Enterocutaneous Fistula in a Patient with Crohn’s Disease After Internalization of a Foreign Body into the Gastrointestinal Tract
Abstract
1. Introduction
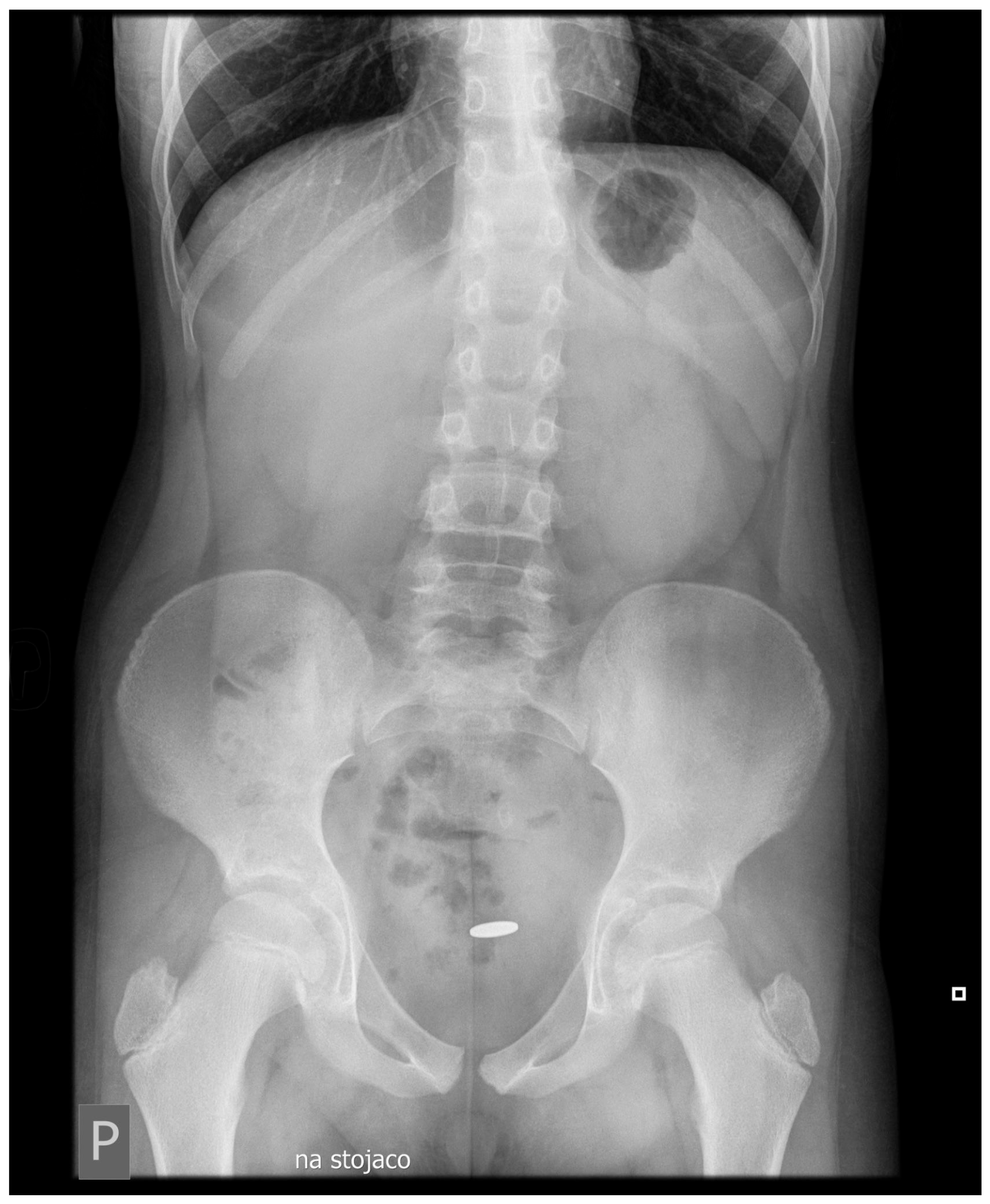
1.1. Case Presentation
1.2. Investigations
2. Discussion
| foreign objects causing fistulisations in Crohn’s patients |
|
| foreign objects mimicking Crohn’s disease |
|
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| ADA | Adalimumab |
| ECF | Enterocutaneous fistula |
| PAF | Perianal fistula |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| US | Ulcerative colitis |
| CT | Computer tomography |
| MR | Magnetic resonance |
References
- Kalla, R.; Ventham, N.T.; Satsangi, J.; Arnott, I.D. Crohn’s disease. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2014, 349, g6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zani, A.; Cozzi, D.A. Giovanni Battista Morgagni and his contribution to pediatric surgery. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2008, 43, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera-Castro, L.; Ferre-Aracil, C.; Garcia-Garcia-de-Paredes, A.; Rodriguez-de-Santiago, E.; Lopez-Sanroman, A. Management of complex perianal Crohn’s disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 30, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier-Massouille, G.; Balde, M.; Salleron, J.; Turck, D.; Dupas, J.L.; Mouterde, O.; Merle, V.; Salomez, J.L.; Branche, J.; Marti, R.; et al. Natural history of pediatric Crohn’s disease: A population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, A.S.; Ledder, O.; Leach, S.T.; Lemberg, D.A. Crohn’s and colitis in children and adolescents. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 5862–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łodyga, M.; Eder, P.; Gawron-Kiszka, M.; Dobrowolska, A.; Gonciarz, M.; Hartleb, M.; Kłopocka, M.; Małecka-Wojciesko, E.; Radwan, P.; Reguła, J.; et al. Guidelines for the management of patients with Crohn’s disease. Recommendations of the Polish Society of Gastroenterology and the Polish National Consultant in Gastroenterology. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2021, 16, 257–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Sandborn, W.J. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2012, 380, 1590–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawryniuk, A.; Rybak, M.; Szwajkosz, K.; Sawicka, K.; Krzyżanowska, E.; Łuczyk, R.; Szymczuk, E.; Tomaszewski, A. Crohn’s disease being caused by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. J. Educ. Health Sport 2017, 7, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petagna, L.; Antonelli, A.; Ganini, C.; Bellato, V.; Campanelli, M.; Divizia, A.; Efrati, C.; Franceschilli, M.; Guida, A.M.; Ingallinella, S.; et al. Pathophysiology of Crohn’s disease inflammation and recurrence. Biol. Direct 2020, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartnik, W.; Szczepanek, M. Wrzodziejące Zapalenie Jelita Grubego [w: Choroby Przewodu Pokarmowego]. 2018. Available online: https://ruj.uj.edu.pl/xmlui/handle/item/145408 (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- Farooqi, N.; Tuma, F. Intestinal Fistula. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tuma, F.; Crespi, Z.; Wolff, C.J.; Daniel, D.T.; Nassar, A.K. Enterocutaneous Fistula: A Simplified Clinical Approach. Cureus 2020, 12, e7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limura, E.; Giordano, P. Modern management of anal fistula. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharl, M.; Rogler, G.; Biedermann, L. Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribovskaja-Rupp, I.; Melton, G.B. Enterocutaneous Fistula: Proven Strategies and Updates. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2016, 29, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redden, M.H.; Ramsay, P.; Humphries, T.; Fuhrman, G.M. The etiology of enterocutaneous fistula predicts outcome. Ochsner J. 2013, 13, 507–511. [Google Scholar]
- Asghar, J.I.; Crosby, J.; Beilman, G.J. Enterocutaneous fistula as early presentation of Crohn’s disease in an adult woman. Case Rep. 2012, 2012, bcr1120115265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavricka, S.R.; Rogler, G. Fistula treatment: The unresolved challenge. Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyemura, M.C. Foreign body ingestion in children. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 72, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quitadamo, P.; Battagliere, I.; Del Bene, M.; Caruso, F.; Gragnaniello, P.; Dolce, P.; Caldore, M.; Bucci, C. Sharp-Pointed Foreign Body Ingestion in Pediatric Age. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 76, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, J.A.; Sollenberger, L.L.; Rege, R.V.; Glenn, J.; Joehl, R.J. External duodenal fistula. Causes, complications, and treatment. Arch. Surg. 1986, 121, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenza, M.; Rossi, D.; De Gruttola, I.; Ballanti, C. Enterocutaneous fistula treatment: Case report and review of the literature. J. Surg.-J. Ital. Surg. Assoc. 2018, 39, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, A.; Koletzko, S.; Turner, D.; Escher, J.C.; Cucchiara, S.; de Ridder, L.; Kolho, K.L.; Veres, G.; Russell, R.K.; Paerregaard, A.; et al. ESPGHAN revised porto criteria for the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vleugels JL, A.; Hazewinkel, Y.; Dekker, E. Morphological classifications of gastrointestinal lesions. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbroja, M.; Cyranka, W.; Kuczyńska, M.; Brodzisz, A.; Maria Woźniak, M. Perianal lesions as an unusual first manifestation of Crohn’s disease in pediatric patients—Case series. J. Ultrason. 2020, 20, e222–e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, L.J.; Mönnink GL, E.; van Dieren, S.; Mundt, M.W.; D’Haens GR, A.M.; Bemelman, W.A.; Buskens, C.J.; van der Bilt, J.D.W. Fistulizing Perianal Disease as a First Manifestation of Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yzet, C.; Sabbagh, C.; Loreau, J.; Turpin, J.; Brazier, F.; Dupas, J.-L.; Nguyen-Khac, É.; Fumery, M. Inflammatory bowel disease symptoms at the time of anal fistula lead to the diagnosis of Crohn’s disease. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2020, 44, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheifetz, A.S. Management of active Crohn disease. JAMA 2013, 309, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberio, B.; Gracie, D.J.; Black, C.J.; Ford, A.C. Efficacy of biological therapies and small molecules in induction and maintenance of remission in luminal Crohn’s disease: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Gut 2023, 72, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Murad, M.H.; Fumery, M.; Sedano, R.; Jairath, V.; Panaccione, R.; Sandborn, W.J.; Ma, C. Comparative efficacy and safety of biologic therapies for moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, T.; Sekulovski, M.; Peshevska-Sekulovska, M. Immunogenicity and Loss of Effectiveness of Biologic Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients Due to Anti-Drug Antibody Development. Antibodies 2024, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Senent, S.; Barreiro-de-Acosta, M.; García-Sánchez, V. Enterocutaneous fistulas and Crohn’s disease: Clinical characteristics and response to treatment. Rev. Esp. Enfermedades Dig. 2013, 105, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirmai, L.; Pelletier, A.L.; Gault, N.; Zallot, C.; Bouguen, G.; Bouchard, D.; Roland Nicaise, P.; Peyneau, M.; Sironneau, S.; Bittencourt, M.C.; et al. Relationship between clinical remission of perianal fistulas in Crohn’s disease and serum adalimumab concentrations: A multi-center cross-sectional study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Inoue, T.; Yorifuji, N.; Iguchi, M.; Sakanaka, T.; Narabayashi, K.; Kakimoto, K.; Nouda, S.; Okada, T.; Abe, Y.; et al. Effect of Adalimumab on an enterocutaneous fistula in patients with Crohn’s disease: A case series. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 2603–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillicuddy, E.A.; Chaar, C.I.; Flynn, C.; Villalona, G.; Longo, W.E. Cologastric fistula with a foreign body in a patient with Crohn’s disease. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2010, 83, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciuto, A.; Aardoom, M.; Orlanski-Meyer, E.; Navon, D.; Carman, N.; Aloi, M.; Bronsky, J.; Däbritz, J.; Dubinsky, M.; Hussey, S.; et al. Predicting outcomes in pediatric crohn’s disease for management optimization: Systematic review and consensus statements from the pediatric inflammatory bowel disease–ahead program. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 403–436.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuenzig, M.E.; Fung, S.G.; Marderfeld, L.; Mak JW, Y.; Kaplan, G.G.; Ng, S.C.; Wilson, D.C.; Cameron, F.; Henderson, P.; Kotze, P.G.; et al. Twenty-first Century Trends in the Global Epidemiology of Pediatric-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1147–1159.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, M.A.; Boyer, R.S.; Jackson, W.D. Toothpick foreign body perforation and migration mimicking Crohn’s disease in a child. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1996, 23, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Lu, X.; Qian, L.; Yu, C.; Xie, J.; Kong, D. Procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, and white blood cell count levels in end-stage cancer patients: A retrospective study on inflammatory markers and their prognostic value. Medicine 2024, 103, e40792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapel, N.; Ouni, H.; Benahmed, N.A.; Barbot-Trystram, L. Fecal Calprotectin for the Diagnosis and Management of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2023, 14, e00617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Chun, S.W.; Kim, H.M.; Cho, J.H. Risk factors for complications associated with upper gastrointestinal foreign bodies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8125–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, G.; Calabrese, C.; Conti Nibali, R.; De Matteis, A.; Casciani, E.; Martemucci, L.; Pagliaro, G.; Pagano, N. Enteroscopy in children. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpias Kamiya, K.J.; Hosoe, N.; Takabayashi, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Sun, X.; Miyanaga, R.; Fukuhara, K.; Fukuhara, S.; Naganuma, M.; Nakayama, A.; et al. Endoscopic removal of foreign bodies: A retrospective study in Japan. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 12, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, A.K.; Choday, P.; Buitrago, C.; Saffouri, G. Navigating the Hazards: A Case Study on the Complexities of Battery Ingestion in an Adult. Clin. Case Rep. 2025, 13, e70184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenstein, A.J.; Sachar, D.B.; Mann, D.; Lachman, P.; Heimann, T.; Aufses, A.H., Jr. Spontaneous free perforation and perforated abscess in 30 patients with Crohn’s disease. Ann. Surg. 1987, 205, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, I.R.; Tian, C.; Hsu, R. Crohn disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK436021/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- O’Donnell, M.E.; Gibson, N.; Sharif, M.A.; Spence, R.A.; Lee, J. Crohn’s disease of the terminal ileum: A cheap diagnosis. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 177, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, O.; Kakoutis, E.; Sakkas, L.; Konstantara, A.; Chatzopoulos, S.; Kotronis, A.; Makrantonakis, N. Ingested toothpick fistula of the ileum mimicking Crohn’s disease. Acta Gastro-Enterol. Belg. 2010, 73, 527–529. [Google Scholar]
- Montacer, K.E.; Haddad, F.; Mansouri, S.E.; Tahiri, M.; Hliwa, W.; Bellabah, A.; Badre, W. An ileo-caecal foreign body mimicking a Crohn disease: Case report. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2018, 31, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visagan, R.; Grossman, R.; Dimitriadis, P.A.; Desai, A. ‘Crohn’z meanz Heinz’: Foreign body inflammatory mass mimicking Crohn’s disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2013009603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, J.R.; Ding, A.; Herzlinger, M.; Subedi, S.; Alverson, B. Pen Foreign Body Ingestion Mimicking Crohn’s Disease in a Pediatric Patient. Rhode Isl. Med. J. 2013, 105, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wadham, B.; Connolly, T.; Ledda, V.; Satchidanand, R.Y. Radiolucent foreign bodies presenting as inflammatory bowel disease: The case of an ingested plastic straw disguising as Crohn’s. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2022, 104, e147–e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dines, J.T.; Harvey, A. Chronic intentional chicken bone ingestion mimicking inflammatory bowel disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e239022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surlin, V.; Georgescu, E.; Comănescu, V.; Mogoantă, S.S.; Georgescu, I. Ileal iterative spontaneous perforation from foreign body granuloma: Problems of histopathologic diagnosis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2009, 50, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Diagnosis | On Admission | During Hospitalization | Operation Day | Follow-Up | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.2021 | 09.2023 | 09.2023 | 10.2023 | 10.2023 | 11.2024 | 03.2025 | |
| Calprotectin [µg/g] | 796 | - | 63 | - | - | 92 | 132 |
| CRP [mg/L] | 17 | 29.5 | 10 | 2.5 | 6.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 |
| WBC [×103/µL] | 10.53 | 9.43 | 7.01 | 6.92 | - | 6.51 | 5.05 |
| ESR [mm/h] | 39 | 44 | - | - | - | 7 | 8 |
| Procalcitonin [ng/mL] | - | - | - | - | 0.02 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buzun, W.H.; Pełka, K.I.; Złotowska, A.; Łuczak, J.; Patkowski, D.; Pytrus, T.; Kofla-Dłubacz, A. Enterocutaneous Fistula in a Patient with Crohn’s Disease After Internalization of a Foreign Body into the Gastrointestinal Tract. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072327
Buzun WH, Pełka KI, Złotowska A, Łuczak J, Patkowski D, Pytrus T, Kofla-Dłubacz A. Enterocutaneous Fistula in a Patient with Crohn’s Disease After Internalization of a Foreign Body into the Gastrointestinal Tract. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072327
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuzun, Wiktoria Hanna, Karolina Izabela Pełka, Aleksandra Złotowska, Justyna Łuczak, Dariusz Patkowski, Tomasz Pytrus, and Anna Kofla-Dłubacz. 2025. "Enterocutaneous Fistula in a Patient with Crohn’s Disease After Internalization of a Foreign Body into the Gastrointestinal Tract" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072327
APA StyleBuzun, W. H., Pełka, K. I., Złotowska, A., Łuczak, J., Patkowski, D., Pytrus, T., & Kofla-Dłubacz, A. (2025). Enterocutaneous Fistula in a Patient with Crohn’s Disease After Internalization of a Foreign Body into the Gastrointestinal Tract. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072327





