Repeatability of Intraoral Scanners for Complete Arch Scan of Partially Edentulous Dentitions: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
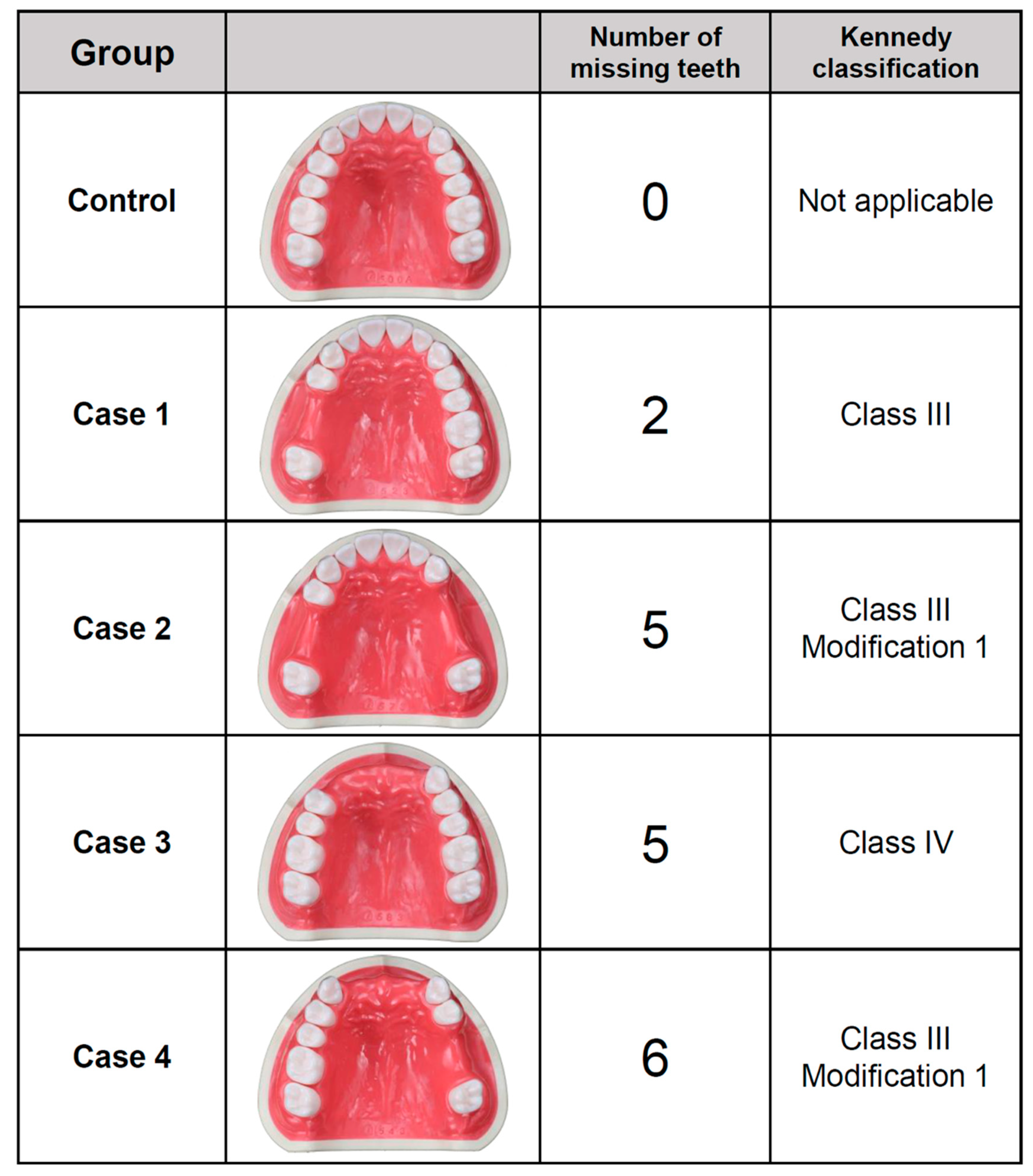
2.1. Evaluated Scenarios
2.2. Use of Intraoral Scanners
2.3. Precision Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
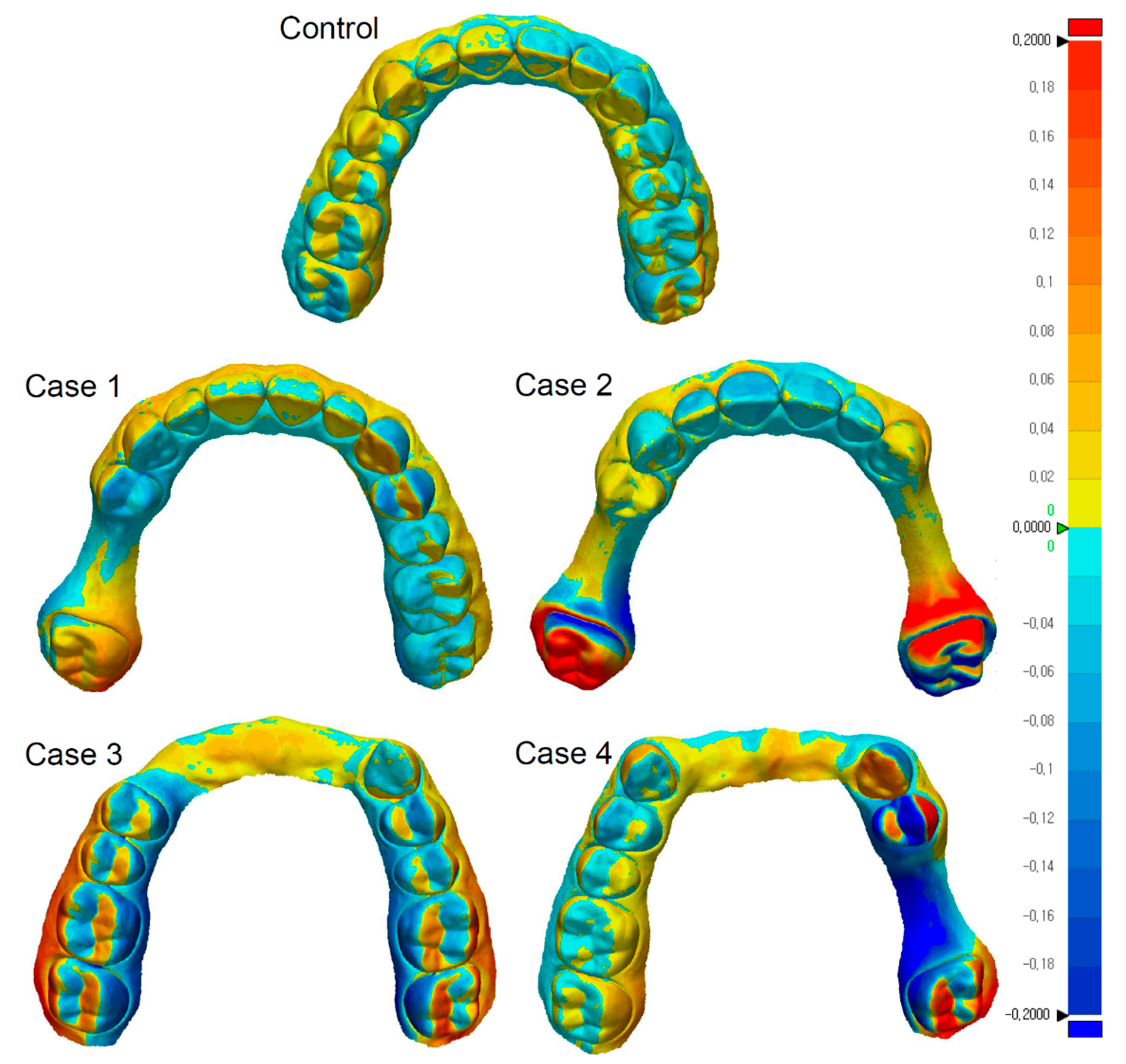
- In the scanning of partially edentulous dentitions, the repeatability of complete-arch scan data acquired by intraoral scanners was reduced in the cases having relatively large edentulous sites;
- Surface deviations were mainly observed on the side that included the partially edentulous area in the scanned dental arch;
- Regardless of the type of intraoral scanners used, a similar trend was observed in the repeatability of complete-arch scan data obtained for partially edentulous dentitions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blatz, M.B.; Conejo, J. The Current State of Chairside Digital Dentistry and Materials. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 63, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervino, G.; Fiorillo, L.; Arzukanyan, A.V.; Spagnuolo, G.; Cicciu, M. Dental Restorative Digital Workflow: Digital Smile Design from Aesthetic to Function. Dent. J. (Basel) 2019, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, E.; Nesbit, M.; Petridis, H. Survey on the use of CAD-CAM technology by UK and Irish dental technicians. Br. Dent. J. 2017, 222, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.; Nesbit, M.; Petridis, H. Survey of UK dentists regarding the use of CAD/CAM technology. Br. Dent. J. 2016, 221, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herford, A.S.; Miller, M.; Lauritano, F.; Cervino, G.; Signorino, F.; Maiorana, C. The use of virtual surgical planning and navigation in the treatment of orbital trauma. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2017, 20, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaizer, M.R.; Gierthmuehlen, P.C.; Dos Santos, M.B.; Cava, S.S.; Zhang, Y. Speed sintering translucent zirconia for chairside one-visit dental restorations: Optical, mechanical, and wear characteristics. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 10999–11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, H.; Durand, J.C.; Jacquot, B.; Fages, M. Dental biomaterials for chairside CAD/CAM: State of the art. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2017, 9, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejatidanesh, F.; Savabi, G.; Amjadi, M.; Abbasi, M.; Savabi, O. Five year clinical outcomes and survival of chairside CAD/CAM ceramic laminate veneers a retrospective study. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkunas, V.; Geciauskaite, A.; Jegelevicius, D.; Vaitiekunas, M. Accuracy of digital implant impressions with intraoral scanners: A systematic review. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 101–120. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Koizumi, H.; Furuchi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ohkubo, C.; Matsumura, H. Use of digital impression systems with intraoral scanners for fabricating restorations and fixed dental prostheses. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 60, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braian, M.; Wennerberg, A. Trueness and precision of 5 intraoral scanners for scanning edentulous and dentate complete-arch mandibular casts: A comparative in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Organizationfor Standardization. Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results Part. 1: General Principles and Definitions; ISO 5725-1: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Latham, J.; Ludlow, M.; Mennito, A.; Kelly, A.; Evans, Z.; Renne, W. Effect of scan pattern on complete-arch scans with 4 digital scanners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ender, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Mehl, A. Accuracy of complete and partial-arch impressions of actual intraoral scanning systems in vitro. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2019, 22, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukazawa, S.; Odaira, C.; Kondo, H. Investigation of accuracy and reproducibility of abutment position by intraoral scanners. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2017, 61, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, N.; Xiong, Y.; Jiao, T. Accuracy of Intraoral Digital Impressions for Whole Upper Jaws, Including Full Dentitions and Palatal Soft Tissues. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddadi, Y.; Bahrami, G.; Isidor, F. Accuracy of crowns based on digital intraoral scanning compared to conventional impression-a split-mouth randomised clinical study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattadiyil, M.T.; Mursic, Z.; AlRumaih, H.; Goodacre, C.J. Intraoral scanning of hard and soft tissues for partial removable dental prosthesis fabrication. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keul, C.; Guth, J.F. Accuracy of full-arch digital impressions: An in vitro and in vivo comparison. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.J.; Park, J.M.; Shim, J.S. Accuracy of 9 intraoral scanners for complete-arch image acquisition: A qualitative and quantitative evaluation. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Park, J.M.; Kim, M.; Heo, S.J.; Myung, J.Y. Comparison of digital intraoral scanner reproducibility and image trueness considering repetitive experience. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osnes, C.A.; Wu, J.H.; Venezia, P.; Ferrari, M.; Keeling, A.J. Full arch precision of six intraoral scanners in vitro. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treesh, J.C.; Liacouras, P.C.; Taft, R.M.; Brooks, D.I.; Raiciulescu, S.; Ellert, D.O.; Grant, G.T.; Ye, L. Complete-arch accuracy of intraoral scanners. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Russo, L.; Caradonna, G.; Troiano, G.; Salamini, A.; Guida, L.; Ciavarella, D. Three-dimensional differences between intraoral scans and conventional impressions of edentulous jaws: A clinical study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Gallucci, G.O.; Chen, C.J.; Hanssen, S.; Naert, I.; Vandenberghe, B. Digital versus conventional implant impressions for edentulous patients: Accuracy outcomes. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayama, H.; Fueki, K.; Wadachi, J.; Wakabayashi, N. Trueness and precision of digital impressions obtained using an intraoral scanner with different head size in the partially edentulous mandible. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marghalani, A.; Weber, H.P.; Finkelman, M.; Kudara, Y.; El Rafie, K.; Papaspyridakos, P. Digital versus conventional implant impressions for partially edentulous arches: An evaluation of accuracy. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Amelya, A.; Shin, Y.; Shim, J.S. Accuracy of intraoral digital impressions using an artificial landmark. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawafleh, N.A.; Mack, F.; Evans, J.; Mackay, J.; Hatamleh, M.M. Accuracy and reliability of methods to measure marginal adaptation of crowns and FDPs: A literature review. J. Prosthodont. 2013, 22, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Squares | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable: RMS | |||||
| Scanner | 4408.63 | 1 | 4408.63 | 3.68 | 0.057 |
| Case | 94,020.02 | 4 | 23,505.00 | 19.61 *** | <0.001 |
| Scanner × Case | 1262.79 | 4 | 315.70 | 0.26 | 0.901 |
| Error | 167,795.36 | 140 | 1198.54 | ||
| Group | RMS (unit: µm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS3600 | i500 | p * | |||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
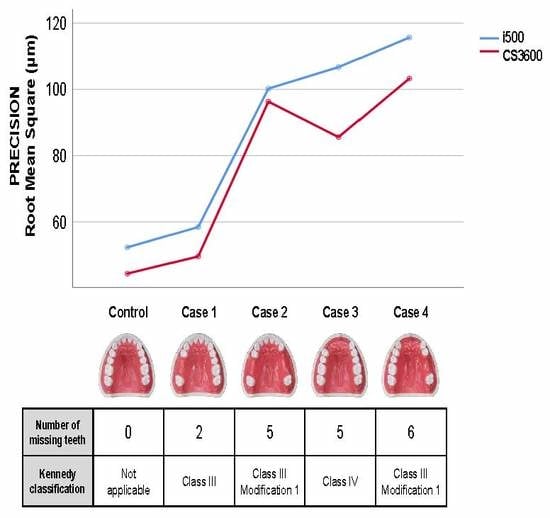
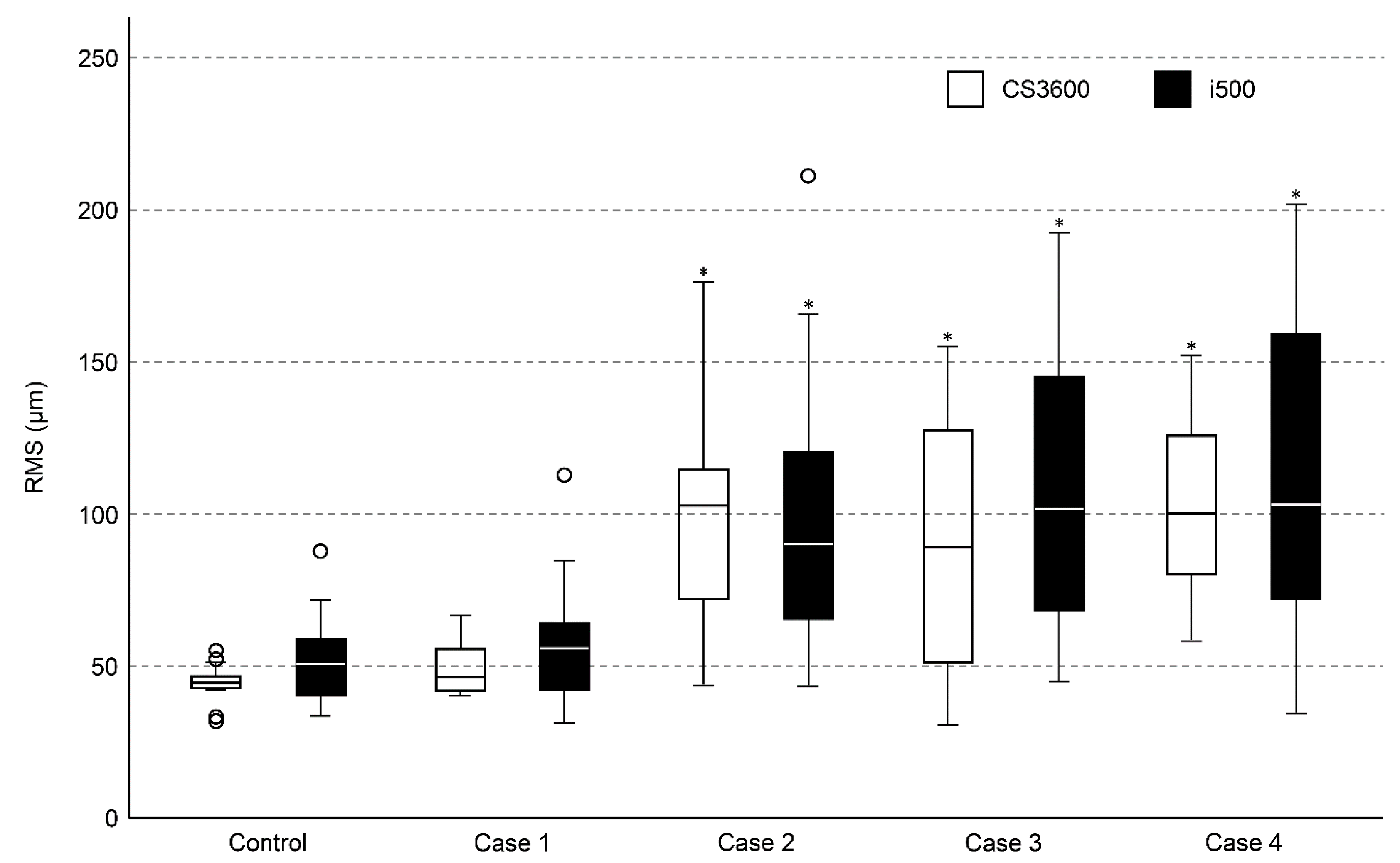
| Control | 44.37 a | 6.04 | 52.30 a | 14.99 | 0.53 |
| Case 1 | 49.57 a | 9.00 | 58.43 a | 21.45 | 0.48 |
| Case 2 | 96.31 b | 35.29 | 100.22 b | 44.74 | 0.76 |
| Case 3 | 85.59 b | 41.85 | 106.71 b | 48.92 | 0.10 |
| Case 4 | 103.28 b | 30.86 | 115.66 b | 53.28 | 0.33 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-H.; Yun, J.-H.; Han, J.-S.; Yeo, I.-S.L.; Yoon, H.-I. Repeatability of Intraoral Scanners for Complete Arch Scan of Partially Edentulous Dentitions: An In Vitro Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081187
Lee J-H, Yun J-H, Han J-S, Yeo I-SL, Yoon H-I. Repeatability of Intraoral Scanners for Complete Arch Scan of Partially Edentulous Dentitions: An In Vitro Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(8):1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081187
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jae-Hyun, Je-Hyeon Yun, Jung-Suk Han, In-Sung Luke Yeo, and Hyung-In Yoon. 2019. "Repeatability of Intraoral Scanners for Complete Arch Scan of Partially Edentulous Dentitions: An In Vitro Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 8: 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081187
APA StyleLee, J.-H., Yun, J.-H., Han, J.-S., Yeo, I.-S. L., & Yoon, H.-I. (2019). Repeatability of Intraoral Scanners for Complete Arch Scan of Partially Edentulous Dentitions: An In Vitro Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(8), 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081187