Simultaneous Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems and the Remote Electrical Neuromodulation (REN) Wearable for Patients with Comorbid Diabetes and Migraine: An Interventional Single-Arm Compatibility Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants and Recruitment
2.3. Sample Size
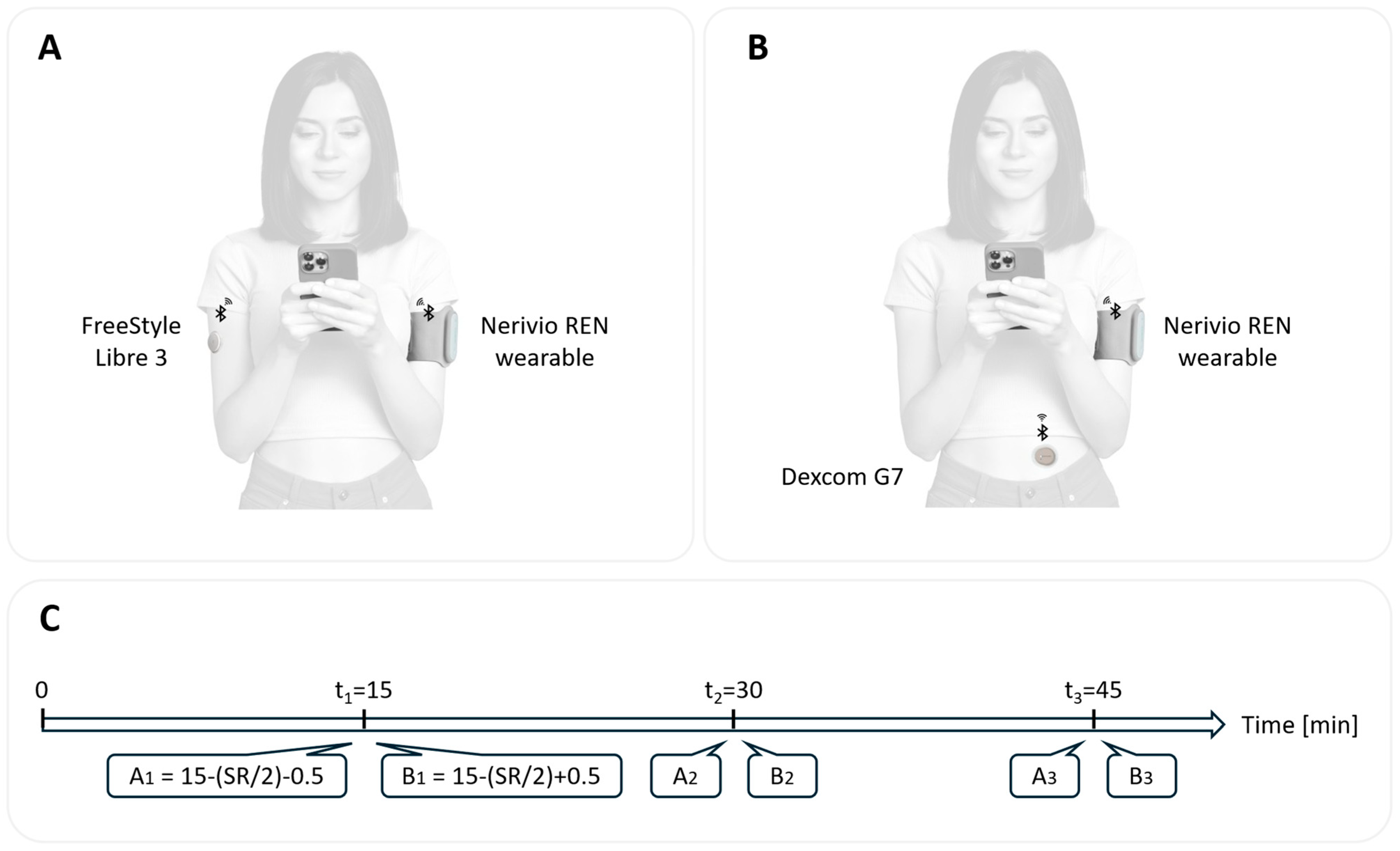
2.4. Study Devices
2.5. Study Procedures
2.6. Outcome Measures
2.7. Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
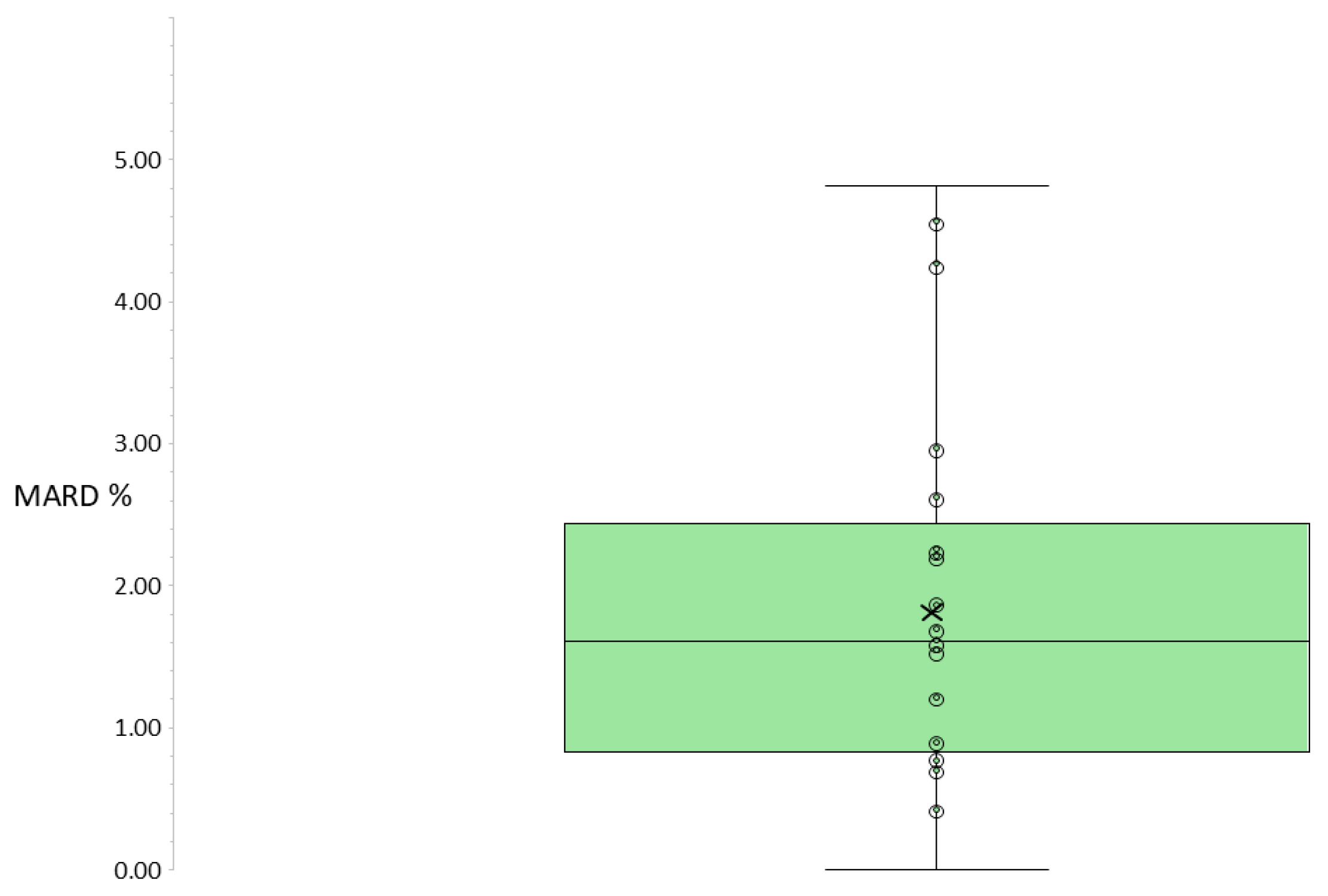
3.2. Primary Outcome: Median MARDREN ON/OFF Across All Participants
3.3. Secondary Outcome: Proportion of Participants with MARDREN ON/OFF < 5%
3.4. Exploratory Subgroup Analysis by Device Family
3.5. Technical and Safety Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings
4.2. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.3. Clinical Implications
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, S.; Qian, G.; Huang, H.; Fu, H. Global trends and future projections of migraine burden in children aged 5 to 14 from 1990 to 2050. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1641599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, W.-S.; Nguyen, V.K.; Chu, M.K. Epidemiological linkage between migraine and diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Headache Pain 2024, 25, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, B.B.; Magliano, D.J.; Boyko, E.J. IDF Diabetes Atlas 11th edition 2025: Global prevalence and projections for 2050. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2025, 41, gfaf177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Manack, A.; Serrano, D.; Turkel, C.; Lipton, R.B. Sociodemographic and comorbidity profiles of chronic migraine and episodic migraine sufferers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Nyholt, D.R. Glucose-Related Traits and Risk of Migraine—A Potential Mechanism and Treatment Consideration. Genes 2022, 13, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Mancilla, E.; Al-Hassany, L.; Villalón, C.M.; Maassen Van Den Brink, A. Metabolic Aspects of Migraine: Association with Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 686398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruijn, N.; Van Lohuizen, R.; Boron, M.; Fitzek, M.; Gabriele, F.; Giuliani, G.; Melgarejo, L.; Řehulka, P.; Sebastianelli, G.; Triller, P.; et al. Influence of metabolic state and body composition on the action of pharmacological treatment of migraine. J. Headache Pain 2024, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Xu, Y.; Ballew, S.H.; Coresh, J.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Selvin, E.; Shin, J.-I. Trends and Disparities in Technology Use and Glycemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2526353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022 Abridged for Primary Care Providers. Clin. Diabetes 2022, 40, 10–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhu, J. A Wearable Integrated Microneedle Electrode Patch for Exercise Management in Diabetes. Research 2024, 7, 0508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnitsky, D.; Dodick, D.W.; Grosberg, B.M.; Burstein, R.; Ironi, A.; Harris, D.; Lin, T.; Silberstein, S.D. Remote Electrical Neuromodulation (REN) Relieves Acute Migraine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Trial. Headache 2019, 59, 1240–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, S.J.; Rabany, L.; Cowan, R.P.; Smith, T.R.; Grosberg, B.M.; Torphy, B.D.; Harris, D.; Vizel, M.; Ironi, A.; Stark-Inbar, A.; et al. Remote electrical neuromodulation for migraine prevention: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Headache 2023, 63, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, M.-P.; Ouellet, S.; Attisso, E.; Supper, W.; Amil, S.; Rhéaume, C.; Paquette, J.-S.; Chabot, C.; Laferrière, M.-C.; Sasseville, M. Wearable Devices for Supporting Chronic Disease Self-Management: Scoping Review. Interact. J. Med. Res. 2024, 13, e55925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafleh, E.A.; Alnaqbi, F.A.; Almaeeni, H.A.; Faqeeh, S.; Alzaabi, M.A.; Al Zaman, K. The Role of Wearable Devices in Chronic Disease Monitoring and Patient Care: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e68921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Applying Human Factors and Usability Engineering to Medical Devices: Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/MedicalDevices/DeviceRegulationandGuidance/GuidanceDocuments/UCM484097.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2026).
- Reddy, N.; Verma, N.; Dungan, K. Monitoring Technologies- Continuous Glucose Monitoring, Mobile Technology, Biomarkers of Glycemic Control. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279046/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Funtanilla, V.D.; Candidate, P.; Caliendo, T.; Hilas, O. Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Review of Available Systems. Pharm. Ther. 2019, 44, 550–553. [Google Scholar]
- Reiterer, F.; Polterauer, P.; Schoemaker, M.; Schmelzeisen-Redecker, G.; Freckmann, G.; Heinemann, L.; Del Re, L. Significance and Reliability of MARD for the Accuracy of CGM Systems. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigersky, R.A.; Shin, J. The Myth of MARD (Mean Absolute Relative Difference): Limitations of MARD in the Clinical Assessment of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2024, 26, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freckmann, G.; Mende, J.; Pleus, S.; Waldenmaier, D.; Baumstark, A.; Jendrike, N.; Haug, C. Mean Absolute Relative Difference of Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems and Relationship to ISO 15197. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2022, 16, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropff, J.; Bruttomesso, D.; Doll, W.; Farret, A.; Galasso, S.; Luijf, Y.M.; Mader, J.K.; Place, J.; Boscari, F.; Pieber, T.R.; et al. Accuracy of two continuous glucose monitoring systems: A head-to-head comparison under clinical research centre and daily life conditions. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services. 21 CFR 862.1355—Integrated Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-H/part-862/subpart-B/section-862.1355 (accessed on 20 January 2026).
- Bailey, T.S.; Alva, S. Landscape of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and Integrated CGM: Accuracy Considerations. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2021, 23, S5–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.; Oliver, N. The role of real-time continuous glucose monitoring in diabetes management and how it should link to integrated personalized diabetes management. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidman, S.; Kainz, W.; Ruggera, P.; Mendoza, G. Wireless Coexistence and EMC of Bluetooth and 802.11b Devices in Controlled Laboratory Settings. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2011, 5, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Al Kalaa, M.O.; Guag, J.; Seidman, S.J.; Ma, Y.; Coder, J. A Case Study of Medical Device Wireless Coexistence Evaluation. IEEE Electromagn. Compat. Mag. 2020, 9, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinemann, L.; Schoemaker, M.; Schmelzeisen-Redecker, G.; Hinzmann, R.; Kassab, A.; Freckmann, G.; Reiterer, F.; Del Re, L. Benefits and Limitations of MARD as a Performance Parameter for Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Interstitial Space. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2020, 14, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Slama, M.Q.; Nicholson, W.T.; Langman, L.; Peyser, T.; Carter, R.; Basu, R. Continuous Glucose Monitor Interference with Commonly Prescribed Medications: A Pilot Study. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Digital Health Technologies for Remote Data Acquisition in Clinical Investigations; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/digital-health-technologies-remote-data-acquisition-clinical-investigations (accessed on 14 January 2026).
| Gender | Age | Race | CGM Type | CGM Location | Diabetes Type | Smartphone Type | Time Wearing CGM Sensor Prior to Trial | HbA1c Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 66 | Caucasian | Dexcom G6 | Abdomen | Type 2 | Android | 3–6 days | 7.1 |
| Female | 60 | Caucasian | Dexcom G6 | Upper arm | Type 2 | iOS | 3–6 days | 5.4 |
| Female | 34 | Hispanic, Latino | Dexcom G7 | Abdomen | Type 2 | Android | <3 days | N/A |
| Female | 40 | Black or African American | Dexcom G7 | Upper arm | Type 2 | Android | <3 days | 5.6 |
| Female | 36 | Black or African American | Dexcom G7 | Abdomen | Type 2 | Android | <3 days | 6.9 |
| Female | 49 | Caucasian | Dexcom G7 | Upper arm | Type 1 | Android | 3–6 days | 7.6 |
| Female | 51 | Caucasian | Dexcom G7 | Abdomen | Type 1 | iOS | 3–6 days | 7.1 |
| Male | 58 | Caucasian | Dexcom G7 | Upper arm | Type 2 | iOS | 3–6 days | 6.5 |
| Male | 31 | Asian | Dexcom G7 | Abdomen | Type 1 | iOS | <3 days | 7.5 |
| Male | 58 | Caucasian | Dexcom G7 | Upper arm | Type 2 | iOS | <3 days | 6.0 |
| Female | 53 | Caucasian | Dexcom G7 | Abdomen | Type 1 | iOS | <3 days | 6.4 |
| Male | 77 | Caucasian | Dexcom G7 | Upper arm | Type 1 | iOS | <3 days | N/A |
| Female | 42 | Caucasian | Dexcom G7 | Upper arm | Type 1 | iOS | 7–9 days | 6.2 |
| Female | 47 | Caucasian | Dexcom G7 | Upper arm | Type 1 | iOS | <3 days | 6.2 |
| Male | 45 | Caucasian | Dexcom G7 | Abdomen | Type 1 | iOS | <3 days | 6.1 |
| Female | 56 | Caucasian | FreeStyle Libre 2 | Upper arm | Type 2 | Android | <3 days | 6.8 |
| Male | 47 | Caucasian | FreeStyle Libre 3 | Upper arm | Type 2 | Android | <3 days | N/A |
| Male | 42 | Hispanic, Latino | FreeStyle Libre 3 | Upper arm | Type 2 | iOS | 3–6 days | N/A |
| Male | 53 | Asian | FreeStyle Libre 3 | Abdomen | Type 2 | iOS | 10–13 days | 6.6 |
| Male | 60 | Caucasian | FreeStyle Libre 3 | Upper arm | Type 2 | iOS | 3–6 days | 7.9 |
| Female | 43 | Caucasian | FreeStyle Libre 3 | Upper arm | Type 1 | iOS | 10–13 days | 6.2 |
| CGM Type | A1 REN ON (mg/dL) | B1 REN OFF (mg/dL) | ARD1 (%) | A2 REN ON (mg/dL) | B2 REN OFF (mg/dL) | ARD2 (%) | A3 REN ON (mg/dL) | B3 REN OFF (mg/dL) | ARD3 (%) | MARD REN ON/OFF % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dexcom G6 | 154 | 156 | 1.28 | 159 | 159 | 0.00 | 160 | 160 | 0.00 | 0.43 |
| Dexcom G6 | 106 | 107 | 0.93 | 108 | 109 | 0.92 | 108 | 109 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| Dexcom G7 | 112 | 113 | 0.88 | 113 | 118 | 4.24 | 118 | 118 | 0.00 | 1.71 |
| Dexcom G7 | 115 | 114 | 0.88 | 113 | 112 | 0.89 | 110 | 109 | 0.92 | 0.90 |
| Dexcom G7 | 115 | 115 | 0.00 | 117 | 117 | 0.00 | 115 | 115 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Dexcom G7 | 127 | 130 | 2.31 | 144 | 153 | 5.88 | 187 | 176 | 6.25 | 4.81 |
| Dexcom G7 | 144 | 150 | 4.00 | 152 | 153 | 0.65 | 146 | 146 | 0.00 | 1.55 |
| Dexcom G7 | 116 | 122 | 4.92 | 134 | 142 | 5.63 | 153 | 158 | 3.16 | 4.57 |
| Dexcom G7 | 228 | 225 | 1.33 | 220 | 213 | 3.29 | 203 | 205 | 0.98 | 1.87 |
| Dexcom G7 | 96 | 95 | 1.05 | 92 | 90 | 2.22 | 91 | 87 | 4.60 | 2.62 |
| Dexcom G7 | 78 | 74 | 5.41 | 72 | 73 | 1.37 | 72 | 72 | 0.00 | 2.26 |
| Dexcom G7 | 74 | 81 | 8.64 | 99 | 100 | 1.00 | 100 | 97 | 3.09 | 4.24 |
| Dexcom G7 | 160 | 164 | 2.44 | 151 | 148 | 2.03 | 141 | 138 | 2.17 | 2.21 |
| Dexcom G7 | 152 | 153 | 0.65 | 150 | 151 | 0.66 | 139 | 139 | 0.00 | 0.44 |
| Dexcom G7 | 114 | 117 | 2.56 | 117 | 120 | 2.50 | 125 | 125 | 0.00 | 1.69 |
| FreeStyle Libre 2 | 164 | 160 | 2.50 | 166 | 167 | 0.60 | 169 | 172 | 1.74 | 1.61 |
| FreeStyle Libre 3 | 154 | 157 | 1.91 | 173 | 175 | 1.14 | 166 | 167 | 0.60 | 1.22 |
| FreeStyle Libre 3 | 89 | 88 | 1.14 | 86 | 86 | 0.00 | 85 | 86 | 1.16 | 0.77 |
| FreeStyle Libre 3 | 141 | 142 | 0.70 | 143 | 142 | 0.70 | 143 | 142 | 0.70 | 0.70 |
| FreeStyle Libre 3 | 225 | 228 | 1.32 | 221 | 221 | 0.00 | 208 | 205 | 1.46 | 0.93 |
| FreeStyle Libre 3 | 99 | 100 | 1.00 | 91 | 95 | 4.21 | 84 | 81 | 3.70 | 2.97 |
| Median | 1.61 | |||||||||
| IQR | 0.84–2.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Asmar, Y.; Stark-Inbar, A.; Wilson, M.C.; Podraza, K.; Treppendahl, C.; Demirci, C.; deMayo, R. Simultaneous Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems and the Remote Electrical Neuromodulation (REN) Wearable for Patients with Comorbid Diabetes and Migraine: An Interventional Single-Arm Compatibility Study. J. Clin. Med. 2026, 15, 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15031097
Asmar Y, Stark-Inbar A, Wilson MC, Podraza K, Treppendahl C, Demirci C, deMayo R. Simultaneous Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems and the Remote Electrical Neuromodulation (REN) Wearable for Patients with Comorbid Diabetes and Migraine: An Interventional Single-Arm Compatibility Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2026; 15(3):1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15031097
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsmar, Yara, Alit Stark-Inbar, Maria Carmen Wilson, Katherine Podraza, Christina Treppendahl, Cem Demirci, and Richelle deMayo. 2026. "Simultaneous Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems and the Remote Electrical Neuromodulation (REN) Wearable for Patients with Comorbid Diabetes and Migraine: An Interventional Single-Arm Compatibility Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 15, no. 3: 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15031097
APA StyleAsmar, Y., Stark-Inbar, A., Wilson, M. C., Podraza, K., Treppendahl, C., Demirci, C., & deMayo, R. (2026). Simultaneous Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems and the Remote Electrical Neuromodulation (REN) Wearable for Patients with Comorbid Diabetes and Migraine: An Interventional Single-Arm Compatibility Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 15(3), 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15031097






