Diagnostic Accuracy of Deep Learning for Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection in Non-Contrast Brain CT Scans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
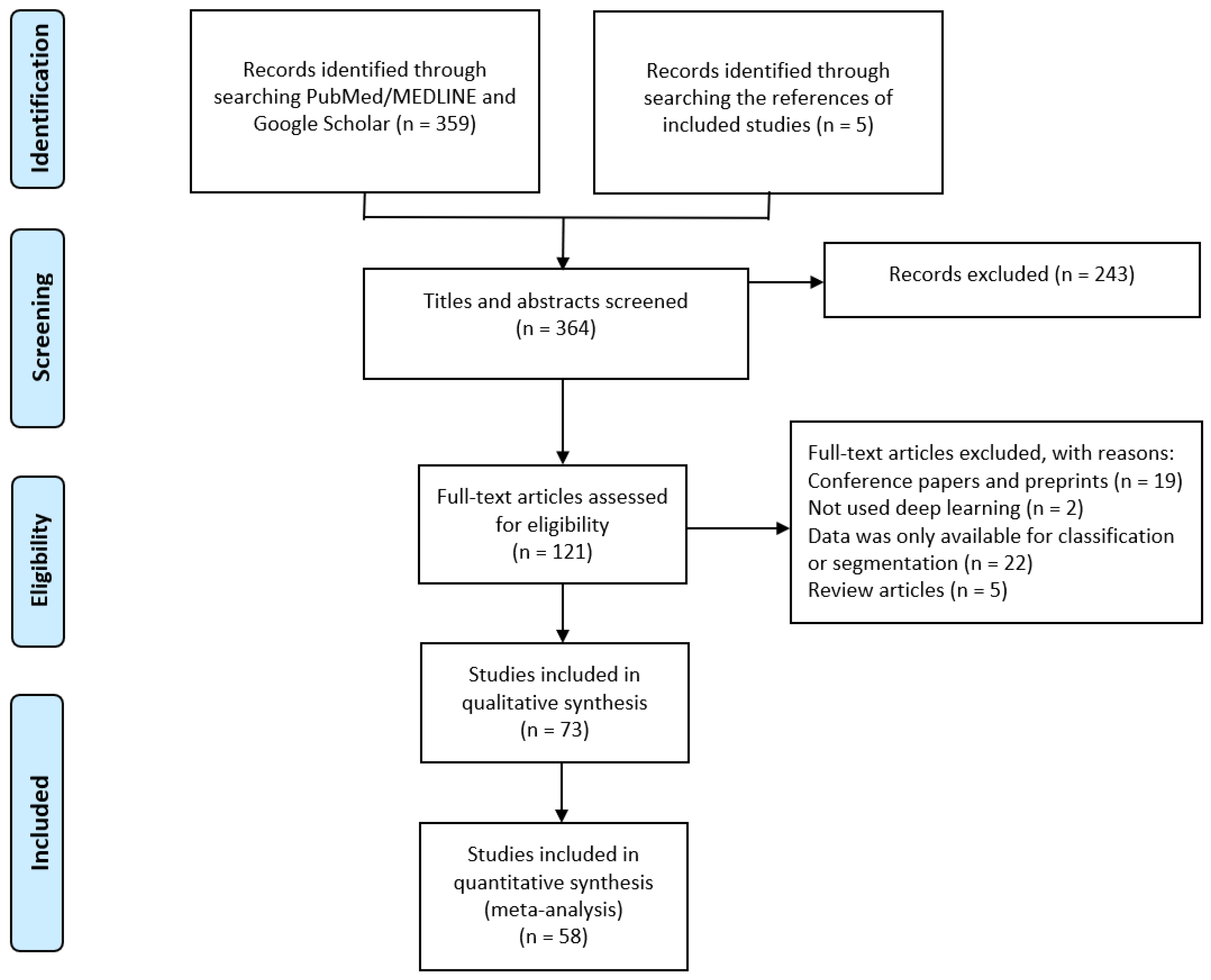
2.1. Search Strategy and Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
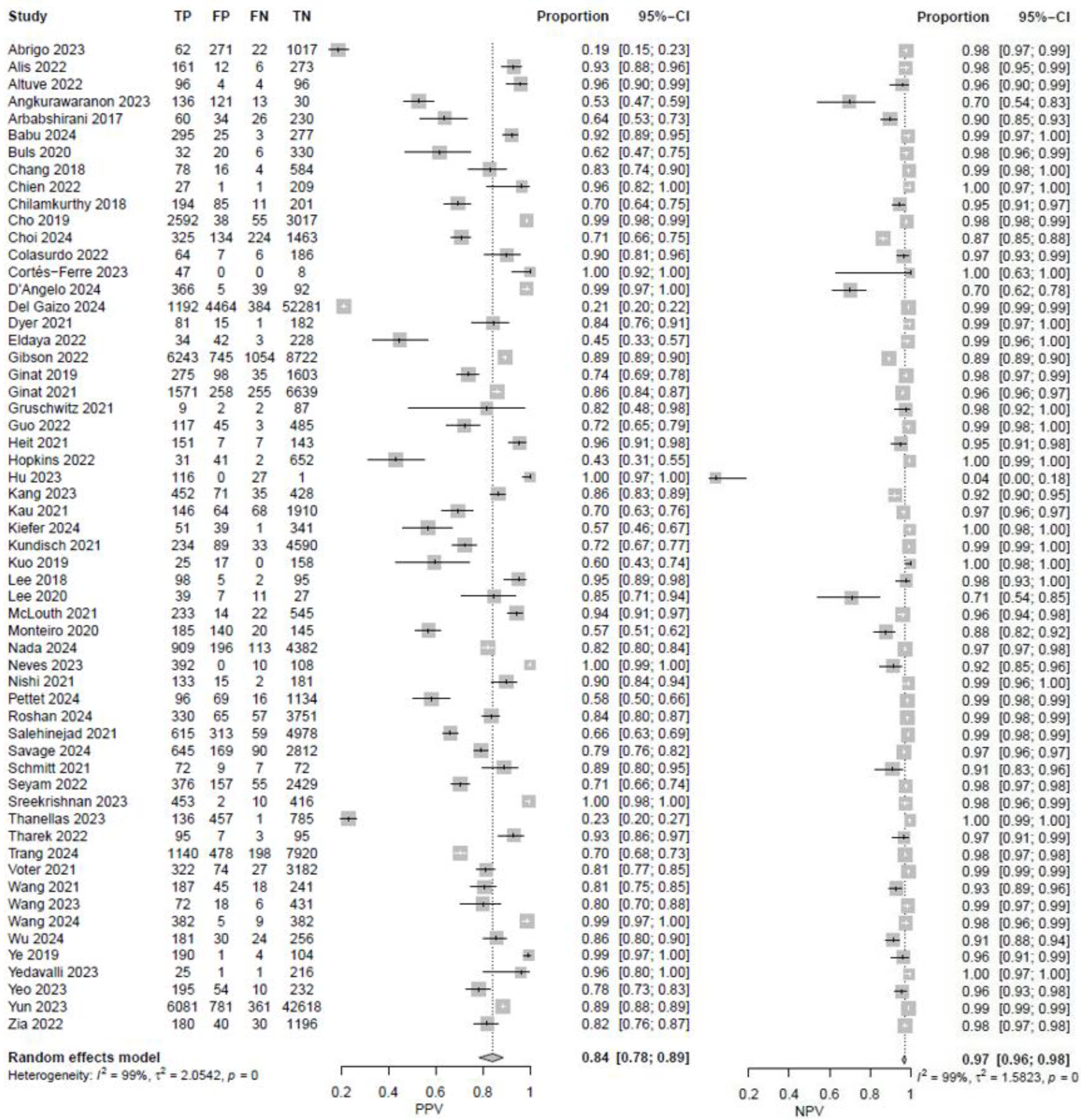
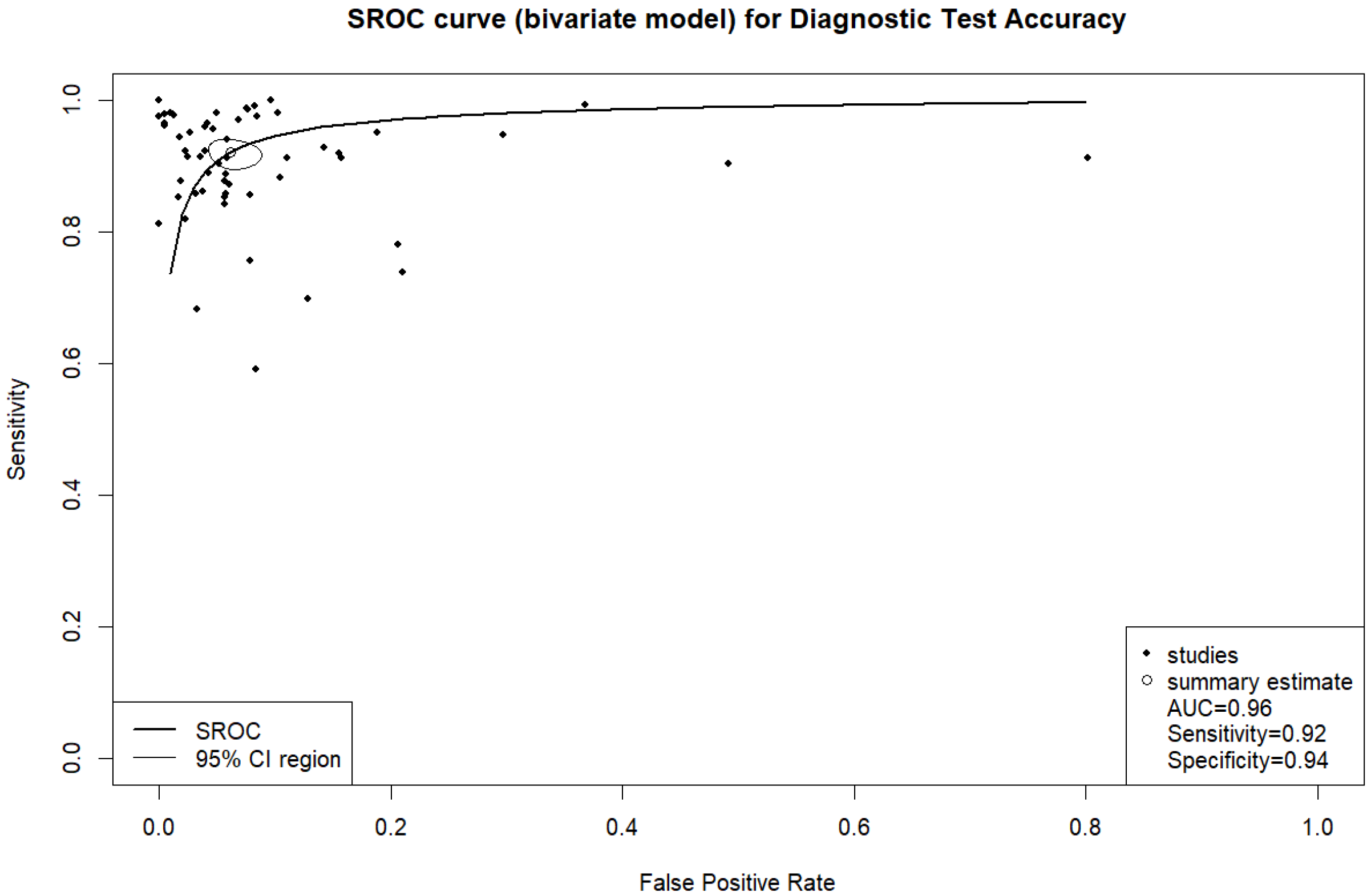
3. Results
3.1. Subgroup Analyses
3.2. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Ethical Implications and Responsibilities
4.3. Directions for Future
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
- The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ICH | Intracranial hemorrhage |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| DL | Deep learning |
| NCCT | Non-contrast computed tomography |
| ANN | Artificial neural networks |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| IPH | Intraparenchymal hemorrhage |
| SDH | Subdural hemorrhage |
| EDH | Epidural hemorrhage |
| IVH | Intraventricular hemorrhage |
| SAH | Subarachnoid hemorrhage |
| AUC | Area under curve |
| TP | True positive |
| TN | True negative |
| FP | False positive |
| FN | False negative |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| RNN | Recurrent neural networks |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| FCN | Fully convolutional networks |
| DCNN | Deep convolutional neural networks |
References
- Caceres, J.A.; Goldstein, J.N. Intracranial hemorrhage. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 30, 771–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, S.M.; Qureshi, D.; Talarico, R.; Tanuseputro, P.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Sood, M.M.; Smith, E.E.; Hill, M.D.; McCredie, V.A.; Scales, D.C.; et al. Intracerebral Hemorrhage Incidence, Mortality, and Association with Oral Anticoagulation Use. Stroke 2021, 52, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, D.; Comeau, M.E.; Venema, S.U.; Anderson, C.D.; Flaherty, M.; Testai, F.; Kittner, S.; Frankel, M.; James, M.L.; Sung, G.; et al. Risk Factors Associated with Mortality and Neurologic Disability After Intracerebral Hemorrhage in a Racially and Ethnically Diverse Cohort. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e221103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.N.; Gilson, A.J. Critical care management of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2011, 13, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobeidi, F.; Aviv, R.I. Emergency Imaging of Intracerebral Haemorrhage. Front. Neurol. Neurosci. 2015, 37, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajashekar, D.; Liang, J.W. Intracerebral Hemorrhage. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553103/ (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Hu, P.; Zhou, H.; Yan, T.; Miu, H.; Xiao, F.; Zhu, X.; Shu, L.; Yang, S.; Jin, R.; Dou, W.; et al. Deep learning-assisted identification and quantification of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in non-contrast CT scans: Development and external validation of Hybrid 2D/3D UNet. Neuroimage 2023, 279, 120321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frija, G.; Blažić, I.; Frush, D.P.; Hierath, M.; Kawooya, M.; Donoso-Bach, L.; Brkljačić, B. How to improve access to medical imaging in low- and middle-income countries? Eclinicalmedicine 2021, 38, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, A.; Badura, P. Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection in Head CT Using Double-Branch Convolutional Neural Network, Support Vector Machine, and Random Forest. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwee, T.C.; Kwee, R.M. Workload of diagnostic radiologists in the foreseeable future based on recent scientific advances: Growth expectations and role of artificial intelligence. Insights Into Imaging 2021, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strub, W.; Leach, J.; Tomsick, T.; Vagal, A. Overnight preliminary head CT interpretations provided by residents: Locations of misidentified intracranial hemorrhage. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 1679–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erly, W.K.; Berger, W.G.; Krupinski, E.; Seeger, J.F.; Guisto, J.A. Radiology resident evaluation of head CT scan orders in the emergency department. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2002, 23, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arendts, G.; Manovel, A.; Chai, A. Cranial CT interpretation by senior emergency department staff. Australas. Radiol. 2003, 47, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amisha Malik, P.; Pathania, M.; Rathaur, V.K. Overview of artificial intelligence in medicine. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 2328–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kuwaiti, A.; Nazer, K.; Al-Reedy, A.; Al-Shehri, S.; Al-Muhanna, A.; Subbarayalu, A.V.; Al Muhanna, D.; Al-Muhanna, F.A. A Review of the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, I.H. Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Overview on Techniques, Taxonomy, Applications and Research Directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Morotti, A.; Mazzacane, F.; Desser, D.; Schlunk, F.; Güttler, C.; Kniep, H.; Penzkofer, T.; Fiehler, J.; Hanning, U.; et al. External Validation and Retraining of DeepBleed: The First Open-Source 3D Deep Learning Network for the Segmentation of Spontaneous Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angkurawaranon, S.; Sanorsieng, N.; Unsrisong, K.; Inkeaw, P.; Sripan, P.; Khumrin, P.; Angkurawaranon, C.; Vaniyapong, T.; Chitapanarux, I. A comparison of performance between a deep learning model with residents for localization and classification of intracranial hemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alis, D.; Alis, C.; Yergin, M.; Topel, C.; Asmakutlu, O.; Bagcilar, O.; Senli, Y.D.; Ustundag, A.; Salt, V.; Dogan, S.N.; et al. A joint convolutional-recurrent neural network with an attention mechanism for detecting intracranial hemorrhage on noncontrast head CT. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurowski, M.A.; Buda, M.; Saha, A.; Bashir, M.R. Deep learning in radiology: An overview of the concepts and a survey of the state of the art with focus on MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 939–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvamangala, D.R.; Kulkarni, R.V. Convolutional neural networks in medical image understanding: A survey. Evol. Intell. 2022, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugunavar, S.; Prabhakar, C.J. Convolutional neural networks for the diagnosis and prognosis of the coronavirus disease pandemic. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art 2021, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuve, M.; Pérez, A. Intracerebral hemorrhage detection on computed tomography images using a residual neural network. Phys Med. 2022, 99, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Park, K.-S.; Karki, M.; Lee, E.; Ko, S.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, D.; Choe, J.; Son, J.; Kim, M.; et al. Improving Sensitivity on Identification and Delineation of Intracranial Hemorrhage Lesion Using Cascaded Deep Learning Models. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaravel, P.; Mohan, S.; Arivudaiyanambi, J.; Shajil, N.; Venkatakrishnan, H.N. A Simplified Framework for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhage in CT Brain Images Using Deep Learning. Curr. Med. Imaging 2021, 17, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, G.; Warman, P.I.; Warman, A.; Warman, R.; Bueso, T.; Vadhan, J.D.; Windisch, T. External Validation of an Artificial Intelligence Device for Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection. World Neurosurg. 2023, 173, e800–e807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’angelo, T.; Bucolo, G.M.; Kamareddine, T.; Yel, I.; Koch, V.; Gruenewald, L.D.; Martin, S.; Alizadeh, L.S.; Mazziotti, S.; Blandino, A.; et al. Accuracy and time efficiency of a novel deep learning algorithm for Intracranial Hemorrhage detection in CT Scans. Radiol. Med. 2024, 129, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.C.; Yang, T.L.; Juang, W.C.; Chen, Y.A.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, C.Y. Pilot Report for Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection with Deep Learning Implanted Head Computed Tomography Images at Emergency Department. J. Med. Syst. 2022, 46, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.M. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melsen, W.G.; Bootsma, M.C.; Rovers, M.M.; Bonten, M.J. The effects of clinical and statistical heterogeneity on the predictive values of results from meta-analyses. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrigo, J.M.; Ko, K.-L.; Chen, Q.; Lai, B.M.; Cheung, T.C.; Chu, W.C.; Yu, S.C. Artificial intelligence for detection of intracranial haemorrhage on head computed tomography scans: Diagnostic accuracy in Hong Kong. Hong. Kong Med. J. 2023, 29, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbabshirani, M.R.; Fornwalt, B.K.; Mongelluzzo, G.J.; Suever, J.D.; Geise, B.D.; Patel, A.A.; Moore, G.J. Advanced machine learning in action: Identification of intracranial hemorrhage on computed tomography scans of the head with clinical workflow integration. Npj Digit. Medicine 2018, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arman, S.E.; Rahman, S.S.; Irtisam, N.; Deowan, S.A.; Islam, A.; Sakib, S.; Hasan, M. Intracranial Hemorrhage Classification From CT Scan Using Deep Learning and Bayesian Optimization. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 83446–83460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.P.S.; Brindha, T. Deep Learning Fusion for Intracranial Hemorrhage Classification in Brain CT Imaging. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. (IJACSA) 2024, 15, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buls, N.; Watté, N.; Nieboer, K.; Ilsen, B.; de Mey, J. Performance of an artificial intelligence tool with real-time clinical workflow integration—Detection of intracranial hemorrhage and pulmonary embolism. Phys. Med. 2021, 83, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Kuoy, E.; Grinband, J.; Weinberg, B.; Thompson, M.; Homo, R.; Chen, J.; Abcede, H.; Shafie, M.; Sugrue, L.; et al. Hybrid 3D/2D Convolutional Neural Network for Hemorrhage Evaluation on Head CT. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamkurthy, S.; Ghosh, R.; Tanamala, S.; Biviji, M.; Campeau, N.G.; Venugopal, V.K.; Mahajan, V.; Rao, P.; Warier, P. Deep learning algorithms for detection of critical findings in head CT scans: A retrospective study. Lancet 2018, 392, 2388–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, H.S.; Lim, S.; Kim, E.H.; Choi, A. Impact of a deep learning-based brain CT interpretation algorithm on clinical decision-making for intracranial hemorrhage in the emergency department. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colasurdo, M.; Leibushor, N.; Robledo, A.; Vasandani, V.; Luna, Z.A.; Rao, A.S.; Garcia, R.; Srinivasan, V.M.; Sheth, S.A.; Avni, N.; et al. Automated detection and analysis of subdural hematomas using a machine learning algorithm. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 138, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coorens, N.A.M.; Lipman, K.G.M.; Krishnam, S.P.M.; Tan, C.O.; Alic, L.; Gupta, R. Intracerebral Hemorrhage Segmentation on Noncontrast Computed Tomography Using a Masked Loss Function U-Net Approach. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2023, 47, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Ferre, L.; Gutiérrez-Naranjo, M.A.; Egea-Guerrero, J.J.; Pérez-Sánchez, S.; Balcerzyk, M. Deep Learning Applied to Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawud, A.M.; Yurtkan, K.; Oztoprak, H. Application of Deep Learning in Neuroradiology: Brain Haemorrhage Classification Using Transfer Learning. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 4629859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaizo, A.J.; Osborne, T.F.; Shahoumian, T.; Sherrier, R. Deep Learning to Detect Intracranial Hemorrhage in a National Teleradiology Program and the Impact on Interpretation Time. Radiol Artif Intell. 2024, 6, e240067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, T.; Chawda, S.; Alkilani, R.; Morgan, T.N.; Hughes, M.; Rasalingham, S. Validation of an artificial intelligence solution for acute triage and rule-out normal of non-contrast CT head scans. Neuroradiology 2022, 64, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldaya, R.W.M.; Kansagra, A.P.; Zei, M.; Mason, E.D.; Holder, D.; Heitsch, L.; Vo, K.D.; Goyal, M.S.M. Performance of Automated RAPID Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection in Real-World Practice: A Single-Institution Experience. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2022, 46, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, E.; Georgescu, B.; Ceccaldi, P.; Trigan, P.-H.; Yoo, Y.; Das, J.; Re, T.J.; Rs, V.; Balachandran, A.; Eibenberger, E.; et al. Artificial Intelligence with Statistical Confidence Scores for Detection of Acute or Subacute Hemorrhage on Noncontrast CT Head Scans. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, e210115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginat, D.T. Analysis of head CT scans flagged by deep learning software for acute intracranial hemorrhage. Neuroradiology. 2020, 62, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginat, D. Implementation of Machine Learning Software on the Radiology Worklist Decreases Scan View Delay for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhage on CT. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruschwitz, P.; Grunz, J.-P.; Kuhl, P.J.; Kosmala, A.; Bley, T.A.; Petritsch, B.; Heidenreich, J.F. Performance testing of a novel deep learning algorithm for the detection of intracranial hemorrhage and first trial under clinical conditions. Neurosci. Inform. 2021, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; He, Y.; He, Y.; Lyu, J.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, D.; Yang, D.; et al. Deep learning with weak annotation from diagnosis reports for detection of multiple head disorders: A prospective, multicentre study. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e584–e593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L. Deep multiscale convolutional feature learning for intracranial hemorrhage classification and weakly supervised localization. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heit, J.; Coelho, H.; Lima, F.; Granja, M.; Aghaebrahim, A.; Hanel, R.; Kwok, K.; Haerian, H.; Cereda, C.; Venkatasubramanian, C.; et al. Automated Cerebral Hemorrhage Detection Using RAPID. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeijer, E.; Tan, C.; van der Heijden, F.; Gupta, R. Crowd-Sourced Deep Learning for Intracranial Hemorrhage Identification: Wisdom of Crowds or Laissez-Faire. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2023, 44, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.S.; Murthy, N.K.; Texakalidis, P.; Karras, C.L.; Mansell, M.; Jahromi, B.S.; Potts, M.B.; Dahdaleh, N.S. Mass Deployment of Deep Neural Network: Real-Time Proof of Concept with Screening of Intracranial Hemorrhage Using an Open Data Set. Neurosurgery 2022, 90, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-W.; Park, G.-H.; Ryu, W.-S.; Schellingerhout, D.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, C.-Y.; Lee, K.-J.; Han, M.-K.; Jeong, H.-G.; et al. Strengthening deep-learning models for intracranial hemorrhage detection: Strongly annotated computed tomography images and model ensembles. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1321964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kau, T.; Ziurlys, M.; Taschwer, M.; Kloss-Brandstätter, A.; Grabner, G.; Deutschmann, H. FDA-approved deep learning software application versus radiologists with different levels of expertise: Detection of intracranial hemorrhage in a retrospective single-center study. Neuroradiology 2022, 64, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, J.; Kopp, M.; Ruettinger, T.; Heiss, R.; Wuest, W.; Amarteifio, P.; Stroebel, A.; Uder, M.; May, M.S. Diagnostic Accuracy and Performance Analysis of a Scanner-Integrated Artificial Intelligence Model for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhages in a Traumatology Emergency Department. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundisch, A.; Hönning, A.; Mutze, S.; Kreissl, L.; Spohn, F.; Lemcke, J.; Sitz, M.; Sparenberg, P.; Goelz, L. Deep learning algorithm in detecting intracranial hemorrhages on emergency computed tomographies. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.; Häne, C.; Mukherjee, P.; Malik, J.; Yuh, E.L. Expert-level detection of acute intracranial hemorrhage on head computed tomography using deep learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22737–22745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yune, S.; Mansouri, M.; Kim, M.; Tajmir, S.H.; Guerrier, C.E.; Ebert, S.A.; Pomerantz, S.R.; Romero, J.M.; Kamalian, S.; et al. An explainable deep-learning algorithm for the detection of acute intracranial haemorrhage from small datasets. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, Y.S. Detection and classification of intracranial haemorrhage on CT images using a novel deep-learning algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Pérez, M.; Schmidt, A.; Wu, Y.; Molina, R.; Katsaggelos, A.K. Deep Gaussian processes for multiple instance learning: Application to CT intracranial hemorrhage detection. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed 2022, 219, 106783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Brattain, L.; Telfer, B.; Farris, C.; Scalera, J. Detecting Intracranial Hemorrhage with Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLouth, J.; Elstrott, S.; Chaibi, Y.; Quenet, S.; Chang, P.D.; Chow, D.S.; Soun, J.E. Validation of a Deep Learning Tool in the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhage and Large Vessel Occlusion. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 656112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, M.; Newcombe, V.F.J.; Mathieu, F.; Adatia, K.; Kamnitsas, K.; Ferrante, E.; Das, T.; Whitehouse, D.; Rueckert, D.; Menon, D.K.; et al. Multiclass semantic segmentation and quantification of traumatic brain injury lesions on head CT using deep learning: An algorithm development and multicentre validation study. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e314–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, A.; Sayed, A.A.; Hamouda, M.; Tantawi, M.; Khan, A.; Alt, A.; Hassanein, H.; Sevim, B.C.; Altes, T.; Gaballah, A. External validation and performance analysis of a deep learning-based model for the detection of intracranial hemorrhage. Neuroradiol. J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, T.; Yamashiro, S.; Okumura, S.; Takei, M.; Tachibana, A.; Akahori, S.; Kaji, M.; Uekawa, K.; Amadatsu, T. Artificial Intelligence Trained by Deep Learning Can Improve Computed Tomography Diagnosis of Nontraumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage by Nonspecialists. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2021, 61, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettet, G.; West, J.; Robert, D.; Khetani, A.; Kumar, S.; Golla, S.; Lavis, R. A retrospective audit of an artificial intelligence software for the detection of intracranial haemorrhage used by a teleradiology company in the United Kingdom. BJR Open. 2024, 6, tzae033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaphuangwittayakul, A.; Guo, Y.; Ying, F.; Dawod, A.Y.; Angkurawaranon, S.; Angkurawaranon, C. An optimal deep learning framework for multi-type hemorrhagic lesions detection and quantification in head CT images for traumatic brain injury. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 7320–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.N.; Mohanty, S.; Sen, K.; Acharya, U.R.; Cheong, K.H.; Sabut, S. Deep Transfer Learning for Automatic Prediction of Hemorrhagic Stroke on CT Images. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 3560507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshan, M.P.; A Al-Shaikhli, S.; Linfante, I.; Antony, T.T.; E Clarke, J.; Noman, R.; Lamy, C.; Britton, S.; Belnap, S.C.; Abrams, K.; et al. Revolutionizing Intracranial Hemorrhage Diagnosis: A Retrospective Analytical Study of Viz.ai ICH for Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy. Cureus 2024, 16, e66449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehinejad, H.; Kitamura, J.; Ditkofsky, N.; Lin, A.; Bharatha, A.; Suthiphosuwan, S.; Lin, H.-M.; Wilson, J.R.; Mamdani, M.; Colak, E. A real-world demonstration of machine learning generalizability in the detection of intracranial hemorrhage on head computerized tomography. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, C.H.; Tanwar, M.; Elkassem, A.A.; Sturdivant, A.; Hamki, O.; Sotoudeh, H.; Sirineni, G.; Singhal, A.; Milner, D.; Jones, J.; et al. Prospective Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence Triage of Intracranial Hemorrhage on Noncontrast Head CT Examinations. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2024, 223, e2431639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, N.; Mokli, Y.; Weyland, C.S.; Gerry, S.; Herweh, C.; Ringleb, P.A.; Nagel, S. Automated detection and segmentation of intracranial hemorrhage suspect hyperdensities in non-contrast-enhanced CT scans of acute stroke patients. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyam, M.; Weikert, T.; Sauter, A.; Brehm, A.; Psychogios, M.-N.; Blackham, K.A. Utilization of Artificial Intelligence-based Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection on Emergent Noncontrast CT Images in Clinical Workflow. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, e210168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhura, C.; Al Fahim, M.; Yalavarthy, P.K.; Gorthi, S. Fully automated sinogram-based deep learning model for detection and classification of intracranial hemorrhage. Med. Phys. 2024, 51, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekrishnan, A.; Giurgiutiu, D.-V.; Kitamura, F.; Martinelli, C.; Abdala, N.; Haerian, H.; Dehkharghani, S.; Kwok, K.; Yedavalli, V.; Heit, J.J. Decreasing false-positive detection of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) using RAPID ICH 3. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2023, 32, 107396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teneggi, J.; Yi, P.H.; Sulam, J. Examination-Level Supervision for Deep Learning-based Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection on Head CT Scans. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2024, 6, e230159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanellas, A.; Peura, H.; Lavinto, M.; Ruokola, T.; Vieli, M.; Staartjes, V.E.; Winklhofer, S.; Serra, C.; Regli, L.; Korja, M. Development and External Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm to Identify and Localize Subarachnoid Hemorrhage on CT Scans. Neurology 2023, 100, e1257–e1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharek, A.; Muda, A.S.; Hudi, A.B.; Hudin, A.B. Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection in Ct Scan Using Deep Learning. Asian J. Med. Technol. 2022, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, A.; Putman, K.; Savani, D.; Chatterjee, D.; Zhao, J.; Kamel, P.; Jeudy, J.J.; Parekh, V.S.; Yi, P.H. Sociodemographic biases in a commercial AI model for intracranial hemorrhage detection. Emerg. Radiol. 2024, 31, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villringer, K.; Sokiranski, R.; Opfer, R.; Spies, L.; Hamann, M.; Bormann, A.; Brehmer, M.; Galinovic, I.; Fiebach, J.B. An Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Integrated into the Clinical Workflow Can Ensure High Quality Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage CT Diagnostic. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2025, 35, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voter, A.F.; Meram, E.; Garrett, J.W.; Yu, J.-P.J. Diagnostic Accuracy and Failure Mode Analysis of a Deep Learning Algorithm for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhage. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2021, 18, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, T.; Yang, S.; Lan, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Han, X. A deep learning algorithm for automatic detection and classification of acute intracranial hemorrhages in head CT scans. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 32, 102785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Jin, R.; Shieh, C.-C.; Ng, A.Y.; Pham, H.; Dugal, T.; Barnett, M.; Winoto, L.; Wang, C.; Barnett, Y. Real world validation of an AI-based CT hemorrhage detection tool. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1177723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-C.; Wang, S.-C.; Xiao, F.; Ho, U.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Yan, J.-L.; Chen, Y.-F.; Ko, L.-W. Development of a Clinically Applicable Deep Learning System Based on Sparse Training Data to Accurately Detect Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage from Non-enhanced Head Computed Tomography. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2025, 65, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Iorga, M.; Badhe, S.; Zhang, J.; Cantrell, D.R.; Tanhehco, E.J.; Szrama, N.; Naidech, A.M.; Drakopoulos, M.; Hasan, S.T.; et al. Precise Image-level Localization of Intracranial Hemorrhage on Head CT Scans with Deep Learning Models Trained on Study-level Labels. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2024, 6, e230296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Gao, F.; Yin, Y.; Guo, D.; Zhao, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Bai, J.; Cao, K.; Song, Q.; et al. Precise diagnosis of intracranial hemorrhage and subtypes using a three-dimensional joint convolutional and recurrent neural network. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 6191–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yedavalli, V.; Heit, J.J.; Dehkharghani, S.; Haerian, H.; Mcmenamy, J.; Honce, J.; Timpone, V.M.; Harnain, C.; Kesselman, A.; Filly, A.; et al. Performance of RAPID noncontrast CT stroke platform in large vessel occlusion and intracranial hemorrhage detection. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1324088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, M.; Tahayori, B.; Kok, H.K.; Maingard, J.; Kutaiba, N.; Russell, J.; Thijs, V.; Jhamb, A.; Chandra, R.V.; Brooks, M.; et al. Evaluation of techniques to improve a deep learning algorithm for the automatic detection of intracranial haemorrhage on CT head imaging. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2023, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.J.; Choi, J.W.; Han, M.; Jung, W.S.; Choi, S.H.; Yoo, R.-E.; Hwang, I.P. Deep learning based automatic detection algorithm for acute intracranial haemorrhage: A pivotal randomized clinical trial. NPJ Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhu, W.; Li, F.; Yuan, M.; Zheng, L.; Liu, X. Transfer Learning of the ResNet-18 and DenseNet-121 Model Used to Diagnose Intracranial Hemorrhage in CT Scanning. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, A.; Fletcher, C.; Bigwood, S.; Ratnakanthan, P.; Seah, J.; Lee, R.; Kavnoudias, H.; Law, M. Retrospective analysis and prospective validation of an AI-based software for intracranial haemorrhage detection at a high-volume trauma centre. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bark, D.; Basu, J.; Toumpanakis, D.; Nyberg, J.B.; Bjerner, T.; Rostami, E.; Fällmar, D. Clinical Impact of an AI Decision Support System for Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhage in CT Scans. Neurotrauma Rep. 2024, 5, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymer, M.M. Hemorrhagic stroke: Intracerebral hemorrhage. Mo. Med. 2011, 108, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.; Smith, M. The acute management of intracerebral hemorrhage: A clinical review. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 110, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warman, R.; Warman, A.; Warman, P.; Degnan, A.; Blickman, J.; Chowdhary, V.; Dash, D.; Sangal, R.; Vadhan, J.; Bueso, T.; et al. Deep Learning System Boosts Radiologist Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhage. Cureus 2022, 14, e30264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nishida, A.; Takahashi, H.; Fujiwara, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Arisawa, A.; Yano, H.; Tomiyama, N.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Improvement of the diagnostic accuracy for intracranial haemorrhage using deep learning-based computer-assisted detection. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, W.; Kovanlikaya, I.; Kovanlikaya, A.; Liu, T.; Wang, S.; Salustri, C.; Wang, Y. Intracranial calcifications and hemorrhages: Characterization with quantitative susceptibility mapping. Radiology 2014, 270, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Study | Design | Type of ICH | Datasets | DL Model | Ground Truth | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy (%) | AUC | Comments on Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abrigo 2023 [32] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on RSNA public dataset/tested on a local dataset consisting of 1372 NCCTs | CNN | Radiologists or senior radiology trainees | 73.8 | 79 | 78.6 | 0.842 | Detection/per-scan |
| Alis 2022 [20] | Prospective | ICH | Local datasets/trained on 49,968 NCCTs/tested on 452 NCCTs | Joint CNN-RNN | Experienced neuroradiologists | 96.41 | 95.79 | 96.02 | 0.961 | Detection/per-scan |
| Altuve 2022 [24] | Retrospective | ICH | Publicly available Kaggle’s Head CT-Hemorrhage database including 200 NCCTs | ResNet-18 (deep residual CNN) | NA | 95.65 | 96.2 | 95.93 | NA | Detection/per-scan/the average performance is reported |
| Angkurawaranon 2023 [19] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset including 300 NCCTs | DL | Experienced neuroradiologists | 82 | 90 | 89 | NA | Detection of ICH/location-level performance is reported |
| Arbabshirani 2017 [33] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/trained on 46,583 NCCTs/tested on 347 NCCTs | CNN with 3D-architecture | Experienced neuroradiologists | 70 | 87 | 84 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Arman 2023 [34] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained and tested on NCCTs from RSNA public dataset | DenseNet | Neuroradiologists | 84.32 | 98.33 | 96.32 | NA | Detection/per-slice |
| Babu 2024 [35] | Retrospective | ICH | Publicly available Kaggle dataset/1600 NCCTs were used for training, 600 images for testing, and 400 images for validation | Hybrid DenseNet 121 + LSTM models | Expert radiologists | 98.99 | NA | 97.5 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Bark 2024 [95] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on a dataset of around 100,000 scans/tested on a local dataset of 2306 head CTs | HealthICH+ version 3.1.24 (3D CNN) | Neuroradiologist | NA | NA | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan/PPV of 82.3% |
| Buls 2020 [36] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 388 NCCTs | Aidoc (CNN) | Board certified experienced neuroradiologists | 84 | 94 | 93 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Chang 2018 [37] | Prospective | ICH | Trained on a local dataset of 10,159 NCCTs/tested on a local dataset including 682 NCCTs | Hybrid 3D/2D mask ROI-based CNN | Board-certified radiologist | 95.1 | 97.3 | 97 | 0.981 | Detection/per-scan The accuracy for ICHs > 25, 5–25, 0.01–5.0, and <0.01 mL is 0.997, 0.977, 0.906, and 0.872, respectively |
| Chien 2022 [29] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 238 NCCTs | Deep-CNN | NA | 96.43 | 99.52 | 99.16 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Chilamkurthy 2018 [38] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on a local dataset (Qure25k dataset) including 21,095 NCCTs/tested on a local dataset (CQ500) including 491 NCCTs | Modified ResNet18 (CNN) | Experienced radiologists | 94.7 | 70.1 | NA | 0.94 | Detection/per-scan |
| Cho 2019 [25] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on a local dataset of 5702 NCCTs | Cascade of CNNs and dual FCNs | A team of experienced neurologist, neurosurgeons, and emergency medicine doctors | 97.91 | 98.76 | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Choi 2024 [39] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 2146 NCCTs | DL | Board-certified neuroradiologists | 59.2 | 91.6 | 83.3 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Colasurdo 2022 [40] | Retrospective | SDH | Local dataset/tested on 263 NCCTs | Deep-CNN | Experienced neuroradiologists | 91.4 | 96.4 | 95.1 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Coorens 2023 [41] | Retrospective | ICH | Local datasets/trained and validated on 16,348 NCCTs/tested on 4095 NCCTs | Masked loss U-Net architecture | NA | 77 | 96.2 | 91.1 | NA | Detection/per-slice |
| Cortés-Ferre 2023 [42] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on the RSNA dataset/55 NCCTs were used for external validation | DL | Experienced radiologists, neurologists and neurocritical doctors | 100 | 100 | 100 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| D’Angelo 2024 [28] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/502 NCCTs | Dense-UNet architecture | Board-certified radiologists | 90.37 | 94.85 | 91.24 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Dawud 2019 [43] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/Trained on 8855 and tested on 3790 NCCTs | AlexNet-SVM | NA | 95 | 90 | 93 | NA | Detection/per-slice |
| Del Gaizo 2024 [44] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/58,321 NCCTs | CINA v1.0 device (DL) | Experienced emergency radiologists | 75.6 | 92.1 | 91.7 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Dyer 2021 [45] | Retrospective | ICH | Tested on a local dataset consisting of 390 NCCTs | EfficientNet neural network architecture | Consultant radiologists and neuroradiologists | 98.8 | 92.5 | NA | 98.8 | Detection/per-scan |
| Eldaya 2022 [46] | Retrospective | ICH | Tested on a local dataset consisting of 307 NCCTs | RAPID AI software (hybrid deep 2D–3D DCNN) | Board-certified or board-eligible neuroradiologists | 91.9 | 84.4 | 85.3 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Gibson 2022 [47] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on 25,946 NCCTs/evaluated on 16,764 NCCTs from RSNA ICH dataset | Deep neural networks | Neuroradiologists | 86 | 92 | NA | 0.95 | Detection/per-scan |
| Ginat 2019 [48] | Prospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 2011 NCCTs | Aidoc (CNN) | Board-certified neuroradiologist | 88.7 | 94.2 | 93.4 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Ginat 2021 [49] | Prospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 8723 NCCTs | Aidoc (CNN) | Radiologist report | 88.4 | 96.1 | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Gruschwitz 2021 [50] | Retrospective/ prospective | ICH | Retrospective (Local dataset/tested on 872 NCCTs) Prospective (Local dataset/tested on 100 NCCTs) | Dense-UNet architecture | A resident radiologist with subsequent supervision of a board-certified radiologist | NA | Detection/per-scan Retrospective (sensitivity = 91.4/specificity = 90.4/accuracy = 90.8) Prospective (sensitivity = 81.8/specificity = 97.8/accuracy = 96) | |||
| Guo 2022 [51] | Prospective | ICH | Trained on a local dataset/tested on a local dataset consisting of 650 NCCTs | RoLo, a novel weakly supervised deep learning algorithm | Expert radiologists | 97.9 | 91.5 | NA | 0.987 | Detection/per-scan |
| He 2024 [52] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained and tested on the ASNR public dataset consisting of 750,000 head CTs | End-to-end deep multiscale convolutional feature fusion framework | Radiologists | NA | NA | NA | 0.988 | Detection/per-slice |
| Heit 2021 [53] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on a local dataset including 805 NCCTs/validated on a local dataset consisting of 308 NCCTs | Hybrid deep 2D–3D CNN | Expert neuroradiologists | 95.6 | 95.3 | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan/performance on validation test is reported |
| Hofmeijer 2023 [54] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained and tested on a local dataset including 134 NCCTs | CNN | Neuroradiologists | NA | NA | NA | 0.82 | Detection/per-scan |
| Hopkins 2022 [55] | Prospective | ICH | Trained on RSNA dataset containing 21,784 NCCTs/tested on a local dataset including 726 NCCTs | CNN | Board-certified radiologists | 94 | 94 | NA | 0.98 | Detection/per-scan |
| Hu 2023 [7] | Ambispective | ICH | Three local datasets for external validation/trained on 931 NCCTs | Hybrid 2D/3D UNet deep-learning framework | Neurosurgeons and radiologists (not well defined) | 81.2 | 99.9 | 99.7 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Kang 2023 [56] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on two publicly available datasets (RSNA and AI-Hub)/two local datasets including 986 NCCTs were used for external testing | 2D U-net with the Inception module + weighted ensemble | Vascular neurologist and neuroradiologists | 92.8 | 85.7 | NA | 95.3 | Detection/per-scan |
| Kau 2021 [57] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 2188 NCCTs | Aidoc (CNN) | Board-certified neuroradiologist | 68.2 | 96.8 | 94 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Kiefer 2024 [58] | Retrospective | ICH | Tested on a local dataset including 432 NCCTs | Dense-UNet architecture | Experienced radiologists | 98.1 | 89.7 | 90.7 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Kumaravel 2020 [26] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained and tested on a publicly available dataset (CQ500 with 451 NCCTs) | DCNN (AlexNet-SVM) | Experienced radiologists | 99.86 | 99.86 | 99.86 | 0.999 | Detection/per-slice |
| Kundisch 2021 [59] | Retrospective | ICH | Tested on a local dataset including 4946 NCCTs | 3D DCNN (Aidoc) | Neuroradiologists | NA | NA | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Kuo 2019 [60] | Retrospective | ICH | Local datasets/Trained on 4396 head CTs/tested on 200 head CTs | Patch-based fully convolutional neural network (PatchFCN) | Board-certified neuroradiologist | 100 | 90 | NA | 0.991 ± 0.006 | Detection/per-scan |
| Lee 2018 [61] | Retrospective | ICH | Local datasets/Trained on 904 NCCTs/tested on 200 head CTs | DCNNs | Board-certified neuroradiologists | 98 | 95 | NA | 99.3 | Detection and classification/per-scan |
| Lee 2020 [62] | Retrospective | ICH | Local datasets/trained on 166 NCCTs/validation set included 84 cases | ANN | Board-certified neuroradiologists | 78 | 80 | NA | 0.859 | Detection/per-scan/performance on validation dataset is reported |
| López-Pérez 2022 [63] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained and tested on RSNA dataset | Multiple Instance Learning based on Deep Gaussian Processes (DGPMIL) | Neuroradiologists | 95.7 | NA | 82.5 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Majumdar 2018 [64] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/trained on 60 NCCTs with ICH/tested on 69 NCCTs | CNN (modified U-Net) | Experienced radiologists | 81 | 98 | NA | NA | Sensitivity per lesion and specificity per normal case |
| McLouth 2021 [65] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 814 NCCTs | CINA v1.0 device (DL) | Board-certified neuroradiologists | 91.4 | 97.5 | 95.6 | NA | Detection/per-scan True positive rate (%) for ICHs < 5, 5–25, and >25 mL is 71.8, 100, and 100, respectively |
| Monteiro 2020 [66] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained and tested on the CENTERTBI dataset (184 NCCTs in the training subset and 655 scans in the test subset)/external validation on a publicly available dataset (CQ500 dataset) | CNN | Experienced radiologists | 90 | 51 | NA | 0.83 | Detection/per-scan/performance on CQ500 dataset is reported |
| Nada 2024 [67] | Prospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 5600 NCCTs | Aidoc (CNN) | Experienced neuroradiologists | 89 | 96 | 94 | 0.954 | Detection/per-scan |
| Neves 2023 [27] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 510 NCCTs | Caire ICH vR1 (Caire Health Inc.) | Experienced radiologists | 97.52 | 100 | 98.05 | 0.9957 | Detection/per-scan |
| Nishi 2021 [68] | Retrospective | Non-traumatic SAH | Local datasets/trained on 757 NCCTs/tested on 331 NCCTs | 3D U-net (CNN) | Neurosurgery specialists | 99 | 92 | 95 | 0.99 | Detection/per-scan |
| Pettet 2024 [69] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset consisting of 1315 NCCTs | CNN (qER, developed by Qure.ai) | Experienced neuroradiologists and general radiologists | 85.7 | 94.3 | 93.5 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Phaphuangwittayakul 2022 [70] | Retrospective | ICH | Two public datasets (RSNA and PhysioNet) and one private dataset (CMU-TBI) including 321 NCCTs | CNN | NA | 95.77 | 96.9 | 96.21 | NA | Detection/per-slice |
| Rao 2022 [71] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset including 1164 NCCT images/Trained on 931 NCCT images/tested on 233 NCCT images | ResNet-based transfer learning model | Radiologists | 99.4 | 99.7 | 99.6 | 100 | Detection/per-slice |
| Roshan 2024 [72] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset including 4203 NCCTs | CNN (Viz.ai ICH) | Experienced neuroradiologists | 85.3 | 98.3 | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan Viz.ai ICH for intraparenchymal ICH >5 mL (99%) showed higher sensitivity than ICH <5 mL (99% and 84%, respectively). For SDH >10 mL it exhibited higher sensitivity than ICH <10 mL (90% and 77%, respectively) |
| Salehinejad 2021 [73] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on 21,784 NCCTs from the RSNA dataset/external validated on a dataset including 5965 NCCTs | DCNN | A trained research assistant | 91.3 | 94.1 | 93.8 | 0.954 | Detection/per-scan/performance on external validation dataset is reported |
| Savage 2024 [74] | Prospective | ICH | Tested on a local dataset consisting of 3716 NCCTs | Aidoc (CNN) | Attending radiologists | 87.8 | 94.3 | 93 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Schmitt 2021 [75] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 160 NCCTs | Brainomix algorithm (DCNN) | Board-certified neuroradiologist | 91 | 89 | NA | 0.9 | Detection/per-scan |
| Seyam 2022 [76] | Prospective | ICH | Local dataset/tested on 3017 NCCTs | Aidoc (CNN) | Board-certified neuroradiologist | 87.2 | 93.9 | 93 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Sindhura 2023 [77] | Retrospective | ICH | RSNA dataset (6122 NCCTs were used for training, 765 NCCTs were used for validation, and 765 NCCTs were used for testing) | Joint CNN-RNN | Neuroradiologists | 93.16 | 97.1 | 95.5 | NA | Detection/patient-level |
| Sreekrishnan 2023 [78] | Retrospective | ICH | Tested on a local dataset including 881 NCCTs | RAPID AI software (hybrid 2D–3D DCNN) | Neuroradiologists | 97.84 | 99.52 | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Teneggi 2024 [79] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on 17,388 NCCTs/tested on two local datasets (CQ500 and CT-ICH with 436 and 75 NCCTs, respectively) | Attention-based CNN | Expert radiologists | NA | NA | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan/for CQ500 datset AUC = 0.92 and for CT-ICH dataset AUC = 0.95) |
| Thanellas 2023 [80] | Retrospective | SAH | Local datasets/trained on 1083 NCCTs/tested on two public external validation datasets (Zurich and CQ500 datasets) including 1379 NCCTs | CNN (U-Net) | NA for Zurich dataset and expert radiologists for CQ500 dataset | 99 | 63 | 67 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Tharek 2022 [81] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained and tested on a public dataset including 200 NCCTs (100 with ICH and 100 without) | CNN | NA | 96.94 | 93.14 | 95 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Trang 2024 [82] | Retrospective | ICH | Tested on a local datset consisting of 9736 NCCTs | Aidoc (CNN) | Board-certified or board-eligible neuroradiologists | 85.2 | 94.3 | 93.1 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Villringer 2024 [83] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on 674,000 NCCT slices from RSNA/tested on 255 NCCTs from a local dataset | CNN + Efficient-Net-B3 architecture | Experienced radiologists | 90 | 96 | 96 | NA | Detection/per-scan/performance is the mean performance of AI vs. expert raters |
| Voter 2021 [84] | Retrospective | ICH | Tested on a local dataset including 3605 NCCTs | Aidoc (CNN) | CAQ-certified neuroradiologist | 92.3 | 97.7 | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Wang 2021 [85] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on RSNA dataset/tested on two publicly available external datasets (PhysioNet-ICH with 75 and CQ500 with 491 NCCTs) | 2D CNN | Experienced radiologists | NA | Detection/per-scan Performance on PhysioNet-ICH (sensitivity = 88.7/specificity = 94.4/AUC = 0.964) Performance on CQ500 dataset is reported (sensitivity = 91.4/specificity = 84.4/AUC = 0.949) | |||
| Wang 2023 [86] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on 20,000 NCCTs from different centers/tested on a local dataset consisting of 527 NCCTs | VeriScout™ tool (CNN) | Radiology trainee with 2 years of specialty experience + a sub-specialty neuroradiologist | 92 | 96 | 96 | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Wang 2024 [87] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained and tested on local datasets/validated on a local dataset including 778 NCCTs | 2D CNN with modifications from U-Net and ResNet architectures | Two radiologists and one neurosurgeon | 97.7 | 98.71 | 98.2 | NA | Detection/per-scan/performance of model on validation dataset is reported |
| Wu 2024 [88] | Retrospective | ICH | Training + Cross-Validation on a local dataset including 10,699 NCCTs/CQ500 dataset including 491 NCCTs used for external testing | Transfer learning with 2D CNN + bidirectional LSTM + attention layer at study level | experienced radiologists | 88.5 | 89.6 | 91.6 | 0.96 | Detection/per-scan/performance of model on external dataset (CQ500) is reported |
| Ye 2019 [89] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on a local dataset containing 2836 NCCTs/tested on 299 NCCTs | 3D Joint CNN-RNN | senior radiologists | 98 | 99 | 99 | 1 | Detection/per-scan |
| Yedavalli 2023 [90] | Retrospective | ICH | Tested on a local dataset including 243 NCCTs | RAPID AI software (hybrid 2D–3D CNN) | board-certified general and neuroradiologists | 96.2 | 99.5 | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan |
| Yeo 2023 [91] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained on the public Kaggle dataset and tested on the CQ500 dataset with 491 NCCTs | Joint CNN-RNN | Experienced radiologists | 95 | 81 | 88 | 0.966 | Detection/per-scan |
| Yun 2023 [92] | Retrospective | ICH | Trained and validated on a local dataset including 104,666 NCCT slices/external validated on a local dataset consisting of 49,841 NCCTs | Joint CNN-RNN | Neuroradiologists | 94.4 | 98.2 | 97.7 | 0.992 | Detection/per-scan |
| Zhou 2022 [93] | Retrospective | ICH | Local dataset/351 NCCTs | DL (Res-Net18 and Dense-Net121) | Experienced radiologists | NA | NA | Detection/per-slice ResNet-18 (sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 87%) DenseNet-121 (sensitivity of 98% and specificity of 79%) | ||
| Zia 2022 [94] | Retrospective/ prospective | ICH | Tested on a local dataset including 1446 NCCTs | Aidoc (CNN) | Board-certified neuroradiologist | 85.7 | 96.8 | NA | NA | Detection/per-scan/performance of prospective dataset is reported |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karamian, A.; Seifi, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Deep Learning for Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection in Non-Contrast Brain CT Scans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072377
Karamian A, Seifi A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Deep Learning for Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection in Non-Contrast Brain CT Scans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072377
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaramian, Armin, and Ali Seifi. 2025. "Diagnostic Accuracy of Deep Learning for Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection in Non-Contrast Brain CT Scans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072377
APA StyleKaramian, A., & Seifi, A. (2025). Diagnostic Accuracy of Deep Learning for Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection in Non-Contrast Brain CT Scans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072377







