Rice-Fallow Targeting for Cropping Intensification through Geospatial Technologies in the Rice Belt of Northeast India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
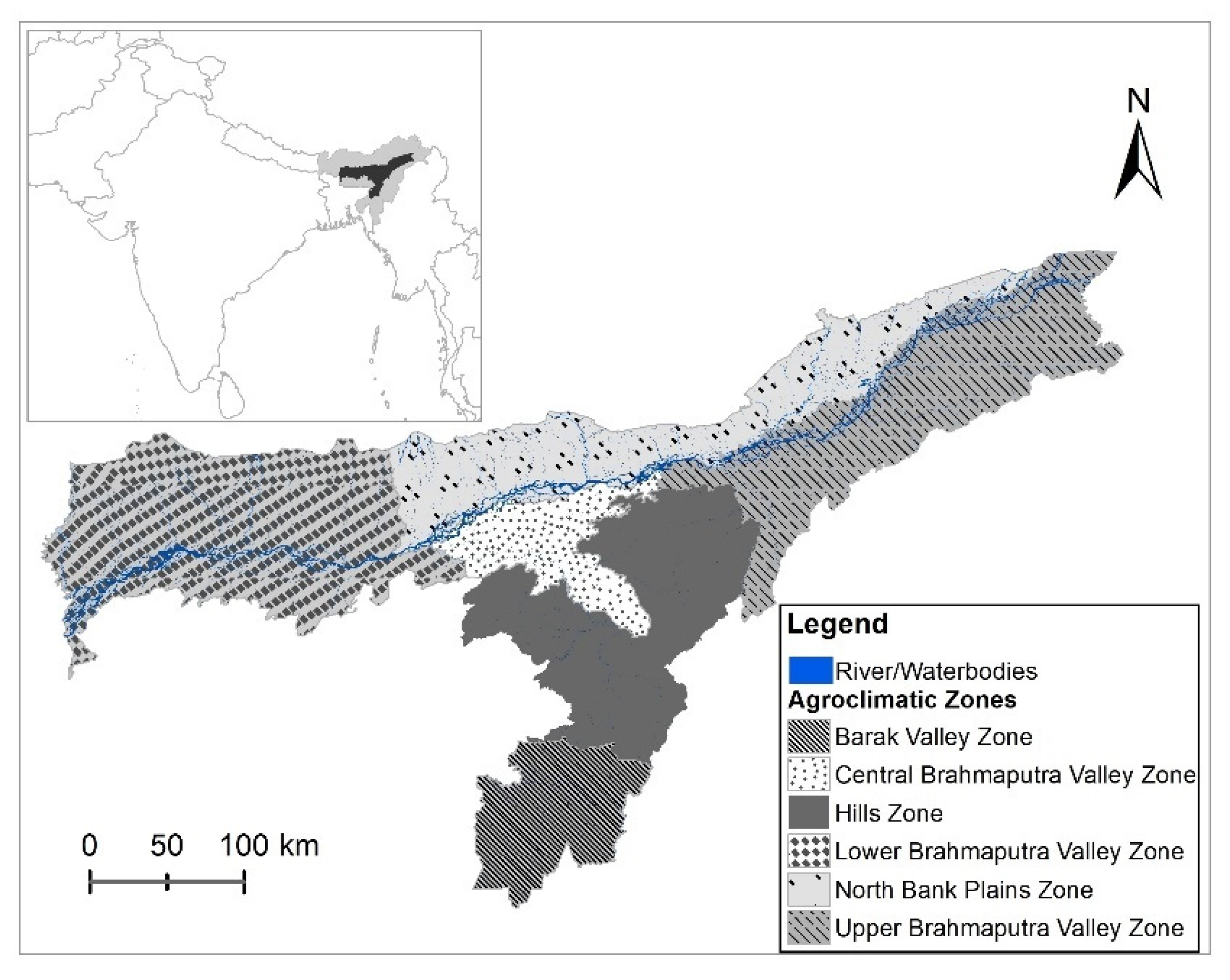
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Ground Data
2.2.2. Earth Observation Data
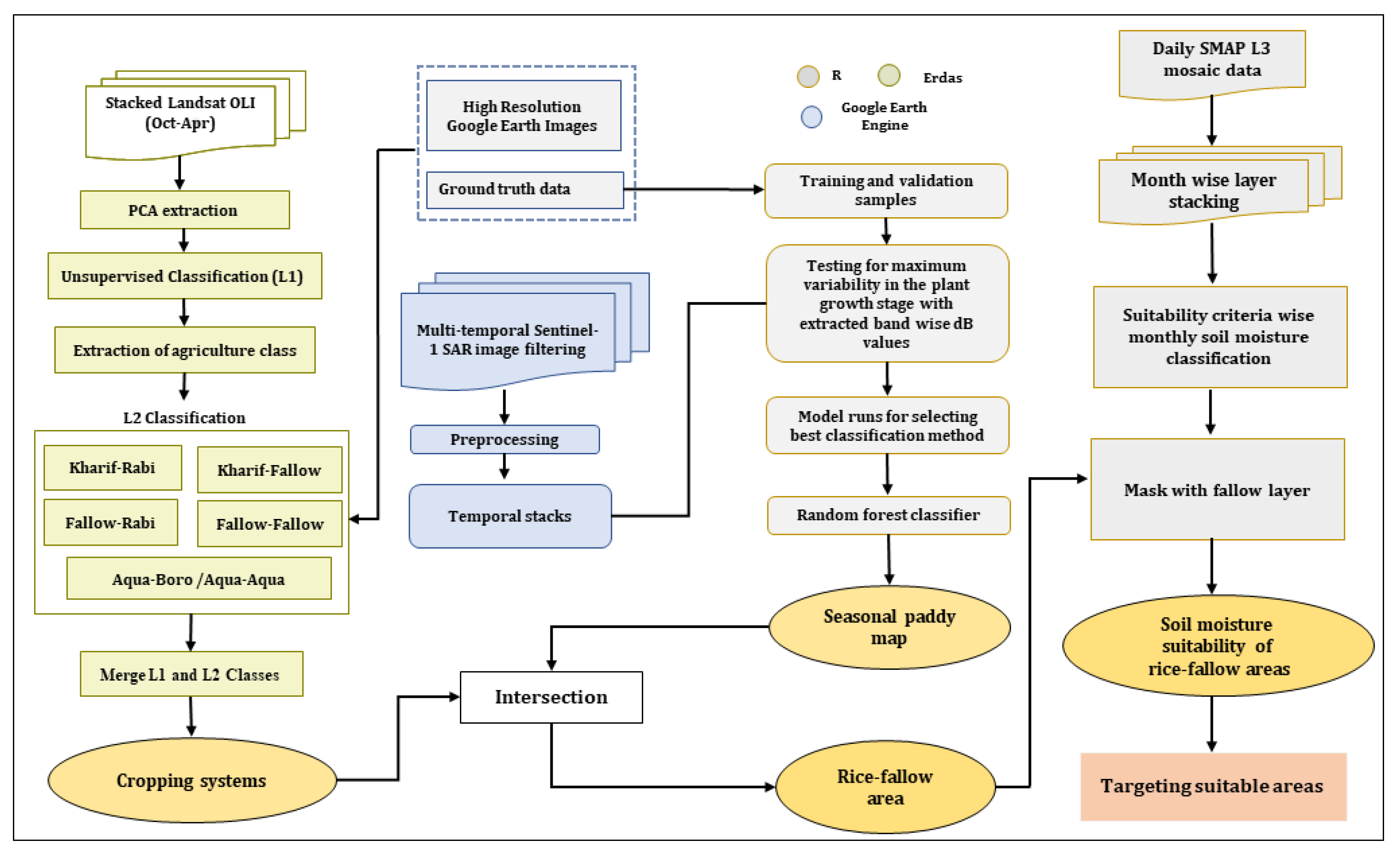
2.3. Mapping
2.3.1. Rice Area Mapping
2.3.2. Rice-Fallow Mapping
2.3.3. Delineating Suitable Rice-Fallow Areas Based on Soil Moisture
2.4. Targeting Suitable Rice-Fallow Areas
3. Results
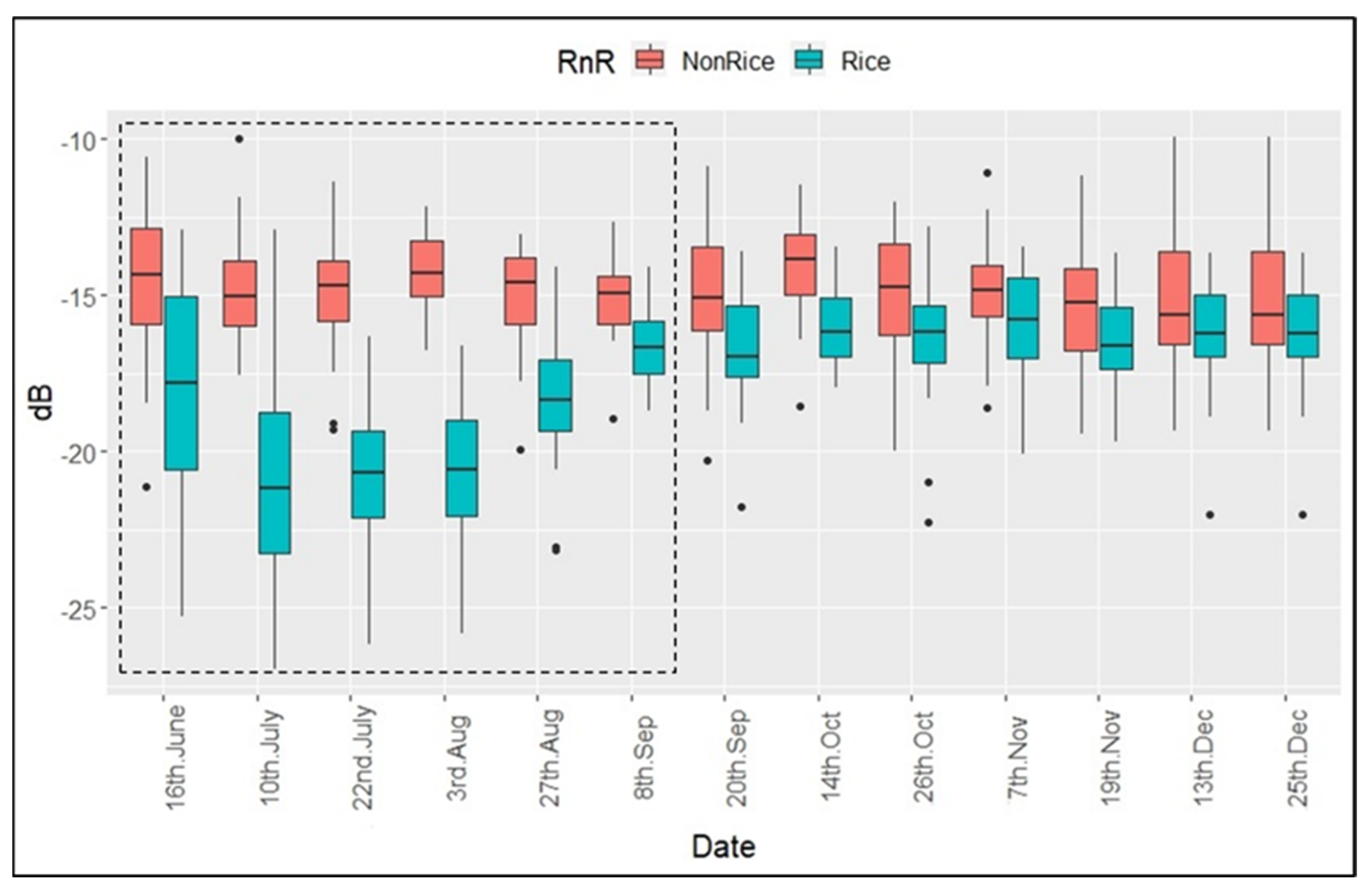
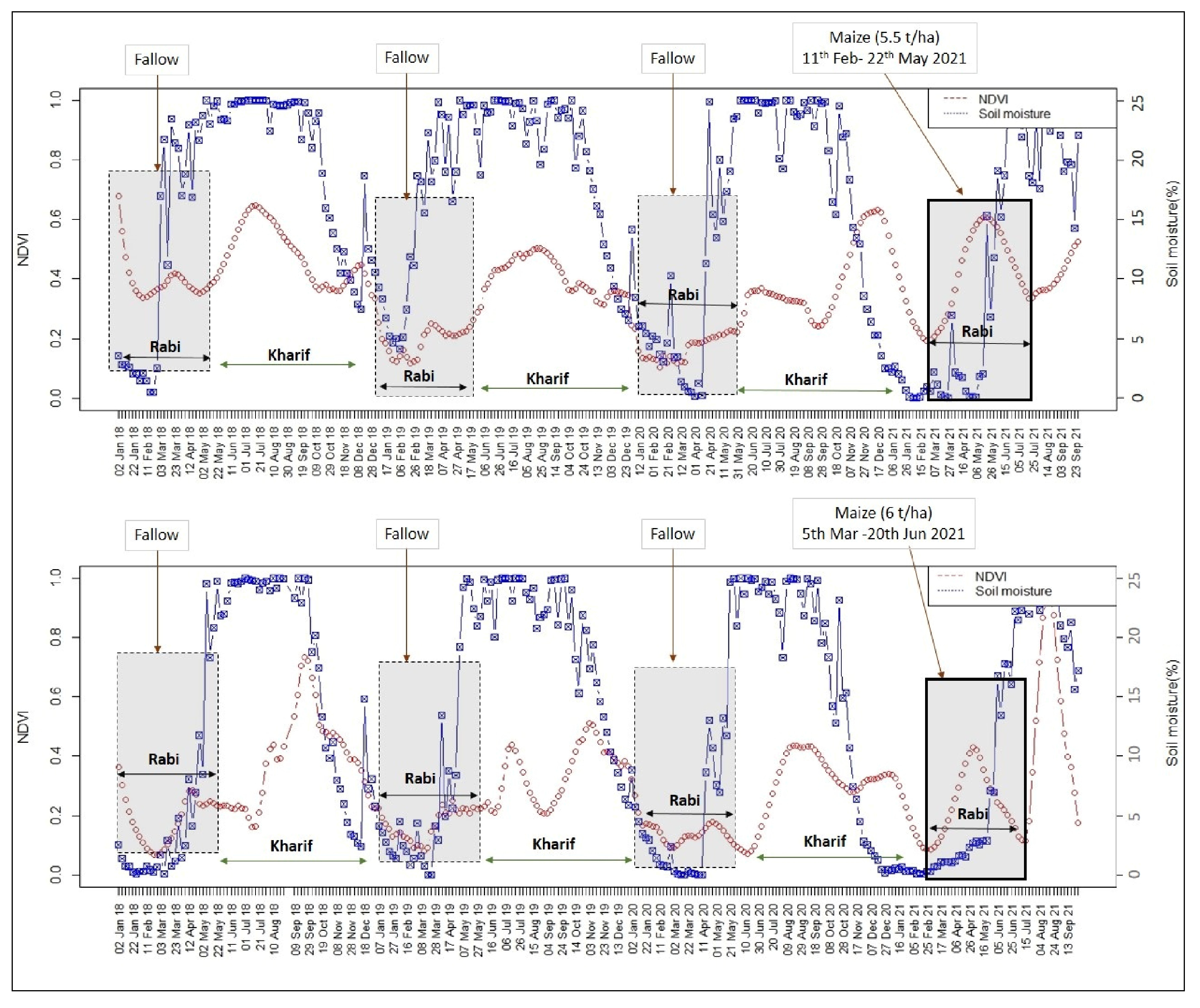
3.1. Variables Governing the Existence of Rice-Fallows
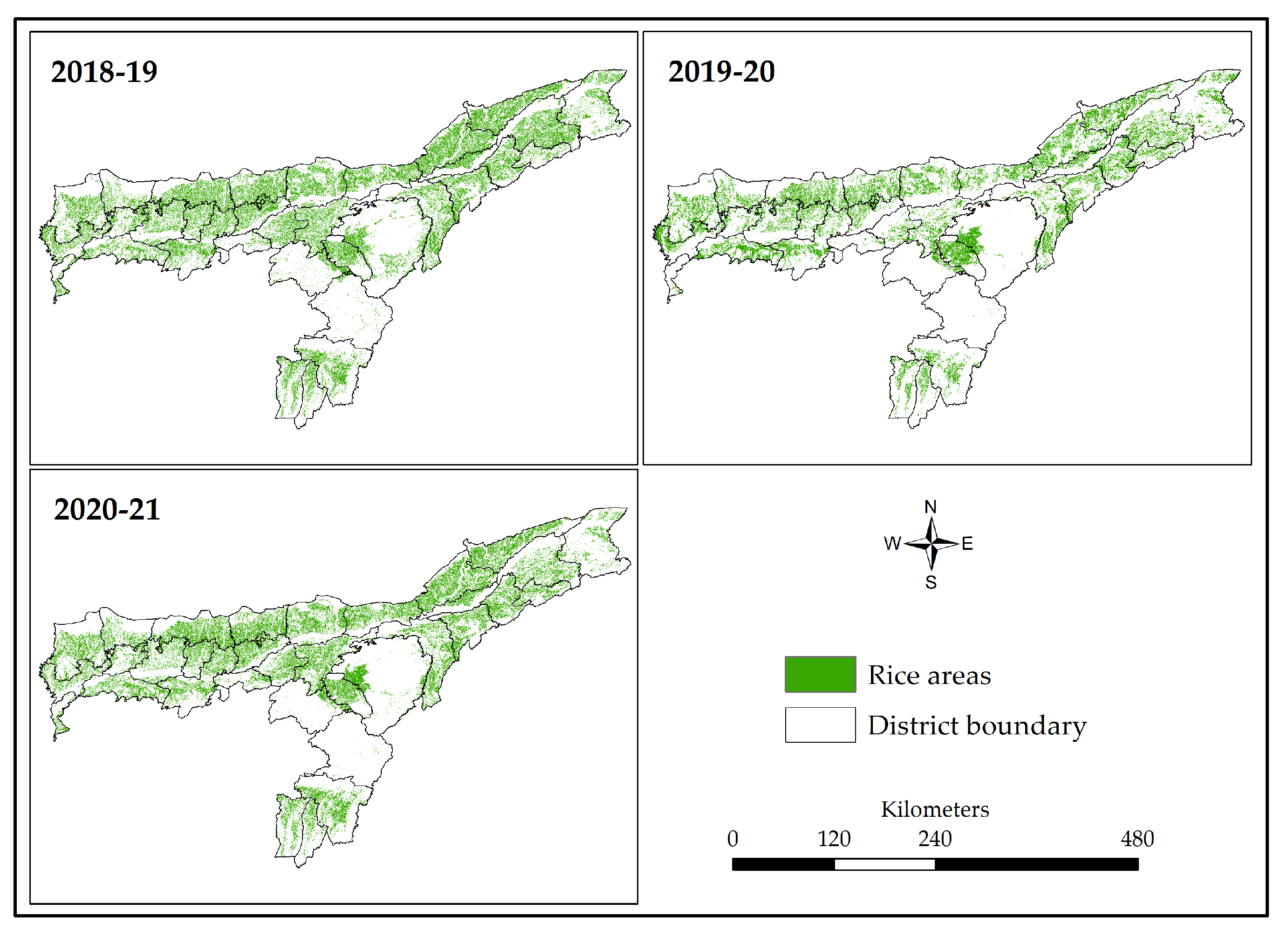
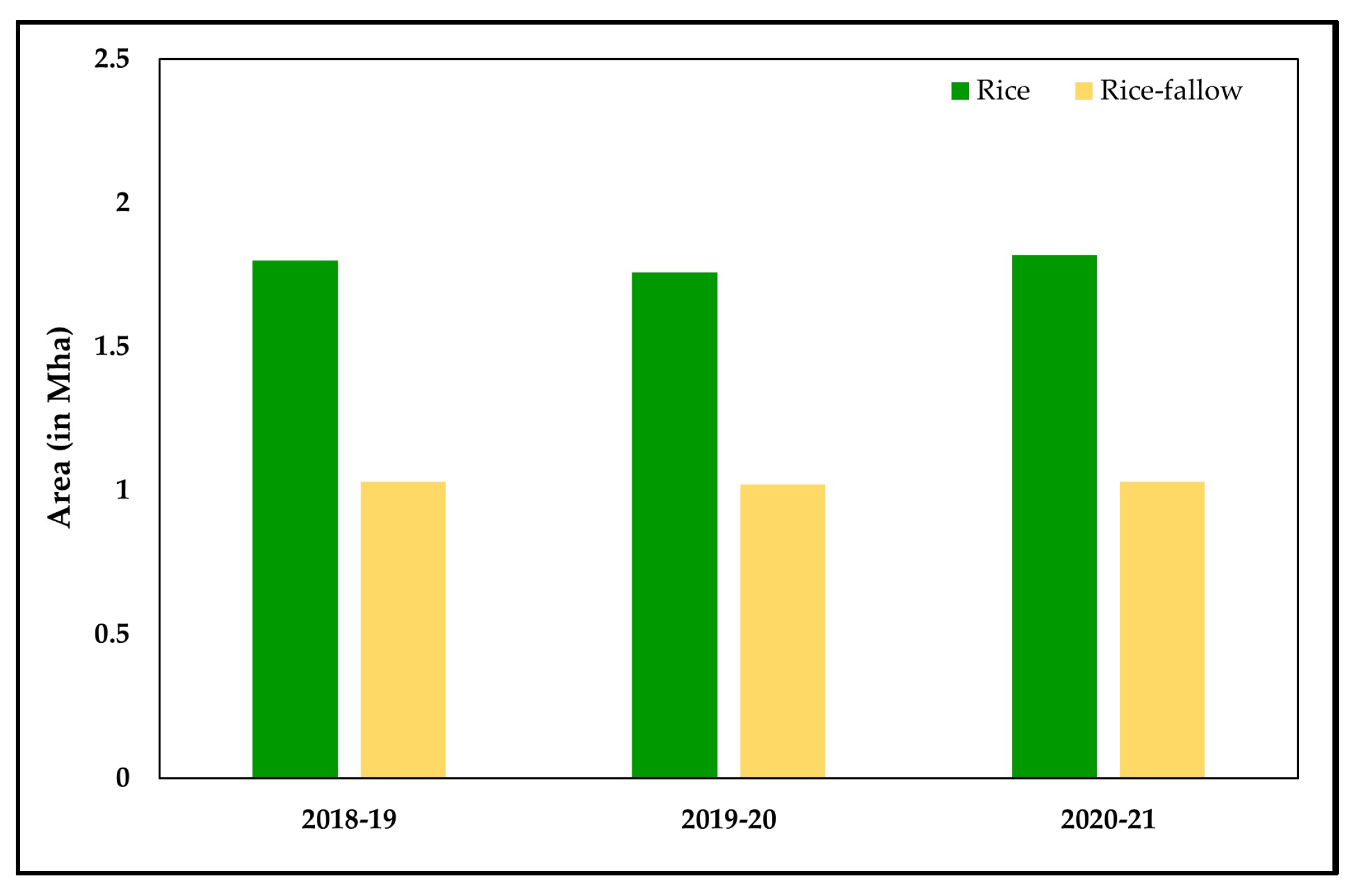
3.2. Rice Area Mapping
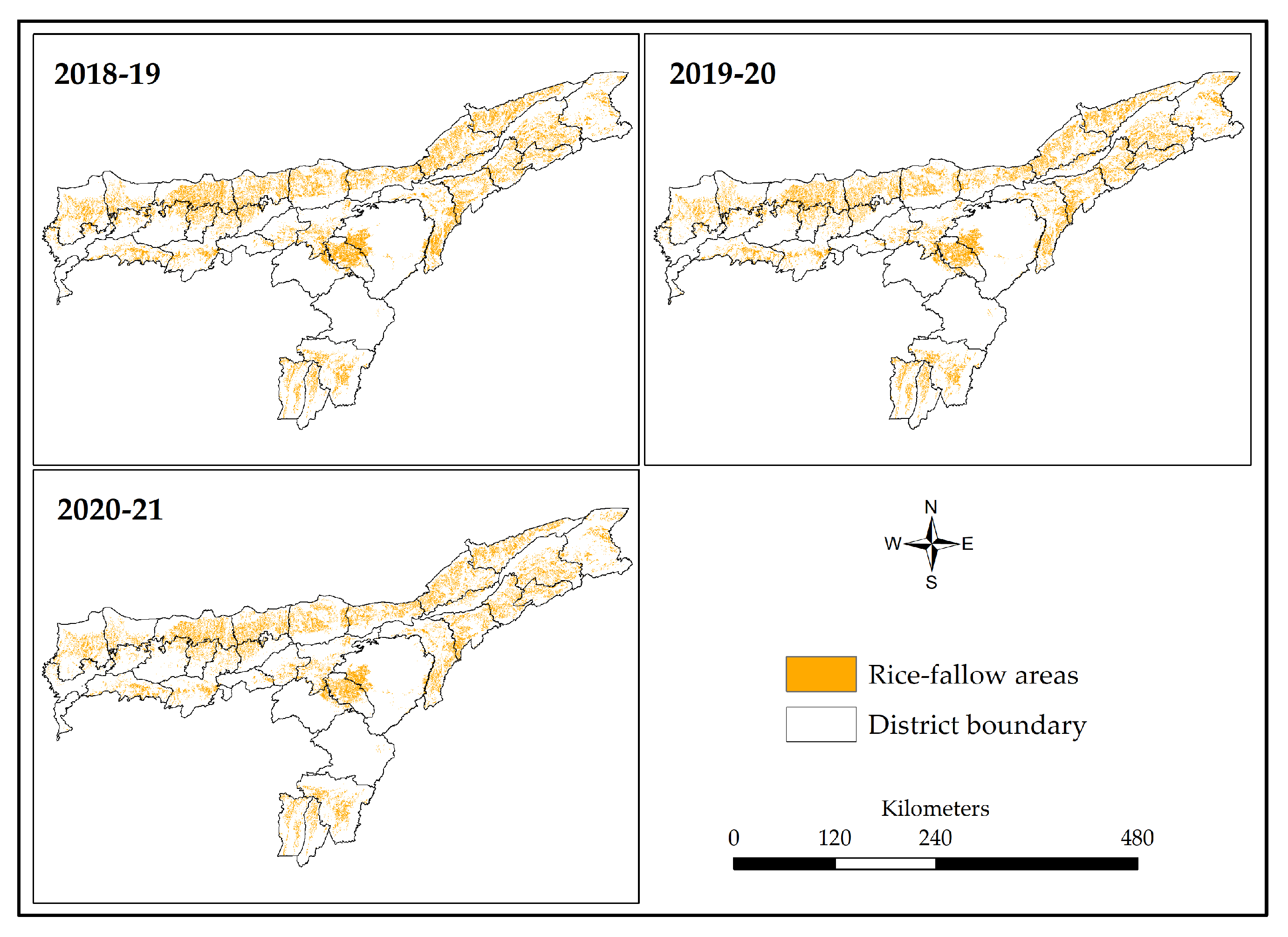
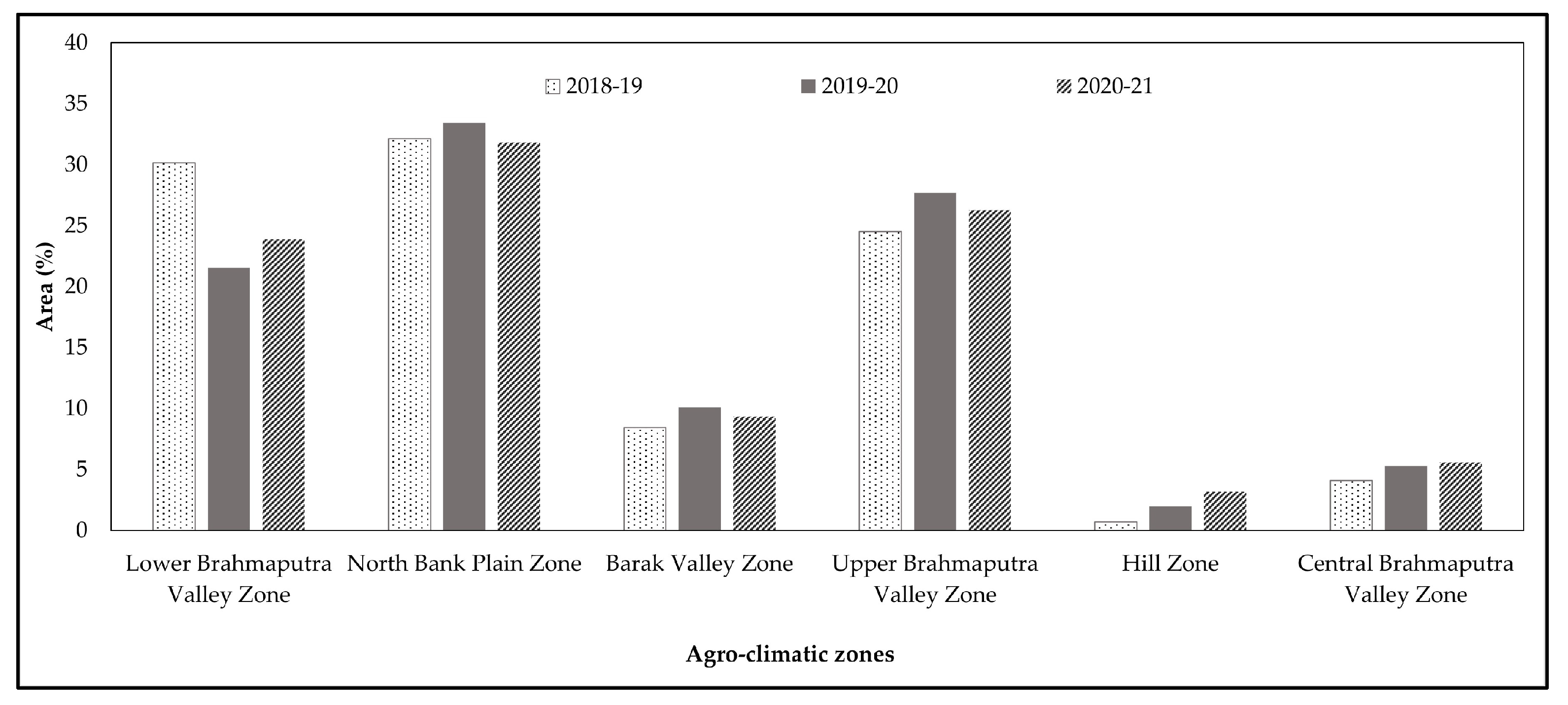
3.3. Rice-Fallow Mapping
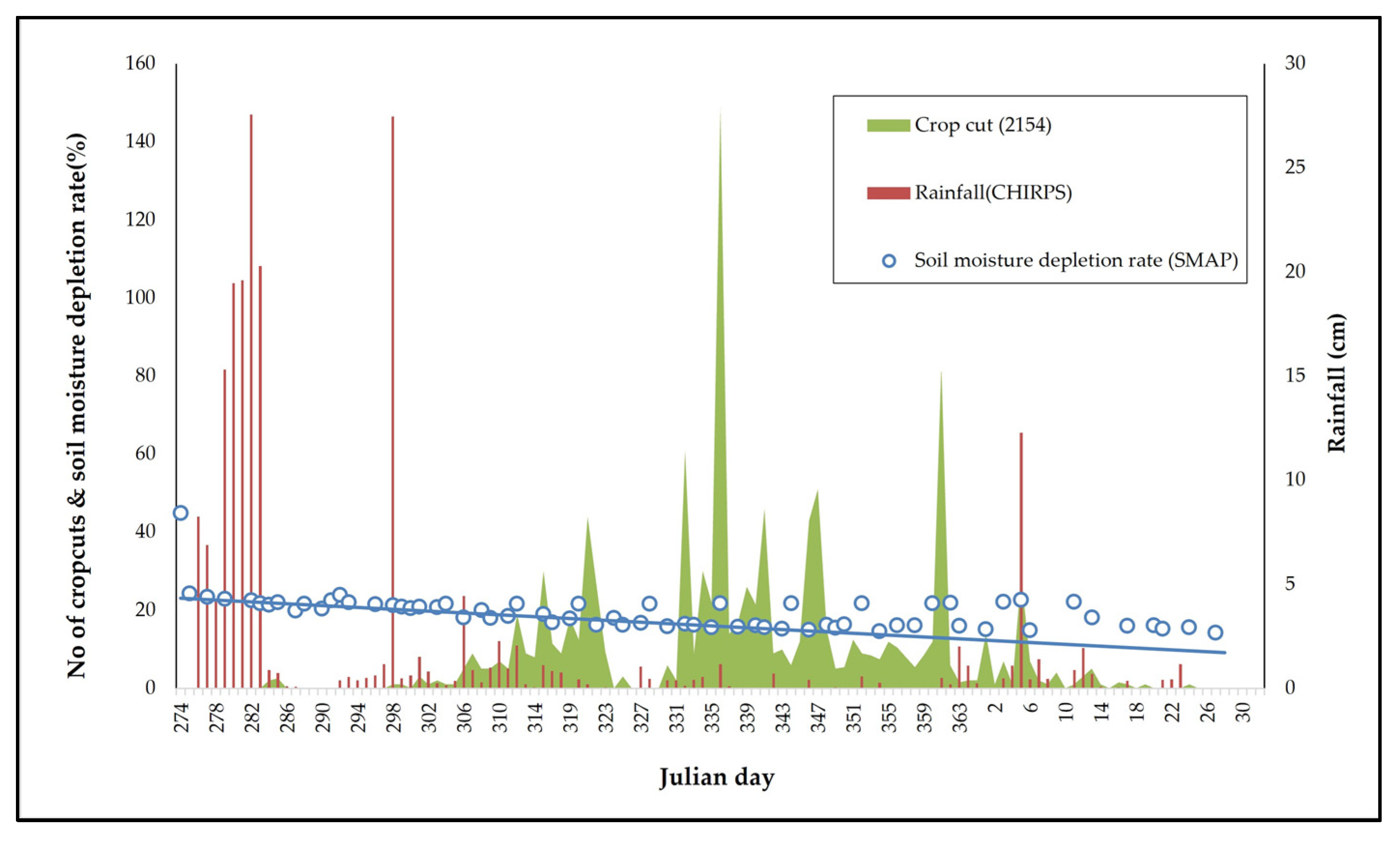
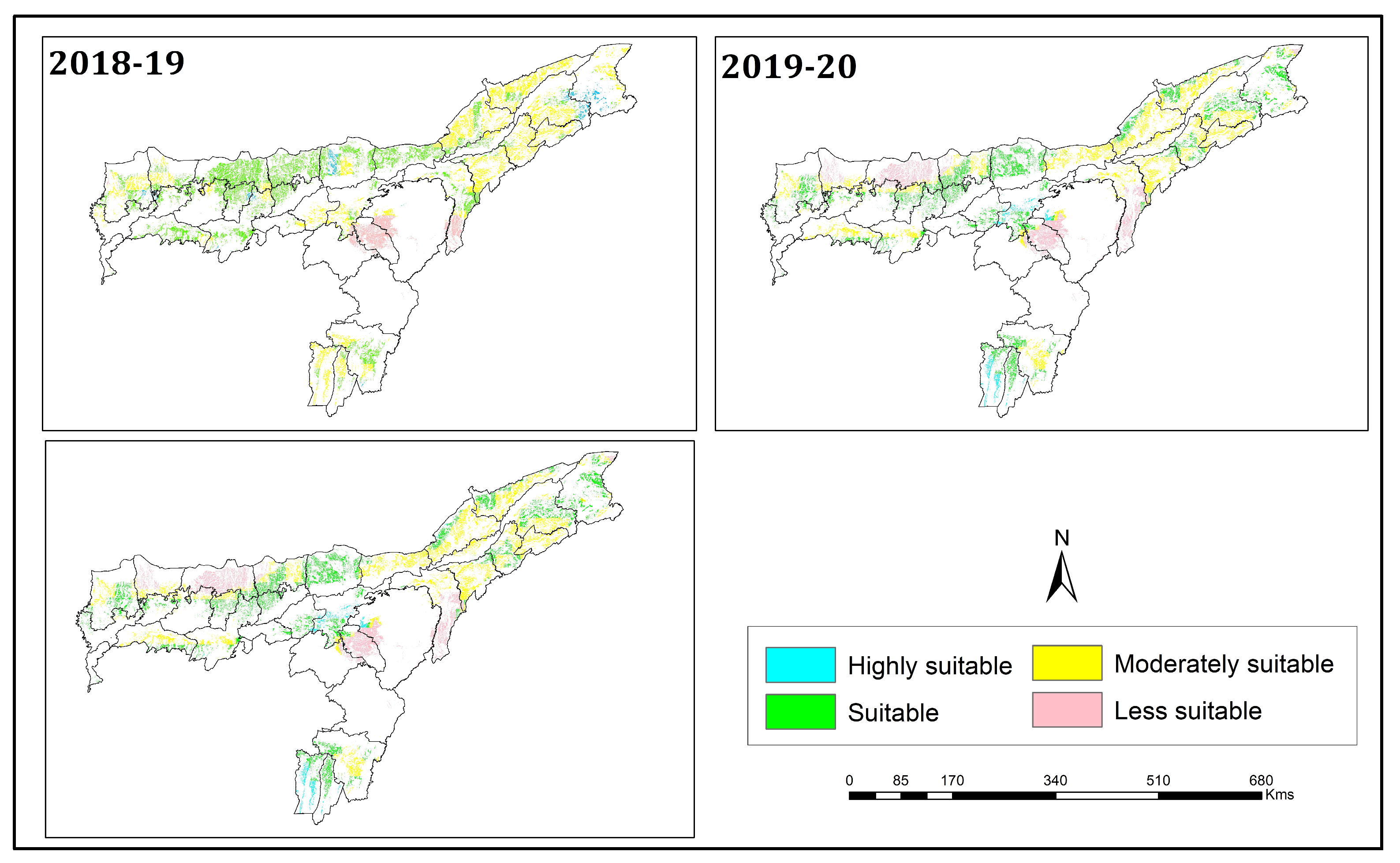
3.4. Soil Moisture Suitability Analysis
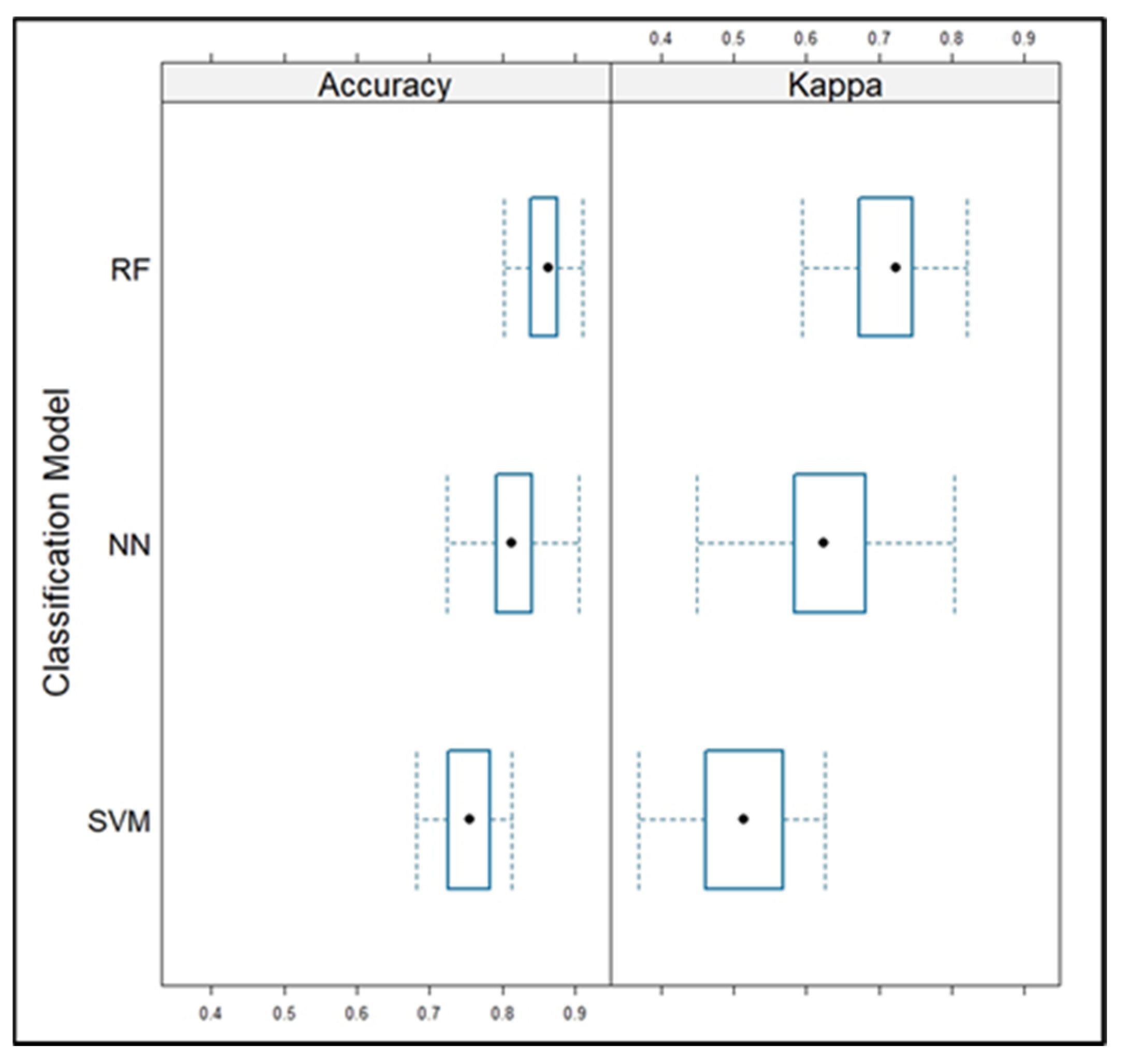
3.5. Accuracy Assessment
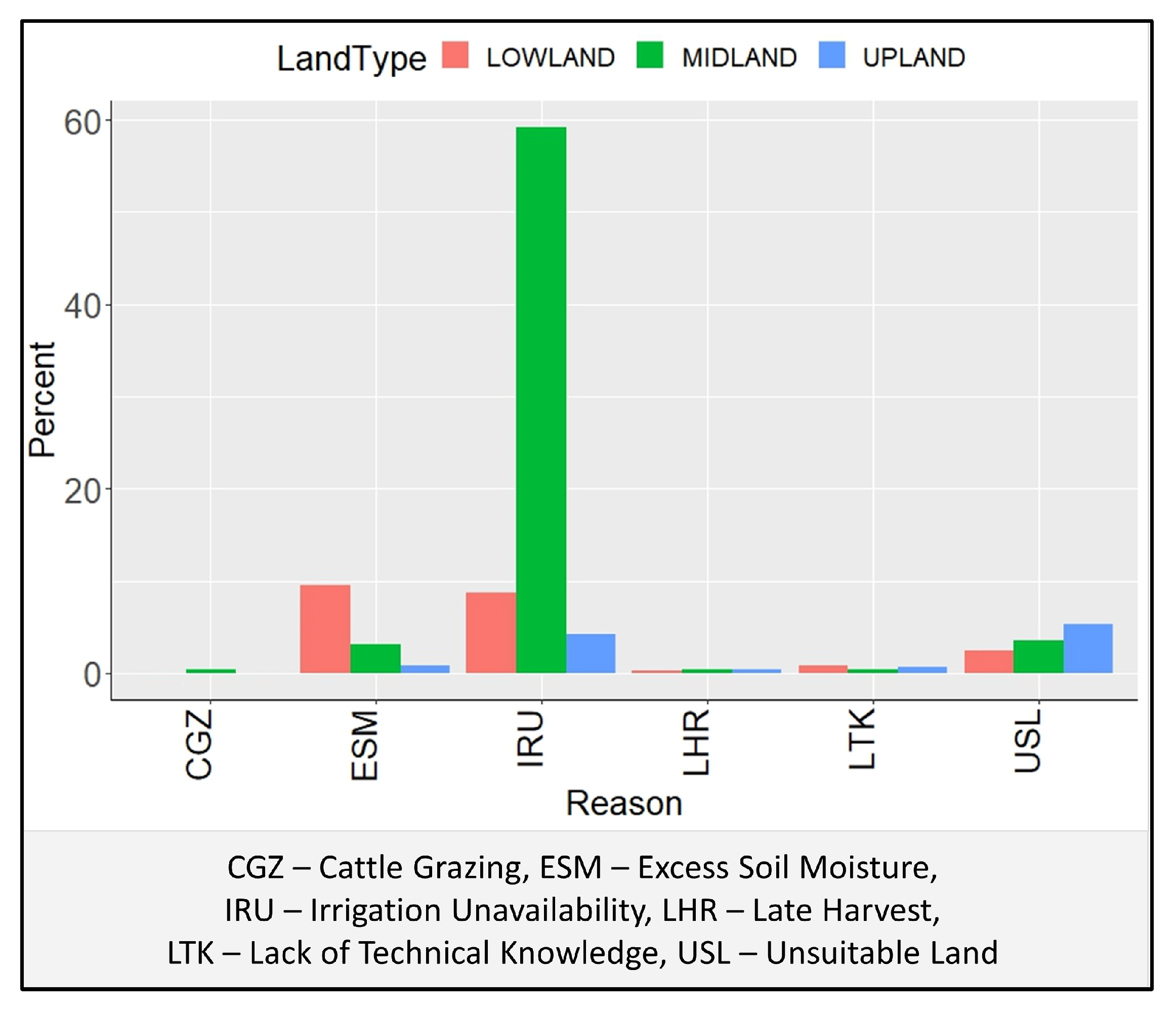
3.6. Targeting Suitable Rice-Fallow Areas through Agronomic Interventions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Burney, J.A.; Davis, S.J.; Lobell, D.B. Greenhouse gas mitigation by agricultural intensification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12052–12057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnett, T.; Appleby, M.C.; Balmford, A.; Bateman, I.J.; Benton, T.G.; Bloomer, P.; Burlingame, B.; Dawkins, M.; Dolan, L.; Fraser, D.; et al. Sustainable Intensification in Agriculture: Premises and Policies. Science 2013, 341, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yu, Q.; You, L.; Chen, K.; Tang, H.; Liu, J. Global cropping intensity gaps: Increasing food production without cropland expansion. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutert, E.; Fairhurst, T.H. Developments in Rice Production in Southeast Asia. Better Crops Int. 2002, 15, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gumma, M.K.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Teluguntla, P.; Rao, M.N.; Mohammed, I.A.; Whitbread, A.M. Mapping rice-fallow cropland areas for short-season grain legumes intensification in South Asia using MODIS 250|m time-series data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 981–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.S.; Lal, R.; Meena, R.S.; Datta, M.; Babu, S.; Das, A.; Layek, J.; Saha, P. Energy budgeting for designing sustainable and environmentally clean/safer cropping systems for rainfed rice fallow lands in India. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 158, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.K.; Mali, S.S.; Jha, B.K.; Kumar, R.; Mondal, S.; Mishra, J.S.; Singh, A.K.; Biswas, A.K.; Choudhary, A.K.; Choudhary, J.S. Intensification of Rice-Fallow Agroecosystem of South Asia with Oilseeds and Pulses: Impacts on System Productivity, Soil Carbon Dynamics and Energetics. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Panda, B.B.; Tripathi, R.; Shahid, M.; Bihari, P.; Guru, P.K.; Singh, T.; Meena, R.L.; Nayak, A.K. Identification of energy and carbon efficient cropping system for ecological sustainability of rice fallow. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Ghosh, P.; Hazra, K. Resource conservation technologies in rice fallow. In Resource Conservation Technology in Pulses, 1st ed.; Ghosh, P.K., Kumar, N., Venkatesh, M.S., Hazra, K.K., Nadarajan, N., Eds.; Scientific Publishers: Jodhpur, India, 2014; pp. 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.P.; Praharaj, C.S.; Sandhu, J.S. Utilizing untapped potential of rice fallow of East and North-east India through pulse production. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2016, 76, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Mishra, J.S.; Rao, K.K.; Mondal, S.; Hazra, K.K.; Choudhary, J.S.; Hans, H.; Bhatt, B.P. Crop rotation and tillage management options for sustainable intensification of rice-fallow agro-ecosystem in eastern India. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Mishra, J.S.; Upadhyay, P.K.; Hans, H. Rice fallows in the eastern India: Problems and prospects. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 89, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Hazra, K.; Nath, C.; Das, A.; Acharya, C. Scope, constraints and challenges of intensifying rice (Oryza sativa) fallows through pulses. Indian J. Agron. 2016, 61, S122–S128. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, G.; Kumar, A. Evaluation of post-rainy season crops with residual soil moisture and different tillage methods in rice fallow of eastern India. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, S.; Sharma, M.; Ghosh, R. Role of Pulses in Sustaining Agricultural Productivity in the Rainfed Rice-Fallow Lands of India in Changing Climatic Scenario. In Proceedings of the National Symposium on Food Security in Context of Changing Climate, CSAUAT, Kanpur, India, 30 October–1 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Mishra, J.S.; Hans, H. Enhancing productivity of rice-fallows of eastern India through inclusion of pulses and oilseeds. Indian Farming 2018, 68, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Mishra, J.S.; Rao, K.K.; Bhatt, B.P.; Hazra, K.K.; Hans, H.; Mondal, S. Sustainable intensification of rice fallows of Eastern India with suitable winter crop and appropriate crop establishment technique. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29409–29423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Chakraborti, M.; Datta, M. Improving Rice-Based Cropping Pattern Through Soil Moisture and Integrated Nutrient Management in Mid-Tropical Plain Zone of Tripura, India. Rice Sci. 2014, 21, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bégué, A.; Arvor, D.; Bellon, B.; Betbeder, J.; de Abelleyra, D.P.D.; Ferraz, R.; Lebourgeois, V.; Lelong, C.; Simões, M.; Verón, S.R. Remote Sensing and Cropping Practices: A Review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duveiller, G.; Defourny, P. A conceptual framework to define the spatial resolution requirements for agricultural monitoring using remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2637–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlow, B.D.; Egbert, S.L.; Kastens, J.H. Analysis of time-series MODIS 250 m vegetation index data for crop classification in the U.S. Central Great Plains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 290–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Xiao, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Bai, X. Multiple cropping intensity in China derived from agro-meteorological observations and MODIS data. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Son, N.T.; Chang, L.Y. Monitoring of rice cropping intensity in the upper Mekong Delta, Vietnam using time-series MODIS data. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, A.; Laborte, A.; Nelson, A.; Singh, R.K. Salinity stress detection in rice crops using time series MODIS VI data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 8186–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, K.K.; Sahoo, R.N.; Singh, R.; Pradhan, S.; Singh, S.; Krishna, G.; Pargal, S.; Mahapatra, S.K. Characterization and crop planning of rabi fallows using remote sensing and GIS. Curr. Sci. 2015, 108, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Gumma, M.K.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Teluguntla, P.; Whitbread, A.M. Monitoring of Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Rabi Rice Fallows in South Asia Using Remote Sensing. In Geospatial Technologies in Land Resources Mapping, Monitoring and Management. Geotechnologies and the Environment; Reddy, G., Singh, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.; Saha, S.K. Remote sensing, spatial multi criteria evaluation (SMCE) and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) in optimal cropping pattern planning for a flood prone area. J. Spat. Sci. 2008, 53, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.; Schönbrodt-Stitt, S.; Löw, F.; Sorokin, D.; Paeth, H. Cropping Intensity in the Aral Sea Basin and Its Dependency from the Runoff Formation 2000–2012. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandna, P.; Ladha, J.K.; Singh, U.P.; Punia, M.; Gupta, R.; Sidhu, B.S. Using remote sensing technologies to enhance resource conservation and agricultural productivity in underutilized lands of South Asia. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, G. Estimation of Soil Moisture from Optical and Thermal Remote Sensing: A Review. Sensors 2016, 16, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolassa, J.; Reichle, R.H.; Draper, C.S. Merging active and passive microwave observations in soil moisture data assimilation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Paul, P.K. Present status of soil moisture estimation by microwave remote sensing. Cogent. Geosci. 2015, 1, 1084669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directorate of Economics and Statistics. Statistical Handbook Assam; Directorate of Economics & Statistics, Govt. of Assam: Guwahati, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, P.K.; Das, A.; Saha, R.; Kharkrang, E.; Tripathi, A.K.; Munda, G.C.; Ngachan, S.V. Conservation agriculture towards achieving food security in North East India. Curr. Sci. 2010, 99, 915–921. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Mandal, R. A generalized stochastic production frontier analysis of technical efficiency of rice farming. Indian Growth Dev. Rev. 2016, 9, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hexagon. ERDAS IMAGINE 2020 Update 1. Hexagon, Stockholm. 2020. Available online: https://bynder.hexagon.com/m/4cce2965b2270e54/original/Hexagon_GSP_ERDAS_IMAGINE_2020_Release_Guide.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- ESRI. ArcGIS Desktop, Release 10.6.; Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc.: Redlands, CA, USA, 2018.
- Nguyen, D.B.; Gruber, A.; Wagner, W. Mapping rice extent and cropping scheme in the Mekong Delta using Sentinel-1A data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K. Random Decision Forest. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandna, P.K.; Mondal, S. Assessment of cropping intensity dynamics in Odisha using multitemporal Landsat TM and OLI images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 018504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.U.; Mohapatra, K.P.; Das, A.; Das, P.T.; Nongkhlaw, L.; Fiyaz, R.A.; Ngachan, S.V.; Hazarika, S.; Rajkhowa, D.J.; Munda, G.C. Spatial variability in distribution of organic carbon stocks in the soils of North East India. Curr. Sci. 2013, 104, 604–614. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, B.R.; Orloff, S.; Peters, D. Monitoring soil moisture helps refine irrigation management. Calif. Agric. 2000, 54, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.V.; Subbaiah, G.; Veeraraghavaiah, R. Productivity and Nutrient Uptake of Rice Fallow Maize (Zea mays L.) as Influenced by Plant Density and Fertilizer N Under No-Till Conditions. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saud, J.; Bezbaruah, M.P. Open grazing and cropping intensity in the Brahmaputra Valley. Agric. Econ. Res. Rev. 2020, 33, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, B.; Ponce-Campos, G.; Zhang, M.; Chang, S.; Tian, F. Mapping up-to-Date Paddy Rice Extent at 10 M Resolution in China through the Integration of Optical and Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, M.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, X. High resolution paddy rice maps in cloud-prone Bangladesh and Northeast India using Sentinel-1 data. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Xu, S.; He, T. Mapping Paddy Rice with Sentinel-1/2 and Phenology-, Object-Based Algorithm—A Implementation in Hangjiahu Plain in China Using GEE Platform. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Lal, R.; Patel, D.P.; Idapuganti, R.G.; Layek, J.; Ngachan, S.V.; Ghosh, P.K.; Bordoloi, J.; Kumar, M. Effects of tillage and biomass on soil quality and productivity of lowland rice cultivation by small scale farmers in North Eastern India. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 143, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Lal, B.; Panda, B.B.; Bihari, P.; Chatterjee, D.; Singh, T.; Nayak, P.K.; Nayak, A.K. Alteration in agronomic practices to utilize rice fallows for higher system productivity and sustainability. Field Crops Res. 2021, 260, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandna, P.K.; Mondal, S. Analyzing multi-year rice-fallow dynamics in Odisha using multi-temporal Landsat-8 OLI and Sentinel-1 Data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Directorate of Agriculture. Irrigation. Available online: https://diragri.assam.gov.in/portlets/irrigation (accessed on 12 May 2023).
| Data | Resolution (m) | Period of Acquisition | Year | No. of Tiles | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 8 OLI | 30 | 1st November–30th April | 2018–2019 2019–2020 2020–2021 | 11 | NASA | Cropping systems mapping |
| Sentinel-1 | 10 | 15th June–15th December | 2018 2019 2020 | 3 | ESA | Rice area mapping |
| SMAP | 9000 | 1st November–30th April | 2018–2019 2019–2020 2020–2021 | 1 | NASA | Soil moisture suitability |
| Random Forest (RF) | Neural Network (NN) | Support Vector Machine (SVM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
| ntree | 500 | Size | 5, 10, 15 | Cost | 0.2, 0,5, 0.1 |
| mtry | 1, 2, 5 | Decay | 0.001, 0.01, 0.1 | ||
| Model | Accuracy | Kappa |
|---|---|---|
| Random Forest (RF) | 0.897 | 0.789 |
| Neural Network (NN) | 0.8031 | 0.597 |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | 0.735 | 0.417 |
| Outputs Generated | Year | User’s Accuracy (%) | Producer’s Accuracy (%) | Overall Accuracy (%) | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | 2018–2019 | 95.3 | 81.8 | 91.9 | 0.83 |
| 2019–2020 | 85.7 | 86.0 | 86.0 | 0.72 | |
| 2020–2021 | 90.2 | 94.0 | 92.0 | 0.84 | |
| Rice-fallow | 2018–2019 | 86.1 | 97.1 | 94.9 | 0.90 |
| 2019–2020 | 87.7 | 85.8 | 90.0 | 0.80 | |
| 2020–2021 | 93.0 | 93.8 | 92.9 | 0.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srivastava, A.K.; Borah, S.B.; Ghosh Dastidar, P.; Sharma, A.; Gogoi, D.; Goswami, P.; Deka, G.; Khandai, S.; Borgohain, R.; Singh, S.; et al. Rice-Fallow Targeting for Cropping Intensification through Geospatial Technologies in the Rice Belt of Northeast India. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13081509
Srivastava AK, Borah SB, Ghosh Dastidar P, Sharma A, Gogoi D, Goswami P, Deka G, Khandai S, Borgohain R, Singh S, et al. Rice-Fallow Targeting for Cropping Intensification through Geospatial Technologies in the Rice Belt of Northeast India. Agriculture. 2023; 13(8):1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13081509
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrivastava, Amit Kumar, Suranjana Bhaswati Borah, Payel Ghosh Dastidar, Archita Sharma, Debabrat Gogoi, Priyanuz Goswami, Giti Deka, Suryakanta Khandai, Rupam Borgohain, Sudhanshu Singh, and et al. 2023. "Rice-Fallow Targeting for Cropping Intensification through Geospatial Technologies in the Rice Belt of Northeast India" Agriculture 13, no. 8: 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13081509
APA StyleSrivastava, A. K., Borah, S. B., Ghosh Dastidar, P., Sharma, A., Gogoi, D., Goswami, P., Deka, G., Khandai, S., Borgohain, R., Singh, S., & Bhattacharyya, A. (2023). Rice-Fallow Targeting for Cropping Intensification through Geospatial Technologies in the Rice Belt of Northeast India. Agriculture, 13(8), 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13081509






