Environmental Impact Decision Support Tools for Horticulture Farming: Evaluation of GHG Calculators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
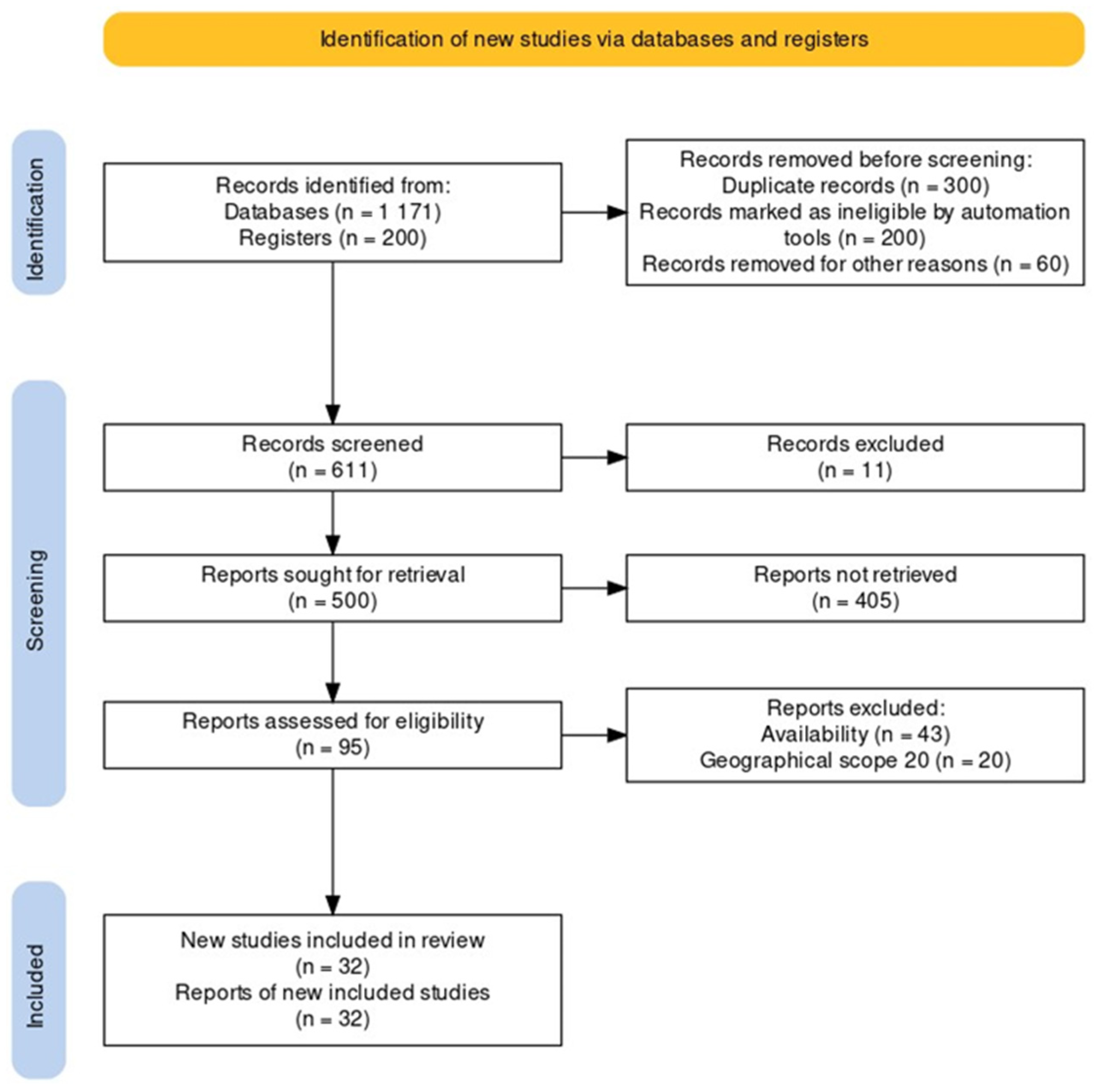
2. Methodology
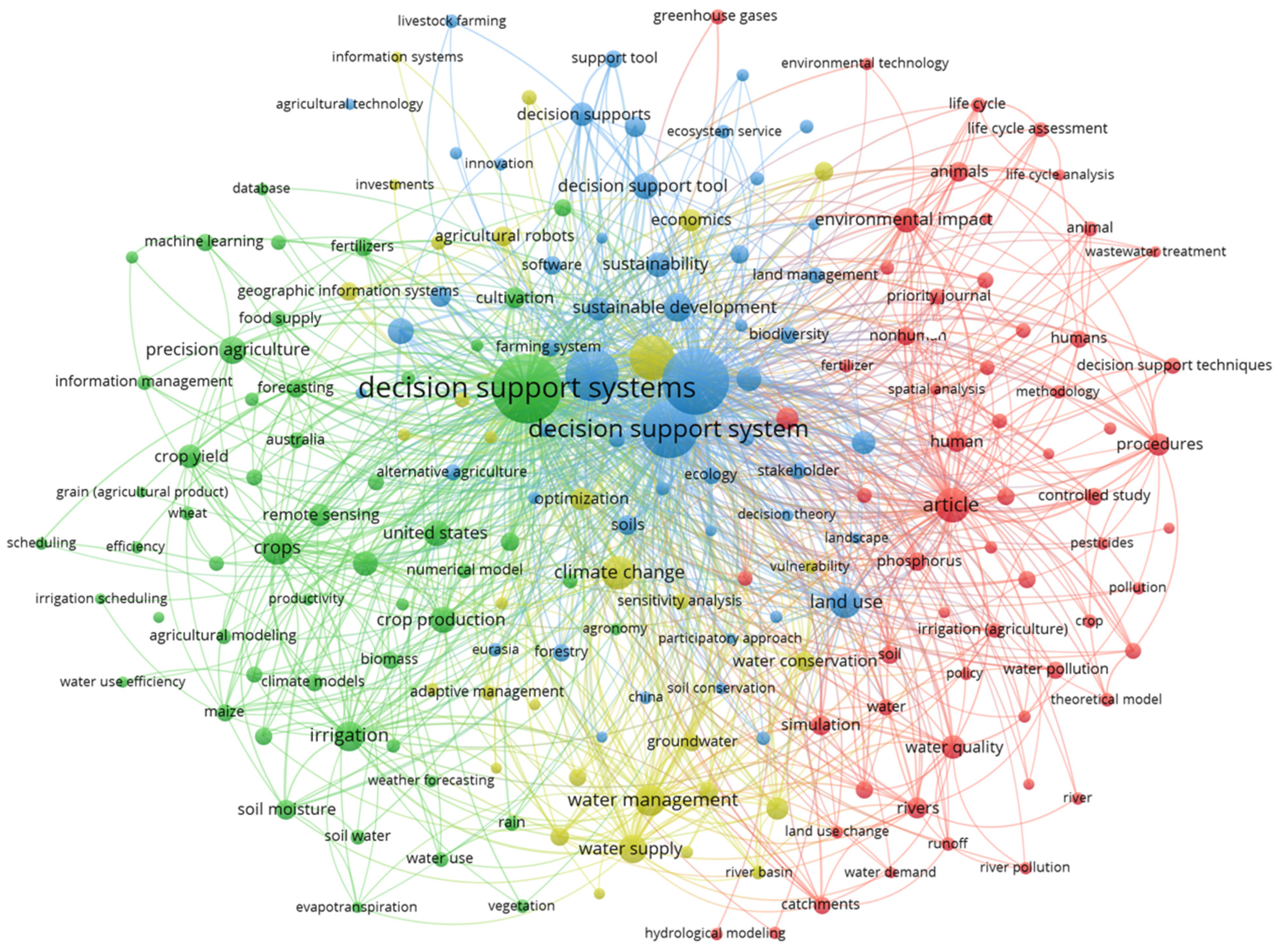
2.1. A Systematic Literature Review on Environmental Impact Decision Support Tools for Horticulture
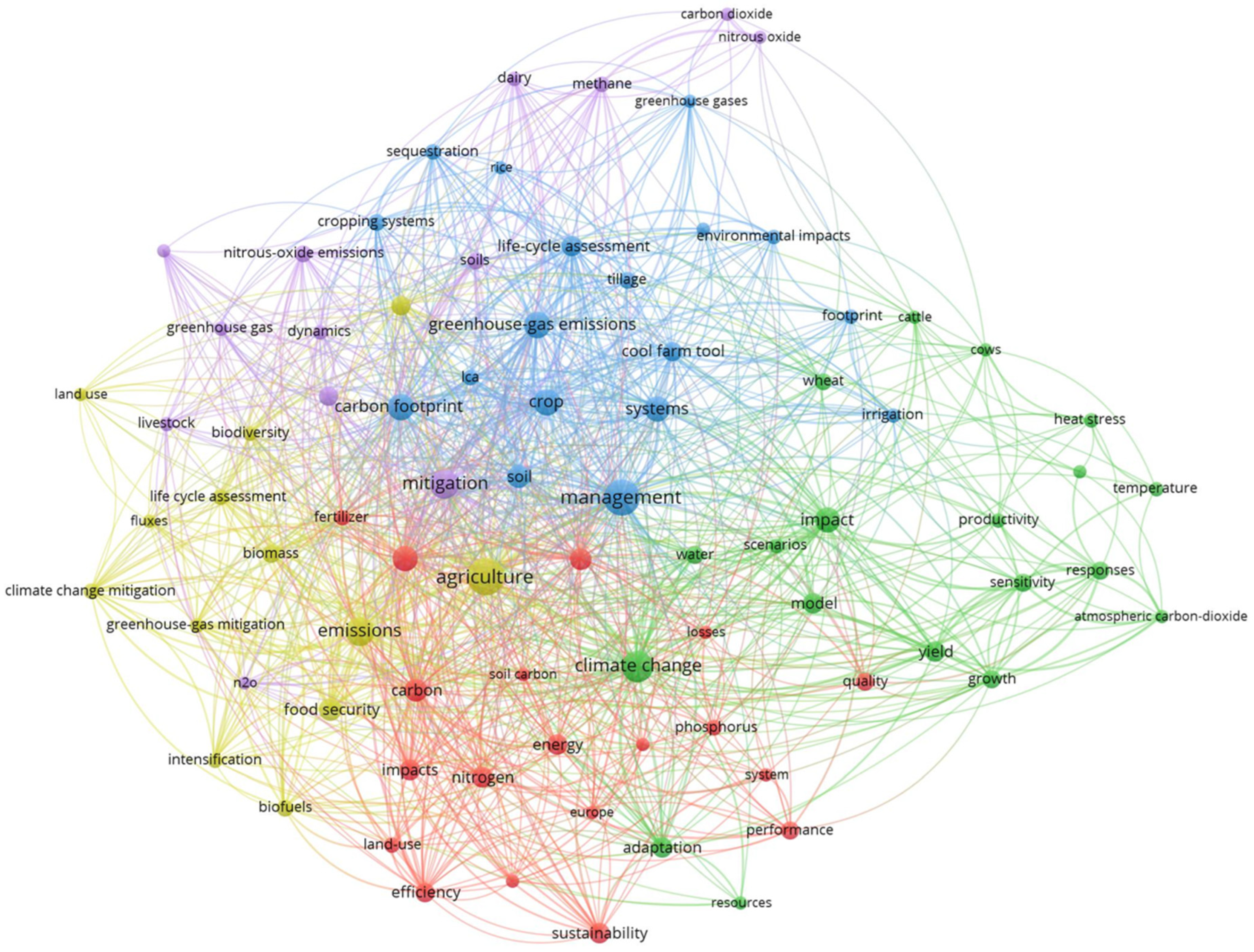
2.2. Selection of Decision Support Tools—GHG Calculators
2.2.1. Bibliographic Analysis of Selected Indicators
2.2.2. In-Depth Analysis: Multicriteria Decision Analysis
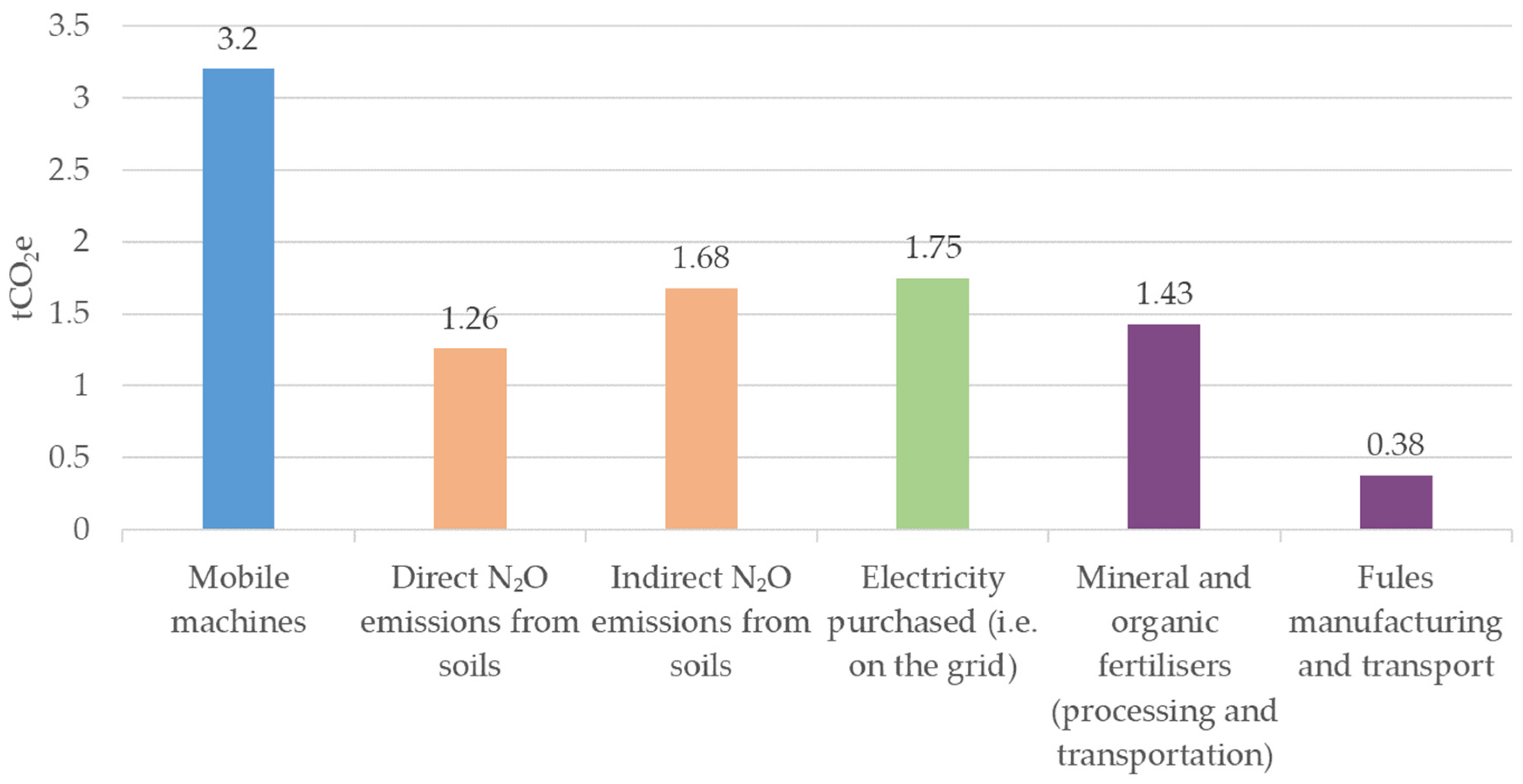
2.3. Case Study Analysis
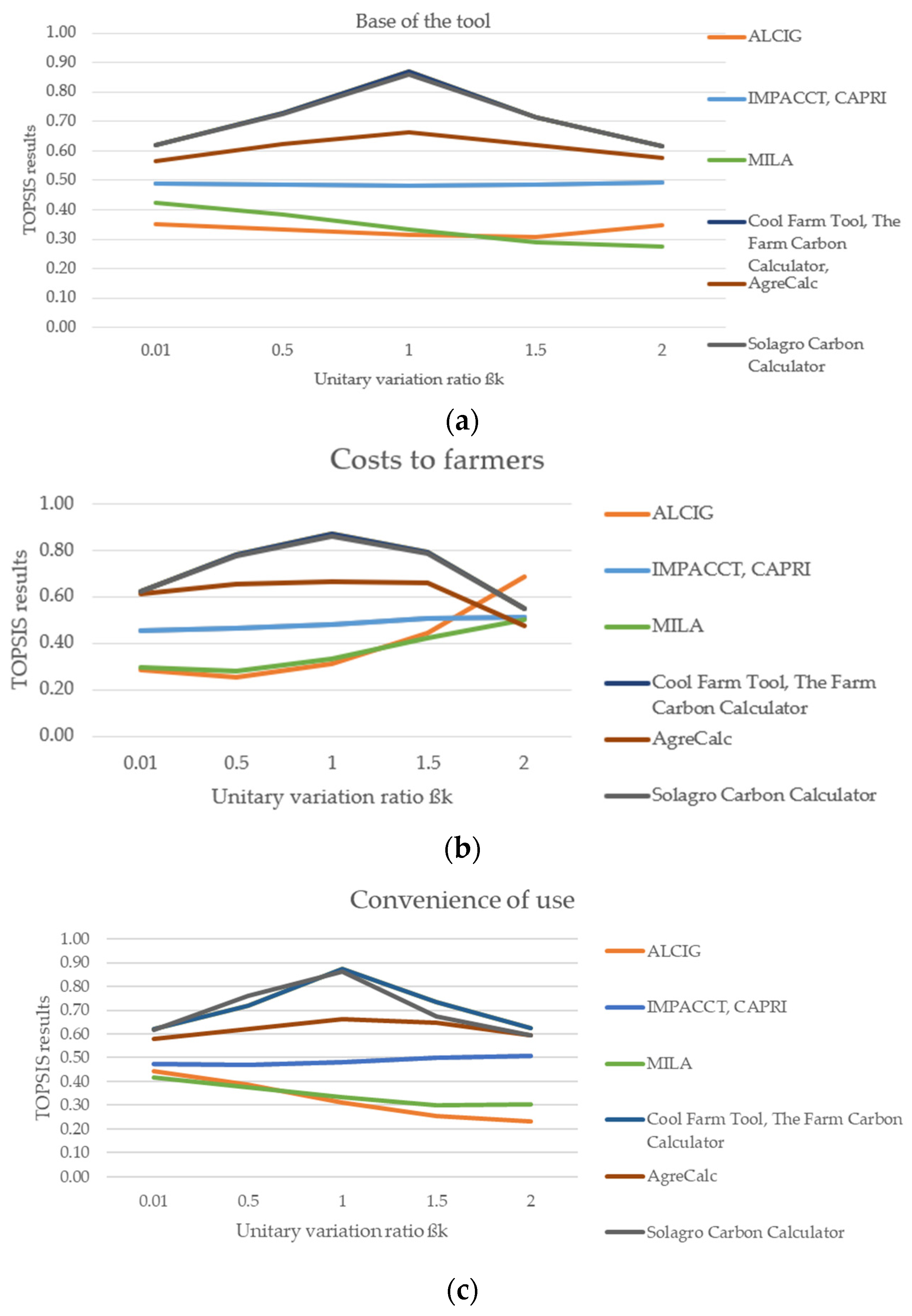
3. Results: Prioritization of GHG Emissions Calculators for the Horticulture Sector
- a—amount of fertilizer used, kg per ha;
- b—amount of fertilizer used, kg;
- c—total area of plants, ha.
- d—amount of fertilizer component, kg per ha;
- e—amount of fertilizer component, %;
- a—amount of fertilizer used, kg per ha.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rose, D.C.; Sutherland, W.J.; Parker, C.; Lobley, M.; Winter, M.; Morris, C.; Twining, S.; Ffoulkes, C.; Amano, T.; Dicks, L.V. Decision support tools for agriculture: Towards effective design and delivery. Agric. Syst. 2016, 149, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; He, Z. Decision Support Systems to Manage Irrigation in Agriculture. Adv. Agron. 2014, 123, 229–279. [Google Scholar]
- García-Vila, M.; Fereres, E. Combining the simulation crop model AquaCrop with an economic model for the optimization of irrigation management at farm level. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 36, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, P.J.; Fragoso, R.; Garcia-Gonzalo, J.; Borges, J.G.; Marques, S.; Lucas, M.R. Assessing impacts of Common Agricultural Policy changes on regional land use patterns with a decision support system: An application in Southern Portugal. For. Policy Econ. 2010, 12, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupnik, R.; Kukar, M.; Vračar, P.; Košir, D.; Pevec, D.; Bosnić, Z. AgroDSS: A decision support system for agriculture and farming. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 161, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Martínez, J.F.; Beltran, V.; Martínez, N.L. Decision support systems for agriculture 4.0: Survey and challenges. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 170, 105256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, D.C.; Harrison, M.T.; Kemmerer, E.P.; Parsons, D. Management opportunities for boosting productivity of cool-temperate dairy farms under climate change. Agric. Syst. 2015, 138, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, I.; Turner, L.; Harrison, M.T.; Monjardino, M.; deVoil, P.; Rodriguez, D. Application, adoption and opportunities for improving decision support systems in irrigated agriculture: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 257, 107161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Parodi, G.; Mach, K.J.; Jagannathan, K.; Sjostrom, K.D. Insights for developing effective decision support tools for environmental sustainability. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 42, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report of Greenhouse Gas Accounting Tools for Agriculture and Forestry Sectors. Available online: https://www.agmrv.org/knowledge-portal/resources/report-of-greenhouse-gas-accounting-tools-for-agriculture-and-forestry-sectors/ (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Arulnathan, V.; Heidari, M.D.; Doyon, M.; Li, E.; Pelletier, N. Farm-level decision support tools: A review of methodological choices and their consistency with principles of sustainability assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde, E.M.; Oudshoorn, F.W.; Sørensen, C.A.G.; Bokkers, E.A.M.; Boer, I.J.M. Assessing sustainability at farm-level: Lessons learned from a comparison of tools in practice. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, C.; McManus, M.C.; Smith, P. A comparison of carbon accounting tools for arable crops in the United Kingdom. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 46, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomb, V.; Touchemoulin, O.; Bockel, L.; Chotte, J.L.; Martin, S.; Tinlot, M.; Bernoux, M. Selection of appropriate calculators for landscape-scale greenhouse gas assessment for agriculture and forestry. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 015029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, C.; Helming, K.; Nendel, C. Do greenhouse gas emission calculations from energy crop cultivation reflect actual agricultural management practices?—A review of carbon footprint calculators. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacSween, K.; Feliciano, D. Info Note. Comparison of Online Greenhouse Gas Accounting Tools for Agriculture. Available online: https://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/handle/2164/11853/CCAFS_Info_Note_Comparison_of_GHG_Accounting_Tools_2018.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Renouf, M.A.; Renaud-Gentié, C.; Perrin, A.; van der Werf, H.M.G.; Kanyarushoki, C.; Jourjon, F. Effectiveness criteria for customised agricultural life cycle assessment tools. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 179, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vibart, R.; de Klein, C.; Jonker, A.; Weerden, T.; Bannink, A.; Bayat, A.R.; Crompton, L.; Durand, A.; Eugène, M.; Klumpp, K.; et al. Challenges and opportunities to capture dietary effects in on-farm greenhouse gas emissions models of ruminant systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumba, D.A.; Lazarova-Molnar, S.; Niloofar, P. Comparative evaluation of data requirements and level of decision support provided by decision support tools for reducing livestock-related greenhouse gas emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzoumanidis, I.; Raggi, A.; Petti, L. Considerations When Applying Simplified LCA Approaches in the Wine Sector. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5018–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, A.; Zambelli, M.; Giovenzana, V.; Tugnolo, A.; Pampuri, A.; Vignati, S.; Beghi, R.; Guidetti, R. Simplified environmental impact tools for agri-food system: A systematic review on trends and future prospective. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 102, 107175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The EU Fruit and Vegetable Sector: Main Features, Challenges and Prospects. Available online: https://policycommons.net/artifacts/1335181/the-eu-fruit-and-vegetable-sector/1941483/#:~:text=The%20EU%20fruit%20and%20vegetable%20sector%3A%20Main%20features%2C,vegetable%20eu%20direct%20payments%20agriculture%20and%20rural%20development (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- From Farm to Fork Strategy. Position Paper. March 2020. Available online: www.eriaff.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/ERIAFF_Position_Paper_F2F_Strategy.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Horticulture Research in Europe—to 2020 and Beyond. Available online: https://epsoweb.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/14_09_11_EPSO_Horticulture-research-in-Europe-to-2020-and-beyond_Draft-White-paper.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Bumbiere, K.; Diaz Sanchez, F.A.; Pubule, J.; Blumberga, D. Development and Assessment of Carbon Farming Solutions. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2022, 26, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PACT. The Role of the Horticulture Sector in a Sustainable EU Food System. Call for a More Plant-Based Future. Available online: https://www.zuid-holland.nl/publish/besluitenattachments/pact-call-for-a-more-plant-based-future/pact-for-a-plant-based-future-eriaff.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Soode, E.; Lampert, P.; Weber-Blaschke, G.; Richter, K. Carbon footprints of the horticultural products strawberries, asparagus, roses and orchids in Germany. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, F.; Blanke, M. Farming and marketing system affects carbon and water footprint—A case study using Hokaido pumpkin. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 28, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; El Khosht, F.F.; Bergkvist, G.; Öborn, I.; Tidåker, P. Effect of short-term perennial leys on life cycle environmental performance of cropping systems: An assessment based on data from a long-term field experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 149, 126888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Navarro, V.; Shahrokh, V.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Acosta, J.A.; Almagro, M.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Boix-Fayos, C.; Díaz-Pereira, E.; Zornoza, R. Perennial alley cropping contributes to decrease soil CO2 and N2O emissions and increase soil carbon sequestration in a Mediterranean almond orchard. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinas, S.; Tiloca, M.T.; Deligios, P.A.; Cossu, M.; Ledda, L. Carbon footprints and social carbon cost assessments in a perennial energy crop system: A comparison of fertilizer management practices in a Mediterranean area. Agric. Syst. 2021, 186, 102989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavifar, H.; Mardani, A. Prognostication of energy consumption and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions analysis of apple production in West Azarbayjan of Iran using Artificial Neural Network. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordikhani, H.; Parashkoohi, M.G.; Zamani, D.M.; Ghahderijani, M. Energy-environmental life cycle assessment and cumulative exergy demand analysis for horticultural crops (Case study: Qazvin province). Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 2899–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostashari-Rad, F.; Nabavi-Pelesaraei, A.; Soheilifard, F.; Hosseini-Fashami, F.; Chau, K. Energy optimization and greenhouse gas emissions mitigation for agricultural and horticultural systems in Northern Iran. Energy 2019, 186, 115845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostashari-Rad, F.; Ghasemi-Mobtaker, H.; Taki, M.; Ghahderijani, M.; Saber, Z.; Chau, K.; Nabavi-Pelesaraei, A. Data supporting midpoint-weighting life cycle assessment and energy forms of cumulative exergy demand for horticultural crops. Data Brief 2020, 33, 106490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, N.; Amano, K.; Shimada, K. Evaluation Of Environmental Load On Friuts and Vegetables Consumption and Its Reduction Potential. Environ. Syst. Res. 2007, 35, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leip, A.; Britz, W.; Weiss, F.; Vries, W. Farm, land, and soil nitrogen budgets for agriculture in Europe calculated with CAPRI. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3243–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, M.; Gocht, A.; Heckelei, T.; Gomez y Paloma, S. Incorporating farm structural change in models assessing the Common Agricultural Policy: An application in the CAPRI farm type model. J. Policy Model. 2016, 38, 1040–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, A.J.; Topp, C.F.E.; Wilson, R.M.; Reid, G.; Rees, R.M. A comparison of farm-level greenhouse gas calculators in their application on beef production systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzilivakis, J.; Lewis, K.; Green, A.; Warner, D. Identifying integrated options for agricultural climate change mitigation. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2014, 6, 192–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, C.; Specka, X.; Aurbacher, J.; Kornatz, P.; Herrmann, C.; Heiermann, M.; Müller, J.; Nendel, C. The MiLA tool: Modeling greenhouse gas emissions and cumulative energy demand of energy crop cultivation in rotation. Agric. Syst. 2017, 152, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayatz, B.; Baroni, G.; Hillier, J.; Lüdtke, S.; Heathcote, R.; Malin, D.; Tonder, C.; Kuster, B.; Freese, D.; Hüttl, R.; et al. Cool Farm Tool Water: A global on-line tool to assess water use in crop production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 1163–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, S.H.; Malin, D.; Smith, P.; Hillier, J. The potential to reduce GHG emissions in egg production using a GHG calculator—A Cool Farm Tool case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak Yetişgin, S.; Morgan-Davies, C.; Önder, H. Comparison of farm-level greenhouse gas emissions in transhumance and semi-intensive sheep production systems in continental rangelands. Animal 2022, 16, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braband, D.; Geier, U.; Köpke, U. Bio-resource evaluation within agri-environmental assessment tools in different European countries. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 98, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicciù, B.; Schramm, F.; Schramm, V.B. Multi-criteria decision making/aid methods for assessing agricultural sustainability: A literature review. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 138, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirpanahi, S.; Almassi, M.; Javadi, A.; Bakhoda, H. Applying multi-criteria decision making method to analyze stability and mechanization patterns in small farms. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2023, 20, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffaroni, M.; Bevacqua, D. Maximize crop production and environmental sustainability: Insights from an ecophysiological model of plant-pest interactions and multi-criteria decision analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 139, 126571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, G.H.; Huang, J.J. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- YaraTera Kristalon 19-6-6 Lilac. Available online: https://vashnil.com/katalog/preparaty-dla-rastenievodstva/mikroudobrenia/yaratera-kristalon-19-6-6-lilac/1752 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Monokālija Fosfāts 25 kg. Available online: http://amozoli.lv/shop/index.php?id_product=17&controller=product&id_lang=6 (accessed on 10 October 2023).

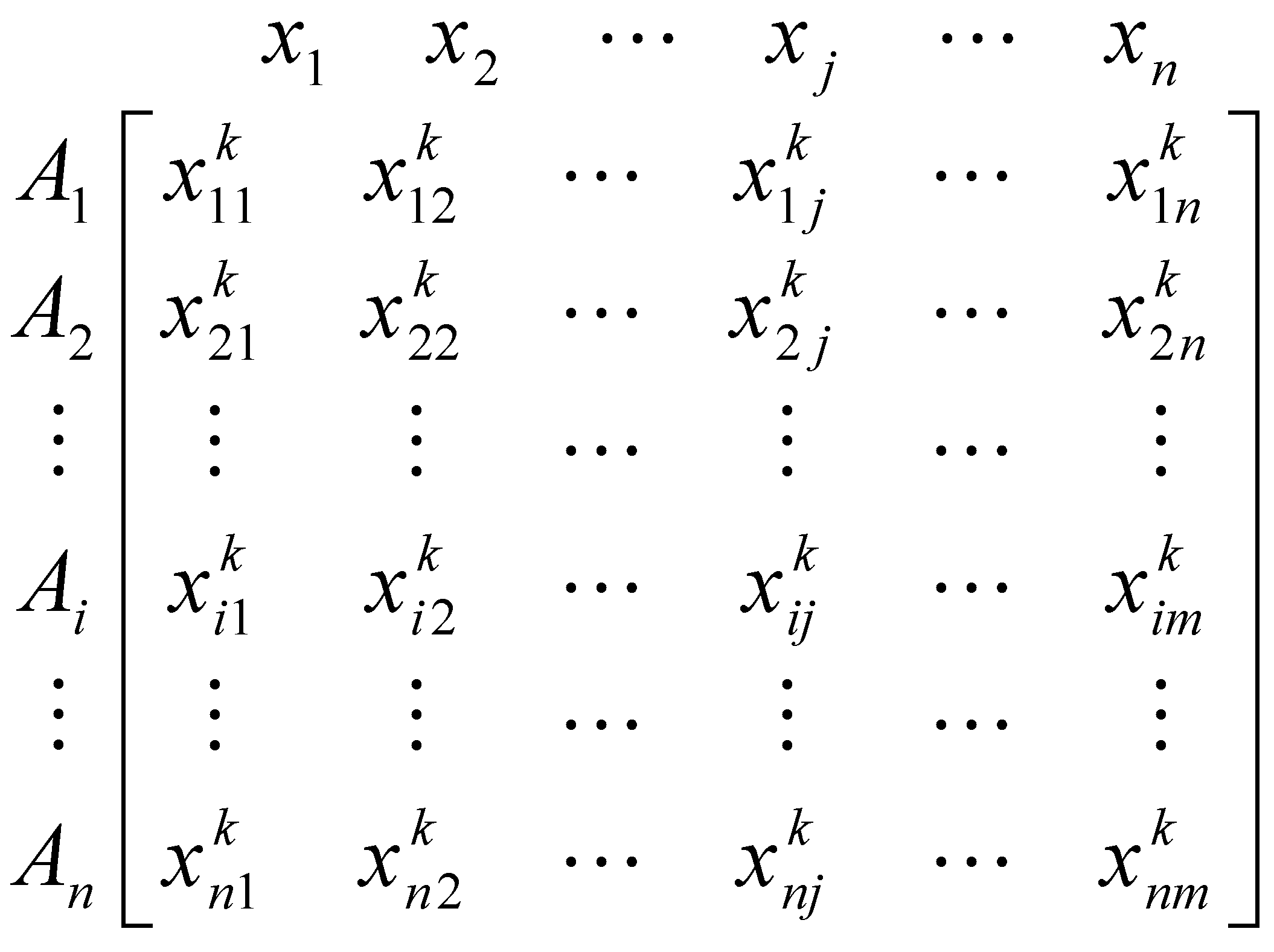
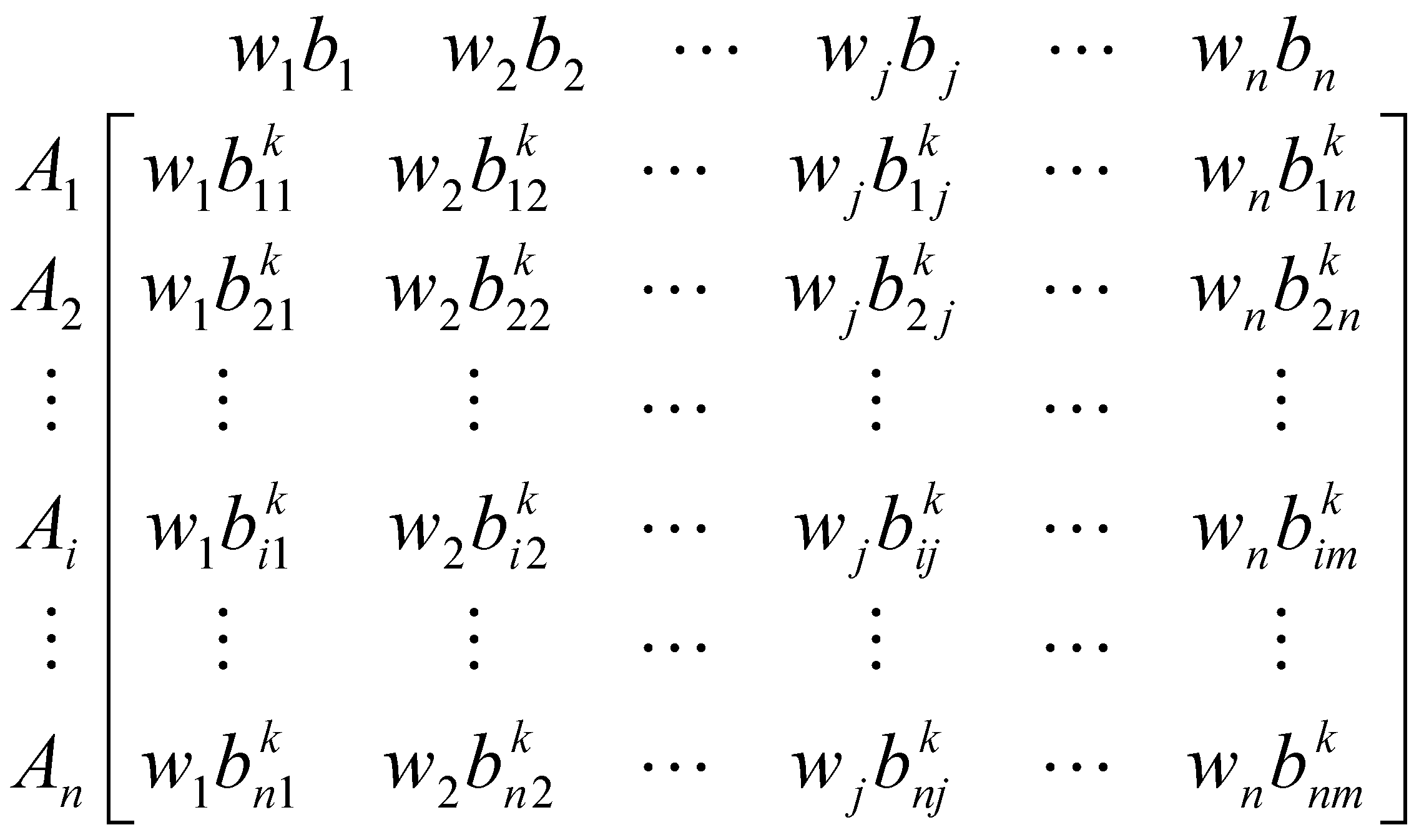


| Publication | Field of Application | Tools Reviewed | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whittaker et al., 2013 | Arable crops in the United Kingdom | 11 | [14] |
| Colomb et al., 2013 | Landscape GHG assessment for agriculture and forestry | 18 | [15] |
| Arzoumanidis et al., 2014 | Application of simplified LCA in the wine sector | 4 | [21] |
| Olde et al., 2016 | Arable and livestock farm assessment in Denmark | 4 | [13] |
| Peter et al., 2017 | Carbon footprint calculators for energy crop cultivation | 18 | [16] |
| MacSween and Feliciano, 2018 | GHG Accounting Tools for Tropical Climate | 6 | [17] |
| Renouf et al., 2018 | Customized agricultural life cycle assessment tools | 14 | [18] |
| Arulnathan et al., 2020 | Farm-level Decision Support Tools | 19 | [11] |
| Vibart et al., 2021 | GHG emission models for dairy cattle systems | 14 | [19] |
| Thumba et al., 2022 | Decision Support Tools in livestock farming | 11 | [19] |
| Casson et al., 2023 | Simplified environmental impact tools for agri-food system | 79 | [22] |
| Unit | Data |
|---|---|
| Total area | 12.5 ha |
| Area of planted sea buckthorn | 10 ha |
| Area of planted quinces | 0.5 ha |
| Unmanaged territory area | 2 ha |
| Number of sea buckthorn plants | 12,500 |
| Number of quinces plants | 1500 |
| Total yield | 31.5 t |
| Total sea buckthorn yield | 30 t |
| Total quinces yield | 1.5 t |
| Soil texture | loam |
| Soil drainage | very good |
| Soil management | no tillage |
| Plant residue management | removed from the field |
| pH | 5.7 |
| Amount of fertilizer—Kristalon Lilac (NPK 19-6-6+micro) [41] | 1400 kg; 140 kg per ha |
| Nitrogen (N) | 19%; 27 kg per ha |
| N (as ammonium N) | 16% |
| N (as nitrate N) | 3% |
| Potassium oxide (K2O) | 6%; 8.4 kg per ha |
| Phosphorus oxide (P2O5) | 6%; 8.4 kg per ha |
| Amount of fertilizer—Monopotassium phosphate [42] | 1000 kg; 100 kg per ha |
| Phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) | 52%; 52 kg per ha |
| Potassium oxide (K2O) | 34%; 34 kg per ha |
| Fuel consumption (tractor, mower, distribution truck) | 1200 L |
| Consumed electricity (drip irrigation system) | 3000 kWh |
| Irrigation amount | 2400 m3 |
| Water source | farm storage pond |
| Calculator | The Base of the Tool | Functional Unit | Sustainability Assessment | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALCIG | Excel, version 2310 | Surface, time | Single indicator | [18,22] |
| CAPRI | Software | Mass | Single indicator | [39,40] |
| The Farm Carbon Calculator | Web-based | Mass, surface | Single indicator | [41] |
| IMPACCT | Software | Mass, surface | Single indicator | [42] |
| MILA | Excel, version 2310 | Mass, surface, energy | Multi indicators | [43] |
| Cool Farm Tool | Web-based | Mass, surface | Multi indicators | [44,45] |
| AgreCalc | Web-based | Mass, surface | Single indicator | [20,46] |
| Solagro Carbon Calculator | Web-based | Mass | Single indicator | [47] |
| Dimension | Indicator | Designation of Indicator | Preferable Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical | The base of the tool | I1 | Max |
| Economic | Costs to farmers | I2 | Min |
| Social | Convenience of use | I3 | Max |
| Recognition by farmers | I4 | Max | |
| Environmental | Transparency of methodology | I5 | Max |
| Calculator | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 | I5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALCIG | 0.0295 | 0.0743 | 0.0645 | 0.0588 | 0.0555 |
| CAPRI | 0.0590 | 0.0743 | 0.0645 | 0.0294 | 0.0555 |
| The Farm Carbon Calculator | 0.0885 | 0.0743 | 0.0806 | 0.0882 | 0.0832 |
| IMPACCT | 0.0590 | 0.0743 | 0.0645 | 0.0588 | 0.0555 |
| MILA | 0.0295 | 0.0743 | 0.0322 | 0.0588 | 0.0555 |
| Cool Farm Tool | 0.0885 | 0.0743 | 0.0806 | 0.0882 | 0.0832 |
| AgreCalc | 0.0885 | 0.0371 | 0.0645 | 0.0882 | 0.0832 |
| Solagro Carbon Calculator | 0.0885 | 0.0743 | 0.0967 | 0.0735 | 0.0832 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dzalbs, A.; Bimbere, M.; Pubule, J.; Blumberga, D. Environmental Impact Decision Support Tools for Horticulture Farming: Evaluation of GHG Calculators. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122213
Dzalbs A, Bimbere M, Pubule J, Blumberga D. Environmental Impact Decision Support Tools for Horticulture Farming: Evaluation of GHG Calculators. Agriculture. 2023; 13(12):2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122213
Chicago/Turabian StyleDzalbs, Arnis, Madara Bimbere, Jelena Pubule, and Dagnija Blumberga. 2023. "Environmental Impact Decision Support Tools for Horticulture Farming: Evaluation of GHG Calculators" Agriculture 13, no. 12: 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122213
APA StyleDzalbs, A., Bimbere, M., Pubule, J., & Blumberga, D. (2023). Environmental Impact Decision Support Tools for Horticulture Farming: Evaluation of GHG Calculators. Agriculture, 13(12), 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13122213





