Approach to the Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patient
Abstract
:1. Background on ALL Work-Up and Follow-Up
2. Standard Chemotherapy Regimens
3. Management of CNS Involvement
4. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Ph-Positive ALL
5. Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for ALL
6. Immunotherapy for ALL
7. Measurable Residual Disease
8. Conclusions
9. Practice Points
10. Future Directions
- Clarify the clinical significance of the provisional entities: B-cell ALL with intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21, and BCR-ABL1-like B-cell ALL.
- Clarify the appropriate therapy strategies for adolescents and young adult ALL patients, which fall between the standard categories of pediatric or adult ALL.
- Expand the use of CAR-T cells and assess the use of CAR-T cells as upfront therapy.
- Establish the role of MRD monitoring beyond studies and clinical trials.
- Set up the best standard-of-care for adolescents and young adults with ALL.
- Set up the best standard-of-care for older adults with ALL.
- Define the best treatment options or Ph-positive ALL in the era of TKIs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunger, S.P.; Mullighan, C.G. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herold, T.; Baldus, C.D.; Gökbuget, N. Ph-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.; Carol, H.; Evans, K.; Richmond, J.; Houghton, P.J.; Smith, M.A.; Lock, R.B. A Review of New Agents Evaluated against Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia by the Pediatric Preclinical Testing Program. Leukemia 2016, 30, 2133–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortelazzo, S.; Ferreri, A.; Hoelzer, D.; Ponzoni, M. Lymphoblastic Lymphoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 113, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graubert, T.A. A Call to Action for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1064–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.G.; Li, Y.; Payne-Turner, D.; Harvey, R.C.; Yang, Y.-L.; Pei, D.; McCastlain, K.; Ding, L.; Lu, C.; Song, G.; et al. Targetable Kinase-Activating Lesions in Ph-like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terwilliger, T.; Abdul-Hay, M. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Comprehensive Review and 2017 Update. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranger, L.; Cuccuini, W.; Lefebvre, C.; Luquet, I.; Perot, C.; Radford, I.; Lafage-Pochitaloff, M. Cytogenetics in the Management of Children and Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): An Update by the Groupe Francophone de Cytogénétique Hématologique (GFCH). Ann. Biol. Clin. 2016, 74, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, M.J. How to Manage Asparaginase Hypersensitivity in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 2615–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, R.; Marks, D.I. Who Should Receive a Transplant for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia? Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2017, 12, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoh, A.E.J.; Lu, Y.; Chin, W.H.N.; Chiew, E.K.H.; Lim, E.H.; Li, Z.; Kham, S.K.Y.; Chan, Y.H.; Abdullah, W.A.; Lin, H.P.; et al. Intensifying Treatment of Childhood B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia With IKZF1 Deletion Reduces Relapse and Improves Overall Survival: Results of Malaysia-Singapore ALL 2010 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2726–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofran, Y.; Izraeli, S. BCR-ABL (Ph)-like Acute Leukemia-Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapeutic Options. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullighan, C.G. The Genomic Landscape of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children and Young Adults. Hematology 2014, 2014, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Kantarjian, H.; Jabbour, E.J. Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 1645–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wasserman, R.; Li, Y.S.; Shinton, S.A.; Carmack, C.E.; Manser, T.; Wiest, D.L.; Hayakawa, K.; Hardy, R.R. A Novel Mechanism for B Cell Repertoire Maturation Based on Response by B Cell Precursors to Pre-B Receptor Assembly. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobucci, I.; Mullighan, C.G. Genetic Basis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelzer, D.; Thiel, E.; Löffler, H.; Büchner, T.; Ganser, A.; Heil, G.; Koch, P.; Freund, M.; Diedrich, H.; Rühl, H. Prognostic Factors in a Multicenter Study for Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults. Blood 1988, 71, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; O’Brien, S.; Smith, T.L.; Cortes, J.; Giles, F.J.; Beran, M.; Pierce, S.; Huh, Y.; Andreeff, M.; Koller, C.; et al. Results of Treatment with Hyper-CVAD, a Dose-Intensive Regimen, in Adult Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafers, H.; Hamm, M.; Wagner, T. Gianturco Self-Expanding Metallic Stents. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 1992, 6, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstone, A.H.; Richards, S.M.; Lazarus, H.M.; Tallman, M.S.; Buck, G.; Fielding, A.K.; Burnett, A.K.; Chopra, R.; Wiernik, P.H.; Foroni, L.; et al. In Adults with Standard-Risk Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, the Greatest Benefit Is Achieved from a Matched Sibling Allogeneic Transplantation in First Complete Remission, and an Autologous Transplantation Is Less Effective than Conventional Consolidation/Maintenance Chemotherapy in All Patients: Final Results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993). Blood 2008, 111, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamps, W.A.; Bökkerink, J.P.; Hählen, K.; Hermans, J.; Riehm, H.; Gadner, H.; Schrappe, M.; Slater, R.; van den Berg-de Ruiter, E.; Smets, L.A.; et al. Intensive Treatment of Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia According to ALL-BFM-86 without Cranial Radiotherapy: Results of Dutch Childhood Leukemia Study Group Protocol ALL-7 (1988–1991). Blood 1999, 94, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volejnikova, J.; Jarosova, M.; Pospisilova, D.; Novak, Z.; Vrbkova, J.; Hajduch, M.; Mihal, V. Treatment and Prognosis of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia on Protocols ALL-BFM 90, 95 and ALL IC-BFM 2002: A Retrospective Single-Center Study from Olomouc, Czech Republic. Neoplasma 2016, 63, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toft, N.; Birgens, H.; Abrahamsson, J.; Griškevičius, L.; Hallböök, H.; Heyman, M.; Klausen, T.W.; Jónsson, Ó.G.; Palk, K.; Pruunsild, K.; et al. Results of NOPHO ALL2008 Treatment for Patients Aged 1–45 Years with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2018, 32, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muffly, L.; Lichtensztajn, D.; Shiraz, P.; Abrahão, R.; McNeer, J.; Stock, W.; Keegan, T.; Gomez, S.L. Adoption of Pediatric-Inspired Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Regimens by Adult Oncologists Treating Adolescents and Young Adults: A Population-Based Study. Cancer 2017, 123, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskarsson, T.; Söderhäll, S.; Arvidson, J.; Forestier, E.; Montgomery, S.; Bottai, M.; Lausen, B.; Carlsen, N.; Hellebostad, M.; Lähteenmäki, P.; et al. Relapsed Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the Nordic Countries: Prognostic Factors, Treatment and Outcome. Haematologica 2016, 101, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedtke, M.; Dunn, T.; Dinner, S.; Coutré, S.E.; Berube, C.; Gotlib, J.; Patel, S.; Medeiros, B. Salvage Therapy with Mitoxantrone, Etoposide and Cytarabine in Relapsed or Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanada, M.; Naoe, T. Imatinib Combined Chemotherapy for Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Major Challenges in Current Practice. Leuk. Lymphoma 2006, 47, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, S.; Marable, M.; Huang, R.S. The Promise of Pharmacogenomics in Reducing Toxicity During Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Maintenance Treatment. Genomics Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, R.Q.; Li, L.; Yuan, W.; Shord, S.S.; Nie, L.; Habtemariam, B.A.; Przepiorka, D.; Farrell, A.T.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Tocilizumab for Treatment of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell-Induced Severe or Life-Threatening Cytokine Release Syndrome. Oncologist 2018, 23, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, K.A. Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurotoxicity after CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified (CAR-) T Cell Therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 183, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Rivière, I.; Gonen, M.; Wang, X.; Sénéchal, B.; Curran, K.J.; Sauter, C.; Wang, Y.; Santomasso, B.; Mead, E.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of CD19 CAR Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, E.; Longo, D.L.; Urba, W.J. A Milestone for CAR T Cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2593–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelzer, D.; Bassan, R.; Dombret, H.; Fielding, A.; Ribera, J.M.; Buske, C.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia in Adult Patients: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, v69–v82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, C.-H.; Robison, L.L.; Look, A.T. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Lancet 2008, 371, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldoss, I.T.; Marcucci, G.; Pullarkat, V. Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults: Applying Lessons Learned in Children. Oncology 2016, 30, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, N.A.; Akasha, D.; Rowe, J.M. Advances in the Genetics of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adults and the Potential Clinical Implications. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2018, 11, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitz, M.J.; Wood, B.L.; Devidas, M.; Loh, M.L.; Raetz, E.A.; Salzer, W.L.; Nachman, J.B.; Carroll, A.J.; Heerema, N.A.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Minimal Residual Disease in High Risk B-ALL: A Report from Children’s Oncology Group Study AALL0232. Blood 2015, 126, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakrishnan, J.; Kumar, R.; Henrion, M.Y.R.; Moorman, A.V.; Rachakonda, P.S.; Hosen, I.; da Silva Filho, M.I.; Holroyd, A.; Dobbins, S.E.; Koehler, R.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Risk Loci for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia at 10q26.13 and 12q23.1. Leukemia 2017, 31, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.A. Managing CNS Disease in Adults with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Tomuleasa, C.; Florian, I.-A.; Shen, J.; Florian, I.-S.; Zdrenghea, M.; Dima, D. Advances in the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Blood Res. 2017, 52, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zając-Spychała, O.; Pawlak, M.A.; Karmelita-Katulska, K.; Pilarczyk, J.; Derwich, K.; Wachowiak, J. Long-Term Brain Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Cognitive Functioning in Children Treated for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with High-Dose Methotrexate Chemotherapy Alone or Combined with CNS Radiotherapy at Reduced Total Dose to 12 Gy. Neuroradiology 2017, 59, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, P.C.; Whitcomb, T.; Wolters, P.L.; Steinberg, S.M.; Balis, F.M.; Brouwers, P.; Hunsberger, S.; Feusner, J.; Sather, H.; Miser, J.; et al. Very High-Dose Methotrexate (33.6 g/m(2)) as Central Nervous System Preventive Therapy for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Results of National Cancer Institute/Children’s Cancer Group Trials CCG-191P, CCG-134P and CCG-144P. Leuk. Lymphoma 2006, 47, 2488–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökbuget, N.; Dombret, H.; Ribera, J.-M.; Fielding, A.K.; Advani, A.; Bassan, R.; Chia, V.; Doubek, M.; Giebel, S.; Hoelzer, D.; et al. International Reference Analysis of Outcomes in Adults with B-Precursor Ph-Negative Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulhern, R.K.; Fairclough, D.; Ochs, J. A Prospective Comparison of Neuropsychologic Performance of Children Surviving Leukemia Who Received 18-Gy, 24-Gy, or No Cranial Irradiation. J. Clin. Oncol. 1991, 9, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krull, K.R.; Hardy, K.K.; Kahalley, L.S.; Schuitema, I.; Kesler, S.R. Neurocognitive Outcomes and Interventions in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winick, N.; Devidas, M.; Chen, S.; Maloney, K.; Larsen, E.; Mattano, L.; Borowitz, M.J.; Carroll, A.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Heerema, N.A.; et al. Impact of Initial CSF Findings on Outcome Among Patients With National Cancer Institute Standard- and High-Risk B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münch, V.; Trentin, L.; Herzig, J.; Demir, S.; Seyfried, F.; Kraus, J.M.; Kestler, H.A.; Köhler, R.; Barth, T.F.E.; Te Kronnie, G.; et al. Central Nervous System Involvement in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Is Mediated by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Blood 2017, 130, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudichon, J.; Jakobczyk, H.; Debaize, L.; Cousin, E.; Galibert, M.-D.; Troadec, M.-B.; Gandemer, V. Mechanisms of Extramedullary Relapse in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Reconciling Biological Concepts and Clinical Issues. Blood Rev. 2019, 36, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, C.S.; DeFilipp, Z.; Inamoto, Y.; Johnston, L.; Nagler, A.; Savani, B.N.; Carpenter, P.A.; Perales, M.-A. ASBMT Statement on Routine Prophylaxis for Central Nervous System Recurrence of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, e86–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshein, E.; Kalathil, S.; Gharibo, M. Prolonged Survival of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Intrathecal Treatments for Isolated Central Nervous System Relapse. Case Rep. Hematol. 2018, 2018, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dara, A.; Mook, B.B.; Doorduijn, J.K.; van den Bent, M.J.; Dinmohamed, A.G.; Bromberg, J.E.C. Efficacy of Intrathecal Chemotherapy in Patients with Central Nervous System Involvement of Hematological Malignancies: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 139, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.K.; Aguilar, A.; Feusner, J. Unifying the Diagnosis of Isolated Central Nervous System Relapse in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Based on Minimal Residual Disease Testing. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 1026–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomuleasa, C.; Fuji, S.; Berce, C.; Onaciu, A.; Chira, S.; Petrushev, B.; Micu, W.-T.; Moisoiu, V.; Osan, C.; Constantinescu, C.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cells for the Treatment of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tat, T.; Li, H.; Constantinescu, C.-S.; Onaciu, A.; Chira, S.; Osan, C.; Pasca, S.; Petrushev, B.; Moisoiu, V.; Micu, W.-T.; et al. Genetically Enhanced T Lymphocytes and the Intensive Care Unit. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16557–16572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribera, J.-M. Efficacy and Safety of Bispecific T-Cell Engager Blinatumomab and the Potential to Improve Leukemia-Free Survival in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2017, 10, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, K.C.; Duncan, B.B.; Lee, D.W. CAR-T Cell Therapy for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Transforming the Treatment of Relapsed and Refractory Disease. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2018, 13, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eapen, M.; Zhang, M.-J.; Devidas, M.; Raetz, E.; Barredo, J.C.; Ritchey, A.K.; Godder, K.; Grupp, S.; Lewis, V.A.; Malloy, K.; et al. Outcomes after HLA-Matched Sibling Transplantation or Chemotherapy in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Second Remission after an Isolated Central Nervous System Relapse: A Collaborative Study of the Children’s Oncology Group and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. Leukemia 2008, 22, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, S.M. Ponatinib: A Review of Its Use in Adults with Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia or Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Drugs 2014, 74, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Kim, D.-W.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; le Coutre, P.; Paquette, R.; Chuah, C.; Nicolini, F.E.; Apperley, J.F.; Khoury, H.J.; Talpaz, M.; et al. A Phase 2 Trial of Ponatinib in Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Leukemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpaz, M.; Shah, N.P.; Kantarjian, H.; Donato, N.; Nicoll, J.; Paquette, R.; Cortes, J.; O’Brien, S.; Nicaise, C.; Bleickardt, E.; et al. Dasatinib in Imatinib-Resistant Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Leukemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H.; Ravandi, F.; Thomas, D.; Huang, X.; Faderl, S.; Pemmaraju, N.; Daver, N.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Sasaki, K.; et al. Combination of Hyper-CVAD with Ponatinib as First-Line Therapy for Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A Single-Centre, Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Jabbour, E.J.; Ravandi, F.; Short, N.J.; Thomas, D.A.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Daver, N.G.; Kadia, T.M.; Konopleva, M.Y.; Jain, N.; et al. Hyper-CVAD plus Ponatinib versus Hyper-CVAD plus Dasatinib as Frontline Therapy for Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Propensity Score Analysis. Cancer 2016, 122, 3650–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieduwilt, M.J. How Should We Treat Older Adults with Ph+ Adult ALL and What Novel Approaches Are Being Investigated? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2017, 30, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousselot, P.; Delannoy, A. Optimal Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia in the Elderly. Drugs Aging 2011, 28, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousselot, P.; Coudé, M.M.; Gokbuget, N.; Gambacorti Passerini, C.; Hayette, S.; Cayuela, J.-M.; Huguet, F.; Leguay, T.; Chevallier, P.; Salanoubat, C.; et al. Dasatinib and Low-Intensity Chemotherapy in Elderly Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive ALL. Blood 2016, 128, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, A.K.; Rowe, J.M.; Richards, S.M.; Buck, G.; Moorman, A.V.; Durrant, I.J.; Marks, D.I.; McMillan, A.K.; Litzow, M.R.; Lazarus, H.M.; et al. Prospective Outcome Data on 267 Unselected Adult Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Confirms Superiority of Allogeneic Transplantation over Chemotherapy in the Pre-Imatinib Era: Results from the International ALL Trial MRC UKALLXII/ECOG2993. Blood 2009, 113, 4489–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalandon, Y.; Thomas, X.; Hayette, S.; Cayuela, J.-M.; Abbal, C.; Huguet, F.; Raffoux, E.; Leguay, T.; Rousselot, P.; Lepretre, S.; et al. Randomized Study of Reduced-Intensity Chemotherapy Combined with Imatinib in Adults with Ph-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2015, 125, 3711–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottmann, O.G.; Wassmann, B.; Pfeifer, H.; Giagounidis, A.; Stelljes, M.; Dührsen, U.; Schmalzing, M.; Wunderle, L.; Binckebanck, A.; Hoelzer, D.; et al. Imatinib Compared with Chemotherapy as Front-Line Treatment of Elderly Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (Ph+ALL). Cancer 2007, 109, 2068–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foà, R.; Vitale, A.; Vignetti, M.; Meloni, G.; Guarini, A.; De Propris, M.S.; Elia, L.; Paoloni, F.; Fazi, P.; Cimino, G.; et al. Dasatinib as First-Line Treatment for Adult Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2011, 118, 6521–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignetti, M.; Fazi, P.; Cimino, G.; Martinelli, G.; Di Raimondo, F.; Ferrara, F.; Meloni, G.; Ambrosetti, A.; Quarta, G.; Pagano, L.; et al. Imatinib plus Steroids Induces Complete Remissions and Prolonged Survival in Elderly Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia without Additional Chemotherapy: Results of the Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche Dell’Adulto (GIMEMA) LAL0201-B Protocol. Blood 2007, 109, 3676–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, V.; Biondi, A. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in BCR-ABL Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2015, 100, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, A.; Locatelli, F.; Zecca, M.; Sanna, A.; Cimminiello, M.; Raimondi, R.; Gini, G.; Mordini, N.; Balduzzi, A.; Leoni, P.; et al. Imatinib for Refractory Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease with Fibrotic Features. Blood 2009, 114, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topp, M.S.; Kufer, P.; Gökbuget, N.; Goebeler, M.; Klinger, M.; Neumann, S.; Horst, H.-A.; Raff, T.; Viardot, A.; Schmid, M.; et al. Targeted Therapy with the T-Cell-Engaging Antibody Blinatumomab of Chemotherapy-Refractory Minimal Residual Disease in B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Results in High Response Rate and Prolonged Leukemia-Free Survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2493–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrier-De Wilde, S.; Rack, K.; Vannuffel, P.; Delannoy, A.; Hagemeijer, A. Philadelphia-Negative Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Developing in a CML Patient in Imatinib Mesylate-Induced Complete Cytogenetic Remission. Leukemia 2003, 17, 2046–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-S.; Metcalf, C.A.; Sundaramoorthi, R.; Wang, Y.; Zou, D.; Thomas, R.M.; Zhu, X.; Cai, L.; Wen, D.; Liu, S.; et al. Discovery of 3-[2-(Imidazo[1,2-b]Pyridazin-3-Yl)Ethynyl]-4-Methyl-N-{4-[(4-Methylpiperazin-1-Yl)Methyl]-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl}benzamide (AP24534), a Potent, Orally Active Pan-Inhibitor of Breakpoint Cluster Region-Abelson (BCR-ABL) Kinase Including the T315I Gatekeeper Mutant. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4701–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, M.; Pandor, A.; Hamilton, J.; Stevens, J.; Rowntree, C.; Martyn-St James, M.; Rawdin, A.; Wong, R. Ponatinib for Treating Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Single Technology Appraisal. Pharmacoeconomics 2018, 36, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visani, G.; Isidori, A. Resistant Chronic Myeloid Leukemia beyond Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitor Therapy: Which Role for Omacetaxine? Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomuleasa, C.; Dima, D.; Frinc, I.; Patiu, M.; Petrushev, B.; Cucuianu, A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. BCR-ABL1 T315I Mutation, a Negative Prognostic Factor for the Terminal Phase of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Treated with First- and Second-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors, Might Be an Indicator of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant as the Treatment of Choice. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 546–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, F.E.; Basak, G.W.; Kim, D.-W.; Olavarria, E.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Apperley, J.F.; Hughes, T.; Niederwieser, D.; Mauro, M.J.; Chuah, C.; et al. Overall Survival with Ponatinib versus Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Leukemias with the T315I Mutation. Cancer 2017, 123, 2875–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, N.J.; Kantarjian, H.; Pui, C.-H.; Goldstone, A.; Jabbour, E. SOHO State of the Art Update and Next Questions: Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018, 18, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.E.; Kim, D.-W.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; le Coutre, P.D.; Paquette, R.; Chuah, C.; Nicolini, F.E.; Apperley, J.F.; Khoury, H.J.; Talpaz, M.; et al. Ponatinib Efficacy and Safety in Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Leukemia: Final 5-Year Results of the Phase 2 PACE Trial. Blood 2018, 132, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fakih, R.; Ahmed, S.; Alfraih, F.; Hanbali, A. Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Adult Patients. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2017, 10, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Fakih, R.; Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; Aljurf, M. Refining the Role of Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia as Novel Therapies Emerge. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökbuget, N. Treatment of Older Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Progr. 2016, 2016, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Stein, A.S.; Bargou, R.C.; Grande Garcia, C.; Larson, R.A.; Stelljes, M.; Gökbuget, N.; Zugmaier, G.; Benjamin, J.E.; Zhang, A.; et al. Blinatumomab Treatment of Older Adults with Relapsed/Refractory B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Results from 2 Phase 2 Studies. Cancer 2016, 122, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.T.; Hayes-Lattin, B. Reduced Intensity Conditioning Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia; Current Evidence, and Improving Outcomes Going Forward. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2018, 13, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akahoshi, Y.; Mizuta, S.; Shimizu, H.; Uchida, N.; Fukuda, T.; Kanamori, H.; Onizuka, M.; Ozawa, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Ohta, S.; et al. Additional Cytogenetic Abnormalities with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia on Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Era. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejanyan, N.; Zhang, M.-J.; Wang, H.-L.; Lazaryan, A.; de Lima, M.; Marks, D.I.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Bachanova, V.; Rowe, J.; Tallman, M.; et al. Pretransplant Consolidation Is Not Beneficial for Adults with ALL Undergoing Myeloablative Allogeneic Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortuza, F.Y.; Papaioannou, M.; Moreira, I.M.; Coyle, L.A.; Gameiro, P.; Gandini, D.; Prentice, H.G.; Goldstone, A.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Foroni, L. Minimal Residual Disease Tests Provide an Independent Predictor of Clinical Outcome in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüggemann, M.; Raff, T.; Flohr, T.; Gökbuget, N.; Nakao, M.; Droese, J.; Lüschen, S.; Pott, C.; Ritgen, M.; Scheuring, U.; et al. Clinical Significance of Minimal Residual Disease Quantification in Adult Patients with Standard-Risk Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2006, 107, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassan, R.; Spinelli, O.; Oldani, E.; Intermesoli, T.; Tosi, M.; Peruta, B.; Rossi, G.; Borlenghi, E.; Pogliani, E.M.; Terruzzi, E.; et al. Improved Risk Classification for Risk-Specific Therapy Based on the Molecular Study of Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). Blood 2009, 113, 4153–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, M.R.; Logan, B.R.; Gandham, S.; Bolwell, B.J.; Cahn, J.-Y.; Lazarus, H.M.; Litzow, M.R.; Marks, D.I.; Wiernik, P.H.; McCarthy, P.L.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Adults with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia after Autologous or Unrelated Donor Bone Marrow Transplantation: A Comparative Analysis by the National Marrow Donor Program and Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008, 41, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallböök, H.; Hägglund, H.; Stockelberg, D.; Nilsson, P.-G.; Karlsson, K.; Björkholm, M.; Linderholm, M.; Wahlin, A.; Linder, O.; Smedmyr, B.; et al. Autologous and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Adult ALL: The Swedish Adult ALL Group Experience. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005, 35, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunault, M.; Harousseau, J.-L.; Delain, M.; Truchan-Graczyk, M.; Cahn, J.-Y.; Witz, F.; Lamy, T.; Pignon, B.; Jouet, J.-P.; Garidi, R.; et al. Better Outcome of Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia after Early Genoidentical Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) than after Late High-Dose Therapy and Autologous BMT: A GOELAMS Trial. Blood 2004, 104, 3028–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, D.I.; Aversa, F.; Lazarus, H.M. Alternative Donor Transplants for Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A Comparison of the Three Major Options. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006, 38, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, J.J.; van der Holt, B.; Verhoef, G.E.G.; van’t Veer, M.B.; van Oers, M.H.J.; Schouten, H.C.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Sonneveld, P.; Maertens, J.; van Marwijk Kooy, M.; et al. Myeloablative Allogeneic versus Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Adult Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in First Remission: A Prospective Sibling Donor versus No-Donor Comparison. Blood 2009, 113, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiehl, M.G.; Kraut, L.; Schwerdtfeger, R.; Hertenstein, B.; Remberger, M.; Kroeger, N.; Stelljes, M.; Bornhaeuser, M.; Martin, H.; Scheid, C.; et al. Outcome of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in Adult Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: No Difference in Related Compared with Unrelated Transplant in First Complete Remission. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2816–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlke, J.; Kröger, N.; Zabelina, T.; Ayuk, F.; Fehse, N.; Wolschke, C.; Waschke, O.; Schieder, H.; Renges, H.; Krüger, W.; et al. Comparable Results in Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia after Related and Unrelated Stem Cell Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006, 37, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiwaki, S.; Miyamura, K.; Ohashi, K.; Kurokawa, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Fukuda, T.; Ikegame, K.; Takahashi, S.; Mori, T.; Imai, K.; et al. Impact of a Donor Source on Adult Philadelphia Chromosome-Negative Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Retrospective Analysis from the Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Working Group of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friberg, G.; Reese, D. Blinatumomab (Blincyto): Lessons Learned from the Bispecific t-Cell Engager (BiTE) in Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL). Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.C.; Weiss, S.L.; Maude, S.L.; Barrett, D.M.; Lacey, S.F.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Shaw, P.; Berg, R.A.; June, C.H.; Porter, D.L.; et al. Cytokine Release Syndrome After Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, e124–e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy-Simon, T.; Tatar, A.-S.; Craciun, A.-M.; Vulpoi, A.; Jurj, M.-A.; Florea, A.; Tomuleasa, C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Astilean, S.; Boca, S. Antibody Conjugated, Raman Tagged Hollow Gold-Silver Nanospheres for Specific Targeting and Multimodal Dark-Field/SERS/Two Photon-FLIM Imaging of CD19(+) B Lymphoblasts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21155–21168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatar, A.-S.; Nagy-Simon, T.; Tomuleasa, C.; Boca, S.; Astilean, S. Nanomedicine Approaches in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Control. Release 2016, 238, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Oriol, A.; Nahi, H.; San-Miguel, J.; Bahlis, N.J.; Usmani, S.Z.; Rabin, N.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Komarnicki, M.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Daratumumab, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palumbo, A.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Weisel, K.; Nooka, A.K.; Masszi, T.; Beksac, M.; Spicka, I.; Hungria, V.; Munder, M.; Mateos, M. V; et al. Daratumumab, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, D. Haematological Cancer: Improvements with Daratumumab. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bride, K.L.; Vincent, T.L.; Im, S.-Y.; Aplenc, R.; Barrett, D.M.; Carroll, W.L.; Carson, R.; Dai, Y.; Devidas, M.; Dunsmore, K.P.; et al. Preclinical Efficacy of Daratumumab in T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2018, 131, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganzel, C.; Kharit, M.; Duksin, C.; Rowe, J.M. Daratumumab for Relapsed/Refractory Philadelphia-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2018, 103, e489–e490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonda, A.; Punatar, S.; Gokarn, A.; Mohite, A.; Shanmugam, K.; Nayak, L.; Bopanna, M.; Cheriyalinkal Parambil, B.; Khattry, N. Daratumumab at the Frontiers of Post-Transplant Refractory T-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia-a Worthwhile Strategy? Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018, 53, 1487–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.A.; O’Brien, S.; Faderl, S.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Ferrajoli, A.; Wierda, W.; Ravandi, F.; Verstovsek, S.; Jorgensen, J.L.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with a Modified Hyper-CVAD and Rituximab Regimen Improves Outcome in de Novo Philadelphia Chromosome-Negative Precursor B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3880–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maury, S.; Chevret, S.; Thomas, X.; Heim, D.; Leguay, T.; Huguet, F.; Chevallier, P.; Hunault, M.; Boissel, N.; Escoffre-Barbe, M.; et al. Rituximab in B-Lineage Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.; Thomas, D.; Jorgensen, J.; Jabbour, E.; Kebriaei, P.; Rytting, M.; York, S.; Ravandi, F.; Kwari, M.; Faderl, S.; et al. Inotuzumab Ozogamicin, an Anti-CD22-Calecheamicin Conjugate, for Refractory and Relapsed Acute Lymphocytic Leukaemia: A Phase 2 Study. Lancet. Oncol. 2012, 13, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Stelljes, M.; Martinelli, G.; Liedtke, M.; Stock, W.; Gökbuget, N.; O’Brien, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, T.; et al. Inotuzumab Ozogamicin versus Standard Therapy for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y. Novel Immunotherapies for Adult Patients with B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennink, J.R.; Doherty, P.C. Different Rules Govern Help for Cytotoxic T Cells and B Cells. Nature 1978, 276, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrelha, J.; Meng, Y.; Kettyle, L.M.; Luis, T.C.; Norfo, R.; Alcolea, V.; Boukarabila, H.; Grasso, F.; Gambardella, A.; Grover, A.; et al. Hierarchically Related Lineage-Restricted Fates of Multipotent Haematopoietic Stem Cells. Nature 2018, 554, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkernagel, R.M. On ‘Reactivity’ versus ‘Tolerance’. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kündig, T.M.; Bachmann, M.F.; Ohashi, P.S.; Pircher, H.; Hengartner, H.; Zinkernagel, R.M. On T Cell Memory: Arguments for Antigen Dependence. Immunol. Rev. 1996, 150, 63–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Han, W. Chimeric Antigen Receptors Modified T-Cells for Cancer Therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tvedt, T.H.A.; Ersvaer, E.; Tveita, A.A.; Bruserud, Ø. Interleukin-6 in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: Its Possible Importance for Immunoregulation and As a Therapeutic Target. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Ding, L.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Huang, H. Advances of CD19-Directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells in Refractory/Relapsed Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luskin, M.R.; DeAngelo, D.J. Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Clinical Practice. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2017, 12, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haso, W.; Lee, D.W.; Shah, N.N.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Yuan, C.M.; Pastan, I.H.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Morgan, R.A.; FitzGerald, D.J.; Barrett, D.M.; et al. Anti-CD22-Chimeric Antigen Receptors Targeting B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran, K.J.; Pegram, H.J.; Brentjens, R.J. Chimeric Antigen Receptors for T Cell Immunotherapy: Current Understanding and Future Directions. J. Gene Med. 2012, 14, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledford, H. Engineered Cell Therapy for Cancer Gets Thumbs up from FDA Advisers. Nature 2017, 547, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Sim, S.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Singh, R.; Hwang, S.; Kim, Y.I.; Park, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.G.; Oh, H.S.; et al. Desensitized Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Selectively Recognize Target Cells with Enhanced Antigen Expression. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Maatman, T.; Hari, P.; Johnson, B. Multi Targeted CAR-T Cell Therapies for B-Cell Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oak, J.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Sahaf, B.; Natkunam, Y.; Long, S.R.; Hossain, N.; Mackall, C.L.; Kong, K.A.; Miklos, D.B. Target Antigen Downregulation and Other Mechanisms of Failure after Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (CAR19) Therapy. Blood 2018, 132, 4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoiber, S.; Cadilha, B.L.; Benmebarek, M.-R.; Lesch, S.; Endres, S.; Kobold, S. Limitations in the Design of Chimeric Antigen Receptors for Cancer Therapy. Cells 2019, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majzner, R.G.; Mackall, C.L. Tumor Antigen Escape from CAR T-Cell Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, J.W.; Martens, A.C.; Hagenbeek, A. Detection of Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Leukemia by Flow Cytometry. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1986, 468, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drach, J.; Drach, D.; Glassl, H.; Gattringer, C.; Huber, H. Flow Cytometric Determination of Atypical Antigen Expression in Acute Leukemia for the Study of Minimal Residual Disease. Cytometry 1992, 13, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dongen, J.J.; Seriu, T.; Panzer-Grümayer, E.R.; Biondi, A.; Pongers-Willemse, M.J.; Corral, L.; Stolz, F.; Schrappe, M.; Masera, G.; Kamps, W.A.; et al. Prognostic Value of Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia in Childhood. Lancet 1998, 352, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavé, H.; van der Werff ten Bosch, J.; Suciu, S.; Guidal, C.; Waterkeyn, C.; Otten, J.; Bakkus, M.; Thielemans, K.; Grandchamp, B.; Vilmer, E.; et al. Clinical Significance of Minimal Residual Disease in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Childhood Leukemia Cooperative Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porwit-MacDonald, A.; Björklund, E.; Lucio, P.; van Lochem, E.G.; Mazur, J.; Parreira, A.; van den Beemd, M.W.; van Wering, E.R.; Baars, E.; Gaipa, G.; et al. BIOMED-1 Concerted Action Report: Flow Cytometric Characterization of CD7+ Cell Subsets in Normal Bone Marrow as a Basis for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL). Leukemia 2000, 14, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucio, P.; Gaipa, G.; van Lochem, E.G.; van Wering, E.R.; Porwit-MacDonald, A.; Faria, T.; Bjorklund, E.; Biondi, A.; van den Beemd, M.W.; Baars, E.; et al. BIOMED-I Concerted Action Report: Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping of Precursor B-ALL with Standardized Triple-Stainings. BIOMED-1 Concerted Action Investigation of Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Leukemia: International Standardization and Clinical Evaluation. Leukemia 2001, 15, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Krampera, M.; Perbellini, O.; Vincenzi, C.; Zampieri, F.; Pasini, A.; Scupoli, M.T.; Guarini, A.; De Propris, M.S.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Campana, D.; et al. Methodological Approach to Minimal Residual Disease Detection by Flow Cytometry in Adult B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2006, 91, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, S.D.; Al-Allawi, N.A.S.; Al Doski, A.A.S. Immunophenotypic Aberrancies in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia from 282 Iraqi Patients. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2017, 39, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lochem, E.G.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Wind, H.K.; te Marvelde, J.G.; Westerdaal, N.A.C.; van Dongen, J.J.M. Immunophenotypic Differentiation Patterns of Normal Hematopoiesis in Human Bone Marrow: Reference Patterns for Age-Related Changes and Disease-Induced Shifts. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2004, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, L.; López, O.; Martino, R.; Brunet, S.; Bellido, M.; Rubiol, E.; Sierra, J.; Nomdedéu, J.F. Combined Use of Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction and Flow Cytometry to Study Minimal Residual Disease in Philadelphia Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2000, 85, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Huang, C.; Tang, G.; Cheng, H.; Liu, M.; Ding, J.; Gong, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; et al. Impact of Clinical Utility of MRD Assessment with Different Techniques on Survival in Acute B Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, J.; Feng, J.; Dickstein, J.I.; Le Beau, M.M.; Rubin, C.M.; Larson, R.A.; Rowley, J.D.; Vardiman, J.W. Lineage Involvement by BCR/ABL in Ph+ Lymphoblastic Leukemias: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Presenting in Lymphoid Blast vs. Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 1996, 10, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ravandi, F.; Jorgensen, J.L.; Thomas, D.A.; O’Brien, S.; Garris, R.; Faderl, S.; Huang, X.; Wen, S.; Burger, J.A.; Ferrajoli, A.; et al. Detection of MRD May Predict the Outcome of Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive ALL Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors plus Chemotherapy. Blood 2013, 122, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theunissen, P.; Mejstrikova, E.; Sedek, L.; van der Sluijs-Gelling, A.J.; Gaipa, G.; Bartels, M.; Sobral da Costa, E.; Kotrová, M.; Novakova, M.; Sonneveld, E.; et al. Standardized Flow Cytometry for Highly Sensitive MRD Measurements in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherian, S.; Miller, V.; McCullouch, V.; Dougherty, K.; Fromm, J.R.; Wood, B.L. A Novel Flow Cytometric Assay for Detection of Residual Disease in Patients with B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma Post Anti-CD19 Therapy. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susman, S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Petrushev, B.; Pirlog, R.; Florian, I.-S.; Mihu, C.-M.; Berce, C.; Craciun, L.; Grewal, R.; Tomuleasa, C. The Role of the Pathology Department in the Preanalytical Phase of Molecular Analyses. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.; Tomuleasa, C.; Bojan, A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Boca, S.; Astilean, S. Design of FLT3 Inhibitor - Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates as Potential Therapeutic Agents for the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarasan, S.; Simon, T.; Boca, S.; Tomuleasa, C.; Astilean, S. Gelatin-Coated Gold Nanoparticles as Carriers of FLT3 Inhibitors for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treatment. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 87, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrushev, B.; Boca, S.; Simon, T.; Berce, C.; Frinc, I.; Dima, D.; Selicean, S.; Gafencu, G.-A.; Tanase, A.; Zdrenghea, M.; et al. Gold Nanoparticles Enhance the Effect of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 641–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafencu, G.A.; Tomuleasa, C.I.; Ghiaur, G. PARP Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Therapy: How a Synthetic Lethality Approach Can Be a Valid Therapeutic Alternative. Med. Hypotheses 2017, 104, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dima, D.; Oprita, L.; Rosu, A.-M.; Trifa, A.; Selicean, C.; Moisoiu, V.; Frinc, I.; Zdrenghea, M.; Tomuleasa, C. Adult Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia: Rare Association with Cytopenias of Undetermined Significance and P210 and P190 BCR-ABL Transcripts. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 5047–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.Y.; Ferracin, M.; Pileczki, V.; Chen, B.; Redis, R.; Fabris, L.; Zhang, X.; Ivan, C.; Shimizu, M.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; et al. Cancer-Associated Rs6983267 SNP and Its Accompanying Long Noncoding RNA CCAT2 Induce Myeloid Malignancies via Unique SNP-Specific RNA Mutations. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaver, A.C.; Greig, B.W.; Mosse, C.A.; Seegmiller, A.C. B-ALL Minimal Residual Disease Flow Cytometry: An Application of a Novel Method for Optimization of a Single-Tube Model. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 143, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behjati, S.; Tarpey, P.S. What Is next Generation Sequencing? Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. Ed. 2013, 98, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop, L.-A.; Puscas, E.; Pileczki, V.; Cojocneanu-Petric, R.; Braicu, C.; Achimas-Cadariu, P.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Quality Control of Ion Torrent Sequencing Library. Cancer Biomark. 2014, 14, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahassi, E.M.; Stambrook, P.J. Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies: Breaking the Sound Barrier of Human Genetics. Mutagenesis 2014, 29, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitz, M.J.; Devidas, M.; Hunger, S.P.; Bowman, W.P.; Carroll, A.J.; Carroll, W.L.; Linda, S.; Martin, P.L.; Pullen, D.J.; Viswanatha, D.; et al. Clinical Significance of Minimal Residual Disease in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Its Relationship to Other Prognostic Factors: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. Blood 2008, 111, 5477–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conter, V.; Bartram, C.R.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Schrauder, A.; Panzer-Grümayer, R.; Möricke, A.; Aricò, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Mann, G.; De Rossi, G.; et al. Molecular Response to Treatment Redefines All Prognostic Factors in Children and Adolescents with B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Results in 3184 Patients of the AIEOP-BFM ALL 2000 Study. Blood 2010, 115, 3206–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, A.C.; Zhang, B.; Narasimhan, B.; Carlton, V.; Zheng, J.; Moorhead, M.; Krampf, M.R.; Jones, C.D.; Waqar, A.N.; Faham, M.; et al. Minimal Residual Disease Quantification Using Consensus Primers and High-Throughput IGH Sequencing Predicts Post-Transplant Relapse in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faham, M.; Zheng, J.; Moorhead, M.; Carlton, V.E.H.; Stow, P.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Pui, C.-H.; Campana, D. Deep-Sequencing Approach for Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 5173–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladetto, M.; Brüggemann, M.; Monitillo, L.; Ferrero, S.; Pepin, F.; Drandi, D.; Barbero, D.; Palumbo, A.; Passera, R.; Boccadoro, M.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing and Real-Time Quantitative PCR for Minimal Residual Disease Detection in B-Cell Disorders. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Emerson, R.O.; Sherwood, A.; Loh, M.L.; Angiolillo, A.; Howie, B.; Vogt, J.; Rieder, M.; Kirsch, I.; Carlson, C.; et al. Detection of Minimal Residual Disease in B Lymphoblastic Leukemia by High-Throughput Sequencing of IGH. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4540–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotrova, M.; Muzikova, K.; Mejstrikova, E.; Novakova, M.; Bakardjieva-Mihaylova, V.; Fiser, K.; Stuchly, J.; Giraud, M.; Salson, M.; Pott, C.; et al. The Predictive Strength of Next-Generation Sequencing MRD Detection for Relapse Compared with Current Methods in Childhood ALL. Blood 2015, 126, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulsipher, M.A.; Carlson, C.; Langholz, B.; Wall, D.A.; Schultz, K.R.; Bunin, N.; Kirsch, I.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Borowitz, M.; Desmarais, C.; et al. IgH-V(D)J NGS-MRD Measurement Pre- and Early Post-Allotransplant Defines Very Low- and Very High-Risk ALL Patients. Blood 2015, 125, 3501–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawad, C.; Pepin, F.; Carlton, V.E.H.; Klinger, M.; Logan, A.C.; Miklos, D.B.; Faham, M.; Dahl, G.; Lacayo, N. Massive Evolution of the Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Locus in Children with B Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 4407–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabovsky, S.; Folber, F.; Horacek, J.M.; Stehlikova, O.; Jelinkova, H.; Salek, C.; Doubek, M.; Czech Leukemia Study Group for Life. Comparison of Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction and Eight-Color Flow Cytometry in Assessment of Minimal Residual Disease in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma. Myeloma Leuk. 2018, 18, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keegan, A.; Charest, K.; Schmidt, R.; Briggs, D.; Deangelo, D.J.; Li, B.; Morgan, E.A.; Pozdnyakova, O. Flow Cytometric Minimal Residual Disease Assessment of Peripheral Blood in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Patients Has Potential for Early Detection of Relapsed Extramedullary Disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denys, B.; van der Sluijs-Gelling, A.J.; Homburg, C.; van der Schoot, C.E.; de Haas, V.; Philippé, J.; Pieters, R.; van Dongen, J.J.M.; van der Velden, V.H.J. Improved Flow Cytometric Detection of Minimal Residual Disease in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2013, 27, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökbuget, N.; Dombret, H.; Bonifacio, M.; Reichle, A.; Graux, C.; Faul, C.; Diedrich, H.; Topp, M.S.; Brüggemann, M.; Horst, H.-A.; et al. Blinatumomab for Minimal Residual Disease in Adults with B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2018, 131, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomuleasa, C.; Selicean, C.; Cismas, S.; Jurj, A.; Marian, M.; Dima, D.; Pasca, S.; Petrushev, B.; Moisoiu, V.; Micu, W.-T.; et al. Minimal Residual Disease in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Consensus Paper That Presents the Clinical Impact of the Presently Available Laboratory Approaches. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurj, A.; Pop, L.; Petrushev, B.; Pasca, S.; Dima, D.; Frinc, I.; Deak, D.; Desmirean, M.; Trifa, A.; Fetica, B.; et al. Exosome-Carried MicroRNA-Based Signature as a Cellular Trigger for the Evolution of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia into Richter Syndrome. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciufu, C.; Arama, V.; Bumbea, H.; Dobrea, C.; Ion, I.; Vladareanu, A.M. Correlations of hematological parameters with bone marrow findings in chroniclymphoproliferative disorders associated with hepatitis viruses. J. Med. Life 2013, 6, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chira, S.; Gulei, D.; Hajitou, A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Restoring the p53 ‘Guardian’ Phenotype in p53-Deficient Tumor Cells with CRISPR/Cas9. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
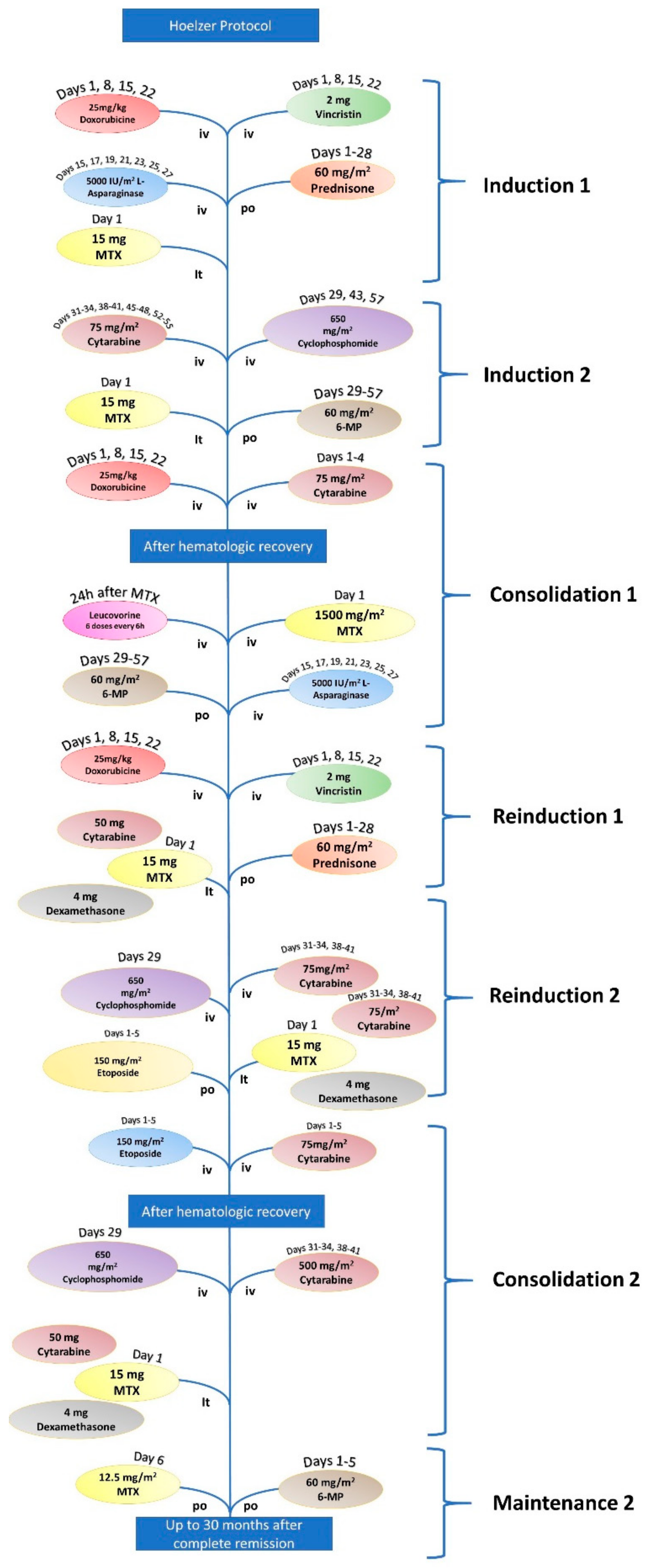

| Hoeltzer Protocol for ALL | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction 1 | Vincristine | 2 mg | Days 1, 18,15, and 22 |
| Doxorubicin | 25 mg/m2 | Days 1, 8, 15, and 22 | |
| L-Asparaginase | 5.000 UI/m2 | Days 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, and 27 | |
| Prednisone | 60 mg/m2 | Days 1–28 | |
| Methotrexate (it) | 15 mg | Day 1 | |
| Induction 2 | Cyclophosphamide | 650 mg/m2 | Days 29, 43, and 57 |
| Cytarabine | 75 mg/m2 | Days 31–34, 38–41, 45–48, and 52–55 | |
| 6-mercaptopurine | 60 mg/m2 | Days 29–57 | |
| Methotrexate (it) | 15 mg | Days 31, 38, 45, and 52 | |
| Consolidation 1 | Cytarabine | 1000 mg/m2 | Days 1–4 |
| Doxorubicin | 30 mg/m2 | Days 3–5 | |
| Methotrexate + Leucovorin | 1500 mg/m2 | ||
| L-Asparaginase | 10.000 UI/m2 | Days 2 and 16 | |
| 6-mercaptopurine | 25 mg/m2 | Days 1–5 and 15–19 | |
| Reinduction 1 | Vincristine | 2 mg/m2 | Days 1, 8, 15, and 22 |
| Doxorubicin | 2 mg/m2 | Days 1, 8, 15, and 22 | |
| Prednisone | 60 mg/m2 | Days 1–28 | |
| Methotrexate (it) | 15 mg | Day 1 | |
| Cytarabine (it) | 50 mg | Day 1 | |
| Dexamethasone (it) | 4 mg | Day 1 | |
| Reinduction 2 | Cyclophosphamide | 650 mg/m2 | Day 29 |
| Cytarabine | 75 mg/m2 | Days 31–34 and 38–41 | |
| 6-thiguanine | 60 mg/m2 | Days 29–57 | |
| Methotrexate (it) | 15 mg | Day 1 | |
| Cytarabine (it) | 50 mg | Day 1 | |
| Dexamethasone (it) | 4 mg | Day 1 | |
| Consolidation 2 | Etoposide | 100 mg/m2 | Days 1–5 |
| Cytarabine | 150 mg/m2 | Days 1–5 | |
| Maintenance | 6-mercaptopurine | 60 mg/m2 | Days 1–5 |
| Methotrexate | 12.5 mg/m2 | Days 1–5 | |
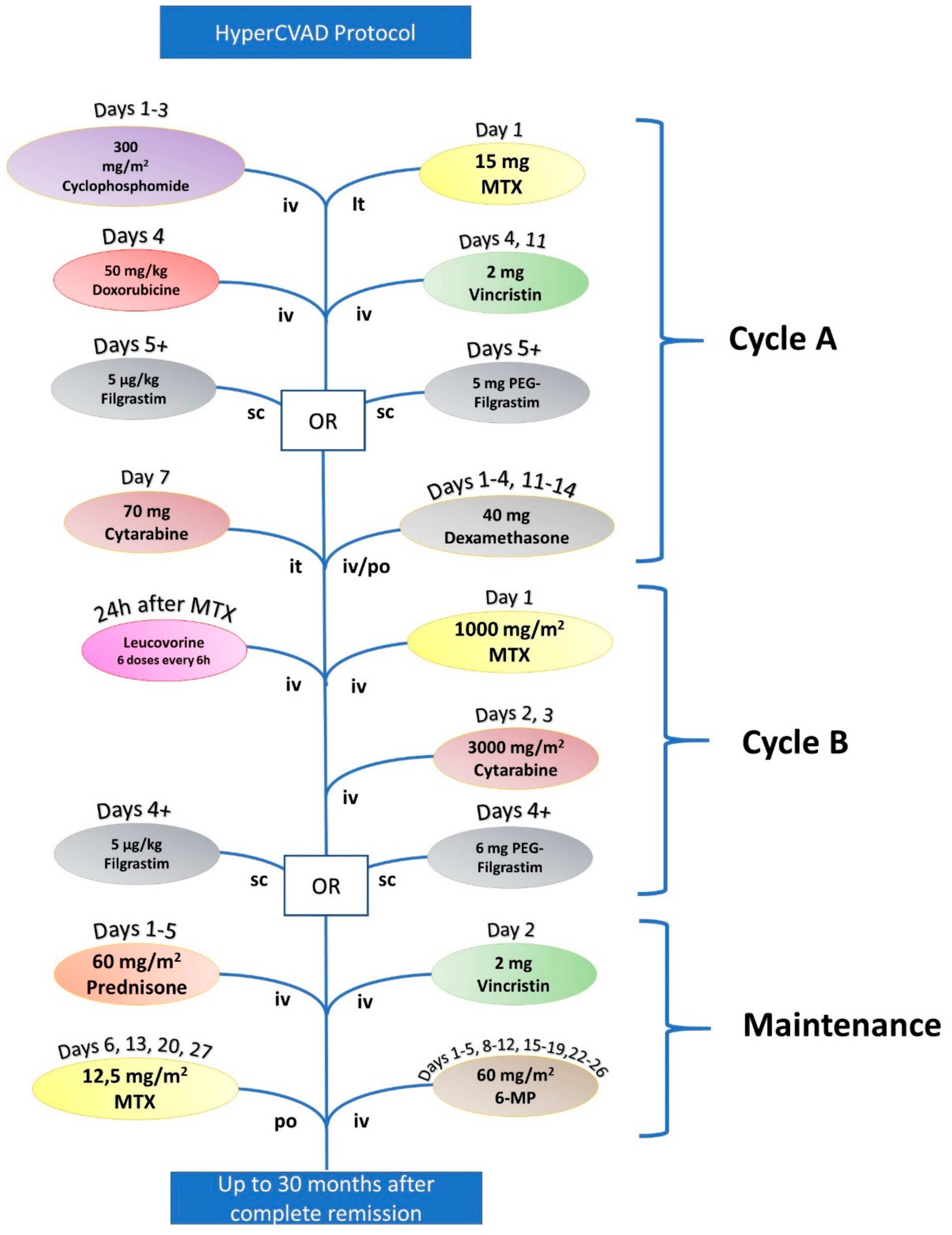
| HyperCVAD | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle A | Cyclophosphamide | 300 mg/m2 | Days 1, 2, and 3 |
| Doxorubicin | 50 mg/m2 | Day 4 | |
| Vincristine | 2 mg | Days 4 and 11 | |
| Filgrastim or pegylated Filgrastim | 5 μg/kg (Filgrastim) or 6 mg (PEG Filgrastim) | Starting Day 5 | |
| Dexamethasone | 40 mg | Days 1–4 and 11–14 | |
| Cytarabine (it) | 70 mg | Day 7 | |
| Methotrexate (it) | 15 mg | Day 2 | |
| Cycle B | Methotrexate (+Leucovorin) | 1000 mg/m2 | Day 1 |
| Cytarabine | 6000 mg/m2 | Days 2 and 3 | |
| Filgrastim or PEG Filgrastim | 5 μg/kg (Filgrastim) or 6 mg (PEG Filgrastim) | Starting Day 4 (Filgrastim) or at Day 4 (PEG Filgrastim) | |
| Maintenance | Vincristine | 2 mg | Day 2 |
| Prednisone | 60 mg/m2 | Days 1–5 | |
| 6-mercaptopurine | 60 mg/m2 | Days 1–5, 8–12, 15–19, and 22–26 | |
| Methotrexate (it) | 12.5 mg/m2 | Days 6, 13, 20, and 27 | |
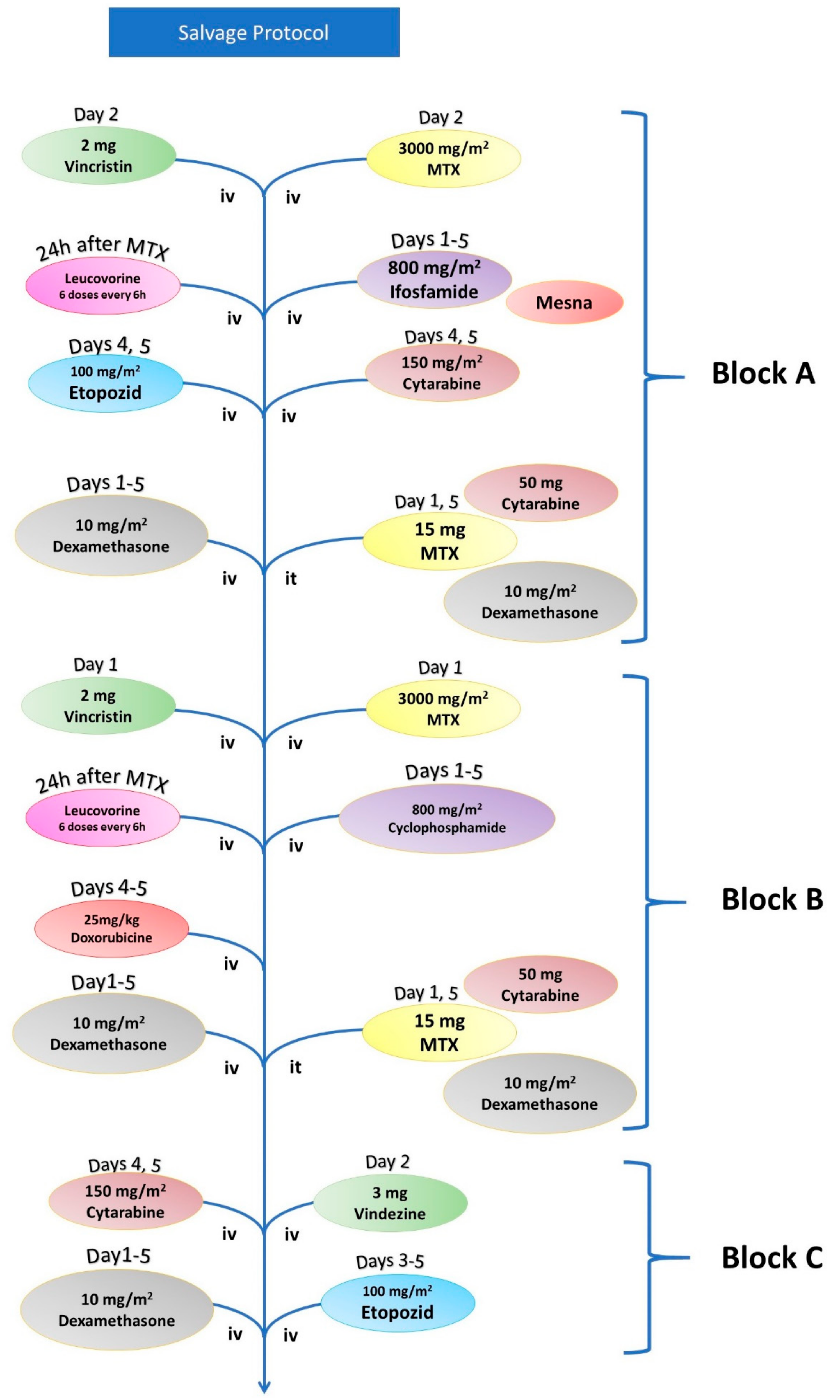
| Salvage Chemotherapy | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Block A | Vincristine | 2 mg | Day 1 |
| Methotrexate (+Leucovorin) | 3000 mg/m2 | Day 1 | |
| Ifosfamide (+Mesna) | 800 mg/m2 | Days 1–5 | |
| Etoposide | 100 mg/m2 | Days 4 and 5 | |
| Cytarabine | 150 mg/m | Days 4 and 5 | |
| Dexamethasone | 10 mg/m2 | Days 1–5 | |
| Methotrexate (it) | 15 mg | Day 1 and 5 | |
| Cytarabine (it) | 50 mg | Day 1 and 5 | |
| Dexamethasone (it) | 8 mg | Day 1 and 5 | |
| Block B | Vincristine | 2 mg | Day 1 |
| Methotrexate (+Leucovorin) | 3000 mg/m2 | Day 1 | |
| Cytarabine | 200 mg/m | Days 1–5 | |
| Doxorubicin | 25 mg/m2 | Days 4 and 5 | |
| Dexamethasone | 10 mg/m2 | Days 1–5 | |
| Methotrexate (it) | 15 mg | Day 1 and 5 | |
| Cytarabine (it) | 50 mg | Day 1 and 5 | |
| Dexamethasone (it) | 8 mg | Day 1 and 5 | |
| Block C | Vindesine | 3 mg | Day 1 |
| Cytarabine | 2000 mg/m2 | Day 1 | |
| Etoposide | 150 mg/m2 | Days 3–5 | |
| Dexamethasone | 10 mg/m2 | Day 1–5 | |
| Philadelphia Positive ALL | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction | Vincristine | 2 mg | Days 1, 8, 15, and 28 |
| Adriblastin | 30 mg/m2 | Days 1–3 | |
| Cytarabine | 1200 mg/m2 | Day 1 | |
| Dexamethasone | 8 mg/m2 | Days 1–28 | |
| Imatinib | 600 mg | Days 8–63 | |
| Methotrexate (it) | 15 mg | Day 29 | |
| Cytarabine (it) | 50 mg | Day 29 | |
| Dexamethasone (it) | 8 mg | Day 29 | |
| Consolidation 1 | Methotrexate | 1 g/m2 | Day 1 |
| Cytarabine | 2 g/m2 | Days 2–3 | |
| Dexamethasone | 8 mg/m2 | Days 1–3 | |
| Methotrexate (it) | 15 mg | Day 29 | |
| Cytarabine (it) | 50 mg | Day 29 | |
| Dexamethasone (it) | 8 mg | Day 29 | |
| Consolidation 2 | Imatinib | 600 mg | Days 1–28 |
| Cytarabine (it) | 50 mg | Day 1 | |
| Dexamethasone (it) | 8 mg | Day 1 | |
| Maintenance | Imatinib | 600 mg | A la longue |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sas, V.; Moisoiu, V.; Teodorescu, P.; Tranca, S.; Pop, L.; Iluta, S.; Pasca, S.; Blag, C.; Man, S.; Roman, A.; et al. Approach to the Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patient. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081175
Sas V, Moisoiu V, Teodorescu P, Tranca S, Pop L, Iluta S, Pasca S, Blag C, Man S, Roman A, et al. Approach to the Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patient. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(8):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081175
Chicago/Turabian StyleSas, Valentina, Vlad Moisoiu, Patric Teodorescu, Sebastian Tranca, Laura Pop, Sabina Iluta, Sergiu Pasca, Cristina Blag, Sorin Man, Andrei Roman, and et al. 2019. "Approach to the Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patient" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 8: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081175
APA StyleSas, V., Moisoiu, V., Teodorescu, P., Tranca, S., Pop, L., Iluta, S., Pasca, S., Blag, C., Man, S., Roman, A., Constantinescu, C., Rus, I., Buse, M., Fetica, B., Marian, M., Selicean, C., Berindan-Neagoe, I., Petrushev, B., Bumbea, H., ... for Bone Marrow Transplantation, R.-J. W. G. o. t. R. S. (2019). Approach to the Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patient. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(8), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081175







