Relationship between Evaluations of Tracheal Tube Position Using Ultrasound and Fluoroscopy in an Infant and Pediatric Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Protocol
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Sample Size
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Implication Statement
References
- Miller, A.; Mandeville, J. Predicting and measuring fluid responsiveness with echocardiography. Echo. Res. Pract. 2016, 3, G1–G12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J.A.; Fredricks, B.J.; Best, C.J. Evaluation of a new method for determining tracheal tube length in children. Anaesthesia 1995, 50, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loew, A.; Thibeault, D.W. A new and safe method to control the depth of endotracheal intubation in neonates. Pediatrics 1974, 54, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, E.A.; Arheart, K.L.; Penning, D.H. Endotracheal tube malposition within the pediatric population: A common event despite clinical evidence of correct placement. Can. J. Anaesth. 2008, 55, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verghese, S.T.; Hannallah, R.S.; Slack, M.C.; Cross, R.R.; Patel, K.M. Auscultation of bilateral breath sounds does not rule out endobronchial intubation in children. Anesth. Analg. 2004, 99, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsingh, D.; Frank, E.; Haughton, R.; Schilling, J.; Gimenez, K.M.; Banh, E.; Rinehart, J.; Cannesson, M. Auscultation versus Point-of-care Ultrasound to Determine Endotracheal versus Bronchial Intubation: A Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Anesth. 2016, 124, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshy, T.; Misra, S.; Chatterjee, N.; Dharan, B.S. Accuracy of a Chest X-Ray-Based Method for Predicting the Depth of Insertion of Endotracheal Tubes in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2016, 30, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, J.J.; McKay, W.P.; Wang, A.F.; Yip, K.A.; O’Brien, J.M.; Plewes, C.E. Three-finger tracheal palpation to guide endotracheal tube depth in children. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2014, 24, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Yokoyama, K. Displacement of the endotracheal tube caused by change of head position in pediatric anesthesia: Evaluation by fiberoptic bronchoscopy. Anesth. Analg. 1996, 82, 251–253. [Google Scholar]
- Tessaro, M.O.; Salant, E.P.; Arroyo, A.C.; Haines, L.E.; Dickman, E. Tracheal rapid ultrasound saline test (T.R.U.S.T.) for confirming correct endotracheal tube depth in children. Resuscitation 2015, 89, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeel, P.; Sheth, M.; Nguyen, J. Ultrasonography for endotracheal tube position in infants and children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2017, 176, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhry, R.; Dangman, B.; Pinheiro, J.M. The concordance of ultrasound technique versus X-ray to confirm endotracheal tube position in neonates. J. Perinatol. 2015, 35, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerrey, B.T.; Geis, G.L.; Quinn, A.M.; Hornung, R.W.; Ruddy, R.M. A prospective comparison of diaphragmatic ultrasound and chest radiography to determine endotracheal tube position in a pediatric emergency department. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.R.; McCurdy, M.T.; Zubrow, M.T.; Papali, A.; Mallemat, H.A.; Verceles, A.C. Tele-intensivists can instruct non-physicians to acquire high-quality ultrasound images. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Feinn, R. Using Effect Size-or Why the P Value Is Not Enough. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, F.; Matyal, R.; Skubas, N.; Montealegre-Gallegos, M.; Swaminathan, M.; Denault, A.; Sniecinski, R.; Mitchell, J.D.; Taylor, M.; Haskins, S.; et al. Perioperative Ultrasound Training in Anesthesiology: A Call to Action. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122, 1794–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Anesthesiology. Available online: https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramRequirements/040Anesthesiology2018TCC.pdf?ver=2018-06-14-143123-497 (accessed on 1 December 2019).

| Characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|
| N | Count | 41 |
| Age (in years) | Median (25th Percentile, 75th Percentile) | 3.00 (1.50, 7.00) |
| 0–2 years | Count (Percentage) | 18 (44%) |
| 3–6 years | Count (Percentage) | 11 (27%) |
| 7–10 years | Count (Percentage) | 12 (29%) |
| Sex (M:F) | Count (Percentage) | 21 (51%):20 (49%) |
| Weight (in kilograms) | Median (25th Percentile, 75th Percentile) | 14.30 (9.20, 22.60) |
| Height (in centimeters) | Median (25th Percentile, 75th Percentile) | 96.00 (79.50, 123.00) |
| ASA (2:3:4) | Count (Percentage) | 17 (42%):23 (56%):1 (2%) |
| Location of Esophagus at Second Tracheal Ring via POCUS Exam Left: Right: Middle | Count (Percentage) | 31 (76%):8 (20%):2 (5%) |
| POCUS Image Quality Scores (1—Low to 5—High) | Count (Percentage) | 1 (0%):2 (0%):3 (0%):4 (0%):5 (100%) |
| POCUS Examination Time (in seconds) | Median (25th Percentile, 75th Percentile) | 112.00 (80.00, 156.00) |
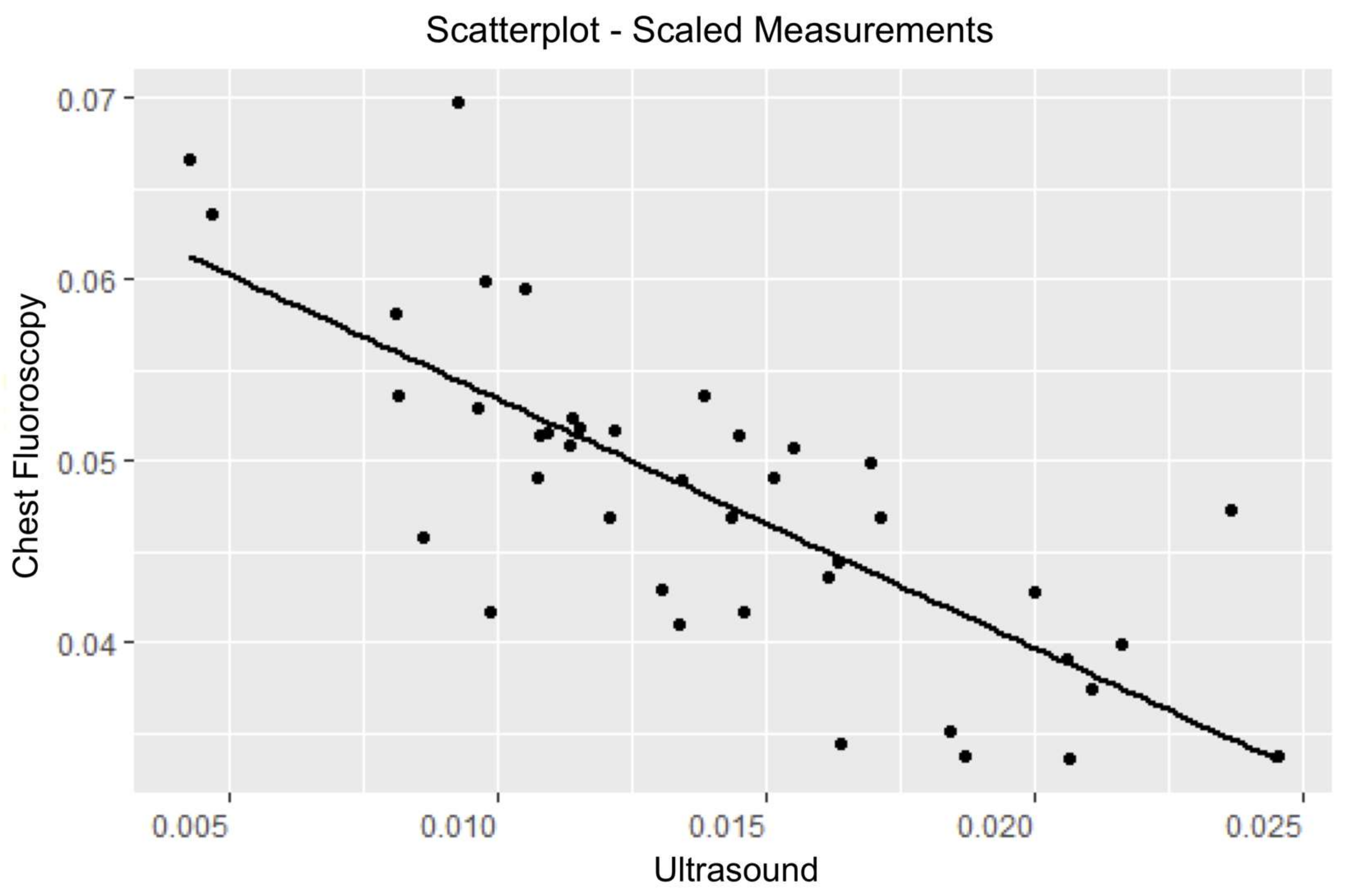
| Coefficients | Estimates | Standard Error | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.07086 | 0.002903 | <0.0001 |
| Ultrasound | −1.4231 | 0.2057 | <0.0001 |
| Age | −0.0008130 | 0.0002909 | 0.008130 |
| R-Squared of Model | 0.7094 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramsingh, D.; Ghazal, E.; Gordon, B.; Ross, P.; Goltiao, D.; Alschuler, M.; Pugh, J.; Holsclaw, M.; Mason, L. Relationship between Evaluations of Tracheal Tube Position Using Ultrasound and Fluoroscopy in an Infant and Pediatric Population. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061707
Ramsingh D, Ghazal E, Gordon B, Ross P, Goltiao D, Alschuler M, Pugh J, Holsclaw M, Mason L. Relationship between Evaluations of Tracheal Tube Position Using Ultrasound and Fluoroscopy in an Infant and Pediatric Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(6):1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061707
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamsingh, Davinder, Elizabeth Ghazal, Brent Gordon, Philip Ross, Darren Goltiao, Matt Alschuler, Justin Pugh, Matthew Holsclaw, and Linda Mason. 2020. "Relationship between Evaluations of Tracheal Tube Position Using Ultrasound and Fluoroscopy in an Infant and Pediatric Population" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 6: 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061707
APA StyleRamsingh, D., Ghazal, E., Gordon, B., Ross, P., Goltiao, D., Alschuler, M., Pugh, J., Holsclaw, M., & Mason, L. (2020). Relationship between Evaluations of Tracheal Tube Position Using Ultrasound and Fluoroscopy in an Infant and Pediatric Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(6), 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061707





