Effects of Oxygen–Ozone Injections in Upper Limb Disorders: Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
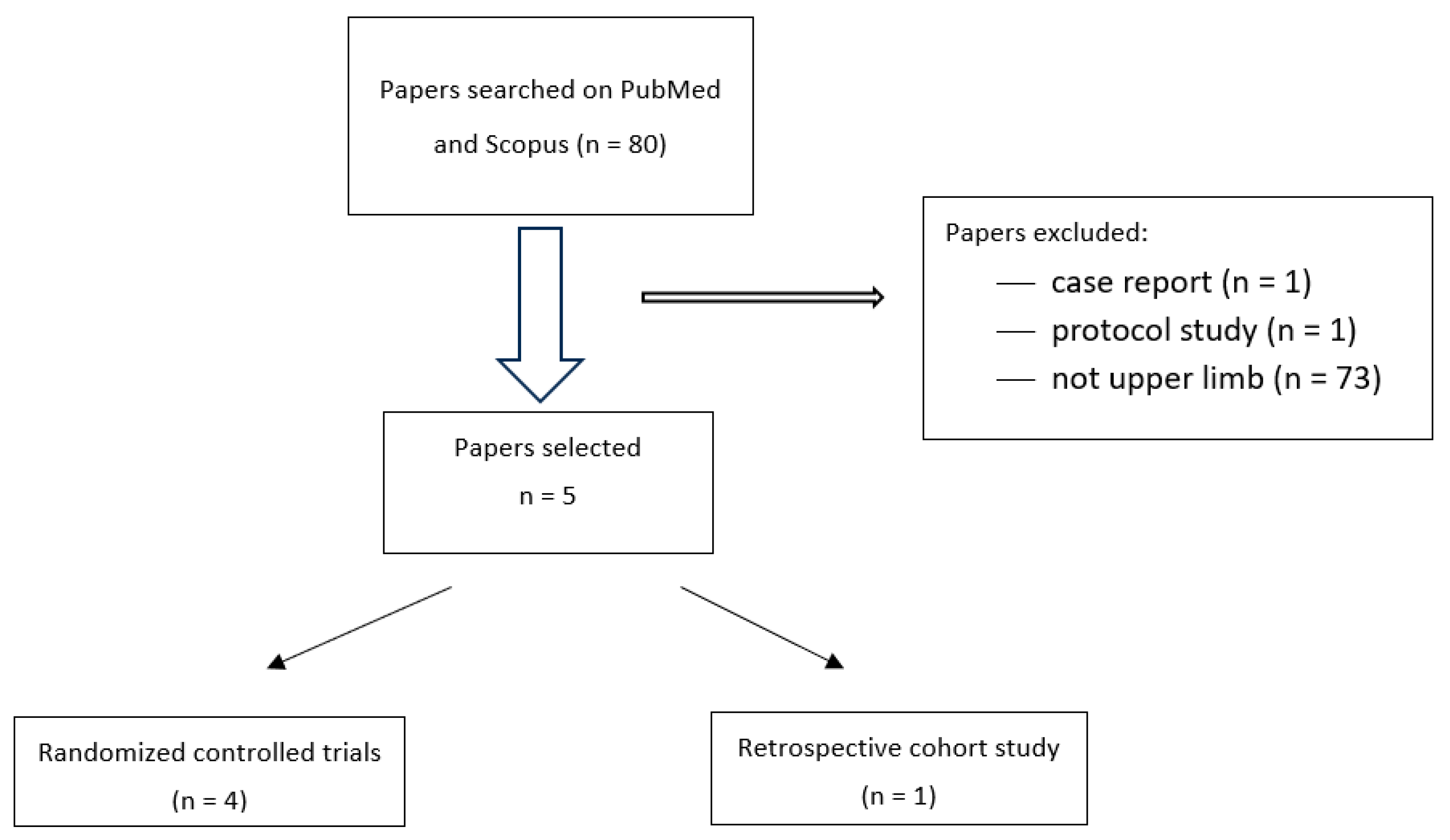
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limits
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babaei-Ghazani, A.; Fadavi, H.R.; Eftekharsadat, B.; Ebadi, S.; Ahadi, T.; Ghazaei, F.; Khabbaz, M.S. A Randomized Control Trial of Comparing Ultrasound-Guided Ozone (O2-O3) vs Corticosteroid Injection in Patients With Shoulder Impingement. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 98, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyam, O.; Smith, N.L.; Reid, I.; Gandhi, J.; Jiang, W.; Khan, S.A. Clinical utility of ozone therapy for musculoskeletal disorders. Med. Gas. Res. 2018, 8, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lino, V.T.S.; Marinho, D.S.; Rodrigues, N.C.P.; Andrade, C.A.F. Efficacy and safety of ozone therapy for knee osteoarthritis: An umbrella review of systematic reviews. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1348028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Sire, A.; Agostini, F.; Lippi, L.; Mangone, M.; Marchese, S.; Cisari, C.; Bernetti, A.; Invernizzi, M. Oxygen-Ozone Therapy in the Rehabilitation Field: State of the Art on Mechanisms of Action, Safety and Effectiveness in Patients with Musculoskeletal Disorders. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
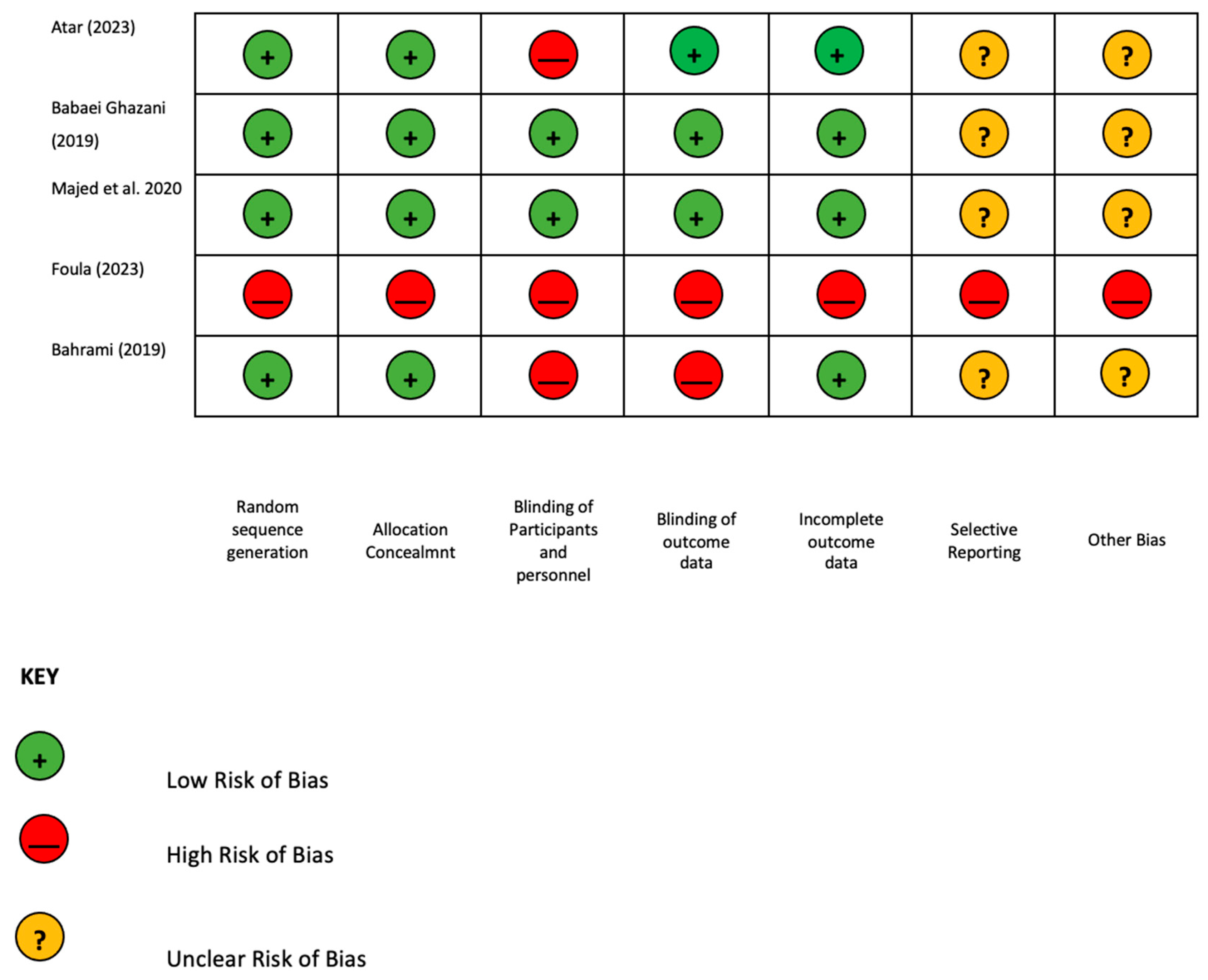
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar]
- Atar, M.Ö.; Korkmaz, N.; Aslan, S.G.; Tezen, Ö.; Köylü, S.U.; Demir, Y.; Kesikburun, S. Comparison of ultrasound-guided subacromial corticosteroid and ozone (O2-O3) injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: A randomized clinical trial. Korean J. Pain 2023, 36, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Foula, A.S.; Sabry, L.S.; Elmulla, A.F.; Kamel, M.A.; Hozien, A.I. Ultrasound-guided Shoulder Intraarticular Ozone Injection Versus Pulsed Radiofrequency Application for Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain Physician 2023, 26, E329–E340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, M.H.; Raeissadat, S.A.; Nezamabadi, M.; Hojjati, F.; Rahimi-Dehgolan, S. Interesting effectiveness of ozone injection for carpal tunnel syndrome treatment: A randomized controlled trial. Orthop. Res. Rev. 2019, 11, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ulusoy, G.R.; Bilge, A.; Öztürk, Ö. Comparison of corticosteroid injection and ozone injection for relief of pain in chronic lateral epicondylitis. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2019, 85, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Jiang, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, J. Intra-articular Steroid Injection for Frozen Shoulder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials With Trial Sequential Analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogu, B.; Yucel, S.D.; Sag, S.Y.; Bankaoglu, M.; Kuran, B. Blind or ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injections and short-term response in subacromial impingement syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, prospective study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronconi, G.; Codazza, S.; Panunzio, M.; La Cagnina, F.; Ariani, M.; Gatto, D.M.; Coraci, D.; Ferrara, P.E. The Effects of Ultrasound-Guided Intra-Articular Injections with Hyaluronic Acid and Corticosteroids in Patients with Hip Osteoarthritis: A Long-Term Real-World Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Say, F.; Gurler, D.; Bulbul, M. Platelet-rich plasma versus steroid injection for subacromial impingement syndrome. J. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 24, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.M.; Yoo, S.J.; Choi, S.; Park, Y.G. Current Trends for Treating Lateral Epicondylitis. Clin. Shoulder Elb. 2019, 22, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chou, L.C.; Liou, T.H.; Kuan, Y.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, H.C. Autologous blood injection for treatment of lateral epicondylosis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phys. Ther. Sport 2016, 18, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, J.A.; Olson, M.A.; Tao, M.A.; Burcal, C.J. Platelet-Rich Plasma versus Corticosteroid Injection for the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2021, 16, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferrara, P.E.; Codazza, S.; Coraci, D.; Malerba, G.; Ferriero, G.; Ronconi, G. State of art in intra-articular hip injections of different medications for osteoarthritis: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ashworth, N.L.; Bland, J.D.; Chapman, K.M.; Tardif, G.; Albarqouni, L.; Nagendran, A. Local corticosteroid injection versus surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2024, 8, CD015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Author (Years) | Design of the Study | Pathology | Study Group | Control Group | Control Group | Outcome Mesaures | Follow-Up | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atar 2022 [6] | Randomized clinical trial | Chronic supraspinatus tendinopathy | Three sessions (1 session/week) of 5 mL of ozone (O2-O3) (with a concentration of 10 μg/mL in the first session, 15 μg/ mL in the second session, and 20 μg/mL in the third session) N patient: 20 M/F: 6/14 Mean age (SD): 48. (10.38) | A mixture of 1 mL corticosteroid (betamethasone 3 mg/mL) and 1 mL lidocaine (20 mg) N patient: 20 M/F: 11/9 Mean age (SD): 50.15 (12.75) | - | WORC, SPADI, VAS | T0: baseline T1: 4 weeks T3: weeks | No differences between groups until T3 in pain quality of life and function. |
| Babaei-Ghazani 2019 [1] | Double-blind randomized controlled trial | Shoulder impingement | 1 injection of 8 mL of ozone (O2-O3) with a concentration of 12 μg/mL and 2 mL of lidocaine 1%, plus 20 min local cold pack, plus physical therapy N patients: 15 M/F: 2/13 Mean age (SD): 59.40 (10.31) | 1 injection of a mixture of 1 mL of triamcinolone 40 mg/mL with 2 mL of lidocaine 1%, plus 20 min local cold pack, plus physical therapy N patients: 15 M/F: 6/9 Mean age (SD): 58.80 (14.72) | - | VAS, Constant score, SPADI | T0: Postinjection T1: 2 weeks T2: 2 months | Corticosteroid injection improves (VAS p level 0.109, SPADI p level 0.295) the pain and disability scores more significantly than a one-time ozone injection. |
| Foula 2023 [7] | Double-blind randomized controlled trial | Shoulder adhesive capsulitis | Intra-articular injection of 10 mL of an oxygen–ozone mixture (15 μg/mL), plus 5 mL of 0.125% bupivacaine N patients: 15 M/F: 3/12 Mean age: 48 (SD) | Intra-articular injection of 40 mg triamcinolone, plus 5 mL of 0.125% bupivacaine N patients: 15 M/F: 3/12 Mean age: 42 (SD) | One session of radiofrequency (PRP), plus intra-articular injection of 5 mL of 0.125% bupivacaine PRP application N patients: 15 M/F: 7/8 Mean age: 46 (SD) | VAS during movement (VASm) and during rest (VASr), ROM, SPADI, inflammatory biomarkers (ICAM 1, hs-CPR) | T0: Preinjection T1: 2 h posttherapy T2: 1° week T3: 2° week T4: 4° week T5: 8° week | No differences between groups in VASm and VASr until T4. Significantly better scores at T5 in the PRP group. Significant improvement in VAS in “within analysis”. After T2 better results in VASr in steroid treatment group. Statistically significant ROM improvement in PRP group until T5. No differences between groups in SPADI. No differences in all groups in ICAM and hs-CRP at T0 and T4. Within analysis showed statistically significant (p level 0.001) improvement in both ICAM-1 and hs-CRP in all groups. |
| Ulusoy et al. 2019 [9] | Retrospective cohort study | Chronic lateral epicondylitis | 6–8 injections with 3-day intervals, aliquots of 3 mL O2-O3) (concentration of 30 μg/mL) N patients: 42 M/F: 11/31 Mean age (SD): 45.1 (8.1) | 1 injection every 3 weeks: 1 mL of betamethasone dipropionate (6.43 mg) and betamethasone sodium phosphate (2.63 mg) N patients: 38 M/F: 13/25 Mean age (SD): 46.4 (6.8) | - | Pain at rest. Pain on compression and during activity. All scores examined by modified Verhaar criteria | T0: After the injection of corticosteroid or ozone T1: 3 months after injection T2: 6 months after injection T3: 9 months after injection | At T0 and T1 there was no difference between corticosteroid and ozone groups with respect to pain. Analysis of pain at T1, T2, T3 demonstrated that ozone group had significantly better scores (p level < 0.001). |
| Bahrami et al. 2019 [8] | Randomized controlled trial | Mild or moderate carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) | Wrist resting splint + a single local injection of 4 mL ozone (10 micrograms/dl) plus 1 mL lidocaine (1%) N patients: 18 M/F: 0/18 Mean age (SD): 48.27 (3.33) | Wrist resting splint: eight weeks N patients: 20 M/F: 0/18 Mean age (SD): 46.35 (6.3) | - | VAS, BQ symptom severity (BQ-SSS), functional status (BQ-FSS), median NCS (CMAP and SNAP) | T0: Baseline T1: 10 weeks | Significant improvement in study group after T1 in pain (VAS p level 0.42), BQ-SSS (p level 0.62), BQ-FSS (0.30) No differences in median NCS in groups. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ronconi, G.; Mariantonietta, A.; Codazza, S.; Cutaia, A.; Zeni, A.; Forastiere, L.; Ferriero, G.; Ferrara, P.E. Effects of Oxygen–Ozone Injections in Upper Limb Disorders: Scoping Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072452
Ronconi G, Mariantonietta A, Codazza S, Cutaia A, Zeni A, Forastiere L, Ferriero G, Ferrara PE. Effects of Oxygen–Ozone Injections in Upper Limb Disorders: Scoping Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072452
Chicago/Turabian StyleRonconi, Gianpaolo, Ariani Mariantonietta, Sefora Codazza, Alberto Cutaia, Alessandra Zeni, Lucia Forastiere, Giorgio Ferriero, and Paola Emilia Ferrara. 2025. "Effects of Oxygen–Ozone Injections in Upper Limb Disorders: Scoping Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072452
APA StyleRonconi, G., Mariantonietta, A., Codazza, S., Cutaia, A., Zeni, A., Forastiere, L., Ferriero, G., & Ferrara, P. E. (2025). Effects of Oxygen–Ozone Injections in Upper Limb Disorders: Scoping Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072452