Large Pontine Cavernoma with Hemorrhage: Case Report on Surgical Approach and Recovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
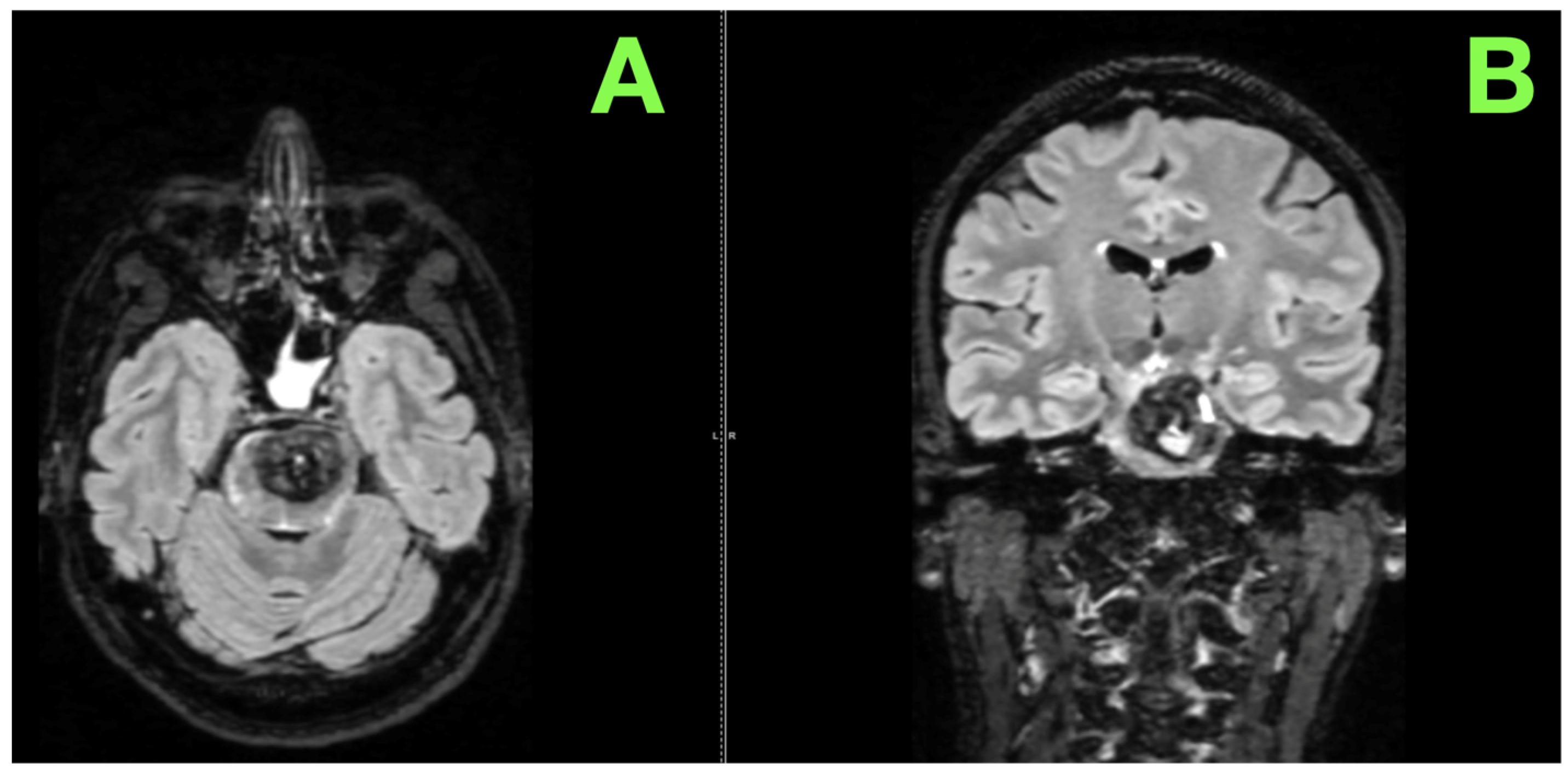
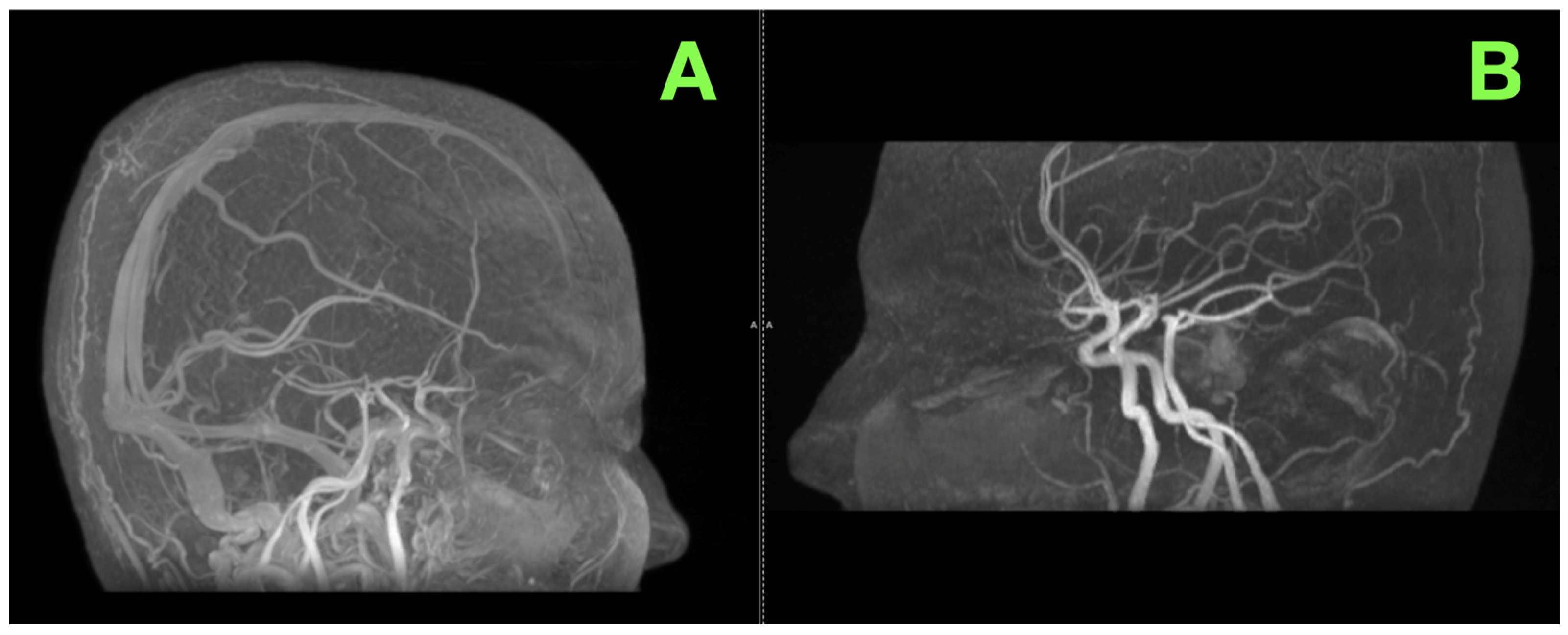
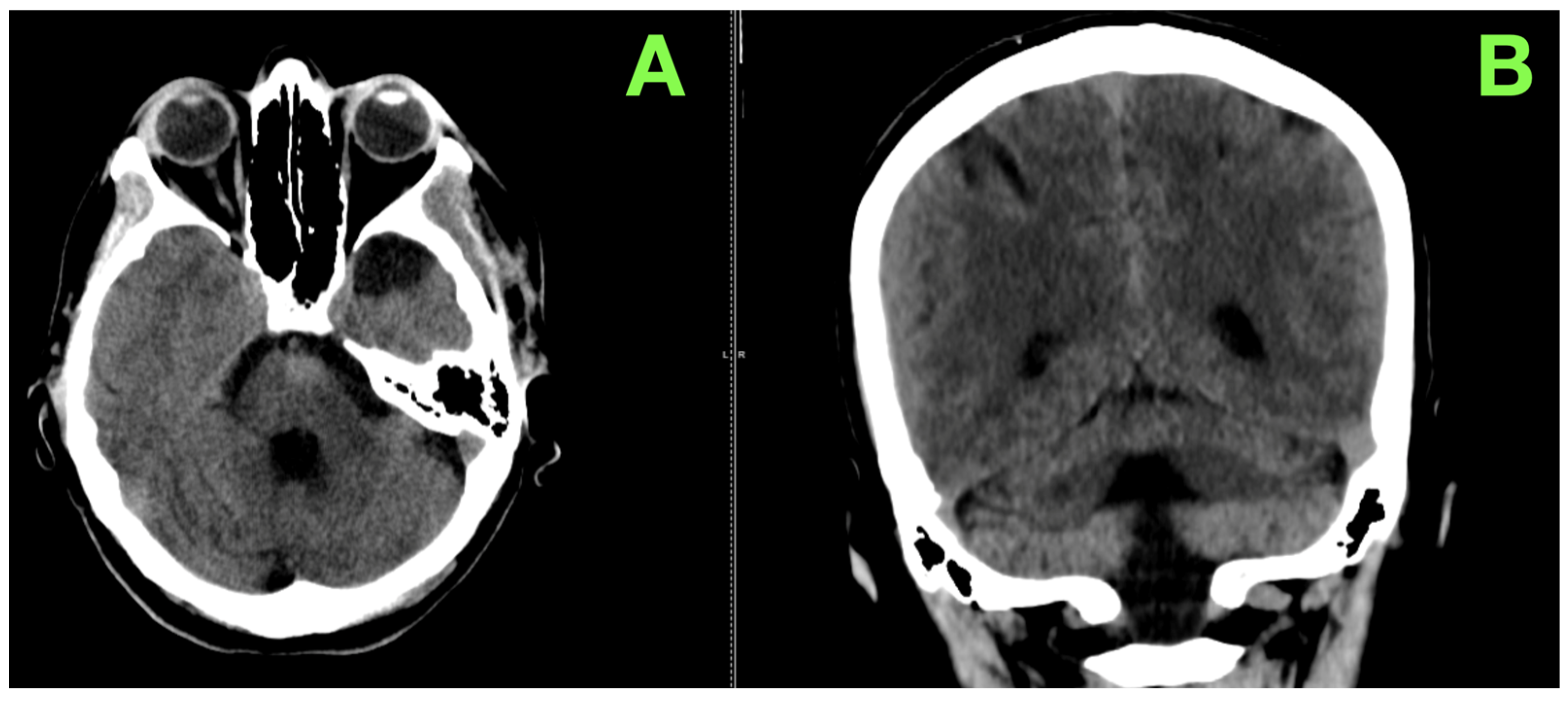
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamamoto, D.; Shibahara, I.; Hyakutake, Y.; Inukai, M.; Sato, S.; Koizumi, H.; Kumabe, T. Complete removal of a cavernous malformation in the dorsal pons, in contact with the expanded transpontine vein: Illustrative case. J. Neurosurg. Case Lessons 2024, 8, CASE24314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashant, G.N.; Dehdashti, A.R. One-point technique in brainstem cavernous malformation surgery: Evaluation of approaches and outcomes from a different perspective. Oper. Neurosurg. Hagerstown Md. 2024, 27, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashti, M.; Di, L.; Daftari, M.; Jaman, E.; Cardinal, T.; Robinson, M.W.; Robinson, M. Intraparenchymal chordoma in the brain stem: A review of surgical management and case highlight. Cureus 2024, 16, e67937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotakopoulos, G.; Andrade-Barazarte, H.; Kivelev, J.; Tjahjadi, M.; Goehre, F.; Hernesniemi, J. Brainstem cavernous malformations management: Microsurgery vs. radiosurgery, a meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 2022, 8, 630134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayawansa, S.; Dumot, C.; Mantziaris, G.; Xu, Z.; Pikis, S.; Peker, S.; Sheehan, J.P. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for patients with brainstem cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs): An international, multicentric study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, K.D.; Brown, R.D.; Lanzino, G. Contemporary cohort of cerebral cavernous malformations: Natural history and utility of follow-up MRI. J. Neurosurg. 2024, 141, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.S.; Bakir, A.; Sidow, N.O.; Erkok, U.; Ahmed, S.A.; Abshir, M.D.; Köksal, A.A. Etiology, risk factors and outcome of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in young adults admitted to tertiary care hospital in mogadishu, Somalia. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 2865–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischer, J.M.; Göd, S.; Gruber, A.; Saringer, W.; Grabner, G.; Gatterbauer, B.; Trattnig, S. Susceptibility-weighted imaging at 7 T: Improved diagnosis of cerebral cavernous malformations and associated developmental venous anomalies. NeuroImage Clin. 2012, 1, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- alco, J.; Broggi, M.; Acerbi, F.; Schiariti, M.; Moretti, M.E.; Restelli, F.; Ferroli, P. Surgery of brainstem cavernous malformations: Surgical nuances and outcomes of a monocentric series of 34 patients. Neurol. Sci. Off. J. Ital. Neurol. Soc. Ital. Soc. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2024, 46, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toader, C.; Serban, M.; Covache-Busuioc, R.A.; Radoi, M.P.; Aljboor, G.S.R.; Costin, H.P.; Gorgan, R.M. Cerebellar cavernoma resection: Case report with long-term follow-up. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Rodriguez, M.; Ross, D.; Ghahreman, A. Concurrent multiple cerebral cavernous malformations and cauda equina paraganglioma: Illustrative case. J. Neurosurg. Case Lessons 2024, 8, CASE24102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaussenot, A.; Ayrignac, X.; Chatron, N.; Granchon-Riolzir, T.; Labauge, P.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Riant, F. Loss of heterozygosity in CCM2 cDNA revealing a structural variant causing multiple cerebral cavernous malformations. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 32, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente-Herraiz, L.; Cuesta, A.M.; Granado, J.; Recio-Poveda, L.; Botella, L.-M.; Albiñana, V. Molecular and cellular characterization of primary endothelial cells from a familial cavernomatosis patient. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, D.T.F.; Zenonos, G.A.; Barrios-Martinez, J.; Bonhomme, G.R.; Yeh, F.C.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Friedlander, R.M. Implementation of high-definition fiber tractography for preoperative evaluation and surgical planning of brainstem cavernous malformation: Long-term outcomes. J. Neurosurg. 2024, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradac, O.; Majovsky, M.; de Lacy, P.; Benes, V. Surgery of brainstem cavernous malformations. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoubash, L.; Baldauf, J.; Matthes, M.; Kirsch, M.; Rath, M.; Felbor, U.; Schroeder, H.W. Long-term outcome and quality of life after CNS cavernoma resection: Eloquent vs. non-eloquent areas. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donofrio, C.A.; Arnautovic, K.; Riccio, L.; Badaloni, F.; Roncaroli, F.; Servadei, F.; Fioravanti, A. Neurological and functional outcomes of 32 patients with hemorrhagic brainstem cavernous malformations: A practical guide for surgical planning. J. Neurosurg. 2025, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Tang, C.; Ma, C. Fully endoscopic approach for resection of brainstem cavernous malformations: A systematic review of the literature. BMC Surg. 2024, 24, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.M.; Ha, B.J.; Cheong, J.H.; Ryu, J.I.; Won, Y.D.; Han, M.-H. Identification of predictive factors for better outcomes in LINAC-based radiation treatment for cerebral cavernous malformation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.H.; Wang, L.; Liu, P.P.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, L.W.; Zhang, J.T.; Li, D. Hemorrhagic outcome of brainstem cavernous malformations following radiosurgery: Dose-response relationship. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2024, 102, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajlan, A.; Basindwah, S.; Yaghmoor, W.; Albakr, A.; Alsaleh, S.; Alrasheed, A.; Alqurashi, A. The 100 most cited articles in endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery: A bibliometric analysis. World Neurosurg. 2023, 171, e363–e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabarkheel, R.; Li, L.; Frankfurter, M.; Zhang, D.Y.; Gajjar, A.; Muhammad, N.; Kahn, M. Untangling sporadic brain arteriovenous malformations: Towards targeting the KRAS/MAPK pathway. Front. Surg. 2024, 11, 1504612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tos, S.M.; Mantziaris, G.; Shaaban, A.; Sheehan, J.P. Stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial cavernous malformations of the deep-seated locations: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Rev. 2024, 47, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandmann, A.C.A.; Kempeneers, M.A.; van den Berg, R.; Verbaan, D.; Vandertop, W.P.; Coutinho, J.M. Clinical course of patients with conservatively managed cerebral cavernous malformations. Eur. Stroke J. 2024, 9, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, C.G.; Radatz, M.W.R. SRS for cavernous malformations: Myths and realities. Neurol. India 2023, 71 (Suppl. 1), S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salihi, M.M.; Al-Jebur, M.S.; Al-Salihi, Y.; Saha, R.; Daie, M.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Ayyad, A. Diffusion tensor imaging with tractography in surgical resection of brainstem cavernous malformations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Neurosci. 2024, 134, 1075–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meessen, J.M.; Abete-Fornara, G.; Zarino, B.; Castori, M.; Tassi, L.; Carriero, M.R.; Latini, R. Patient-reported outcome measures in patients with familial cerebral cavernous malformations: Results from the treat_CCM trial. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1338941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Schwendner, M.; Grziwotz, M.; Wiestler, B.; Wostrack, M.; Meyer, B.; Ille, S. Improving tractography in brainstem cavernoma patients by distortion correction. Brain Spine 2023, 3, 102685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, W.S.; Fonoff, E.T.; dos Santos Silva, R.P.; Schiavao, L.; Brunoni, A.R.; de Almeida, C.C.; Júnior, C.C. Preoperative cortical mapping for brain tumor surgery using navigated transcranial stimulation: Analysis of accuracy. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.R.; Chiluwal, A.K.; Nouri, M.; Prashant, G.N.; Dehdashti, A.R. Retrosigmoid transhorizontal fissure approach to lateral pontine cavernous malformation: Comparison to transpetrosal presigmoid retrolabyrinthine approach. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 136, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, D.D.; Figueiredo, E.G.; Preul, M.C.; Spetzler, R.F. Anatomical and objective evaluation of the main surgical approaches to pontine Intra-axial lesions. World Neurosurg. 2019, 121, e207–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunoda, S.; Inoue, T.; Segawa, M.; Akabane, A. Anterior transpetrosal resection of the lower ventral pontine cavernous malformation: A technical case report with operative video. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, B.A.; Du, R. Hemorrhage from cerebral cavernous malformations: A systematic pooled analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, S.; Meng, G.; Xiao, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J. Surgical management of brainstem cavernous malformation: Report of 67 patients. World Neurosurg. 2019, 122, e1162–e1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroli, P.; Sinisi, M.; Franzini, A.; Giombini, S.; Solero, C.L.; Broggi, G. Brainstem cavernomas: Long–term results of microsurgical resection in 52 patients. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulakci, M.; Kalelioglu, T.; Kiris, A. The importance of susceptibility-weighted imaging in familial cerebral cavernous malformation. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1376–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, M.T.; Lang, M.J. The future of open vascular neurosurgery: Perspectives on cavernous malformations, AVMs, and bypasses for complex aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 130, 1409–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abla, A.A.; Lekovic, G.P.; Turner, J.D.; de Oliveira, J.G.; Porter, R.; Spetzler, R.F. Advances in the treatment and outcome of brainstem cavernous malformation surgery: A single-center case series of 300 surgically treated patients. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samii, M.; Eghbal, R.; Carvalho, G.A.; Matthies, C. Surgical management of brainstem cavernomas. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 95, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramina, R.; Mattei, T.A.; de Aguiar, P.H.P.; Meneses, M.S.; Ferraz, V.R.; Aires, R.; de Carvalho Kirchhoff, D. Surgical management of brainstem cavernous malformations. Neurol. Sci. Off. J. Ital. Neurol. Soc. Ital. Soc. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 32, 1013–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiesen, T.; Edner, G.; Kihlström, L. Deep and brainstem cavernomas: A consecutive 8-year series. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 99, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogswell, P.M.; Pillai, J.J.; Lanzino, G.; Flemming, K.D. Prevalence of developmental venous anomalies in association with sporadic cavernous malformations on 7T MRI. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2023, 45, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhuo, L.; Kang, Y.; Liu, P.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Lin, F. Prevalence, genetic and clinical characteristics in first-degree relatives of patients with familial cerebral cavernous malformations in China. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2025, 10, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudnall, R.; Chen, E.X.; Opperman, P.J.; Kelly, S.; Cramer, J.A.; Surdell, D.L. A series of 14 representative presentations of cerebral cavernous malformations. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2021, 26, 101298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellings, D.A.; Hong, C.C.; Ren, A.A.; Lopez-Ramirez, M.A.; Girard, R.; Srinath, A.; Kahn, M.L. Cerebral cavernous malformation: From mechanism to therapy. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, T.; Chernov, M.; Alshebib, Y.A.; Kubota, Y.; Matsuo, S.; Shiramizu, H.; Okada, Y. Long-term outcomes after surgery for brainstem cavernous malformations: Analysis of 46 consecutive cases. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 138, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jones, P.; Zhao, M. Identifying potential (re)hemorrhage among sporadic cerebral cavernous malformations using machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh, K.; Akhlaghdoust, M.; Zali, A. Advances in artificial intelligence, robotics, augmented and virtual reality in neurosurgery. Front. Surg. 2023, 10, 1241923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Rota, A.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; Iovene, E.; De Momi, E. Recent advancements in augmented reality for robotic applications: A survey. Actuators 2023, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfranconi, S.; Scola, E.; Meessen, J.M.; Pallini, R.; Bertani, G.A.; Salman, R.A.S.; Zarino, B. Safety and efficacy of propranolol for treatment of familial cerebral cavernous malformations (Treat_CCM): A randomised, open-label, blinded-endpoint, phase 2 pilot trial. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author(s) and Year | Study Type | Population | Key Findings | Relevance to This Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross et al. (2017) [33] | Retrospective cohort | 168 patients with brainstem cavernomas | Early surgical intervention in symptomatic cavernomas reduces long-term morbidity; favorable outcomes in 78% of patients. | Supports the decision for early intervention in symptomatic cases, as in this patient with acute neurological deterioration. |
| Gui et al. (2019) [34] | Retrospective cohort | 67 patients | Surgery improved functional outcomes in 85% of patients with hemorrhagic cavernomas; mortality rate of 1.3%. | Reinforces the benefits of surgical resection in hemorrhagic lesions while highlighting low perioperative mortality risks. |
| Ferroli et al. (2005) [35] | Case series | 52 patients with brainstem cavernomas | Subtotal resection achieves excellent symptom relief while minimizing postoperative deficits in eloquent brainstem areas. | Validates the subtotal resection approach taken in this case to balance effective decompression and functional preservation. |
| Bulakci et al. (2012) [36] | Case Report | Focused on imaging modalities | SWI is critical for detecting hemosiderin deposits and hemorrhagic activity; fluid-fluid levels indicate active hemorrhage. | Highlights the role of advanced imaging, particularly SWI, in guiding surgical urgency and trajectory in this case. |
| Lawton et al. (2019) [37] | Single-center cohort | 300 brainstem cavernomas | The pterional transsylvian approach provided safe access to ventral pontine lesions; good outcomes in 89% of cases. | Demonstrates the efficacy of the pterional approach used in this case to access and decompress a ventrally located lesion. |
| Abla et al. (2014) [38] | Multicenter review | 300 patients with resected cavernomas | Risk of recurrence reduced with subtotal or gross resection; early intervention improves recovery. | Highlights the long-term stability achieved with subtotal resection and supports the surgical timing in this patient’s case. |
| Samii et al. (2001) [39] | Prospective study | 101 brainstem cavernomas | Surgical outcomes improved with anatomical tailoring of approach; retrosigmoid best for dorsal lesions, pterional for ventral. | Supports the selection of the pterional route in this patient, optimizing access to the ventral pontine lesion. |
| Ramina et al. (2011) [40] | Retrospective cohort | 43 patients with brainstem cavernomas | Microsurgical techniques (e.g., high-res microscopes) and neurophysiological monitoring reduce risks in brainstem surgery. | Reinforces the importance of precision and safety during resection in complex anatomical areas like the brainstem. |
| Mathiesen et al. (2003) [41] | Retrospective cohort | 68 patients with brainstem lesions | Observation is appropriate for minimally symptomatic lesions; surgery reserved for recurrent or progressive symptoms. | Contrasts with the decision for urgent surgery in this case, highlighting the need for tailored management based on symptoms. |
| Falco et al. (2019) [9] | Monocentric series | 34 cases analyzed | Emphasized role of multidisciplinary teams; perioperative care critical to reducing complications and enhancing outcomes. | Highlights the need for the integrated care provided in this patient’s surgical and postoperative management. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toader, C.; Serban, M.; Eva, L.; Costea, D.; Covache-Busuioc, R.-A.; Radoi, M.P.; Ciurea, A.V.; Dumitru, A.V. Large Pontine Cavernoma with Hemorrhage: Case Report on Surgical Approach and Recovery. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072358
Toader C, Serban M, Eva L, Costea D, Covache-Busuioc R-A, Radoi MP, Ciurea AV, Dumitru AV. Large Pontine Cavernoma with Hemorrhage: Case Report on Surgical Approach and Recovery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072358
Chicago/Turabian StyleToader, Corneliu, Matei Serban, Lucian Eva, Daniel Costea, Razvan-Adrian Covache-Busuioc, Mugurel Petrinel Radoi, Alexandru Vlad Ciurea, and Adrian Vasile Dumitru. 2025. "Large Pontine Cavernoma with Hemorrhage: Case Report on Surgical Approach and Recovery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072358
APA StyleToader, C., Serban, M., Eva, L., Costea, D., Covache-Busuioc, R.-A., Radoi, M. P., Ciurea, A. V., & Dumitru, A. V. (2025). Large Pontine Cavernoma with Hemorrhage: Case Report on Surgical Approach and Recovery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072358






