Kidney Disease in HIV Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of CKD in the Setting of HIV Infection
3. HIV Involvement in Kidney Disease
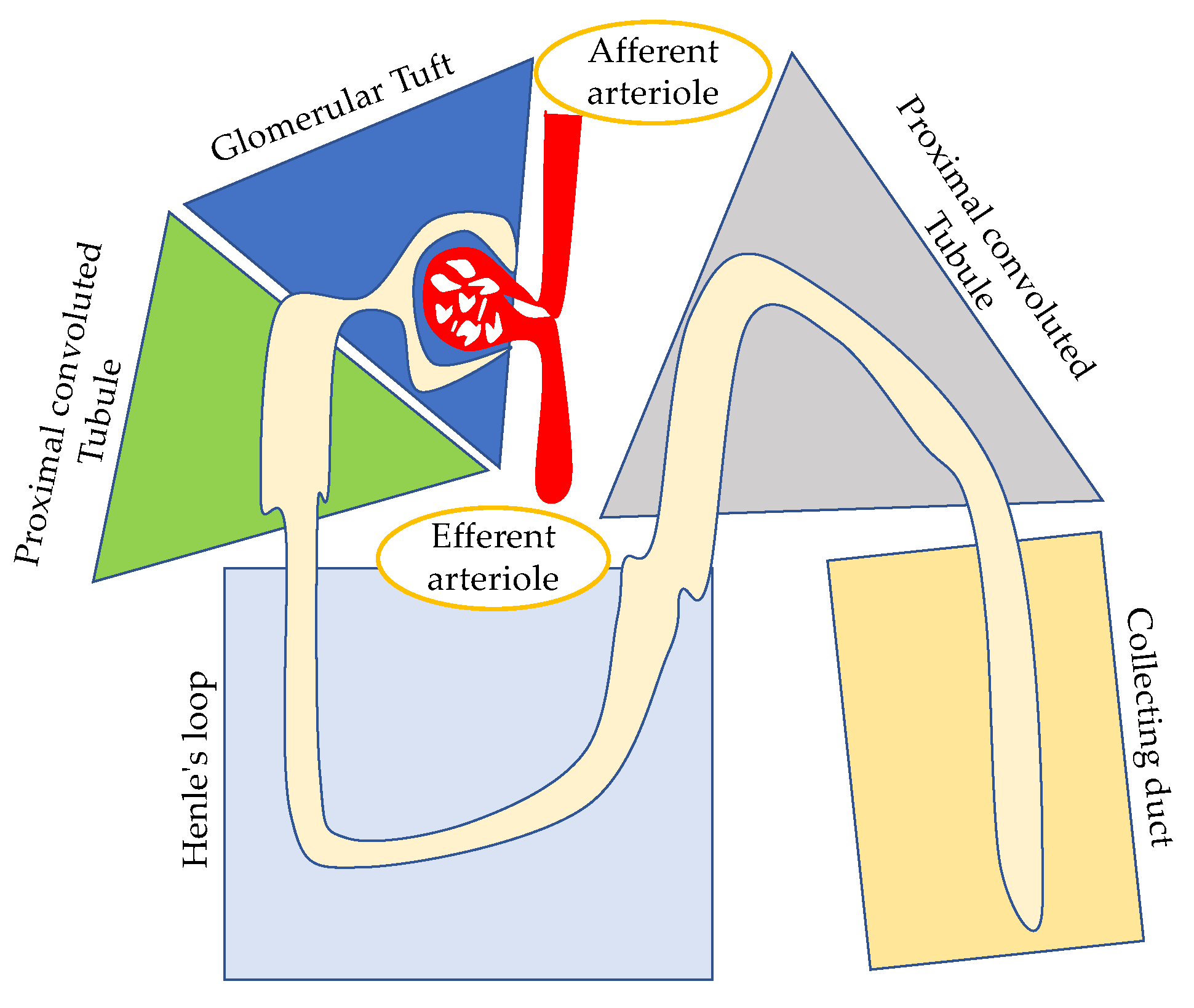
3.1. Glomerular-Dominant HIV-Related Diseases
3.2. Tubulointerstitial-Dominant HIV-Related Diseases
3.3. Vascular-Dominant HIV-Related Diseases
3.4. Other, in the Setting of HIV Infection
4. Nephrotoxicity of ART
5. Direct Mechanism
5.1. Tenofovir
5.2. Tenofovir Alafenamide
5.3. Protease Inhibitors
5.4. Integrase Inhibitor
5.5. Cobicistat
6. Indirect Mechanism of Nephrotoxicity
7. Emerging Therapy
8. Treatment of CKD
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Data and Statistics. Available online: http://www.who.int/hiv/data/en/ (accessed on 9 July 2019).
- Gueler, A.; Moser, A.; Calmy, A.; Günthard, H.F.; Bernasconi, E.; Furrer, H.; Fux, C.A.; Battegay, M.; Cavassini, M.; Vernazza, P.; et al. Life expectancy in HIV-positive persons in Switzerland: Matched comparison with general population. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2017, 31, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.-Y.; Hung, C.-C.; Liu, W.-C.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Sun, H.-Y.; Lu, C.-L.; Wu, H.; Chien, K.-L. Metabolic syndrome among HIV-infected Taiwanese patients in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy: Prevalence and associated factors. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, A.G.; Althoff, K.N.; Jing, Y.; Estrella, M.M.; Kitahata, M.M.; Wester, C.W.; Bosch, R.J.; Crane, H.; Eron, J.; Gill, M.J.; et al. End-stage renal disease among HIV-infected adults in North America. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2015, 60, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, E.J.; Szczech, L.A.; Ross, M.J.; Klotman, M.E.; Winston, J.A.; Klotman, P.E. Highly active antiretroviral therapy and the epidemic of HIV+ end-stage renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2005, 16, 2412–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilma, D.; Abdissa, A.; Kæstel, P.; Tesfaye, M.; Olsen, M.F.; Girma, T.; Ritz, C.; Friis, H.; Andersen, Å.B.; Kirk, O. Serum creatinine and estimated glomerular filtration rates in HIV positive and negative adults in Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagneux-Brunon, A.; Mariat, C.; Delanaye, P. Cystatin C in HIV-infected patients: Promising but not yet ready for prime time. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.-Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2012, 27, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A. Estimating GFR Using the CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) Creatinine Equation: More Accurate GFR Estimates, Lower CKD Prevalence Estimates, and Better Risk Predictions. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2010, 55, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cockcroft, D.W.; Gault, M.H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 1976, 16, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekrikpo, U.E.; Kengne, A.P.; Bello, A.K.; Effa, E.E.; Noubiap, J.J.; Salako, B.L.; Rayner, B.L.; Remuzzi, G.; Okpechi, I.G. Chronic kidney disease in the global adult HIV-infected population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, G.M.; Mehta, S.H.; Atta, M.G.; Kirk, G.D.; Galai, N.; Vlahov, D.; Moore, R.D. End-stage renal disease and chronic kidney disease in a cohort of African-American HIV-infected and at-risk HIV-seronegative participants followed between 1988 and 2004. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2007, 21, 2435–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansi, L.; Hughes, A.; Bhagani, S.; Mackie, N.E.; Leen, C.; Levy, J.; Edwards, S.; Connolly, J.; Holt, S.G.; Hendry, B.M.; et al. Clinical epidemiology of HIV-associated end-stage renal failure in the UK. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2009, 23, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazancioğlu, R. Risk factors for chronic kidney disease: An update. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocroft, A.; Lundgren, J.D.; Ross, M.; Law, M.; Reiss, P.; Kirk, O.; Smith, C.; Wentworth, D.; Neuhaus, J.; Fux, C.A.; et al. Development and validation of a risk score for chronic kidney disease in HIV infection using prospective cohort data from the D:A:D study. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouatou, Y.; Gayet Ageron, A.; Bernasconi, E.; Battegay, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Staehelin, C.; Merz, L.; Kovari, H.; Fux, C.; de Seigneux, S.; et al. Lipodystrophy Increases the Risk of CKD Development in HIV-Positive Patients in Switzerland: The LIPOKID Study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucas, G.M.; Lau, B.; Atta, M.G.; Fine, D.M.; Keruly, J.; Moore, R.D. Chronic Kidney Disease Incidence, and Progression to End-Stage Renal Disease, in HIV-Infected Individuals: A Tale of Two Races. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althoff, K.N.; Gebo, K.A.; Moore, R.D.; Boyd, C.M.; Justice, A.C.; Wong, C.; Lucas, G.M.; Klein, M.B.; Kitahata, M.M.; Crane, H.; et al. Contributions of traditional and HIV-related risk factors on non-AIDS-defining cancer, myocardial infarction, and end-stage liver and renal diseases in adults with HIV in the USA and Canada: A collaboration of cohort studies. Lancet HIV 2019, 6, e93–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.J.; Foley, R.N.; Chavers, B.; Gilbertson, D.; Herzog, C.; Johansen, K.; Kasiske, B.; Kutner, N.; Liu, J.; St Peter, W.; et al. United States Renal Data System 2011 Annual Data Report: Atlas of chronic kidney disease & end-stage renal disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2012, 59, A7. [Google Scholar]
- Eggers, P.W.; Kimmel, P.L. Is there an epidemic of HIV Infection in the US ESRD program? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2004, 15, 2477–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Bosch, J.P.; Lewis, J.B.; Greene, T.; Rogers, N.; Roth, D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: A new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B.I.; Limou, S.; Ma, L.; Kopp, J.B. APOL1-Associated Nephropathy: A Key Contributor to Racial Disparities in CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2018, 72, S8–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purswani, M.U.; Patel, K.; Winkler, C.A.; Spector, S.A.; Hazra, R.; Seage, G.R.; Mofenson, L.; Karalius, B.; Scott, G.B.; Van Dyke, R.B.; et al. Brief Report: APOL1 Renal Risk Variants Are Associated With Chronic Kidney Disease in Children and Youth With Perinatal HIV Infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1999 2016, 73, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atta, M.G.; Estrella, M.M.; Skorecki, K.L.; Kopp, J.B.; Winkler, C.A.; Wasser, W.G.; Shemer, R.; Racusen, L.C.; Kuperman, M.; Foy, M.C.; et al. Association of APOL1 Genotype with Renal Histology among Black HIV-Positive Patients Undergoing Kidney Biopsy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2016, 11, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, R.; Granich, R.M.; Gupta, S.; Williams, B.G. CD4 Cell Count: Declining Value for Antiretroviral Therapy Eligibility. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2016, 62, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swanepoel, C.R.; Atta, M.G.; D’Agati, V.D.; Estrella, M.M.; Fogo, A.B.; Naicker, S.; Post, F.A.; Wearne, N.; Winkler, C.A.; Cheung, M.; et al. Kidney disease in the setting of HIV infection: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, C.M.; Klotman, P.E.; D’Agati, V.D. HIV-Associated Nephropathy: Clinical Presentation, Pathology, and Epidemiology in the Era of Antiretroviral Therapy. Semin. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopp, J.B.; Nelson, G.W.; Sampath, K.; Johnson, R.C.; Genovese, G.; An, P.; Friedman, D.; Briggs, W.; Dart, R.; Korbet, S.; et al. APOL1 genetic variants in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and HIV-associated nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2011, 22, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasembeli, A.N.; Duarte, R.; Ramsay, M.; Mosiane, P.; Dickens, C.; Dix-Peek, T.; Limou, S.; Sezgin, E.; Nelson, G.W.; Fogo, A.B.; et al. APOL1 Risk Variants Are Strongly Associated with HIV-Associated Nephropathy in Black South Africans. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2015, 26, 2882–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, J.A.; Klotman, M.E.; Klotman, P.E. HIV-associated nephropathy is a late, not early, manifestation of HIV-1 infection. Kidney Int. 1999, 55, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anochie, I.C.; Eke, F.U.; Okpere, A.N. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated nephropathy (HIVAN) in Nigerian children. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2008, 23, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Appel, R.G.; Neill, J. A steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 1990, 113, 892–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Pawar, R.; Carey, J.T.; Graham, R.C.; Jacobs, G.H.; Menon, A.; Salata, R.A.; Seliga, R.; Kalayjian, R.C. Effect of corticosteroid therapy on human immunodeficiency virus-associated nephropathy. Am. J. Med. 1994, 97, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, W.A.; Tanawattanacharoen, S.; Choi, M.J.; Scheel, P.J.; Nadasdy, T.; Racusen, L. Clinicopathologic correlates of prednisone treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-associated nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 1996, 28, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattana, J.; Siegal, F.P.; Schwarzwald, E.; Molho, L.; Sankaran, R.T.; Gooneratne, R.; Ahuja, T.S.; Singhal, P.C. AIDS-associated membranous nephropathy with advanced renal failure: Response to prednisone. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 1997, 30, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustace, J.A.; Nuermberger, E.; Choi, M.; Scheel, P.J.; Moore, R.; Briggs, W.A. Cohort study of the treatment of severe HIV-associated nephropathy with corticosteroids. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucas, G.M.; Ross, M.J.; Stock, P.G.; Shlipak, M.G.; Wyatt, C.M.; Gupta, S.K.; Atta, M.G.; Wools-Kaloustian, K.K.; Pham, P.A.; Bruggeman, L.A.; et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of chronic kidney disease in patients infected with HIV: 2014 update by the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2014, 59, e96–e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.F.; Scriven, J.; Meintjes, G.; Wilkinson, R.J. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV-infected patients. HIVAIDS Auckl. NZ 2015, 7, 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A.H.; Nast, C.C. HIV-associated nephropathy. A unique combined glomerular, tubular, and interstitial lesion. Mod. Pathol. 1988, 1, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, J.W.; Hamzah, L.; Jose, S.; Horsfield, C.; O’Donnell, P.; McAdoo, S.; Kumar, E.A.; Turner-Stokes, T.; Khatib, N.; Das, P.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of HIV-associated immune complex kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alpers, C.E. Light at the end of the TUNEL: HIV-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jehle, A.W.; Khanna, N.; Sigle, J.-P.; Glatz-Krieger, K.; Battegay, M.; Steiger, J.; Dickenmann, M.; Hirsch, H.H. Acute renal failure on immune reconstitution in an HIV-positive patient with miliary tuberculosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2004, 38, e32–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafrani, L.; Coppo, P.; Dettwiler, S.; Molinier-Frenkel, V.; Agbalika, F.; Guiard-Schmid, J.-B.; Pialoux, G.; Xu-Dubois, Y.-C.; Rondeau, E.; Hertig, A. Nephropathy associated with the diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Hansson, G.K. Leducq Transatlantic Network on Atherothrombosis Inflammation in atherosclerosis: From pathophysiology to practice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, N.S.; Grobbee, D.E.; Burgner, D.; Cheung, M.M.H.; Kurniati, N.; Uiterwaal, C.S.P.M. Effects of paediatric HIV infection on childhood vasculature. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 3610–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S. HIV associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Postgrad. Med. J. 2002, 78, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.D.; Kimmel, P.L. Immune Complex Renal Disease and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. Semin. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, K.R.; Elhadad, S.; Copertino, D.; Laurence, J. Thrombotic Microangiopathy in the Setting of HIV Infection: A Case Report and Review of the Differential Diagnosis and Therapy. AIDS Patient Care STDs 2016, 30, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.T.; Cole, S.R.; Li, X.; Kingsley, L.A.; Palella, F.J.; Riddler, S.A.; Visscher, B.R.; Margolick, J.B.; Dobs, A.S. Antiretroviral therapy and the prevalence and incidence of diabetes mellitus in the multicenter AIDS cohort study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, S.; Aldous, C.; Mahomed, F. A deadly combination—HIV and diabetes mellitus: Where are we now? S. Afr. Med. J. Suid-Afr. Tydskr. Vir Geneeskd. 2016, 106, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallipattu, S.K.; Liu, R.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, E.Y.; D’Agati, V.; Kaufman, L.; Ma’ayan, A.; Klotman, P.E.; Chuang, P.Y.; He, J.C. Expression of HIV transgene aggravates kidney injury in diabetic mice. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sax, P.E.; Gallant, J.E.; Klotman, P.E. Renal safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. AIDS Read. 2007, 17, 90–92, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, M.R.; Katlama, C.; Montaner, J.S.; Cooper, D.A.; Gazzard, B.; Clotet, B.; Lazzarin, A.; Schewe, K.; Lange, J.; Wyatt, C.; et al. The safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HIV infection in adults: The first 4 years. AIDS 2007, 21, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, J.E.; Parish, M.A.; Keruly, J.C.; Moore, R.D. Changes in renal function associated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate treatment, compared with nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor treatment. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2005, 40, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, A.; Amin, J.; Mallon, P.; Marriott, D.; Carr, A.; Cooper, D.A.; Emery, S. Minor changes in calculated creatinine clearance and anion-gap are associated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-containing highly active antiretroviral therapy. HIV Med. 2006, 7, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchacz, K.; Young, B.; Baker, R.K.; Moorman, A.; Chmiel, J.S.; Wood, K.C.; Brooks, J.T. Renal function in patients receiving tenofovir with ritonavir/lopinavir or ritonavir/atazanavir in the HIV Outpatient Study (HOPS) cohort. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1999 2006, 43, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, C.A.; Simcock, M.; Wolbers, M.; Bucher, H.C.; Hirschel, B.; Opravil, M.; Vernazza, P.; Cavassini, M.; Bernasconi, E.; Elzi, L.; et al. Tenofovir use is associated with a reduction in calculated glomerular filtration rates in the Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Antivir. Ther. 2007, 12, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Goicoechea, M.; Liu, S.; Best, B.; Sun, S.; Jain, S.; Kemper, C.; Witt, M.; Diamond, C.; Haubrich, R.; Louie, S.; et al. Greater tenofovir-associated renal function decline with protease inhibitor-based versus nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor-based therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.M.; Hendry, B.M.; Nitsch, D.; Connolly, J.O. Tenofovir-associated kidney toxicity in HIV-infected patients: A review of the evidence. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2011, 57, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.D.; Wiebe, N.; Smith, N.; Keiser, P.; Naicker, S.; Tonelli, M. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Renal Safety of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in HIV-Infected Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, J.E.; Staszewski, S.; Pozniak, A.L.; DeJesus, E.; Suleiman, J.M.A.H.; Miller, M.D.; Coakley, D.F.; Lu, B.; Toole, J.J.; Cheng, A.K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Tenofovir DF vs Stavudine in Combination Therapy in Antiretroviral-Naive Patients: A 3-Year Randomized Trial. JAMA 2004, 292, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, J.E.; DeJesus, E.; Arribas, J.R.; Pozniak, A.L.; Gazzard, B.; Campo, R.E.; Lu, B.; McColl, D.; Chuck, S.; Enejosa, J.; et al. Tenofovir DF, emtricitabine, and efavirenz vs. zidovudine, lamivudine, and efavirenz for HIV. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapadula, G.; Bernasconi, D.P.; Casari, S.; Maggiolo, F.; Cauda, R.; Pietro, M.D.; Ladisa, N.; Sighinolfi, L.; Zoppo, S.D.; Sabbatini, F.; et al. Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease among Patients Developing Mild Renal Impairment during Tenofovir-Containing Antiretroviral Treatment. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, M.; Khaykin, P.; Stephan, C.; Schmidt, K.; Buettner, M.; Amann, K.; Lutz, T.; Gute, P.; Haberl, A.; Geiger, H.; et al. Acute kidney injury caused by tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and diclofenac co-administration. HIV Med. 2013, 14, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzedine, H.; Hulot, J.S.; Vittecoq, D.; Gallant, J.E.; Staszewski, S.; Launay-Vacher, V.; Cheng, A.; Deray, G. Study 903 Team Long-term renal safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in antiretroviral-naive HIV-1-infected patients. Data from a double-blind randomized active-controlled multicentre study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2005, 20, 743–746. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, W.J.; Jang, J.Y.; Park, W.Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Cha, S.-W.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Effect of tenofovir on renal function in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourret, J.; Deray, G.; Isnard-Bagnis, C. Tenofovir Effect on the Kidneys of HIV-Infected Patients: A Double-Edged Sword? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallant, J.E.; Moore, R.D. Renal function with use of a tenofovir-containing initial antiretroviral regimen. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2009, 23, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.L.; Tan, J.M.E.; Jonker, M.J.; Jongejan, A.; Buissink, T.; Veldhuijzen, S.; van Kampen, A.H.C.; Brul, S.; van der Spek, H. Beyond the polymerase-γ theory: Production of ROS as a mode of NRTI-induced mitochondrial toxicity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, D.; Monge, M.; Meynard, J.-L.; Fouqueray, B.; Mougenot, B.; Girard, P.-M.; Ronco, P.; Rossert, J. Fanconi syndrome and renal failure induced by tenofovir: A first case report. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2002, 40, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 16th CROI Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections Montreal, Canada; 8–11 February 2009 Tenofovir and PI Use Are Associated with an Increased Prevalence of Proximal Renal Tubular Dysfunction in the Swiss HIV Cohort Study: Boosted PI+TDF Associated with Renal Function. Available online: http://www.natap.org/2009/CROI/croi_144.htm (accessed on 6 January 2019).
- Fux, C.A.; Rauch, A.; Simcock, M.; Bucher, H.C.; Hirschel, B.; Opravil, M.; Vernazza, P.; Cavassini, M.; Bernasconi, E.; Elzi, L.; et al. Tenofovir use is associated with an increase in serum alkaline phosphatase in the Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Antivir. Ther. 2008, 13, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, P.M.; Cotter, A.G. Tenofovir and Bone Health. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2016, 11, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irizarry-Alvarado, J.M.; Dwyer, J.P.; Brumble, L.M.; Alvarez, S.; Mendez, J.C. Proximal tubular dysfunction associated with tenofovir and didanosine causing Fanconi syndrome and diabetes insipidus: A report of 3 cases. AIDS Read. 2009, 19, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, K.; Nagata, M.; Watanabe, S.; Nishi, S. Distal renal tubular acidosis without renal impairment after use of tenofovir: A case report. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauss, S.; Berger, F.; Schmutz, G. Antiretroviral therapy with tenofovir is associated with mild renal dysfunction. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2005, 19, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Stebbing, J.; Nelson, M.; Moyle, G.; Bower, M.; Mandalia, S.; Gazzard, B. Renal dysfunction with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-containing highly active antiretroviral therapy regimens is not observed more frequently: A cohort and case-control study. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1999 2004, 37, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.; Buchacz, K.; Baker, R.K.; Moorman, A.C.; Wood, K.C.; Chmiel, J.; Brooks, J.T. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators Renal function in Tenofovir-exposed and Tenofovir-unexposed patients receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy in the HIV Outpatient Study. J. Int. Assoc. Physicians AIDS Care Chic. Ill 2002 2007, 6, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlitz, L.C.; Mohan, S.; Stokes, M.B.; Radhakrishnan, J.; D’Agati, V.D.; Markowitz, G.S. Tenofovir nephrotoxicity: Acute tubular necrosis with distinctive clinical, pathological, and mitochondrial abnormalities. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.E.; Pizzoferrato, T.; Bedford, J.; Morris, A.; Hoffman, R.; Braden, G. Tenofovir-associated acute and chronic kidney disease: A case of multiple drug interactions. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2006, 42, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, K.; van Agtmael, M.A.; Carr, A. Incomplete reversibility of tenofovir-related renal toxicity in HIV-infected men. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1999 2010, 55, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, S.; Domingo, P.; Palacios, R.; Santos, J.; Falcó, V.; Murillas, J.; Estrada, V.; Ena, J.; Alvarez, M.L. Recover Study Group Renal safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in HIV-1 treatment-experienced patients with adverse events related to prior NRTI use: Data from a prospective, observational, multicenter study. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1999 2006, 42, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents Living with HIV. Available online: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- Lisowska-Myjak, B. Serum and urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Blood Purif. 2010, 29, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, T.; Kurosawa, T.; Tanaka, N.; Kawasaki, Y.; Kikuchi, Y.; Oka, S.; Gatanaga, H. Urinary β2 microglobulin can predict tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-related renal dysfunction in HIV-1-infected patients who initiate tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-containing antiretroviral therapy. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2016, 30, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.A.; He, G.-X.; Eisenberg, E.; Cihlar, T.; Swaminathan, S.; Mulato, A.; Cundy, K.C. Selective intracellular activation of a novel prodrug of the human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase inhibitor tenofovir leads to preferential distribution and accumulation in lymphatic tissue. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruane, P.J.; DeJesus, E.; Berger, D.; Markowitz, M.; Bredeek, U.F.; Callebaut, C.; Zhong, L.; Ramanathan, S.; Rhee, M.S.; Fordyce, M.W.; et al. Antiviral activity, safety, and pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of tenofovir alafenamide as 10-day monotherapy in HIV-1-positive adults. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1999 2013, 63, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.S.; Fordyce, M.W.; Hitchcock, M.J.M. Tenofovir alafenamide: A novel prodrug of tenofovir for the treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Antiviral Res. 2016, 125, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stray, K.M.; Park, Y.; Babusis, D.; Callebaut, C.; Cihlar, T.; Ray, A.S.; Perron, M. Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) does not deplete mitochondrial DNA in human T-cell lines at intracellular concentrations exceeding clinically relevant drug exposures. Antiviral Res. 2017, 140, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, J.R.; Thompson, M.; Sax, P.E.; Haas, B.; McDonald, C.; Wohl, D.A.; DeJesus, E.; Clarke, A.E.; Guo, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Brief Report: Randomized, Double-Blind Comparison of Tenofovir Alafenamide (TAF) vs Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (TDF), Each Coformulated With Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, and Emtricitabine (E/C/F) for Initial HIV-1 Treatment: Week 144 Results. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1999 2017, 75, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnell, K.L.; Vibhakar, S.; Glowacki, R.C.; Gallagher, M.A.; Osei, A.M.; Huhn, G. Nephrotoxicity Associated with Concomitant Use of Ledipasvir-Sofosbuvir and Tenofovir in a Patient with Hepatitis C Virus and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Coinfection. Pharmacotherapy 2016, 36, e148–e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novick, T.K.; Choi, M.J.; Rosenberg, A.Z.; McMahon, B.A.; Fine, D.; Atta, M.G. Tenofovir alafenamide nephrotoxicity in an HIV-positive patient: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017, 96, e8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, N.C.; Yarlagadda, S.G. Fanconi Syndrome and Tenofovir Alafenamide: A Case Report. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzedine, H.; Lescure, F.X.; Bonnet, F. HIV medication-based urolithiasis. Clin. Kidney J. 2014, 7, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viraben, R.; Aquilina, C. Indinavir-associated lipodystrophy. AIDS Lond. Engl. 1998, 12, F37–F39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattevin, P.; Revest, M.; Chapplain, J.-M.; Ratajczak-Enselme, M.; Arvieux, C.; Michelet, C. Increased risk of renal stones in patients treated with atazanavir. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2013, 56, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, Y.; Nishijima, T.; Watanabe, K.; Komatsu, H.; Tsukada, K.; Teruya, K.; Gatanaga, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Oka, S. High incidence of renal stones among HIV-infected patients on ritonavir-boosted atazanavir than in those receiving other protease inhibitor-containing antiretroviral therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2012, 55, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzigou, C.; Daudon, M.; Meynard, J.L.; Lebas, F.B.; Higueret, D.; Escaut, L.; Zucman, D.; Liotier, J.-Y.; Quencez, J.-L.; Asselah, K.; et al. Urolithiasis in HIV-Positive Patients Treated with Atazanavir. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, e105–e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Updated Recommendations on First-Line and Second-Line Antiretroviral Regimens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis and Recommendations on Early Infant Diagnosis of HIV: Interim Guidance; (WHO/CDS/HIV/18.18). Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Milburn, J.; Jones, R.; Levy, J.B. Renal effects of novel antiretroviral drugs. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2017, 32, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellbrink, H.-J.; Reynes, J.; Lazzarin, A.; Voronin, E.; Pulido, F.; Felizarta, F.; Almond, S.; St Clair, M.; Flack, N.; Min, S.; et al. Dolutegravir in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1: 96-week results from a randomized dose-ranging study. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2013, 27, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Bang, T.J. Prevention of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy (CIN) in Interventional Radiology Practice. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 27, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koteff, J.; Borland, J.; Chen, S.; Song, I.; Peppercorn, A.; Koshiba, T.; Cannon, C.; Muster, H.; Piscitelli, S.C. A phase 1 study to evaluate the effect of dolutegravir on renal function via measurement of iohexol and para-aminohippurate clearance in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raffi, F.; Rachlis, A.; Stellbrink, H.-J.; Hardy, W.D.; Torti, C.; Orkin, C.; Bloch, M.; Podzamczer, D.; Pokrovsky, V.; Pulido, F.; et al. Once-daily dolutegravir versus raltegravir in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 infection: 48 week results from the randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority SPRING-2 study. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2013, 381, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, E.D. Cobicistat: A review of its use as a pharmacokinetic enhancer of atazanavir and darunavir in patients with HIV-1 infection. Drugs 2014, 74, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegar, D.A.; Knight, A.M.; Monolakis, J.S. Antiretroviral medication errors among hospitalized patients with HIV infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2006, 43, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, L.A.; Coresh, J.; Greene, T.; Levey, A.S. Assessing kidney function--measured and estimated glomerular filtration rate. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckard, A.R.; McComsey, G.A. The Role of Statins in the Setting of HIV Infection. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015, 12, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koubar, S.H.; Estrella, M.M.; Warrier, R.; Moore, R.D.; Lucas, G.M.; Atta, M.G.; Fine, D.M. Rhabdomyolysis in an HIV cohort: Epidemiology, causes and outcomes. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, L.R.; Schrier, P.B.; Shah, H.H. Severe recurrent rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury in a HIV-infected patient on antiretroviral therapy. Ren. Fail. 2013, 35, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Pinto, A.; Grant, A.; Edwards, S.; Weller, I. Lactic acidosis in HIV infected patients: A systematic review of published cases. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2003, 79, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, J.; Mocroft, A.; Ryom, L. Contemporary protease inhibitors and cardiovascular risk. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryom, L.; Lundgren, J.D.; El-Sadr, W.; Reiss, P.; Kirk, O.; Law, M.; Phillips, A.; Weber, R.; Fontas, E.; d’ Arminio Monforte, A.; et al. Cardiovascular disease and use of contemporary protease inhibitors: The D:A:D international prospective multicohort study. Lancet HIV 2018, 5, e291–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddler, S.A.; Smit, E.; Cole, S.R.; Li, R.; Chmiel, J.S.; Dobs, A.; Palella, F.; Visscher, B.; Evans, R.; Kingsley, L.A. Impact of HIV infection and HAART on serum lipids in men. JAMA 2003, 289, 2978–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llibre, J.M.; Hill, A. Abacavir and cardiovascular disease: A critical look at the data. Antiviral Res. 2016, 132, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombier, M.-A.; Molina, J.-M. Doravirine: A review. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2018, 13, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effect Of Severe Renal Impairment On Doravirine Pharmacokinetics. CROI Conference. Available online: http://www.croiconference.org/sessions/effect-severe-renal-impairment-doravirine-pharmacokinetics (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- Kaplon, H.; Reichert, J.M. Antibodies to watch in 2019. MAbs 2019, 11, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llibre, J.M.; Hung, C.-C.; Brinson, C.; Castelli, F.; Girard, P.-M.; Kahl, L.P.; Blair, E.A.; Angelis, K.; Wynne, B.; Vandermeulen, K.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of dolutegravir-rilpivirine for the maintenance of virological suppression in adults with HIV-1: Phase 3, randomised, non-inferiority SWORD-1 and SWORD-2 studies. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2018, 391, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, P.; Madero, J.S.; Arribas, J.R.; Antinori, A.; Ortiz, R.; Clarke, A.E.; Hung, C.-C.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Girard, P.-M.; Sievers, J.; et al. Dolutegravir plus lamivudine versus dolutegravir plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 infection (GEMINI-1 and GEMINI-2): Week 48 results from two multicentre, double-blind, randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 trials. The Lancet 2019, 393, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Schloth, T.; Genabe, I.; Pilgrim, W.; Jorden, A.; Fein, P.A.; Avram, M.M. Peritonitis and the patient with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Adv. Perit. Dial. Conf. Perit. Dial. 1992, 8, 250–252. [Google Scholar]
- Dressler, R.; Peters, A.T.; Lynn, R.I. Pseudomonal and candidal peritonitis as a complication of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Am. J. Med. 1989, 86, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, J.E.; Gustafson, S.; Mehta, S.; Reed, R.D.; Shelton, B.; MacLennan, P.A.; Durand, C.; Snyder, J.; Salkowski, N.; Massie, A.; et al. Survival Benefit of Kidney Transplantation in HIV-Infected Patients. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, J.E.; Mehta, S.; Reed, R.D.; MacLennan, P.; Massie, A.; Nellore, A.; Durand, C.; Segev, D.L. A National Study of Outcomes among HIV-Infected Kidney Transplant Recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2015, 26, 2222–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wearne, N.; Okpechi, I.G.; Swanepoel, C.R. Nephrology in South Africa: Not Yet ubuntu. Kidney Dis. Basel Switz. 2019, 5, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Kilonzo, K.G.; Jones, E.S.W.; Okpechi, I.G.; Wearne, N.; Barday, Z.; Swanepoel, C.R.; Yeates, K.; Rayner, B.L. Disparities in dialysis allocation: An audit from the new South Africa. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaud, G.; Dejucq-Rainsford, N.; Avettand-Fenoël, V.; Viard, J.-P.; Anglicheau, D.; Bienaimé, F.; Muorah, M.; Galmiche, L.; Gribouval, O.; Noël, L.-H.; et al. The kidney as a reservoir for HIV-1 after renal transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2014, 25, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HIV-Related Kidney Disease | Directly Related to HIV Infection | First-Line Treatment * | Second-Line Treatment | Adjunctive Therapies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I. Glomerular-dominant | ||||
| a. Podocytopaties (e.g. HIVAN, FSGS) | X | ART | Steroid, Cys A | ACEi or ARB |
| b. Immune complex-mediated glomerular disease (e.g. MPGN, IgAN) | ART | Steroid | ACEi or ARB | |
| II. Tubulointerstitial-dominant | ||||
| a. Tubulointerstitial injury in the setting of classic HIVAN | X | ART | Steroid | |
| b. Acute tubular injury or acute tubular necrosis (associated with ART) | Stop offending drug | |||
| c. Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (other than ART) | Stop offending drug | Steroid | ||
| d. Direct renal parenchymal infection by pathogens | Treat the underling infection | |||
| e. Imuunologic dysfunction-related tubulointerstitial inflammation | ||||
|
|
| II. NSAID (risk of nephrotoxicity), thalidomide, hydroxychloroquine, anti-TNFalpha | |
| f. Other tubulointerstitial inflammation in the setting of HIV | Treat underlining disease | |||
| III. Vascular-dominant | ||||
| a. Thrombotic microangiopathy in the setting of HIV | ||||
|
|
| I. Rituximab, bortezomib, Cys A | I. Sterodi/antiplatelet agents |
| b. Arteriosclerosis | X § | ART/reduce risk factors for atherosclerosis | ||
| IV. Other, in the setting of HIV | ||||
| a. Diabetic nephrolopathy | Treat diabetes | ACEi or ARB | ||
| b. Age-related nephrosclerosis | ART | ART/reduce risk factors for atherosclerosis | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfano, G.; Cappelli, G.; Fontana, F.; Di Lullo, L.; Di Iorio, B.; Bellasi, A.; Guaraldi, G. Kidney Disease in HIV Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081254
Alfano G, Cappelli G, Fontana F, Di Lullo L, Di Iorio B, Bellasi A, Guaraldi G. Kidney Disease in HIV Infection. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(8):1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081254
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfano, Gaetano, Gianni Cappelli, Francesco Fontana, Luca Di Lullo, Biagio Di Iorio, Antonio Bellasi, and Giovanni Guaraldi. 2019. "Kidney Disease in HIV Infection" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 8: 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081254
APA StyleAlfano, G., Cappelli, G., Fontana, F., Di Lullo, L., Di Iorio, B., Bellasi, A., & Guaraldi, G. (2019). Kidney Disease in HIV Infection. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(8), 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081254






