The Association Between Delivery of Small-for-Gestational-Age Neonate and Their Risk for Long-Term Neurological Morbidity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Statistical Analysis
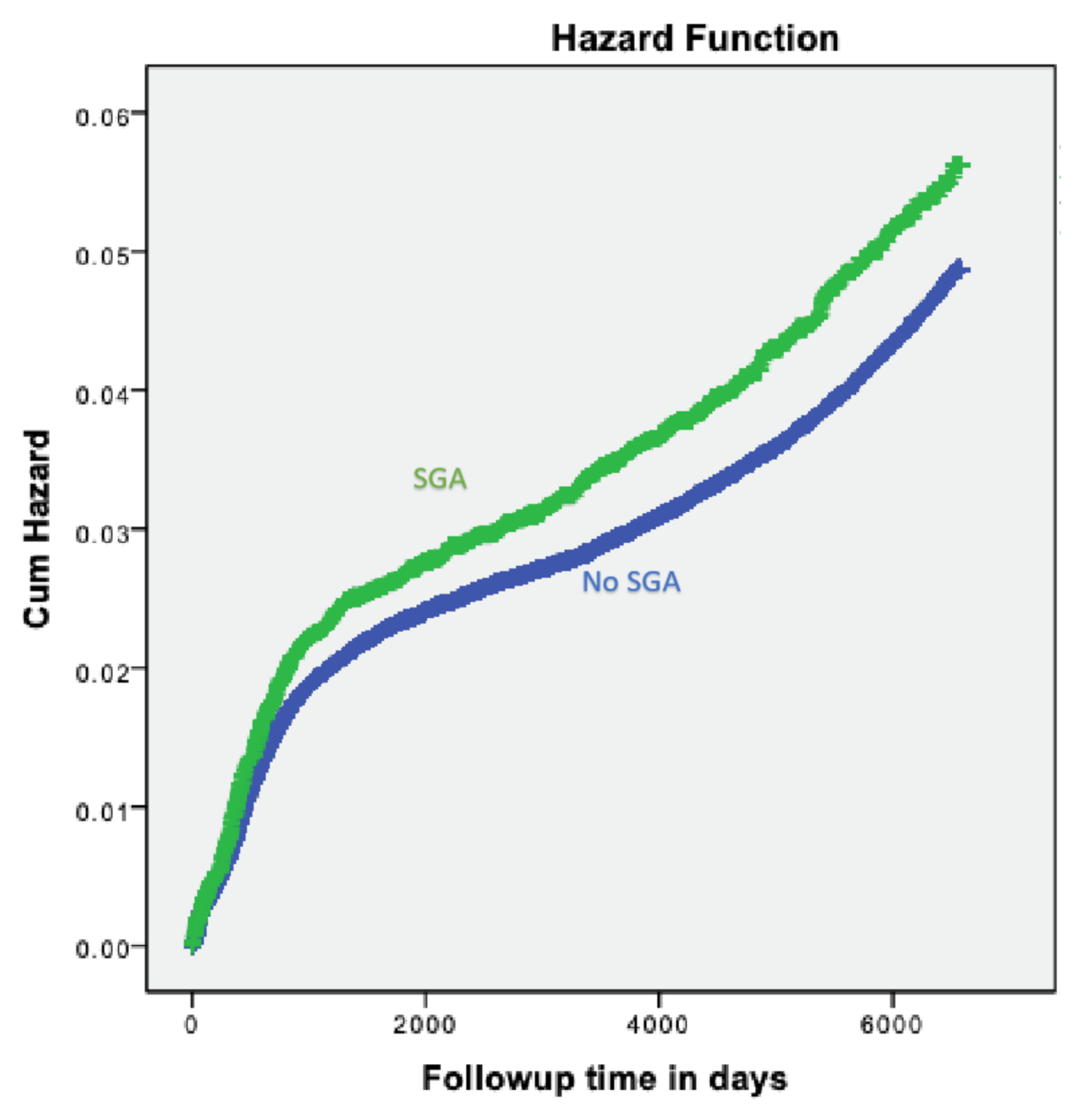
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clausson, B.; Gardosi, J.; Francis, A.; Cnattingius, S. Perinatal outcome in SGA births defined by customised versus population-based birthweight standards. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2001, 108, 830–834. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, N.; Wainstock, T.; Sheiner, E.; Segal, I.; Landau, D.; Walfisch, A. Small for gestational age as an independent risk factor for long-term pediatric gastrointestinal morbidity of the offspring. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2017, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gur, Z.; Tsumi, E.; Wainstock, T.; Walter, E.; Sheiner, E. Association between delivery of small-for-gestational-age neonate and long-term pediatric ophthalmic morbidity. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 298, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, A.; Ellington, S.; Shapiro-Mendoza, C.; Barfield, W.; Kourtis, A. Full-term small-for-gestational-age newborns in the U.S.: Characteristics, trends, and morbidity. Matern. Child. Health J. 2017, 21, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaudecker, E.P.; Munoz, F.M.; Bardají, A.; Boghossian, N.S.; Khalil, A.; Mousa, H. Small for gestational age: Case definition & guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of maternal immunisation safety data. Vaccine 2017, 4, 6518–6528. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, D.J.; Winter, P.D.; Osmond, C.; Margetts, B.; Simmonds, S.J. Weight in infancy and death from ischaemic heart disease. Lancet 1989, 2, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, J.G.; Forsén, T.; Tuomilehto, J.; Osmond, C.; Barker, D.J.P. Early growth and coronary heart disease in later life: Longitudinal study. BMJ 2001, 322, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, E.; Shoham-Vardi, I.; Sergienko, R.; Landau, D.; Sheiner, E. The association between birth weight at term and long-term endocrine morbidity of the offspring. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2018, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallard, C.; Loeliger, M.; Copolov, D.; Rees, S. Reduced number of neurons in the hippocampus and the cerebellum in the postnatal guinea-pig following intrauterine growth-restriction. Neuroscience 2000, 100, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashima, L.; Nakata, M.; Anno, K.; Sugino, N.; Kato, H. Prenatal influence of ischemia-hypoxia-induced intrauterine growth retardation on brain development and behavioral activity in rats. Neonatology 2001, 80, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, H.P.; Welch, N.N.; Dabiere, C.S.; Vasan, N.S.; Butterfield, L.J. Alterations in human brain biochemistry following intrauterine growth retardation. Pediatrics 1972, 50, 403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suffren, S.; Angulo, D.; Ding, Y.; Reyes, P.; Marin, J.; Hernandez, J.T. Long-term attention deficits combined with subcortical and cortical structural central nervous system alterations in young adults born small for gestational age. Early Hum. Dev. 2017, 110, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isabelle, G.; Alexandre, L.; Sylvain, R.; Marie-Laure, C.; Jean-Christophe, R.; Stéphane, M. Neurologic outcomes at school age in very preterm infants born with severe or mild growth restriction. Pediatrics 2011, 127, e891. [Google Scholar]
- Alkandari, F.; Ellahi, A.; Aucott, L.; Devereux, G.; Turner, S. Fetal Ultrasound Measurements and Associations with Postnatal Outcomes in Infancy and Childhood: A Systematic Review of an Emerging Literature. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2015, 69, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Das, M.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Bhattacharyya, A. WHO child growth standards. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, S.M.; Hannon, G.; Khashan, A.S.; Hourihane, J.O.; Kenny, L.C.; Kiely, M. Thin-for-gestational age infants are at increased risk of neurodevelopmental delay at 2years. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2017, 102, F197–F202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, J.; Silva, P.; Brooke, M. Growth, development and behaviour in adolescents born small-for-gestational-age. J. Paediatr. Child Health 1995, 31, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanis, J.C.; Van Braeckel Koenraad, N.J.A.; Kerstjens Jorien, M.; Bocca-Tjeertes Inger, F.A.; Reijneveld Sijmen, A.; Bos Arend, F. Functional outcomes at age 7 years of moderate preterm and full term children born small for gestational age. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, B.; Edmonds, C.J. School age neurological and cognitive outcomes of fetal growth retardation or small for gestational age birth weight. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.H.; Yi, Y.Y.; Hwang, I.T. Behavioral and intelligence outcome in 8- to 16-year-old born small for gestational age. Korean J. Pediatr. 2016, 59, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.; Thornburg, K. The obstetric origins of health for a lifetime. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 56, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, R.L.; Culhane, J.F.; Iams, J.D.; Romero, R. Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth. Lancet 2008, 371, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damti, P.; Friger, M.; Landau, D.; Sergienko, R.; Sheiner, E. Offspring of women following bariatric surgery and those of patients with obesity are at an increased risk for long-term pediatric endocrine morbidity. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2019, 300, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, Z.F.; Gutvirtz, G.; Pariente, G.; Wainstock, T.; Landau, D.; Sheiner, E. Maternal obesity and long-term neuropsychiatric morbidity of the offspring. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2020, 301, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, J.F.; Fink, E.L.; Hartman, M.E.; Angus, D.C.; Bell, M.J.; Linde-Zwirble, W.T. Hospitalizations of children with neurological disorders in the United States. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 14, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardon, L.; Picciolini, O.; Squarza, C.; Frigerio, A.; Giannì, M.L.; Gangi, S. Neurodevelopmental outcome and adaptive behaviour in extremely low birth weight infants at 2 years of corrected age. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 128, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnoudse-Moens, C.S.H.; Weisglas-Kuperus, N.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Oosterlaan, J. Meta-analysis of neurobehavioural outcomes in very preterms and/or very low birth weight children. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordijn, S.J.; Beune, I.M.; Thilaganathan, B.; Papageorghiou, A.; Baschat, A.A.; Baker, P.N. Consensus definition of fetal growth restriction: A Delphi procedure. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 48, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| p-Value | SGA Newborns (N = 11,290) % (n) | Not SGA Newborns (N = 221,978) % (n) | Maternal and Newborn Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| <0.001 | 26.76 ± 5.880 | 28.11 ± 5.793 | Maternal age (years, mean ± SD) |
| <0.001 | 39.20 ± 2.150 | 39.09 ± 1.978 | Gestational age (weeks, mean ± SD) |
| <0.001 | 2399.95 ± 435.724 | 3201.58 ± 371.473 | Birth weight (grams, mean ± SD) |
| Parity (%) | |||
| <0.001 | 37.7 (4258) | 23.5 (52,095) | 1 |
| 43.2 (4879) | 51.6 (114,574) | 2–4 | |
| 19.1 (2151) | 24.9 (55,259) | 5+ | |
| 0.13 | 6.6 (743) | 7.0 (15,439) | Preterm (<37) |
| <0.001 | 2.4 (274) | 4.6 (10,300) | Diabetes mellitus 1 |
| <0.001 | 8.7 (986) | 4.7 (10,591) | Hypertensive disorders 2 |
| <0.001 | 52.0 (5870) | 4.7 (10,487) | Low birth weight (≤2500 g) |
| <0.001 | 2.9 (327) | 0.5 (1115) | Very Low Birth Weight Group (<1500 g) |
| <0.001 | 5.5 (618) | 2.1 (4723) | Apgar scores <7 at 5 min (%) |
| <0.001 | 2.6 (292) | 0.5 (1003) | Perinatal mortality |
| p-Value | OR; 95% Confidence Interval | SGA N = 10,998 N (%) | No SGA N = 220,975 N (%) | Neurological Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.408 | 1.827 (0.43–7.76) | 2 (0.02) | 22 (0.01) | Autism |
| 0.511 | 0.849 (0.52–1.38) | 17 (0.13) | 402 (0.18) | Eating disorders |
| 0.057 | 2.393 (0.94–6.05) | 5 (0.04) | 42 (0.018) | Sleep disorders |
| 0.497 | 1.094 (0.84–1.42) | 60 (0.54) | 1102 (0.50) | Psychiatric emotional |
| 0.901 | 1.050 (0.49–2.24) | 7 (0.06) | 134 (0.06) | ADHD |
| <0.001 | 2.527 (1.68–3.82) | 26 (0.24) | 207 (0.09) | Developmental disorders |
| 0.007 | 2.048 (1.12–3.47) | 15 (0.13) | 148 (0.06) | Degenerative, Demyelination |
| 0.049 | 1.843 (0.99–3.42) | 11 (0.10) | 120 (0.05) | Myopathy |
| <0.001 | 1.204 (1.09–1.33) | 406 (3.71) | 6820 (3.10) | Total neurologic hospitalizations |
| Variables | Adjusted HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | |||
| SGA (vs. AGA) | 1.18 | 1.07–1.31 | <0.001 | |
| Maternal age (years) | 0.997 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.116 | |
| Hypertensive disorders 1 | 1.130 | 1.03–1.24 | 0.018 | |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 0.930 | 0.93–0.94 | <0.001 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hadar, O.; Sheiner, E.; Wainstock, T. The Association Between Delivery of Small-for-Gestational-Age Neonate and Their Risk for Long-Term Neurological Morbidity. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103199
Hadar O, Sheiner E, Wainstock T. The Association Between Delivery of Small-for-Gestational-Age Neonate and Their Risk for Long-Term Neurological Morbidity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(10):3199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103199
Chicago/Turabian StyleHadar, Omer, Eyal Sheiner, and Tamar Wainstock. 2020. "The Association Between Delivery of Small-for-Gestational-Age Neonate and Their Risk for Long-Term Neurological Morbidity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 10: 3199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103199
APA StyleHadar, O., Sheiner, E., & Wainstock, T. (2020). The Association Between Delivery of Small-for-Gestational-Age Neonate and Their Risk for Long-Term Neurological Morbidity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(10), 3199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103199






