Real-World Evidence of Administration of Biologic Agents in Patients with Severe Asthma: An Analysis of the Respiratory Department of University Hospital of Patras Asthma Registry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
Study Design and Patient Selection
3. Outcome Measures
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Results
5.1. Baseline Patient Characteristics
5.2. Treatment Modalities Pre-Biologic Agents
5.3. Biologic Administration
5.4. Patient Characteristics by Biologic Use
5.5. Biologic Efficacy and Safety Profiles
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brusselle, G.G.; Koppelman, G.H. Biologic Therapies for Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settipane, R.A.; Kreindler, J.L.; Chung, Y.; Tkacz, J. Evaluating direct costs and productivity losses of patients with asthma receiving GINA 4/5 therapy in the United States. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 123, 564–572.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzGerald, J.M.; Tran, T.N.; Alacqua, M.; Altraja, A.; Backer, V.; Bjermer, L.; Bjornsdottir, U.; Bourdin, A.; Brusselle, G.; Bulathsinhala, L.; et al. International severe asthma registry (ISAR): Protocol for a global registry. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2020, 20, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguin, F.; Cardet, J.C.; Chung, K.F.; Diver, S.; Ferreira, D.S.; Fitzpatrick, A.; Gaga, M.; Kellermeyer, L.; Khurana, S.; Knight, S.; et al. Management of severe asthma: A European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society guideline. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.; Stewart, K.; Misirovs, R.; Lipworth, B.J. Targeting Downstream Type 2 Cytokines or Upstream Epithelial Alarmins for Severe Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Corren, J.; Bourdin, A.; Chupp, G.; Israel, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E.; Griffiths, J.M.; Hellqvist, A.; Bowen, K.; et al. Tezepelumab in Adults and Adolescents with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, G.J.; Neffen, H.; Castro-Rodriguez, J.A. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous omalizumab vs placebo as add-on therapy to corticosteroids for children and adults with asthma: A systematic review. Chest 2011, 139, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.; Cabrera, P.; Berkman, N.; Buhl, R.; Holgate, S.; Wenzel, S.; Fox, H.; Hedgecock, S.; Blogg, M.; Cioppa, G.D. The effect of treatment with omalizumab, an anti-IgE antibody, on asthma exacerbations and emergency medical visits in patients with severe persistent asthma. Allergy 2005, 60, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel, E.H.; Wenzel, S.E.; Thompson, P.J.; Prazma, C.M.; Keene, O.N.; Yancey, S.W.; Ortega, H.G.; Pavord, I.D.; Investigators, S. Oral glucocorticoid-sparing effect of mepolizumab in eosinophilic asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleecker, E.R.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Chanez, P.; Papi, A.; Weinstein, S.F.; Barker, P.; Sproule, S.; Gilmartin, G.; Aurivillius, M.; Werkstrom, V.; et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for patients with severe asthma uncontrolled with high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta(2)-agonists (SIROCCO): A randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2115–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, J.M.; Bleecker, E.R.; Nair, P.; Korn, S.; Ohta, K.; Lommatzsch, M.; Ferguson, G.T.; Busse, W.W.; Barker, P.; Sproule, S.; et al. Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin-5 receptor alpha monoclonal antibody, as add-on treatment for patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma (CALIMA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2128–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Colice, G.; Griffiths, J.M.; Almqvist, G.; Ponnarambil, S.; Kaur, P.; Ruberto, G.; Bowen, K.; Hellqvist, A.; Mo, M.; et al. NAVIGATOR: A phase 3 multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tezepelumab in adults and adolescents with severe, uncontrolled asthma. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Parnes, J.R.; Wang, L.; Mo, M.; Roseti, S.L.; Griffiths, J.M.; van der Merwe, R. Tezepelumab in Adults with Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.; Castro, M.; Corren, J.; Maspero, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Pirozzi, G.; Sutherland, E.R.; Evans, R.R.; Joish, V.N.; et al. Dupilumab efficacy and safety in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma despite use of medium-to-high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus a long-acting beta2 agonist: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled pivotal phase 2b dose-ranging trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledford, D.K.; Soong, W.; Carr, W.; Trevor, J.; Tan, L.; Carstens, D.; Ambrose, C.S. Real-world severe asthma biologic administration and adherence differs by biologic: CHRONICLE study results. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 131, 598–605.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.F.; Wenzel, S.E.; Brozek, J.L.; Bush, A.; Castro, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2024 Gina Severe Asthma. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/severe-asthma/ (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Papaioannou, A.I.; Mplizou, M.; Porpodis, K.; Fouka, E.; Zervas, E.; Samitas, K.; Markatos, M.; Bakakos, P.; Papiris, S.; Gaga, M.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with allergic asthma: A real-life study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2021, 42, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarraf, H.N.; Masoud, H.H.; Zidan, M.; Wahba, B. Effectiveness and safety of omalizumab in severe, persistent IgE-mediated asthma in pediatric and adult patients: A real-world observational study in Egyptian population. J. Asthma 2020, 57, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilette, C.; Canonica, G.W.; Chaudhuri, R.; Chupp, G.; Lee, F.E.; Lee, J.K.; Almonacid, C.; Welte, T.; Alfonso-Cristancho, R.; Jakes, R.W.; et al. REALITI-A Study: Real-World Oral Corticosteroid-Sparing Effect of Mepolizumab in Severe Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 2646–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallieri, M.; Zervas, E.; Fouka, E.; Porpodis, K.; Mitrova, M.H.; Tzortzaki, E.; Makris, M.; Ntakoula, M.; Papaioannou, A.I.; Lyberopoulos, P.; et al. RELIght: A two-year REal-LIfe study of mepolizumab in patients with severe eosinophilic asTHma in Greece: Evaluating the multiple components of response. Allergy 2022, 77, 2848–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, J.; Steffens, A.; Chastek, B.; Deb, A. Real-World Effectiveness of Mepolizumab in Patients with Allergic and Non-Allergic Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2024, 17, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzella, F.; Ruggiero, P.; Galeone, C.; Scelfo, C.; Bagnasco, D.; Facciolongo, N. Significant improvement in lung function and asthma control after benralizumab treatment for severe refractory eosinophilic asthma. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 64, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langton, D.; Politis, J.; Collyer, T.; Khung, S.W.; Bardin, P. Benralizumab and mepolizumab treatment outcomes in two severe asthma clinics. Respirology 2023, 28, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maglio, A.; Vitale, C.; Pelaia, C.; D’Amato, M.; Ciampo, L.; Sferra, E.; Molino, A.; Pelaia, G.; Vatrella, A. Severe Asthma Remissions Induced by Biologics Targeting IL5/IL5r: Results from a Multicenter Real-Life Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, J.E.; Hearn, A.P.; Dhariwal, J.; d’Ancona, G.; Douiri, A.; Roxas, C.; Fernandes, M.; Green, L.; Thomson, L.; Nanzer, A.M.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness of Benralizumab in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Chest 2021, 159, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancor, D.; Bautista, S.; Lopez-Rodriguez, R.; Valverde-Monge, M.; Fernandez-Nieto, M.; Rial, M.J. Four-month real-life response to Tezepelumab in patients with multi-failure to other biologics. Allergol. Immunopathol 2024, 52, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greig, R.; Chan, R.; Fardon, T.C.; Lipworth, B.J. Real-world effects of tezepelumab on small airway dysfunction in severe refractory asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, T.M.; Vanden Berghe, E.; Kraft, M.; Vonk, J.M.; Nawijn, M.C.; Siddiqui, S.; Sun, K.; Fabbri, L.M.; Rabe, K.F.; Chung, K.F.; et al. Predictors and associations of the persistent airflow limitation phenotype in asthma: A post-hoc analysis of the ATLANTIS study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Tran, T.N.; Heaney, L.G.; Jones, R.C.; Menzies-Gow, A.N.; Busby, J.; Jackson, D.J.; Pfeffer, P.E.; Rhee, C.K.; et al. Characterization of Severe Asthma Worldwide: Data From the International Severe Asthma Registry. Chest 2020, 157, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larenas-Linnemann, D.; Rhee, C.K.; Altraja, A.; Busby, J.; Tran, T.N.; Wang, E.; Popov, T.A.; Mitchell, P.D.; Pfeffer, P.E.; Pleasants, R.A.; et al. International Severe Asthma Registry (ISAR): 2017–2024 Status and Progress Update. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | (N, %) |
|---|---|
| Total number of patients | 80 |
| Age (95% CI) | 67.0 (61.0 to 70.0) |
| Male/female | 28 (35.0%)/52 (65.0%) |
| Current smokers/ex-smokers | 9 (11.2%)/30 (37.5%) |
| Never smokers | 41 (51.3%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) ± SD | 28.29 ± 5.90 |
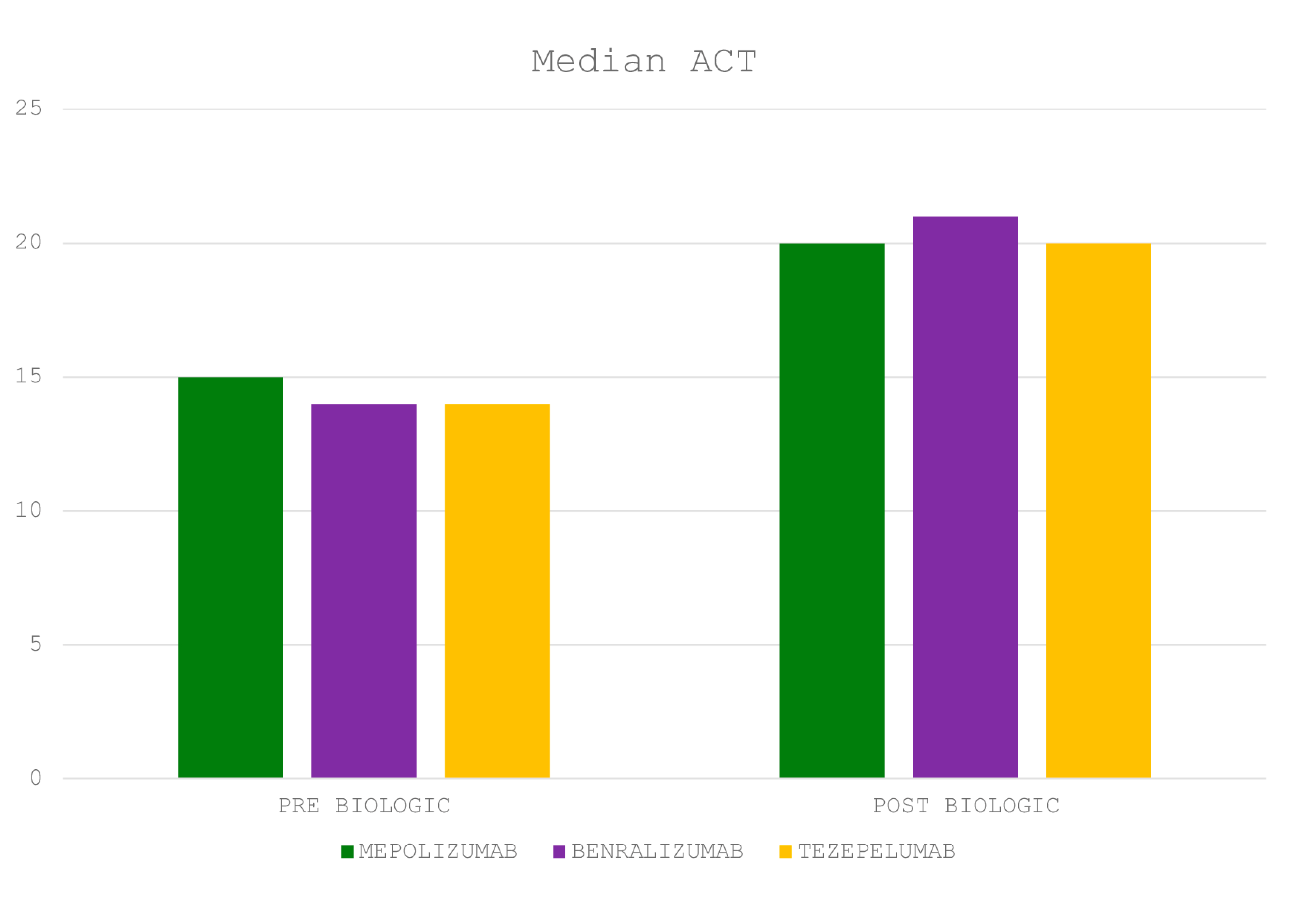
| ACT (95% CI) | 15 (15 to 16) |
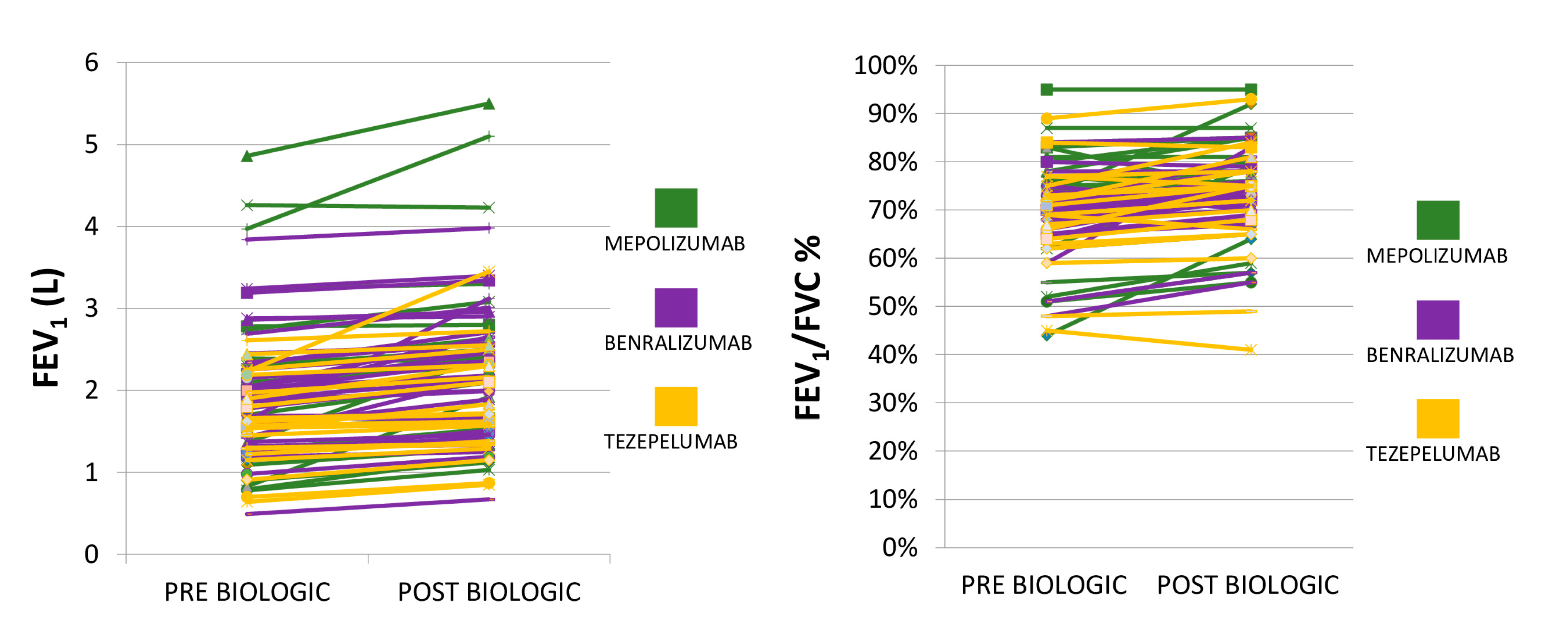
| FEV1/FVC (95% CI) | 0.71 (0.69 to 0.73) |
| FEV1% predicted ± SD | 68.9 ± 22.0 |
| PAL phenotype | 29 (36.3%) |
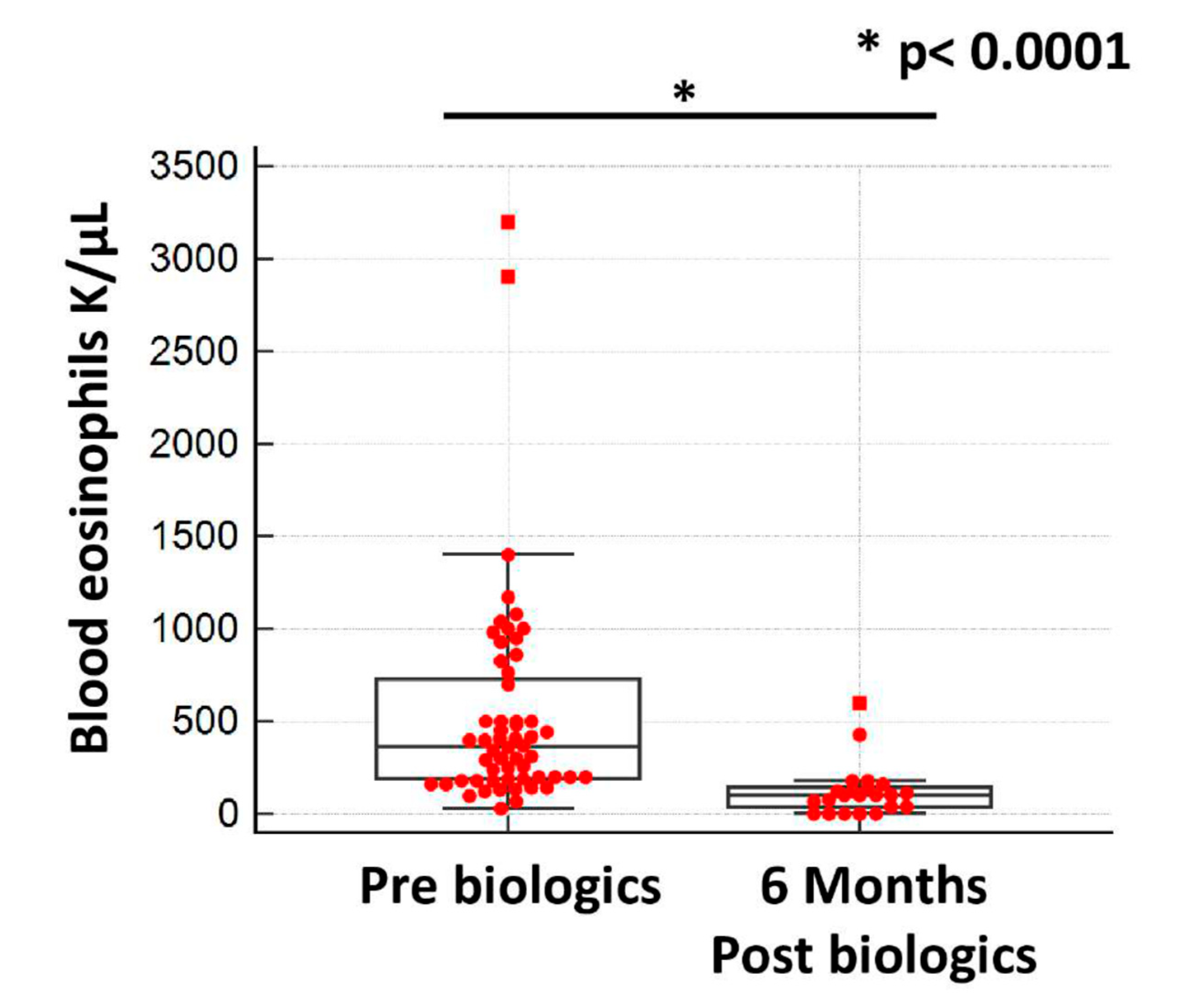
| Eosinophils (K/μL) (95% CI) | 365 (252 to 448) |
| FeNO (ppb) ± SD | 26.3 ± 17.9 |
| IgE (IU/mL) (95% CI) | 266 (20 to 1099) |
| Positive SPTs | 19 (23.8%) |
| Arterial hypertension | 29 (36.3%) |
| Dyslipidemia | 27 (33.8%) |
| Chronic heart disease | 17 (21.3%) |
| Nasal polypoids | 9 (11.3%) |
| GERD | 6 (7.5%) |
| Bronchiectasis | 6 (7.5%) |
| Hospitalization due to exacerbation in the previous year | 29 (36.3%) |
| Baseline Phenotypic Characteristics | Anti-IL-5 (Mepolizumab) N = 23 | Anti-IL-5R (Benralizumab) N = 33 | Anti-TSLP (Tezepelumab) N = 21 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (95% CI) | 61.0 (51.0 to 70.7) | 65.0 (61.0 to 71.0) | 70.0 (63.2 to 71.0) |
| Male/female | 11 (47.8%)/12 (52.2%) | 10 (30.3%)/23 (69.7%) | 6 (28.6%)/15 (71.4%) |
| Current smokers/ex-smokers | 2 (8.7%)/9 (39.1%) | 3 (9.1%)/9 (27.3%) | 3 (14.3%)/11 (52.4%) |
| Never smokers | 12 (52.2%) | 21 (63.6%) | 7 (33.3%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) ± SD | 27.02 ± 4.4 | 28.55 ± 6.6 | 30.52 ± 5.41 |
| FEV1/FVC (95% CI) | 0.73 (0.62 to 0.80) | 0.71 (0.67 to 0.73) | 0.70 (0.63 to 0.74) |
| FEV1% predicted ± SD | 69.57 ± 20.62 | 70.87 ± 21.21 | 65.53 ± 26.10 |
| Eosinophils (K/μL) (95% CI) | 425 (340 to 935) | 420 (200 to 741) | 260 (160 to 370) |
| Nasal polypoids | 5 (21.7%) | 1 (3.0%) | 1 (4.8%) |
| Positive SPTs | 4 (17.4%) | 5 (15.2%) | 4 (19.0%) |
| Hospitalization/exacerbation in the previous year | 15 (65.2%) | 9 (27.3%) | 4 (19.0%) |
| Oral corticosteroids (longitudinal use) | 5 (21.7%) | 2 (6.0%) | 2 (9.5%) |
| Characteristics | (N, %) |
|---|---|
| ACT (95% CI) | 20 (20 to 21) |
| FEV1/FVC (95% CI) | 0.74 (0.73 to 0.76) |
| FEV1% predicted ± SD | 77.6 ± 25.2 |
| Eosinophils (K/μL) (95% CI) | 100 (40 to 121) |
| Severe exacerbations/Hospitalizations | 2/80 (2.5%) |
| Oral corticosteroids (longitudinal use 7.5 mg/day prednisone-concomitant autoimmune disease) | 3/80 (3.8%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papaioannou, O.; Christopoulos, I.; Tsiri, P.; Sampsonas, F.; Karkoulias, K.; Lykouras, D.; Sotiropoulou, V.; Theohari, E.; Papalexatos, D.; Komninos, D.; et al. Real-World Evidence of Administration of Biologic Agents in Patients with Severe Asthma: An Analysis of the Respiratory Department of University Hospital of Patras Asthma Registry. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072174
Papaioannou O, Christopoulos I, Tsiri P, Sampsonas F, Karkoulias K, Lykouras D, Sotiropoulou V, Theohari E, Papalexatos D, Komninos D, et al. Real-World Evidence of Administration of Biologic Agents in Patients with Severe Asthma: An Analysis of the Respiratory Department of University Hospital of Patras Asthma Registry. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072174
Chicago/Turabian StylePapaioannou, Ourania, Ioannis Christopoulos, Panagiota Tsiri, Fotios Sampsonas, Kyriakos Karkoulias, Dimosthenis Lykouras, Vasilina Sotiropoulou, Eva Theohari, Dionysios Papalexatos, Dimitrios Komninos, and et al. 2025. "Real-World Evidence of Administration of Biologic Agents in Patients with Severe Asthma: An Analysis of the Respiratory Department of University Hospital of Patras Asthma Registry" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072174
APA StylePapaioannou, O., Christopoulos, I., Tsiri, P., Sampsonas, F., Karkoulias, K., Lykouras, D., Sotiropoulou, V., Theohari, E., Papalexatos, D., Komninos, D., Christopoulos, A., & Tzouvelekis, A. (2025). Real-World Evidence of Administration of Biologic Agents in Patients with Severe Asthma: An Analysis of the Respiratory Department of University Hospital of Patras Asthma Registry. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072174







