Abatacept, Golimumab, and Sarilumab as Selected Bio-Originator Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs with Diverse Mechanisms of Action in Their Current Use in Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Tender Joint Count (TJC)—number of tender joints out of 28 assessed joints.
- Swollen Joint Count (SJC)—number of swollen joints out of 28 assessed joints.
- ESR or CRP.
- Patient Global Assessment (PGA)—patient’s self-reported assessment of disease activity, rated on a Visual Analog Scale (VAS) from 0 to 100 mm.
- TJC—number of tender joints out of 28 assessed joints.
- SJC—number of swollen joints out of 28 assessed joints.
- PGA—on a 0–10 cm (0–100 mm) Visual Analog Scale.
- Evaluator Global Assessment (EGA)—physician’s assessment of disease activity on a 0–10 cm VAS;
2. Bio-Originator Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (boDMARDs)
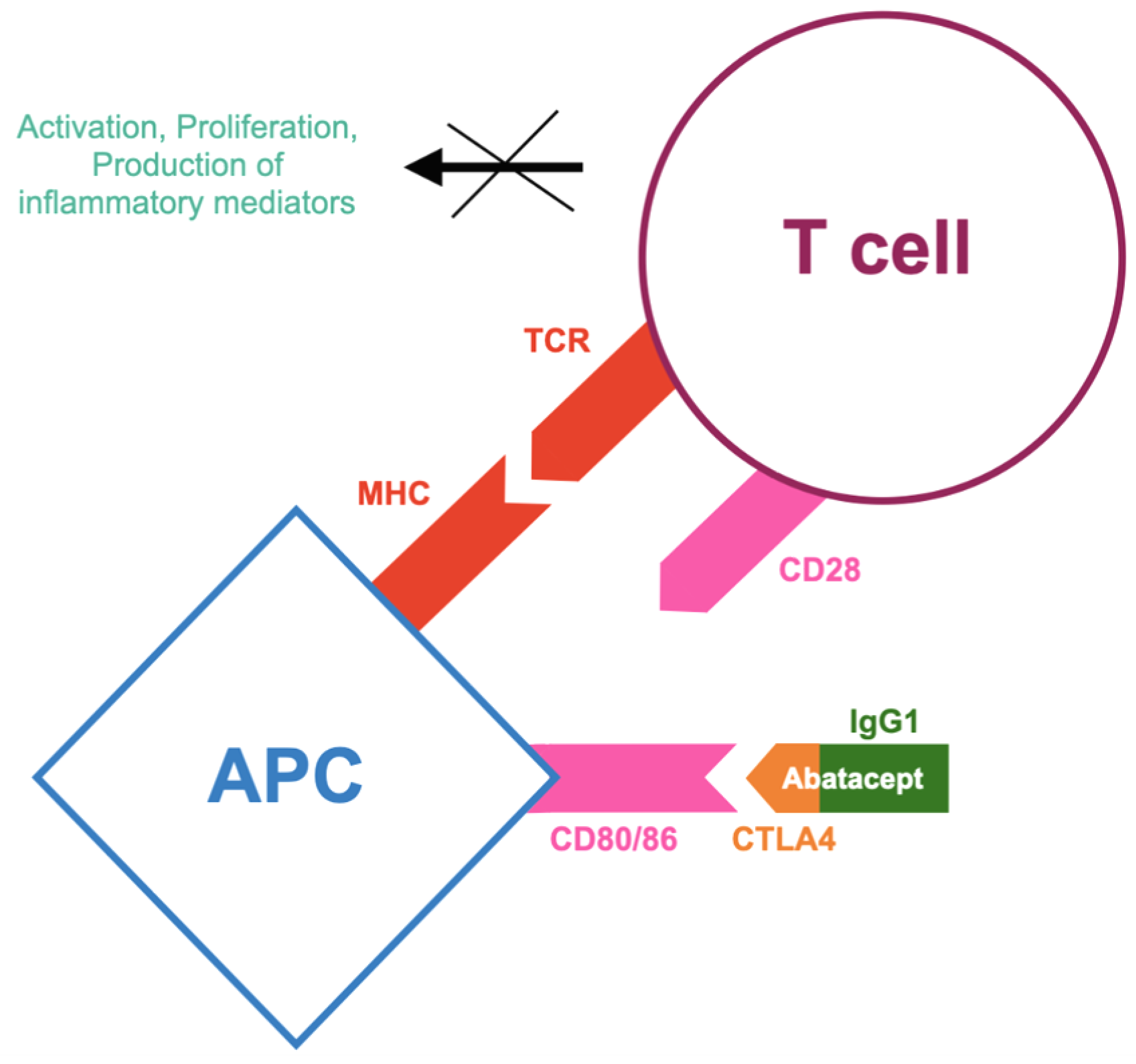
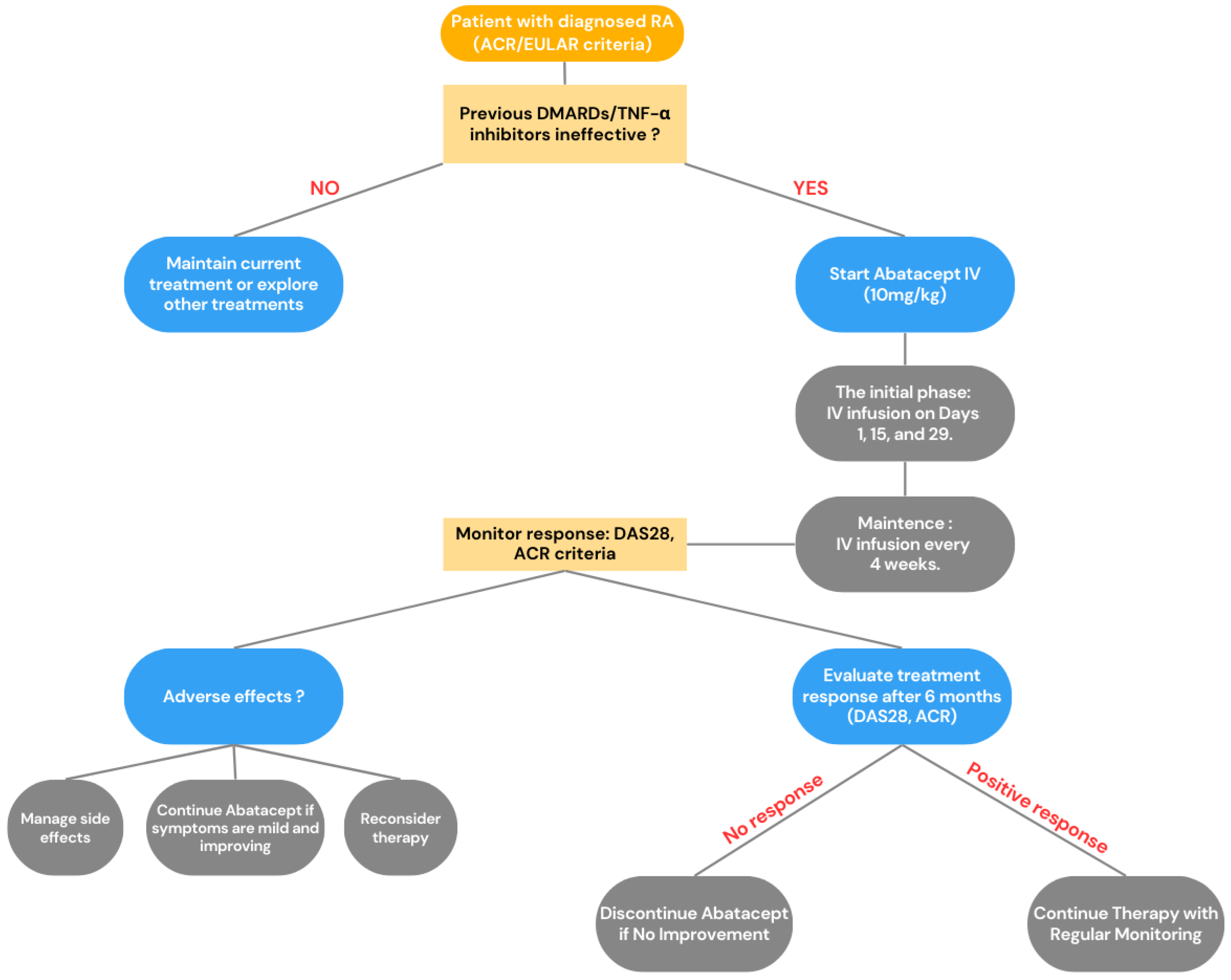
2.1. Co-Stimulation Inhibitor (CTLA4-Ig)—Abatacept
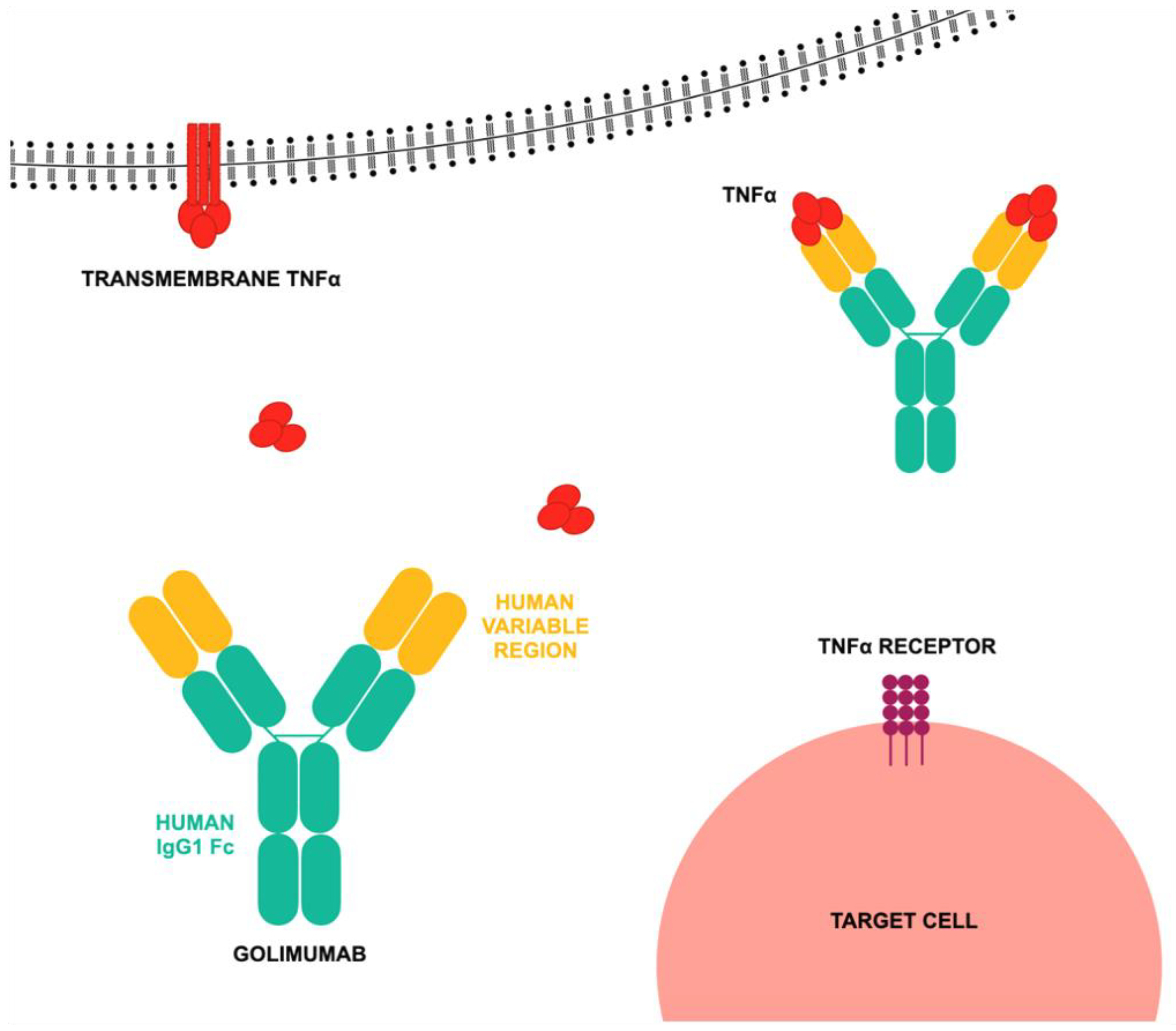
2.2. TNF Inhibitor—Golimumab
2.3. IL-6R Inhibitor—Sarilumab
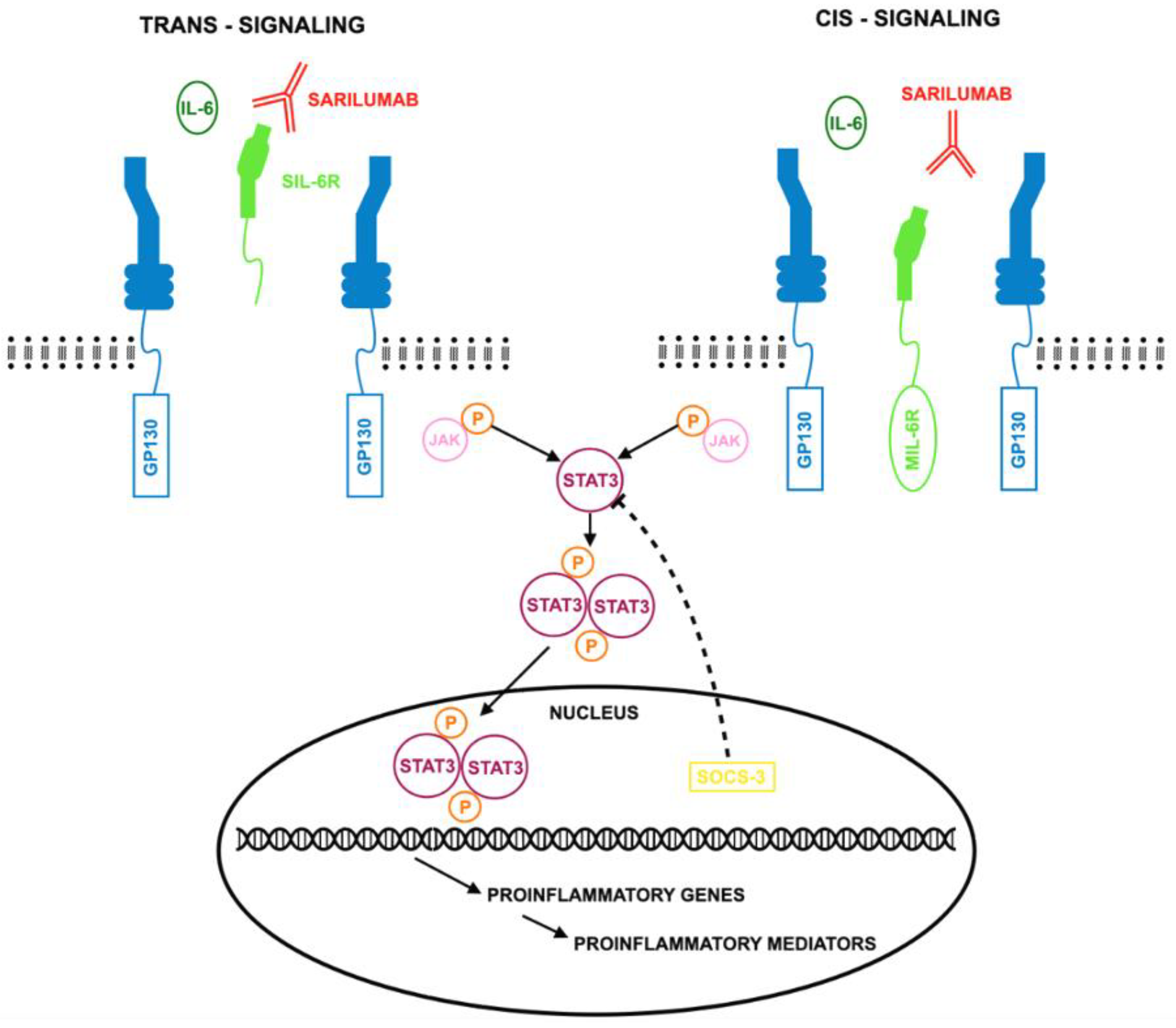
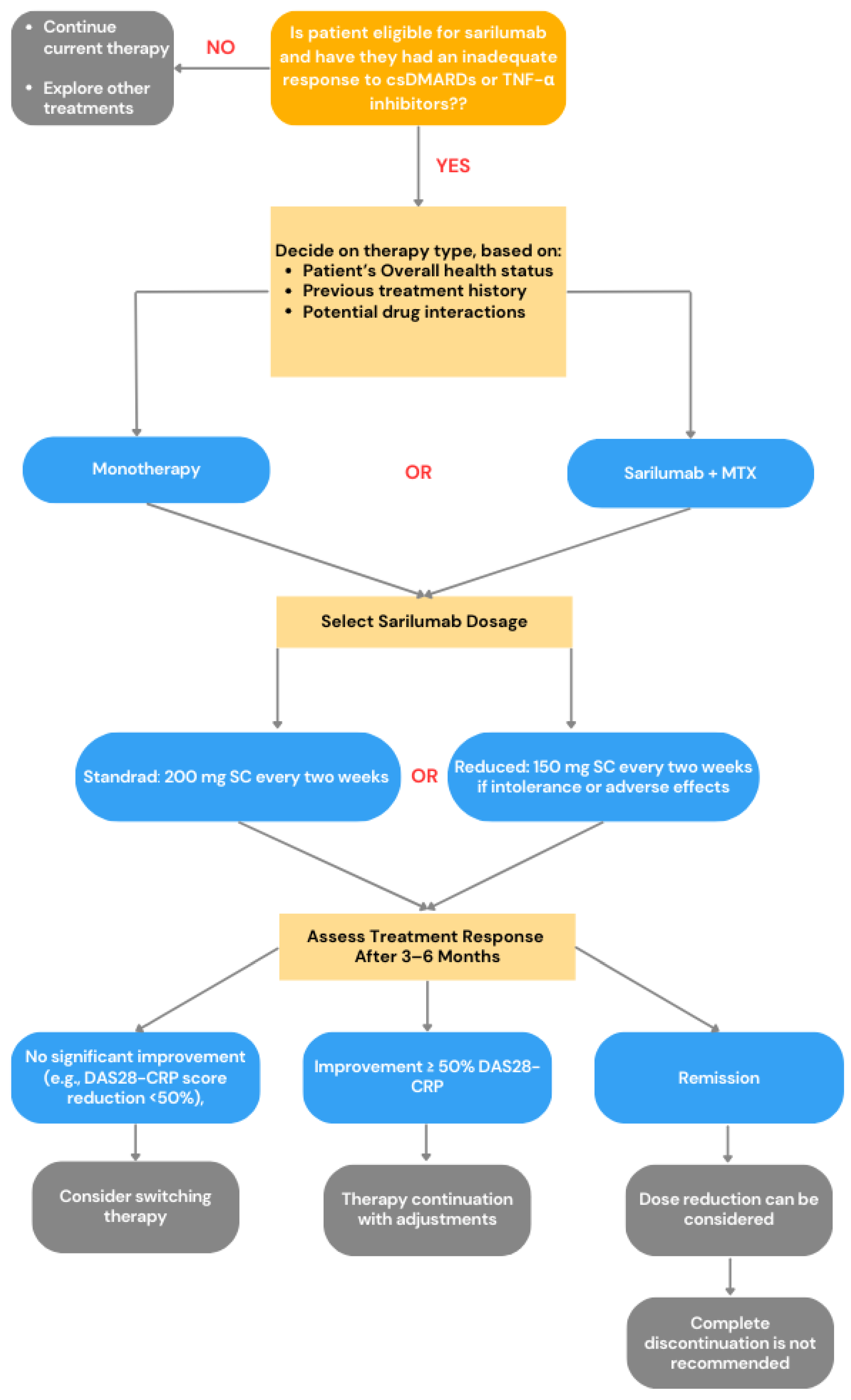
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases. Available online: https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/arthritis-and-rheumatic-diseases (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Sharma, A.; Goel, A. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and its treatment with anti-inflammatory natural products. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 4687–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, R.; Berney, S.M. Clinical aspects of rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology 2005, 12, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, J.; Basu, N.; Schlachetzki, J.C.M.; Schett, G.; McInnes, I.B.; Cavanagh, J. Immune mechanisms of depression in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, C.-E.; Popescu, C.C.; Agache, M.; Dinache, G.; Codreanu, C. Depression in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Narrative Review-Diagnostic Challenges, Pathogenic Mechanisms and Effects. Medicina 2022, 58, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bungau, S.G.; Behl, T.; Singh, A.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Chigurupati, S.; Vijayabalan, S.; Das, S.; Palanimuthu, V.R. Targeting Probiotics in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, P.; Guo, S.; Schrodi, S.J.; He, D. Apoptosis, Autophagy, NETosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis Mediated Programmed Cell Death as Targets for Innovative Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 809806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, S.; Schrodi, S.J.; He, D. Molecular and Cellular Heterogeneity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 790122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, Z.; Schmalzing, M.; Dörner, T.; Tony, H.-P.; Muhammad, K. Therapeutic Cytokine Inhibition Modulates Activation and Homing Receptors of Peripheral Memory B Cell Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 572475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, C.; Falcone, M. The role of invariant NKT cells in organ-specific autoimmunity. Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; van der Heijde, D.; Machold, K.P.; Aletaha, D.; Landewé, R. Proposal for a new nomenclature of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Cui, S.; Yang, L.; Cui, J.; Wang, X.; Ding, M.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Chang, F.; Jin, H.; et al. Efficacy of non-conventional synthetic DMARDs for patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. RMD Open 2023, 9, e003487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bergstra, S.A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Aletaha, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Hyrich, K.L.; Pope, J.E.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biolog-ical disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Kumar, H.; Handa, R.; Talapatra, P.; Ray, S.; Gupta, V. Use of clinical disease activity index score for assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: An Indian experience. Arthritis 2011, 2011, 146398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaffi, F.; Cimmino, M.A.; Leardini, G.; Gasparini, S.; Grassi, W. Disease activity assessment of rheumatoid arthritis in daily practice: Validity, internal consistency, reliability and congruency of the Disease Activity Score including 28 joints (DAS28) compared with the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI). Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, 552–559. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, J.A. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, ITC1–ITC16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Queiroz, M.J.; de Castro, C.T.; Albuquerque, F.C.; Brandão, C.C.; Gerlack, L.F.; Pereira, D.C.R.; Barros, S.C.; Andrade, W.W.; Bastos, E.A.; Azevedo, J.N.B.; et al. Safety of biological therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in administrative health databases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 928471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiro, S.; Sepriano, A.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Nam, J.L.; Smolen, J.S.; van der Heijde, D.; Dougados, M.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Burmester, G.R.; et al. Safety of synthetic and biological DMARDs: A systematic literature review informing the 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1101–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Kanbori, M.; Ishii, Y. Effectiveness of golimumab in rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate response to first-line biologic therapy: Results from a Japanese post-marketing surveillance study. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, K.; Gill, H.; Singh, N. Long-term safety of biologic and targeted synthetic disease modifying drugs in rheumatology. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2024, 36, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, L.; Singh, J.A. Abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 2009, CD007277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, M.; Scheinecker, C. How does abatacept really work in rheumatoid arthritis? Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Beaumont, G.; Martínez Calatrava, M.J.; Castañeda, S. Abatacept mechanism of action: Concordance with its clinical profile. Reumatol. Clin. 2012, 8, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderman, E.R.; Pope, R.M. Drug Insight: Abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2006, 2, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, Y.; Hu, S. A review on applications of abatacept in systemic rheumatic diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, R.; Moilanen, E. Abatacept, a novel CD80/86-CD28 T cell co-stimulation modulator, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 104, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinia, A.; Gharibia, T.; Marofib, F.; Babaloo, Z.; Baradarana, B. CTLA-4: From mechanism to autoimmune therapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felson, D.; Smolen, J.S. Trial of Upadacitinib or Abatacept in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombo-Suarez, M.; Gomez-Reino, J.J. Abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, A.P.; Jasenecova, M.; Vasconcelos, J.C.; Filer, A.; Raza, K.; Qureshi, S.; D’Agostino, M.A.; McInnes, I.B.; Isaacs, J.D.; Pratt, A.G.; et al. Abatacept in individuals at high risk of rheumatoid arthritis (APIPPRA): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, parallel, placebo-controlled, phase 2b clinical trial. Lancet 2024, 403, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, H.A.; Deeks, E.D. Abatacept: A Review in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drugs 2017, 77, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soubrier, M.; Lahaye, C.; Tatar, Z. Abatacept for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Special Focus on the Elderly. Drugs Aging 2018, 35, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, H.I.; Wong, R.; Nys, M.; Kou, T.D.; Dominique, A.; Martini, A.; Lovell, D.J.; Ruperto, N.; Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation (PRINTO) and the Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study Group (PRCSG). Abatacept: A Review of the Treatment of Polyarticular-Course Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Paediatr. Drugs 2020, 22, 653–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goettel, A.M.; DeClercq, J.; Choi, L.; Graham, T.B.; Mitchell, A.A. Efficacy and Safety of Abatacept, Adalimumab, and Etanercept in Pediatric Patients With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 26, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliesi, A.; de Oliveira, A.B.; Oliveira, A.B.; Xavier, R.; da Mota, L.M.H.; Bertolo, M.B.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Citera, G.; de Carvalho, L.S.F. Compared efficacy of rituximab, abatacept, and tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to methotrexate or TNF inhibitors agents: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Adv. Rheumatol. 2023, 63, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Rheumatology 20/50/70 Response Criteria (ACR20/50/70). Available online: https://eprovide.mapi-trust.org/instruments/american-college-of-rheumatology-20-50-70-response-criteria (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Mohamed Ahamada, M.; Wu, X. Analysis of efficacy and safety of abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2023, 41, 1882–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizzo, G.; Gremese, E.; Ferraccioli, G. Abatacept in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: Biological and clinical profiles of the responders. Immunotherapy 2018, 10, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussirot, E.; Michaud, M.; Wendling, D.; Devauchelle, V. Abatacept as Adjunctive Therapy in Refractory Polymyalgia Rheumatica. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 1888–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, M.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Rudin, A.; Hetland, M.L.; Heiberg, M.S.; Nordström, D.C.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Gudbjornsson, B.; Ørnbjerg, L.M.; Bøyesen, P.; et al. Certolizumab pegol, abatacept, tocilizumab or active conventional treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis: 48-week clinical and radiographic results of the investigator-initiated randomised controlled NORD-STAR trial. Ann Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, B.; Qayed, M.; McCracken, C.; Bratrude, B.; Betz, K.; Suessmuth, Y.; Yu, A.; Sinclair, S.; Furlan, S.; Bosinger, S.; et al. Phase II Trial of Costimulation Blockade With Abatacept for Prevention of Acute GVHD. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, A.G.; Kim, H.T.; Liegel, J.; Arnason, J.; Ho, V.T.; Antin, J.H.; Joyce, R.; Cutler, C.; Gooptu, M.; Nikiforow, S.; et al. Phase 2 clinical trial evaluating abatacept in patients with steroid-refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2023, 141, 2932–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunandan, S.; Gorfinkel, L.; Graiser, M.; Bratrude, B.; Suessmuth, Y.; Gillespie, S.; Westbrook, A.L.; Williams, K.M.; Schoettler, M.L.; Kean, L.S.; et al. Abatacept for the prevention of GVHD in patients receiving mismatched unrelated transplants: A real-world analysis. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 4395–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel-Quiroz, V.R.; Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Alarcón, G.S. Abatacept for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2016, 25, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerola, A.M.; Kauppi, M.J. Abatacept as a successful therapy for myositis—A case-based review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, W.E.; Bundy, B.N.; Anderson, M.S.; Cooney, L.A.; Gitelman, S.E.; Goland, R.S.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Haller, M.J.; Krischer, J.P.; et al. Abatacept for Delay of Type 1 Diabetes Progression in Stage 1 Relatives at Risk: A Randomized, Double-Masked, Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachid, O.; Osman, A.; Abdi, R.; Haik, Y. CTLA4-Ig (abatacept): A promising investigational drug for use in type 1 diabetes. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatomi, H.; Yamashita, D.; Kitao, R.; Nishioka, H. Abatacept-associated panniculitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 16, e256197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariette, X.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Ravaud, P.; Combe, B. Registries in rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmune diseases: Data from the French registries. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, M.; Gujral, A.; Barakoti, B.; Magaliff, E. Abatacept-Induced Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder-Like Syndrome Without a History of Transplant. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, S488–S490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbert-Roth, A.; Enejosa, J.; Pangan, A.L.; Haraoui, B.; Rischmueller, M.; Khan, N.; Zhang, Y.; Martin, N.; Xavier, R.M. Trial of Upadacitinib or Abatacept in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelechas, E.; Voulgari, P.V.; Drosos, A.A. Golimumab for Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.C.; Keystone, E.C. Intravenous golimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, M.; Archer, R.; Tosh, J.; Simpson, E.; Everson-Hock, E.; Stevens, J.; Hernandez-Alava, M.; Paisley, S.; Dickinson, K.; Scott, D.; et al. Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, tocilizumab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis not previously treated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and after the failure of conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs only: Systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 2016, 20, 1–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltis, D.; Settas, L.; Georgiadis, A.; Koukli, E.; Bounas, A.; Livieratos, A.; Petrikkou, E.; Kalogiannaki, H.; Repa, A.; Vassilopoulos, D.; et al. The effects of golimumab on patient centric outcomes amongst rheumatoid arthritis patients in Greece. The GO-Q study. Rheumatol. Int. 2022, 42, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, E.G.; Halilovic, J.; Stan-Ugbene, O. Golimumab: Review of the efficacy and tolerability of a recently approved tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor. Clin. Ther. 2010, 32, 1681–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.E. Golimumab: A Review in Inflammatory Arthritis. BioDrugs 2017, 31, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanowska-Próchnicka, K.; Felis-Giemza, A.; Olesińska, M.; Wojdasiewicz, P.; Paradowska-Gorycka, A.; Szukiewicz, D. The Role of TNF-α and Anti-TNF-α Agents during Preconception, Pregnancy, and Breastfeeding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitoma, H.; Horiuchi, T.; Tsukamoto, H.; Ueda, N. Molecular mechanisms of action of anti-TNF-α agents—Comparison among therapeutic TNF-α antagonists. Cytokine 2018, 101, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Panaccione, N.; Whitmire, N.; Dulai, P.S.; Vande Casteele, N.; Singh, S.; Boland, B.S.; Collins, A.; Sandborn, W.J.; Panaccione, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of simultaneous treatment with two biologic medications in refractory Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, T.J.; Kavanaugh, A. Golimumab in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamant, M.; Paul, S.; Roblin, X. Golimumab for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slevin, S.M.; Egan, L.J. New Insights into the Mechanisms of Action of Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Monoclonal Antibodies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2909–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urdaneta, M.; Jethwa, H.; Sultan, R.; Abraham, S. A review on golimumab in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. Immunotherapy 2017, 9, 871–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, D.A.; Bathon, J.M.; Hanicq, D.; Yasothan, U.; Kirkpatrick, P. Golimumab. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgari, P.V. Golimumab: A new anti-TNF-alpha agent for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagoras, C.; Voulgari, P.V.; Drosos, A.A. Golimumab, the newest TNF-α blocker, comes of age. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 570–577. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, A.T.; Campanilho-Marques, R.; Fonseca, J.E. Golimumab (anti-TNF monoclonal antibody): Where we stand today. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2021, 17, 1586–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, V.; Plosker, G.L. Golimumab: In the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. BioDrugs 2009, 23, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, S.; Greenwald, D. Golimumab. mAbs 2009, 1, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, M.; Viapiana, O.; Orsolini, G.; Fracassi, E.; Idolazzi, L.; Gatti, D.; Adami, S.; Govoni, M. Why golimumab in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis? Reumatismo. 2015, 66, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios Rodriguez, V.; Poddubnyy, D. Golimumab for treatment of axial spondyloarthritis. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svedbom, A.; Storck, C.; Kachroo, S.; Govoni, M.; Khalifa, A. Persistence with golimumab in immune-mediated rheumatic diseases: A systematic review of real-world evidence in rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, and psoriatic arthritis. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2017, 11, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husni, M.E.; Deodhar, A.; Schwartzman, S.; Chakravarty, S.D.; Hsia, E.C.; Leu, J.H.; Zhou, Y.; Lo, K.H.; Kavanaugh, A. Pooled safety results across phase 3 randomized trials of intravenous golimumab in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.P.; Kumar, N.; Srinivasa, K.; Gande, A.; Anusha, M.; Dar, H.; Baji, D.B. The Role of Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e33293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Leu, J.; Watson, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, H. Investigation of the Mechanism of Therapeutic Protein-Drug Interaction Between Methotrexate and Golimumab, an Anti-TNFα Monoclonal Antibody. AAPS J. 2018, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toussirot, E.; Vauchy, C.; Binda, D.; Michel, F. Golimumab in radiographic and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: A review of clinical trials. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrin, T.; Haller, M.J.; Steck, A.K.; Felner, E.I.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Leu, J.H.; Zoka, R.; Hedrick, J.A.; Rigby, M.R.; et al. Golimumab and Beta-Cell Function in Youth with New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.A.; Noorbaloochi, S.; Singh, G. Golimumab for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidi, I.; Bouaziz, A.; Mnif, W.; Bartegi, A.; Al-Hizab, F.A.; Amor, N.B. Golimumab Therapy of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Scand. J. Immunol. 2010, 72, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kavanaugh, A. Adverse effects of golimumab in the treatment of rheumatologic diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2014, 13, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, J.; Archer, R.; Davis, S.; Stevenson, M.; Stevens, J.W. Golimumab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure of previous disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: A NICE single technology appraisal. Pharmacoeconomics 2013, 31, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chovel-Sella, A.; Karplus, R.; Sella, T.; Amital, H. Clinical efficacy and adverse effects of golimumab in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2012, 14, 390–394. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y.; Senoo, A.; Fujii, H.; Baker, D. Evaluation of golimumab for the treatment of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Kanbori, M.; Ishii, Y. Effect of Golimumab Dose Escalation in Japanese Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Post-Hoc Analysis of Post-Marketing Surveillance Data. Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadwell, A.; Schechtman, J.; Conaway, D.; Kivitz, A.; Shiff, N.J.; Black, S.; Xu, S.; Langholff, W.; Schwartzman, S.; Curtis, J.R. Effectiveness and safety of intravenous golimumab with and without concomitant methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the prospective, noninterventional AWARE study. BMC Rheumatol. 2023, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.; Ishii, Y.; Masuda, J. Persistence and Safety of Golimumab in Elderly Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Renal Dysfunction in a Real-World Setting. Drugs Real World Outcomes 2023, 10, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, C.L.J.; Meehan, A.G.; Lin, J.; Briscoe, S.D.; Govoni, M. Long-term golimumab persistence: Five-year treatment retention data pooled from pivotal Phase III clinical trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 3397–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.; Tirri, E.; Giardino, A.M.; De Rosa, T.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Dagna, L.; Santo, L.; Ciccia, F.; Frediani, B.; Govoni, M.; et al. Real-world effectiveness and persistence of golimumab as second-line anti-TNFα drug in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and axial spondyloarthritis patients in Italy: GO-BEYOND, a 12-month prospective observational study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 27, e15091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keystone, E.C.; Genovese, M.C.; Klareskog, L.; Hsia, E.C.; Hall, S.T.; Miranda, P.C.; Pazdur, J.; Bae, S.C.; Palmer, W.; Zrubek, J.; et al. Golimumab, a human antibody to tumour necrosis factor {alpha} given by monthly subcutaneous injections, in active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate therapy: The GO-FORWARD Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriols-Lisart, R.; Ferriols-Lisart, F. Dose modifications of anti-TNF drugs in rheumatoid arthritis patients under real-world settings: A systematic review. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 1193–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, D.; Robinson, A. Efficacy and safety of sarilumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2018, 10, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfi, F.; Franza, L.; Carusi, V.; Altamura, S.; Andriollo, G.; Nucera, E. Interleukin-6 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Martin Mola, E. IL-6 targeting compared to TNF targeting in rheumatoid arthritis: Studies of olokizumab, sarilumab and sirukumab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1595–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderman, E.M. Rheumatoid arthritis: IL-6 inhibition in RA—déjà vu all over again? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuora, S. Rheumatoid arthritis: Sarilumab more effective than adalimumab. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondo, M.G.; Biggioggero, M.; Crotti, C.; Becciolini, A.; Favalli, E.G. Profile of sarilumab and its potential in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussar, D.A.; Lee, Y.F. Crisaborole, Dupilumab, and Sarilumab. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2017, 57, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, R.R.; Olsen, N.J. Room for more IL-6 blockade? Sarilumab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Rafique, A.; Potocky, T.; Paccaly, A.; Nolain, P.; Lu, Q.; Iglesias-Rodriguez, M.; St John, G.; Nivens, M.C.; Kanamaluru, V.; et al. Differential Binding of Sarilumab and Tocilizumab to IL-6Rα and Effects of Receptor Occupancy on Clinical Parameters. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 61, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, F.; Nucera, V.; Masala, I.F.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Bonitta, G. Il-6 Involvement in pain, fatigue and mood disorders in rheumatoid arthritis and the effects of Il-6 inhibitor sarilumab. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 149, 104402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Guo, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; De, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Sun, R.; Lv, Y.; Liang, Y.; et al. Current Evidence of Interleukin-6 Signaling Inhibitors in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 615972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Geng, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y. Role of IL-6 inhibitor in treatment of COVID-19-related cytokine release syndrome. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- REMAP-CAP Investigators; Gordon, A.C.; Mouncey, P.R.; Al-Beidh, F.; Rowan, K.M.; Nichol, A.D.; Arabi, Y.M.; Annane, D.; Beane, A.; van Bentum-Puijk, W.; et al. Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiali, S.; Rezagholizadeh, A.; Entezari-Maleki, T. A comprehensive review on sarilumab in COVID-19. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Munafò, A.; Augello, E.; Bellanca, C.M.; Bonomo, C.; Ceccarelli, M.; Musso, N.; Cantarella, G.; Cacopardo, B.; Bernardini, R. Sarilumab Administration in COVID-19 Patients: Literature Review and Considerations. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Feist, E.; Pope, J.E.; Nash, P.; Sibilia, J.; Caporali, R.; Balsa, A. What have we learnt from the inhibition of IL-6 in RA and what are the clinical opportunities for patient outcomes? Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2024, 16, 1759720X241283340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J. Sarilumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, Y.N.; Deeks, E.D. Sarilumab: A Review in Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drugs 2018, 78, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, E.G.; Rogan, E.L.; Vyas, D.; Prasad, N.; Mai, Y. Sarilumab: Review of a Second IL-6 Receptor Antagonist Indicated for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2018, 52, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.B. A review of sarilumab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunotherapy 2018, 10, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Buch, M.H.; Tanaka, Y.; Kameda, H.; Praestgaard, A.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Fernandez-Nebro, A.; Huizinga, T. Sarilumab monotherapy vs sarilumab and methotrexate combination therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2596–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Broeder, N.; den Broeder, A.A.; Verhoef, L.M.; van den Hoogen, F.H.J.; van der Maas, A.; van den Bemt, B.J.F. Non-Medical Switching from Tocilizumab to Sarilumab in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Low Disease Activity, an Observational Study. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 114, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshimoto, K.; Kondo, Y.; Kikuchi, J.; Hanaoka, H.; Kaneko, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Differences in the strength of inhibition of interleukin-6 signalling by subcutaneous sarilumab and tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2023, 41, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E.; Freemantle, N.; Proudfoot, C.; Chen, C.-I.; Pollissard, L.; Kuznik, A.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Mangan, E.; Carita, P.; Huynh, T.M. Indirect Treatment Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab Monotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Inadequate Response to Conventional Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotti, C.; Biggioggero, M.; Becciolini, A.; Favalli, E.G. Sarilumab: Patient-reported outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis. Patient Relat. Outcome Meas. 2018, 9, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermejo, I.; Ren, S.; Simpson, E.; Clowes, M.; Scott, D.L.; Young, A.; Stevenson, M. Sarilumab for Previously-Treated Moderate or Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Single Technology Appraisal. Pharmacoeconomics 2018, 36, 1427–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Su, Y.; Paccaly, A.; Kanamaluru, V. Population Pharmacokinetics of Sarilumab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, E.; Freemantle, N.; Proudfoot, C.; Chen, C.-I.; Pollissard, L.; Kuznik, A.; Van Hoogstraten, H.; Mangan, E.; Carita, P.; Huynh, T.M. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of sarilumab combination therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs or tumour necrosis factor α inhibitors: Systematic literature review and network meta-analyses. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Wada, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Hagino, O.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Graham, N.M.H.; Kameda, H. Sarilumab plus methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to methotrexate: Results of a randomized, placebo-controlled phase III trial in Japan. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossec, L.; Strand, V.; Proudfoot, C.; Chen, C.-I.; Guillonneau, S.; Kimura, T.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Mangan, E.; Reaney, M. Effects of Sarilumab on Rheumatoid Arthritis as Reported by Patients Using the Rheumatoid Arthritis Impact of Disease Scale. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, P.; Rondon, J.; Parrino, J.; Lin, Y.; Pena-Rossi, C.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Graham, N.M.H.; Liu, N.; Paccaly, A.; Wu, R.; et al. Safety and tolerability of subcutaneous sarilumab and intravenous tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, P.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Thangavelu, K.; Mangan, E.; St John, G.; Verschueren, P. Subcutaneous Sarilumab in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis who Previously Received Subcutaneous Sarilumab or Intravenous Tocilizumab: An Open-Label Extension of a Randomized Clinical Trial. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020, 2, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.F.; Parrino, J.; Mangan, E.K.; Paccaly, A.; Lin, Y.; Xu, C.; Fan, C.; Graham, N.M.H.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Torri, A. Immunogenicity of Sarilumab Monotherapy in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Who Were Inadequate Responders or Intolerant to Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs. Rheumatol. Ther. 2019, 6, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, R.; Genovese, M.C.; Lin, Y.; St John, G.; van der Heijde, D.; Wang, S.; Gomez-Reino, J.J.; Maldonado-Cocco, J.A.; Stanislav, M.; Kivitz, A.J.; et al. Long-term safety of sarilumab in rheumatoid arthritis: An integrated analysis with up to 7 years’ follow-up. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, H.-P.; Feist, E.; Aries, P.M.; Zinke, S.; Krüger, K.; Ahlers, J.; Albrecht, I.; Barrionuevo, C.; Kalus, S.; Burkhardt, H. Sarilumab reduces disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate response to janus kinase inhibitors or tocilizumab in regular care in Germany. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2022, 6, rkac002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, Y.; Maeyama, A.; Hagio, T.; Sakai, M.; Maruyama, A.; Yamamoto, T. Usefulness of Sarilumab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis after Regression of Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2023, 2023, 5780733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraenkel, L.; Bathon, J.M.; Englan, B.R.; E St Clair, E.W.; Arayssi, T.; Carandang, K.; Deane, K.D.; Genovese, M.; Huston, K.K.; Kerr, G.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainz, L.; Riera, P.; Moya, P.; Bernal, S.; Casademont, J.; Díaz-Torné, C.; Millán, A.M.; Park, H.S.; Lasa, A.; Corominas, H. Impact of IL6R genetic variants on treatment efficacy and toxicity response to sarilumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, M.; Schwarz, T.; Wehkamp, U.; Bohne, A.-S.; Drerup, K. Rheumatoid neutrophilic dermatosis under treatment with the interleukin-6-receptor-antagonist sarilumab in a patient with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2023, 50, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmester, G.R.; Strand, V.; Kivitz, A.J.; Hu, C.-C.; Wang, S.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Klier, G.L.; Fleischmann, R. Long-term safety and efficacy of sarilumab with or without background csDMARDs in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 3268–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisell, T.; Bower, H.; Morin, M.; Baecklund, E.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Delcoigne, B.; Feltelius, N.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H.; Lindqvist, E.; Lindström, U.; et al. Safety of biological and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis as used in clinical practice: Results from the ARTIS programme. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiera, R.F.; Unizony, S.; Warrington, K.J.; Sloane, J.; Giannelou, A.; Nivens, M.C.; Akinlade, B.; Wong, W.; Bhore, R.; Lin, Y.; et al. Sarilumab for Relapse of Polymyalgia Rheumatica during Glucocorticoid Taper. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Bergstra, S.A.; Smolen, J.S.; van der Heijde, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Verschueren, P.; de Souza, S.; Pope, J.E.; et al. Efficacy of synthetic and biological DMARDs: A systematic literature review informing the 2022 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Criterion | Category | Points |
|---|---|---|
| Joint involvement | 1 large joint | 0 |
| 2–10 large joints | 1 | |
| 1–3 small joints (with or without large joints) | 2 | |
| 4–10 small joints (with or without large joints) | 3 | |
| More than 10 joints (including at least 1 small joint) | 5 | |
| Serology (RF or ACPAs) | Negative | 0 |
| Low-positive | 2 | |
| High-positive | 3 | |
| Acute-phase reactants (CRP or ESR) | Normal | 0 |
| Abnormal | 1 | |
| Symptom duration | Less than 6 weeks | 0 |
| 6 weeks or more | 1 |
| Step | Action | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Diagnosis | Confirm RA by using ACR/EULAR criteria | Assess joint involvement, serology, and inflammatory markers |
| 2. Initial treatment | Start MTX ± short-term glucocorticoids | If MTX is contraindicated, use leflunomide or sulfasalazine |
| 3. Monitoring (3–6 months) | Assess DAS28 or CDAI | If no improvement at 3 months, adjust treatment |
| 4. Escalation | Add bDMARD or tsDMARD in high-risk patients | Consider JAK inhibitors with caution |
| 5. Failure of advanced therapy | Switch to another bDMARD or tsDMARD | Choose a drug with a different mechanism of action |
| 6. Remission and Tapering | Reduce DMARD dose gradually | Complete discontinuation is not recommended |
| Disease Activity Level | DAS28 Score Range | Mean DAS28 ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Remission | <2.6 | 1.99 ± 0.38 |
| Low Disease Activity | 2.6–3.2 | 3.04 ± 0.17 |
| Moderate Disease Activity | 3.2–5.1 | 4.25 ± 0.58 |
| High Disease Activity | >5.1 | 6.38 ± 0.87 |
| Disease Activity Level | CDAI Score Range | Mean CDAI ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Remission | <2.8 | 0.90 ± 0.65 |
| Low Disease Activity | 2.8–10 | 6.45 ± 2.35 |
| Moderate Disease Activity | 10–22 | 16.46 ± 3.31 |
| High Disease Activity | >22 | 38.56 ± 11.88 |
| Criterion Category | Parameters | Score |
|---|---|---|
| ACR20 | ≥20% improvement in Tender Joint Count (TJC) and Swollen Joint Count (SJC), plus ≥20% improvement in at least 3 of the 5 additional indicators listed above | ≥20% improvement |
| ACR50 | ≥50% improvement in TJC and SJC, plus ≥50% improvement in at least 3 of the 5 additional indicators listed above | ≥50% improvement |
| ACR70 | ≥70% improvement in TJC and SJC, plus ≥70% improvement in at least 3 of the 5 additional indicators listed above | ≥70% improvement |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawczak, P.; Feszak, I.J.; Bączek, T. Abatacept, Golimumab, and Sarilumab as Selected Bio-Originator Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs with Diverse Mechanisms of Action in Their Current Use in Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062107
Kawczak P, Feszak IJ, Bączek T. Abatacept, Golimumab, and Sarilumab as Selected Bio-Originator Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs with Diverse Mechanisms of Action in Their Current Use in Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062107
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawczak, Piotr, Igor Jarosław Feszak, and Tomasz Bączek. 2025. "Abatacept, Golimumab, and Sarilumab as Selected Bio-Originator Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs with Diverse Mechanisms of Action in Their Current Use in Treatment" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062107
APA StyleKawczak, P., Feszak, I. J., & Bączek, T. (2025). Abatacept, Golimumab, and Sarilumab as Selected Bio-Originator Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs with Diverse Mechanisms of Action in Their Current Use in Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062107








