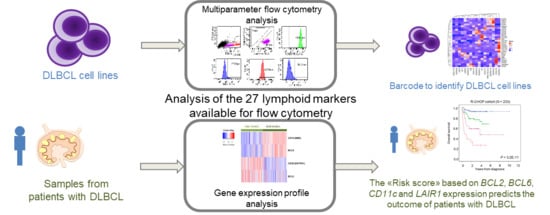
Phenotypic Characterization of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cells and Prognostic Impact
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Gene Expression Profiling and Statistical Analyses
2.5. Building the B-Cell Marker Risk Score
2.6. Interaction Effect Quantification
3. Results
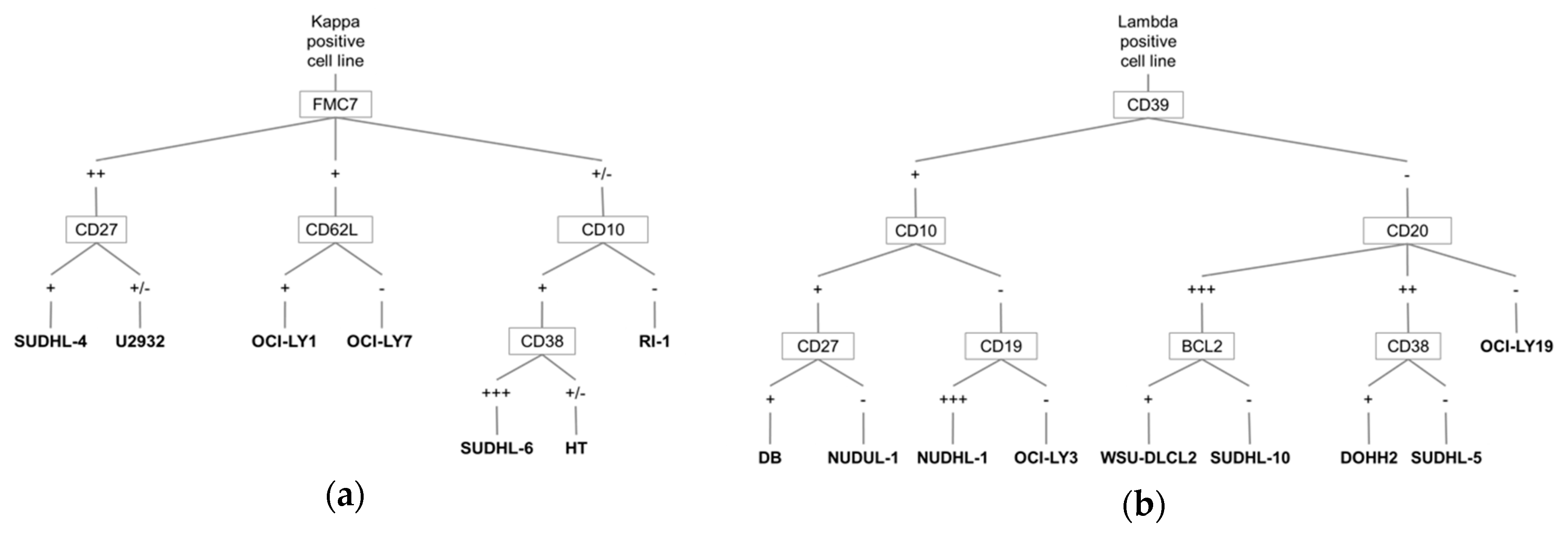
3.1. A Barcode to Identify DLBCL-Derived Cell Lines by MFC
3.2. CD39 is A Useful Marker to Discriminate Between ABC and GCB DLBCL Tumor Samples
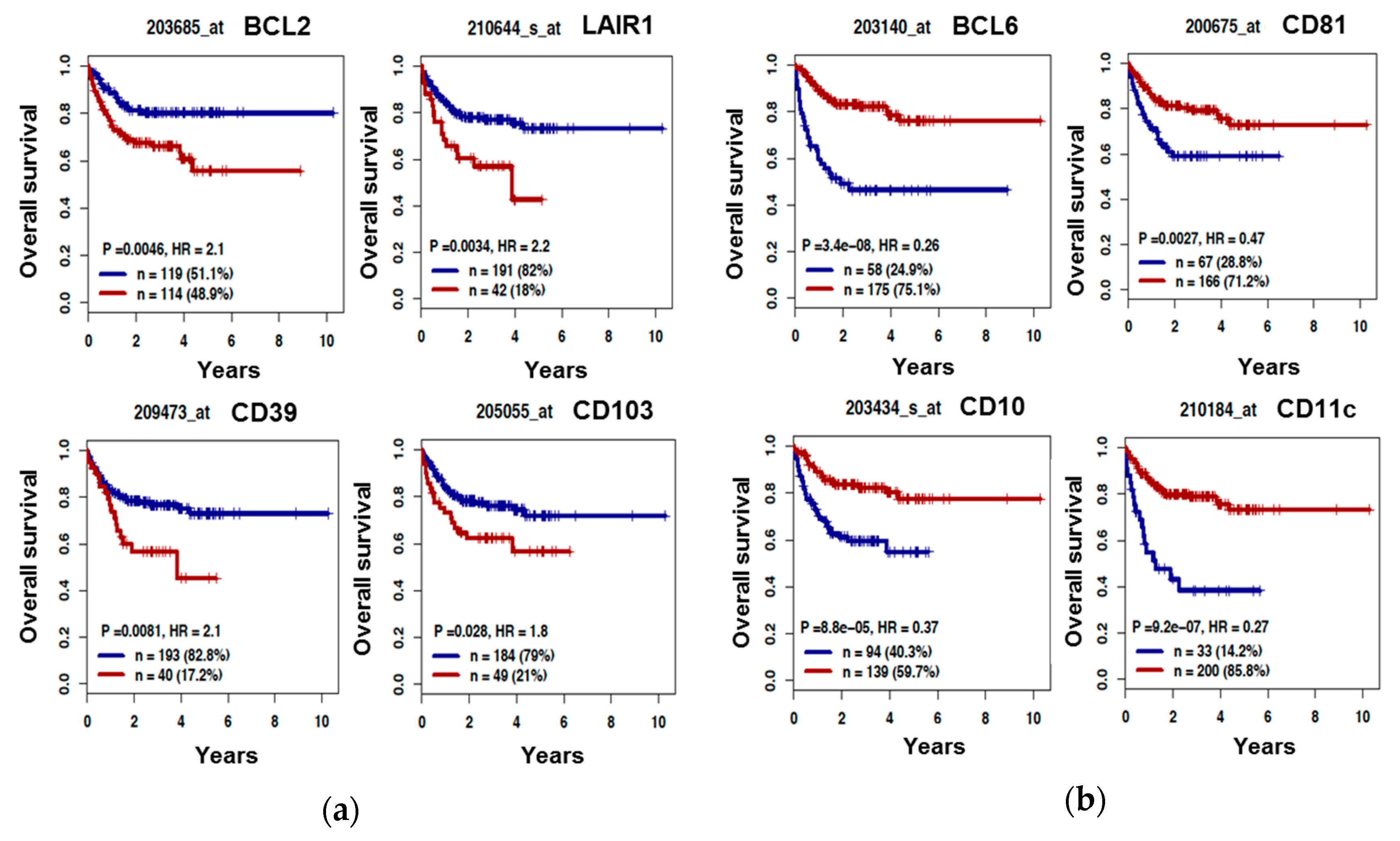
3.3. The B Cell Marker Risk Score
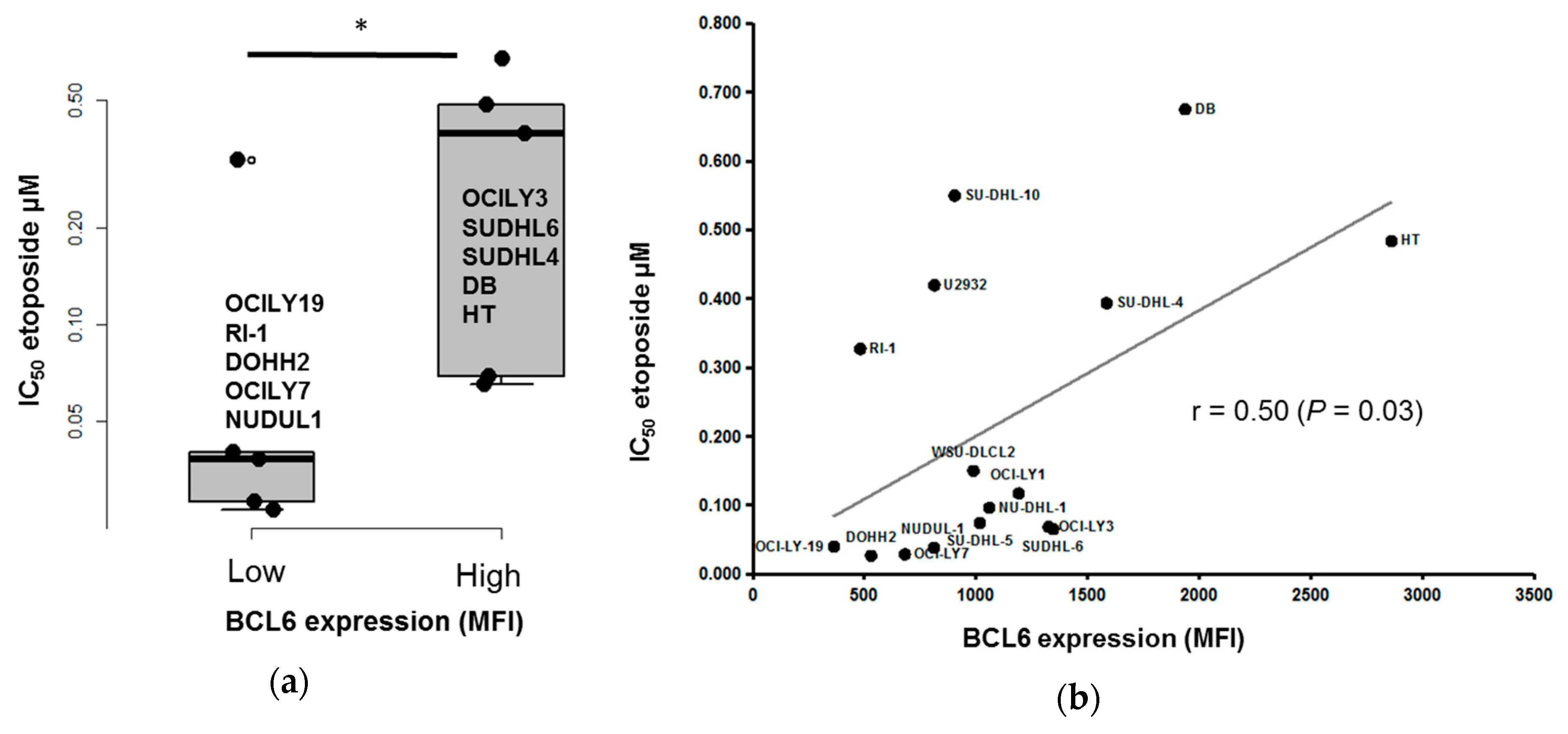
3.4. BCL6 Protein Expression is Correlated with DLBCL Cell Response to Etoposide
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| GEP | Gene expression profiling |
| COO | Cell of origin |
| GCB | Germinal-center B-cell–like subgroup |
| ABC | Activated B cell–like subtype |
| R | Rituximab |
| CHOP | Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone |
| EFS | Event-free survival |
| OS | Overall survival |
| FCM | Flow cytometry |
| FSC | Forward scatter |
| SSC | Side scatter |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kB |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinases |
| IC50 | Inhibitory concentration 50 |
| INPP5D | Src homology 2 domain containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase 1 |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PTPN6 | Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Non-Receptor Type 6 |
| SAM | Significance analysis of microarray |
| STR | Short tandem repeat |
| SYK | Spleen tyrosine kinase |
References
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenwald, A.; Wright, G.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; Campo, E.; Fisher, R.I.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Smeland, E.B.; Giltnane, J.M.; et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roschewski, M.; Staudt, L.M.; Wilson, W.H. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma-treatment approaches in the molecular era. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldman-Jones, M.H.; Lai, Z.; Wappett, M.; Harbron, C.G.; Barrett, J.C.; Harrington, E.A.; Thress, K.S. Reproducible, Quantitative, and Flexible Molecular Subtyping of Clinical DLBCL Samples Using the NanoString nCounter System. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2367–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.W.; Wright, G.W.; Williams, P.M.; Lih, C.-J.; Walsh, W.; Jaffe, E.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Campo, E.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Determining cell-of-origin subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using gene expression in formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissue. Blood 2014, 123, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreaux, J.; Klein, B.; Bataille, R.; Descamps, G.; Maïga, S.; Hose, D.; Goldschmidt, H.; Jauch, A.; Rème, T.; Jourdan, M.; et al. A high-risk signature for patients with multiple myeloma established from the molecular classification of human myeloma cell lines. Haematologica 2011, 96, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bou Samra, E.; Klein, B.; Commes, T.; Moreaux, J. Development of gene expression-based risk score in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia patients. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bret, C.; Klein, B.; Moreaux, J. Gene expression-based risk score in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van Dongen, J.J.M.; Lhermitte, L.; Böttcher, S.; Almeida, J.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Flores-Montero, J.; Rawstron, A.; Asnafi, V.; Lécrevisse, Q.; Lucio, P.; et al. EuroFlow antibody panels for standardized n-dimensional flow cytometric immunophenotyping of normal, reactive and malignant leukocytes. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1908–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, J.J.M.; Orfao, A. EuroFlow: Resetting leukemia and lymphoma immunophenotyping. Basis for companion diagnostics and personalized medicine. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaterre, E.; Raimbault, S.; Garcia, J.-M.; Rème, T.; Requirand, G.; Klein, B.; Moreaux, J. Automated and simplified identification of normal and abnormal plasma cells in Multiple Myeloma by flow cytometry. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2017, 94, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.; Dave, S.S.; Xiao, W.; Powell, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Tan, B.; Goldschmidt, N.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Stromal gene signatures in large-B-cell lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaknovich, R.; Geng, H.; Johnson, N.A.; Tsikitas, L.; Cerchietti, L.; Greally, J.M.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Elemento, O.; Melnick, A. DNA methylation signatures define molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2010, 116, e81–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dybkær, K.; Bøgsted, M.; Falgreen, S.; Bødker, J.S.; Kjeldsen, M.K.; Schmitz, A.; Bilgrau, A.E.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Li, L.; Bergkvist, K.S.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma classification system that associates normal B-cell subset phenotypes with prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A.; Rème, T.; Jourdan, M.; Fest, T.; Hose, D.; Tarte, K.; Klein, B. GenomicScape: An easy-to-use web tool for gene expression data analysis. Application to investigate the molecular events in the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A.; Hose, D.; Moreaux, J.; Walker, B.A.; Protopopov, A.; Reme, T.; Pellestor, F.; Pantesco, V.; Jauch, A.; Morgan, G.; et al. Genes with a spike expression are clustered in chromosome (sub)bands and spike (sub)bands have a powerful prognostic value in patients with multiple myeloma. Haematologica 2012, 97, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothorn, T.; Lausen, B. On the exact distribution of maximally selected rank statistics. Stat. Med. 2012, 3178–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaterre, E.; Raimbault, S.; Goldschmidt, H.; Bouhya, S.; Requirand, G.; Robert, N.; Boireau, S.; Seckinger, A.; Hose, D.; Klein, B.; et al. CD24, CD27, CD36 and CD302 gene expression for outcome prediction in patients with multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 98931–98944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, W.R.; Bravo, G.; Parsons, J.C. The search for synergy: A critical review from a response surface perspective. Pharmacol. Rev. 1995, 47, 331–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Combes, E.; Andrade, A.F.; Tosi, D.; Michaud, H.-A.; Coquel, F.; Garambois, V.; Desigaud, D.; Jarlier, M.; Coquelle, A.; Pasero, P.; et al. Inhibition of Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated and RAD3-related (ATR) overcomes oxaliplatin resistance and promotes anti-tumor immunity in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2933–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, A.L.; Young, R.M.; Staudt, L.M. Pathogenesis of human B cell lymphomas. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 565–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeb, S.J.; D’Souza, R.C.J.; Cox, J.; Schmidt-Supprian, M.; Mann, M. Super-SILAC allows classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma subtypes by their protein expression profiles. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2012, 11, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lausen, B.; Schumacher, M. Maximally Selected Rank Statistics. Biometrics 1992, 48, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Compagno, M.; Lim, W.K.; Grunn, A.; Nandula, S.V.; Scandurra, M.; Bertoni, F.; Ponzoni, M.; Califano, A.; Bhagat, G.; et al. Mutations in Multiple Genes Cause Deregulation of the NFkB Pathway in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2008, 112, 801. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Iqbal, J.; Huang, J.Z.; Zhou, G.; Chan, W.C. BCL2 protein expression parallels its mRNA level in normal and malignant B cells. Blood 2004, 104, 2936–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, M.K.; Perez-Andres, M.; Schmitz, A.; Johansen, P.; Boegsted, M.; Nyegaard, M.; Gaihede, M.; Bukh, A.; Johnsen, H.E.; Orfao, A.; et al. Multiparametric flow cytometry for identification and fluorescence activated cell sorting of five distinct B-cell subpopulations in normal tonsil tissue. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 136, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerchietti, L.C.; Ghetu, A.F.; Zhu, X.; Da Silva, G.F.; Zhong, S.; Matthews, M.; Bunting, K.L.; Polo, J.M.; Farès, C.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of BCL6 kills DLBCL cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, J.R. Human cancer cell lines: Fact and fantasy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, Y.A. Characterization and authentication of cancer cell lines: An overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 731, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maïga, S.; Brosseau, C.; Descamps, G.; Dousset, C.; Gomez-Bougie, P.; Chiron, D.; Ménoret, E.; Kervoelen, C.; Vié, H.; Cesbron, A.; et al. A simple flow cytometry-based barcode for routine authentication of multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma cell lines. Cytom. Part A 2015, 87, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parson, W.; Kirchebner, R.; Mühlmann, R.; Renner, K.; Kofler, A.; Schmidt, S.; Kofler, R. Cancer cell line identification by short tandem repeat profiling: Power and limitations. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, S.C.; Sévigny, J.; Zimmermann, H. The E-NTPDase family of ectonucleotidases: Structure function relationships and pathophysiological significance. Purinergic Signal. 2006, 2, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, C.C.; Auat, M.; Santos-Pirath, I.M.; Rudolf-Oliveira, R.C.M.; da Silva, J.P.; Lange, B.G.; Siegel, D.; de Moraes, A.C.R.; Del Moral, J.A.G.; Santos-Silva, M.C. The importance of CD39, CD43, CD81, and CD95 expression for differentiating B cell lymphoma by flow cytometry. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2017, 94, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-García, G.; Cardesa-Salzmann, T.; Climent, F.; González-Barca, E.; Mercadal, S.; Mate, J.L.; Sancho, J.M.; Arenillas, L.; Serrano, S.; Escoda, L.; et al. Gene-expression profiling and not immunophenotypic algorithms predicts prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy. Blood 2011, 117, 4836–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilly, H.; da Silva, M.G.; Vitolo, U.; Jack, A.; Meignan, M.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Walewski, J.; André, M.; Johnson, P.W.; Pfreundschuh, M.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, v116–v125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.; Tan, B.; Rosenwald, A.; Hurt, E.H.; Wiestner, A.; Staudt, L.M. A gene expression-based method to diagnose clinically distinct subgroups of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9991–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.W.; Emre, N.C.T.; Kohlhammer, H.; Dave, S.S.; Davis, R.E.; Carty, S.; Lam, L.T.; Shaffer, A.L.; Xiao, W.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arise by distinct genetic pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13520–13525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bret, C.; Klein, B.; Cartron, G.; Schved, J.-F.; Constantinou, A.; Pasero, P.; Moreaux, J. DNA repair in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A molecular portrait. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidlin, H.; Diehl, S.A.; Blom, B. New insights into the regulation of human B-cell differentiation. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsi, E.D.; Yegappan, S. Lymphoma immunophenotyping: A new era in paraffin-section immunohistochemistry. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2001, 8, 218–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilalovic, N.; Blystad, A.K.; Golouh, R.; Nesland, J.M.; Selak, I.; Trinh, D.; Torlakovic, E. Expression of bcl-6 and CD10 protein is associated with longer overall survival and time to treatment failure in follicular lymphoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 121, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukema, S.M.; Siebert, R.; Schuuring, E.; van Imhoff, G.W.; Kluin-Nelemans, H.C.; Boerma, E.-J.; Kluin, P.M. Double-hit B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2011, 117, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Young, K.H.; Medeiros, L.J. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Pathology 2018, 50, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.A.; Slack, G.W.; Savage, K.J.; Connors, J.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rogic, S.; Scott, D.W.; Tan, K.L.; Steidl, C.; Sehn, L.H.; et al. Concurrent expression of MYC and BCL2 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3452–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Tzankov, A.; Green, T.; Wu, L.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Liu, W.; Visco, C.; Li, Y.; Miranda, R.N.; et al. MYC/BCL2 protein coexpression contributes to the inferior survival of activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and demonstrates high-risk gene expression signatures: A report from The International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program. Blood 2013, 121, 4021–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuyama, N.; Sakata, S.; Baba, S.; Mishima, Y.; Nishimura, N.; Ueda, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Terui, Y.; Hatake, K.; Kitagawa, M.; et al. BCL2 expression in DLBCL: Reappraisal of immunohistochemistry with new criteria for therapeutic biomarker evaluation. Blood 2017, 130, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souers, A.J.; Leverson, J.D.; Boghaert, E.R.; Ackler, S.L.; Catron, N.D.; Chen, J.; Dayton, B.D.; Ding, H.; Enschede, S.H.; Fairbrother, W.J.; et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, E.D. Venetoclax: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.D.; Johnson, N.A.; Severson, T.M.; Mungall, A.J.; An, J.; Goya, R.; Paul, J.E.; Boyle, M.; Woolcock, B.W.; Kuchenbauer, F.; et al. Somatic mutations altering EZH2 (Tyr641) in follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of germinal-center origin. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandelbaum, J.; Bhagat, G.; Tang, H.; Mo, T.; Brahmachary, M.; Shen, Q.; Chadburn, A.; Rajewsky, K.; Tarakhovsky, A.; Pasqualucci, L.; et al. BLIMP1 is a tumor suppressor gene frequently disrupted in activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Hansen, M.; Berendse, S.; Marafioti, T.; McNamara, C. Does cell-of-origin or MYC, BCL2 or BCL6 translocation status provide prognostic information beyond the International Prognostic Index score in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab and chemotherapy? A systematic review. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 2403–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyaard, L. The inhibitory collagen receptor LAIR-1 (CD305). J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.; Santiago-Schwarz, F.; Al-Abed, Y.; Diamond, B. C1q limits dendritic cell differentiation and activation by engaging LAIR-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3160–E3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Vuurst de Vries, A.R.; Clevers, H.; Logtenberg, T.; Meyaard, L. Leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor-1 (LAIR-1) is differentially expressed during human B cell differentiation and inhibits B cell receptor-mediated signaling. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 3160–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shojaee, S.; Buchner, M.; Geng, H.; Lee, J.W.; Klemm, L.; Titz, B.; Graeber, T.G.; Park, E.; Tan, Y.X.; et al. Signalling thresholds and negative B-cell selection in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 2015, 521, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limnander, A.; Depeille, P.; Freedman, T.S.; Liou, J.; Leitges, M.; Kurosaki, T.; Roose, J.P.; Weiss, A. STIM1, PKC-δ and RasGRP set a threshold for proapoptotic Erk signaling during B cell development. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, S.; Savage, K.J.; Kutok, J.L.; Feuerhake, F.; Kurtin, P.; Mihm, M.; Wu, B.; Pasqualucci, L.; Neuberg, D.; Aguiar, R.C.T.; et al. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood 2005, 105, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.A.; Lee, M.; Hu, Y.; Andreas, J.; Patel, S.J.; Zhang, S.; Chines, P.; Elkahloun, A.; Chandrasekharappa, S.; Gutkind, J.S.; et al. A systems genetics approach identifies CXCL14, ITGAX, and LPCAT2 as novel aggressive prostate cancer susceptibility genes. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umit, E.G.; Baysal, M.; Durmus, Y.; Demir, A.M. CD11c expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia revisited, related with complications and survival. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2017, 39, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, B.; Hu, W.-W.; Chen, L.-J.; Wu, C.-P.; Lu, B.-F.; Shen, Y.-P.; Jiang, J.-T. High expression of CD11c indicates favorable prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 9403–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohl, K.; Schippers, A.; Tenbrock, K. CD11c-Specific Deletion Reveals CREB as a Critical Regulator of DC Function during the Germinal Center Response. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 8947230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, N.; Mueller, M.; Mougiakakos, D.; Ihorst, G.; Marks, R.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Veelken, H. Analysis of dendritic cell subpopulations in follicular lymphoma with respect to the tumor immune microenvironment. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 2150–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Andres, M.; Paiva, B.; Nieto, W.G.; Caraux, A.; Schmitz, A.; Almeida, J.; Vogt, R.F.; Marti, G.E.; Rawstron, A.C.; Van Zelm, M.C.; et al. Human peripheral blood B-cell compartments: A crossroad in B-cell traffic. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2010, 78, S47–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perbellini, O.; Falisi, E.; Giaretta, I.; Boscaro, E.; Novella, E.; Facco, M.; Fortuna, S.; Finotto, S.; Amati, E.; Maniscalco, F.; et al. Clinical significance of LAIR1 (CD305) as assessed by flow cytometry in a prospective series of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2014, 99, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, P.; Vargas, A.; Bueno, C.; Barrena, S.; Almeida, J.; De Santiago, M.; López, A.; Roa, S.; San Miguel, J.F.; Orfao, A. Quantitative analysis of bcl-2 expression in normal and leukemic human B-cell differentiation. Leukemia 2004, 18, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, M.; Moriyama, S.; Ando, Y.; Hikida, M.; Mori, Y.; Kurosaki, T.; Okada, T. Bcl6 protein expression shapes pre-germinal center B cell dynamics and follicular helper T cell heterogeneity. Immunity 2011, 34, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosu, T.; Fukuda, T.; Miki, T.; Miura, O. BCL6 overexpression prevents increase in reactive oxygen species and inhibits apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic reagents in B-cell lymphoma cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 4459–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, T.; Yang, S.N.; Patel, J.; Hatzi, K.; Malik, A.; Tam, W.; Martin, P.; Leonard, J.; Melnick, A.; Cerchietti, L. Selective targeting of BCL6 induces oncogene addiction switching to BCL2 in B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3520–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| A. | Overall Survival (n = 233) | |
| Prognostic Variable | HR | p-Value |
| Age (>60 years) | 2.20 | <0.0001 |
| GCB-ABC molecular subgroups | 2.75 | <0.0001 |
| IPI | 1.79 | <0.0001 |
| DNA repair score | 3.87 | <0.0001 |
| Risk Score | 2.41 | <0.0001 |
| B. | Overall Survival (n = 233) | |
| Prognostic Variable | HR | p-Value |
| Risk Score | 2.248 | <0.0001 |
| Age (>60 years) | 1.846 | 0.03 |
| Risk Score | 2.269 | <0.0001 |
| GCB-ABC molecular subgroups | 1.359 | NS |
| Risk Score | 2.113 | <0.0001 |
| IPI | 1.582 | <0.0001 |
| Risk Score | 2.263 | <0.0001 |
| DNA repair score | 2.909 | <0.0001 |
| C. | Overall Survival (n = 233) | |
| Prognostic Variable | HR | p-Value |
| Age (>60 years) | 1.80 | NS |
| GCB-ABC molecular subgroups | 2.23 | NS |
| IPI | 0.20 | NS |
| DNA repair score | 3.44 | <0.0001 |
| Risk Score | 1.61 | 0.007 |
| A. | Overall Survival (n = 233) | |
| Lymphoid Marker | HR | p-Value |
| BCL2 | 2.11 | 0.006 |
| BCL6 | 0.26 | <0.0001 |
| CD39 | 2.1 | 0.01 |
| CD103 | 1.82 | 0.03 |
| CD11c | 0.27 | <0.0001 |
| LAIR1 | 2.24 | 0.004 |
| CD10 | 0.37 | <0.0001 |
| CD5 | 0.59 | 0.04 |
| B. | Overall Survival (n = 233) | |
| Lymphoid Marker | HR | p-Value |
| BCL2 | 1.96 | 0.01 |
| BCL6 | 0.44 | 0.007 |
| CD39 | 1.22 | NS |
| CD103 | 1.30 | NS |
| CD11c | 0.33 | <0.0001 |
| LAIR1 | 2.82 | 0.002 |
| CD10 | 0.39 | NS |
| CD5 | 0.47 | 0.01 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devin, J.; Kassambara, A.; Bruyer, A.; Moreaux, J.; Bret, C. Phenotypic Characterization of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cells and Prognostic Impact. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071074
Devin J, Kassambara A, Bruyer A, Moreaux J, Bret C. Phenotypic Characterization of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cells and Prognostic Impact. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(7):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071074
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevin, Julie, Alboukadel Kassambara, Angélique Bruyer, Jérôme Moreaux, and Caroline Bret. 2019. "Phenotypic Characterization of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cells and Prognostic Impact" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 7: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071074
APA StyleDevin, J., Kassambara, A., Bruyer, A., Moreaux, J., & Bret, C. (2019). Phenotypic Characterization of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cells and Prognostic Impact. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(7), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071074