Functional and Endoscopic Indicators for Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analyses
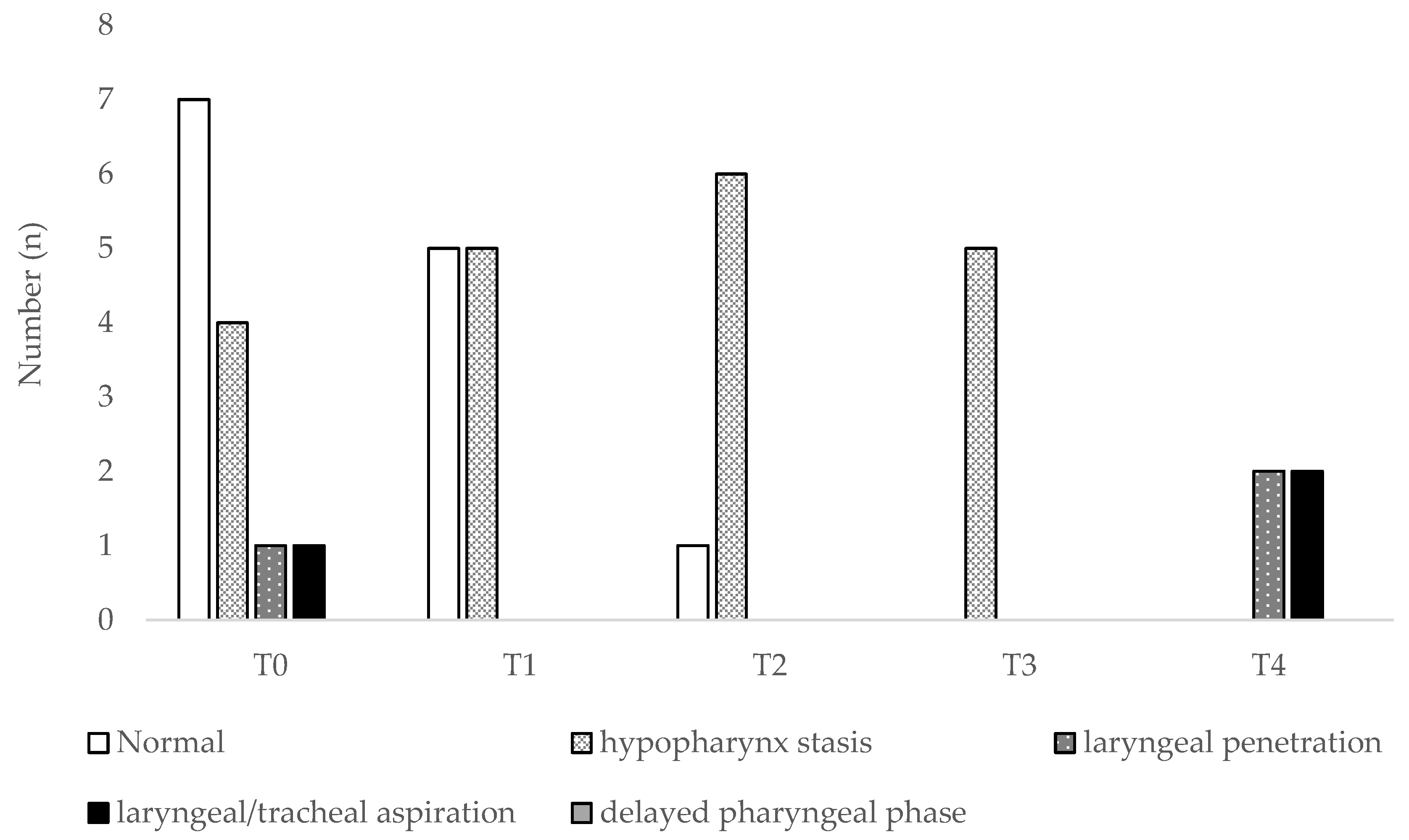
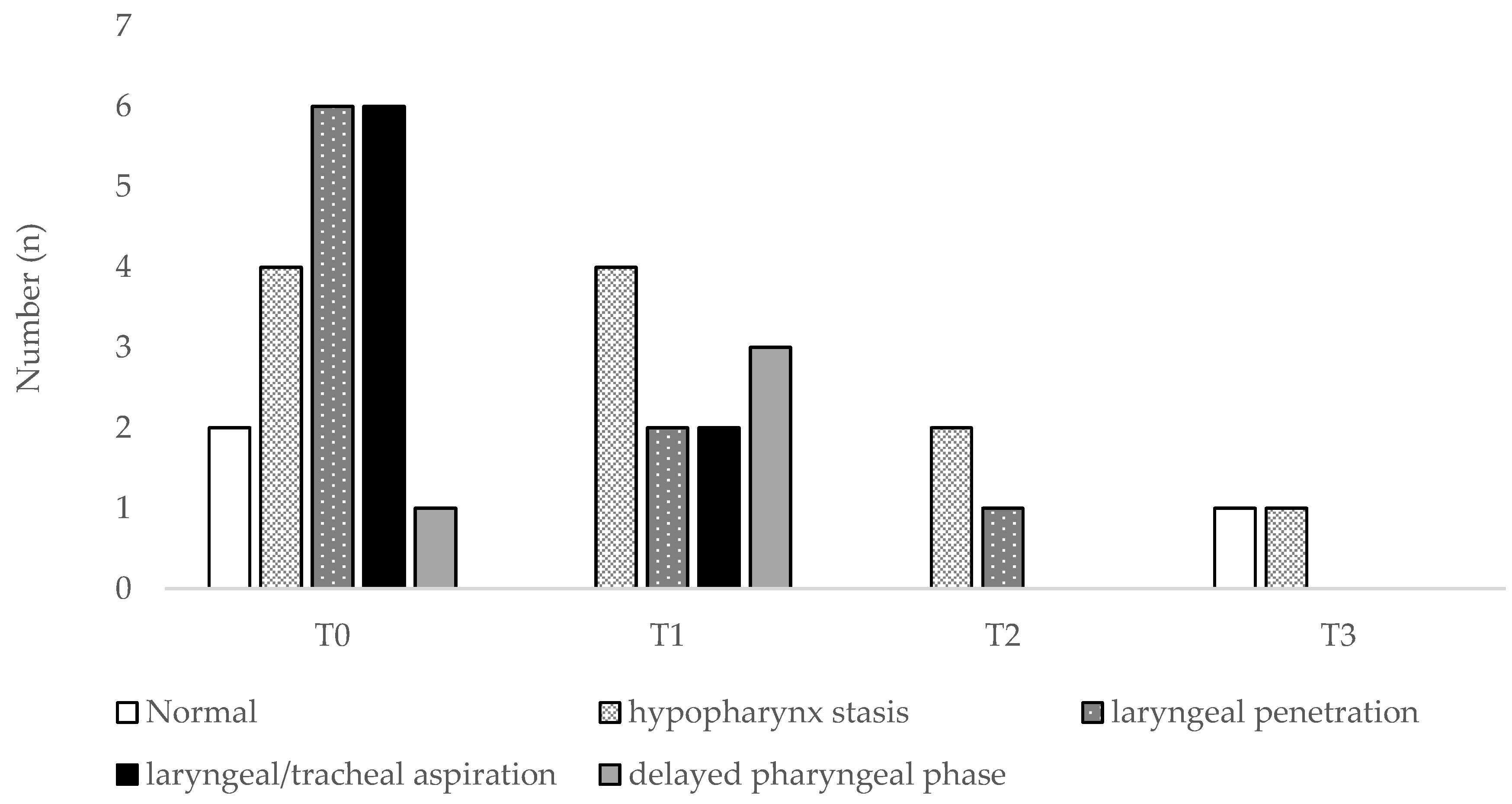
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics and Functional Parameters
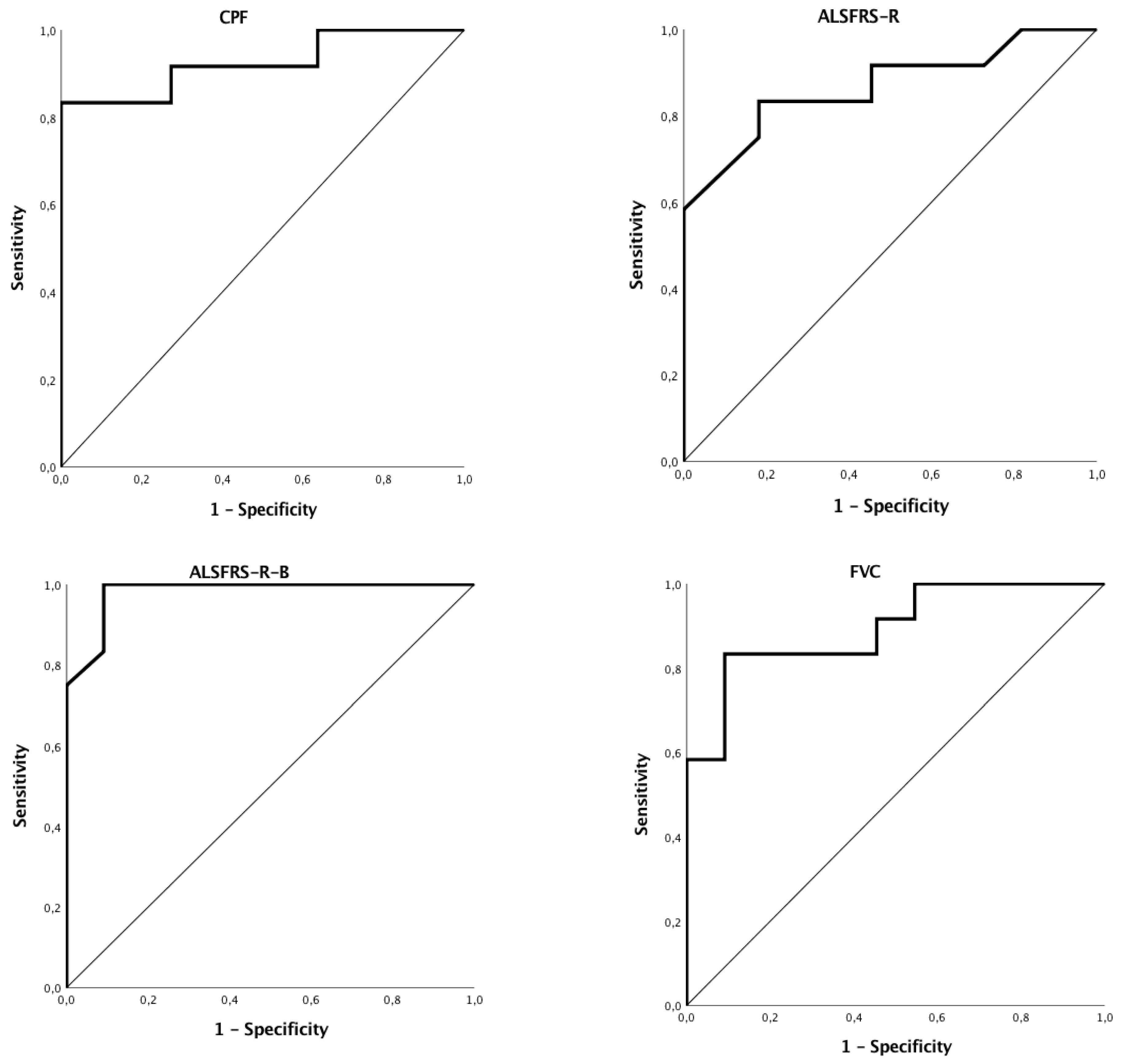
3.2. Discriminant Ability of Functional or Endoscopic Indicators for Predicting PEG
3.3. Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kak, M.; Issa, N.P.; Roos, R.P.; Sweitzer, B.J.; Gottlieb, O.; Guralnick, A.; White, S.R.; Semrad, C.E.; Soliven, B.; Baroody, J.; et al. Gastrostomy tube placement is safe in advanced amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talman, P.; Duong, T.; Vucic, S.; Mathers, S.; Venkatesh, S.; Henderson, R.; Rowe, D.; Schultz, D.; Edis, R.; Needham, M.; et al. Identification and outcomes of clinical phenotypes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease: Australian National Motor Neuron Disease observational cohort. BMJ Open 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieves, J.W.; Gennings, C.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Hupf, J.; Singleton, J.; Sharf, V.; Oskarsson, B.; Filho, J.A.M.F.; Sorenson, E.J.; D’Amico, E.; et al. Association between dietary intake and function in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, R.; Bretón, I.; Cereda, E.; Desport, J.C.; Dziewas, R.; Genton, L.; Gomes, F.; Jésus, P.; Leischker, A.; Muscaritoli, M.; et al. ESPEN guideline clinical nutrition in neurology. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 37, 354–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, C.J. Gastrostomy in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ProGas): A prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 702–709. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, F.; Sun, L.; Xiong, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, X. Therapeutic effects of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy on survival in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Shi, X. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy versus fluoroscopic gastrostomy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) sufferers with nutritional impairment: A meta-analysis of current studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102244–102253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Goshi, S.; Kawauchi, Y.; Nishigaki, Y.; Mizuno, K.-I.; Hashimoto, S.; Takeuchi, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Ozawa, T.; Nishizawa, M.; Aoyagi, Y. Safety of unsedated PEG placement using transoral ultrathin endoscopy in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.G.; Jackson, C.E.; Kasarskis, E.J.; England, J.D.; Forshew, D.; Johnston, W.; Kalra, S.; Katz, J.S.; Mitsumoto, H.; Rosenfeld, J.; et al. Practice parameter update: The care of the patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Multidisciplinary care, symptom management, and cognitive/behavioral impairment (an evidence-based review): Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American of Neurology. Neurology 2009, 73, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.W.; Allen, C.T.; Huang, C.C.; Lee, C.J. Murray secretion scale and fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in predicting aspiration in dysphagic patients. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2017, 274, 2513–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviv, J.E.; Kaplan, S.T.; Thomson, J.E.; Spitzer, J.; Diamond, B.; Close, L.G. The safety of flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing (FEESST): An analysis of 500 consecutive evaluations. Dysphagia 2000, 15, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farneti, D.; Fattori, B.; Nacci, A.; Mancini, V.; Simonelli, M.; Ruoppolo, G.; Genovese, E. The Pooling-score (P-score): Inter- and intra-rater reliability in endoscopic assessment of the severity of dysphagia. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2014, 34, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rooney, J.; Burke, T.; Vajda, A.; Heverin, M.; Hardiman, O. What does the ALSFRS-R really measure? A longitudinal and survival analysis of functional dimension subscores in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plowman, E.K.; Watts, S.A.; Robison, R.; Tabor, L.; Dion, C.; Gaziano, J.; Vu, T.; Gooch, C. Voluntary cough airflow differentiates safe versus unsafe swallowing in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.G.; Blackwell, V.; Marsden, R.; Millard, E.; Lawson, C.; Nickol, A.H.; East, J.E.; Talbot, K.; Allan, P.J.; Turner, M.R. A risk stratifying tool to facilitate safe late-stage percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in ALS. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2017, 18, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winck, J.C.; LeBlanc, C.; Soto, J.L.; Plano, F. The value of cough peak flow measurements in the assessment of extubation or decannulation readiness. Rev. Port. Pneumol. 2015, 21, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, A.A.; Pessolano, F.A.; Monteiro, S.G.; Ferreyra, G.; Capria, M.E.; Mesa, L.; Dubrovsky, A.; De Vito, E.L. Peak flow and peak cough flow in the evaluation of expiratory muscle weakness and bulbar impairment in patients with neuromuscular disease. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 81, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.J.; Whitelaw, W.; Siafakas, N.; Supinski, G.S.; Fitting, J.W.; Bellemare, F.; Loring, S.H.; De Troyer, A.; Grassino, A.E. ATS/ERS Statement on respiratory muscle testing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 518–624. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, E.; Fonseca, L.; Matos, J.; Bernardo, T.; Silva, A. Videoendoscopy of swallowing: Evaluation protocol. Port. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Cervical-Facial Surg. 2012, 50, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Fattori, B.; Siciliano, G.; Mancini, V.; Bastiani, L.; Bongioanni, P.; Ienco, G.E.; Barillari, M.R.; Romeo, S.O.; Nacci, A. Dysphagia in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Relationships between disease progression and Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing. Auris Nasus Larynx 2017, 44, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onesti, E.; Schettino, I.; Gori, M.C.; Frasca, V.; Ceccanti, M.; Cambieri, C.; Ruoppolo, G.; Inghilleri, M. Dysphagia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Impact on patient behavior, diet adaptation, and riluzole management. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabor, L.; Gaziano, J.; Watts, S.; Robison, R.; Plowman, E.K. Defining swallowing-related quality of life profiles in individuals with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilanus, T.B.M.; Groothuis, J.T.; TenBroek-Pastoor, J.M.C.; Feuth, T.B.; Heijdra, Y.F.; Slenders, J.P.L.; Doorduin, J.; van Engelen, B.G.; Kampelmacher, M.J.; Raaphorst, J. The predictive value of respiratory function tests for non-invasive ventilation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Phenotypes | ALS Spinal Onset | ALS Bulbar Onset | ALS Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61.3 ± 8.1 | 69.7 ± 8.3 | 65.4 ± 9.1 |
| Gender | |||
| Males | 10 (83.3%) | 4 (36.4%) | 14 (60.9%) |
| Females | 2 (16.7%) | 7 (63.6%) | 9 (39.1%) |
| FVC (%) | 91.1 ± 18.6 | 77.4 ± 34.0 | 84.6 ± 27.4 |
| PEmax (cm H2O) | 88.4 ± 34.5 | 56.0 ± 45.6 | 72.9 ± 42.6 |
| PImax (cm H2O) | 78.0 ± 20.3 | 34.7 ± 23.5 | 57.3 ± 30.8 |
| CPF (L/min) | 319.6 ± 70.6 | 205.4 ± 147.1 | 265.0 ± 125.4 |
| PEF/CPF | |||
| <1 | 4 (33.3%) | 3 (27.3%) | 7 (30.4%) |
| 0 | 0 | 1 (9.1%) | 1 (4.3%) |
| ≥1 | 8 (66.7%) | 7 (63.6%) | 15 (65.3%) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conde, B.; Martins, N.; Rodrigues, I.; Pimenta, A.C.; Winck, J.C. Functional and Endoscopic Indicators for Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100352
Conde B, Martins N, Rodrigues I, Pimenta AC, Winck JC. Functional and Endoscopic Indicators for Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(10):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100352
Chicago/Turabian StyleConde, Bebiana, Natália Martins, Inês Rodrigues, Ana Cláudia Pimenta, and João Carlos Winck. 2018. "Functional and Endoscopic Indicators for Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 10: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100352
APA StyleConde, B., Martins, N., Rodrigues, I., Pimenta, A. C., & Winck, J. C. (2018). Functional and Endoscopic Indicators for Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(10), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100352






