Estimation and Forecasting of Rice Yield Using Phenology-Based Algorithm and Linear Regression Model on Sentinel-II Satellite Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
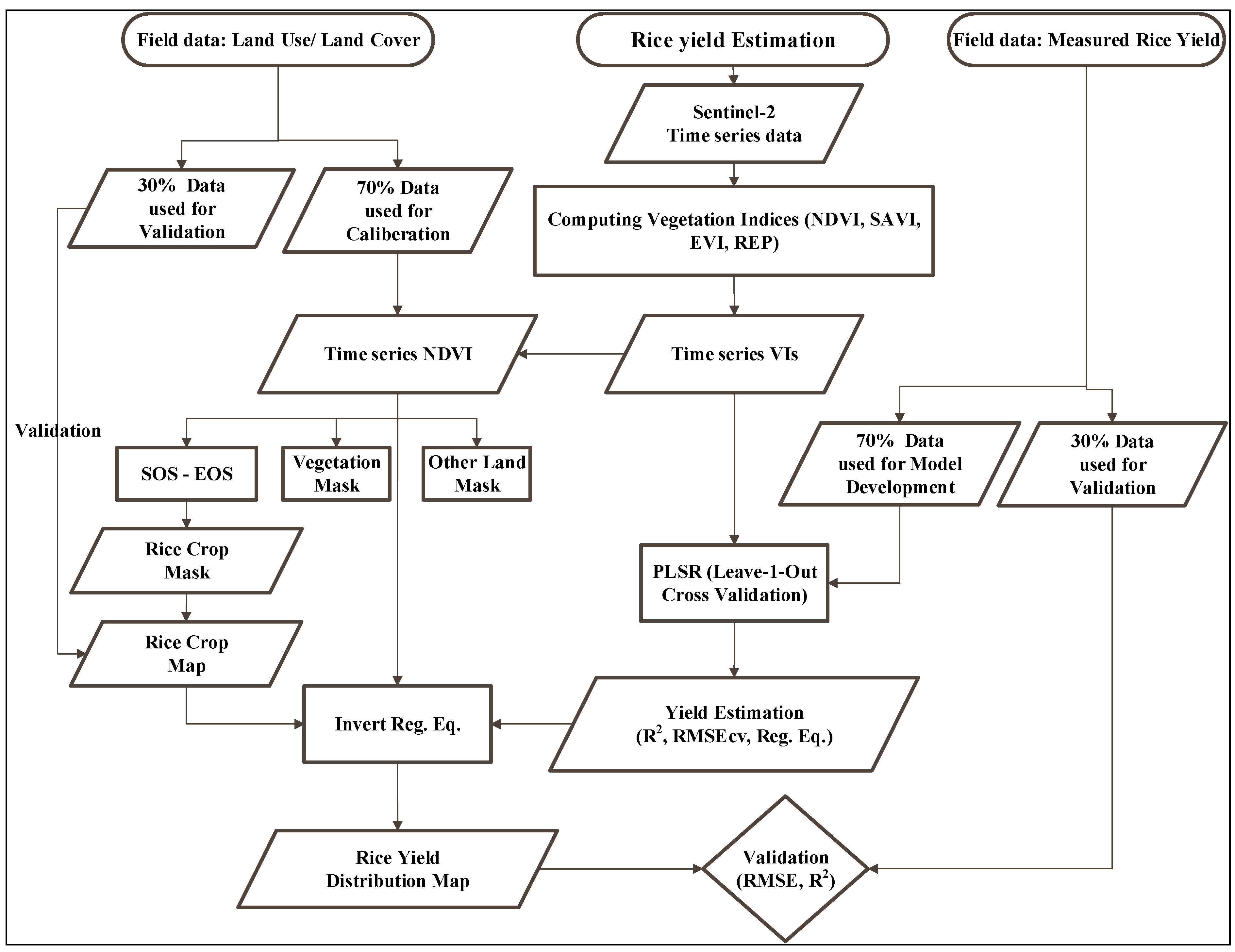
2. Materials and Methods
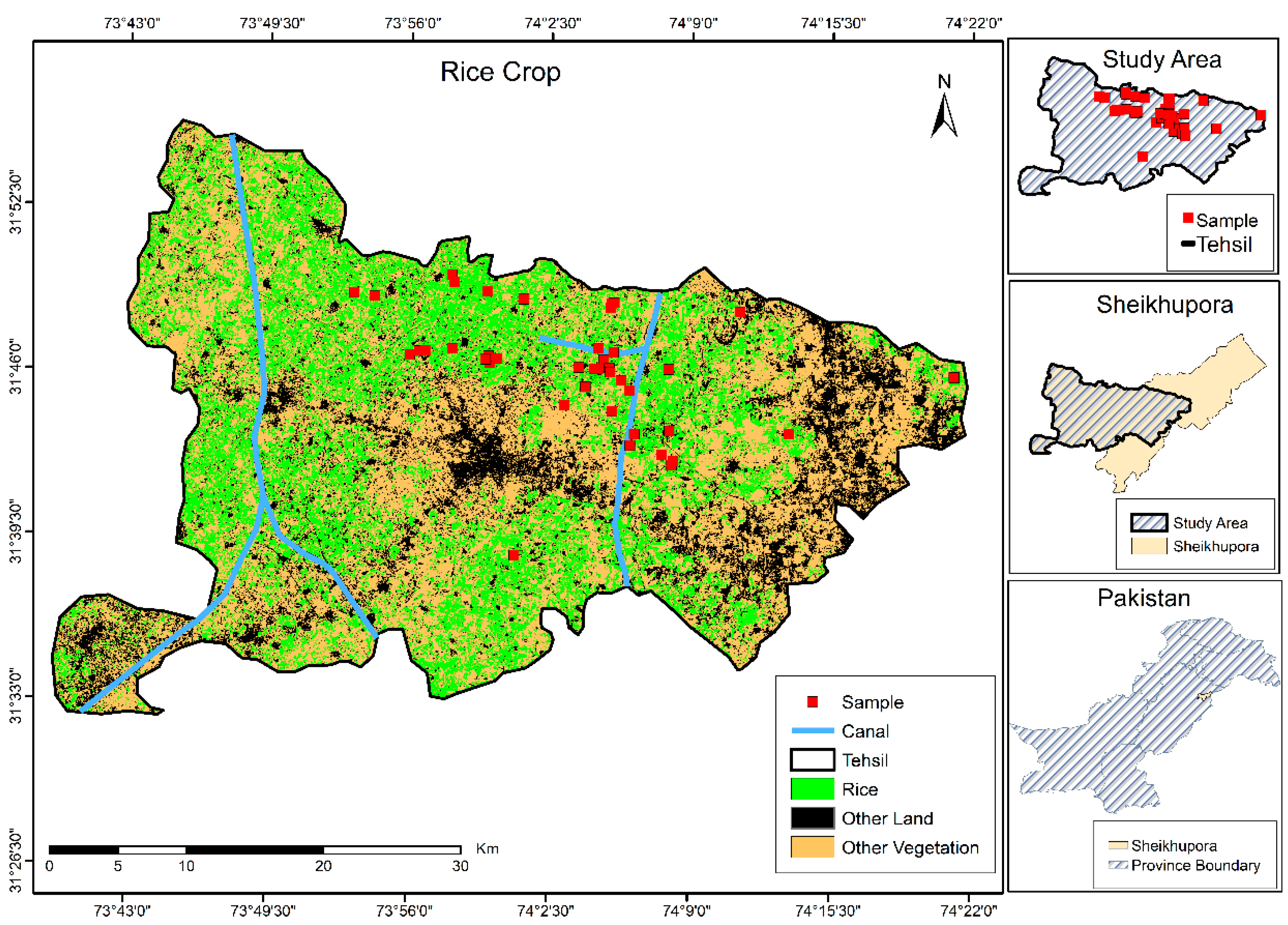
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
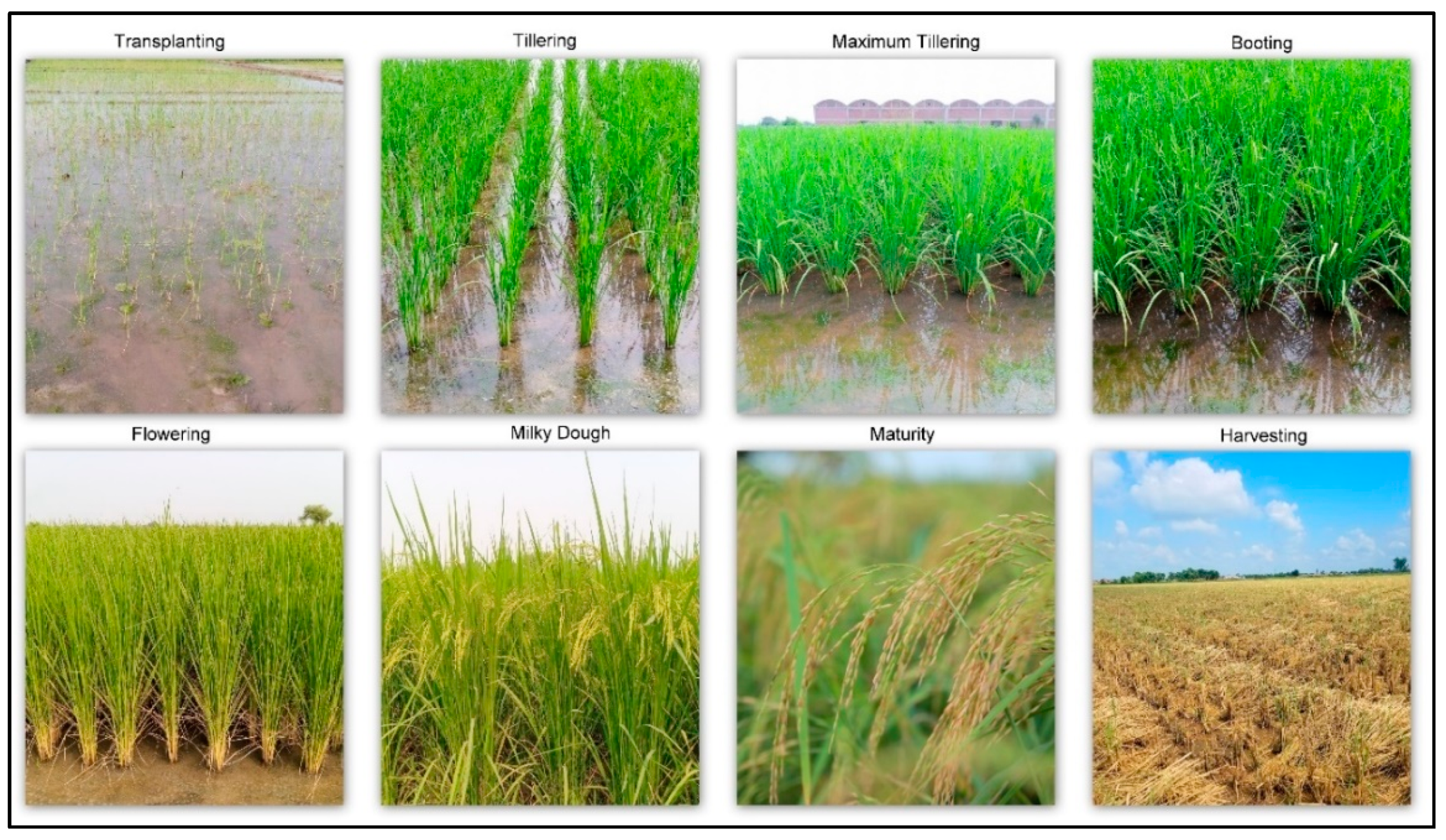
2.2.1. Field Data
2.2.2. Satellite Data Preprocessing and Vegetation Index
2.3. Geo-Statistical Analysis
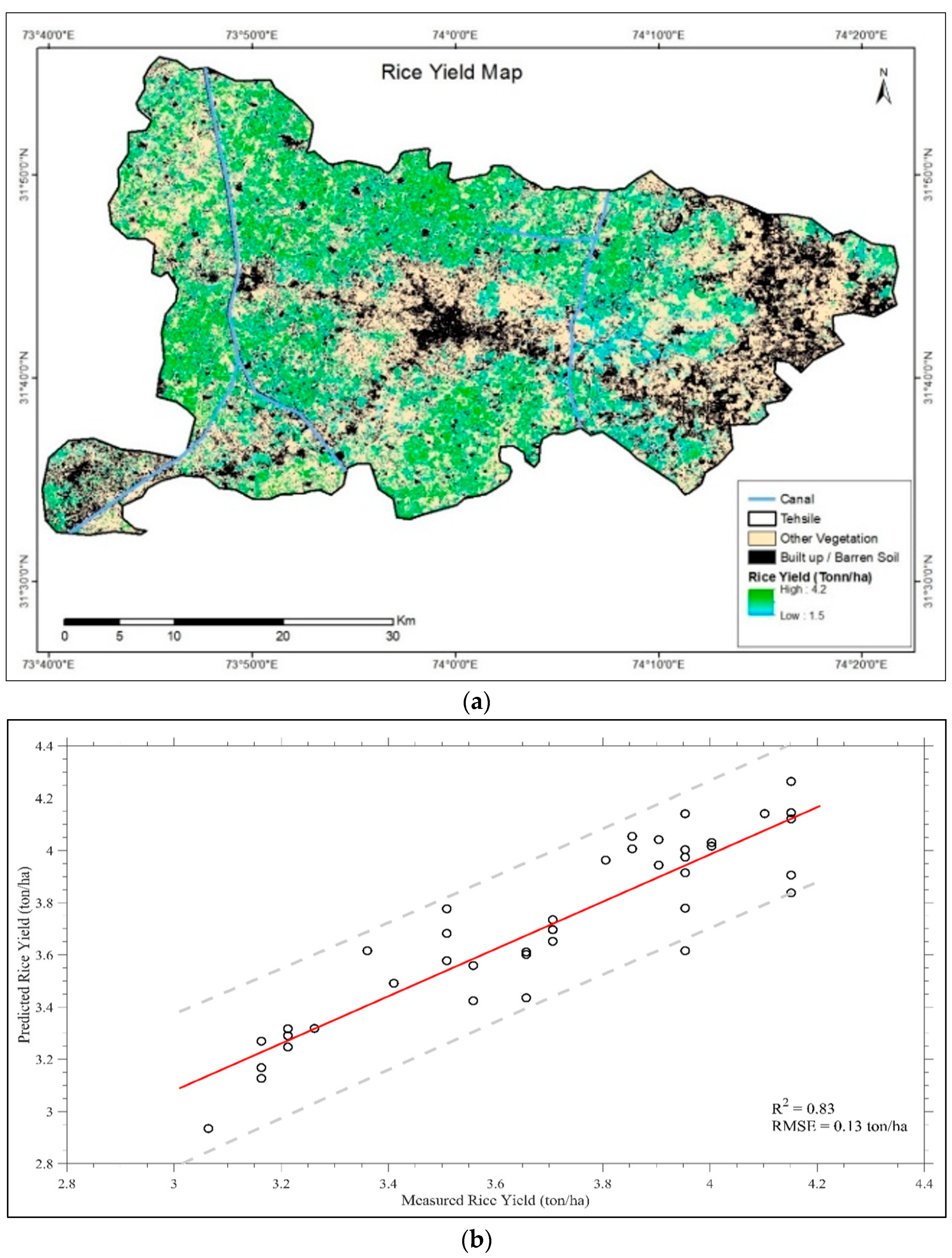
2.4. Spatial Distribution and Mapping of Rice Yield
3. Results
3.1. Rice Yield Estimation (Field Level Data)
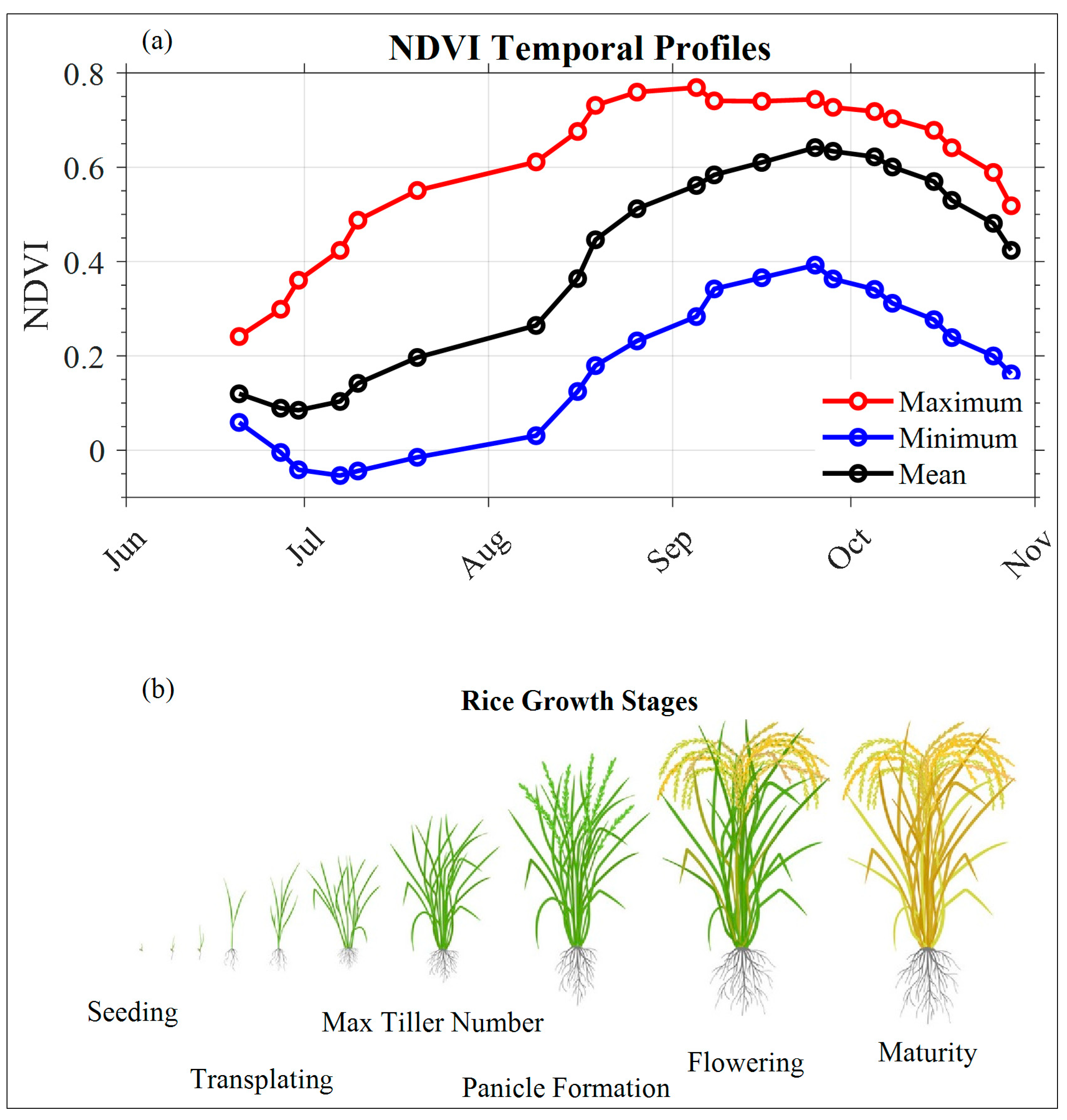
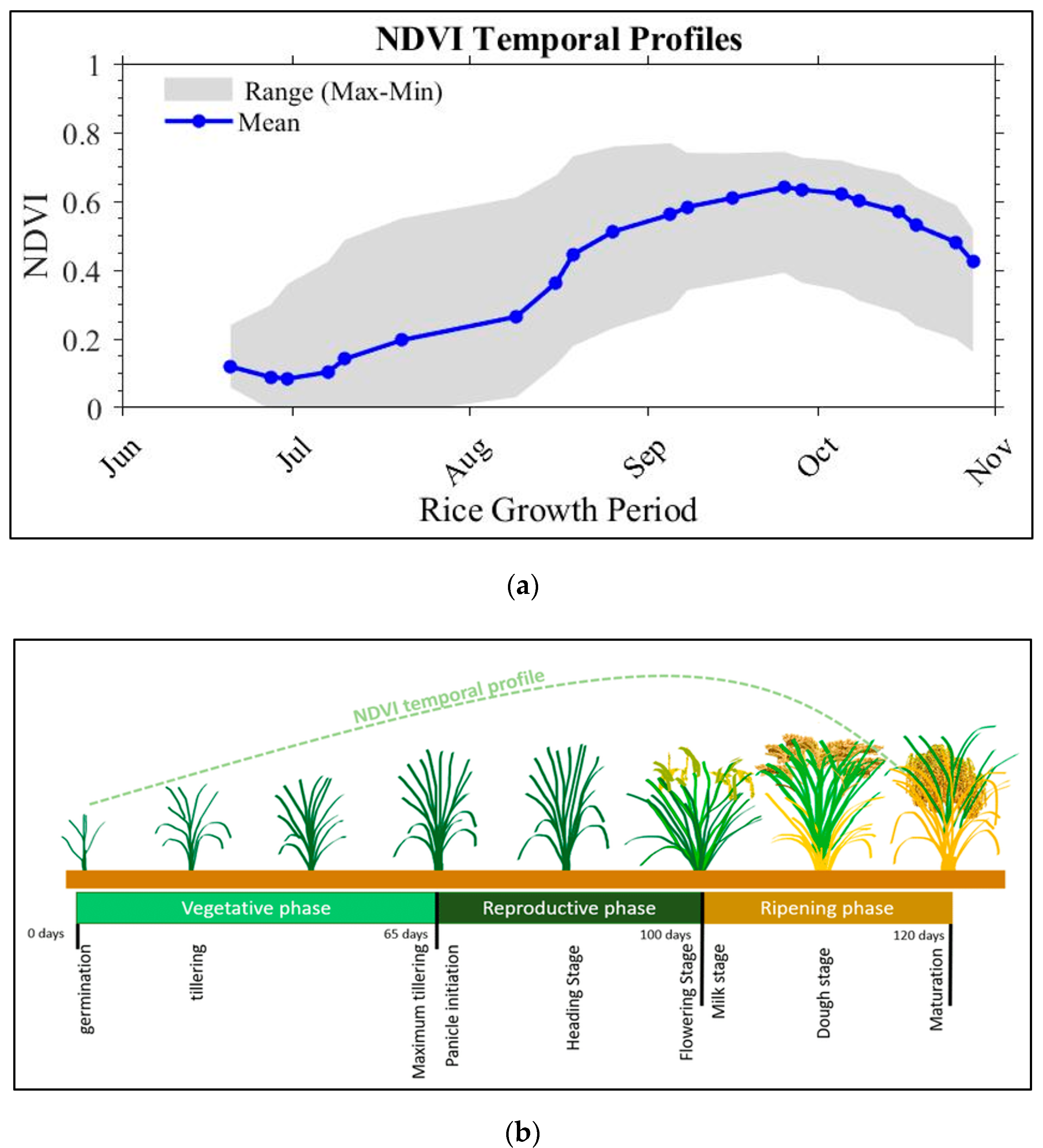
3.2. Variation in Temporal Profiles of Vegetation Indices with Rice Phenology
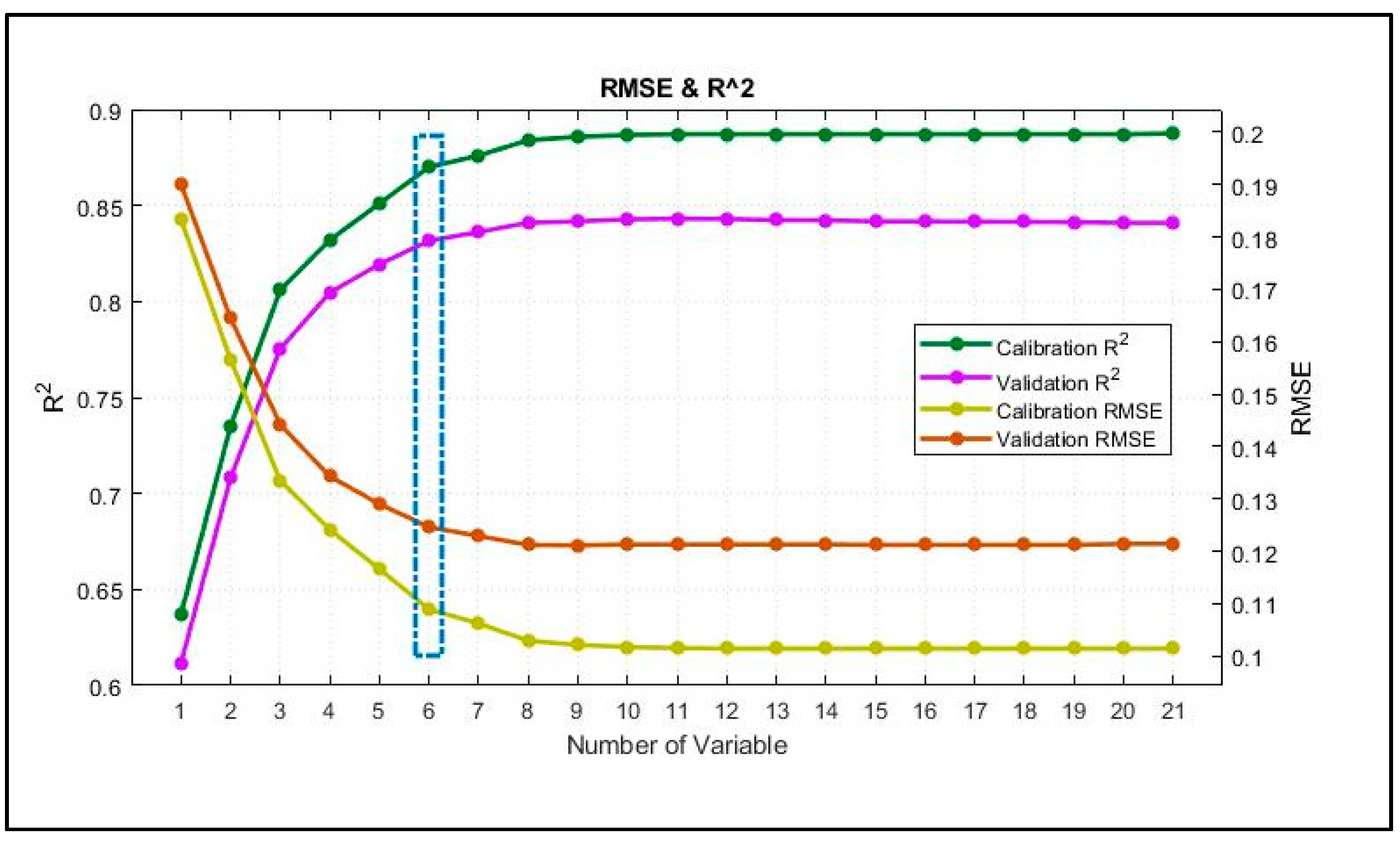
3.3. Prediction of Rice Yield and the Performance of Vegetation Indices
3.4. Spatial Varability in Rice Yield Potential
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food Security: The Challenge of Feeding 9 Billion People. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawe, D. The contribution of rice research to poverty alleviation. In Redesigning Rice Photosynthesis to Increase Yield, Proceedings of the Workshop on the Quest to Reduce Hunger: Redesigning Rice Photosynthesis, Los Baños, Philippines, 30 November–3 December 1999; Sheehy, J.E., Mitchell, P.L., Hardy, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture (SOFA): Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bandumula, N. Rice Production in Asia: Key to Global Food Security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 88, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PBS. Prices of Agricultural Commodities; Agriculture Statistics; Pakistan Bureau of Statistics (PBS): Islamabad, Pakistan, 2019; pp. 124–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Huang, J.; Xie, J. Rice Yield Estimation Using Parcel-Level Relative Spectral Variables From UAV-Based Hyperspectral Imagery. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebbers, R.; Adamchuk, V.I. Precision Agriculture and Food Security. Science 2010, 327, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Prediction of crop yield using phenological information extracted from remote sensing vegetation index. Sensors 2021, 21, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Liang, S.; Hoogenboom, G.; Teasdale, J.; Cavigelli, M. Corn-yield estimation through assimilation of remotely sensed data into the CSM-CERES-Maize model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3011–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B. The use of satellite data for crop yield gap analysis. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 143, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.P.; Zhou, X.X.; Wang, Z.X.; Mao, W.; Li, W.X.; Yun, F.; Guo, W.S.; Tan, C.W. Using HJ-CCD image and PLS algorithm to estimate the yield of field-grown winter wheat. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savin, I.Y.; Isaev, V.A. Rice yield forecast based on satellite and meteorological data. Russ. Agric. Sci. 2010, 36, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, Y.-S.; Chuang, Y.-C. Yield Estimation of Paddy Rice Based on Satellite Imagery: Comparison of Global and Local Regression Models. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, D.; Huang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, F.; Yang, X. Modelling paddy rice yield using MODIS data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 184, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilardelli, C.; Stella, T.; Confalonieri, R.; Ranghetti, L.; Campos-Taberner, M.; García-Haro, F.J.; Boschetti, M. Downscaling rice yield simulation at sub-field scale using remotely sensed LAI data. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 103, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ines, A.V.M.; Das, N.N.; Hansen, J.W.; Njoku, E.G. Assimilation of remotely sensed soil moisture and vegetation with a crop simulation model for maize yield prediction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 138, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Launay, M.; Guerif, M. Assimilating remote sensing data into a crop model to improve predictive performance for spatial applications. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 111, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Fernández, R.; Escalante, O.M.; Mamán, L.; Navarro, G. New capabilities of Sentinel-2A/B satellites combined with in situ data for monitoring small harmful algal blooms in complex coastal waters. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basterrechea, D.A.; Parra, L.; Parra, M.; Lloret, J. A Proposal for Monitoring Grass Coverage in Citrus Crops Applying Time Series Analysis in Sentinel-2 Bands. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Industrial IoT Technologies and Applications, Virtual Event; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 11 December 2020; pp. 193–206. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-71061-3_12 (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Phiri, D.; Simwanda, M.; Salekin, S.; Nyirenda, V.R.; Murayama, Y.; Ranagalage, M. Sentinel-2 data for land cover/use mapping: A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Cheng, T.; Yao, X.; Deng, X.; Tian, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Detection of rice phenology through time series analysis of ground-based spectral index data. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 198, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Qiu, X.; Cheng, T.; Tian, Y. Integrating remote sensing information with crop model to monitor wheat growth and yield based on simulation zone partitioning. Precis. Agric. 2018, 19, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murchie, E.H.; Yang, J.; Hubbart, S.; Horton, P.; Peng, S. Are there associations between grain-filling rate and photosynthesis in the flag leaves of field-grown rice? J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntanos, D.A.; Koutroubas, S.D. Dry matter and N accumulation and translocation for Indica and Japonica rice under Mediterranean conditions. Field Crop. Res. 2002, 74, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.; Suguri, M.; Umeda, M. Multivariate analysis of nitrogen content for rice at the heading stage using reflectance of airborne hyperspectral remote sensing. Field Crop. Res. 2011, 122, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horie, T.; Ohnishi, M.; Angus, J.F.; Lewin, L.G.; Tsukaguchi, T.; Matano, T. Physiological characteristics of high-yielding rice inferred from cross-location experiments. Field Crop. Res. 1997, 52, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Shi, L.; Han, J.; Zha, Y.; Zhu, P. Deep convolutional neural networks for rice grain yield estimation at the ripening stage using UAV-based remotely sensed images. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 235, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PMD-Pakistan Meteorological Department. Decadal Agromet Bulletin of Pakistan; National Agromet Centre (NAMC) Pakistan Meteorological Department: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2019; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Khaliq, T.; Gaydon, D.S.; Ahmad, M.-D.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Gull, U. Analyzing crop yield gaps and their causes using cropping systems modelling–A case study of the Punjab rice-wheat system, Pakistan. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 232, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, W.; Younas, M.; Waseem, M. Price Fluctuations of Rice Crop in District Sheikhupura. J. Agric. Stud. 2019, 7, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transon, J.; D’Andrimont, R.; Maugnard, A.; Defourny, P. Survey of Hyperspectral Earth Observation Applications from Space in the Sentinel-2 context. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohrs, C.W.; Cook, R.L.; Gray, J.M.; Albaugh, T.J. Sentinel-2 Leaf Area Index Estimation for Pine Plantations in the Southeastern United States. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narin, O.G.; Abdikan, S. Monitoring of phenological stage and yield estimation of sunflower plant using Sentinel-2 satellite images. Geocarto. Int. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Smith, R.B.; De Pauw, E. Hyperspectral Vegetation Indices and Their Relationships with Agricultural Crop Characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 71, 158–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W., Jr.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with ERTS; NASA Special Pub-351; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.R. A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Huete, A. A feedback based modification of the NDVI to minimize canopy background and atmospheric noise. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, I.; Penuelas, J. The red edge position and shape as indicators of plant chlorophyll content, biomass and hydric status. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Watanabe, N.; Sakanoue, S.; Lee, H.-J.; Inoue, Y.; Odagawa, S. Testing genetic algorithm as a tool to select relevant wavebands from field hyperspectral data for estimating pasture mass and quality in a mixed sown pasture using partial least squares regression. Grassl. Sci. 2010, 56, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Skidmore, A.K.; Ramoelo, A.; Groen, T.A.; Naeem, M.; Ali, A. Retrieval of leaf water content spanning the visible to thermal infrared spectra. SPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denham, M.C. Choosing the number of factors in partial least squares regression: Estimating and minimizing the mean squared error of prediction. J. Chemom. 2000, 14, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guan, K.; Yu, A.; Peng, B.; Zhao, L.; Li, B.; Peng, J. Toward building a transparent statistical model for improving crop yield prediction: Modeling rainfed corn in the U.S. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 234, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Kawamura, K.; Ishikawa, N.; Goto, M.; Wulan, T.; Alateng, D.; Yin, T.; Ito, Y. MODIS normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and vegetation phenology dynamics in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Z.; Jönsson, P.; Jin, H.; Eklundh, L. Performance of Smoothing Methods for Reconstructing NDVI Time-Series and Estimating Vegetation Phenology from MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laenoi, S.; Rerkasem, B.; Lordkaew, S.; Prom-u-thai, C. Seasonal variation in grain yield and quality in different rice varieties. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 221, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Knauer, K. Remote sensing of rice crop areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2101–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, M.K.; Hassan, Q.K.; Chowdhury, E.H. Application of Remote Sensors in Mapping Rice Area and Forecasting its Production: A Rev. Sensors 2015, 15, 769–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panda, S.S.; Ames, D.P.; Panigrahi, S. Application of Vegetation Indices for Agricultural Crop Yield Prediction Using Neural Network Techniques. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 673–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirasi, A.; Mahmoudi, A.; Navid, H.; Valizadeh Kamran, K.; Asoodar, M.A. Evaluation of sum-NDVI values to estimate wheat grain yields using multi-temporal Landsat OLI data. Geocarto. Int. 2019, 36, 1309–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Ullah, S.; Khurshid, K.; Ali, A. Estimation of leaf water content from mid- and thermal-infrared spectra by coupling genetic algorithm and partial least squares regression. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 022203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-W.; Shen, Y.; Lo, J.-C. Predicting Rice Yield Using Canopy Reflectance Measured at Booting Stage. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Vegetation Indices (VIs) | References |
|---|---|
| Rouse et al. (1974) [35] | |
where L = 0.5, to minimize the brightness effect of soil | Huete (1988) [36] |
where G = 2.5; L = 0.5 (Soil adjusted factor); C1 and C2 are constants to reduce aerosols effects. | Liu and Huete (1995) [37] |
where 704 and 35 represent interpolation constants that can be adjusted according to available band’s wavelength | Filella and Penuelas (1994) [38] |
| Dataset Type | Sample Size (n) | Minimum (ton/ha) | Maximum (ton/ha) | Mean (ton/ha) | SD (ton/ha) | CV (ton/ha) | Graphical Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | 96 | 3.06 | 4.15 | 3.70 | 0.31 | 0.083 | 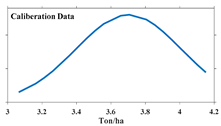 |
| Validation | 41 | 3.16 | 4.15 | 3.71 | 0.29 | 0.078 |  |
| Indices | No. of Latent Variables in PLSR Model | Calibration R2 | RMSEC (ton/ha) | Validation R2 | RMSECV (ton/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | 6 | 0.87 | 0.11 | 0.83 | 0.12 |
| EVI | 6 | 0.85 | 0.12 | 0.80 | 0.14 |
| SAVI | 6 | 0.84 | 0.12 | 0.79 | 0.14 |
| REP | 5 | 0.70 | 0.16 | 0.62 | 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazir, A.; Ullah, S.; Saqib, Z.A.; Abbas, A.; Ali, A.; Iqbal, M.S.; Hussain, K.; Shakir, M.; Shah, M.; Butt, M.U. Estimation and Forecasting of Rice Yield Using Phenology-Based Algorithm and Linear Regression Model on Sentinel-II Satellite Data. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11101026
Nazir A, Ullah S, Saqib ZA, Abbas A, Ali A, Iqbal MS, Hussain K, Shakir M, Shah M, Butt MU. Estimation and Forecasting of Rice Yield Using Phenology-Based Algorithm and Linear Regression Model on Sentinel-II Satellite Data. Agriculture. 2021; 11(10):1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11101026
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazir, Abid, Saleem Ullah, Zulfiqar Ahmad Saqib, Azhar Abbas, Asad Ali, Muhammad Shahid Iqbal, Khalid Hussain, Muhammad Shakir, Munawar Shah, and Muhammad Usman Butt. 2021. "Estimation and Forecasting of Rice Yield Using Phenology-Based Algorithm and Linear Regression Model on Sentinel-II Satellite Data" Agriculture 11, no. 10: 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11101026
APA StyleNazir, A., Ullah, S., Saqib, Z. A., Abbas, A., Ali, A., Iqbal, M. S., Hussain, K., Shakir, M., Shah, M., & Butt, M. U. (2021). Estimation and Forecasting of Rice Yield Using Phenology-Based Algorithm and Linear Regression Model on Sentinel-II Satellite Data. Agriculture, 11(10), 1026. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11101026








