Abstract
Wheat stripe rust (WSR) caused by Puccinia striiformis F. tritici Erikss. (Pst) is one of the serious diseases that affect wheat planting areas around the world. Many efforts have been made to control such a serious disease including using fungicides and breeding highly resistant genotypes. However, due to Pst’s ability to produce new races that overcome these fungicides and break the resistance in the highly resistant genotypes, looking for other effective ways to restrict this disease is urgently required. One of the highly effective ways of controlling crop diseases is using biological control. In this study, the efficiency of three different Trichoderma species (Trichoderma asperellum T34, Trichoderma harzianum (TH), and Trichoderma verdinium (TV)) was tested in a set of 34 wheat genotypes at the seedling stage. The evaluation was conducted in two experiments with two different temperature regimes. In each experiment, four treatments were applied, namely, control, T34, TV, and TH. High genetic variation was found among all genotypes in each experiment and under each Trichoderma treatment. Notably, the symptoms of WSR were affected by temperature under all treatments except T34, which had a stable performance in the two experiments. The 34 studied genotypes were highly diverse, related to ten different countries, and consisted of durum and bread wheat. Out of the three studied Trichoderma species, T34 was able to improve WSR resistance in all the studied genotypes suggesting its effectiveness in inducing the resistance and producing a priming response in different wheat genetic backgrounds. The results of this study provided very useful information on the effectiveness of Trichoderma spp. in controlling WSR.
1. Introduction
Wheat stripe rust (WSR) (caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. Tritici (Pst)) is the most devasting rust disease in many wheat planting areas and causes huge damage to wheat yield [1]. Pst infection can occur at any time during wheat’s life cycle and results in decreasing kernel mass/plant and kernels/head [2]. Usually, new Pst races appear and distribute among a wide range of environmental conditions. As a result, WSR resistance has been broken in many resistant genotypes [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Finding a suitable and successful way to control such a serious disease is urgently needed.
Over the past 75 years, fungicides have been found as a successful method to control the spread of WSR in many planting areas [6,7]. However, due to Pst’s ability to produce new races that overcome these fungicides, as well as the harmful effect of fungicides on the environment and human health, looking for other methods is required. One other possible way to control WSR is breeding resistant genotypes that produce a broad-spectrum resistance against a wide range of Pst races. This is the main goal for wheat breeders in the recent decade. Many efforts have been made to achieve this goal [6,7,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. However, breeding programs need a long time to produce promising resistant genotypes. Furthermore, the Pst pathogen can produce new virulence races that overcome the resistance in the resistant genotypes. Therefore, other controlling techniques should be established.
In the last few years, biological control has been found to be one of the most effective, sustainable, cost-efficient, and environmentally friendly approaches that control many plant diseases [23,24,25]. It is reported as a way to control plant diseases with no environmental concerns and no complexity of use. Bioagents could be bacteria or fungi isolated from the phyllosphere, endosphere, or rhizosphere around the plant. Fungal bioagents, especially Trichoderma spp., are more common in the biological control of plant diseases [26,27,28,29,30,31]. Trichoderma spp. was found to improve plant resistance against different pathogens using two different mechanisms: a direct mechanism by using mycoparasites, and an indirect mechanism by inducing the plant’s systematic defense response [26]. In the indirect mechanism, Trichoderma produces antibodies and uses the mycoparasitic mechanisms to resist the pathogen. During the mycoparasitic mechanism, Trichoderma colonizes the outer layers of the leaves and alters the transcriptome and proteome machinery, therefore increasing plant growth and nutrient uptake [26]. Inducing the plant’s defense system results in stronger plant growth that enables the plant to be ready for any biotic/abiotic stress, a response known as the priming response [32]. During the priming response, plants become ready for abiotic stresses following the category of hardening and biotic stresses following the category of induced defense. The response of plants to Trichoderma could be classified into four different timing stages. In each stage, a different cellular response occurs due to inducing different plant genes. The priming response depends on the genetic control of the plant as specific genes are induced under the effect of Trichoderma spp. [33].
Few efforts have been made in studying the biological control of wheat rust diseases. Some studies have tested the efficiency of bacterial bioagents in controlling wheat rusts [34,35]. Others tested the efficiency of fungal bioagents such as Trichoderma spp. and mycorrhizal fungi [36]. Unlike bacterial bioagents, fungal bioagents have a higher reproductive rate, short generation time, specific target, and survival ability in the absence of their host [26]. These features make fungal bioagents more suitable to be used. Out of the known fungal bioagents, Trichoderma spp. are more common, and many products are commercially available such as Trichoderma asperellum T34, Trichoderma harzianum (TH), and Trichoderma verdinium (TV). The efficiency of these Trichoderma species in controlling cereal crop diseases has been reported previously [37,38,39,40].
In our previous study, T34 was tested in a set of 198 diverse spring wheat genotypes and was found to significantly increase the resistance of WSR in almost all the tested genotypes, except nine genotypes that were still susceptible [33]. Therefore, it was worth testing if there is another Trichoderma spp. that could be more effective than T34 in controlling WSR. The objective of this study is to examine the effect of three Trichoderma spp. (Trichoderma asperellum T34, Trichoderma harzianum, and Trichoderma verdinium) as a bioagent to control WSR under different degrees of temperature.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
In this study, 34 spring wheat genotypes were used. These genotypes were selected from a highly diverse spring wheat panel that was evaluated for stripe rust resistance under Egyptian conditions [6,7]. Furthermore, this panel was evaluated previously for their response to stripe rust under Trichoderma asperellum T34 (T34) treatment [33]. The selected genotypes were susceptible (nine genotypes) and immune genotypes (25 genotypes). Moreover, the 34 genotypes were originated from ten different countries including Australia, Canada, Egypt, Germany, Greece, Iran, Morocco, Oman, the United Kingdom, and the United States, and classified into bread and durum wheat (Table S1).
2.2. Experimental Design, Greenhouse Conditions, and Trichoderma Treatments
In our previous study, T34 was found to be effective against WSR [33]. Therefore, it was worth testing the effectiveness of other Trichoderma spp. in controlling this disease. Moreover, to identify the best Trichoderma spp. that is effective under different temperatures, two different greenhouse chambers having different temperatures were used. Therefore, a total of two experiments were conducted and could identify as follows: (1) Exp. I: under the greenhouse conditions of 80% relative humidity, 16 h of 16,000 lux, and 10–12 °C; and (2) Exp. II: under greenhouse conditions of 80% relative humidity, 16 h of 16,000 lux, and 16–18 °C. In each experiment, four different treatments were applied as follows: (1) Trichoderma asperellum T34 (will be named hereinafter T34), (2) Trichoderma harzianum (will be named hereinafter TH), (3) Trichoderma verdinium (will be named hereinafter TV), and (4) stripe rust infection without any biological control (will be named hereinafter Yr). Both experiments were conducted at the Wheat Disease Research Department, Sakha Agricultural Research Station, Agricultural Research Center, Kafrelsheikh, Egypt. For each treatment, the experimental design was a randomized complete block design (RCBD) with three replications for each experiment.
2.3. Preparation of Trichoderma spp.
TH and TV used in this study were obtained from MTA (Hungarian Academy of Sciences), Budapest, Hungary [41]. T34 was obtained from Biocontrol Technologies S.L. Company, Spain (Local import Shoura chemical company, https://shouraonline.com/) [33]. The three Trichoderma spp. were separately grown on Potato dextrose broth medium and incubated on a rotary shaker at 250 rpm at 28 ± 2 °C for ten days. Spore suspensions of the three isolates were counted and adjusted at (106 spore/mL) each using a hemocytometer [42]. In both experiments, the suspension of T34, TH, and TV treatments was sprayed one day before the Pst inoculation, while seedlings used in the Yr treatment were kept without any treatment until inoculation.
2.4. Stripe Rust Inoculation and Evaluation
For all four treatments, the fresh mixtures of the most recent P. striiformis f. tritici (Pst) spore collected from Egyptian fields in the 2022/2023 growing season were used in seedling inoculation. The race population mainly consists of 78E189 and 262E31 (Samar Esmail, personal communication). The urediniospores were multiplied on “Morocco” susceptible check. The inoculation was performed following Stakman et al.’s (1962) method described in [33]. After 24 h of incubation in the dew chamber at 10 °C, the seedlings were shifted to the greenhouses with the mentioned conditions for each experiment.
Stripe rust symptoms were recorded 10–14 days after inoculation. The symptoms were recorded as infection type (IT) from 0 to 9 [43]. In this scale, genotypes were classified into immune (IT = 0), very resistant (VR, 0 < IT < 1), resistant (R, IT = 2), moderately resistant (MR, 3 < IT < 5), moderately susceptible (MS, 6 < IT < 7), susceptible (S, 7 < IT < 8), and very susceptible (VS, IT = 9). Furthermore, to provide more understanding of the role of the different studied Trichoderma spp. in controlling stripe rust, slow rusting components were calculated. These components were the incubation period (IP), latent period (LP), and pustules density (PD). IP was calculated as the time from inoculation until symptoms are visible [44]. LP was calculated as the time from inoculation to pustule eruption [45]. PD was recorded as the number of pustules/cm2 of the leaf area (2.0 × 0.5 cm) on the upper side of the leaves [46].
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
To examine the growth of T34 hyphae in the leaves of wheat seedlings, five samples of leaves were cut using sterilized scissors and prepared for examination using an electron microscope. The preparation of samples was performed as described in [47]. Scanning was performed using Joel scanning electron microscope (T.330 A) at the central laboratory for inspection and photography of the Faculty of Agriculture, Mansoura University, Egypt.
2.6. Statistical Analysis of Stripe Rust and Slow Rust Components
The analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using BLAPSTAT software [48] following two different models as follows:
where Yijk is an observation of genotype i in replication j, which was planted in experiment k; µ is the general mean; gi, ri, and Ek are the main effects of genotypes (fixed effects), replications, and experiments (random effects), respectively; and eijk is the error. This model was used to identify the differences between the two experiments (Exp. I and Exp. II).
where Yijk is an observation of genotype i in replication j under treatment k, and μ is the general mean; gi, rj, and tk are the main effects of genotypes, replications, and treatment, respectively; and eijk is the error. This model was used to identify the differences between Yr and T34, Yr and TH, and Yr and TV in each experiment, separately.
Yijk = µ + gi + rj + Ek + gyik + eijk
Yijk = µ + rj + tk + gi + tgik + tgrijk + eijk
Broad-sense heritability was calculated using the following formula:
where and are the variance of the lines and the residuals, respectively. r is the number of replicates.
2.7. Genetic Distance between Each Pair of the Tested Genotypes
The tested plant materials were genotyped using 25K i-select SNP array as described in [33,49,50,51]. This sequencing method generated a set of 21,450 SNP markers. Using this marker set, the genetic distance was calculated following the simple matching coefficient method using the R-package “ade4” [52] and visualized as a phylogeny tree using iTol website [53].
3. Results
3.1. Effect of the Different Temperatures on Stripe Rust Infection
The susceptible check “Morocco” showed a highly susceptible response to Pst with IT = 9 in both Exp. I and Exp. II (Table S1). These results indicated the success of the artificial inoculation performed on all genotypes in this study. The ANOVA revealed highly significant differences between the two experiments for stripe rust symptoms (Table 1). Furthermore, highly significant differences were found among the tested genotypes. A significant interaction between the genotypes and experiments (G × E) was found. A high degree of broad-sense heritability (H2) was found with a value of 0.69.

Table 1.
Mean square for stripe rust seedling resistance between the two different temperatures under normal infection.
None of the tested genotypes were found to be immune to Pst in any experiment. In Exp. I, no genotypes were found to be VR (Figure 1a). However, two and five genotypes were found to be R and MR, respectively, in Exp. I. Out of the resistant genotypes, only five (Sohag3, Sohag4, Misr4, Sakha95, and IWA8600840) were found to be MR in both experiments (Figure 1b). On the same pattern, the number of susceptible genotypes was higher in Exp. I than Exp. II. In Exp. I, six, four, and 16 genotypes were found to be MS, S, and VS, respectively, while in Exp. II, five, nine, and eight genotypes were found to be MS, S, and VS, respectively. Most of the susceptible genotypes showed a stable response in both experiments (Figure 1c).
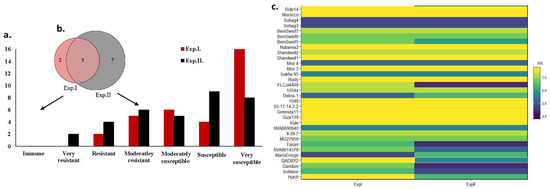
Figure 1.
The response of the 34-tested genotypes to stripe rust in Exp. I and Exp. II: (a) Number of genotypes represent different responses to stripe rust in Exp. I. and Exp. II. (b) Number of common resistant genotypes in Exp. I. and Exp. II. (c) The response of all the tested genotypes in both experiments.
3.2. Effect of the Different Trichoderma spp. on Stripe Rust Symptoms
Due to the presence of highly significant differences between the two experiments for Yr, it was worth investigating the effect of the different Trichoderma spp. on each experiment separately. In Exp. I., the ANOVA revealed highly significant differences among the different treatments (Table 2). Furthermore, highly significant differences were found between IT and slow rusting components under the Yr treatment and each one of the Trichoderma treatments (Table S2). Comparing the IT among the four different treatments, the symptoms of Yr under all three Trichoderma treatments were lower than those that appeared in the Yr treatment (Figure 2a). The T34 treatment was found to have the lowest IT (IT = 1.80). Furthermore, all the Trichoderma spp. increased IP and LP, and decreased PD compared with Yr (Figure 2b–d). The Highest IP and LP, and the lowest PD values, were found under the T34 treatment.

Table 2.
Mean squares for stripe rust seedling resistance among the different Trichoderma species and normal infection in Exp. I.
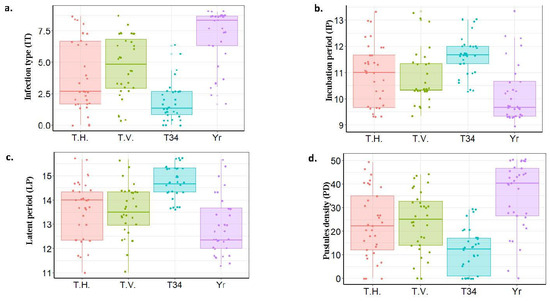
Figure 2.
Boxplots represent stripe rust response of the tested genotypes under different Trichoderma species in Experiment 1. stripe rust symptoms were measured as infection type (a), incubation period (b), latent period (c) and pustules density (d).
Under Exp. II conditions, highly significant differences were found among the four treatments for IT, IP, LP, and PD (Table 3). Furthermore, highly significant differences were found in the IT between Yr and T34, Yr and TH, and Yr and TV (Table S3). Of the four treatments, T34 was found to have the lowest IT average (IT = 1.10), the highest LP and IP, and the lowest PD (Figure 3). TV and TH had almost a similar average of IT with a value of 3.14 and 3.02, respectively (Figure 3a). On the same pattern, TV and TH were found to have almost the same effects on the LP, IP, and PD.

Table 3.
Mean squares for stripe rust seedling resistance among the different Trichoderma species and normal infection in Exp. II.
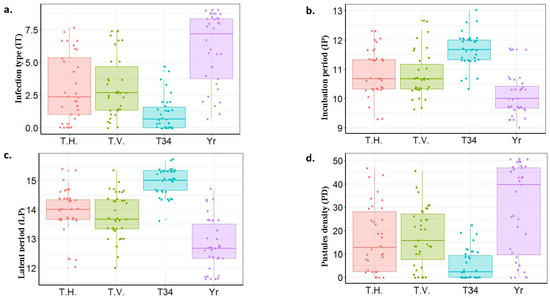
Figure 3.
Boxplots represent stripe rust response of the tested genotypes under different Trichoderma species in Experiment 2. stripe rust symptoms were measured as infection type (a), incubation period (b), latent period (c) and pustules density (d).
To provide more understanding of the effectiveness of the studied Trichoderma spp. on controlling stripe rust, the average of IT under each treatment in both experiments was plotted together in Figure 4a. All the studied Trichoderma spp. decreased the IT compared with Yr. However, the lowest values in both experiments were found under the T34 treatment followed by TH and then TV. The effect of T34 seemed to be more stable under both temperatures’ regimes. The response of all the tested genotypes under each Trichoderma treatment in each year was plotted to compare the stability of the effect of each Trichoderma spp. (Figure 4b and Figure S1). Under the T34 treatment, eleven genotypes showed stable immune or VR response (0 < IT < 1) in both experiments while this number decreased to three and one stable genotypes under the TV and TH treatments, respectively (Figure 4b and Figure S1). Furthermore, the susceptible check “Morocco” was found to be R and VR under T34 in Exp. I and Exp. II, respectively. This susceptible check was still S in both experiments under TH. Furthermore, it was S and MR under the TV treatment in Exp. I and Exp. II, respectively.
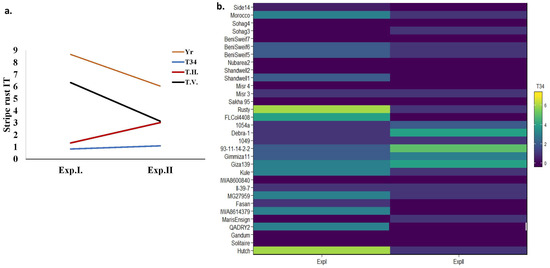
Figure 4.
(a) Average IT scores in both experiments under Yr and three Trichoderma treatments. (b) The response of each of the evaluated genotypes under T34 treatment in both experiments.
3.3. Insights into the Effect of T34 on Stripe Rust Disease
3.3.1. Effectiveness of T34 in Controlling Stripe Rust under Different Temperature Degrees
Under Exp. I conditions, a total number of 7 resistant and 26 susceptible genotypes were found (Figure 5a). However, T34 was able to increase the total number of resistant genotypes to 31, which could be classified into 7 immune, 11 VR, 5 R, and 8 MR ones. Furthermore, it decreased the 26 susceptible genotypes to only 2 MS genotypes. Notably, not all the immune genotypes under T34 were resistant under the Yr treatment. However, two genotypes were susceptible under normal Yr conditions and became immune under T34.
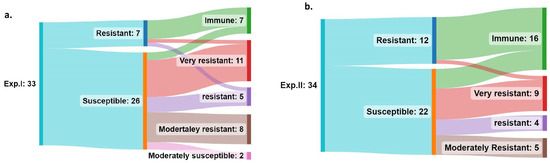
Figure 5.
Effect of T34 on the response of the 34-tested genotypes compared with their response under normal stripe rust infection in Exp. I (a) and Exp. II (b).
Under Exp. II conditions, a total of 12 and 22 genotypes were found to be resistant and susceptible to Pst under Yr treatment. T34 was able to improve the resistance level of the tested material and all the genotypes were found to be resistant with 16 immune, 9 VR, 4 R, and 5 MR ones (Figure 5b). Five genotypes were found to be susceptible under the Yr treatment and became immune under T34.
To provide more understanding of the role that T34 plays in controlling WSR, an electron microscope was used to investigate the development of T34 at different times after treatments (Figure 6). After one day of the T34 treatment, T34 grew and started producing hypha (Figure 6a). These hyphae grew extremely quickly during the first week and spread inside wheat leaf tissues (Figure 6b). Notably, after one day of the T34 treatment, T34 hyphae were able to interact with Pst urediniospores and prevent them from growing (Figure 6c). Hence, an increase in IP and LP, and a decrease in PD were obtained as a result of this interaction.
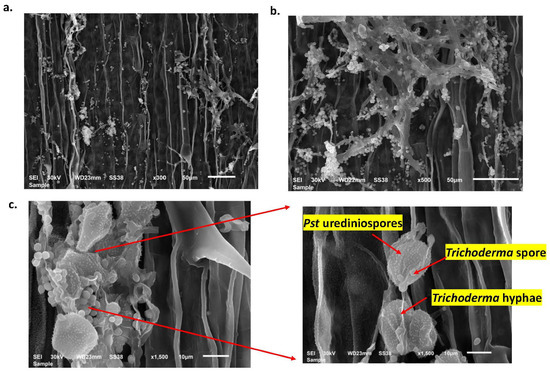
Figure 6.
Growing of Trichoderma asperellum T34 inside wheat seedling leaves after one day (a) and seven days (b) after inoculation. (c) Interaction between T34 spores and hyphae and Puccinia striiformis f. sp. Tritici (Pst) urediniospores after one day after T34 treatment.
3.3.2. Effectiveness of T34 as a Bioagent Controlling Stripe Rust in Different Wheat Genetic Backgrounds
To provide more understanding of the response of different genotypes to the T34 treatment, the genetic distance among the tested genotypes was calculated. The tested genotypes were found to be distributed among three different clusters (Figure 7a). The genetic distance ranged from 0.047 between “Hamira” and “Kule2” to 0.501 between “Debra-1” and “Benisweif6” genotypes (Table S4). Furthermore, these genotypes were distributed among the three clusters far from each other, except for Misr4 and Sakha95, which were closely related. Moreover, the distance between these five immune genotypes ranged from 0.273 between “Misr4” and “Sakha95” to 0.489 between “Solitaire” and “Sohag4”.
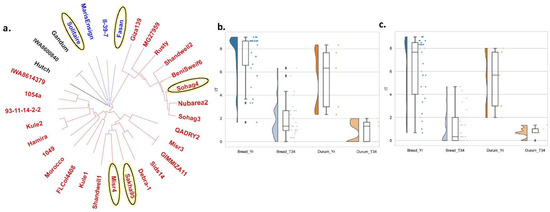
Figure 7.
Genetic diversity of the tested wheat genotypes: (a) genetic distance between each pair of the studied wheat genotypes, highlighted genotypes are the common immune genotypes in both experiments under Trichoderma asperlleum T34 treatment; (b,c) the effect of T34 on stripe rust in fection type in bread and durum wheat under Exp. I. conditions (b) and Exp. II. conditions (c).
Because the tested genotypes contained bread and durum wheat genotypes, the effect of T34 in each species under each experimental condition was investigated separately and is presented in Figure 7b,c. In Exp. I, T34 decreased the average of IT in bread wheat from 7.35 to 1.95 (p-value = 5.15 × 10−15). While it decreased the IT in the durum wheat from 5.53 to 1.00 (p-value = 0.008) (Figure 7b). Under Exp. II conditions, T34 decreased the IT from 6.18 to 1.16 (p-value = 6.10 × 10−12) in bread wheat and from 5.27 to 0.73 (p-value = 0.006) in durum wheat (Figure 7c).
4. Discussion
Wheat stripe rust (WSR) is a serious disease that affects wheat planting areas and causes significant yield losses. Biological control has been reported as an effective way to restrict different fungal diseases in different plants [23,24,25]. Trichoderma spp. are among the effective bioagents that are available at the commercial level [54,55,56,57,58]. In our previous study [33], T34 was found as an effective bioagent in controlling stripe rust in a diverse wheat panel. In this study, we studied the possibility of biological control of this serious disease using three factors: environments (different temperature degrees), bioagents (different Trichoderma spp.), and host plants (different wheat germplasms) (Figure 8).
Figure 8.
Studied factors of the biological control of stripe rust resistance in wheat.
4.1. Factor 1: Testing the Effectiveness of Biological Control in Different Environments
Pst can grow and infect wheat plants in a wide range of environmental conditions. Out of these conditions, temperature and humidity have been recorded as the most important factors that significantly affect the ability of the fungus to grow rapidly and infect more plants [59,60]. Recent studies have mentioned that temperature is more important than humidity [61]. The optimum temperature for Pst ranges from 10 °C to 15 °C [62]. However, the appearance of WSR in warmer environments has recently been reported in many regions around the world [63,64,65]. In this study, two different greenhouse experiments were conducted with two temperature regimes 10–12 °C and 16–18 °C to provide a wide range of environmental conditions that are preferred by Pst. The humidity degree was at optimum in both experiments (>80%). The susceptible check “Morocco” showedVS response in both experiments confirming the success of the artificial inoculation and that both experimental conditions are suitable for the Pst pathogen. The presence of highly significant differences between the two experiments for IT confirmed that the studied temperatures differently affect the virulence of Pst (Table 1). However, the absence of immune genotypes in both experiments and the presence of stableVS genotypes in both experiments confirmed the urgent need for controlling WSR under both conditions. The effect of Trichoderma spp. on reducing the severity of various plant diseases was previously investigated in many crops. However, few studies were performed on wheat plants, which are an important cereal crop. Therefore, Trichoderma seems to be a useful application in fighting against plant diseases in various prominent crops.
4.2. Factor 2: Testing the Effectiveness of Different Bioagents in the Biological Control of WSR
The three tested Trichoderma species were available commercially as bioagents to control different plant fungal diseases [58,66,67,68]. In both experiments, highly significant differences were found among these three Trichoderma treatments and Yr for the IT and slow rusting components suggesting that all the tested Trichoderma treatments could be effective in controlling WSR under different temperature degrees (Table 2, Table 3 and Tables S2 and S3). All the three Trichoderma species were found to decrease the IT, increase LP and IP, and decrease PD compared with Yr (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Out of the three Trichoderma spp., T34 and TH seemed to be more effective in controlling WSR than TV. However, TH was less stable than T34 under different temperatures. TV was able to decrease IT in Exp. II but not effective in Exp. I. Previous studies reported the effectiveness of TV and TH in controlling wheat stem rust disease (Puccinia graminis Pers.:Pers. f. sp. tritici Eriks. and E. Henn. (Pg)) in wheat [36]. Pg requires higher temperatures than Pst to produce infection. In our current study, TV was very effective in controlling WSR in Exp. II, which was performed under a warmer temperature regime. Therefore, TV seems to require a warmer temperature to grow and control rust pathogens. It was found to be an effective bioagent to control leaf rust in summer crops such as soybean [69]. Therefore, TV is not recommended as a bioagent for WSR. Other studies concluded the efficiency of TH in controlling wheat leaf rust disease [70]. Based on our results and previous studies, we can conclude that T34 is the best commercial bioagent in controlling WSR, followed by TH.
T34 was found to greatly increase WSR resistance in both experiments. Under Exp. II conditions, no genotypes were found to be susceptible and only two genotypes were still MS (Figure 5). In our previous study [33], T34 improved WSR in a set of 198 spring wheat genotypes and only nine genotypes were found to be susceptible. That study was conducted under greenhouse conditions similar to Exp. I in the recent study. From our recent study, we found that the efficiency of T34 increases when the temperature becomes warmer. However, it is still effective under cooler temperatures. T34 was reported to resist different plant pathogens using two different mechanisms, direct mechanism and indirect mechanism [26]. Figure 6 represents the direct interaction between T34′ hyphae and Pst urediniospores that prevents Pst urediniospores from growing. The indirect mechanism occurs as a side effect of the growing T34′ hyphae. T34′ hyphae were reported to colonize the outer layers of the leaves and alter the transcriptome and proteome machinery. Therefore, increasing plant growth and nutrient uptake and producing priming response [26].
4.3. Factor 3: Testing the Effectiveness of T34 Bioagent in Controlling WSR in Different Wheat Germplasm
T34 was found to cause a priming response in wheat plants that induce resistance against different pathogens [32]. Priming response mainly depends on inducing specific genes in the plant genome [33]. Without these genes, wheat plants cannot respond to the T34 bioagent. Therefore, understanding the genetic diversity among the tested genotypes is a key point to investigate the effectiveness of T34 in controlling WSR in different wheat genetic backgrounds. In the recent study, different degrees of genetic distance were found among the 34 studied genotypes ranging from very low to high (Table S4). It was reported that high genetic distances were obtained when the studied materials were from different geographic origins [51]. The current studied material was collected from ten different countries around the world (Table S1). They were clustered into three different distinct groups (Figure 7a). Based on the genetic diversity results, the studied materials could be considered as highly genetically diverse germplasm.
Furthermore, the five immune genotypes under T34 in both experiments were found to be located in different subgroups and have a high genetic distance. These results suggested that T34 could induce WSR resistance and produce the priming response in a wide range of wheat genetic backgrounds. Similar results were found in our previous study conducted on 198 spring wheat genotypes originating from 22 different countries. Moreover, in both experiments, T34 was able to improve WSR resistance in bread and durum wheat that contains different genomes. Therefore, we can conclude that T34 seems to be an effective bioagent in controlling WSR in different wheat genetic backgrounds and species.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the two experiments were conducted under two ranges of temperatures that significantly affect WSR symptoms. T34 was found as the best Trichoderma species to control WSR under different environmental conditions followed by TH, which was effective but less stable. TV was found to be effective in controlling WSR under warmer conditions. However, under normal circumstances, it was not effective as a bioagent. T34 was found to be effective in inducing resistance and producing a priming response in different wheat genetic backgrounds. The results of this study provide new and important information on the effectiveness of Trichoderma spp. as a bioagent against Pst. It was noted that not all genotypes have a consistent response to Trichoderma spp. Therefore, the genotypes should be first tested to T34 to confirm their stable response. Such an application will be helpful to improve the resistance of high-yielding wheat genotypes that may have susceptibility to stripe rust races. This is the first study to test the effectiveness of different Trichoderma species in controlling an important wheat disease such as WSR. More studies are needed to provide a better understanding of the effectiveness of T34 in controlling WSR at the adult growth stage and study the limitations of using such an application.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture13091755/s1, Table S1: List of the tested genotypes, their country of origin, wheat type, and response to stripe rust, Trichoderma asperlleum T34, Trichoderma harzianum (TH), and Trichoderma verdinium (TV) under the differnert temperature degrees in Exp. I and Exp. II, Table S2: Mean square between Yr and the different Trichoderma treatments in the tested 34-genotypes under Exp. I conditions, Table S3: Mean square between Yr and the different Trichoderma treatment in the tested 34-genotypes under Exp. II conditions, Table S4: Genetic distance between each pair of the 34-tested genotypes. Figure S1: The response of each of the evaluated genotype under Trichoderma harzianum (T.H) (a), and Trichoderma verdinium TV (b) in both experiments.
Author Contributions
A.M.I.M. designed the experiment, performed the genetic and phenotyping analysis, discussed the results, and drafted the manuscript. A.B. reviewed the manuscript. S.M.E. performed the phenotyping for stripe rust. The authors agreed to be accountable for the content of the work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Marker data were provided by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Costs for open-access publishing were partially funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation, grant 491250510).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Sakha’s station team of wheat breeding for help in conducting the experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
WSR: wheat stripe rust; T34: Trichoderma asperellum T34; TH: Trichoderma harzianum; TV: Trichoderma verdinium.
References
- Yuan, F.P.; Zeng, Q.D.; Wu, J.H.; Wang, Q.L.; Yang, Z.J.; Liang, B.P.; Kang, Z.S.; Chen, X.H.; Han, D.J. QTL mapping and validation of adult plant resistance to stripe rust in chinese wheat landrace humai 15. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.M. Epidemiology and control of stripe rust [Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici] on wheat. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 27, 314–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellings, C.R. Global status of stripe rust: A review of historical and current threats. Euphytica 2011, 179, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markell, S.G.; Milus, E.A. Emergence of a novel population of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in eastern United States. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbasyoni, I.S.; El-Orabey, W.M.; Morsy, S.; Baenziger, P.S.; Al Ajlouni, Z.; Dowikat, I. Evaluation of a global spring wheat panel for stripe rust: Resistance loci validation and novel resources identification. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Zeid, M.A.; Mourad, A.M.I. Genomic regions associated with stripe rust resistance against the Egyptian race revealed by genome-wide association study. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, A.M.I.; Abou-Zeid, M.A.; Eltaher, S.; Baenziger, P.S.; Börner, A. Identification of candidate genes and genomic regions associated with adult plant resistance to stripe rust in spring wheat. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmail, S.M.; Draz, I.S.; Ashmawy, M.A.; El-Orabey, W.M. Emergence of new aggressive races of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici causing yellow rust epiphytotic in Egypt. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 114, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, I.; Esmail, S.; Abou-zeid, M.; Hafez, Y. Changeability in stripe rust infection and grainy Yield of wheat associated to climatic conditions. Environ. Biodiv. Soil Secur. 2019, 2, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoun, M.; Chen, X.; Somo, M.; Xu, S.S.; Li, X.; Elias, E.M. Novel stripe rust all-stage resistance loci identified in a worldwide collection of durum wheat using genome-wide association mapping. Plant Genome 2021, 14, e20136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, Z.; Ali, M.; Mirza, J.I.; Fayyaz, M.; Majeed, K.; Naeem, M.K.; Aziz, A.; Trethowan, R.; Ogbonnaya, F.C.; Poland, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association and Genomic Prediction for Stripe Rust Resistance in Synthetic-Derived Wheats. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvet, L.; Percival-Alwyn, L.; Berry, S.; Fenwick, P.; Mantello, C.C.; Sharma, R.; Holdgate, S.; Mackay, I.J.; Cockram, J. Wheat genetic loci conferring resistance to stripe rust in the face of genetically diverse races of the fungus Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, I.; Saripalli, G.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, A.; Singh, R.; Batra, R.; Sharma, P.K.; Balyan, H.S.; Gupta, P.K. Meta-QTLs and candidate genes for stripe rust resistance in wheat. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tene, M.; Adhikari, E.; Cobo, N.; Jordan, K.W.; Matny, O.; del Blanco, I.A.; Roter, J.; Ezrati, S.; Govta, L.; Manisterski, J.; et al. GWAS for Stripe Rust Resistance in Wild Emmer Wheat (Triticum dicoccoides) Population: Obstacles and Solutions. Crops 2022, 2, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, M.; Zhang, J.; Bulli, P.; Abate, Z.; Chao, S.; Cantu, D.; Bossolini, E.; Chen, X.; Pumphrey, M.; Dubcovsky, J. A Genome-wide association study of resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) in a worldwide collection of hexaploid spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2015, 5, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemui, S.K.; Huluka, A.B.; Tesfayei, K.; Haileselassie, T.; Uauy, C. Genome-wide association mapping identifies yellow rust resistance loci in Ethiopian durum wheat germplasm. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0243675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Messoadi, K.; El Hanafi, S.; El Gataa, Z.; Kehel, Z.; Bouhouch, Y.; Tadesse, W. Genome wide association study for stripe rust resistance in spring bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 104, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, F.; Long, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Genome-wide association mapping reveals potential novel loci controlling stripe rust resistance in a Chinese wheat landrace diversity panel from the southern autumn-sown spring wheat zone. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinnia, F.; Geyer, M.; Schürmann, F.; Rudolphi, S.; Holzapfel, J.; Kempf, H.; Stadlmeier, M.; Löschenberger, F.; Morales, L.; Buerstmayr, H.; et al. Genome-wide association study and genomic prediction of resistance to stripe rust in current Central and Northern European winter wheat germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 3583–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yan, X.; Weldu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, E.; Xia, X.; He, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, D. Genome-wide association mapping of leaf rust and stripe rust resistance in wheat accessions using the 90K SNP array. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1233–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Guan, F.; Duan, L.; Long, L.; Tang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, J.; Qi, P.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Stable Stripe Rust Resistance Loci in a Chinese Wheat Landrace Panel Using the 660K SNP Array. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 783830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavani, S.; Singh, P.K.; Qureshi, N.; He, X.; Biswal, A.K.; Juliana, P.; Dababat, A.; Mourad, A.M.I. Globally Important Wheat Diseases: Status, Challenges, Breeding and Genomic Tools to Enhance Resistance Durability. In Genomic Designing for Biotic Stress Resistant Cereal Crops; Kole, C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: New Delhi, India, 2021; pp. 59–128. ISBN 9783030758790. [Google Scholar]
- Barratt, B.I.P.; Moran, V.C.; Bigler, F.; van Lenteren, J.C. The status of biological control and recommendations for improving uptake for the future. BioControl 2018, 63, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messing, R.; Brodeur, J. Current challenges to the implementation of classical biological control. BioControl 2018, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodeur, J.; Abram, P.K.; Heimpel, G.E.; Messing, R.H. Trends in biological control: Public interest, international networking and research direction. BioControl 2018, 63, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambugala, K.M.; Daranagama, D.A.; Phillips, A.J.L.; Kannangara, S.D.; Promputtha, I. Fungi vs. Fungi in Biocontrol: An Overview of Fungal Antagonists Applied Against Fungal Plant Pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 604923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodaran, T.; Rajan, S.; Manoharan, M.; Gopal, R. Biological Management of Banana Fusarium Wilt Caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense Tropical Race 4 Using Antagonistic Fungal Isolate CSR-T-3 (Trichoderma reesei). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 595845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocurull, M.; Fullana, A.M.; Ferro, M.; Valero, P.; Escudero, N.; Saus, E.; Gabaldón, T.; Sorribas, F.J. Commercial Formulates of Trichoderma Induce Systemic Plant Resistance to Meloidogyne incognita in Tomato and the Effect Is Additive to That of the Mi-1.2 Resistance Gene. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Spada, F.; Stracquadanio, C.; Riolo, M.; Pane, A.; Cacciola, S.O. Trichoderma Counteracts the Challenge of Phytophthora nicotianae Infections on Tomato by Modulating Plant Defense Mechanisms and the Expression of Crinkler, Necrosis-Inducing Phytophthora Protein 1, and Cellulose-Binding Elicitor Lectin Pathogenic Effecto. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 583539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros, H.A.; Vieira, J.; Filho, D.A.; Freitas, L.G. De Tomato progeny inherit resistance to the nematode Meloidogyne javanica linked to plant growth induced by the biocontrol fungus Trichoderma atroviride. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2017, 7, 40216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, N.M.A.; Eraky, A.M.I.; Sallam, A. Effect of Trichoderma spp. on Fusarium wilt disease of tomato. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 4463–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morán-Diez, M.E.; Martínez de Alba, Á.E.; Rubio, M.B.; Hermosa, R.; Monte, E. Trichoderma and the plant heritable priming responses. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmail, S.M.; Omar, G.E.; Mourad, A. In-depth understanding of the genetic control of stripe rust resistance (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) induced in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by Trichoderma asperellum T34. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, T.; Mehboob, F.; Hyder, M.Z.; Zainy, Z.; Xu, L.; Huang, L.; Farrakh, S. Control of stripe rust of wheat using indigenous endophytic bacteria at seedling and adult plant stage. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omara, R.I.; Essa, T.A.; Khalil, A.A.; Elsharkawy, M.M. A case study of non-traditional treatments for the control of wheat stem rust disease. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, H.H.A.; Rashad, Y.M.; Ibrahim, S.A. Biocontrol of stem rust disease of wheat using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Trichoderma spp. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 103, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, Y.; Abdelfatah, A.; El-Nashar, F.; Badr, M.; Elkady, S. Management of barley net blotch using Trichoderma asperellum (T34), eugenol, non-traditional compounds and fungicides. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2019, 29, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degani, O.; Gordani, A. New Antifungal Compound, 6-Pentyl-α-Pyrone, against the Maize Late Wilt Pathogen, Magnaporthiopsis maydis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, G.M.; Shabana, Y.M.; Ismail, A.E.; Rashad, Y.M. Trichoderma harzianum: A biocontrol agent against Bipolaris oryzae. Mycopathologia 2007, 164, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Maheshwari, V. Biological seed treatment for the control of loose smut of wheat. Indian Phytopathol. 2001, 54, 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Bayoumi, Y.; Taha, N.; Shalaby, T.; Alshaal, T.; El-Ramady, H. Sulfur promotes biocontrol of purple blotch disease via Trichoderma spp. and enhances the growth, yield and quality of onion. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 134, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janisiewicz, W.J.; Marchi, A. Control of storage rots on various pear cultivars with a saprophytic strain of Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Dis. 1992, 76, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stakman, E.C.; Stewart, D.M.; Loegering, W.Q. Identification of Physiologic Races of Puccinia Graminis var. tritici; USDA_ARS: Washington, DC, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- McNeal, F.H.; Konzak, C.F.; Smith, E.P.; Tate, W.S.; Russell, T.S. A Uniform System for Recording and Processing Cereal Research Data; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, ARS: Washington, DC, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Katsuya, K.; Green, G.J. Reproductive potentials of races 15B and 56 of wheat stem rust. Can. J. Bot. 1967, 45, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlevliet, J.E.; Ommeren, A.V. Partial resistance of barley to leaf rust, Puccinia hordei. II. Relationship between field trials, micro plot tests and latent period. Euphytica 1975, 24, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, M.; Fergusen, L. Thee of SEM in pollen morphology and plant systemic. In Scanning Electron Microscopy Studies in Taxonomy and Functional Morphology; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1990; pp. 45–68. [Google Scholar]
- Utz, H. PLABSTAT: A Computer Program for Statistical Analysis of Plant Breeding Experiments; Institute of Plant Breeding, Seed Science and Population Genetics: Hohenheim, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrov, V.; Kartseva, T.; Alqudah, A.M.; Kocheva, K.; Tasheva, K.; Börner, A.; Misheva, S. Genetic diversity, linkage disequilibrium and population structure of bulgarian bread wheat assessed by genome-wide distributed SNP markers: From old germplasm to semi-dwarf cultivars. Plants 2021, 10, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amro, A.; Harb, S.; Youssef, K.; Ali, M.M.F.; Mohammed, A.G.; Mourad, A.M.I.; Afifi, M.; Börner, A.; Sallam, A. Growth responses and genetic variation among highly ecologically diverse spring wheat genotypes grown under seawater stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 996538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, A.M.I.; Eltaher, S.; Börner, A.; Sallam, A. Unlocking the genetic control of spring wheat kernel traits under normal and heavy metals stress conditions. Plant Soil 2023, 484, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dray, S.; Dufour, A.B. The ade4 Package: Implementing the Duality Diagram for Ecologists. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordo, C.A.; Monaco, C.I.; Segarra, C.I.; Simon, M.R.; Mansilla, A.Y.; Perelló, A.E.; Kripelz, N.I.; Bayo, D.; Conde, R.D. Trichoderma spp. as elicitors of wheat plant defense responses against Septoria tritici. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boamah, S.; Zhang, S.; Xu, B.; Li, T.; Calderón-Urrea, A. Trichoderma longibrachiatum (TG1) Enhances Wheat Seedlings Tolerance to Salt Stress and Resistance to Fusarium pseudograminearum. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 741231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitti, A.; Bevilacqua, V.; Logozzo, G.; Bochicchio, R.; Amato, M.; Nuzzaci, M. Seed Coating with Trichoderma harzianum T-22 of Italian Durum Wheat Increases Protection against Fusarium culmorum-Induced Crown Rot. Agriculture 2022, 12, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segarra, G.; Van Der Ent, S.; Trillas, I.; Pieterse, C.M.J. MYB72, a node of convergence in induced systemic resistance triggered by a fungal and a bacterial beneficial microbe. Plant Biol. 2009, 11, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, Y.M.; El-Nagar, A.S.; Elzaawely, A.A.; Kamel, S.; Maswada, H.F. Biological control of podosphaera xanthii the causal agent of squash powdery mildew disease by upregulation of defense-related enzymes. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2018, 28, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Khan, M.I.; Shahbaz, M.; Nabi, G.; Zeeshan, M.; Aleem, S.; Hussain, M.; Saadia. Environmental Factors and Yellow Rust Epidemic on Wheat Varieties in Punjab, Pakistan. J. Agric. Food 2022, 3, 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- Grabow, B.S.; Shah, D.A.; DeWolf, E.D. Environmental conditions associated with stripe rust in kansas winter wheat, Kansas State University. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 2306–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Liao, Z.; Wu, S.; Nobis, M.P.; Wang, J.; Wu, N. Impact of climate change on wheat security through an alternate host of stripe rust. Food Energy Secur. 2022, 11, e356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, D. The Wheat Rusts—Breeding for Resistance; Frnakel, R., Grossma, M., Mgliga, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; ISBN 9781425803780. [Google Scholar]
- Hovmøller, M.S.; Walter, S.; Bayles, R.A.; Hubbard, A.; Flath, K.; Sommerfeldt, N.; Leconte, M.; Czembor, P.; Rodriguez-Algaba, J.; Thach, T.; et al. Replacement of the European wheat yellow rust population by new races from the centre of diversity in the near-Himalayan region. Plant Pathol. 2016, 65, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, A.; Lewis, C.M.; Yoshida, K.; Ramirez-Gonzalez, R.H.; de Vallavieille-Pope, C.; Thomas, J.; Kamoun, S.; Bayles, R.; Uauy, C.; Saunders, D.G.O. Field pathogenomics reveals the emergence of a diverse wheat yellow rust population. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milus, E.A.; Kristensen, K.; Hovmøller, M.S. Evidence for increased aggressiveness in a recent widespread strain of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici causing stripe rust of wheat. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kazzaz, M.K.; Ghoniem, K.E.; Ashmawy, M.A.; Omar, G.E.; Hafez, Y.M. Suppression of wheat strip rust disease caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. Tritici by eco-friendly bio-control agents correlated with yield improvement. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 8385–8393. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, A.F. Genetic variation and biological control of Fusarium graminearum isolated from wheat in Assiut-Egypt. Plant Pathol. J. 2016, 32, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omara, R.I.; El-Kot, G.A.; Fadel, F.M.; Abdelaal, K.A.A.; Saleh, E.M. Efficacy of certain bioagents on patho-physiological characters of wheat plants under wheat leaf rust stress. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 106, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martanto, E.A.; Tanati, A.E.; Baan, S.; Tata, H.R.; Murdjoko, A. Effectiveness of biological control of trichoderma harzianum on soybean leaf rust disease and the production in west papua lowland, indonesia. Biodiversitas 2020, 21, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Haroon, A.; Hussain, M.A.; Chaudary, A.-U.-R.; Bashir, M.A.; Atta, S.; Bashir, S.; Bodlah, M.A. Potential of Trichoderma Isolates to Control Plant Pathogen, Leaf Rust on Different Commercial Wheat Varieties/Genotypes. In Wheat-Recent Advances; Ansari, M.-R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; pp. 197–212. ISBN 978-1-80355-523-2. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).