Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Prescription According to Reimbursement Constraints and Guideline Recommendations in Catalonia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Variables
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
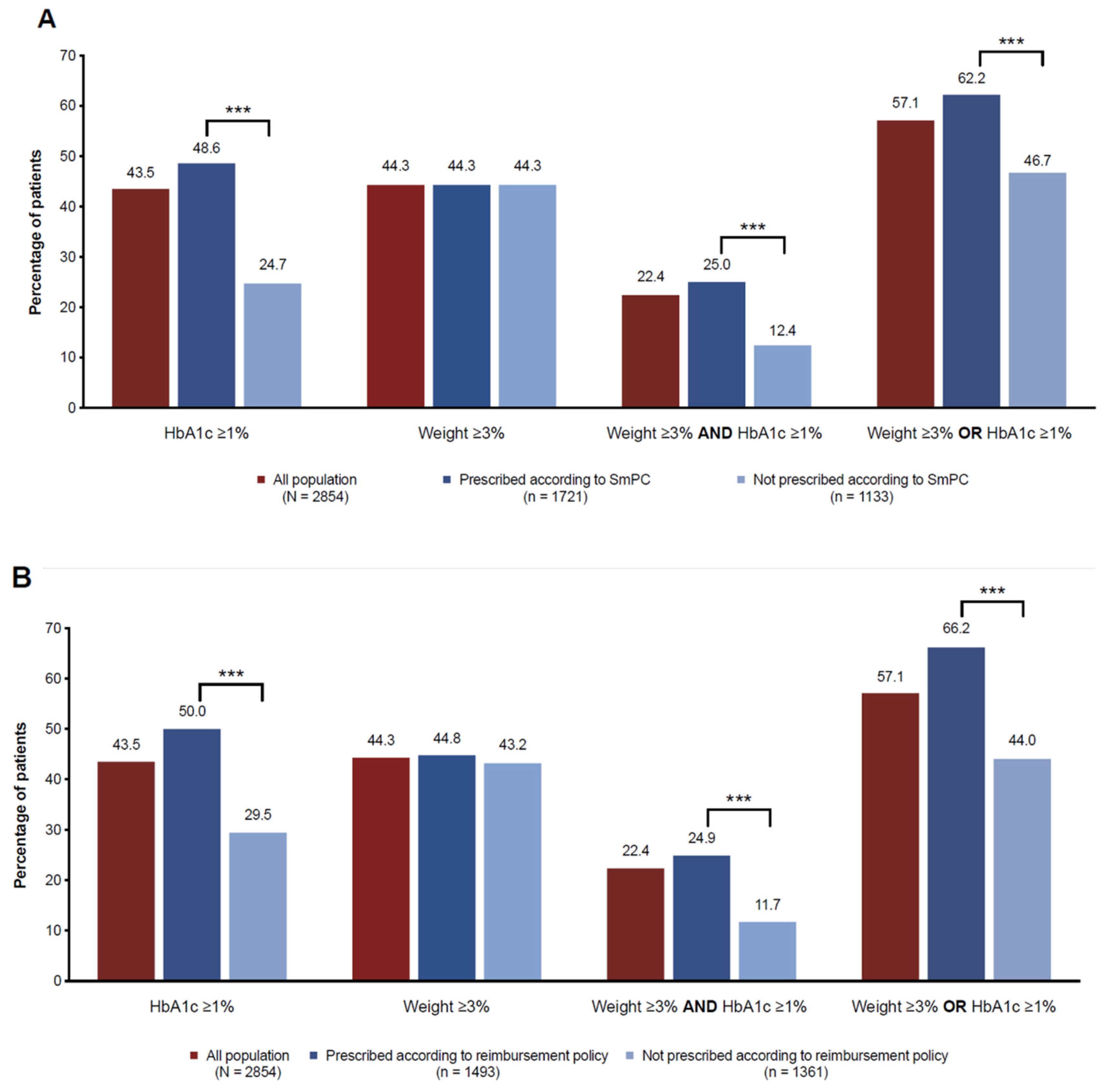
3.2. Adequacy to GLP-1RAs SmPC and Local Health Policy Requirements for Reimbursement
3.3. Treatment Response after Six and Twelve Months of GLP-1RA Initiation
3.4. Assessment of Beneficial Response
3.5. Medication Persistence and Adherence
3.6. Adverse Events
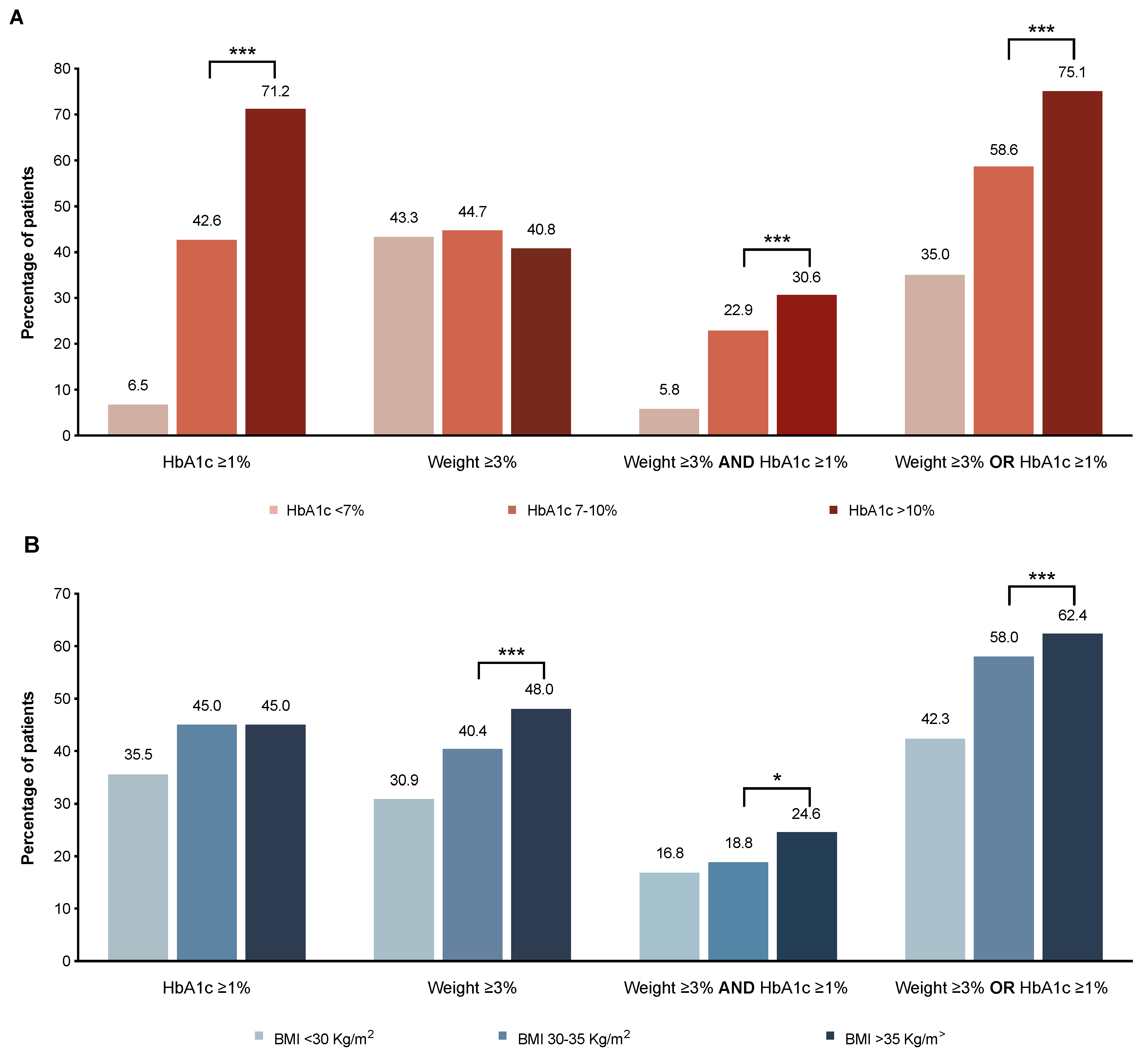
3.7. Variables Associated with Beneficial HbA1c Reduction and Weight Loss after Therapy with GLP-1RAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mechanick, J.I.; Garber, A.J.; Grunberger, G.; Handelsman, Y.; Garvey, W.T. Dysglycemia-Based Chronic Disease: An American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Position Statement. Endocr. Pract. 2018, 24, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.A. Defining and characterizing the progression of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, S151–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.J.; Abrahamson, M.J.; Barzilay, J.I.; Blonde, L.; Bloomgarden, Z.T.; Bush, M.A.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Einhorn, D.; Fonseca, V.A.; et al. Consensus Statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the Comprehensive Type 2 Diabetes Management Algorithm--2016 Executive Summary. Endocr. Pract. 2016, 22, 84–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADA (American Diabetes Association). 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S90–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Fradkin, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; Rossing, P.; Tsapas, A.; Wexler, D.J.; Buse, J.B. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanna, S.; Christensen, M.; Holst, J.J.; Laferrere, B.; Gluud, L.L.; Vilsboll, T.; Knop, F.K. Secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analyses of clinical studies. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, D.A.; D’Alessio, D.A. Physiology of proglucagon peptides: Role of glucagon and GLP-1 in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 513–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnen, D. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, H.; Nayar, R.; Rajeswaran, C.; Jandhyala, R. Long-term management of type 2 diabetes with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Diabetes. Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2017, 10, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzucchi, S.E.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buse, J.B.; Diamant, M.; Ferrannini, E.; Nauck, M.; Peters, A.L.; Tsapas, A.; Wender, R.; Matthews, D.R. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: A patient-centered approach: Update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.J.; Abrahamson, M.J.; Barzilay, J.I.; Blonde, L.; Bloomgarden, Z.T.; Bush, M.A.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Einhorn, D.; Fonseca, V.A.; et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm-2018 executive summary. Endocr. Pract. 2018, 24, 91–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, Association. 8. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, S73–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meece, J. Basal Insulin Intensification in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Review. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.N.; Tang, T.; Halapy, H.; Thorpe, K.; Yu, C.H. Initiating insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2012, 184, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad-Reddy, L.; Isaacs, D. A clinical review of GLP-1 receptor agonists: Efficacy and safety in diabetes and beyond. Drugs Context 2015, 4, 212283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htike, Z.Z.; Zaccardi, F.; Papamargaritis, D.; Webb, D.R.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and mixed-treatment comparison analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, M.E. Major adverse cardiovascular event reduction with GLP-1 and SGLT2 agents: Evidence and clinical potential. Ther. Adv. Chronic. Dis. 2018, 9, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heile, M.; Wyne, K.; Billings, L.K.; Cannon, A.; Handelsman, Y.; Shannon, M. Cardiovascular Outcomes with Once-Weekly GLP-1 RAs: Clinical and Economic Implications. J. Manag. Care. Spec. Pharm. 2018, 24, S42–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K. What have we learnt from "real world" data, observational studies and meta-analyses. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htike, Z.Z.; Zaccardi, F.; Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) therapy in management of type 2 diabetes: Choosing the right agent for individualised care. Br. J. Diabetes 2016, 16, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Guideline NG28. NICE. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Type 2 diabetes in adults: Management. 2015. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng28 (accessed on 24 July 2018).
- Generalitat de Catalunya. Pautes per al tractament farmacològic de la diabetis mellitus tipus 2. Barcelona: Agència de Qualitat i Avaluació Sanitàries de Catalunya. Departament de Salut. Generalitat de Catalunya, 2013; (Programa d’Harmonització Farmacoterapèutica de Medicaments en l’Àmbit de l’Atenció Primària i Comunitària del Servei Català de la Salut; 1/2013). Available online: www.gencat.cat/catsalut (accessed on 24 July 2018).
- Vinagre, I.; Mata-Cases, M.; Hermosilla, E.; Morros, R.; Fina, F.; Rosell, M.; Castell, C.; Franch-Nadal, J.; Bolibar, B.; Mauricio, D. Control of glycemia and cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes in primary care in Catalonia (Spain). Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolibar, B.; Fina Aviles, F.; Morros, R.; Garcia-Gil Mdel, M.; Hermosilla, E.; Ramos, R.; Rosell, M.; Rodriguez, J.; Medina, M.; Calero, S.; et al. SIDIAP database: Electronic clinical records in primary care as a source of information for epidemiologic research. Med. Clin. (Barc.) 2012, 138, 617–621. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, P.A.; Nguyen, H.; Wittbrodt, E.T.; Kim, S.C. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: A systematic review of comparative effectiveness research. Diabetes. Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2017, 10, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Shenouda, S.K.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buse, J.B.; Glass, L.C.; Heilmann, C.R.; Kwan, A.Y.; MacConell, L.A.; Hoogwerf, B.J. Baseline factors associated with glycemic control and weight loss when exenatide twice daily is added to optimized insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, S.A.; Lefrandt, J.D.; Petersen, J.F.; Boersma, H.H.; Mulder, D.J.; Hoogenberg, K. The effects of GLP-1 analogues in obese, insulin-using type 2 diabetes in relation to eating behaviour. Int J. Clin. Pharm 2016, 38, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, A.S.; Ganz, M.L.; Benjamin, N.; Langer, J.; Hammer, M. Clinical effectiveness of liraglutide across body mass index in patients with type 2 diabetes in the United States: A retrospective cohort study. Adv. Ther. 2014, 31, 986–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostawal, A.; Mocevic, E.; Kragh, N.; Xu, W. Clinical Effectiveness of Liraglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Treatment in the Real-World Setting: A Systematic Literature Review. Diabetes Ther. 2016, 7, 411–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezquita-Raya, P.; Reyes-Garcia, R.; Moreno-Perez, O.; Escalada-San Martin, J.; Angel Rubio Herrera, M.; Lopez de la Torre Casares, M. Clinical Effects of Liraglutide in a Real-World Setting in Spain: eDiabetes-Monitor SEEN Diabetes Mellitus Working Group Study. Diabetes Ther. 2015, 6, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thong, K.Y.; Gupta, S.P.; Cull, L.M.; Adamson, K.; Dove, S.D.; Rowles, W.S.; Tarpey, S.; Duncan, C.; Chalmers, J.; Harper, R.; et al. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes—NICE Guidelines Versus Clinical Practice. Br. J. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. 2014, 14, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, K.; D’Oca, K.; Leigh, P.; Murray-Thomas, T. Adherence to NICE guidance on glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: An evaluation using the Clinical Practice Research Datalink. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; McEwan, P.; O’Shea, R.; George, L. A retrospective, case-note survey of type 2 diabetes patients prescribed incretin-based therapies in clinical practice. Diabetes Ther. 2013, 4, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, A.; Maor, Y.; Goldstein, I.; Todorova, L.; Schertz-Sternberg, P.; Karasik, A. Efficacy of liraglutide in a real-life cohort. Diabetes Ther. 2014, 5, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conget, I.; Mauricio, D.; Ortega, R.; Detournay, B.; on Behalf of the CHADIG Study Investigators. Characteristics of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus newly treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists (CHADIG Study): A cross-sectional multicentre study in Spain. BMJ Open 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, S.; Wei, W.; Buysman, E.; Brekke, L.; Crown, W.; Grabner, M.; Raparla, S.; Quimbo, R.; Cziraky, M.J.; Hu, W.; et al. The INITIATOR study: Pilot data on real-world clinical and economic outcomes in US patients with type 2 diabetes initiating injectable therapy. Adv. Ther. 2013, 30, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Inoue, K.; Maeda, N.; Fujishima, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Nagao, H.; Yamaoka, M.; Hirata, A.; Nishizawa, H.; Funahashi, T.; Shimomura, I. Long-term impact of liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue, on body weight and glycemic control in Japanese type 2 diabetes: An observational study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilsboll, T.; Christensen, M.; Junker, A.E.; Knop, F.K.; Gluud, L.L. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on weight loss: Systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2012, 344, d7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tong, Y.; Su, N.; Li, Y.; Tang, L.; Huang, L.; Tong, N. Weight loss effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 mimetics on obese/overweight adults without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Diabetes 2015, 7, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, N.; Reining, F.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, C.; Burkhardt, T.; Aberle, J. Off-label antiobesity treatment in patients without diabetes with GLP-1 agonists in clinical practice. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015, 47, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, K.S.; Botros, F.T.; Haupt, A.; Woodward, B.; Lage, M.J. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Use and Renal Impairment: A Retrospective Analysis of an Electronic Health Records Database in the U.S. Population. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, B.P.; Alicic, R.Z.; Tuttle, K.R. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease: From the Patient-Side to the Bench-Side. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, J.; Heng, J.; Newsholme, P.; Carlessi, R. Pleiotropic Effects of GLP-1 and Analogs on Cell Signaling, Metabolism, and Function. Front. Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, G.C.; McMahon, A.D.; Dain, M.P.; Wang, E.; Home, P.D. Primary-care observational database study of the efficacy of GLP-1 receptor agonists and insulin in the UK. Diabet. Med. 2013, 30, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkovic, M.C.; Bilic-Curcic, I.; Herman Mahecic, D.; Gradiser, M.; Grgurevic, M.; Bozek, T. Long-term effectiveness of liraglutide in association with patients’ baseline characteristics in real-life setting in Croatia: An observational, retrospective, multicenter study. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ouyang, J.; Perkins, K.; Nair, S.; Joseph, F. Determining predictors of early response to exenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 162718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monami, M.; Dicembrini, I.; Nreu, B.; Andreozzi, F.; Sesti, G.; Mannucci, E. Predictors of response to glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: A meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Acta Diabetol. 2017, 54, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihan, H.; Ng, W.L.; Magliano, D.J.; Shaw, J.E. Predictors of efficacy of GLP-1 agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors: A systematic review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 121, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simioni, N.; Berra, C.; Boemi, M.; Bossi, A.C.; Candido, R.; Di Cianni, G.; Frontoni, S.; Genovese, S.; Ponzani, P.; Provenzano, V.; et al. Predictors of treatment response to liraglutide in type 2 diabetes in a real-world setting. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadini, G.P.; Simioni, N.; Frison, V.; Dal Pos, M.; Bettio, M.; Rocchini, P.; Avogaro, A. Independent glucose and weight-reducing effects of Liraglutide in a real-world population of type 2 diabetic outpatients. Acta Diabetol. 2013, 50, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpierrez, G.E.; Pantalone, K.M.; Kwan, A.Y.; Zimmermann, A.G.; Zhang, N.; Fernandez Lando, L. Relationship between weight change and glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving once-weekly dulaglutide treatment. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, J.P.; Miller-Jones, D.; Hanif, W.; Hicks, D.; Evans, M.; Leslie, D.; Bain, S.C.; Barnett, A.H. The new NICE guidelines for type 2 diabetes—A critical analysis. The British Journal of Diabetes 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlqvist, S.; Ahlen, E.; Filipsson, K.; Gustafsson, T.; Hirsch, I.B.; Tuomilehto, J.; Imberg, H.; Ahren, B.; Attvall, S.; Lind, M. Variables associated with HbA1c and weight reductions when adding liraglutide to multiple daily insulin injections in persons with type 2 diabetes (MDI Liraglutide trial 3). BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2018, 6, e000464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | N | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD), years | 2854 | 59.5 (9.8) |
| Gender (male) | 2854 | 50.6% |
| Diabetes duration, mean (SD), years | 9.2 (8.6) | |
| <5 years | 705 | 24.7% |
| 5–10 years | 950 | 33.3% |
| >10 years | 1199 | 42.0% |
| Weight, mean (SD), kg | 2296 | 99.7 (18.5) |
| BMI, mean (SD), kg/m2 | 2304 | 37.1 (5.9) |
| HbA1c, %, mean (SD) [mmol/mol] | 2206 | 8.74 (1.6). (72.0 (17.5)) |
| Total Cholesterol, mean (SD), mg/dL | 1909 | 180 (37.6) |
| HDL-cholesterol, mean (SD), mg/dL | 1909 | 44.9 (11.2) |
| LDL-cholesterol, mean (SD), mg/dL | 1909 | 99.6 (32.2) |
| Triglycerides, mean (SD), mg/dL | 2133 | 218 (179) |
| Heart rate, mean (SD), bpm | 2105 | 80 (12.6) |
| SBP, mean (SD), mmHg | 2456 | 135 (15.1) |
| DBP, mean (SD), mmHg | 2456 | 78.3 (9.9) |
| eGFR, mean (SD), mL/min/1.73 m2 | 2153 | 85.7 (20.4) |
| eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 10 | 0.5% |
| eGFR 30–44 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 86 | 4.0% |
| eGFR 45–59 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 184 | 8.5% |
| eGFR ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 1873 | 87.0% |
| Complications, n (%) | ||
| Peripheral artery disease | 180 | 6.3% |
| Ischemic heart disease | 420 | 14.7% |
| Heart failure | 185 | 6.5% |
| Stroke | 177 | 6.2% |
| AD treatment | ||
| No pharmacologic treatment | 95 | 3.3% |
| 1 agent (excluding insulin) | 1246 | 43.7% |
| 1 agent (including insulin) | 1454 | 50.9% |
| ≥2 agents (including insulin) | 1305 | 45.7% |
| AD treatment by drug class | ||
| Insulin | 1483 | 52.0% |
| Metformin | 2316 | 81.1% |
| Sulphonylureas | 777 | 27.2% |
| DPP4i | 749 | 26.2% |
| GLP-1RA prescribed | ||
| Liraglutide | 1575 | 56.0% |
| Exenatide * | 668 | 23.8% |
| Lixisenatide | 569 | 20.2% |
| Clinical Variable | Endpoint | Overall Mean Change (SD) n = 2251 | Prescribed According to SmPC? * | Prescribed According to Reimbursement Policy? ** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes n = 1721 | No n = 1133 | p-Value | Yes n = 1493 | No n = 1361 | p-Value | |||
| HbA1c, % | 6 months | −0.84 (1.66) | −0.99 (1.68) | −0.28 (1.46) | <0.001 | −1.02 (1.70) | −0.46 (1.51) | <0.001 |
| 12 months | −0.88 (1.57) | −1.03 (1.59) | −0.36 (1.39) | <0.001 | −1.03 (1.61) | −0.57 (1.45) | <0.001 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 6 months | −1.01 (2.36) | −0.99 (2.25) | −1.04 (2.55) | 0.674 | −1.08 (2.23) | −0.87 (2.59) | 0.062 |
| 12 months | −1.08 (2.22) | −1.07 (2.15) | −1.10 (2.35) | 0.826 | −1.17 (2.08) | −0.89 (2.48) | 0.035 | |
| Weight, kg | 6 months | −2.73 (6.44) | −2.67 (6.17) | −2.85 (6.90) | 0.559 | −2.87 (6.01) | −2.47 (7.19) | 0.212 |
| 12 months | −2.86 (5.99) | −2.79 (5.86) | −2.97 (6.25) | 0.598 | −3.06 (5.57) | −2.44 (6.77) | 0.081 | |
| Total-Cholesterol, mg/dL | 6 months | −6.86 (35.9) | −7.59 (35.6) | −4.13 (36.9) | 0.129 | −8.05 (36.5) | −4.31 (34.6) | 0.052 |
| 12 months | −7.64 (35.3) | −8.31 (35.0) | −5.32 (36.6) | 0.263 | −9.11 (35.5) | −4.57 (34.8) | 0.049 | |
| HDL-Cholesterol, mg/dL | 6 months | 0.09 (7.14) | 0.12 (7.01) | −0.02 (7.58) | 0.764 | 0.14 (7.02) | −0.02 (7.38) | 0.696 |
| 12 months | −0.05 (7.10) | 0.01 (6.96) | −0.27 (7.56) | 0.612 | −0.03 (7.13) | −0.11 (7.04) | 0.859 | |
| LDL-Cholesterol, mg/dL | 6 months | −5.07 (31.2) | −5.60 (30.8) | −3.08 (32.8) | 0.212 | −5.65 (31.6) | −3.83 (30.4) | 0.278 |
| 12 months | −5.83 (30.5) | −6.21 (29.9) | −4.51 (32.6) | 0.471 | −6.42 (30.8) | −4.60 (30.0) | 0.360 | |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 6 months | −16.42 (166) | −20.52 (181) | −1.28 (90.3) | 0.004 | −22.41 (174) | −4.50 (149) | 0.022 |
| 12 months | −21.30 (156) | −27.16 (170) | −1.29 (91.6) | 0.001 | −29.41 (163) | −5.59 (141) | 0.006 | |
| SBP, mmHg | 6 months | −0.90 (17.6) | −0.77 (17.3) | −1.11 (18.1) | 0.659 | −1.01 (17.4) | −0.73 (17.7) | 0.710 |
| 12 months | −1.97 (15.7) | −1.92 (15.9) | −2.05 (15.3) | 0.864 | −2.05 (16.1) | −1.83 (15.1) | 0.777 | |
| DBP, mmHg | 6 months | −0.33 (10.5) | −0.32 (10.1) | −0.36 (11.1) | 0.938 | −0.42 (10.2) | −0.21 (10.9) | 0.643 |
| 12 months | −1.07 (9.46) | −1.05 (9.15) | −1.11 (9.98) | 0.917 | −1.11 (9.24) | −1.01 (9.80) | 0.839 | |
| Heart rate, bpm | 6 months | 0.68 (12.8) | 0.58 (12.4) | 0.86 (13.5) | 0.664 | 0.64 (12.4) | 0.73 (13.4) | 0.897 |
| 12 months | 0.55 (11.6) | 0.26 (11.1) | 1.08 (12.6) | 0.250 | 0.36 (11.1) | 0.87 (12.5) | 0.466 | |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 6 months | −1.63 (11.1) | −1.86 (10.8) | −0.65 (12.1) | 0.083 | −1.70 (11.0) | −1.48 (11.4) | 0.689 |
| 12 months | −1.19 (10.5) | −1.38 (10.5) | −0.41 (10.7) | 0.169 | −1.16 (10.6) | −1.24 (10.3) | 0.884 | |
| Clinical Variable | After 6 Months | After 6–12 Months | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduction in HbA1c ≥ 1% | Reduction in Weight ≥ 3% | Reduction in HbA1c ≥ 1% AND Weight ≥ 3% | Reduction in HbA1c ≥ 1%, Weight ≥ 3%OR Both | Reduction in HbA1c ≥ 1% | Reduction in Weight ≥ 3% | Reduction in HbA1c ≥ 1% AND Weight ≥ 3% | Reduction in HbA1c ≥ 1%, Weight ≥ 3%OR Both | |
| Male gender | – | – | – | – | – | 0.73 (0.54–0.97) p = 0.036 | – | – |
| T2D duration (10–20 years) | 0.64 (0.43–0.97) p = 0.036 | – | – | 0.67 (0.46–0.96) p = 0.031 | – | – | 2.81* (1.02-7.61) p = 0.042 | – |
| HbA1c | 2.06 (1.83–2.33) p < 0.001 | – | 1.25 (1.12–1.40) p < 0.001 | 1.41 (1.28–1.56) p < 0.001 | 2.14 (1.85–2.48) p < 0.001 | – | 1.42 (1.22–1.66) p < 0.001 | 1.35 (1.22–1.50) p < 0.001 |
| BMI | – | 1.03 (1.01–1.05) p = 0.014 | 1.03 (1.00–1.06) p = 0.032 | 1.02 (1.00–1.05) p = 0.043 | – | 1.04 (1.02–1.07) p = 0.001 | 1.06 (1.02–1.10) p = 0.003 | 1.03 (1.01–1.06) p = 0.005 |
| DBP | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1.03 (1.01–1.06) p = 0.018 | – |
| eGFR | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1.01 (1.00–1.03) p = 0.042 | – |
| Prescribed according to HPR | – | – | – | 1.60 (1.04-2.45) p = 0.031 | – | – | – | – |
| AUC of the model | 0.78 | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.79 | 0.63 | 0.74 | 0.67 |
| (0.76–0.79) | (0.59–0.62) | (0.65–0.69) | (0.66–0.69) | (0.77–0.80) | (0.61–0.65) | (0.71–0.76) | (0.65–0.68) | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franch-Nadal, J.; Mata-Cases, M.; Ortega, E.; Real, J.; Gratacòs, M.; Vlacho, B.; Vallés, J.A.; Mauricio, D. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Prescription According to Reimbursement Constraints and Guideline Recommendations in Catalonia. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091389
Franch-Nadal J, Mata-Cases M, Ortega E, Real J, Gratacòs M, Vlacho B, Vallés JA, Mauricio D. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Prescription According to Reimbursement Constraints and Guideline Recommendations in Catalonia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(9):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091389
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranch-Nadal, Josep, Manel Mata-Cases, Emilio Ortega, Jordi Real, Mònica Gratacòs, Bogdan Vlacho, Joan Antoni Vallés, and Dídac Mauricio. 2019. "Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Prescription According to Reimbursement Constraints and Guideline Recommendations in Catalonia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 9: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091389
APA StyleFranch-Nadal, J., Mata-Cases, M., Ortega, E., Real, J., Gratacòs, M., Vlacho, B., Vallés, J. A., & Mauricio, D. (2019). Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Prescription According to Reimbursement Constraints and Guideline Recommendations in Catalonia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(9), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091389







