Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring in Full-Endoscopic Cervical Endoscopic ULBD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Retrospective Evaluation
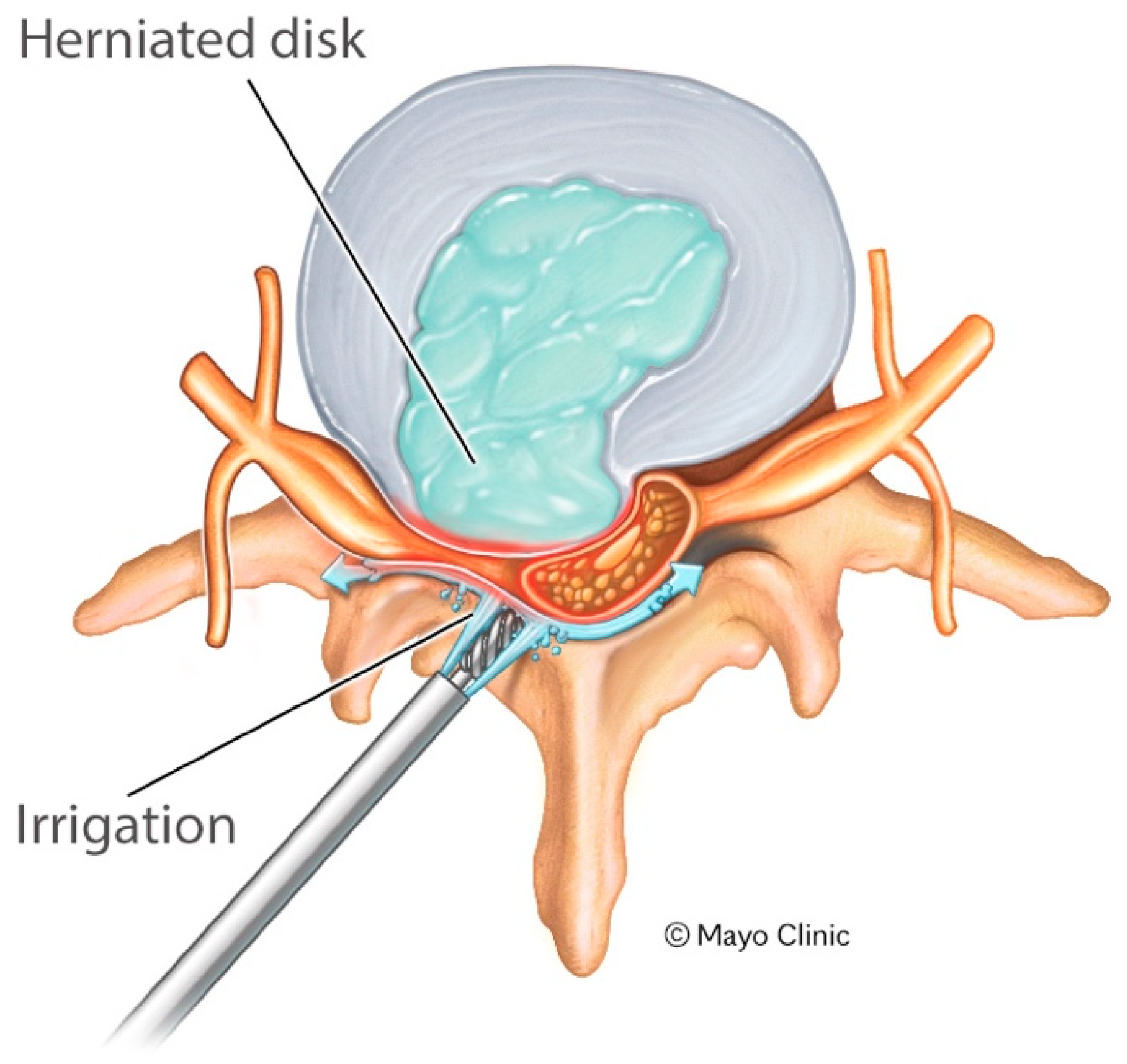
2.3. Surgical Technique
2.4. Neuromonitoring Reports
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CE-ULBD | Cervical Endoscopic Unilateral Laminotomy for Bilateral Decompression |
| IONM | Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| MEP | Motor Evoked Potential |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| mJOA | Modified Japanese Orthopedic Association (score) |
References
- Foley, T.K.; Smith, M.M. Micro Endoscopic Discectomy (MED). Tech. Neurosurg. 1997, 3, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, A.T. The Evolution and Advancement of Endoscopic Foraminal Surgery: One Surgeon’s Experience Incorporating Adjunctive Techologies. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2007, 1, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konakondla, S.; Sofoluke, N.; Xia, J.; Grant, R.; Telfeian, A.E.; Hofstetter, C.P.; Slotkin, J.R. Transforaminal Endoscopic Approach for Large-Sample Tumor Biopsy using Beveled Working Channel for Core Technique: A Technical Note. World Neurosurg. 2020, 141, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruetten, S.; Komp, M.; Merk, H.; Godolias, G. Use of newly developed instruments and endoscopes: Full-endoscopic resection of lumbar disc herniations via the interlaminar and lateral transforaminal approach. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2007, 6, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.; Lee, S.H.; Raiturker, P.P.; Lee, S.; Chae, Y.S. Percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for intracanalicular disc herniations at L5-S1 using a rigid working channel endoscope. Neurosurgery 2006, 58, ONS59-68, discussion ONS59-68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.T.; Choi, K.C.; Shim, H.K.; Lee, D.C.; Kim, J.S. Full-endoscopic versus microscopic unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis at L4–L5: Comparative study. Int. Orthop. 2022, 46, 2887–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, L.B.; White-Dzuro, G.A.; Hofstetter, C.P. Comparison of clinical outcomes following minimally invasive or lumbar endoscopic unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 30, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitha, R.; Mahan, M.A.; Patel, R.P.; Colan, J.A.; Leyendecker, J.; Zaki, M.M.; Harake, E.S.; Kathawate, V.; Kashlan, O.; Konakondla, S.; et al. Lumbar Endoscopic Unilateral Laminectomy for Bilateral Decompression in Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. World Neurosurg. 2024, 191, e644–e651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, D.C.; Rogers-LaVanne, M.P.; Satin, A.M.; Yap, N.; Khan, I.; Kim, P.; Hofstetter, C.P.; Derman, P.B. Learning curve for endoscopic posterior cervical foraminotomy. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 32, 2670–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, D.A.; Abecassis, I.J.; Hofstetter, C.P. Full endoscopic unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of the cervical spine: Surgical technique and early experience. J. Spine Surg. 2020, 6, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyendecker, J.; Prasse, T.; Park, C.; Köster, M.; Rumswinkel, L.; Shenker, T.; Bieler, E.; Eysel, P.; Bredow, J.; Zaki, M.M.; et al. 90-Day Emergency Department Utilization and Readmission Rate After Full-Endoscopic Spine Surgery: A Multicenter, Retrospective Analysis of 821 Patients. Neurosurgery 2024, 96, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju CIl Kim, P.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.M. Complications of Cervical Endoscopic Spinal Surgery: A Systematic Review and Narrative Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2023, 178, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandrowski, K.U.; Telfeian, A.E.; Hellinger, S.; León, J.F.R.; de Carvalho, P.S.T.; Ramos, M.R.; Kim, H.S.; Hanson, D.W.; Salari, N.; Yeung, A. Difficulties, Challenges, and the Learning Curve of Avoiding Complications in Lumbar Endoscopic Spine Surgery. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2021, 15, S21–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Koh, Y.H.; Hur, S.; Kim, S.J.; Chai, J.W.; Kang, H.S. New MRI grading system for the cervical canal stenosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, W134–W140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Hofstetter, C.P.; Wang, M.Y. Innovations in Spinal Endoscopy. World Neurosurg. 2022, 160, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, S.N.; Dinh, H.T. The first experience with fully endoscopic posterior cervical foraminotomy and discectomy for radiculopathy performed in Viet Duc University Hospital. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodwad, S.J.M.; Dodwad, S.N.M.; Prasarn, M.L.; Savage, J.W.; Patel, A.A.; Hsu, W.K. Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy Indications, Technique, and Outcomes. Clin. Spine Surg. 2016, 29, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovrlj, B.; Gologorsky, Y.; Haque, R.; Fessler, R.G.; Qureshi, S.A. Complications, outcomes, and need for fusion after minimally invasive posterior cervical foraminotomy and microdiscectomy. Spine J. 2014, 14, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Huang, X.; Yu, J.; Ye, X. Posterior Percutaneous Endoscopic Cervical Diskectomy: A Single-Center Experience of 252 Cases. World Neurosurg. 2018, 120, e63–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.I.; Lee, S.M. Complications and Management of Endoscopic Spinal Surgery. Neurospine 2023, 20, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Wu, P.H.; Jang, I.T. Lumbar Endoscopic Unilateral Laminotomy for Bilateral Decompression Outside-In Approach: A Proctorship Guideline With 12 Steps of Effectiveness and Safety. Neurospine 2020, 17, S99–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, J.H.; Heo, D.H.; Son, S.K.; Park, C.K. Percutaneous biportal endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: A technical note and preliminary clinical results. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 24, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.; Kang, H.Y.; Modi, H.N.; Prada, N.; Nicolau, R.J.; Joh, J.Y.; Pan, W.J.; Lee, S.-H. Risk of Developing Seizure After Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2011, 24, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haijun, M.; Xiaobing, Z.; Bin, G.; Jinwen, H.; Dacheng, Z.; Shenghong, W.; Honggang, Z.; Yayi, X. Trans-interlamina percutaneous endoscopic cervical discectomy for symptomatic cervical spondylotic radiculopathy using the new Delta system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.-M.; Yu, K.-X.; Deng, R.; Long, Q.-Y.; Chu, L.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, B.; Chen, L.; Yan, Z.-J.; Deng, Z.-L. Comparative Review Modified K-Hole Percutaneous Endoscopic Surgery for Cervical Foraminal Stenosis: Partial Pediculectomy Approach. Pain Physician 2019, 22, E407–E416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, A.; Chabbra, R.P.; Mehta, V.S.; Gaikwad, S.; Pandey, R.M. Effect of intramedullary signal changes on the surgical outcome of patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine J. 2003, 3, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedantam, A.; Rajshekhar, V. Does the type of T2-weighted hyperintensity influence surgical outcome in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy? A review. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Grade 0 | No Stenosis | |
|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Mild Stenosis | >50% thecal Sac compression without cord deformity |
| Grade 2 | Moderate Stenosis | Cord Deformity without signal Change |
| Grade 3 | Severe Stenosis | Cord Signal Change |
| Demographic | Result |
|---|---|
| Male | 23 (69.7%) |
| Female | 10 (30.3%) |
| Mean Age (years) | |
| Male | 69.13 ± 2.1 |
| Female | 72.5 ± 2.9 |
| BMI Mean | 29.6 ± 1.1 |
| Primary Pre-op Diagnosis | |
| Cervical Stenosis | 33 |
| Preoperative Weakness | |
| Yes | 20 (60.6%) |
| No | 13 (39.4%) |
| Operative Data | Result |
|---|---|
| Number of Operative Levels | |
| One | 16 |
| Two | 14 |
| Three | 2 |
| Four | 1 |
| Average Time per level (min) | 91.8 |
| Average Blood Loss (mL) | 9.5 |
| CE-ULBD Procedural Levels | |
| C2-C3 | 2 |
| C3-C4 | 20 |
| C4-C5 | 13 |
| C5-C6 | 9 |
| C6-C7 | 10 |
| Total | 54 |
| New Post-Procedural Weakness | |
| Yes | 4 (12.1%) |
| Mean blood loss (mL) | 6.75 |
| Time per Level (min) | 75 |
| No | 28 (82.4%) |
| Mean blood loss (mL) | 9.9 |
| Time per level (min) | 94.1 |
| Highest Degree of Stenosis Per Patient | Patients With New Post-Op Weakness | |
|---|---|---|
| Central Stenosis | ||
| Grade 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Grade 2 | 11 | 0 |
| Grade 3 | 21 | 4 (19%) |
| Surgical Levels | Pre-Operative Weakness | Stenosis Grade | Pre-Operative Exam | Two-Week Post-Operative Exam |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3-C5 | No | 3 | Intact | Right: 4+/5 Bicep, 4+/5 Triceps, Remainder Intact Left: Intact |
| C3-C4 | Yes | 3 | 3+/5 Bilateral Upper extremities 4/5 bilateral dorsiflexion, plantar flexion, knee hip flexion Left Knee flexion 3+/5, Right Knee flexion 4/5 | Right: 2/5 deltoids, 3/5 triceps, 3+/5 biceps, 0/5 intrinsics, 0/5 grip. 3+/5 dorsiflexion, 4/5 knee flexion, knee extension and hip flexion. Left: 3+/5 deltoids, 3+/5 triceps, 3+/5 biceps, 3+/5 intrinsics, 2/5 grip. 4/5 in left dorsiflexion. 4/5 knee flexion, knee extension and hip flexion |
| C3-C5 | No | 3 | Intact | Right: Intact Left 4+/5 deltoid, Remainder of exam intact |
| C3-C4 | Yes | 3 | Right: Bicep 4/5, Triceps 4/5, Deltoid 4/5, 4+/5 Hand intrinsics, Remainder of exam intact Left: 5/5 except Hand intrinsics 3/5 | Right: Bicep 4/5, Triceps 3/5, Deltoid 2/5. Wrist extension 5/5, Flexor Digitorum Profundus 4/5, Abductor Digiti Minimi 2/5, Remainder of exam intact Left: Bicep 2/5, Triceps 2/5, Deltoid 2/5, Wrist extension 2/5, Flexor Digitorum Profundus 4/5, Abductor Digiti Minimi 2/5, Remainder of exam intact |
| Procedure | Procedural Level | Pre-Op Weakness | Highest Stenosis Grade | Intra-Op IONM Results | New Post-Op Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE-ULBD | C3-C4 | Yes | 3 | Sustained MEP Decreased | Yes |
| CE-ULBD | C3-C5 | No | 3 | Sustained MEP Decrease | Yes |
| CE-ULBD | C3-C5 | No | 3 | Sustained MEP Decrease | Yes |
| CE-ULBD | C3-C4 | Yes | 3 | Sustained MEP Decrease | Yes |
| CE-ULBD | C4-C5 | No | 3 | Sustained MEP-Decrease | No |
| CE-ULBD | C4-C5 | Yes | 3 | Temporary MEP Decrease | No |
| CE-ULBD | C3-C5 | Yes | 3 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C3-C5 | Yes | 3 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C2-C3 | No | 2 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C3-C5 | Yes | 2 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C5-C7 | Yes | 2 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C5-C7 | Yes | 3 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C3-C4 | Yes | 3 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C6-C7 | No | 3 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C3-C4 | Yes | 1 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C4-C7 | No | 2 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C4-C6 | No | 3 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C3-C6 | No | 2 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C5-C7 | Yes | 2 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C3-C4, C6-C7 | No | 2 | EMG Firing | No |
| CE-ULBD | C5-C7 | Yes | 3 | EMG Firing | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Hudson, M.; Esposito, S.; Zaki, M.M.; Glynn, S.M.; Kashlan, O.N.; Ogunlade, J.; Krishna, C.; Bakhsheshian, J.; Hofstetter, C.P. Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring in Full-Endoscopic Cervical Endoscopic ULBD. J. Clin. Med. 2026, 15, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010327
Hudson M, Esposito S, Zaki MM, Glynn SM, Kashlan ON, Ogunlade J, Krishna C, Bakhsheshian J, Hofstetter CP. Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring in Full-Endoscopic Cervical Endoscopic ULBD. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2026; 15(1):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010327
Chicago/Turabian StyleHudson, Miles, Sarah Esposito, Mark M. Zaki, Simon M. Glynn, Osama N. Kashlan, John Ogunlade, Chandan Krishna, Joshua Bakhsheshian, and Christoph P. Hofstetter. 2026. "Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring in Full-Endoscopic Cervical Endoscopic ULBD" Journal of Clinical Medicine 15, no. 1: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010327
APA StyleHudson, M., Esposito, S., Zaki, M. M., Glynn, S. M., Kashlan, O. N., Ogunlade, J., Krishna, C., Bakhsheshian, J., & Hofstetter, C. P. (2026). Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring in Full-Endoscopic Cervical Endoscopic ULBD. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 15(1), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010327






