Retrospective Analysis of Predictive Biomarkers of Survival in Acute Exacerbation of Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease: A Single-Center Study in Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
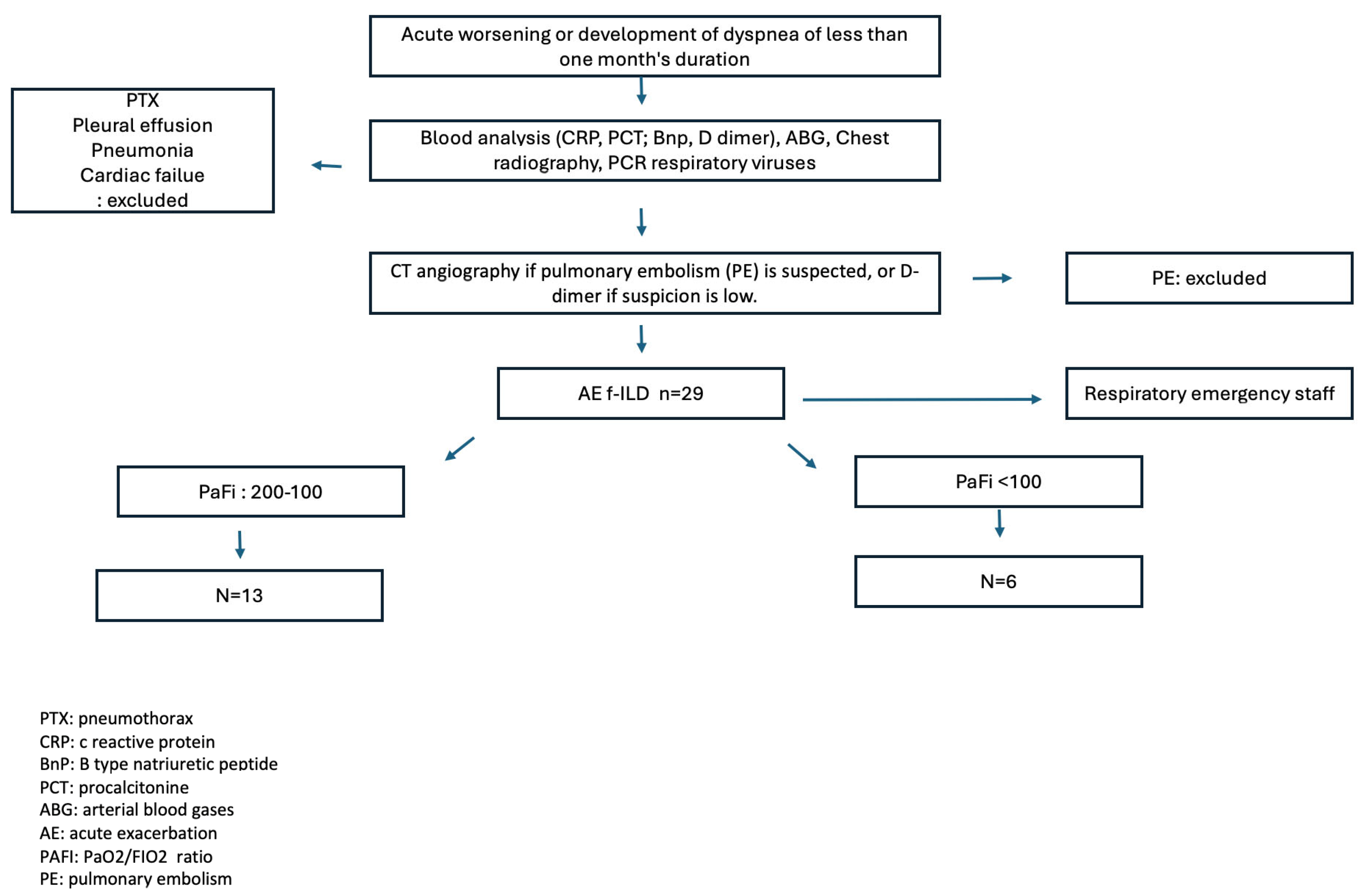
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Variables Studied
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE-f-ILD | Acute exacerbation fibrosing interstitial lung disease |
| AE-IPF | Acute exacerbation idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| f-ILD | fibrosing interstitial lung disease |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| UIP | Usual interstitial pneumonia |
References
- George, P.M.; Spagnolo, P.; Kreuter, M.; Altinisik, G.; Bonifazi, M.; Martinez, F.J.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Renzoni, E.A.; Richeldi, L.; Tomassetti, S.; et al. ILD working group. Progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease: Clinical uncertainties, consensus recommendations, and research priorities. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Wollin, L.; Fischer, A.; Quaresma, M.; Stowasser, S.; Harari, S. Fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: Knowns and unknowns. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 180100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.K.; Martinez, F.J.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Thannickal, V.J.; Prasse, A.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Goeldner, R.G.; Clerisme-Beaty, E.; Tetzlaff, K.; Cottin, V.; et al. The natural history of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishaba, T. Current perspective of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung disease. Respir. Investig. 2022, 60, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambly, N.; Farooqi, M.M.; Dvorkin-Gheva, A.; Donohoe, K.; Garlick, K.; Scallan, C.; Chong, S.G.; MacIsaac, S.; Assayag, D.; Johannson, K.A.; et al. Prevalence and characteristics of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease in a prospective registry. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.; Vašáková, M. The natural history of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, B.F.; Luppi, F. Diagnosis and Management of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases. Clin. Chest Med. 2021, 42, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, R.; Brown, K.K.; Yamano, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Yokoyama, T.; Matsuda, T.; Kimura, T.; Suzuki, A.; Furukawa, T.; Fukuoka, J.; et al. Prevalence and prognosis of chronic fibrosing interstitial lung diseases with a progressive phenotype. Respirology 2022, 27, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.S.; Choe, J.; Chae, E.J.; Hwang, H.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Song, J.W. Progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease: Prevalence and clinical outcome. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuschner, G.; Behr, J. Acute Exacerbation in Interstitial Lung Disease. Front. Med. 2017, 3, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Choe, J.; Chae, E.J.; Song, J.W. Acute exacerbation of fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Incidence and outcomes. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, M.; Bondue, B.; Pesci, A.; Miyazaki, Y.; Song, J.W.; Bhatt, N.Y.; Huggins, J.T.; Oldham, J.M.; Padilla, M.L.; Roman, J.; et al. Acute exacerbations of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, R.; Takemura, T.; Misumi, T.; Nagasawa, R.; Iwasawa, T.; Baba, T.; Hagiwara, E.; Ogura, T. Acute Exacerbation and Proposed Criteria for Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Patients with Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respiration 2023, 102, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collard, H.R.; Moore, B.B.; Flaherty, K.R.; Brown, K.K.; Kaner, R.J.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lasky, J.A.; Loyd, J.E.; Noth, I.; Olman, M.A.; et al. Acute Exacerbations of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 18–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, Y.; Cottin, V.; Brown, K.K. Recent lessons learned in the management of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.W.; Ryerson, C.J.; Guler, S.A. Progression of fibrosing interstitial lung disease. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, T.M.; Wuyts, W. Management of Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 1518–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, D.; Benden, C.; Corris, P.A.; Dark, J.H.; Davis, R.D.; Keshavjee, S.; Lederer, D.J.; Mulligan, M.J.; Patterson, G.A.; Singer, L.G.; et al. A consensus document for the selection of lung transplant candidates: 2014—An update from the Pulmonary Transplantation Council of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2015, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Kim, H.C.; Shim, T.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Huh, J.W.; Hong, S.B.; Lee, G.D.; Kim, D.K.; Park, S.I.; Choi, S. Clinical impact of pre-existing acute exacerbation in patients with interstitial lung disease who underwent lung transplantation. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.H.; Kuo, C.W.; Chen, C.W.; Tseng, Y.L.; Wu, C.L.; Lin, S.H. Baseline plasma KL-6 level predicts adverse outcomes in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis receiving nintedanib: A retrospective real-world cohort study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Clynick, B.; Corte, T.J.; Jo, H.E.; Stewart, I.; Glaspole, I.N.; Grainge, C.; Maher, T.M.; Navaratnam, V.; Hubbard, R.; Hopkins, P.M.A.; et al. Biomarker signatures for progressive idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2101181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, C.; Seeliger, B.; Jäger, B.; Fuge, J.; Welte, T.; Terwolbeck, O.; Freise, J.; van Moorsel, C.H.M.; Zhang, Y.; Prasse, A. Genetic Variation in CCL18 Gene Influences CCL18 Expression and Correlates with Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis—Part B. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, S.; Szewczyk, K.; Jerczyńska, H.; Miłkowska-Dymanowska, J.; Białas, A.J.; Gwadera, Ł.; Piotrowski, W.J. Longitudinal and Comparative Measures of Serum Chitotriosidase and YKL-40 in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 760776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, N.D.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Antonelli, M.; Anzueto, A.; Beale, R.; Brochard, L.; Brower, R.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; et al. The Berlin definition of ARDS: An expanded rationale, justification, and supplementary material. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markin, A.M.; Markina, Y.V.; Bogatyreva, A.I.; Tolstik, T.V.; Chakal, D.A.; Breshenkov, D.G.; Charchyan, E.R. The Role of Cytokines in Cholesterol Accumulation in Cells and Atherosclerosis Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangemi, R.; Calvieri, C.; Falcone, M.; Bucci, T.; Bertazzoni, G.; Scarpellini, M.G.; Barillà, F.; Taliani, G.; Violi, F.; SIXTUS Study Group. Relation of Cardiac Complications in the Early Phase of Community-Acquired Pneumonia to Long-Term Mortality and Cardiovascular Events. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cangemi, R.; Casciaro, M.; Rossi, E.; Calvieri, C.; Bucci, T.; Calabrese, C.M.; Taliani, G.; Falcone, M.; Palange, P.; Bertazzoni, G.; et al. Platelet Activation Is Associated with Myocardial Infarction in Patients with Pneumonia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Badimon, J.J. The Sum of Two Evils. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 1926–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, C.; Anderson, R. Prevalence, pathogenesis, therapy, and prevention of cardiovascular events in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Pneumonia 2016, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, M.; Hayakawa, H.; Urano, T.; Sato, A.; Chida, K.; Nakamura, H.; Takada, A. Relevance of Tissue Factor and Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor for Hypercoagulable State in the Lungs of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Throm. Res. 2000, 99, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, I.; Sato, A.; Hayakawa, H.; Urano, T.; Takada, Y.; Takada, A. Increased procoagulant and antifibrinolytic activities in the lungs with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Throm. Res. 1995, 77, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senoo, T.; Hattori, N.; Tanimoto, T.; Furonaka, M.; Ishikawa, N.; Fujitaka, K.; Haruta, Y.; Murai, H.; Yokoyama, A.; Kohno, N. Suppression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by RNA interference attenuates pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2010, 65, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, H.; Nakayama, K.; Yanai, M.; Suzuki, T.; Yamaya, M.; Watanabe, M.; Sasaki, H. Anticoagulant Therapy for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2005, 128, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.S.; Freiheit, E.; Brown, A.W.; Shlobin, O.A.; Aryal, S.; Ahmad, K.; Khangoora, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Venuto, D.; Nathan, S.D. Association between Anticoagulation and Survival in Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest 2021, 159, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, M.G.; Hart, S.P. Coagulation and anticoagulation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.G.; Feldbrügge, L.; Tapper, E.B.; Popov, Y.; Ghaziani, T.; Afdhal, N.; Robson, S.C.; Mukamal, K.J. Aspirin use is associated with lower liver fibrosis indices among adults in the United States. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, I.; Tacconelli, S.; Bruno, A.; Contursi, A.; Mucci, L.; Hu, X.; Xie, Y.; Chakraborty, R.; Jain, K.; Sacco, A.; et al. Low-dose Aspirin prevents hypertension and cardiac fibrosis when thromboxane A2 is unrestrained. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Deng, J.; Yang, S.; Xiang, Z.; Guo, H.; Xi, H.; Sang, M.; Zhang, W. Aspirin inhibits endometrial fibrosis by suppressing theTGF-β1-Smad2/Smad3 pathway in intrauterine adhesions. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, K.G.; Acosta-Jaquez, H.A.; Romeo, Y.; Ekim, B.; Soliman, G.A.; Carriere, A.; Roux, P.P.; Ballif, B.A.; Fingar, D.C. Regulation of mTOR Complex 1 (mTORC1) by Raptor Ser863 and Multisite Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Lyu, X.; Gong, H.; Tan, S.; Dong, L.; Sanders, Y.Y.; Zhang, X. Aspirin alleviates pulmonary fibrosis through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy pathway. Exp. Geront. 2023, 172, 112085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J.; Corte, T.J.; Jenkins, G.; Kondoh, Y.; Lederer, D.J.; Lee, J.S.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M.; et al. Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An International Working Group Report. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amratia, D.A.; Viola, H.; Ioachimescu, O.C. Glucocorticoid Therapy in Respiratory Illness: Bench to Bedside. J. Investig. Med. 2022, 70, 1662–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Cottin, V. Spectrum of Fibrotic Lung Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Demographic Data | Total (n: 29) | Non-IPF (n: 22) | IPF (n: 7) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male, n, % | 21 (72.4%) | 14 (63.6%) | 7 (100%) | 0.0608 |
| Age, mean (SD) | 70.5 (8.6) | 69.1 (8.1) | 74.9 (9.2) | 0.1137 |
| Smoking status, n, % | ||||
| Non-smoker | 7 (24.1%) | 7 (31.8%) | 0 (0%) | 0.1768 |
| Active smoker | 1 (3.4%) | 1 (4.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Ex-smoker | 21 (72.4%) | 14 (63.6%) | 7 (100%) | |
| Charlson Index, mean (SD) | 2.8 (1.7) | 2.9 (1.9) | 2.3 (1.1) | 0.6365 |
| Prior f-ILD (n, %) | ||||
| No | 4 (13.8%) | 4 (18.2%) | 0 (0%) | 0.5461 |
| Yes | 25 (86.2%) | 18 (81.8%) | 7 (100%) | |
| Prior f-ILD diagnosis (n, %) | ||||
| f-NSIP | 5 (17.2%) | |||
| f-HP | 4 (13.8%) | |||
| SRIF | 3 (10.3%) | |||
| IPF | 7 (24.1%) | |||
| CPFE | 2 (6.9%) | |||
| f-Drug-induced interstitial pneumonitis | 2 (6.9%) | |||
| f-Sjögren’s syndrome lung disease | 1 (3.4%) | |||
| f-COP | 1 (3.4%) | |||
| f-ILD sequelae of distress syndrome | 1 (3.4%) | |||
| f-Unclassifiable interstitial lung disease | 3 (10.3%) | |||
| Spirometry, FVC (%), mean (SD) | 65.4 (17.5) | 66.1 (17.6) | 62.7 (18.6) | 0.6440 |
| Prior chest CT (percent glass) | 0.0675 | |||
| No | 8 (27.6%) | 3 (13.6%) | 5 (71.4%) | |
| <25% | 9 (31%) | 8 (36.4%) | 1 (14.3%) | |
| 25–50% | 5 (17.2%) | 4 (18.2%) | 1 (14.3%) | |
| 50–75% | 2 (6.9%) | 2 (9.1%) | 0 (0%) | |
| >75% | 5 (17.2%) | 5 (22.7%) | 0 (0%) | |
| UIP pattern present (n, %) | <0.0001 | |||
| No | 21 (75%) | 21 (95.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Yes | 7 (25%) | 1 (4.5%) | 6 (100%) | |
| Laboratory data (mean, SD) | ||||
| ESR | 37.9 (30.8) | 44.9 (32.2) | 16.8 (11.4) | 0.0444 |
| LDL | 537.7 (173.2) | 549.4 (186.6) | 507.2 (146.7) | 0.9215 |
| Treatments received (n, %) | ||||
| Prior immunosuppressants, n, % | 17 (60.7%) | 12 (54.5%) | 5 (83.3%) | 0.3547 |
| Prior immunosuppressants (types) | ||||
| Mycophenolate | 2 (16.7%) | 1 (20%) | 0.61026 | |
| Prednisone | 5 (41.7%) | 4 (80%) | ||
| Methylprednisolone | 2 (16.7%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Mycophenolate + prednisone | 3 (25%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Prior antifibrotics | 2 (9.1%) | 4 (66.7%) | ||
| Prior LTOT (n, %) | 0.986 | |||
| No | 7 (31.8%) | 2 (33.3%) | ||
| Resting LTOT | 14 (63.6%) | 4 (66.7%) | ||
| Exercise-induced LTOT | 1 (4.5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Data | Total | Subgroup | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-IPF | IPF | |||
| Trigger (n, %) | 9 (33.3%) | 7 (31.8%) | 2 (40%) | 1.0001 |
| PAFI (mean, SD) | 132.3 (48.5) | 133.3 (47.8) | 124.0 (75) | 0.94695 |
| Severity level of PAFI (n, %) | ||||
| 2 | 13 (68.4%) | 12 (70.6%) | 1 (50%) | 1.0001 |
| 3 | 6 (31.6%) | 5 (29.4%) | 1 (50%) | |
| Laboratory (mean, SD) | ||||
| ESR | 37.9 (30.8) | 44.9 (32.2) | 16.8 (11.4) | 0.0444 |
| LDL | 537.7 (173.2) | 549.4 (186.6) | 507.2 (146.7) | 0.9215 |
| Leukocytes × 109 | 13.9 (4.0) | 13.6 (3.8) | 15.2 (5.1) | 0.6144 |
| Neutrophils × 109 | 11.6 (3.6) | 11.4 (3.6) | 12.4 (3.6) | 0.4495 |
| Lymphocytes × 109 | 1.3 (0.9) | 1.2 (0.5) | 1.7 (1.7) | 0.9777 |
| Platelets × 109 | 277.0 (85.5) | 284.5 (78.6) | 250.7 (110.9) | 0.4310 |
| Fibrinogen | 5.2 (1.1) | 5.2 (1.2) | 5.0 (0.9) | 0.5946 |
| D-dimer | 866.8 (756.7) | 662.4 (544.2) | 1412.0 (1101.6) | 0.1531 |
| Data | Subgroup | Total | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-IPF | IPF | |||
| Cumulative Cortisone Dose (mg), (mean, SD) | 937.6 (785.5) | 540.0 (242.8) | 854.8 (721.4) | 0.2707 |
| Cortisone Dose (mg), (n, %) | ||||
| ≤500 | 5 (26.3%) | 2 (40%) | 7 (29.2%) | 0.967 |
| 501–≤1000 | 9 (47.4%) | 3 (60%) | 12 (50%) | |
| 1001–1500 | 2 (10.5%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (8.3%) | |
| >1501 | 3 (15.8%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (12.5%) | |
| Respiratory Support (n, %) | ||||
| HFNC | 20 (95.2%) | 6 (85.7%) | 26 (92.9%) | 0.4445 |
| NIV | 2 (9.5%) | 1 (16.7%) | 3 (11.1%) | 0.5454 |
| IMV-IOT | 4 (19%) | 1 (16.7%) | 5 (18.5%) | 0.987 |
| Total | 22 (75.9%) | 7 (24.1%) | 29 (100%) | |
| Clinical Data | N Subjects | N Deaths | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (n) | |||
| Female | 8 | 7 | 0.0072 |
| Male | 21 | 12 | |
| Smoking Status (n) | |||
| Non-smoker | 7 | 6 | 0.06 |
| Active smoker | 1 | 0 | |
| Ex-smoker | 21 | 13 | |
| History of Ischemic Heart Disease (n) | |||
| No | 19 | 15 | 0.029 |
| Yes | 10 | 4 | |
| Prior Immunosuppression (n) | |||
| No | 11 | 8 | 0.2402 |
| Yes | 17 | 11 | |
| Prior Antifibrotics (n) | |||
| No | 22 | 14 | 0.3287 |
| Yes | 6 | 5 | |
| Use of LTOT (n) | |||
| No | 9 | 6 | 0.0558 |
| LTOT at rest | 18 | 12 | |
| LTOT only with effort | 1 | 1 | |
| Trigger (n) | |||
| No | 18 | 10 | 0.0291 |
| Yes | 9 | 9 | |
| Cumulative Cortisone Dose (n) | |||
| ≤500 | 7 | 6 | 0.0029 |
| 501–≤1000 | 12 | 6 | |
| 1001–1500 | 2 | 1 | |
| >1501 | 3 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreiro-Posse, A.; Granados, G.; Salvador, S.; Pilia, M.F.; Espejo, D.; Romero, C.; Ojanguren, I.; Muñoz, X.; Villar, A. Retrospective Analysis of Predictive Biomarkers of Survival in Acute Exacerbation of Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease: A Single-Center Study in Spain. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061974
Ferreiro-Posse A, Granados G, Salvador S, Pilia MF, Espejo D, Romero C, Ojanguren I, Muñoz X, Villar A. Retrospective Analysis of Predictive Biomarkers of Survival in Acute Exacerbation of Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease: A Single-Center Study in Spain. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061974
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreiro-Posse, Antía, Galo Granados, Sara Salvador, Maria Florencia Pilia, David Espejo, Christian Romero, Iñigo Ojanguren, Xavier Muñoz, and Ana Villar. 2025. "Retrospective Analysis of Predictive Biomarkers of Survival in Acute Exacerbation of Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease: A Single-Center Study in Spain" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061974
APA StyleFerreiro-Posse, A., Granados, G., Salvador, S., Pilia, M. F., Espejo, D., Romero, C., Ojanguren, I., Muñoz, X., & Villar, A. (2025). Retrospective Analysis of Predictive Biomarkers of Survival in Acute Exacerbation of Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease: A Single-Center Study in Spain. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061974






