Exploring the Muscle-to-Fat Ratio of Pediatric Patients with Thyroid Disorders and Its Interaction with Thyroid Function and Metabolic Syndrome Components
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Body Composition Assessment
2.5. Definition of Study Variables
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, M.; Asuka, E.; Fingeret, A. Physiology, Thyroid Function; StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, R.; Balci, M.K.; Altunbas, H.; Karayalcin, U. The Effect of Body Weight and Weight Loss on Thyroid Volume and Function in Obese Women. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2003, 59, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Cho, J.-H.; Lee, D.Y.; Park, S.E.; Park, C.-Y.; Lee, W.-Y.; Oh, K.-W.; Park, S.-W.; Rhee, E.-J. Association between Thyroid Hormone Levels, Body Composition and Insulin Resistance in Euthyroid Subjects with Normal Thyroid Ultrasound: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2018, 89, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangierski, A.; Ruchała, M.; Krauze, T.; Moczko, J.; Guzik, P. Treatment of Severe Thyroid Function Disorders and Changes in Body Composition. Endokrynol. Pol. 2016, 67, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roef, G.; Lapauw, B.; Goemaere, S.; Zmierczak, H.-G.; Toye, K.; Kaufman, J.-M.; Taes, Y. Body Composition and Metabolic Parameters Are Associated with Variation in Thyroid Hormone Levels among Euthyroid Young Men. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 167, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, A.; Pingitore, A.; Pearce, S.H.S.; Zaman, A.; Iervasi, G.; Razvi, S. Thyroid Hormones and Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiano, F.; Rochira, A.; Gnoni, A.; Siculella, L. Action of Thyroid Hormones, T3 and T2, on Hepatic Fatty Acids: Differences in Metabolic Effects and Molecular Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duntas, L.H.; Brenta, G. A Renewed Focus on the Association between Thyroid Hormones and Lipid Metabolism. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brener, A.; Peleg, I.; Rosenfeld, T.; Kern, S.; Uretzky, A.; Elkon-Tamir, E.; Rosen, G.; Levinson, H.; Israeli, G.; Interator, H.; et al. Beyond Body Mass Index—Body Composition Assessment by Bioimpedance in Routine Endocrine Practice. Endocr. Pract. 2021, 27, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Trotsenburg, P.; Stoupa, A.; Léger, J.; Rohrer, T.; Peters, C.; Fugazzola, L.; Cassio, A.; Heinrichs, C.; Beauloye, V.; Pohlenz, J.; et al. Congenital Hypothyroidism: A 2020–2021 Consensus Guidelines Update-An ENDO-European Reference Network Initiative Endorsed by the European Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and the European Society for Endocrinology. Thyroid 2021, 31, 387–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollowell, J.G.; Staehling, N.W.; Flanders, W.D.; Hannon, W.H.; Gunter, E.W.; Spencer, C.A.; Braverman, L.E. Serum TSH, T(4), and Thyroid Antibodies in the United States Population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strich, D.; Edri, S.; Gillis, D. Current Normal Values for TSH and FT3 in Children Are Too Low: Evidence from over 11,000 Samples. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 25, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lem, A.J.; de Rijke, Y.B.; van Toor, H.; de Ridder, M.A.J.; Visser, T.J.; Hokken-Koelega, A.C.S. Serum Thyroid Hormone Levels in Healthy Children from Birth to Adulthood and in Short Children Born Small for Gestational Age. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3170–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.S.; Burch, H.B.; Cooper, D.S.; Greenlee, M.C.; Laurberg, P.; Maia, A.L.; Rivkees, S.A.; Samuels, M.; Sosa, J.A.; Stan, M.N.; et al. 2016 American Thyroid Association Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Hyperthyroidism and Other Causes of Thyrotoxicosis. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1343–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, W.A.; Tanner, J.M. Variations in the Pattern of Pubertal Changes in Boys. Arch. Dis. Child. 1970, 45, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, W.A.; Tanner, J.M. Variations in Pattern of Pubertal Changes in Girls. Arch. Dis. Child. 1969, 44, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolanowski, M.; Nilsson, B.E. Assessment of Human Body Composition Using Dual-Energy x-Ray Absorptiometryand Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2001, 7, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, H.D.; Samani-Radia, D.; Jebb, S.A.; Prentice, A.M. Skeletal Muscle Mass Reference Curves for Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2014, 9, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burck, L. Characterization and Classification of Geographical Units by Thesocio-Economic Level of the Population 2015; Report No.: 1765; Central Bureauof Statistics: Jerusalem, Israel, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kuczmarski, R.J.; Ogden, C.L.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M.; Flegal, K.M.; Guo, S.S.; Wei, R.; Mei, Z.; Curtin, L.R.; Roche, A.F.; Johnson, C.L. CDC Growth Charts: United States. Adv. Data 2000, 314, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, J.M.; Goldstein, H.; Whitehouse, R.H. Standards for Children’s Height at Ages 2-9 Years Allowing for Heights of Parents. Arch. Dis. Child. 1970, 45, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.T.; Kaelber, D.C.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Blowey, D.; Carroll, A.E.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dionne, J.M.; Falkner, B.; Flinn, S.K.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shypailo, R.J. Age-Based Pediatric Blood Pressure Reference Charts. Baylor College of Medicine, Children’s Nutrition Research Center, Body Composition Laboratory. 2018. Available online: https://www.bcm.edu/bodycomplab/BPappZjs/BPvAgeAPPz.html (accessed on 26 October 2024).
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 Acc/Aha/Aapa/Abc/Acpm/Ags/Apha/Ash/Aspc/Nma/Pcna Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2018, 71, 1269–1324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Segni, M. Disorders of the Thyroid Gland in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Kaltsas, G., Koch, C., Kopp, P., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, G.R. Thyroid Hormone Actions in Cartilage and Bone. Eur. Thyroid J. 2013, 2, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, D.; Raychaudhuri, M. Hypothyroidism and Obesity: An Intriguing Link. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 20, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, L.; Anania, C.; Ferraro, F.; Andreoli, G.M.; Chiesa, C. Thyroid Function in Childhood Obesity and Metabolic Comorbidity. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livadas, S.; Magiakou, M.A.; Mengreli, C.; Girginoudis, P.; Galani, C.; Smyrnaki, P.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C.; Xekouki, P.; Chrousos, G.P.; Dacou-Voutetakis, C. Obesity and Attenuated Adiposity Rebound in Children with Congenital Hypothyroidism. Normalization of BMI Values in Adolescents. Horm. Metab. Res. 2007, 39, 524–528. [Google Scholar]
- Mazza, E.; Troiano, E.; Ferro, Y.; Lisso, F.; Tosi, M.; Turco, E.; Pujia, R.; Montalcini, T. Obesity, Dietary Patterns, and Hormonal Balance Modulation: Gender-Specific Impacts. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Li, Q.; Guan, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhong, F.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, H.; Song, Y.; et al. Association between Different Obesity Phenotypes and Hypothyroidism: A Study Based on a Longitudinal Health Management Cohort. Endocrine 2021, 72, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.Y. Prevalence of Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Obese Children or Adolescents and Association between Thyroid Hormone and the Components of Metabolic Syndrome. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2018, 54, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salton, N.; Kern, S.; Interator, H.; Lopez, A.; Moran-Lev, H.; Lebenthal, Y.; Brener, A. Muscle-to-Fat Ratio for Predicting Metabolic Syndrome Components in Children with Overweight and Obesity. Child. Obes. 2022, 18, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
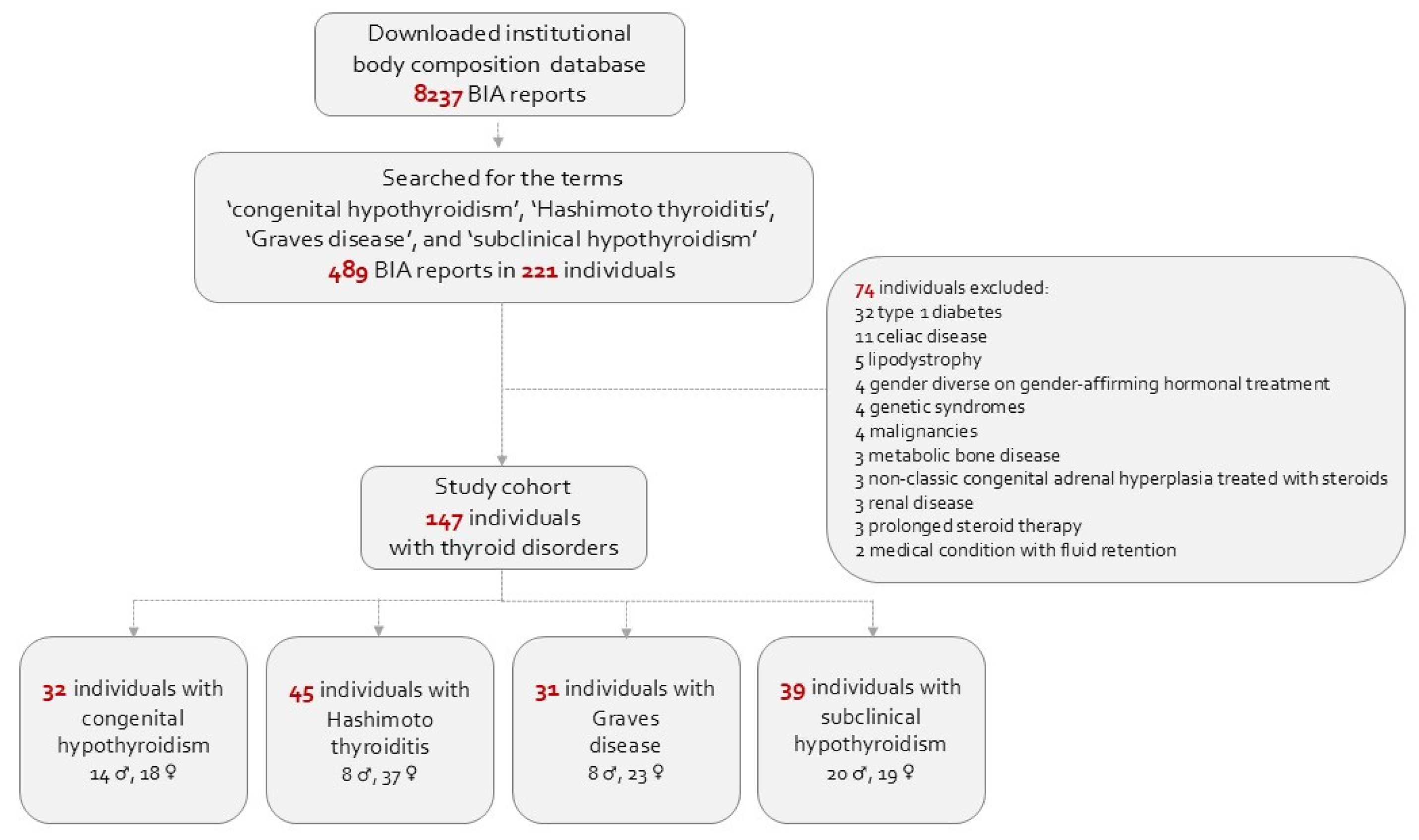
| Congenital Hypothyroidism, n = 32 | Hashimoto Thyroiditis, n = 45 | Graves’ Disease, n = 31 | Subclinical Hypothyroidism, n = 39 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |||||
| Males (%) | 14/32 (43.8) ab | 8/45 (17.8) c | 8/31 (25.8) bc | 20/39 (51.3) a | 0.005 |
| Females (%) | 18/32 (56.2) | 37/45 (82.2) | 23/31 (74.2) | 19/39 (48.7) | |
| Socioeconomic position | |||||
| Cluster, median [IQR] | 8 [6, 9] | 8 [7, 9] | 8 [6, 9] | 8 [7, 9] | 0.445 |
| Index, median [IQR] | 1.17 [0.23, 173] | 1.469 [0.571, 1.805] | 1.143 [0.559, 1.776] | 1.259 [0.786, 1.769] | 0.562 |
| Low (1–4) | 6/32 (18.8) | 2/45 (4.4) | 3/31 (9.7) | 2/39 (5.1) | 0.431 |
| Medium (5–7) | 8/32 (25.0) | 13/45 (28.9) | 10/31 (23.2) | 12/39 (30.8) | |
| High (8–10) | 18/32 (56.2) | 30/45 (66.6) | 18/31 (58.1) | 25/39 (64.1) | |
| Children in the family | |||||
| Number | 2 [2, 3] | 3 [2, 3] | 2 [2, 3] | 3 [2, 3] | 0.783 |
| Birth order | 2 [1, 3] | 2 [1, 2] | 2 [1, 2] | 2 [1, 2] | 0.677 |
| Conception, n (%) | |||||
| Spontaneous | 29/31 (93.5) | 38/42 (90.5) | 28/28 (100) | 31/36 (86.1) | 0.330 |
| IVF | 2/31 (6.5) | 4/42 (9.5) | 0 (0) | 4/36 (11.1) | |
| Adopted | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1/36 (2.8) | |
| Maternal conditions, n (%) | |||||
| GDM | 1/31 (3.2) | 5/42 (11.9) | 2/28 (7.1) | 0/36 (0) | 0.307 |
| Mode of delivery, n (%) | |||||
| Spontaneous vaginal | 25/30 (83.3) | 36/42 (85.7) | 23/27 (85.2) | 23/34 (67.6) | 0.296 |
| Elective C-section | 3/30 (10.0) | 5/42 (11.9) | 3/27 (11.1) | 10/34 (29.4) | |
| Urgent C-section | 2/30 (6.7) | 1/42 (2.4) | 1/27 (3.7) | 1/34 (2.9) | |
| Gestational age classifications, n (%) | |||||
| GA, weeks | 40 [38, 40] | 40 [38, 40] | 40 [38, 40] | 38.5 [37.3, 40] | 0.439 |
| Preterm, <37 wks | 16/32 (50.0) | 16/45 (35.5) | 24/31 (77.4) | 15/39 (38.5) | 0.132 |
| Term, 38–42 wks | 3/32 (9.4) | 3/45 (6.7) | 1/31 (3.2) | 2/39 (5.1) | |
| Postterm, ≥42 wks | 2/32 (6.2) | 3/45 (6.7) | 1/31 (3.2) | 7/39 (17.9) | |
| Birth parameters and categories | |||||
| Birth weight, grams | 2930 [2732, 3215] | 3282 [3006, 3550] | 3100 [3000, 3300] | 3160 [2800, 3390] | 0.072 |
| Birth weight, z-score | −0.49 ± 0.88 | 0.07 ± 0.90 | −0.09 ± 0.78 | −0.23 ± 0.90 | 0.061 |
| SGA, n (%) | 3/32 (9.4) | 2/45 (4.4) | 1/31 (3.2) | 3/39 (7.7) | 0.911 |
| AGA, n (%) | 27/32 (84.4) | 40/45 (88.9) | 29/31 (93.6) | 33/39 (84.6) | |
| LGA, n (%) | 2/32 (6.2) | 3/45 (6.7) | 1/31 (3.2) | 3/39 (7.7) | |
| Congenital Hypothyroidism n = 32 | Hashimoto Thyroiditis n = 45 | Grave’s Disease n = 31 | Subclinical Hypothyroidism n = 39 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current age, years | 9.4 [7.2, 11.7] a | 15.7 [11.4, 17.2] bc | 16.5 [14.1, 18.3] c | 13.5 [11.1, 16.4] b | <0.001 |
| Pubertal status, n (%) | |||||
| Prepubertal (Tanner 1) | 21 (66) b | 9 (20) a | 2 (6.5) a | 8 (20.5) a | <0.001 |
| In puberty (Tanner 2–4) | 8 (25) | 9 (20) | 4 (13) | 15 (38.5) | |
| Fully pubertal (Tanner 5) | 3 (9) | 27 (30) | 25 (80.5) | 16 (41) | |
| Anthropometric measurements | |||||
| Height, z-score | −0.30 ± 1.21 | −0.90 ± 0.86 | 0.22 ± 1.00 | 0.16 ± 0.98 | 0.076 |
| MPHt, z-score | −0.24 ± 0.80 | −0.02 ± 0.68 | 0.05 ± 0.89 | −0.20 ± 0.96 | 0.551 |
| Delta height, z-score | −0.13 [−1.00, 0.67] | 0.07 [−0.72, 0.49] | 0.23 [−0.31, 0.55] | 0.37 [−0.35, 0.98] | 0.064 |
| Weight, z-score | −0.03 ± 1.50 | 0.52 ± 1.23 | 0.12 ± 0.89 | 0.43 ± 1.83 | 0.112 |
| BMI, z-score | 0.26 [−0.24, 1.20] ab | 1.07 [−0.05, 1.39] a | −0.09 [−0.58, 0.49] b | 0.61 [−0.25, 1.36] ab | 0.010 |
| Body composition components | |||||
| Fat percentage | 24.3 ± 6.2 a | 29.5 ± 7.7 b | 24.5 ± 7.7 a | 25.0 ± 6.5 ab | 0.002 |
| Truncal fat percentage | 19.0 ± 6.0 a | 24.1 ± 7.4 b | 19.3 ± 7.6 a | 19.7 ± 6.0 a | 0.001 |
| ASMM, z-score | −0.65 ± 1.00 | −0.03 ± 1.09 | −0.18 ± 0.68 | −0.24 ± 1.03 | 0.058 |
| MFR, z-score | −0.66 ± 0.73 a | −0.77 ± 0.76 a | −0.12 ± 1.12 b | −0.72 ± 0.75 a | 0.003 |
| Thyroid function tests at body composition assessment | |||||
| TSH, mIU/L | 6.69 [3.54, 11.38] a | 5.97 [3.08, 9.80] a | 1.50 [0.89, 3.41] b | 4.57 [2.44, 7.29] a | <0.001 |
| Free T4, ng/dL | 1.28 [1.17, 1.35] b | 1.18 [0.98, 1.24] a | 1.13 [1.02, 1.30] ab | 1.10 [1.02, 1.22] a | <0.001 |
| Lipid profile at body composition assessment | |||||
| Cholesterol, mg/dL | 172.3 ± 28.7 a | 176.9 ± 31.5 a | 142.3 ± 27.5 b | 167.2 ± 24.0 a | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 61.8 ± 18.5 a | 101.0 ± 29.5 b | 71.9 ± 22.3 ab | 70.8 ± 20.9 ab | <0.001 |
| HDL-c, mg/dL | 61.2 ± 12.5 a | 53.9 ± 11.6 ab | 49.6 ± 12.9 b | 59.6 ± 15.2 ab | 0.044 |
| LDL-c, mg/dL | 99.9 ± 22.1 a | 102.9 ± 24.0 a | 79.7 ± 25.2 b | 92.9 ± 20.2 ab | <0.001 |
| Non-HDL-c, mg/dL | 113.9 ± 21.6 a | 122.7 ± 23.3 a | 95.1 ± 27.4 b | 107.7 ± 20.2 ab | <0.001 |
| TG:HDL | 1.11 ± 0.45 a | 1.90 ± 0.91 b | 1.66 ± 0.68 ab | 1.39 ± 0.89 ab | <0.001 |
| TSH | FT4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | |
| BMI, z-score | 0.238 | 0.005 | −0.165 | 0.057 |
| ASMM, z-score | 0.091 | 0.291 | −0.255 | 0.003 |
| MFR, z-score | −0.215 | 0.012 | 0.042 | 0.628 |
| Metabolic outcomes | ||||
| Systolic blood pressure, % | 0.032 | 0.708 | 0.122 | 0.161 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, % | −0.046 | 0.592 | 0.113 | 0.194 |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol | 0.472 | <0.001 | −0.244 | 0.052 |
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol | 0.084 | 0.500 | 0.036 | 0.779 |
| Triglycerides | 0.232 | 0.050 | −0.145 | 0.239 |
| TG/HDL-c | 0.077 | 0.536 | −0.103 | 0.414 |
| ASMM, z-Score | MFR, z-Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | |
| Systolic blood pressure, % | 0.104 | 0.211 | −0.161 | 0.052 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, % | −0.029 | 0.724 | −0.179 | 0.030 |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol | 0.066 | 0.595 | −0.217 | 0.078 |
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol | −0.311 | 0.010 | 0.395 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides | 0.274 | 0.019 | −0.454 | <0.001 |
| TG/HDL-c | 0.307 | 0.011 | −0.459 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brener, A.; Stark, Y.; Friedman Miron, G.; Averbuch, S.; Elkon-Tamir, E.; Borger, O.; Lebenthal, Y. Exploring the Muscle-to-Fat Ratio of Pediatric Patients with Thyroid Disorders and Its Interaction with Thyroid Function and Metabolic Syndrome Components. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041255
Brener A, Stark Y, Friedman Miron G, Averbuch S, Elkon-Tamir E, Borger O, Lebenthal Y. Exploring the Muscle-to-Fat Ratio of Pediatric Patients with Thyroid Disorders and Its Interaction with Thyroid Function and Metabolic Syndrome Components. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(4):1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041255
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrener, Avivit, Yuval Stark, Gal Friedman Miron, Shay Averbuch, Erella Elkon-Tamir, Ophir Borger, and Yael Lebenthal. 2025. "Exploring the Muscle-to-Fat Ratio of Pediatric Patients with Thyroid Disorders and Its Interaction with Thyroid Function and Metabolic Syndrome Components" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 4: 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041255
APA StyleBrener, A., Stark, Y., Friedman Miron, G., Averbuch, S., Elkon-Tamir, E., Borger, O., & Lebenthal, Y. (2025). Exploring the Muscle-to-Fat Ratio of Pediatric Patients with Thyroid Disorders and Its Interaction with Thyroid Function and Metabolic Syndrome Components. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041255






