Effect of Soil and Foliar Silicon Application on the Reduction of Zinc Toxicity in Wheat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pot Experiment
- (1)
- 0: control without Zn and Si
- (2)
- Zn: 600 mg kg−1 Zn applied to the soil
- (3)
- ZnSi1-soil: 600 mg kg−1 Zn to the soil + 200 mg kg−1 Si to the soil
- (4)
- ZnSi2-soil: 600 mg kg−1 Zn to the soil + 400 mg kg−1 Si to the soil
- (5)
- ZnSi1-foliar: 600 mg kg−1 Zn to the soil + triple foliar spray with 2 mM L−1 Si
- (6)
- ZnSi2-foliar: 600 mg kg−1 Zn to the soil + triple foliar spray with 6 mM L−1 Si
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. Calculation of the Bioaccumulation and Translocation Factor
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
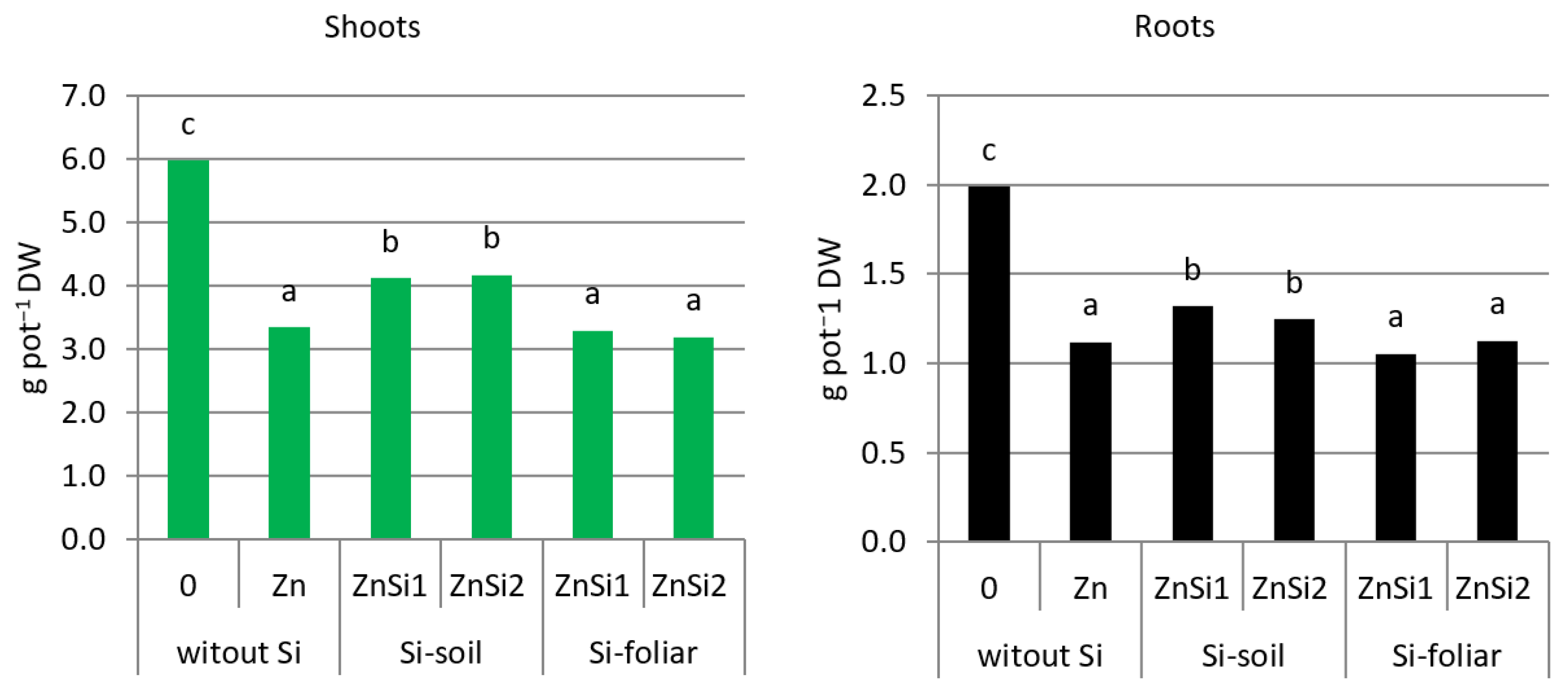
3.1. Plants Biomass
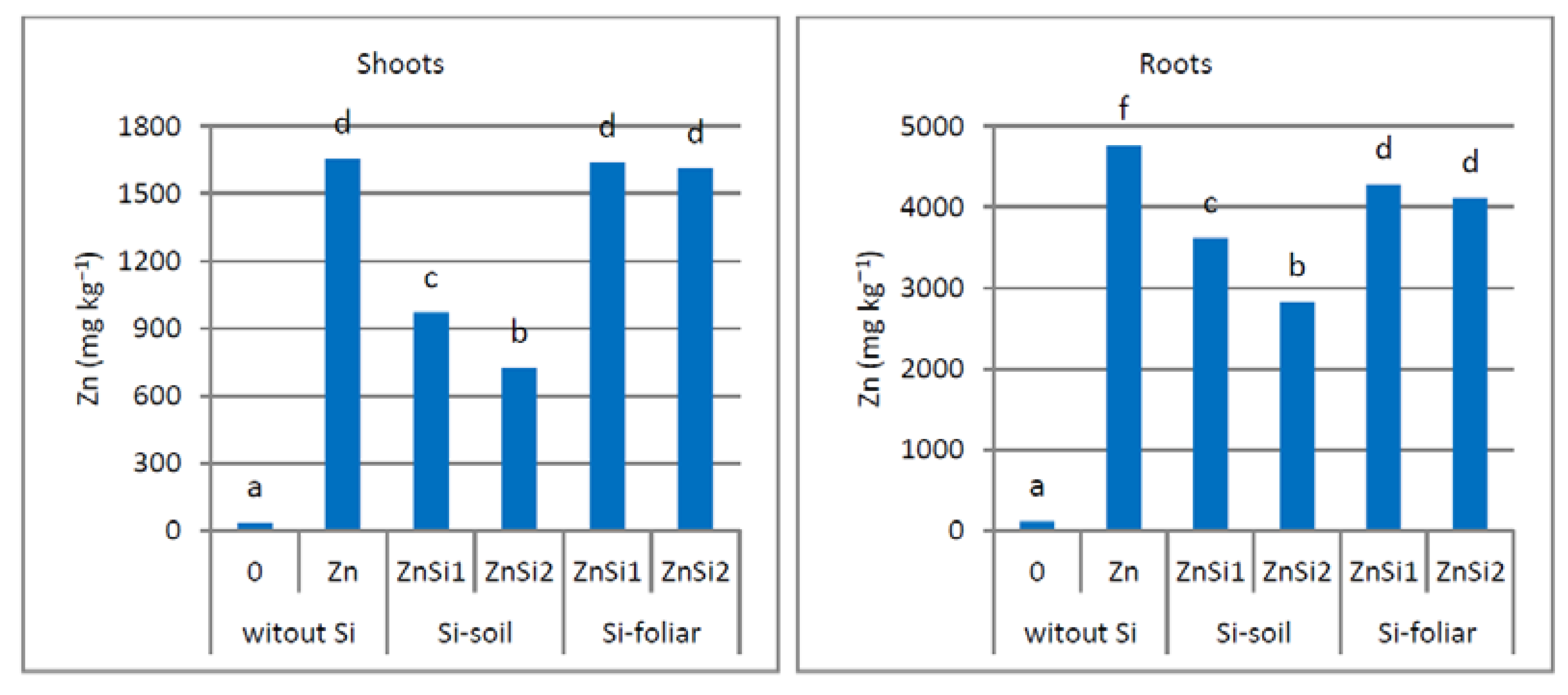
3.2. Zn Concentration in Shoots and Roots
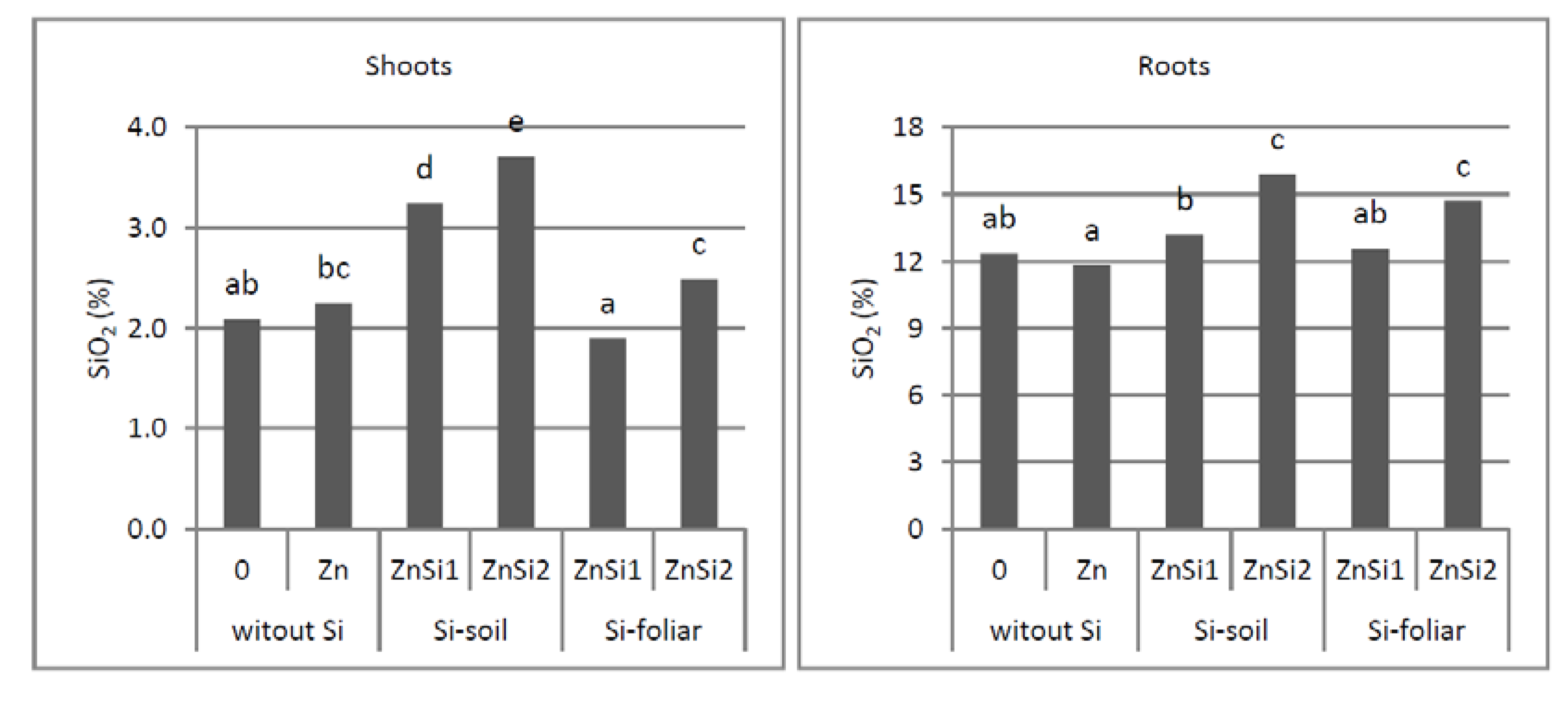
3.3. Si Concentration in Shoots and Roots
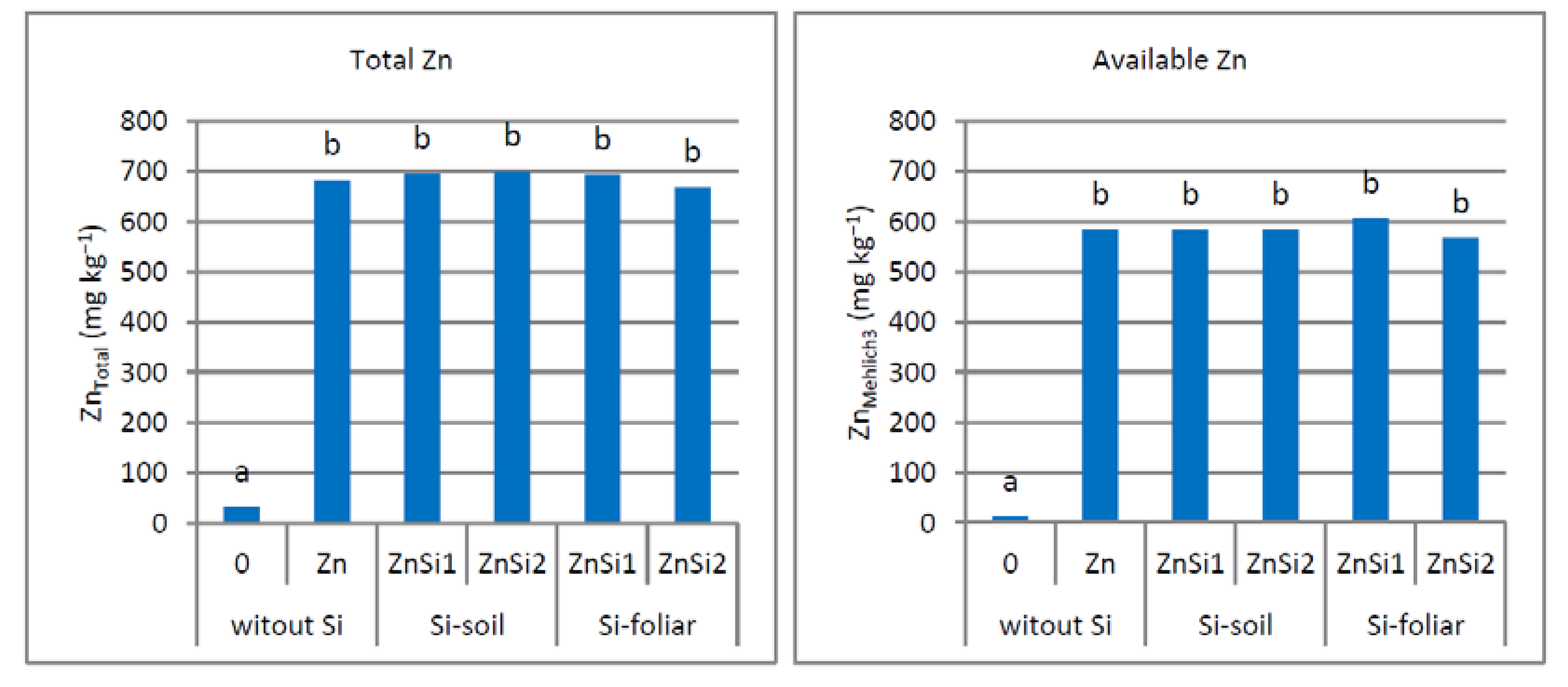
3.4. Zn Concentration in Soil
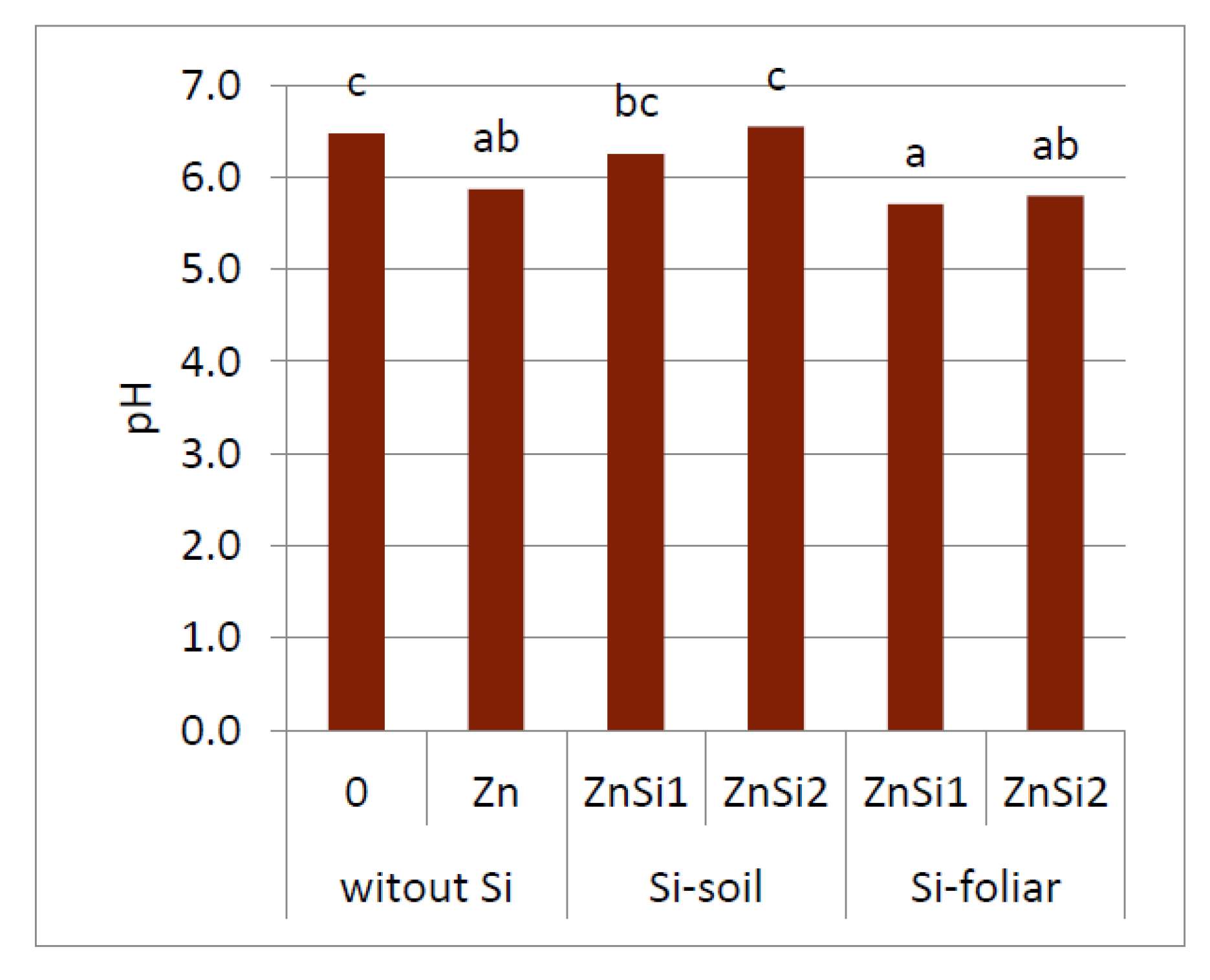
3.5. Soil pH
3.6. Zn Bioaccumulation and Translocation
4. Discussion
4.1. Plant Biomass
4.2. Zn Concentration in Shoots and Roots
4.3. Si Concentration in Shoots and Roots
4.4. Zn Concertation in Soil
4.5. Zn Transfer from Roots to Shoots
4.6. The Joint Effect of Si and pH Changes in Alleviating Zn Toxicity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaney, R.Á. Zinc phytotoxicity. In Zinc in Soils and Plants; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 135–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ciarkowska, K.; Gambus, F.; Antonkiewicz, J.; Koliopoulos, T. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and heavy metal contents in the urban soils in southern Poland. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Lin, C.; Cheng, H.; Duan, X.; Lei, K. Contamination and health risks of soil heavy metals around a lead/zinc smelter in southwestern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noulas, C.; Tziouvalekas, M.; Karyotis, T. Zinc in soils, water and food crops. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 49, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliszewska-Kordybach, B.; Smreczak, B.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A. Zagrożenie zanieczyszczeniami chemicznymi gleb na obszarach rolniczych w Polsce w świetle badan IUNG-PIB w Puławach (Threat of chemical contamination in agricultural areas in Poland in the context of research of IUNG-PIB in Pulawy). Studia Rap. IUNG-PIB 2013, 35, 97–118. [Google Scholar]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, G.R.; Das, P. Effect of metal toxicity on plant growth and metabolism: I. Zinc. In Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 873–884. [Google Scholar]
- Anwaar, S.A.; Ali, S.; Ali, S.; Ishaque, W.; Farid, M.; Farooq, M.A.; Najeeb, U.; Abbas, F.; Sharif, M. Silicon (Si) alleviates cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) from zinc (Zn) toxicity stress by limiting Zn uptake and oxidative damage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3441–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Li, P.; Fan, F.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y. The effect of silicon on photosynthesis and expression of its relevant genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under high-zinc stress. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E. Silicon. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1999, 50, 641–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E. The anomaly of silicon in plant biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E.; Bloom, A.J. Mineral Nutrition of Plants: Principles and Perspectives, 2nd ed.; Sinauer: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhu, Y.G.; Christie, P. Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of abiotic stresses in higher plants: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.A.; Dietz, K.J. Silicon as versatile player in plant and human biology: Overlooked and poorly understood. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guével, M.H.; Menzies, J.G.; Bélanger, R.R. Effect of root and foliar applications of soluble silicon on powdery mildew control and growth of wheat plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 119, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Yamaji, N. Silicon uptake and accumulation in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, S.B.; Saiyad, M.; Dhruve, J.J. Effect of foliar application of silicon on growth and development of okra fruit. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2019, 8, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, A.; Ayed, S.; Bezzin, O.; Farooq, M.; Ayed-Slama, O.; Slim-Amara, H.; Younes, M.B. Effect of Silicon Supply Methods on Durum Wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) Response to Drought Stress. Silicon 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Cheema, M.A.; Sher, A.; Ijaz, M.; Wasaya, A.; Yasir, T.A.; Abbas, T.; Hussain, M. Foliar Applied Silicon Improves Water Relations, Stay Green and Enzymatic Antioxidants Activity in Late Sown Wheat. Silicon 2020, 12, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntzer, F.; Keller, C.; Meunier, J.D. Benefits of plant silicon for crops: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Mitani, N.; Nagao, S.; Konishi, S.; Tamai, K.; Iwashita, T.; Yano, M. Characterization of the silicon uptake system and molecular mapping of the silicon transporter gene in rice. Plant. Physiol. 2004, 136, 3284–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, M.A.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Ahmad, R.; Waraich, E.A.; Hameed, M. Improving drought tolerance potential in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) through exogenous silicon supply. Pak. J. Bot. 2015, 47, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Ibrahim, M.; Farid, M.; Adrees, M.; Bharwana, S.A.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Abbas, F. Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of drought and salt stress in plants: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15416–15431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sienkiewicz-Cholewa, U.; Sumisławska, J.; Sacała, E.; Dziągwa-Becker, M.; Kieloch, R. Influence of silicon on spring wheat seedlings under salt stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2018, 40, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Gong, H.J.; Yin, J.L. Role of silicon in mediating salt tolerance in plants: A review. Plants 2019, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, N. Silicon control of bacterial and viral diseases in plants. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2016, 56, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.X.; Wang, Y.C.; Gong, H.J. Mechanisms of enhanced heavy metal tolerance in plants by silicon: A review. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wong, J.W.C.; Wei, L. Silicon-mediated enhancement of cadmium tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Ghafoor, A.; Farooq, M. Suppression of cadmium concentration in wheat grains by silicon is related to its application rate and cadmium accumulating abilities of cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Meunier, J.D.; Miche, H.; Keller, C. Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F. Effect of Si on the distribution of Cd in rice seedlings. Plant Soil. 2005, 272, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xue, G.; Fan, F.; Liang, Y. Silicon-enhanced resistance to cadmium toxicity in Brassica chinensis L. is attributed to Si-suppressed cadmium uptake and transport and Si-enhanced antioxidant defense capacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Guo, L.; Yang, D.; He, N.; Ying, B.; Wang, Y. Influence of silicon on cadmium availability and cadmium uptake by rice in acid and alkaline paddy soils. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Farooq, M.A.; Yasmeen, T.; Hussain, S.; Arif, M.S.; Abbas, F.; Bharwana, S.A.; Zhang, G. The influence of silicon on barley growth, photosynthesis and ultra-structure under chromium stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 89, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Liao, X.; Wang, R. Silicon Mediated the Detoxification of Cr on Pakchoi (Brassica Chinensis L.) in Cr-contaminated Soil. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hou, Y.L.; Wang, S.G.; Zhu, Y.G. Effect of silicate on the growth and arsenate uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings in solution culture. Plant Soil. 2005, 272, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmiroli, M.; Pigoni, V.; Savo-Sardaro, M.L.; Marmiroli, N. The effect of silicon on the uptake and translocation of arsenic in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 99, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ullah, N.; Bharwana, S.A.; Waseem, M.; Farooq, M.A.; Abbasi, G.H.; Farid, M. Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of silicon-induced copper stress tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, B.; Doelsch, E.; Keller, C.; Cazevieille, P.; Tella, M.; Chaurand, P.; Panfili, F.; Hazemann, J.L.; Meunier, J.D. Evidence of sulfur-bound reduced copper in bamboo exposed to high silicon and copper concentrations. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokor, B.; Vaculík, M.; Slováková, Ľ.; Masarovič, D.; Lux, A. Silicon does not always mitigate zinc toxicity in maize. Acta Physiol Plant. 2014, 36, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.H.; Qiu, H.; Tian, T.; Zhan, S.S.; Chaney, R.L.; Wang, S.Z.; Tang, Y.T.; Morel, J.L.; Qiu, R.L. Mitigation effects of silicon rich amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on multi-metal contaminated acidic soil. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, C.; Tuna, A.L.; Sonmez, O.; Ince, F.; Higgs, D. Mitigation effects of silicon on maize plants grown at high zinc. J. Plant Nutr. 2009, 32, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabanjoubani, P.; Abdolzadeh, A.; Sadeghipour, H.R.; Aghdasi, M. Impacts of silicon nutrition on growth and nutrient status of rice plants grown under varying zinc regimes. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2015, 27, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Fan, F.; Nikolic, M.; Liang, Y. The alleviation of zinc toxicity by silicon is related to zinc transport and antioxidative reactions in rice. Plant Soil. 2011, 344, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira da Cunha, K.; Williams Araújo do Nascimento, C.; José da Silva, A. Silicon alleviates the toxicity of cadmium and zinc for maize (Zea mays L.) grown on a contaminated soil. J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sci. 2008, 171, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polish Committee for Standardization. PN-R-04033:1998. Soil and Mineral Soil Materials: Particle Size Distribution on Soil Classes; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1998. (In Polish)
- International Standardization Organization. ISO 10390:2005. Soil Quality: Determination of pH; International Standardization Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Polish Committee for Standardization. PN-ISO-14235:2003. Soil Quality: Determination of Organic Carbon in Soil by Sulfochromic Oxidation; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2003. (In Polish)
- Polish Committee for Standardization. PN-R-04022:1996. Agrochemical Soil Analyse: Determination of Available Potassium Content in Mineral Soils; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1996. (In Polish)
- Polish Committee for Standardization. PN-R-04020:1994. Agrochemical Soil Analyse: Determination of Available Magnesium Content in Mineral Soils; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1994. (In Polish)
- International Standardization Organization. ISO 11466:1995. Soil Quality: Extraction of Trace Elements Soluble in Aqua Regia; International Standardization Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Korzeniowska, J.; Stanisławska-Glubiak, E. Comparison of 1 M HCl and Mehlich 3 for assessment of the micronutrient status of polish soils in the context of winter wheat nutritional demands. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzeniowska, J.; Stanislawska-Glubiak, E.; Lipinski, W. Development of the limit values of micronutrient deficiency in soil determined using Mehlich 3 extractant for Polish soil conditions. Part I. Wheat. Soil Sci. Annu. 2019, 70, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polish Committee for Standardization. PN-R-04014:1991. Agrochemical Plant Analyse. Methods of Mineralization of Plant Material for Determination Macro- and Microelements; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1991. (In Polish)
- Yoshida, S.; Forno, D.A.; Cock, J.H.; Gomez, K.A. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice, 3rd ed.; Intemational Rice Research Institute: Los Banos, Laguna, Philippines, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, E.E.C.; Costa, E.T.S.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; Faquin, V.; Nascimento, C.W.A. Accumulation of arsenic and nutrients by castor bean plants grown on an As-enriched nutrient solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.H.; Zhan, S.S.; Wang, S.Z.; Tang, Y.T.; Chaney, R.L.; Fang, X.H. Silicon-mediated amelioration of zinc toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Plant Soil. 2012, 350, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, G. Silicon supplementation improves drought tolerance in canola plants. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 61, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.A.; Balal, R.M.; Pervez, M.A.; Abbas, T.; AQUEEL, M.A.; Javaid, M.M.; Garcia-Sanchez, F. Foliar spray of phyto-extracts supplemented with silicon: An efficacious strategy to alleviate the salinity-induced deleterious effects in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Turk. J. Bot. 2015, 39, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenidou, S.; Cavins, T.J.; Marek, S. Silicon supplements affect floricultural quality traits and elemental nutrient concentrations of greenhouse produced gerbera. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 123, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon, C.; Soratto, R.P.; Moreno, L.A. Effects of soil and foliar application of soluble silicon on mineral nutrition, gas exchange, and growth of potato plants. Crop. Sci. 2013, 53, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Mukherjee, A.B. Trace Elements from Soil to Human; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Masarovič, D.; Slováková, Ľ.; Bokor, B.; Bujdoš, M.; Lux, A. Effect of silicon application on Sorghum bicolor exposed to toxic concentration of zinc. Biologia 2012, 67, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| pH KCl | Sand | Silt | Clay | Corg | P1 | K 1 | Mg 2 | Zn 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | mg kg−1 | |||||||
| 6.5 | 70 | 26 | 4 | 0.7 | 150 | 284 | 116 | 33 |
| Treatment | BFshoot | BFroot | TF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn-without Si | 2.42 | 7.00 | 0.35 |
| ZnSi1-soil | 1.39 | 5.21 | 0.27 |
| ZnSi2-soil | 1.08 | 4.08 | 0.26 |
| ZnSi1-foliar | 2.35 | 6.17 | 0.38 |
| ZnSi2-foliar | 2.39 | 6.16 | 0.39 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zajaczkowska, A.; Korzeniowska, J.; Sienkiewicz-Cholewa, U. Effect of Soil and Foliar Silicon Application on the Reduction of Zinc Toxicity in Wheat. Agriculture 2020, 10, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10110522
Zajaczkowska A, Korzeniowska J, Sienkiewicz-Cholewa U. Effect of Soil and Foliar Silicon Application on the Reduction of Zinc Toxicity in Wheat. Agriculture. 2020; 10(11):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10110522
Chicago/Turabian StyleZajaczkowska, Aleksandra, Jolanta Korzeniowska, and Urszula Sienkiewicz-Cholewa. 2020. "Effect of Soil and Foliar Silicon Application on the Reduction of Zinc Toxicity in Wheat" Agriculture 10, no. 11: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10110522
APA StyleZajaczkowska, A., Korzeniowska, J., & Sienkiewicz-Cholewa, U. (2020). Effect of Soil and Foliar Silicon Application on the Reduction of Zinc Toxicity in Wheat. Agriculture, 10(11), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10110522






