The Vagus Nerve Can Predict and Possibly Modulate Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases: Introducing a Neuroimmunological Paradigm to Public Health
Abstract
1. The Problem
2. Oxidative Stress and Chronic Diseases
3. Inflammation and Chronic Diseases
4. Excessive Sympathetic Nervous System Activity and Chronic Diseases
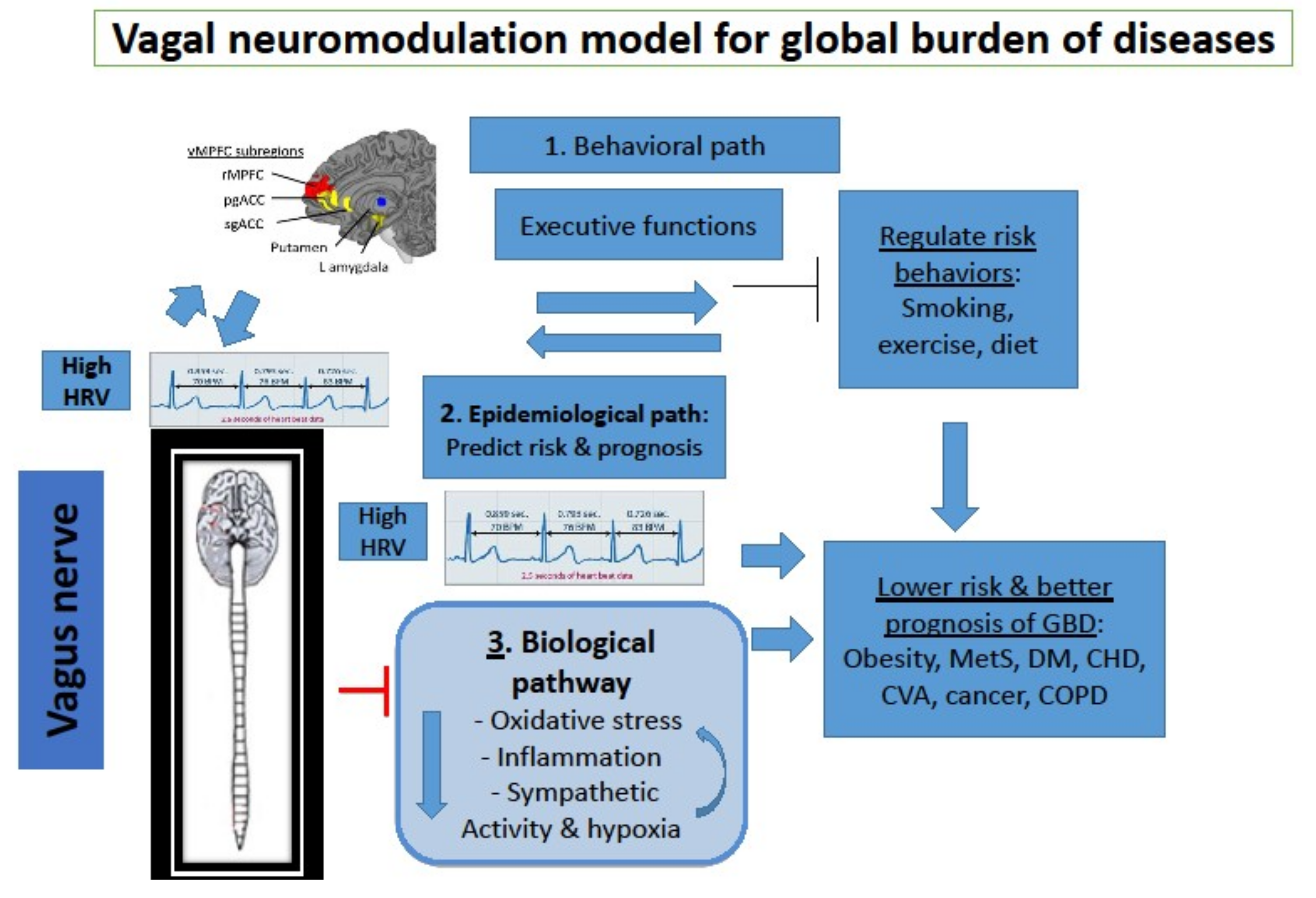
5. Introducing Neuro-Immunology and Neuro-Modulation to Public Health
6. Epidemiological Path: Vagal Nerve Activity Predicts Risk and prognosis of Chronic Diseases
7. Biological Path: The Vagus Nerve Inhibits Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Sympathetic Activity
8. Behavioral Path: Effects of Vagal Activity on Lifestyle Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases
9. Implications for Prevention and Treatment: Activating the Vagal Nerve for Health
10. Note of Caution
11. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1151–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1659–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, J. Physical activity in the prevention of the most frequent chronic diseases: An analysis of the recent evidence. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2007, 8, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Africa Working Group. Trends in obesity and diabetes across Africa from 1980 to 2014: An analysis of pooled population-based studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, A.E.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Ezzati, M.; Flaxman, A.; Murray, C.J.; Naghavi, M. The global burden of ischemic heart disease in 1990 and 2010: The Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Circulation 2014, 129, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.M.; Woo, H.; Jung, S.J.; Jung, K.W.; Shin, H.R.; Shin, A. Colorectal cancer incidence in 5 Asian countries by subsite: An analysis of Cancer Incidence in Five Continents (1998–2007). Cancer Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubisse-Marliac, L.; Delafosse, P.; Boitard, J.B.; Poncet, F.; Grosclaude, P.; Colonna, M. Breast cancer incidence and time trend in France from 1990 to 2007: A population-based study from two French cancer registries. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2016 DALYs and HALE Collaborators. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1260–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Campos, J.L.; Tan, W.; Soriano, J.B. Global burden of COPD. Respirology 2016, 21, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidron, Y.; Perry, H.; Glennie, M. The Vagus may inform the brain about sub-clinical tumours and modulate them: An Hypothesis. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Couck, M.; Mravec, B.; Gidron, Y. You may need the vagus nerve to understand pathophysiology and to treat diseases. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdrel, T.; Bind, M.A.; Béjot, Y.; Morel, O.; Argacha, J.F. Cardiovascular effects of air pollution. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 110, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Øvrevik, J.; Refsnes, M.; Låg, M.; Brinchmann, B.C.; Schwarze, P.E.; Holme, J.A. Triggering Mechanisms and Inflammatory Effects of Combustion Exhaust Particles with Implication for Carcinogenesis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 121, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Kwong, J.C.; Copes, R.; Hystad, P.; van Donkelaar, A.; Tu, K.; Brook, J.R.; Goldberg, M.S.; Martin, R.V.; Murray, B.J.; et al. Exposure to ambient air pollution and the incidence of dementia: A population-based cohort study. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, J. Associations of job stress indicators with oxidative biomarkers in Japanese men and women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 6662–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, E.H.; Epel, E.S. Telomeres and adversity: Too toxic to ignore. Nature 2012, 490, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, S.G.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J.; Roy, S.; Shinkle, J.; Sabarinathan, M.; Argos, M.; Tong, L.; Ahmed, A.; Islam, M.T.; et al. The association between telomere length and mortality in Bangladesh. Aging 2017, 9, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikarsky, E.; Porat, R.M.; Stein, I.; Abramovitch, R.; Amit, S.; Kasem, S.; Gutkovich-Pyest, E.; Urieli-Shoval, S.; Galun, E.; Ben-Neriah, Y. NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature 2004, 431, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voronov, E.; Shouval, D.S.; Krelin, Y.; Cagnano, E.; Benharroch, D.; Iwakura, Y.; Dinarello, C.A.; Apte, R.N. IL-1 is required for tumour invasiveness and angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disease. Am. Heart J. 1999, 138, S419–S420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidron, Y.; Kupper, N.; Kwaijtaal, M.; Winter, J.; Denollet, J. Vagus-brain communication in atherosclerosis-related inflammation: A neuroimmunomodulation perspective of CAD. Atherosclerosis 2007, 195, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.; Liu, T.; Fan, H.; Chen, F.; Ding, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Hou, S. Inflammatory Markers and the Risk of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Song, C.; Lin, A.; de Jongh, R.; van Gastel, A.; Kenis, G.; Bosmans, E.; de Meester, I.; Benoy, I.; Neels, H.; et al. The effects of psychological stress on humans: Increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and a Th1-like response in stress-induced anxiety. Cytokine 1998, 10, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remme, W.J. The sympathetic nervous system and ischaemic heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 1998, 19, F62–F71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Entschladen, F.; Drell, T.L.; Lang, K.; Joseph, J.; Zaenker, K.S. Tumour-cell migration, invasion, and metastasis: Navigation by neurotransmitters. Lancet Oncol. 2004, 5, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, S.; Haarmann, H.; Klarner, S.; Hasenfuss, G.; Raupach, T. Increased sympathetic nerve activity in COPD is associated with morbidity and mortality. Lung 2014, 192, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yufu, K.; Okada, N.; Ebata, Y.; Murozono, Y.; Shinohara, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Takahashi, N. Plasma norepinephrine is an independent predictor of adverse cerebral and cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetic patients without structural heart disease. J. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowska, J.; Krajewski, W.; Bolanowski, M.; Kręcicki, T.; Zatoński, T. Diabetes and Cancer: A Review of Current Knowledge. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2016, 124, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idris, M.A.; Dollard, M.F.; Winefield, A.H. The effect of globalization on employee psychological health and job satisfaction in Malaysian workplaces. J. Occup. Health 2011, 53, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, G.W.; Carrère, S. Traffic congestion, perceived control, and psychophysiological stress among urban bus drivers. J. Appl. Psychol. 1991, 76, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadgar, I.; Norström, T. Short-term and long-term effects of GDP on traffic deaths in 18 OECD countries, 1960–2011. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2017, 71, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, T.B.; Lai, C.J.; Huang, Y.T.; Yang, C.C. Regression analysis between heart rate variability and baroreflex-related vagus nerve activity in rats. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2005, 16, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.S.; Thayer, J.F.; Rudat, M.; Wirtz, P.H.; Zimmermann-Viehoff, F.; Thomas, A.; Perschel, F.H.; Arck, P.C.; Deter, H.C. Low vagal tone is associated with impaired post stress recovery of cardiovascular, endocrine, and immune markers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, H.; Matsunaga, M.; Osumi, T.; Fukuyama, S.; Shinoda, J.; Yamada, J.; Gidron, Y. Vagal nerve activity as a moderator of brain-immune relationships. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 260, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licht, C.M.; Vreeburg, S.A.; van Reedt Dortland, A.K.; Giltay, E.J.; Hoogendijk, W.J.; DeRijk, R.H.; Vogelzangs, N.; Zitman, F.G.; de Geus, E.J.; Penninx, B.W. Increased sympathetic and decreased parasympathetic activity rather than changes in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity is associated with metabolic abnormalities. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 2458–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, J.M.; Schouten, E.G.; Klootwijk, P.; Pool, J.; Swenne, C.A.; Kromhout, D. Heart rate variability from short electrocardiographic recordings predicts mortality from all causes in middle-aged and elderly men. The Zutphen Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buccelletti, E.; Gilardi, E.; Scaini, E.; Galiuto, L.; Persiani, R.; Biondi, A.; Basile, F.; Silveri, N.G. Heart rate variability and myocardial infarction: Systematic literature review and metanalysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 13, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Fu, W. Heart rate variability in the prediction of survival in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychosom. Res. 2016, 89, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Couck, M.D.; Maréchal, R.; Moorthamers, S.; Laethem, J.-L.V.; Gidron, Y. Vagal nerve activity predicts overall survival in metastatic pancreatic cancer, mediated by inflammation. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perugini, R.A.; Li, Y.; Rosenthal, L.; Gallagher-Dorval, K.; Kelly, J.J.; Czerniach, D.R. Reduced heart rate variability correlates with insulin resistance but not with measures of obesity in population undergoing laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2010, 6, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissinger, A.; Ruxer, J.; Ahmed, R.B.; Lubinski, A. Heart rate turbulence in patients with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus type 2. Arch. Med. Sci. 2014, 10, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, R.; Poanta, L.; Rusu, D.; Albu, A. The role of heart rate variability in assessing the evolution of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 50, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, T.; Ide, T.; Yamato, M.; Kudou, W.; Andou, M.; Hirooka, Y.; Utsumi, H.; Tsutsui, H.; Sunagawa, K. Modulation of the myocardial redox state by vagal nerve stimulation after experimental myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 77, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, O.C.; França, C.M.; Rocha, J.A.; Neves, G.A.; Souza, P.R.M.; Teixeira Gomes, M.; Malfitano, C.; Loleiro, T.C.A.; Dourado, P.M.; Llesuy, S.; et al. Cholinergic stimulation improves oxidative stress and inflammation in experimental myocardial infarction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ek, M.; Kurosawa, M.; Lundeberg, T.; Ericsson, A. Activation of vagal afferents after intravenous injection of interleukin-1beta: Role of endogenous prostaglandins. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9471–9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracey, K.J. Reflex control of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Ballina, M.; Olofsson, P.S.; Ochani, M.; Valdés-Ferrer, S.I.; Levine, Y.A.; Reardon, C.; Tusche, M.W.; Pavlov, V.A.; Andersson, U.; Chavan, S.; et al. Acetylcholine-synthesizing T cells relay neural signals in a vagus nerve circuit. Science 2011, 334, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saku, K.; Kishi, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Hosokawa, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Murayama, Y.; Kakino, T.; Ikeda, M.; Ide, T.; Sunagawa, K. Afferent vagal nerve stimulation resets baroreflex neural arc and inhibits sympathetic nerve activity. Physiol. Rep. 2014, 2, e12136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feliciano, L.; Henning, R.J. Vagal nerve stimulation releases vasoactive intestinal peptide which significantly increases coronary artery blood flow. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 40, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupel, P.; Mayer, A. Hypoxia in cancer: Significance and impact on clinical outcome. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007, 26, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarry, T.; Biniecka, M.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. Hypoxia, oxidative stress and inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodin, F.; McIntyre, K.M.; Schwartz, J.E.; McKinley, P.S.; Cardetti, C.; Shapiro, P.A.; Gorenstein, E.; Sloan, R.P. The Association of Cigarette Smoking with High-Frequency Heart Rate Variability: An Ecological Momentary Assessment Study. Psychosom. Med. 2017, 79, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzman, J.B.; Bridgett, D.J. Heart rate variability indices as bio-markers of top-down self-regulatory mechanisms: A meta-analytic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 74, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggs, N.R.; Huh, J.; Chou, C.P.; Spruijt-Metz, D.; Pentz, M.A. Executive function and latent classes of childhood obesity risk. J. Behav. Med. 2012, 35, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, P.A.; Fong, G.T.; Epp, L.J.; Elias, L.J. Executive function moderates the intention-behavior link for physical activity and dietary behavior. Psychol. Health 2008, 23, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, T.; Hösl, K.; Kiess, O.; Schanze, A.; Kornhuber, J.; Forster, C. BOLD fMRI deactivation of limbic and temporal brain structures and mood enhancing effect by transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation. J. Neural Transm. 2007, 114, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badran, B.W.; Dowdle, L.T.; Mithoefer, O.J.; LaBate, N.T.; Coatsworth, J.; Brown, J.C.; DeVries, W.H.; Austelle, C.W.; McTeague, L.M.; George, M.S. Neurophysiologic effects of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) via electrical stimulation of the tragus: A concurrent taVNS/fMRI study and review. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziomber, A.; Juszczak, K.; Kaszuba-Zwoinska, J.; Machowska, A.; Zaraska, K.; Gil, K.; Thor, P. Magnetically induced vagus nerve stimulation and feeding behavior in rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meule, A.; Freund, R.; Skirde, A.K.; Vögele, C.; Kübler, A. Heart rate variability biofeedback reduces food cravings in high food cravers. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2012, 37, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, S.U.; Hare, T.A. Higher heart-rate variability is associated with ventromedial prefrontal cortex activity and increased resistance to temptation in dietary self-control challenges. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinmäki, K.; Rusko, H. Time-frequency analysis of heart rate variability during immediate recovery from low and high intensity exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 102, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberstein, S.D.; Mechtler, L.L.; Kudrow, D.B.; Calhoun, A.H.; McClure, C.; Saper, J.R.; Liebler, E.J.; Rubenstein Engel, E.; Tepper, S.J.; ACT1 Study Group. Non-Invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation for the ACute Treatment of Cluster Headache: Findings from the Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled ACT1 Study. Headache 2016, 56, 1317–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerman, I.; Hauger, R.; Sorkin, L.; Proudfoot, J.; Davis, B.; Huang, A.; Lam, K.; Simon, B.; Baker, D.G. Noninvasive Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Decreases Whole Blood Culture-Derived Cytokines and Chemokines: A Randomized, Blinded, Healthy Control Pilot Trial. Neuromodulation 2016, 19, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hein, E.; Nowak, M.; Kiess, O.; Biermann, T.; Bayerlein, K.; Kornhuber, J.; Kraus, T. Auricular transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in depressed patients: A randomized controlled pilot study. J. Neural Transm. 2013, 120, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhai, X.; Li, S.; McCabe, M.F.; Wang, X.; Rong, P. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation induces tidal melatonin secretion and has an antidiabetic effect in Zucker fatty rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, R.P.; Floras, J.S.; Ahmed, L.; Harvey, P.J.; Hiscock, N.; Hendrickx, H.; Talbot, D. Behavioural modification of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory response to C-reactive protein in patients with hypertension. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 272, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Couck, M.; de Leeuw, I.; Blase, K.M.; Reiman, E.; van Acker, L.; Gidron, Y. Effects of HRV-biofeedback on the tumor marker CEA in patients with metastatic colon cancer: A controlled pilot study. Manuscript under review.
- Tyagi, A.; Cohen, M. Yoga and heart rate variability: A comprehensive review of the literature. Int. J. Yoga 2016, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, I.S.; Didier, S.; Murray, D.W.; Turner, T.H.; Issaivanan, M.; Ruggieri, R.; Al-Abed, Y.; Symons, M. Semapimod sensitizes glioblastoma tumors to ionizing radiation by targeting microglia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimura, T.; Saku, K.; Kakino, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Tohyama, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Kishi, T.; Ide, T.; Sunagawa, K. Intravenous electrical vagal nerve stimulation prior to coronary reperfusion in a canine ischemia-reperfusion model markedly reduces infarct size and prevents subsequent heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 227, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodaparast, N.; Hays, S.A.; Sloan, A.M.; Fayyaz, T.; Hulsey, D.R.; Rennaker, R.L., II; Kilgard, M.P. Vagus nerve stimulation delivered during motor rehabilitation improves recovery in a rat model of stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2014, 28, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malbert, C.H.; Picq, C.; Divoux, J.L.; Henry, C.; Horowitz, M. Obesity-associated alterations in glucose metabolism are reversed by chronic bilateral stimulation of the abdominal vagus verve. Diabetes 2017, 66, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, A.; Nilsson, L.; Nylund, G.; Khorram-Manesh, A.; Nordgren, S.; Delbro, D.S. Is acetylcholine an autocrine/paracrine growth factor via the nicotinic alpha7-receptor subtype in the human colon cancer cell line HT-29? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 609, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.R.; Richbart, S.D.; Merritt, J.C.; Brown, K.C.; Nolan, N.A.; Akers, A.T.; Lau, J.K.; Robateau, Z.R.; Miles, S.L.; Dasgupta, P. Acetylcholine signaling system in progression of lung cancers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlsen, J.; Kaijer, M.N.; Mehlsen, A.B. Autonomic and electrocardiographic changes in cardioinhibitory syncope. Europace 2008, 10, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.K.; Tucker, K.L.; O’Neill, M.S.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Hu, H.; Schwartz, J. Fruit, vegetable, and fish consumption and heart rate variability: The Veterans Administration Normative Aging Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidron, Y.; Davidson, K.; Bata, I. The short-term effects of a hostility-reduction intervention on male coronary heart disease patients. Health Psychol. 1999, 18, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gidron, Y.; Deschepper, R.; De Couck, M.; Thayer, J.F.; Velkeniers, B. The Vagus Nerve Can Predict and Possibly Modulate Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases: Introducing a Neuroimmunological Paradigm to Public Health. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100371
Gidron Y, Deschepper R, De Couck M, Thayer JF, Velkeniers B. The Vagus Nerve Can Predict and Possibly Modulate Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases: Introducing a Neuroimmunological Paradigm to Public Health. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(10):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100371
Chicago/Turabian StyleGidron, Yori, Reginald Deschepper, Marijke De Couck, Julian F. Thayer, and Brigitte Velkeniers. 2018. "The Vagus Nerve Can Predict and Possibly Modulate Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases: Introducing a Neuroimmunological Paradigm to Public Health" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 10: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100371
APA StyleGidron, Y., Deschepper, R., De Couck, M., Thayer, J. F., & Velkeniers, B. (2018). The Vagus Nerve Can Predict and Possibly Modulate Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases: Introducing a Neuroimmunological Paradigm to Public Health. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(10), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100371




