Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated Gene Expression in Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Participants
2.3. RNA Isolation of the Study
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
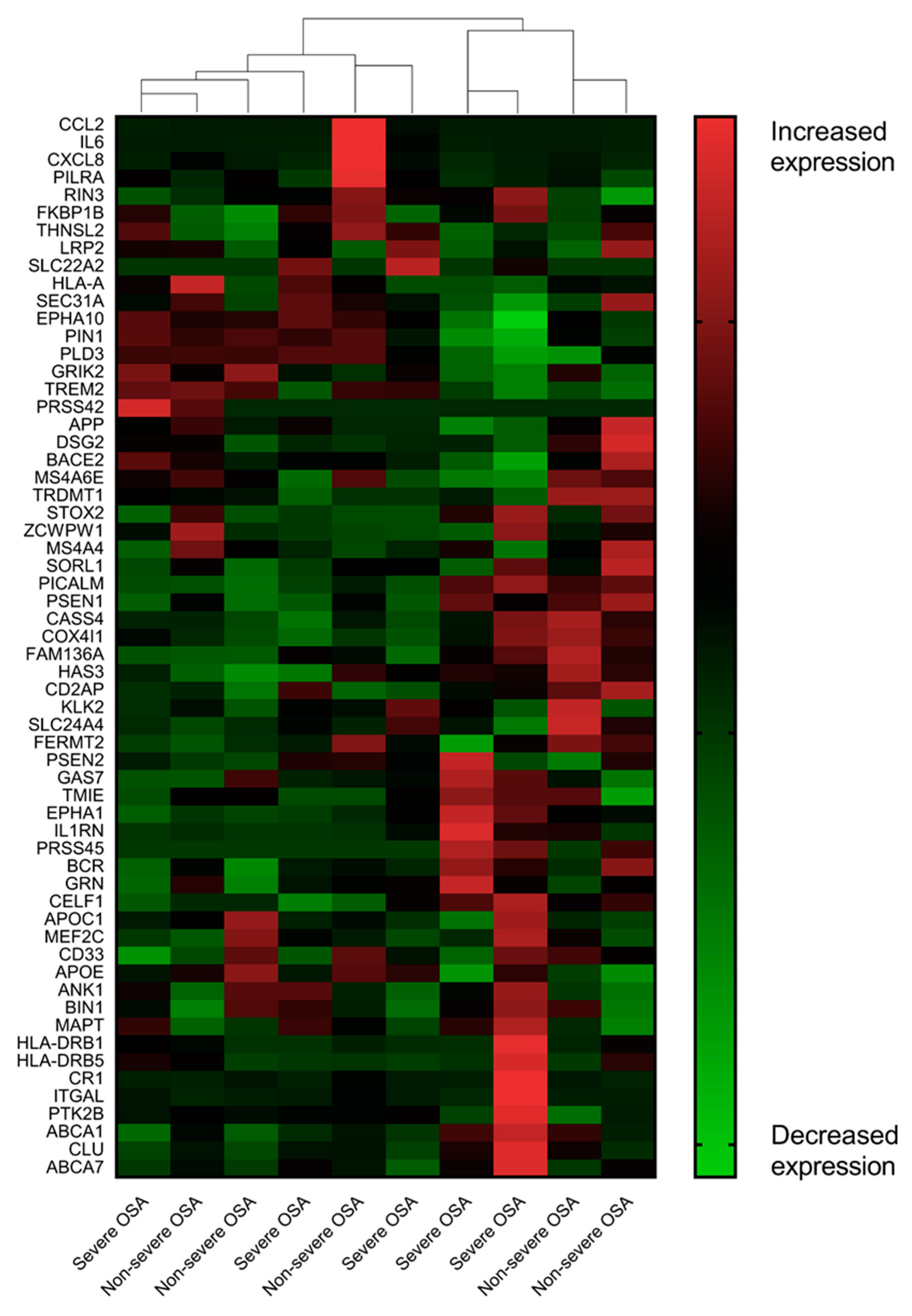
3.2. AD-Associated Transcriptomic Expression in the Uvular Tissue of the Patients with Severe OSA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenzweig, I.; Glasser, M.; Polsek, D.; Leschziner, G.D.; Williams, S.C.R.; Morrell, M.J. Sleep apnoea and the brain: A complex relationship. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Kastin, A.J. Can sleep apnea cause Alzheimer’s disease? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 47, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.P.; Liu, M.E.; Chang, W.C.; Yang, A.C.; Ku, Y.C.; Pai, J.T.; Huang, H.L.; Tsai, S.J. Sleep apnea and the risk of dementia: A population-based 5-year follow-up study in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Yang, S.W.; Ju, Y.J.; Ki, S.K.; Chun, K.H. Sleep-disordered breathing and Alzheimer’s disease: A nationwide cohort study. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 273, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubu, O.M.; Brannick, M.; Mortimer, J.; Umasabor-Bubu, O.; Sebastiao, Y.V.; Wen, Y.; Schwartz, S.; Borenstein, A.R.; Wu, Y.; Morgan, D.; et al. Sleep, Cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep 2017, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Chen, S.-J.; Ma, M.-Y.; Bao, Y.-P.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.-M.; Shi, J.; Vitiello, M.V.; Lu, L. Sleep disturbances increase the risk of dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 40, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, A.C.; Balouch, S.; Tabet, N. Is Sleep Disruption a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 58, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guffanti, A.; Simchovitz, A.; Soreq, H. Emerging bioinformatics approaches for analysis of NGS-derived coding and non-coding RNAs in neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cruchaga, C.; Karch, C.M.; Jin, S.C.; Benitez, B.A.; Cai, Y.; Guerreiro, R.; Harari, O.; Norton, J.; Budde, J.; Bertelsen, S.; et al. Rare coding variants in the phospholipase D3 gene confer risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2014, 505, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gant, J.C.; Blalock, E.M.; Chen, K.C.; Kadish, I.; Porter, N.M.; Norris, C.M.; Thibault, O.; Landfield, P.W. FK506-binding protein 1b/12.6: A key to aging-related hippocampal Ca2+ dysregulation? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 739, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sun, Q.; Xie, N.; Tang, B.; Li, R.; Shen, Y. Alzheimer’s Disease: From Genetic Variants to the Distinct Pathological Mechanisms. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2015 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 332–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingworth, P.; Harold, D.; Sims, R.; Gerrish, A.; Lambert, J.C.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Abraham, R.; Hamshere, M.L.; Pahwa, J.S.; Moskvina, V.; et al. Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wavrant-De Vrieze, F.; Compton, D.; Womick, M.; Arepalli, S.; Adighibe, O.; Li, L.; Perez-Tur, J.; Hardy, J. ABCA1 polymorphisms and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 416, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, S.; Song, J.H.; Tan, M.S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.X.; Jiang, T.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T. Association of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism in ANK1 with Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease in Han Chinese. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 6476–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, T.; Brookes, K.J.; Turton, J.; Chaudhury, S.; Guetta-Baranes, T.; Guerreiro, R.; Bras, J.; Hernandez, D.; Singleton, A.; Francis, P.T.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing of the BDR cohort: evidence to support the role of the PILRA gene in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Liu, C.C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Lv, D.; Zhang, J. Meta-analysis of BACE1 gene rs638405 polymorphism and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in Caucasion and Asian population. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 616, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, S.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Ikram, M.A.; DeStefano, A.L.; Gudnason, V.; Boada, M.; Bis, J.C.; Smith, A.V.; Carassquillo, M.M.; Lambert, J.C.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of genetic loci associated with Alzheimer disease. JAMA 2010, 303, 1832–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.C.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Harold, D.; Naj, A.C.; Sims, R.; Bellenguez, C.; DeStafano, A.L.; Bis, J.C.; Beecham, G.W.; Grenier-Boley, B.; et al. Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flex, A.; Giovannini, S.; Biscetti, F.; Liperoti, R.; Spalletta, G.; Straface, G.; Landi, F.; Angelini, F.; Caltagirone, C.; Ghirlanda, G.; et al. Effect of proinflammatory gene polymorphisms on the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener. Dis. 2014, 13, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naj, A.C.; Jun, G.; Beecham, G.W.; Wang, L.S.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Buros, J.; Gallins, P.J.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Jarvik, G.P.; Crane, P.K.; et al. Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harold, D.; Abraham, R.; Hollingworth, P.; Sims, R.; Gerrish, A.; Hamshere, M.L.; Pahwa, J.S.; Moskvina, V.; Dowzell, K.; Williams, A.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.C.; Heath, S.; Even, G.; Campion, D.; Sleegers, K.; Hiltunen, M.; Combarros, O.; Zelenika, D.; Bullido, M.J.; Tavernier, B.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wang, K.; Rodova, M.; Esteves, R.; Berry, D.; Lezi, E.; Crafter, A.; Barrett, M.; Cardoso, S.M.; Onyango, I.; et al. Polymorphic variation in cytochrome oxidase subunit genes. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 21, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalli, M.A.; Garcia, G.; Madrigal, L.; Arcos-Burgos, M.; Arcila, M.L.; Kosik, K.S.; Lopera, F. Exploratory data from complete genomes of familial alzheimer disease age-at-onset outliers. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, K.; Friedman, B.A.; Larson, J.L.; Lauffer, B.E.; Goldstein, L.D.; Appling, L.L.; Borneo, J.; Poon, C.; Ho, T.; Cai, F.; et al. Untangling the brain’s neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative transcriptional responses. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.C.; Pastor, P.; Cooper, B.; Cervantes, S.; Benitez, B.A.; Razquin, C.; Goate, A.; Ibero-American Alzheimer Disease Genetics Group Researchers; Cruchaga, C. Pooled-DNA sequencing identifies novel causative variants in PSEN1, GRN and MAPT in a clinical early-onset and familial Alzheimer’s disease Ibero-American cohort. Alzheimer’s Res. 2012, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.; Delabio, R.; Horiguchi, L.; Mizumoto, I.; Terazaki, C.R.; Mazzotti, D.; Bertolucci, P.H.; Pinhel, M.A.; Souza, D.; Krieger, H.; et al. Association between interleukin 6 gene haplotype and Alzheimer’s disease: A Brazilian case-control study. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 36, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Pan, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.D.; Deng, Y.L.; Ren, R.J.; Xu, W.; Ma, J.F.; Wang, G.; Chen, S.D. A single nucleotide polymorphism in LRP2 is associated with susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease in the Chinese population. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, K.; Giordano, T.; Brady, D.R.; Stoll, J.; Martin, L.J.; Rapoport, S.I. Impairment in mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase gene expression in Alzheimer disease. Mol. Brain Res. 1994, 24, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, B.; Bulbarelli, A.; Bastias Candia, S.; Lonati, E.; Mastronardi, L.; Romualdi, P.; Candeletti, S.; Gussago, C.; Galimberti, D.; Scarpini, E.; et al. Pin1 contribution to Alzheimer’s disease: Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms in patients with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener. Dis. 2012, 10, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, R.; Wojtas, A.; Bras, J.; Carrasquillo, M.; Rogaeva, E.; Majounie, E.; Cruchaga, C.; Sassi, C.; Kauwe, J.S.; Younkin, S.; et al. TREM2 variants in Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarkowski, E.; Liljeroth, A.-M.; Nilsson, Å.; Minthon, L.; Blennow, K. Decreased Levels of Intrathecal Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist in Alzheimer’s Disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2001, 12, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashutosh; Kou, W.; Cotter, R.; Borgmann, K.; Wu, L.; Persidsky, R.; Sakhuja, N.; Ghorpade, A. CXCL8 protects human neurons from amyloid-beta-induced neurotoxicity: Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listi, F.; Candore, G.; Balistreri, C.R.; Grimaldi, M.P.; Orlando, V.; Vasto, S.; Colonna-Romano, G.; Lio, D.; Licastro, F.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Association between the HLA-A2 allele and Alzheimer disease. Rejuvenation Res. 2006, 9, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Harold, D.; Williams, J. Genetic evidence for the involvement of lipid metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.-H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.; Seo, H.S.; Bang, S.; Kim, S.E.; Greve, D.N.; Au, R.; Shin, C. Amyloid burden in obstructive sleep apnea. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 59, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.E.S.; Finn, M.B.; Sutphen, C.L.; Herries, E.M.; Jerome, G.M.; Ladenson, J.H.; Crimmins, D.L.; Fagan, A.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Obstructive sleep apnea decreases central nervous system-derived proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, R.S.; Ayappa, I.; Mantua, J.; Gumb, T.; Varga, A.; Mooney, A.M.; Burschtin, O.E.; Taxin, Z.; During, E.; Spector, N. The interaction between sleep-disordered breathing and apolipoprotein E genotype on cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in cognitively normal elderly individuals. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubu, O.M.; Pirraglia, E.; Andrade, A.G.; Sharma, R.A.; Gimenez-Badia, S.; Umasabor-Bubu, O.Q.; Hogan, M.M.; Shim, A.M.; Mukhtar, F.; Sharma, N. Obstructive sleep apnea and longitudinal Alzheimer’s disease biomarker changes. Sleep 2019, 42, zsz048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, C.; Mercuri, N.B.; Izzi, F.; Romigi, A.; Cordella, A.; Sancesario, G.; Placidi, F. Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with early but possibly modifiable Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers changes. Sleep 2017, 40, zsx011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimon, N.; Hanly, P.J. Does snoring intensity correlate with the severity of obstructive sleep apnea? J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2010, 6, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audic, S.; Claverie, J.M. The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res. 1997, 7, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann Stat. 2001, 29, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T.; et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D480–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.K.; Gim, J.A.; Yeo, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Integrated late onset Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD) susceptibility genes: Cholesterol metabolism and trafficking perspectives. Gene 2017, 597, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payao, S.L.; Goncalves, G.M.; de Labio, R.W.; Horiguchi, L.; Mizumoto, I.; Rasmussen, L.T.; de Souza Pinhel, M.A.; Silva Souza, D.R.; Bechara, M.D.; Chen, E.; et al. Association of interleukin 1beta polymorphisms and haplotypes with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 247, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, A.; Xiong, X.; Shi, M.; Xu, H. Roles of interleukin (IL)-6 gene polymorphisms, serum IL-6 levels, and treatment in obstructive sleep apnea: A meta-analysis. Sleep Breath 2016, 20, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, L.P.; Chen, N.H.; Lin, Y.; Ko, W.S.; Pang, J.H. Increased MCP-1 gene expression in monocytes of severe OSA patients and under intermittent hypoxia. Sleep Breath 2016, 20, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, T.; Hatta, K.; Hitomi, Y.; Kambayashi, Y.; Hibino, Y.; Konoshita, T.; Nakamura, H. Increased systemic inflammatory interleukin-1ss and interleukin-6 during agitation as predictors of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2013, 28, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimberti, D.; Fenoglio, C.; Lovati, C.; Venturelli, E.; Guidi, I.; Corra, B.; Scalabrini, D.; Clerici, F.; Mariani, C.; Bresolin, N.; et al. Serum MCP-1 levels are increased in mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.S.; Beiser, A.S.; Vasan, R.S.; Roubenoff, R.; Dinarello, C.A.; Harris, T.B.; Benjamin, E.J.; Au, R.; Kiel, D.P.; Wolf, P.A.; et al. Inflammatory markers and the risk of Alzheimer disease: The Framingham Study. Neurology 2007, 68, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattlecker, M.; Khondoker, M.; Proitsi, P.; Williams, S.; Soininen, H.; Kloszewska, I.; Mecocci, P.; Tsolaki, M.; Vellas, B.; Lovestone, S.; et al. Longitudinal Protein Changes in Blood Plasma Associated with the Rate of Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 49, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Crupi, R.; Di Paola, R.; Ontario, M.L.; Bella, R.; Calabrese, E.J.; Crea, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Calabrese, V. Inflammasomes, hormesis, and antioxidants in neuroinflammation: Role of NRLP3 in Alzheimer disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamian, F.; Khazaie, H.; Tahmasian, M.; Leschziner, G.D.; Morrell, M.J.; Hsiung, G.Y.; Rosenzweig, I.; Sepehry, A.A. The Association Between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis Perspective. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancoli-Israel, S.; Klauber, M.R.; Butters, N.; Parker, L.; Kripke, D.F. Dementia in Institutionalized Elderly: Relation to Sleep Apnea. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Severe OSA | Non-Severe OSA | Effect Size | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | n = 5 | n = 5 | ||
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 34.6 (4.2) | 41.2 (12.0) | 0.73 | 0.07 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 5 (100) | 4 (80) | >0.99 | |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 26.4 (3.2) | 25.5 (2.9) | 0.30 | 0.07 |
| AHI (events/h), mean (SD) | 60.6 (21.2) | 7.0 (4.3) | 3.50 | <0.001 |
| Minimum SpO2 (%), mean (SD) | 79.0 (6.0) | 85.2 (2.3) | 1.37 | 0.06 |
| Time SpO2 < 85% (%), mean (SD) | 1.66 (2.3) | 0.04 (0.04) | 1.00 | 0.15 |
| Gene Symbol | Expression | Log2(Fold Change) | Regulation | Probability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severe OSA | Non-Severe OSA | ||||
| Early-onset Alzheimer’s disease | |||||
| APP | 382.418 | 587.644 | −0.619 | Down | 0.503 |
| PSEN1 | 12.776 | 14.876 | −0.220 | Down | 0.286 |
| PSEN2 | 7.204 | 6.208 | 0.215 | Up | 0.265 |
| FKBP1B | 3.786 | 4.126 | −0.124 | Down | 0.216 |
| Late-onset Alzheimer’s disease | |||||
| CCL2 | 12.992 | 116.716 | −3.167 | Down | 0.868 a |
| IL6 | 2.854 | 33.06 | −3.534 | Down | 0.857 a |
| CXCL8 | 2.042 | 20.058 | −3.296 | Down | 0.824 a |
| HLA-A | 1.272 | 14.006 | −3.460 | Down | 0.811 a |
| IL1RN | 239.35 | 57.236 | 2.064 | Up | 0.806 a |
| CLU | 490.412 | 308.192 | 0.670 | Up | 0.522 |
| BIN1 | 23.218 | 18.884 | 0.298 | Up | 0.335 |
| APOE | 24.526 | 29.308 | −0.257 | Down | 0.318 |
| SORL1 | 8.136 | 9.338 | −0.199 | Down | 0.267 |
| PICALM | 56.394 | 52.512 | 0.103 | Up | 0.233 |
| Term | Count | Percentage | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malaria | 3 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 0.007 a |
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 3 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 0.005 a |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 3 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 0.008 a |
| Chagas disease | 3 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 0.008 a |
| Influenza A | 3 | 0.8 | 0.002 | 0.02 a |
| Herpes simplex infection | 3 | 0.8 | 0.002 | 0.02 a |
| Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction | 3 | 0.8 | 0.003 | 0.02 a |
| Graft-versus-host disease | 2 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.09 |
| Legionellosis | 2 | 0.5 | 0.02 | 0.12 |
| Pertussis | 2 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 0.15 |
| Salmonella infection | 2 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.15 |
| Amoebiasis | 2 | 0.5 | 0.045 | 0.18 |
| TNF signaling pathway | 2 | 0.5 | 0.045 | 0.18 |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 2 | 0.5 | 0.045 | 0.18 |
| Hepatitis B | 2 | 0.5 | 0.06 | 0.22 |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | 2 | 0.5 | 0.06 | 0.21 |
| Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | 2 | 0.5 | 0.07 | 0.22 |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | 2 | 0.5 | 0.08 | 0.23 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.-Y.; Tsai, M.-S.; Huang, C.-G.; Wang, R.Y.L.; Chuang, L.-P.; Chen, N.-H.; Liu, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-M.; Cheng, W.-N.; Lee, L.-A. Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated Gene Expression in Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091361
Li H-Y, Tsai M-S, Huang C-G, Wang RYL, Chuang L-P, Chen N-H, Liu C-H, Hsu C-M, Cheng W-N, Lee L-A. Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated Gene Expression in Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(9):1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091361
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hsueh-Yu, Ming-Shao Tsai, Chung-Guei Huang, Robert Y. L. Wang, Li-Pang Chuang, Ning-Hung Chen, Chi-Hung Liu, Cheng-Ming Hsu, Wen-Nuan Cheng, and Li-Ang Lee. 2019. "Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated Gene Expression in Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 9: 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091361
APA StyleLi, H.-Y., Tsai, M.-S., Huang, C.-G., Wang, R. Y. L., Chuang, L.-P., Chen, N.-H., Liu, C.-H., Hsu, C.-M., Cheng, W.-N., & Lee, L.-A. (2019). Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated Gene Expression in Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(9), 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091361








