High Tibial Osteotomy Is Associated with Improvements in Both Knee and Ankle Alignment in Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Preoperative Assessment and Surgical Procedure
2.3. Clinical and Radiological Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOFAS | American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society |
| HKA | Hip–knee–ankle angle |
| LDTA | Lateral distal tibial angle |
| JLCA | Joint line convergence angle |
| MPTA | Medial proximal tibial angle |
| MOWHTO | Medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy |
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| TKA | Total knee arthroplasty |
References
- Van Oevelen, A.; Burssens, A.; Krähenbühl, N.; Barg, A.; Bevernage, B.D.; Audenaert, E.; Hintermann, B.; Victor, J. Osteotomies around the knee alter alignment of the ankle and hindfoot: A systematic review of biomechanical and clinical studies. EFORT Open Rev. 2023, 8, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agneskirchner, J.D.; Hurschler, C.; Wrann, C.D.; Lobenhoffer, P. The effects of valgus medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy on articular cartilage pressure of the knee: A biomechanical study. Arthroscopy 2007, 23, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.H.; Wang, H.-Y.; Tzeng, S.-C.; Hsu, K.-H.; Wang, J.-H. Knee-ankle joint line angle: A significant contributor to high-degree knee joint line obliquity in medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maione, A.; Minoli, C.; Parmigiani, M.D.; Travi, M.; Calanna, F.; Marcolli, D.; Compagnoni, R.; Ferrua, P.; Berruto, M.; Randelli, P.S. Knee osteotomies significantly influence coronal ankle alignment: A radiographic analysis. J. Exp. Orthop. 2025, 12, e70252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.O.; Kim, T.Y.; Baek, J.H.; Jung, H.; Song, S.H. Following the correction of varus deformity of the knee through total knee arthroplasty, significant compensatory changes occur not only at the ankle and subtalar joint, but also at the foot. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 3230–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, T.; Ikoma, K.; Ohashi, S.; Arai, Y.; Hara, Y.; Ueshima, K.; Sawada, K.; Shirai, T.; Fujiwara, H.; Kubo, T. Hindfoot alignment at one year after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 2442–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Ma, J.; Sun, W.; Guo, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, W. Radiographic assessment of knee-ankle alignment after total knee arthroplasty for varus and valgus knee osteoarthritis. Knee 2017, 24, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.K.; Bansal, S.; Pranav, J.; Raja, B.S.; Gupta, T.; Paul, S.; Gupta, K.; Kalia, R.B. Increased medial talar tilt may incite ankle pain and predispose ankle osteoarthritis after correction of severity of knee varus deformity among patients undergoing bilateral total knee arthroplasty: A prospective observation. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2024, 36, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Lee, S.C.; Jin, H.; Ahn, H.S.; Nam, C.H. Open-wedge high tibial osteotomy for the treatment of osteoarthritis of both knee and ankle in the same leg: A report of two cases. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e04140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.M.; Aidenlou, A.; Qoreishi, M.; Minaie, R. High Tibial Osteotomy Effects on Subtalar Joint in Patients with Genu Varum. Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2022, 10, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev, G.P.; Telang, M.; Landzhov, B.; Olewnik, Ł.; Slavchev, S.A.; LaPrade, R.F.; Ruzik, K.; Tubbs, R.S. The novel epiligament theory: Differences in healing failure between the medial collateral and anterior cruciate ligaments. J. Exp. Orthop. 2022, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, F.; Takagi, H. Evaluation of postoperative orientation of the knee and ankle joint after open wedge high tibial osteotomy. Asia Pac. J. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rehabil. Technol. 2022, 29, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.W.; Yang, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Yun, H.H.; Lee, Y.I.; Chae, J.E.; Yoon, J.R. Changes in coronal alignment of the ankle joint after high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, A.; Dincel, Y.M.; Cetin, M.U.; Kilinc, S.; Gunaydin, B.; Ozdemir, M. Comparison of changes in the ankle after unicondylar knee arthroplasty and high tibial osteotomy. Acta Ortop. Bras. 2022, 30, e245842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivoto, T.; Lúcio, A.D. Metan: An R package for multi-environment trial analysis. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, M.D.; M’BArki, H.; Haque, O.; Vincent, A.; Abouali, J.; Belzile, E.L.; Matache, B.A. High Tibial Osteotomy Improves Function and Alignment in Patients Above and Below 50 Years: A Systematic Review. J. Orthop. Rep. 2025, 100789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suero, E.M.; Sabbagh, Y.; Westphal, R.; Hawi, N.; Citak, M.; Wahl, F.M.; Krettek, C.; Liodakis, E. Effect of medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy on intraarticular knee and ankle contact pressures. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyung, M.G.; Cho, Y.J.; Hwang, S.; Lee, M.C.; Lee, D.Y. Change in intersegmental foot and ankle motion after a high tibial osteotomy in genu varum patients. J. Orthop. Res. 2021, 39, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.M.; Roberts, J.; Picard, F. Ankle and Hindfoot Symptoms after Medial Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. J. Knee Surg. 2019, 32, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, M.; Mohammed, A.L.S.; Elsheikh, A.; Ahmed, M.A. Ankle pain and orientation after high tibial osteotomy as a treatment of medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. SICOT J 2025, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.O.; SooHoo, N.F. Ankle Deformity After High Tibial Osteotomy for Correction of Varus Knee: A Case Report. Foot Ankle Int. 2014, 35, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.H.; Seo, K.D.; Yoo, H.J.; Jang, M.G.; Park, J.S.; Song, J.H. Effects of high tibial osteotomy on the coronal, sagittal, and axial alignments of the ankle joint. J. Orthop. Surg. 2024, 32, 10225536241273889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
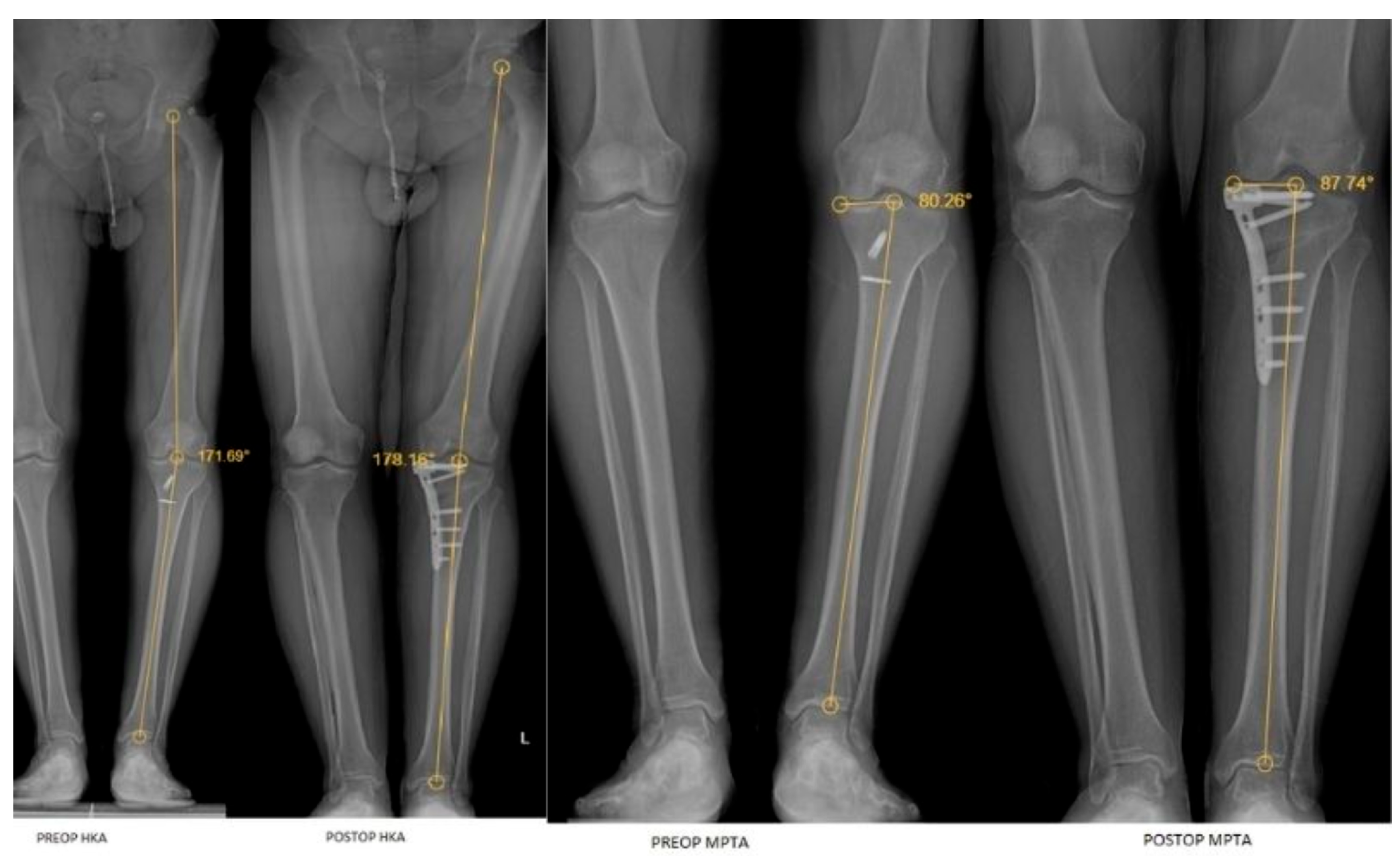
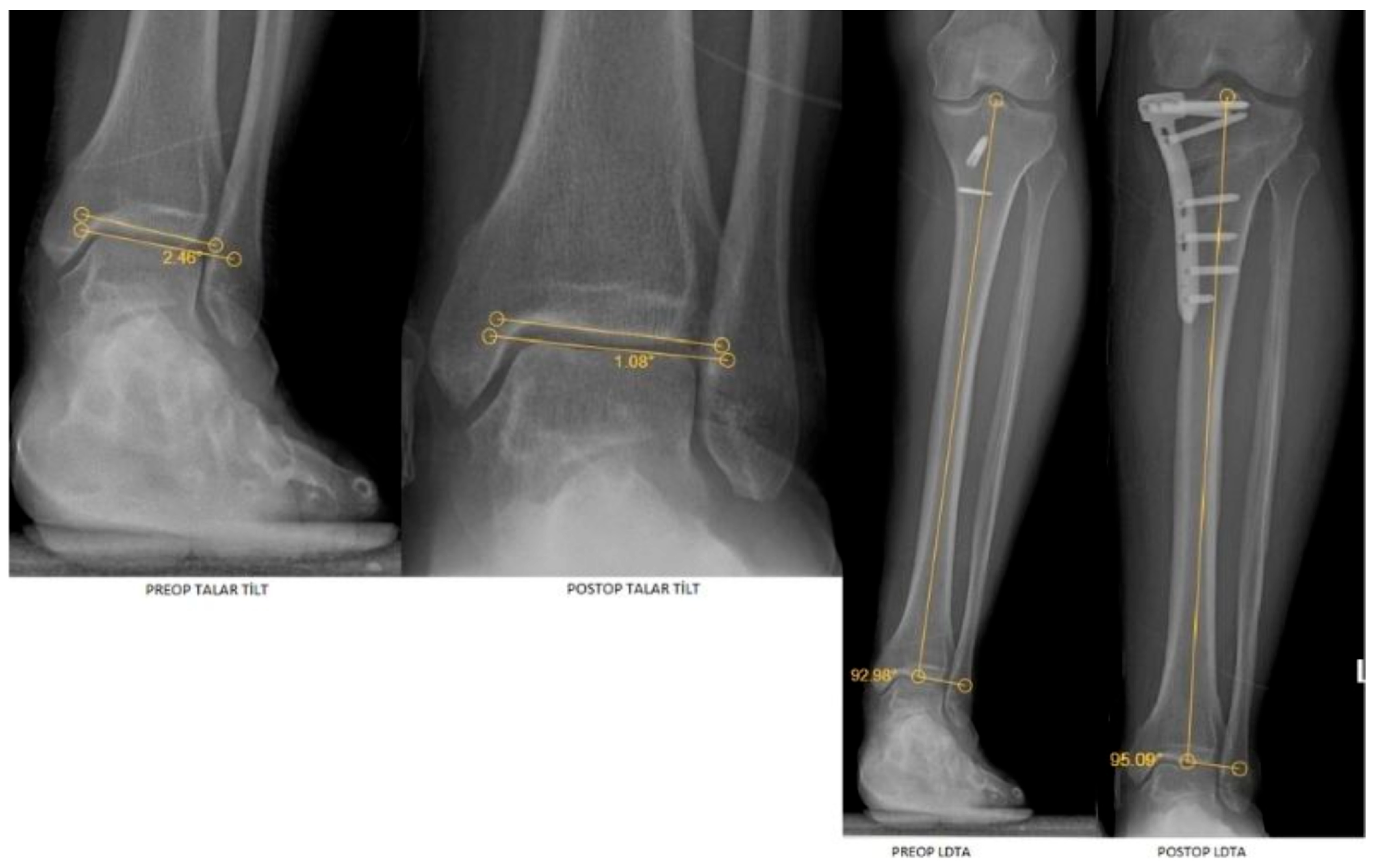
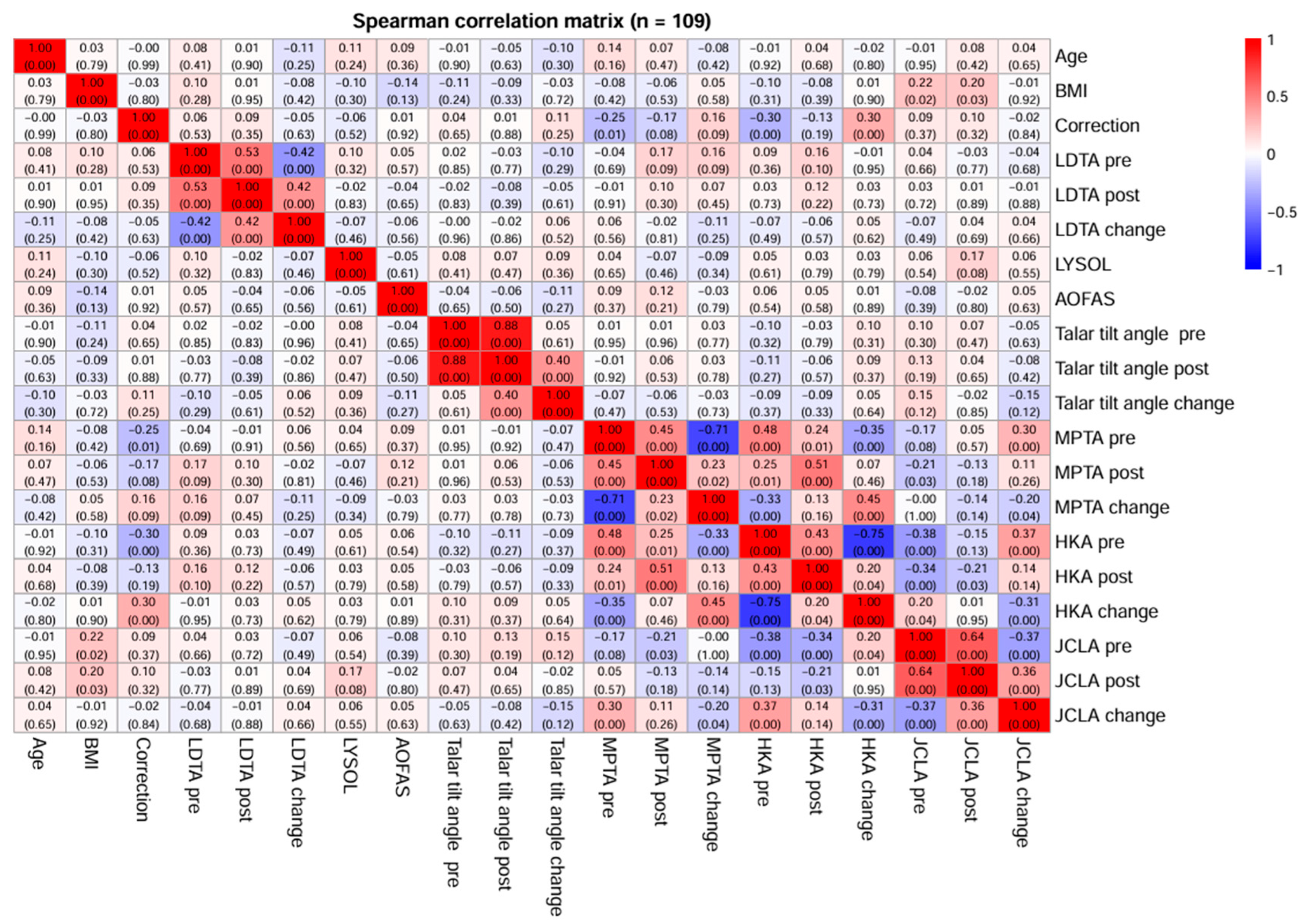
| Variables | Participants (n = 110) | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 28 (25.5%) |
| Female | 82 (74.54%) | |
| Side | Right | 46 (41.81%) |
| Left | 64 (58.2%) | |
| Kellgren–Lawrence | 2 | 36 (32.7%) |
| 3 | 71 (64.5%) | |
| 4 | 3 (2.7%) | |
| Age | 52 (11) | |
| Body Mass Index | 29.4 (4) | |
| Correction (mm) | 10 (2) | |
| Baseline | Postop 1 Year | p-Value | Effect Size | ICC (95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDTA | 87.25 (2.76) | 88.14 (2.24) | 0.018 a | 0.225 | 0.690 (0.577–0.776) |
| MPTA | 83 (4.53) | 87.40 (2.71) | <0.001 a | 0.838 | 0.441 (0.277–0.579) |
| HKA | 171.44 ± 3.35 | 177.11 ± 2.32 | <0.001 b | −1.804 | 0.404 (0.235–0.549) |
| JLCA | 3.18 (1.94) | 1.95 (1.12) | <0.001 a | 0.798 | 0.692 (0.580–0.778) |
| Talar tilt | 0.85 (0.51) | 0.70 (0.52) | <0.001 a | 0.752 | 0.863 (0.806–0.904) |
| Variables | <10 mm (n = 50) | 10 mm (n = 60) | 95% CI (Mean Difference) | p-Value | Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 52.50 (13) | 52 (10) | 1.0 (−2.0–4.0) | 0.467 a | 0.069 |
| BMI | 29.15 (4.5) | 29.55 (3.5) | −2.34 × 10−5 (−1.00–0.90) | 0.993 a | 0.000 |
| Gender Male Female | 9 (18%) 41 (82%) | 19 (31.7%) | - | 0.156 b | −0.156 |
| Kellgren grade 2 3 4 | 18 (36%) 30 (60%) 2 (4%) | 18 (30%) 41 (68.3%) 1 (1.7%) | - | 0.601 c | 0.102 |
| AOFAS | 100 (3) | 100 (10) | −1.68 × 10−5 (−8.18 × 10−6–3.83 × 10−5) | 0.861 a | 0.017 |
| LYSHOLM | 90 (19) | 90 (23) | 4.15 × 10−5 (−3–4) | 0.880 a | 0.014 |
| JCLA_percent change | −36.26 (26.19) | −37.07 (26.74) | 1.129 (−7.850–8.130) | 0.785 a | 0.026 |
| LDTA_percent change | 0.55 (2.46) | 0.65 (3.27) | −0.25 (−1.06–0.579) | 0.606 a | 0.049 |
| Talar tilt_percent_change | −13.03 (14.06) | −9.11 (16.30) | 0.020 (−0.01–0.05) | 0.204 a | 0.121 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Oktem, U.; Dastan, M.C.; Avci, H.; Bulut, M.; Ozaltin, G.E.; Ocguder, D.A.; Tecimel, O.; Bingol, I. High Tibial Osteotomy Is Associated with Improvements in Both Knee and Ankle Alignment in Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2026, 15, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010315
Oktem U, Dastan MC, Avci H, Bulut M, Ozaltin GE, Ocguder DA, Tecimel O, Bingol I. High Tibial Osteotomy Is Associated with Improvements in Both Knee and Ankle Alignment in Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2026; 15(1):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010315
Chicago/Turabian StyleOktem, Umut, Muhammed Cihan Dastan, Hanife Avci, Mustafa Bulut, Gulfem Ezgi Ozaltin, Durmus Ali Ocguder, Osman Tecimel, and Izzet Bingol. 2026. "High Tibial Osteotomy Is Associated with Improvements in Both Knee and Ankle Alignment in Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 15, no. 1: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010315
APA StyleOktem, U., Dastan, M. C., Avci, H., Bulut, M., Ozaltin, G. E., Ocguder, D. A., Tecimel, O., & Bingol, I. (2026). High Tibial Osteotomy Is Associated with Improvements in Both Knee and Ankle Alignment in Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 15(1), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm15010315






