increasing the Cu concentration in the substrate did not cause a reduction in the DW of the root and cane as reported by other authors who used a hydroponic solution in their experiments [17]. The 5BB rootstock with increasing Cu concentration in the substrate showed increasing cane, root, and biomass DW in Cu-oxychloride (p = 0.001, p = 0.006 and p = 0.001, respectively), and in Cu-gluconate (p = 0.044, p = 0.003 and p = 0.019, respectively) (Table 1; 5BB Oxy and Glu data). The DW of the whole graft biomass was the highest when Cu was added in Cu-gluconate form, but differences between formulations were not significant (p ≤ 0.05). The same trends as in 5BB were also seen in the SO4 rootstock, except in the case of Cu-oxychloride where the differences in root DW were not observed (Table 1; SO4 Oxy and Glu data). This rootstock showed similar trends with Cu-gluconate, and it was observed that all its grafts failed in the pots with the highest Cu concentrations (Glu-1000) after the one month of growth (at 25–30 cm of shoot length). Whether this was due to the high concentration of copper should be examined in the future. We assume that the translocation rate of systemic acting Cu-gluconate to grapevine graft organs was so high that the concentrations in these organs reached a lethal level. We assume that in the first month of the trial, Cu-gluconate present in the growing substrate was not transformed into other copper forms that do not have such a high rate of systemic movement in the graft tissues. In pot trials conducted by Toselli et al. [11], the shoot inhibiting threshold of 1.16 mg of CaCl2-extractable Cu and 141 mg of DTPA-extractable Cu/kg soil DW was established for rooted grafts in pots in sand-enriched soil after 1 year of exposure. Concentrations of copper measured in roots in that trial were higher than in our trial, but the plants survived the toxic effects. Our grafts were potted directly after callusing (without developed roots), and inhibition at the beginning of graft growth at the time of adventitious root formation is perhaps more severe than later when the grafts have a bigger root mass.

Table 1.
Root, rootstock trunk, and cane dry weight (DW), and biomass (mean ± SE; n = 4) for grafts of Sauvignon Blanc grafted on 5BB and SO4 rootstocks grown in pots with various Cu concentrations in substrate after 6 months (oxy = Cu-oxychloride, glu = Cu-gluconate).
Due to the limited amount of data in the literature, especially the lack of data for different grapevine rootstocks, the copper concentrations in grapevines observed in the present study can only be compared with those of grapevine cuttings grown in hydroponic media. Juang et al. [17], found that the cytotoxic damage in grapevine rhizodermal cells caused by Cu in a hydroponic medium was most evident in the 25 to 50 µM concentration range. The threshold value of Cu shown to have a measurable inhibitory effect on the root growth of the grapevine was 10 µM, and the root growth was totally stunted at a concentration of 50 µM. In other plants (grass species), the lowest concentration that inhibited root growth was between 0.1 μM [30] and 5 μM [27]. Some plant species were free of any inhibition of root growth, even at exposure to a concentration of 10 µM of Cu [15]. Steffens and Rasmussen [42] also reported that nutrient and heavy metal stress conditions increase adventitous root development.
3.2. Cu in Graft Organs
The Cu concentrations in grafts were the highest in the roots and decreased gradually to the rootstock trunk and cane (Figure 2). The Cu accumulation within the roots generally increased with increasing Cu concentration in the substrate for both rootstocks and Cu formulations: Cu-oxychloride (p = 0.0001), and Cu-gluconate (p = 0.001, p = 0.022). Practically all lines in Figure 2 have an upward trend. The trend of increasing Cu concentrations in the rootstock trunks was similar to the increase in roots when the grafts were grown in substrate with the Cu-oxychloride for both rootstocks: p = 0.045 (5BB), and p = 0.0001 (SO4). (Compare the lines with rectangles and diamonds in Figure 2.) In the case of Cu-gluconate, differences in the Cu concentrations in the trunks of grafts grown in substrates with increasing Cu concentration were not significant, but the retention of Cu in the rootstock trunk was more pronounced in 5BB (p = 0.450) than in SO4 (p = 0.074). (Compare the lines on left and right side of Figure 2.) Generally, the Cu concentration in the canes was not influenced by the Cu concentration in the substrate, except for the SO4 rootstock with Cu-gluconate (p = 0.002). (See correlation lines in Figure 3.) This indicates that most of the Cu is retained by the roots, but in the case of Cu-gluconate, its translocation to the canes of grafts is still higher in the SO4 rootstock than in the 5BB rootstock.
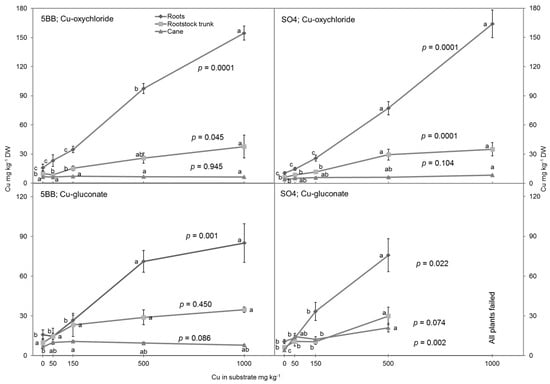
Figure 2.
Copper content in DW of roots, rootstock trunks, and canes of Sauvignon Blanc grafts on the 5BB and SO4 rootstocks exposed to various Cu concentrations and formulations in the substrate in a pot-based trial. Different letters indicate significant differences between copper content in specific tissues (root, rootstock trunk, cane) and in a specific combinations of rootstock variety and Cu formulation at p ≤ 0.05, according to the LSD tests.
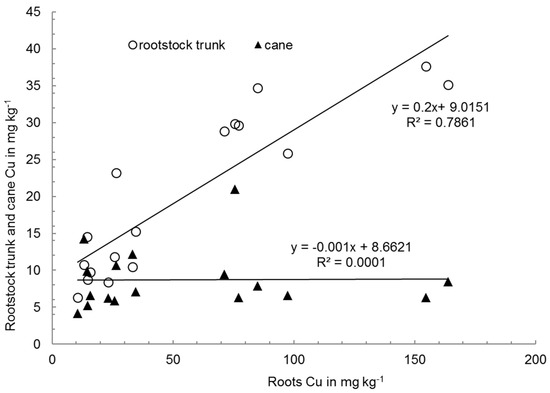
Figure 3.
Correlations between Cu concentration (mg kg−1) in roots and in the rootstock trunk and canes of Sauvignon Blanc grafts exposed to various Cu concentrations and formulations in the substrate (p ≤ 0.05).
In comparison with the canes, the roots accumulated relatively higher amounts of Cu, from 11 to 164 mg kg−1 DW, regardless of exposure concentrations in the substrate (Figure 2). Meanwhile, the Cu concentrations for rootstock trunks ranged from 6 to 38 mg kg−1 DW and from 4 to 21 mg kg−1 DW for canes (Figure 2). The tendency observed in the present study for vines to accumulate Cu in certain graft organs was in agreement with the research reported by other authors [34,40]. Significantly higher Cu concentrations were observed in the roots and rootstock trunks compared with in canes. At the highest Cu concentrations (1000 mg kg−1) in the substrate, the Cu amounts in the roots were four times higher than in the rootstock trunks and sixteen times higher than in the canes in both rootstocks (5BB, SO4) when the Cu-oxycloride formulations were used (Figure 2). The copper content was the highest in treatments with the higher concentrations (Oxy-500 and Oxy-1000), which was expected based on the findings of other researchers [17]. In the roots and in the rootstock trunks, the Cu concentration was eight times and four times higher, respectively, compared with the control grafts. In canes, the differences were minimal in all Cu treatments. The exception was at the higher concentration of Cu-gluconate in the substrate for the SO4 rootstock (p = 0.002). In the roots, the Cu concentration was lower when Cu-gluconate was used, whereas it was higher in the canes. Treatment Glu-500 resulted in a significant increase in the amount of Cu accumulated in the canes of the SO4 rootstock (21 mg kg−1). This was more than two times higher than in canes of 5BB (9.43 mg kg−1 DW) and three times more than with Cu-oxychloride in both rootstocks: 6.4 mg kg−1 DW (SO4) and 6.58 mg kg−1 DW (5BB). These results confirm the increased translocation of Cu from the roots to the shoots as a result of the systemic activity of this Cu gluconate form.
Grapevine grafts accumulated most of the Cu in their roots, thereby reducing its translocation to canes and avoiding excessive uptake of Cu, which is consistent with numerous previous studies [17,30]. This is confirmed by our findings that the amounts of Cu in the canes and roots do not correlate well (Figure 3). A highly significant correlation between the amounts of Cu in the rootstock trunks and roots was observed, which confirms the higher Cu translocation from the roots to the rootstock trunk than further to the canes (See Section 3.3). These results demonstrate the different nature of Cu-gluconate, where the increased translocation of Cu from the graft roots to the canes was observed. Our findings suggest that grapevine grafts accumulate most of the Cu in their roots (and also in the rootstock trunk), and are somehow able to reduce its translocation in the growing season to other plant parts (shoots and leaves) and thereby avoid excessive uptake of Cu.
3.3. Bioaccumulation and Translocation of Cu
By definition, the BAF represents the capacity for a specific species to accumulate a compound, and thus, it is highly species-specific. In general, the Cu accumulation in roots (BAFroot) was higher in grafts of 5BB than in SO4 rootstock in the Cu-oxycloride treatments (Figure 4), but the differences were not significant (p ≤ 0.05). The decreasing BAF rates of the 5BB and SO4 rootstocks were similar except for Cu-gluconate in canes. In this case, the BAFs for 5BB were lower at all Cu substrate concentrations, and in pots with 500 mg Cu kg−1 of substrate, the BAF of 5BB was two times lower than that for SO4. A comparison between the rootstocks in the pot with 1000 mg Cu kg−1 of substrate was not possible as in these pots, all the grafts of SO4 rootstock failed in the first month of the experiment. This suggests that the toxicity limit of grafts for this form of Cu was exceeded. Differences in the BAF values of the cane for different substrate Cu-concentration levels were determined in both rootstocks and Cu-formulations at a significance level of p ≤ 0.004 (Figure 4), which means that both rootstocks reduced the accumulation of Cu in the canes, regardless of the concentration in the substrate, but the reduction in Cu accumulation was less pronounced in SO4, and therefore, SO4 suffered total damage at Cu-1000-gluconate. The Cu-formulation also influenced the BAF of cane. It was, on average, 0.042 and 0.112 for the Cu-oxychloride and Cu-gluconate formulations, respectively (p = 0.006).
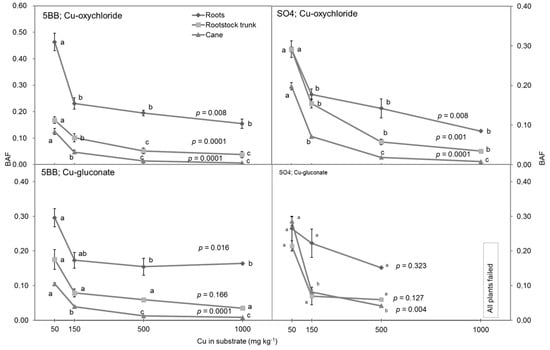
Figure 4.
Bioaccumulation factors (BAF) for roots, rootstock trunk, and canes of grapevine grafts of Sauvignon Blanc grafted on 5BB and SO4 rootstocks grown in pots in response to treatment with a range of internal Cu concentrations (mg kg−1) in substrate. Different letters indicate significant differences between the BAF values in specific tissues (root, rootstock trunk, cane) and in specific combinations of type of rootstock and Cu formulation at p ≤ 0.05, according to the LSD tests. Values represent mean ± SE, n = 4.
With increasing Cu concentrations in the substrate, translocation factor (TF) values were decreased. More significant differences were observed for the TF canes/roots (Table 2). Similar relationships are found for TFs of rootstock trunks (rootstock trunk/roots) of grafts. This suggests that the rootstock may also retain some excess Cu and limit further translocation to the green organs of the vine graft. These results further confirmed that grapevines are a typical metal excluder when exposed to excessive Cu and revealed that the Cu absorbed by the grapevine remains mainly in the roots. Therefore, the role of rootstocks should not be ignored, but there are still insufficient results available. Even the arrangement of the roots vertically along the soil horizon can affect the uptake of metals. The differences between the rootstocks were significant in regard to TFs for canes and roots (p = 0.043). This suggests that the rootstock 5BB is more Cu-exclusive than SO4, regardless of Cu formulation (Table 2). In the first step of Cu translocation in grafts, from roots to rootstock trunks, the differences between TFs were not significant for different Cu concentrations in the substrate, except for the more mobile Cu form (Cu-gluconate) in the SO4 rootstock.

Table 2.
Translocation factors (TFs) of roots to rootstock trunk and rootstock trunk to cane of grapevine grafts of Sauvignon Blanc grafted on 5BB and SO4 rootstocks grown in pots in response to treatment with a range of internal Cu concentrations (mg kg−1) in substrate. (oxy = Cu-oxychloride, glu = Cu-gluconate).
Cu translocation was influenced by Cu formulation, with higher values identified for Cu-gluconate, both for the different substrates and different rootstocks. In general, in both rootstocks, the average TF values were higher with Cu-gluconate in comparison with Cu-oxychloride. The TF values for rootstock trunk/roots were 12% (SO4) and 67% (5BB) higher. The TF values for cane/roots were 17% (SO4) and 21% (5BB) higher, and those for cane/rootstock trunk were 18% (5BB) and 140% (SO4) higher. This suggests that 5BB rootstocks also translocated less Cu from the rootstock trunk to the canes. The average cane/rootstock trunk TF for Cu-gluconate was 0.599 in 5BB in comparison to a TF of 1.086 in the SO4 rootstock (p = 0.05). The values of TF higher than 1 indicate a high mobility of Cu from the rootstock trunk into canes for the SO4 rootstock. Differences in TF values for Cu-oxychloride were not significant for the 5BB and SO4 rootstocks, with values of 0.505 and 0.452, respectively.
In practice, however, other environmental factors should also be taken into consideration due to the complex field conditions. Based on the BAFs and TFs, the grapevine could be considered a Cu-exclusive plant, as found by Juang et al. [17]. We can only speculate about the physiological background of the limited translocation of copper from roots to canes. We suggest that copper is complexed to immobile non-soluble complexes which cannot be transported from the root by the xylem stream to the upper parts of the plant. These complexes are likely incorporated into the cell walls, as proposed by Toselli et al. [11], who cited the research of Iwasaki et al. [43]. Substances for the forming of complexes may be present in the vascular root tissue or can be transported there from aboveground parts in the context of plant defence mechanisms which remain unfamiliar (for example, excessive suberisation of cell walls of root cells).
4. Conclusions
In this study, the bioaccumulation, translocation, and phytotoxicity of Cu in grapevine grafts were investigated. The dose–response relationship between Cu concentration in the substrate and the rate of inhibition of shoot and root growth was not found to be significant. Roots accumulated a relatively higher rate of Cu than the rootstock trunk and canes. Our results indicate that Sauvignon Blanc grafted on 5BB and SO4 rootstocks does not, when grown in substrate containing from 50 to 1000 mg Cu kg−1 DW, show a significant reduction in growth vigour, despite the high accumulation rate of copper in the roots and rootstock trunk. We suggest that the resistance to growth retardation is based on the low translocation rate of copper to aboveground parts, even in the case of systemic-acting Cu-gluconate. It is also necessary to mention the increased amount of copper in the rootstock trunks, which was also associated with lower translocation of copper into the canes at the end of the growing season. This needs to be considered when extrapolating our findings to other rootstocks. The failure of grafts on SO4 rootstock when grown in the substrate spiked to 1000 g of Cu-gluconate kg−1 DW demonstrates that the form of copper could play an important role in the toxicity level.
The results of our study show quite a high tolerance of grafts after callusing to elevated copper concentrations in the growing substratum. The treatment consisting of 500 mg of Cu kg−1 still did not cause a reduction in shoot growth. Considering the statistics on copper residues in grape-growing areas, which show that only a small proportion of soils contain more than 500 mg of Cu kg−1, we expect that in most of the moderately contaminated soils, young grape plants do not suffer growth inhibition related to sub-lethal copper toxicity effects. We are aware that conclusions obtained in pot trials cannot be directly extrapolated to the conditions for development of grafts in vineyard soils contaminated with Cu.
Based on our results, further research should be carried out in the future with other cultivars and rootstocks, and especially with even higher concentrations of copper, which are reported in the soil in some wine-growing countries. Since in our research, grafts were used in the most sensitive phase of development, i.e., immediately after callus formation, it would make sense to also include in further trials already rooted grafts which are ready for planting in vineyards. Our results contribute to knowledge about Cu impacts on the development of grape grafts grown in graft nurseries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.V.; Formal analysis, A.P. and B.P.; Funding acquisition, S.V.; Investigation, M.G.; Methodology, S.V. and B.P.; Visualization, S.V.; Writing—original draft, S.V.; Writing—review and editing, S.V. and M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Slovenian national research agency and the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Food of the Republic of Slovenia (grant no. CRP V4-0475) via the project “Determining the optimal grape production technology in terms of predicted climate changes and the future of Slovenian viticulture”.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the authors.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by University centre of Viticulture and Enology, Faculty of Agriculture and Life Sciences, University of Maribor.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Brun, L.A.; Maillet, J.; Hinsinger, P.; Pepin, M. Evaluation of Copper Availability to Plants in Copper-Contaminated Vineyard Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 111, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Esparza, M.A.; Capri, E.; Pirzadeh, P.; Trevisan, M. Copper Content of Grape and Wine from Italian Farms. Food Addit. Contam. 2006, 23, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casali, C.A.; Moterle, D.F.; Rheinheimer, D.D.; Brunetto, G.; Corcini, A.L.M.; Kaminski, J.; de Melo, G.W.B. Copper Forms and Desorption in Soils under Grape Vine in the Serra Gaucha of Rio Grande Do Sul. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2008, 32, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačič, R.G.; Lešnik, M.; Vršič, S. An Overview of the Copper Situation and usage in Viticulture. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 19, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Chaignon, V.; Sanchez-Neira, I.; Jaillard, B.; Hinsinger, P. Copper Bioavailability and Extractability as Related to Chemical Properties of Contaminated Soils from a Vine-Growing Area. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 123, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirlean, N.; Roisenberg, A.; Chies, J.O. Metal Contamination of Vineyard Soils in Wet Subtropics (Southern Brazil). Environ. Pollut. 2007, 149, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Gabbay, J. Copper as a Biocidal Tool; Cupron Inc., Publications: Gibton, Israel, 2007; 42p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, G.W.; Whitacre, D.M. The Pesticide Book, 6th ed.; MeisterPro Information Resources: Willoughby, OH, USA, 2004; 487p. [Google Scholar]
- Helling, B.; Reineeke, S.; Reineeke, A.J. Effects of the Fungicide Copper Oxychloride on the Growth and Reproduction of Eisena (Oligochaeta). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000, 46, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoffer, J.T.; Sauvé, S.; Neaman, A.; Ginocchio, R. Role of Leaf Litter on the Incorporation of Copper-Containing Pesticides into Soils Under Fruit Production: A Review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toselli, M.; Baldi, E.; Marcolini, G.; Malaguti, D.; Quartieri, M.; Sorrenti, G.; Marangoni, B. Response of Potted Grapevines to Increasing Soil Copper Concentration. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2009, 15, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vršič, S.; Ivanćić, A.; Pulko, B.; Valdhuber, J. Effect of Soil Management Systems on Erosion and Nutrition Loss in Vineyards on Steep Slopes. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Mengel, K.E.; Kirkbiy, A.; Kosegarten, H.; Appel, T. Principles of Plant Nutrition; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 2001; pp. 537–549. [Google Scholar]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Menzies, N.W. Effect of Cu Toxicity on Growth of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Plant Soil 2006, 27, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourato, M.P.; Martins, L.L.; Campos-Andrada, M.P. Physiological Responses of Lupinus luteus to Different Copper Concentrations. Biol. Plant. 2009, 53, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, Y.S.; Li, P.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, T. Root Growth Inhibition and Induction of DNA Damage in Soybean (Glycine max) by Chlorobenzenes in Contaminated Soil. Chemosphere 2009, 57, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, K.W.; Lee, Y.I.; Lai, H.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, B.C. Copper Accumulation, Translocation, and Toxic Effects in Grapevine Cuttings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, M.J.; Smolders, E.; Merckx, R. Soil Root Interface: Physicochemical Processes. In Soil Chemistry and Ecosystem Health; Huang, P.M., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1998; Volume 52, pp. 233–277. [Google Scholar]
- Romić, M.; Romić, D.; Ondrašek, G. Heavy Metals Accumulation in Topsoil from the Wine Growing Regions Part 2, Relationships between Soil Properties and Extractable Copper Contents. Agric. Conspec. Scentificus 2004, 69, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Beni, C.; Rossi, G. Conventional and Organic Farming: Estimation of some Effects on Soil, Copper Accumulation and Wine in a Central Italy Vineyard. Agrochimica 2009, 53, 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta, J.R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; Tiemann, K.J.; Gomez, E.; Arteaga, S.; Rascon, E.; Parsons, J.G. Uptake and Effects of five Heavy Metals on Seed Germination and Plant Growth in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 66, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.J.; Yang, X.E.; Römheld, V. Growth and Nutrient Composition of Elsholtzia splendens Nakai under Copper Toxicity. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 25, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.B.; Vajpayee, P.; Tripathi, R.D.; Rai, U.N.; Singh, S.N.; Singh, S.P. Phytoremediation of Lead, Nickel and Copper by Salix acmophylla Boiss: Role of Antioxidant Enzymes and Antioxidant Substances. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 70, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, K.A.; Marhan, S.; Ditterich, F.; Schmidt, H.P.; Kandeler, E. The Effects of Biochar and Compost Amendments on Copper Immobilization and Soil Microorganisms in a Temperate Vineyard. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 201, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khellaf, N.; Zerdaoui, M. Growth Response of the Duckweed Lemna gibba L. to Copper and Nickel Phytoaccumulation. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, E.I.B.; Marin, B.; Mkoungafoko, R.; Rigaux, A.; Hopgood, M.J.; Delannoy, E.; Cances, B.; Laurain, M. Factors Affecting Distribution and Mobility of Trace Elements (Cu, Pb, Zn) in a Perennial Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) in the Champagne Region of France. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Shen, Z. Copper Accumulation and Tolerance in Chrysanthemum coronarium L., and Sorghum sudanense L. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 55, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Hua, L.; Mclaughlin, M.J. Identification of Hydroxyl Copper Toxicity to Barley (Hordeum vulgare) Root Elongation in Solution Culture. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, K.W.; Lai, H.Y.; Chen, B.C. Coupling Bioaccumulation and Phytotoxicity to Predict Copper Removal by Switchgrass Grown Hydroponically. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, A.M.; Chappellaz, C.; Hinsinger, P. Copper Phytotoxicity Affects Root Elongation and Iron Nutrition in Durum Wheat (Triticum turgidum durum L.). Plant Soil 2008, 310, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, L.A.; Maillet, J.; Richarte, J.; Herrmann, P.; Remy, J.C. Relationships between Extractable Copper, Soil Properties and Copper Uptake by Wild Plants in Vineyard Soils. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 102, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devez, A.; Gomez, E.; Gilbin, R.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Persin, F.; Andrieux, P.; Casellas, C. Assessment of Copper Bioavailability and Toxicity in Vineyard Runoff Waters by DPASV and Algal Bioassay. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 348, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, K.; De Schamphelaere, K.A.C.; Becaus, S.; Criel, P.; Van Eeckhout, H.; Janssen, C.R. Development and Validation of a Terrestrial Biotic Ligand Model Predicting the Effect of Cobalt on Root Growth of Barley (Hordeum vulgare). Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, V.R.; Ivanov, A.S.; Braikov, D.M. Heavy Metals (Pb, Cu, Zn and Cd) in the System Soil-Grapevine-Grape. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, B.G.; Vogeler, I.; Bolan, N.S.; Clothier, B.; Green, S.; Kennedy, J. Mobility of Copper, Chromium and Arsenic from Treated Timber into Grapevines. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 388, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandy, S.; Schulin, R.; Nowack, B. The Influence of EDDS on the Uptake of Heavy Metals in Hydroponically Grown Sunflowers. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Lee, Y.I.; Chenc, B.C.; Juang, K.W. Effects of Calcium on Rhizotoxicity and the Accumulation and Translocation of Copper by Grapevines. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 73, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vršič, S. Soil Erosion and Earthworm Population Responses to Soil Management Systems in Steep-Slope Vineyards. Plant Soil Environ. 2011, 57, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnik, V.; Gaberšek, V.; Unuk, T.; Tojnko, S.; Vogrin, A.; Vajs, S.; Lešnik, M. Influence of Alternative Copper Fungicide Formulations on Copper Content in Apple Fruits. Erwerbs-Obstbau 2012, 54, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.Y.; Juang, K.W.; Chen, B.C. Copper Concentrations in Grapevines and Vineyard Soils in Central Taiwan. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 56, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busuioc, G.; Elekes, C.C.; Stihi, C.; Lordache, S.; Ciulei, S.C. The Bioaccumulation and Translocation of Fe, Zn, and Cu in Species of Mushrooms from Russula Genus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, B.; Rasmussen, A. The physiology of adventitious roots. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, K.; Sakurai, K.; Takahashi, E. Copper Binding by the Root Cell Walls on Italian Reygrass and Red Clover. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1990, 36, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).