Extraradicular Infection and Apical Mineralized Biofilm: A Systematic Review of Published Case Reports
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Report Review
Selection of Case Reports
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Cases and Analysis of Extraradicular Infections
3.1.1. Demographics and Patient Characteristics
3.1.2. Root Canal Conditions and Periapical Diagnoses
3.1.3. Adjunctive Procedures and Treatment Approaches
3.1.4. Extraradicular Biofilm and Calculus Formation
3.1.5. Comparison Across Studies
4. Discussion
4.1. Etiology
4.2. Clinical Signs and Symptoms
4.3. Radiographic Assessment
4.4. Treatment of the Extraradicular Infection
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
- Development of novel antibiofilm agents specifically targeting extraradicular biofilms while preserving host tissue integrity.
- Advancements in imaging techniques, such as AI-assisted CBCT analysis, to enhance the detection of persistent periapical infections and mineralized apical biofilms.
- Longitudinal clinical studies evaluating the efficacy of non-surgical treatments, including photodynamic therapy, nanoparticle-based disinfection, and laser-assisted techniques for persistent apical periodontitis cases.
- Genetic and molecular studies aimed at identifying bacterial resistance mechanisms and potential biomarkers for predicting treatment outcomes.
- Exploration of bioceramic sealers and bioactive endodontic materials that promote periapical healing and inhibit bacterial adhesion, particularly in the apical region.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANP | apical negative pressure |
| FISH | fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| OCT | optical coherence tomography |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PUI | passive ultrasonic irrigation |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
References
- Gaeta, C.; Malvicini, G.; Di Lascio, D.; Martignoni, M.; Ragucci, G.; Grandini, S.; Marruganti, C. Lifestyle, caries, and apical periodontitis: Results from a university-based cross-sectional study. Int. Endod. J. 2025, 58, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricucci, D.; Milovidova, I.; Rôças, I.N.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Surgical management of a lateral lesion refractory to root canal retreatment caused by an extraradicular calculus. A case report. Aust. Endod. J. 2023, 49, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricucci, D.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Apical actinomycosis as a continuum of intraradicular and extraradicular infection: Case report and critical review on its involvement with treatment failure. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricucci, D.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Biofilms and apical periodontitis: Study of prevalence and association with clinical and histopathologic findings. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricucci, D.; Lopes, W.S.P.; Loghin, S.; Rocas, I.N.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Large Bacterial Floc Causing an Independent Extraradicular Infection and Posttreatment Apical Periodontitis: A Case Report. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricucci, D.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Lopes, W.S.; Vieira, A.R.; Rocas, I.N. Extraradicular infection as the cause of persistent symptoms: A case series. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricucci, D.; Candeiro, G.T.; Bugea, C.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Complex Apical Intraradicular Infection and Extraradicular Mineralized Biofilms as the Cause of Wet Canals and Treatment Failure: Report of 2 Cases. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, L.L.; Vaishnavi, C. Endodontic microbiology. J. Conserv. Dent. 2010, 13, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, J.S.; Bakaletz, L.O.; Wozniak, D.J. What’s on the Outside Matters: The Role of the Extracellular Polymeric Substance of Gram-negative Biofilms in Evading Host Immunity and as a Target for Therapeutic Intervention. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12538–12546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Hou, B. Diverse bacterial profile in extraradicular biofilms and periradicular lesions associated with persistent apical periodontitis. Int. Endod. J. 2021, 54, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Crincoli, V.; Laino, L.; Alovisi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Lo Muzio, L.; Troiano, G. Prevalence of Bacteria of Genus Actinomyces in Persistent Extraradicular Lesions-Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez de Paz, L.E.; Davies, J.R.; Bergenholtz, G.; Svensater, G. Strains of Enterococcus faecalis differ in their ability to coexist in biofilms with other root canal bacteria. Int. Endod. J. 2015, 48, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, M.; Schneider, R.; Bhattarai, B.; Currie, H.; Chavez, B.; Christopher, G.; Rumbaugh, K.; Gordon, V. Perspective: The viscoelastic properties of biofilm infections and mechanical interactions with phagocytic immune cells. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1102199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Vásquez, J.L. The Biomineralization Conundrum of Calcified Extraradicular Deposits on the Apical Root Surface of Teeth: A Case Report. Open Dent. J. 2023, 17, e187421062309191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.A.M.; Harun, N.; Reduwan, N.H.; Al-Bayaty, F.; Ariffin, F. Role of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Leading to the Finding of Actinomycosis Mimicking Periodontitis. J. Int. Dent. Med. Res. 2020, 13, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Signoretti, F.G.; Endo, M.S.; Gomes, B.P.; Montagner, F.; Tosello, F.B.; Jacinto, R.C. Persistent extraradicular infection in root-filled asymptomatic human tooth: Scanning electron microscopic analysis and microbial investigation after apical microsurgery. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1696–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricucci, D.; Martorano, M.; Bate, A.L.; Pascon, E.A. Calculus-like deposit on the apical external root surface of teeth with post-treatment apical periodontitis: Report of two cases. Int. Endod. J. 2005, 38, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Gao, Y.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Yu, Q. Surgical endodontic treatment of refractory periapical periodontitis with extraradicular biofilm. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 110, e40–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronstad, L.; Barnett, F.; Cervone, F. Periapical bacterial plaque in teeth refractory to endodontic treatment. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 1990, 6, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricucci, D.; Loghin, S.; Gonçalves, L.S.; Rôças, I.N.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Histobacteriologic conditions of the apical root canal system and periapical tissues in teeth associated with sinus tracts. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitjean, E.; Mavridou, A.; Li, X.; Hauben, E.; Cotti, E.; Lambrechts, P. Multimodular assessment of a calcified extraradicular deposit on the root surfaces of a mandibular molar. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, B.C.; Gomes, F.A.; Ferreira, C.M.; Rocha, M.; Barros, E.B.; Albuquerque, D.S. Persistent extra-radicular bacterial biofilm in endodontically treated human teeth: Scanning electron microscopy analysis after apical surgery. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2017, 80, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, J. Imaging of extraradicular biofilm using combined scanning electron microscopy and stereomicroscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2013, 76, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhu, C.; Liang, J. Bacterial flora and extraradicular biofilm associated with the apical segment of teeth with post-treatment apical periodontitis. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-Q.; Yang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Hou, B. Microbial Communities in the Extraradicular and Intraradicular Infections Associated With Persistent Apical Periodontitis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 798367. [Google Scholar]
- Ricucci, D.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Bate, A.L.; Pitt Ford, T.R. Histologic investigation of root canal-treated teeth with apical periodontitis: A retrospective study from twenty-four patients. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noiri, Y.; Ehara, A.; Kawahara, T.; Takemura, N.; Ebisu, S. Participation of bacterial biofilms in refractory and chronic periapical periodontitis. J. Endod. 2002, 28, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, P.N. Pathogenesis of apical periodontitis and the causes of endodontic failures. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2004, 15, 348–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byström, A.; Happonen, R.P.; Sjögren, U.; Sundqvist, G. Healing of periapical lesions of pulpless teeth after endodontic treatment with controlled asepsis. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 1987, 3, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran Nair, P.N.; Schroeder, H.E. Periapical actinomycosis. J. Endod. 1984, 10, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshberg, A.; Tsesis, I.; Metzger, Z.; Kaplan, I. Periapical actinomycosis: A clinicopathologic study. Oral Surg Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2003, 95, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronstad, L.; Barnett, F.; Riso, K.; Slots, J. Extraradicular endodontic infections. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 1987, 3, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunde, P.T.; Olsen, I.; Debelian, G.J.; Tronstad, L. Microbiota of periapical lesions refractory to endodontic therapy. J. Endod. 2002, 28, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, J.J.; Dobeck, J.M.; Smith, C.; White, R.R.; Socransky, S.S.; Skobe, Z. Bacteria of asymptomatic periradicular endodontic lesions identified by DNA-DNA hybridization. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 2000, 16, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade, K.Q.; Almeida-da-Silva, C.L.C.; Coutinho-Silva, R. Immunological Pathways Triggered by Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum: Therapeutic Possibilities? Mediat. Inflamm 2019, 2019, 7241312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, Z.; Lin, Y.Y.; Dimeo, F.; Ambrose, W.W.; Trope, M.; Arnold, R.R. Synergistic pathogenicity of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum in the mouse subcutaneous chamber model. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, D.; Wilensky, A.; Shapira, L.; Halabi, A.; Goldstein, D.; Weiss, E.I.; Houri-Haddad, Y. Mouse model of experimental periodontitis induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis/Fusobacterium nucleatum infection: Bone loss and host response. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Almeida-da-Silva, C.L.C.; Takiya, C.M.; Figliuolo, V.R.; Rocha, G.M.; Weissmüller, G.; Scharfstein, J.; Coutinho-Silva, R.; Ojcius, D.M. Oral infection of mice with Fusobacterium nucleatum results in macrophage recruitment to the dental pulp and bone resorption. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Zhu, X.; Pan, J. Regulatory Mechanisms and Promising Applications of Quorum Sensing-Inhibiting Agents in Control of Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 589640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.J. Dental calculus: Recent insights into occurrence, formation, prevention, removal and oral health effects of supragingival and subgingival deposits. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1997, 105, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.L.; Mann, V.; Gulabivala, K. A prospective study of the factors affecting outcomes of nonsurgical root canal treatment: Part 1: Periapical health. Int. Endod. J. 2011, 44, 583–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshargawi, W.K.; Alghamdi, F.M.; Alziyad, S.A.; Ramadan, F.L.; Alamoudi, A.I.; Alotni, S.I.; Saad, R.M.; Alsayegh, A.s.; Altwalah, A.A.; Alharbi, R.F.; et al. Impact of diabetes mellitus on endodontic treatment outcomes. Int. J. Community Med. Public Health 2024, 11, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Qasim, A.; Al-Hajji, Z.; Almutairy, Y.; Shahrkhani, A.; Al Eid, F.; Hawsawi, M.M.; Aljishi, R.A.; Alzahrani, M.; Alnassaralhassn, H.; Al-Fadhel, N.; et al. The Impact of Systemic Diseases on Endodontic Treatment Outcomes. J. Healthc. Sci. 2023, 3, 765–770. [Google Scholar]
- Svetlozarova, S. Association between Systemic Diseases and Endodontic Treatment Outcome-Review of Literature. Adv. Dent. Oral Health 2019, 11, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Segura-Egea, J.J.; Martin-Gonzalez, J.; Castellanos-Cosano, L. Endodontic medicine: Connections between apical periodontitis and systemic diseases. Int. Endod. J. 2015, 48, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.R.; Ricucci, D.; Vieira, G.C.S.; Provenzano, J.C.; Alves, F.R.F.; Marceliano-Alves, M.F.; Rôças, I.N.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Cleaning, Shaping, and Disinfecting Abilities of 2 Instrument Systems as Evaluated by a Correlative Micro-computed Tomographic and Histobacteriologic Approach. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Rocas, I.N. Microbiology and treatment of acute apical abscesses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliga, A.; Imre, M.; Grandini, S.; Marruganti, C.; Gaeta, C.; Bodnar, D.; Dimitriu, B.A.; Foschi, F. The Limitations of Periapical X-ray Assessment in Endodontic Diagnosis—A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukumbuzya, M.; Schmid, M.; Pjevac, P.; Daims, H.A. Multicolor Fluorescence in situ Hybridization Approach Using an Extended Set of Fluorophores to Visualize Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, M. Biofilm biodiversity presented by fluorescent in situ hybridisation. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, Wroclaw, Poland, 24 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Depetris, A.; Wiedmer, A.; Wagner, M.; Schäfer, S.; Battin, T.J.; Peter, H. Automated 3D Optical Coherence Tomography to Elucidate Biofilm Morphogenesis Over Large Spatial Scales. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2019, 150, e59356. [Google Scholar]
- Toth, L.; Vajas, A.; Csomor, P.; Berta, A.; Sziklai, I.; Karosi, T. Optical coherence tomography for biofilm detection in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2013, 270, 555–563. [Google Scholar]
- Narciso, D.A.C.; Pereira, A.; Dias, N.O.; Melo, L.F.; Martins, F.G. Characterization of biofilm structure and properties via processing of 2D optical coherence tomography images in BISCAP. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demidov, V.V.; Demidova, N.; Hazem, D.; Craig, L.P.; Gunn, J.R.; Jackson, O.P.; Gitajn, I.L.; Vitkin, A.I.; Elliott, J.T. Optical coherence tomography-based detection of orthopaedic implant biofilms formed by Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). In Proceedings of the BiOS, Manchester, UK, 11–12 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Barbero-Navarro, I.; Sofian-Pauliuc, I.; Irigoyen-Camacho, M.E.; Zepeda-Zepeda, M.A.; Ribas-Perez, D.; Castaño-Seiquer, A.L. Evaluating the Preventive and Therapeutic Roles of Active Irrigation Systems in Root Canal Treatment: A Narrative Review and Critical Appraisal of Theory and Methodology. Dent. J. 2024, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Rôças, I.N. Present status and future directions: Microbiology of endodontic infections. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55 (Suppl. S3), 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Pérez, A.R.; Marceliano-Alves, M.F.; Provenzano, J.C.; Silva, S.G.; Pires, F.R.; Vieira, G.C.S.; Rôças, I.N.; Alves, F.R.F. What happens to unprepared root canal walls: A correlative analysis using micro-computed tomography and histology/scanning electron microscopy. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera, J.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Ricucci, D.; Loghin, S.; Fernandez, N.; Flores, B.; Cruz, A.G. One- versus two-visit endodontic treatment of teeth with apical periodontitis: A histobacteriologic study. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaneo, I.; Vieira, G.C.S.; Perez, A.R.; Alves, F.R.F.; Goncalves, L.S.; Mdala, I.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Rocas, I.N. Root Canal Disinfection by Single- and Multiple-instrument Systems: Effects of Sodium Hypochlorite Volume, Concentration, and Retention Time. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Strategies to treat infected root canals. J. Calif. Dent. Assoc. 2001, 29, 825–837. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, D.; Marques, A.; Pereira, J.F.; Palma, P.J.; Santos, J.M. Long-Term Prognosis of Endodontic Microsurgery—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2020, 56, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coria-Valdiosera, F.E.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, D.R.; Ruiz-Reyes, H. Persistent Apical Periodontitis: Bacterial Taxonomic Analysis and Treatment Through Intentional Replantation. J. Dent. Oral Sci. 2020, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.H.; Rajkumar, K.; Pavithra, G.; Ramadoss, R.; Shankar, S.; Janani, K.; Chandan Srivastava, K.; Shrivastava, D.; Rokaya, D. Antibiofilm efficiency of silver and copper nanoparticle incorporated calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament: An in vitro study. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2025, 15, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandras, N.; Pasqualini, D.; Roana, J.; Tullio, V.; Banche, G.; Gianello, E.; Bonino, F.; Cuffini, A.M.; Berutti, E.; Alovisi, M. Influence of Photon-Induced Photoacoustic Streaming (PIPS) on Root Canal Disinfection and Post-Operative Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordea, I.R.; Hanna, R.; Chiniforush, N.; Grădinaru, E.; Câmpian, R.S.; Sîrbu, A.; Amaroli, A.; Benedicenti, S. Evaluation of the outcome of various laser therapy applications in root canal disinfection: A systematic review. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 29, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josic, U.; Mazzitelli, C.; Maravic, T.; Fidler, A.; Breschi, L.; Mazzoni, A. Biofilm in Endodontics: In Vitro Cultivation Possibilities, Sonic-, Ultrasonic- and Laser-Assisted Removal Techniques and Evaluation of the Cleaning Efficacy. Polymers 2022, 14, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prati, C.; Gandolfi, M.G. Calcium silicate bioactive cements: Biological perspectives and clinical applications. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


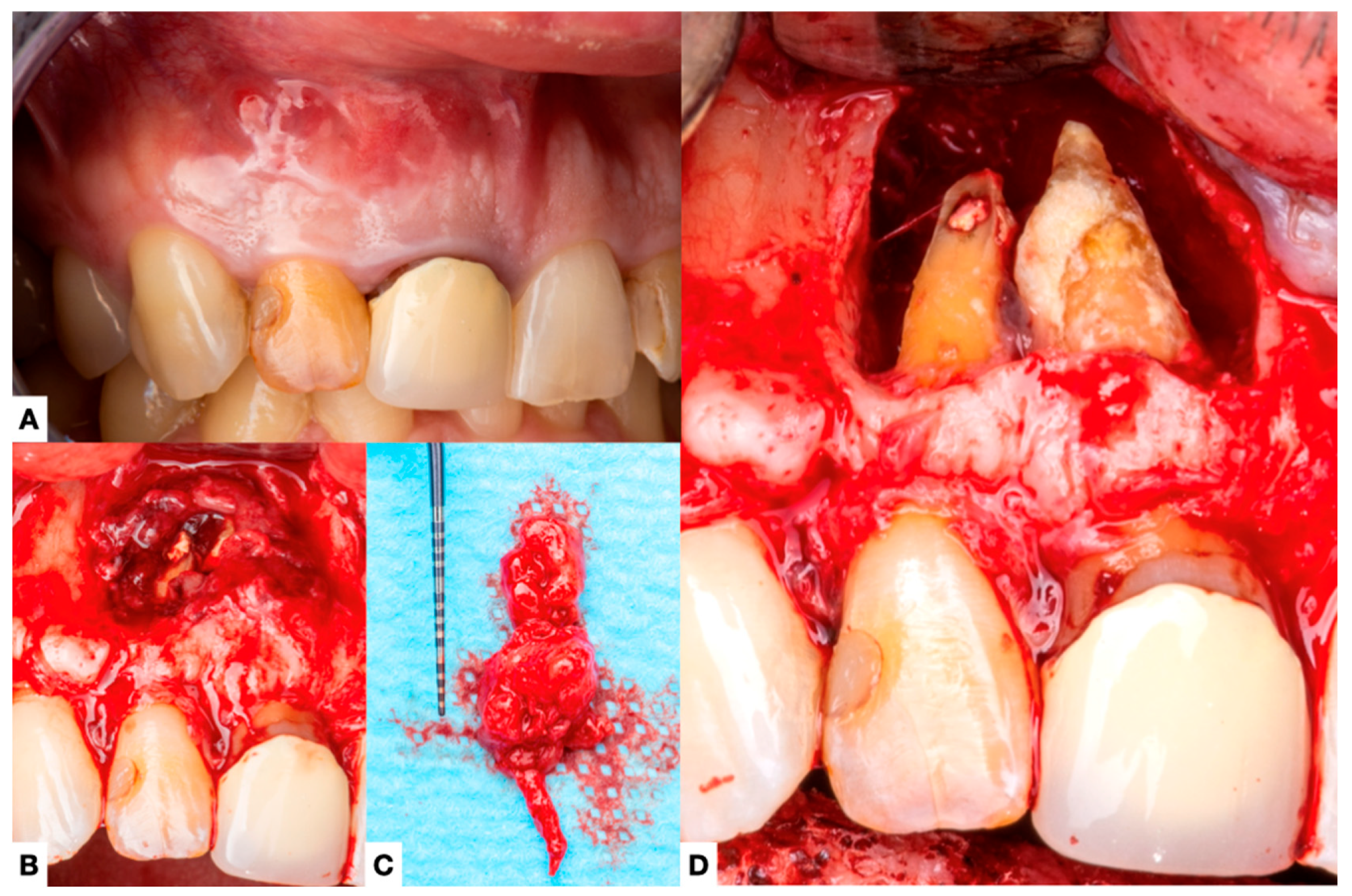
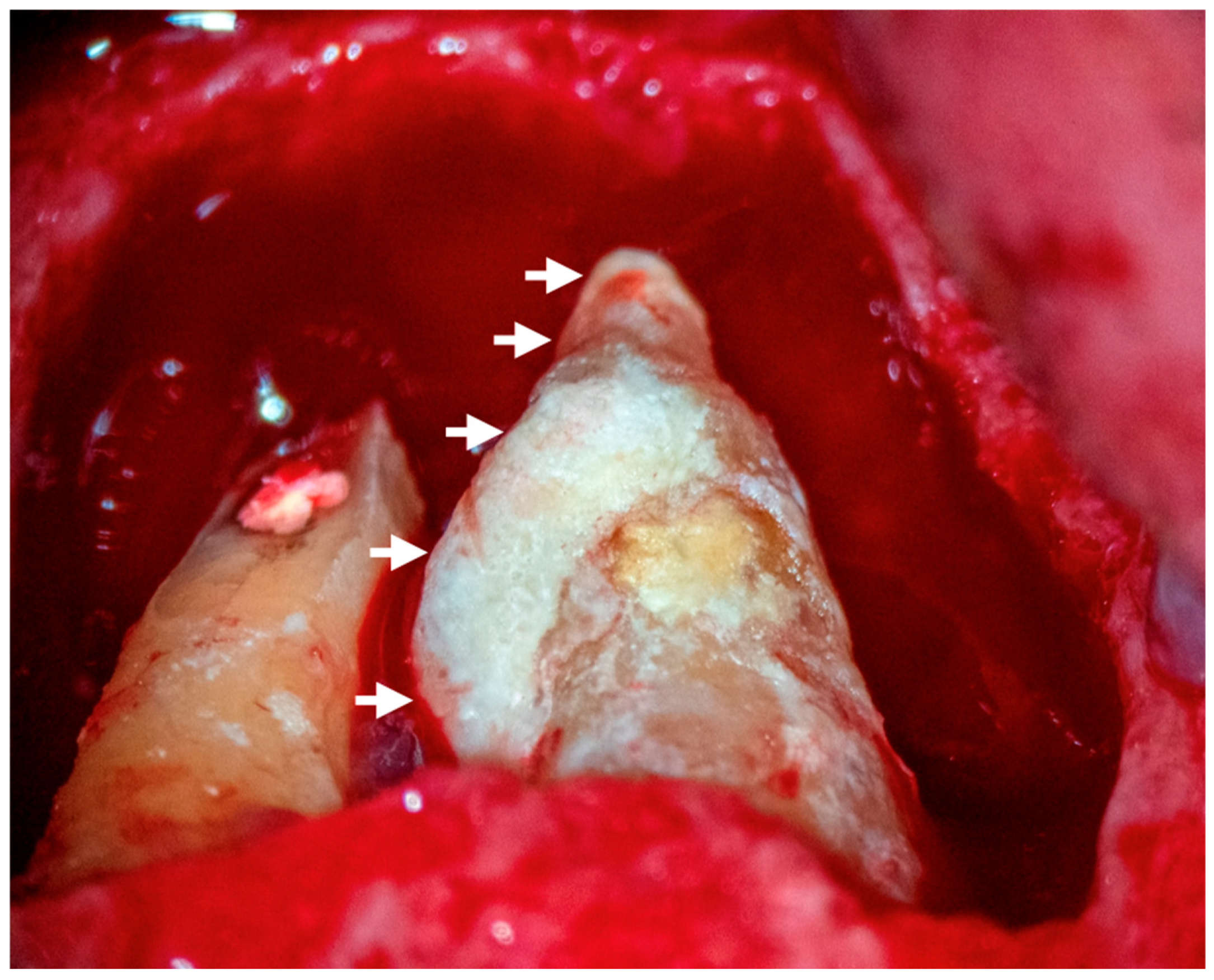
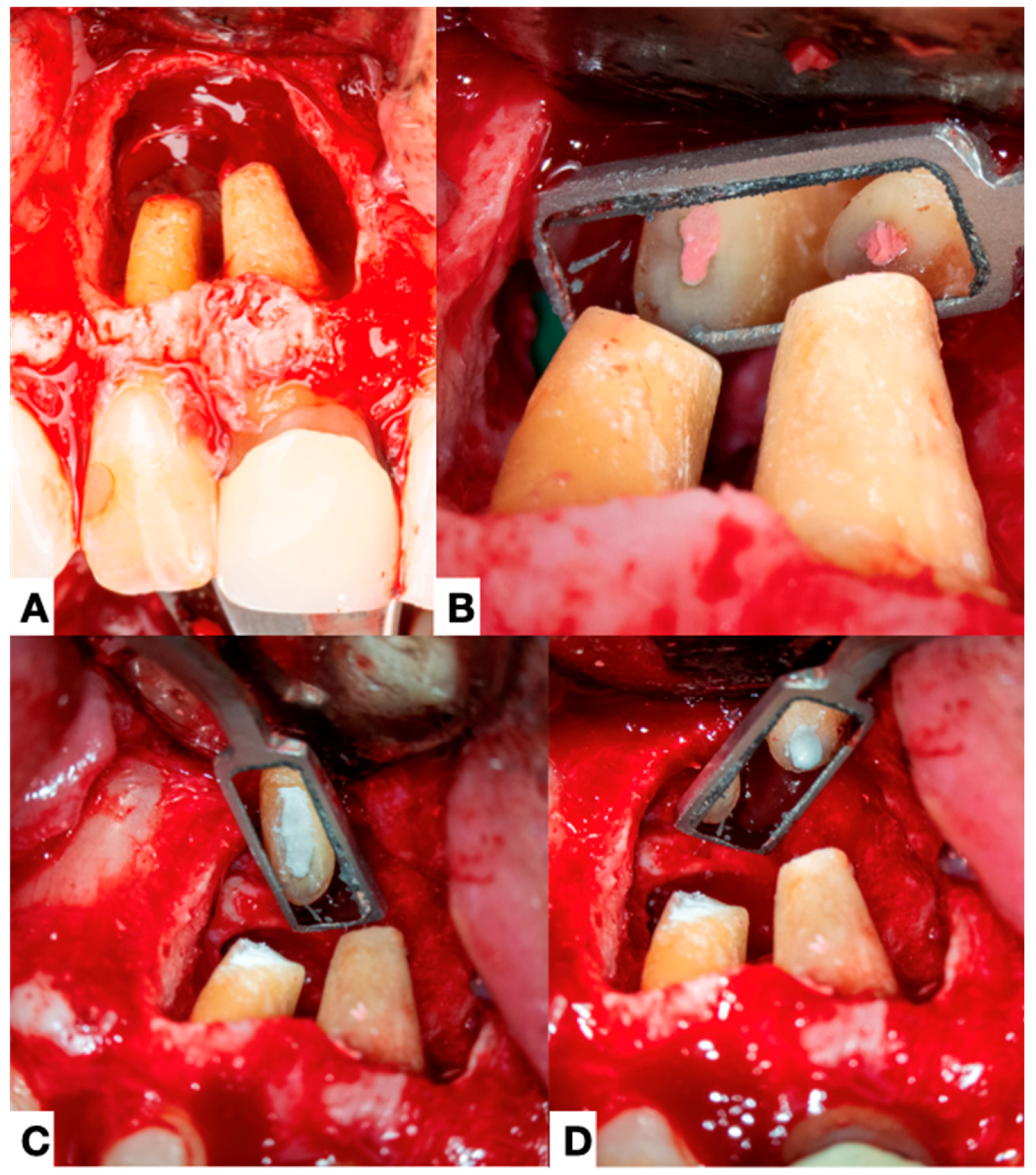

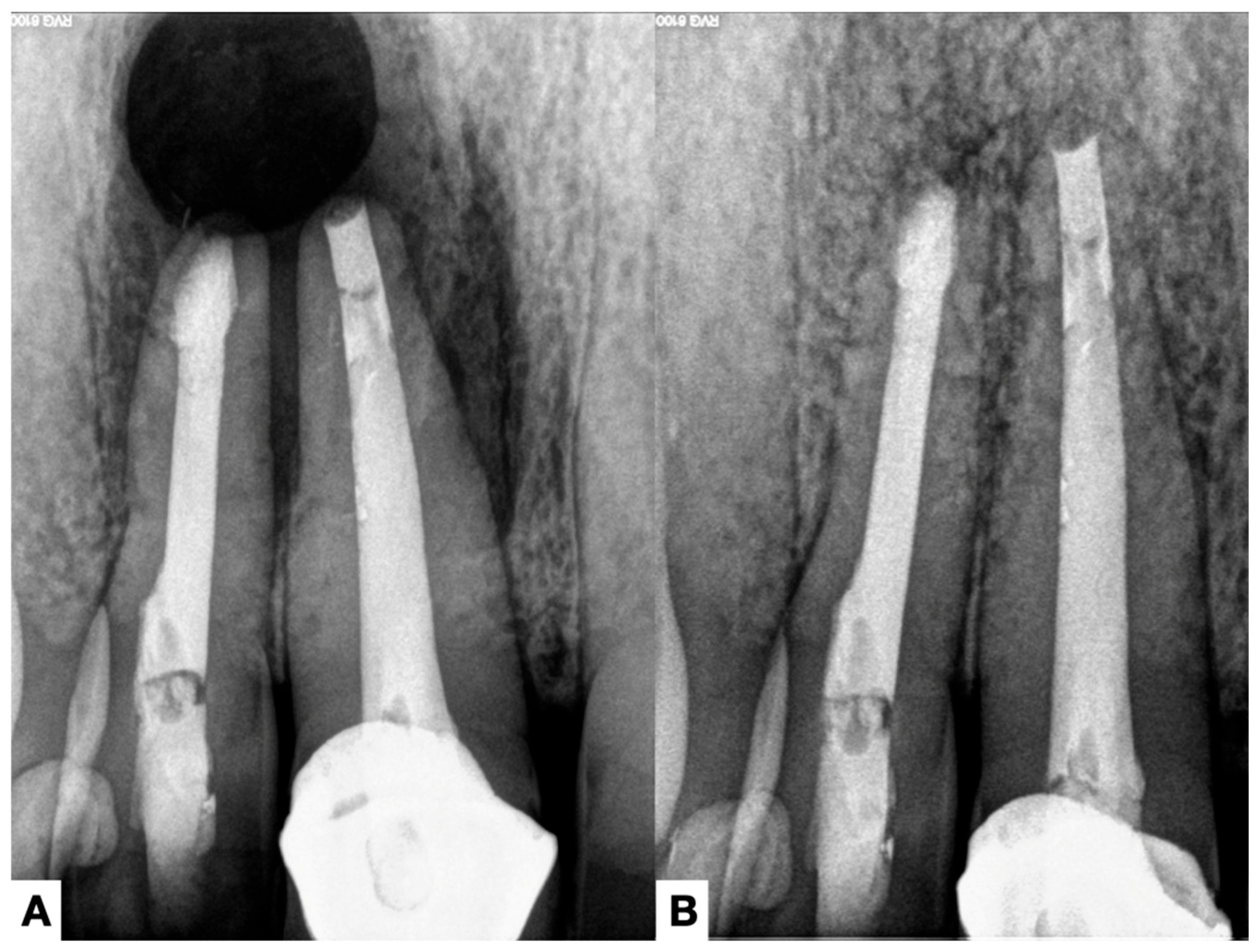
| Author, Year | Teeth | Gender | Age | Signs/Symptoms | Root Canal Conditions | Periapical Diagnosis | Adjunctive Procedures | Extraradicular Biofilm and Calculus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tronstad et al., 1990 [19] | 25 | F | 60 | Sinus tractNo periodontal probing | Treated | AAP | CH (3m), Formo, Amonio quater. | yes/no |
| Ricucci et al., 2005 [17] | 13 | M | 22 | Sinus tract, pain, no periodontal probing | Necrotic | SAP | CH (3w) | yes/yes |
| 5 | F | 51 | Sinus tract, no periodontal probing | Treated | AAP | CH (4w) | yes/yes | |
| Ricucci & Siqueira, 2008 [3] | 7 | F | 32 | Sinus tractPain | Necrotic | SAP | CH (5w) | yes/no |
| Su et al., 2010 [18] | 24 | F | 33 | Sinus tract and pain | Treated | SAP | CH (15w) | yes/no |
| 25 | F | 33 | Sinus tract and pain | Treated | SAP | CH (15w) | yes/no | |
| Signoretti et al., 2011 [16] | 19 | F | 38 | Sinus tractNo periodontal probing | Treated | AAP | None | yes/no |
| Ricucci, et al., 2015 [6] | 24–25 | M | 35 | Pain and swelling | Incompletely treated | SAP | CH (4w) | yes/no |
| 25 | M | 42 | Swelling | Treated | AAP | CH (3w) and PUI | yes/no | |
| 9 | M | 42 | Pain and swelling | Necrotic | SAP | CH (8w) PUI | yes/yes | |
| Ricucci, et al., 2016 [7] | 7 | M | 29 | Sinus tract, swelling and no periodontal probing | Necrotic | AAP | CH (12w) | yes/yes |
| 29 | M | 70 | No pain | Treated | AAP | PUIANP | yes/yes | |
| Ricucci et al., 2018 [20] | 9 | F | 18 | No pain | Necrotic | AAP | CH(2w) and PUI | yes/no |
| 10 | F | 18 | Swelling | Necrotic | AAP | yes/no | ||
| Ricucci et al., 2023 [2] | 10 | M | 61 | Sinus tract | Treated | AAP | PUI, CH (1w) | yes/yes |
| Characteristic | Dependent | Independent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Originates from and depends on an intraradicular infection; bacteria migrate from the canal into periapical tissues. | Persists independently of an intraradicular infection; bacteria are self-sustaining in periapical tissues. |
| Etiology | Typically occurs in cases of acute apical abscesses or chronic apical periodontitis where canal infection spreads beyond the apex. | Associated with extraradicular biofilm formation, where bacteria adhere to the root apex or surrounding periapical tissues without ongoing intraradicular infection. |
| Microbial features | Microorganisms are predominantly facultative and obligate anaerobes that originate from the infected root canal system. | Microbial composition includes Gram-positive bacteria (e.g., Actinomyces spp.), capable of surviving independently outside the root canal system. |
| Histologic findings | Bacteria are found within inflammatory infiltrates, often alongside immune cells attempting to eliminate the infection. | Biofilms form directly on the root surface, sometimes undergoing mineralization (apical calculus-like deposits), making them resistant to host clearance. |
| Response to endodontic treatment | Resolves with intracanal disinfection using effective irrigation. | Does not respond to intracanal disinfection alone, as bacteria survive outside the root canal system. |
| Clinical signs | Frequently presents with pain, sinus tracts, swelling, and purulent drainage due to the connection between intra- and extraradicular infection. | May be asymptomatic or persist despite successful root canal treatment, leading to treatment failure and chronic apical periodontitis. |
| Treatment approach | Requires root canal treatment and antimicrobial strategies to eliminate the intraradicular source of infection. | Often necessitates apical surgery to remove biofilms and mineralized calculus, as endodontic retreatment alone is ineffective. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez, A.R.; Rendón, J.; Ortolani-Seltenerich, P.S.; Pérez-Ron, Y.; Cardoso, M.; Noites, R.; Loroño, G.; Vieira, G.C.S. Extraradicular Infection and Apical Mineralized Biofilm: A Systematic Review of Published Case Reports. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072335
Pérez AR, Rendón J, Ortolani-Seltenerich PS, Pérez-Ron Y, Cardoso M, Noites R, Loroño G, Vieira GCS. Extraradicular Infection and Apical Mineralized Biofilm: A Systematic Review of Published Case Reports. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072335
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez, Alejandro R., Jaime Rendón, P. S. Ortolani-Seltenerich, Yetzangel Pérez-Ron, Miguel Cardoso, Rita Noites, Gaizka Loroño, and Gaya C. S. Vieira. 2025. "Extraradicular Infection and Apical Mineralized Biofilm: A Systematic Review of Published Case Reports" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072335
APA StylePérez, A. R., Rendón, J., Ortolani-Seltenerich, P. S., Pérez-Ron, Y., Cardoso, M., Noites, R., Loroño, G., & Vieira, G. C. S. (2025). Extraradicular Infection and Apical Mineralized Biofilm: A Systematic Review of Published Case Reports. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072335







