Comprehensive Genomic Characterization and Expression Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Watermelon under Hormonal Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of LOX Gene Family Members in Watermelon
2.2. Analysis of Protein Properties, Phylogenetic Tree and Conserved Motifs
2.3. Analysis of the Gene Structure and Putative Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements
2.4. Chromosome Mapping, Duplication and Synteny Analysis
2.5. Expression Analysis of Watermelon LOX Genes Based on RNA-Seq Data
2.6. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.7. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of LOX Genes in Watermelon
3.2. Evolutionary Relationship among LOX Family Members in Various Plant Species
3.3. Characterization and Conserved Domain Analysis of Watermelon LOX Proteins
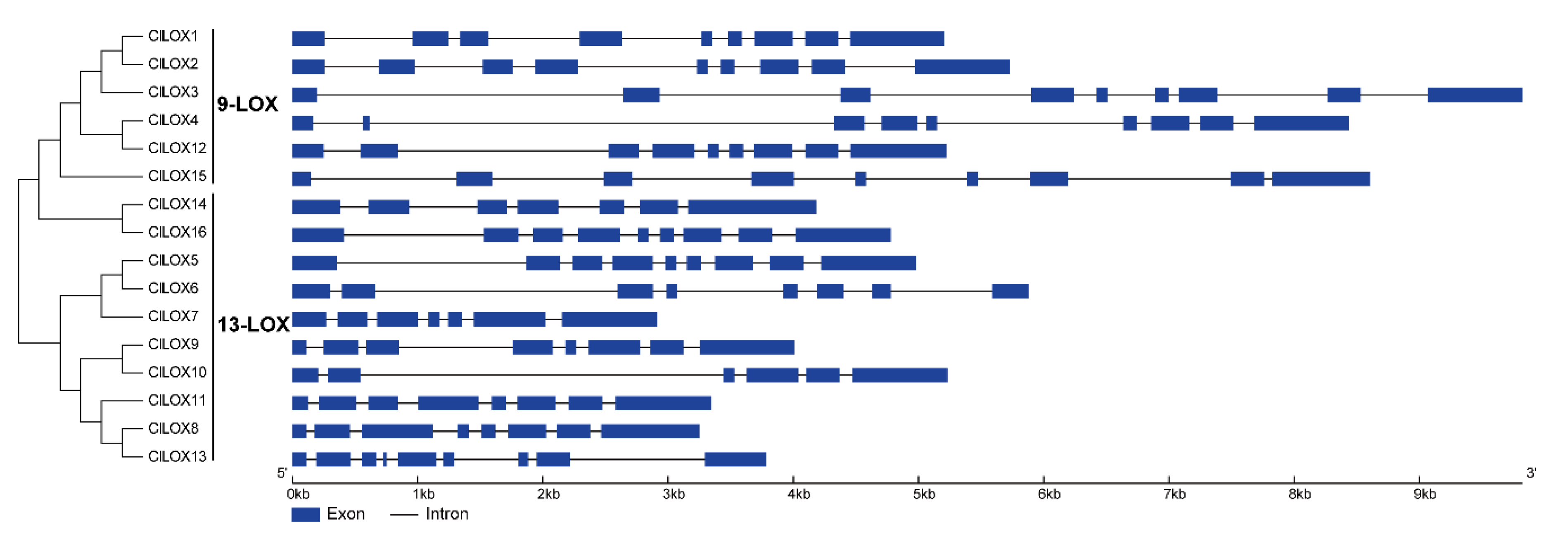
3.4. Intrachromosomal Localization and Structural Analysis of Watermelon LOX Genes
3.5. Cis-Element Analysis in the Promoter Regions of ClLOX Genes
3.6. Expression Analysis of ClLOX Genes in Different Tissues and during Fruit Development
3.7. Expression Analysis of Several Watermelon ClLOX Genes in Response to JA, SA and ET Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Porta, H.; Rocha-Sosa, M. Plant lipoxygenases. Physiological and molecular features. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feussner, I.; Wasternack, C. The lipoxygenase pathway. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennman, A.; Oliw, E.H.; Karkehabadi, S.; Chen, Y. Crystal structure of manganese lipoxygenase of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 8130–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banthiya, S.; Kalms, J.; Yoga, E.G.; Ivanov, I.; Carpena, X.; Hamberg, M.; Kuhn, H.; Scheerer, P. Structural and functional basis of phospholipid oxygenase activity of bacterial lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, P.; Li, C.; Han, S.; Lopez-Baltazar, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Identification of lipoxygenase (LOX) genes from legumes and their responses in wild type and cultivated peanut upon Aspergillus flavus infection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Guang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Ahammed, G.J.; Yang, Y. The CYP74 gene family in watermelon: Genome-wide identification and expression profiling under hormonal stress and root-knot nematode infection. Agronomy 2019, 9, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanath, K.K.; Varakumar, P.; Pamuru, R.R.; Basha, S.J.; Mehta, S.; Rao, A.D. Plant lipoxygenases and their role in plant physiology. J. Plant. Biol. 2020, 63, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolley, J.P.; Nagashima, Y.; Gorman, Z.; Kolomiets, M.V.; Koiwa, H. Isoform-specific subcellular localization of Zea mays lipoxygenases and oxo-phytodienoate reductase 2. Plant Gene 2018, 13, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, A.; Feussner, I. Lipoxygenases—Structure and reaction mechanism. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, D.; Lv, S.; Tan, A. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of lipoxygenase genes in Tartary buckwheat. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2020, 34, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Yan, H.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Cai, R.; Xiang, Y. The lipoxygenase gene family in poplar: Identification, classification, and expression in response to MeJA treatment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannenberg, G.; Martinez, M.; Hamberg, M.; Castresana, C. Diversity of the enzymatic activity in the lipoxygenase gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Lipids 2009, 44, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarde, S.J.; Kumar, A.; Remme, R.N.; Dicke, M. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression of lipoxygenase gene family in pepper. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 98, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Li, F.; Yan, X.; Liu, S.; Wei, C. Characterization and alternative splicing profiles of the lipoxygenase gene family in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 1765–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hu, T.; Wang, W.; Hu, H.; Wei, Q.; Wei, X.; Bao, C. Bioinformatics analysis of the lipoxygenase gene family in radish (Raphanus sativus) and functional characterization in response to abiotic and biotic stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunola, O.F.; Hawkins, L.K.; Mylroie, E.; Kolomiets, M.V.; Borrego, E.; Tang, J.D.; Williams, W.P.; Warburton, M.L. Characterization of the maize lipoxygenase gene family in relation to aflatoxin accumulation resistance. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umate, P. Genome-wide analysis of lipoxygenase gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Mattoo, A.K. Genome-wide identification of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) lipoxygenases coupled with expression profiles during plant development and in response to methyl-jasmonate and wounding. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 231, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolyan, A.; White, J.; Jordan, B.; Winefield, C. Identification of the lipoxygenase gene family from Vitis vinifera and biochemical characterisation of two 13-lipoxygenases expressed in grape berries of Sauvignon Blanc. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Cao, S.; Qi, H. The phylogeny and expression profiles of the lipoxygenase (LOX) family genes in the melon (Cucumis melo L.) genome. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 170, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Liu, X.H.; Jiang, L.W. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of the lipoxygenase gene family in cucumber. Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 2613–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, L.; Dunwell, J.M.; Qiao, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S. Characterization of the lipoxygenase (LOX) gene family in the Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) and comparison with other members of the Rosaceae. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldelari, D.; Wang, G.; Farmer, E.E.; Dong, X. Arabidopsis lox3 lox4 double mutants are male sterile and defective in global proliferative arrest. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 75, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayen, D.; Ali, N.; Sarkar, S.N.; Datta, S.K.; Datta, K. Down-regulation of lipoxygenase gene reduces degradation of carotenoids of golden rice during storage. Planta 2015, 242, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarde, S.J.; Bouwmeester, K.; Venegas-Molina, J.; David, A.; Boland, W.; Dicke, M. Involvement of sweet pepper CaLOX2 in jasmonate-dependent induced defence against Western flower thrips. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Ban, Q.; Meng, K.; He, Y.; Han, S.; Jin, M.; Rao, J. Overexpression of persimmon 9-lipoxygenase DkLOX3 confers resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 and Botrytis cinerea in Arabidopsis. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 84, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Meng, K.; Han, Y.; Ban, Q.; Wang, B.; Suo, J.; Lv, J.; Rao, J. The persimmon 9-lipoxygenase gene DkLOX3 plays positive roles in both promoting senescence and enhancing tolerance to abiotic stress. Front Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools—An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wan, C.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of the Dof gene family related to abiotic stress in watermelon. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Identification and expression analysis of two allene oxide cyclase (AOC) genes in watermelon. Agriculture 2019, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban, M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Sun, H.; Ullah, A.; Zhu, L. Genome-wide identification of lipoxygenase gene family in cotton and functional characterization in response to abiotic stresses. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steczko, J.; Donoho, G.P.; Clemens, J.C.; Dixon, J.E.; Axelrod, B. Conserved histidine residues in soybean lipoxygenase: Functional consequences of their replacement. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 4053–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, W.; Su, C.; Ma, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Tandem 13-lipoxygenase genes in a cluster confers yellow-green leaf in cucumber. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloane, D.L.; Leung, R.; Craik, C.S.; Sigal, E. A primary determinant for lipoxygenase positional specificity. Nature 1991, 354, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Hou, Y.; Huber, D.J.; Dong, X.; Ban, Q.; Chang, X.; Zhang, T.; Rao, J. Molecular cloning, structural characterization, and ripening-related expression of lipoxygenase genes from three persimmon cultivars differing in postharvest ripening rate. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 34, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.T.; Zhang, M.; Fu, C.H.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.J. Molecular cloning and characterization of two 9-lipoxygenase genes from Taxus chinensis. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 30, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, M.N.; Hernández, M.L.; Sanz, C.; Martínez-Rivas, J.M. Molecular cloning, functional characterization and transcriptional regulation of a 9-lipoxygenase gene from olive. Phytochemistry 2012, 74, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, E.; Walther, M.; Kühn, H.; Feussner, I. Conversion of cucumber linoleate 13-lipoxygenase to a 9-lipoxygenating species by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4192–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, J.; Hileman, L. Functional evolution in the plant SQUAMOSA-PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) gene family. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Evolution by gene duplication: An update. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, K.; Bowen, J.; Allan, A.; Espley, R.; Karunairetnam, S.; Ferguson, I. Differential expression within the LOX gene family in ripening kiwifruit. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 3825–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, A.; Barry, C.; Alpuche-Solis, A.G.; Grierson, D. Ethylene and developmental signals regulate expression of lipoxygenase genes during tomato fruit ripening. J. Exp. Bot. 1999, 50, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Ángel-Coronel, O.A.; León-García, E.; Vela-Gutiérrez, G.; Rojas-Reyes, J.O.; Gómez-Lim, M.Á.; García, H.S. Lipoxygenase activity associated to fruit ripening and senescence in chayote (Sechium edule Jacq. Sw. cv. “virens levis”). J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.; Creelman, R.A.; Mullet, J.E. A chloroplast lipoxygenase is required for wound-induced jasmonic acid accumulation in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8675–8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Han, X.; Feng, D.; Yuan, D.; Huang, L.J. Signaling crosstalk between salicylic acid and ethylene/jasmonate in plant defense: Do we understand what they are whispering? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, X.; Gomila, J.; Takken, F.L.W. Involvement of salicylic acid, ethylene and jasmonic acid signalling pathways in the susceptibility of tomato to Fusarium oxysporum. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaler, J.S.; Humphrey, P.T.; Whiteman, N.K. Evolution of jasmonate and salicylate signal crosstalk. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Shen, W.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Su, N.; Wan, J. A novel lipoxygenase gene from developing rice seeds confers dual position specificity and responds to wounding and insect attack. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 66, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Han, B. Differential expression pattern of an acidic 9/13-lipoxygenase in flower opening and senescence and in leaf response to phloem feeders in the tea plant. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.A.; Nemchenko, A.; Borrego, E.; Murray, I.; Sobhy, I.S.; Bosak, L.; DeBlasio, S.; Erb, M.; Robert, C.A.; Vaughn, K.A.; et al. The maize lipoxygenase, ZmLOX10, mediates green leaf volatile, jasmonate and herbivore-induced plant volatile production for defense against insect attack. Plant J. 2013, 74, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Borrego, E.J.; Gorman, Z.; Huang, P.C.; Kolomiets, M.V. Relative contribution of LOX10, green leaf volatiles and JA to wound-induced local and systemic oxylipin and hormone signature in Zea mays (maize). Phytochemistry 2020, 174, 112334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, Z.; Christensen, S.A.; Yan, Y.; He, Y.; Borrego, E.; Kolomiets, M.V. Green leaf volatiles and jasmonic acid enhance susceptibility to anthracnose diseases caused by Colletotrichum graminicola in maize. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Handa, A.K.; Mattoo, A.K. Transcript Abundance Patterns of 9- and 13-Lipoxygenase Subfamily Gene Members in Response to Abiotic Stresses (Heat, Cold, Drought or Salt) in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Highlights Member-Specific Dynamics Relevant to Each Stress. Genes 2019, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Nomenclature | Locus | Predicted LOX Class | Chromosomal Position | gDNA (bp) | CDS (bp) | Protein Properties | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (aa) | MW (KDa) | Domain | pI | GRAVY | Subcellular Localization | |||||||
| LH2 | LOX | |||||||||||
| ClLOX1 | Cla019908 | 9-LOX | Chr2: 25963474 .. 25968681 (+) | 5208 | 2628 | 875 | 99.03 | 40–181 | 192–858 | 6.14 | −0.365 | Cytoplasm |
| ClLOX2 | Cla019907 | 9-LOX | Chr2: 25991122 .. 25996850 (+) | 5729 | 2640 | 879 | 99.70 | 40–181 | 192–862 | 5.41 | −0.364 | Cytoplasm |
| ClLOX3 | Cla019897 | 9-LOX | Chr2: 26087261 .. 26097084 (−) | 9824 | 2589 | 862 | 97.49 | 18–162 | 173–845 | 5.67 | −0.432 | Cytoplasm |
| ClLOX4 | Cla019896 | 9-LOX | Chr2: 26108726 .. 26117164 (−) | 8439 | 2259 | 752 | 85.95 | 7–97 | 82–735 | 5.13 | −0.361 | Cytoplasm |
| ClLOX5 | Cla008520 | 13-LOX | Chr2: 33497808 .. 33502790 (−) | 4983 | 2709 | 902 | 102.74 | 74–207 | 218–885 | 5.76 | −0.413 | Chloroplast |
| ClLOX6 | Cla008519 | 13-LOX | Chr2: 33513361 .. 33519238 (−) | 5878 | 1686 | 561 | 63.98 | 66–187 | 342–561 | 6.16 | −0.187 | Cytoplasm |
| ClLOX7 | Cla008517 | 13-LOX | Chr2: 33543209 .. 33546121 (−) | 2913 | 2355 | 784 | 89.41 | 1–89 | 100–767 | 5.44 | −0.447 | Chloroplast |
| ClLOX8 | Cla008516 | 13-LOX | Chr2: 33565766 .. 33569015 (−) | 3250 | 2511 | 836 | 95.13 | 3–129 | 142–819 | 5.72 | −0.579 | Chloroplast |
| ClLOX9 | Cla003211 | 13-LOX | Chr2: 33577155 .. 33581164 (−) | 4010 | 2493 | 830 | 94.30 | 3–129 | 140–813 | 7.02 | −0.483 | Chloroplast |
| ClLOX10 | Cla003210 | 13-LOX | Chr2: 33590798 .. 33596027 (−) | 5230 | 1989 | 662 | 75.43 | 1–68 | 79–645 | 6.57 | −0.448 | Chloroplast |
| ClLOX11 | Cla003209 | 13-LOX | Chr2: 33605180 .. 33608524 (−) | 3345 | 2574 | 857 | 97.86 | 7–140 | 151–840 | 6.02 | −0.558 | Chloroplast |
| ClLOX12 | Cla009402 | 9-LOX | Chr6: 6667738 .. 6672962 (+) | 5225 | 2652 | 883 | 100.89 | 36–180 | 191–861 | 6.00 | −0.352 | Cytoplasm |
| ClLOX13 | Cla005400 | 13-LOX | Chr7: 27624656 .. 27628437 (+) | 3782 | 1755 | 584 | 67.73 | 4–128 | 158–584 | 6.55 | −0.581 | Chloroplast |
| ClLOX14 | Cla015542 | 13-LOX | Chr9: 581154 .. 585338 (−) | 4185 | 2787 | 928 | 103.02 | 80–234 | 245–911 | 6.65 | −0.376 | Cytoplasm |
| ClLOX15 | Cla014845 | 9-LOX | Chr9: 6640629 .. 6649232 (−) | 8604 | 2517 | 838 | 96.18 | 16–143 | 154–816 | 6.61 | −0.459 | Cytoplasm |
| ClLOX16 | Cla022987 | 13-LOX | Chr11: 16214820 .. 16219598 (+) | 4779 | 2787 | 928 | 105.04 | 105–229 | 240–911 | 8.83 | −0.475 | Cytoplasm |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y. Comprehensive Genomic Characterization and Expression Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Watermelon under Hormonal Treatments. Agriculture 2020, 10, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10100429
Liu J, Zhou Y, Li J, Wang F, Yang Y. Comprehensive Genomic Characterization and Expression Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Watermelon under Hormonal Treatments. Agriculture. 2020; 10(10):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10100429
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jianping, Yong Zhou, Jingwen Li, Feng Wang, and Youxin Yang. 2020. "Comprehensive Genomic Characterization and Expression Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Watermelon under Hormonal Treatments" Agriculture 10, no. 10: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10100429
APA StyleLiu, J., Zhou, Y., Li, J., Wang, F., & Yang, Y. (2020). Comprehensive Genomic Characterization and Expression Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Watermelon under Hormonal Treatments. Agriculture, 10(10), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10100429







