Retinal Vascular Density and Thickness in Long-Term Type 1 Diabetes Without Visible Vascular Signs of Retinopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
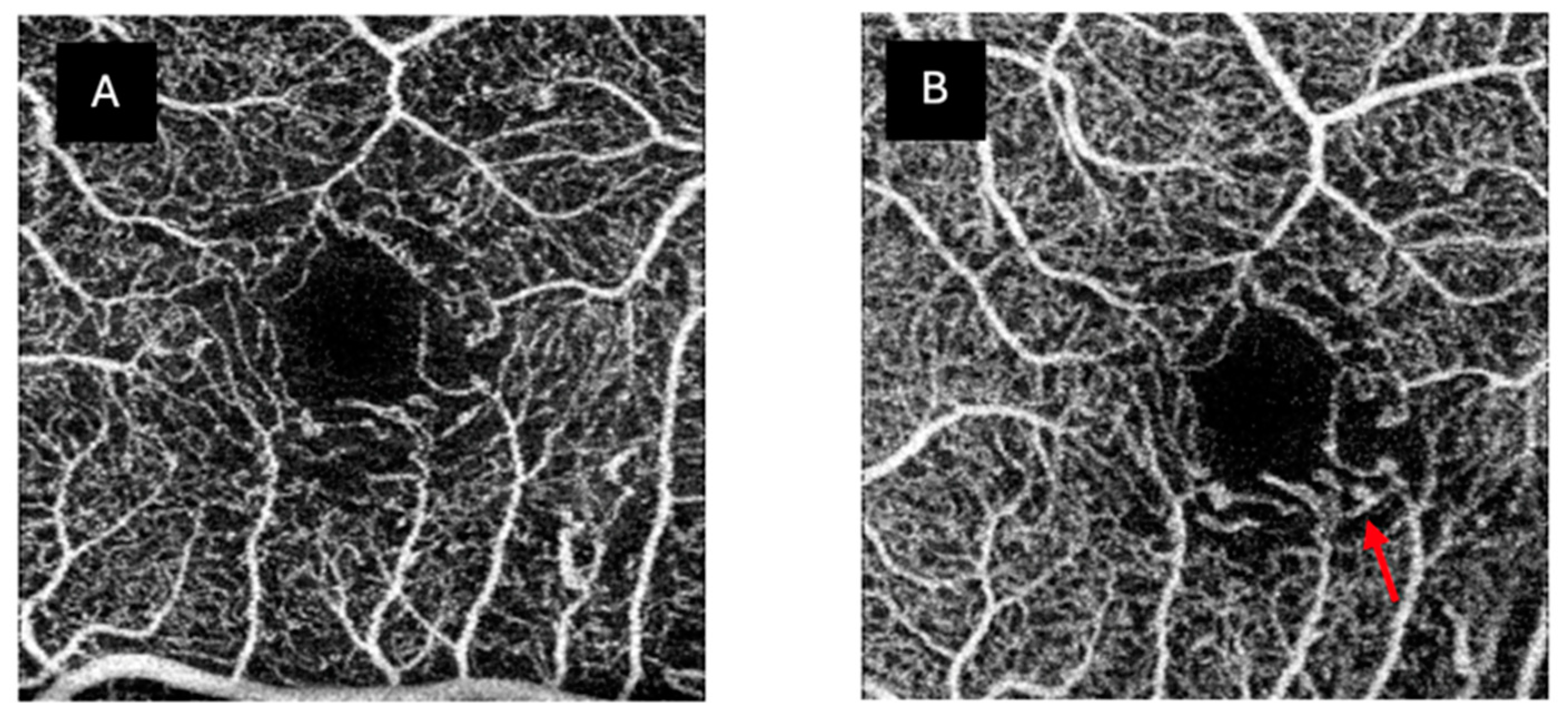
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solomon, S.D.; Chew, E.; Duh, E.J.; Sobrin, L.; Sun, J.K.; VanderBeek, B.L.; Wykoff, C.C.; Gardner, T.W. Diabetic Retinopathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.; Karuranga, S.; Malanda, B.; Saeedi, P.; Basit, A.; Besançon, S.; Bommer, C.; Esteghamati, A.; Ogurtsova, K.; Zhang, P.; et al. Global and Regional Estimates and Projections of Diabetes-Related Health Expenditure: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.; Airey, M.; Baxter, H.; Forrester, J.; Kennedy-Martin, T.; Girach, A. Epidemiology of Diabetic Retinopathy and Macular Oedema: A Systematic Review. Eye 2004, 18, 963–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. Early Detection of Microvascular Impairments with Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Diabetic Patients Without Clinical Retinopathy: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 222, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, H.W.; Verbraak, F.D.; Stehouwer, M.; Kok, P.H.B.; Garvin, M.K.; Sonka, M.; DeVries, J.H.; Schlingemann, R.O.; Abràmoff, M.D. Association of Visual Function and Ganglion Cell Layer Thickness in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and No or Minimal Diabetic Retinopathy. Vision Res. 2011, 51, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinilla, I.; Idoipe, M.; Perdices, L.; Sanchez-Cano, A.; Acha, J.; Lopez-Galvez, M.I.; Cuenca, N.; Abecia, E.; Orduna-Hospital, E. Changes in total and inner retinal thicknesses in type 1 diabetes with no retinopathy after 8 years of follow-up. Retina 2020, 40, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dijk, H.W.; Verbraak, F.D.; Kok, P.H.B.; Garvin, M.K.; Sonka, M.; Lee, K.; Devries, J.H.; Michels, R.P.J.; van Velthoven, M.E.J.; Schlingemann, R.O.; et al. Decreased Retinal Ganglion Cell Layer Thickness in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3660–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.K.; Keenan, H.A.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Asztalos, B.F.; Schaefer, E.J.; Sell, D.R.; Strauch, C.M.; Monnier, V.M.; Doria, A.; Aiello, L.P.; et al. Protection from Retinopathy and Other Complications in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes of Extreme Duration: The Joslin 50-Year Medalist Study. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachin, J.M.; McGee, P.; Palmer, J.P. Impact of C-Peptide Preservation on Metabolic and Clinical Outcomes in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes 2014, 63, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujosevic, S.; Muraca, A.; Alkabes, M.; Villani, E.; Cavarzeran, F.; Rossetti, L.; De Cilla, S. Early Microvascular and Neural Changes in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus without Clinical Signs of Diabetic Retinopathy. Retina 2019, 39, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simó, R.; Stitt, A.W.; Gardner, T.W. Neurodegeneration in Diabetic Retinopathy: Does It Really Matter? Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacconi, R.; Tombolini, B.; Cartabellotta, A.; Zerbini, G.; Bandello, F.; Querques, G. Structural and Functional Characterization of Retinal Impairment in T1DM Patients without Diabetic Retinopathy: A 3-Year Longitudinal Study. Acta Diabetol. 2024, 61, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschauer, J.; Pollreisz, A.; Karst, S.; Hülsmann, M.; Hajdu, D.; Datlinger, F.; Egner, B.; Kriechbaum, K.; Pablik, E.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.M. Longitudinal Analysis of Microvascular Perfusion and Neurodegenerative Changes in Early Type 2 Diabetic Retinal Disease. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, I.P.; Alves, D.; Santos, T.; Mendes, L.; Lobo, C.; Santos, A.R.; Durbin, M.; Cunha-Vaz, J. Characterization of Disease Progression in the Initial Stages of Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes: A 2-Year Longitudinal Study. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaey, C.; van de Voorde, J. Regulatory Mechanisms in the Retinal and Choroidal Circulation. Ophthalmic Res. 2000, 32, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feke, G.T.; Buzney, S.M.; Ogasawara, H.; Fujio, N.; Goger, D.G.; Spack, N.P.; Gabbay, K.H. Retinal Circulatory Abnormalities in Type 1 Diabetes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 2968–2975. [Google Scholar]
- Clermont, A.C.; Aiello, L.P.; Mori, F.; Aiello, L.M.; Bursell, S.-E. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Severity of Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Mediate Retinal Hemodynamics In Vivo: A Potential Role for Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in the Progression of Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1997, 124, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, J.E.; Riva, C.E.; Baine, J.; Brucker, A.J. Total Retinal Volumetric Blood Flow Rate in Diabetic Patients with Poor Glycemic Control. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 356–363. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, T.M.; Gardiner, T.A.; Stitt, A.W. Microvascular Lesions of Diabetic Retinopathy: Clues towards Understanding Pathogenesis? Eye 2009, 23, 1496–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholfield, C.N.; McGeown, J.G.; Curtis, T.M. Cellular Physiology of Retinal and Choroidal Arteriolar Smooth Muscle Cells. Microcirculation 2007, 14, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaey, C.; Boussery, K.; Van de Voorde, J. A Retinal-Derived Relaxing Factor Mediates the Hypoxic Vasodilation of Retinal Arteries. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 3555–3560. [Google Scholar]
- Nesper, P.L.; Roberts, P.K.; Onishi, A.C.; Chai, H.; Liu, L.; Jampol, L.M.; Fawzi, A.A. Quantifying Microvascular Abnormalities with Increasing Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, BIO307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, A.C.; Nesper, P.L.; Roberts, P.K.; Moharram, G.A.; Chai, H.; Liu, L.; Jampol, L.M.; Fawzi, A.A. Importance of Considering the Middle Capillary Plexus on OCT Angiography in Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, J.X.; Fawzi, A.A. Perspectives on Diabetic Retinopathy from Advanced Retinal Vascular Imaging. Eye 2022, 36, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, R.B.; Andrade Romo, J.S.; Krawitz, B.D.; Mo, S.; Fawzi, A.A.; Linderman, R.E.; Carroll, J.; Pinhas, A.; Chui, T.Y.P.P. Earliest Evidence of Preclinical Diabetic Retinopathy Revealed Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Perfused Capillary Density. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 203, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Mucollari, I.; Kwan, C.C.; Dingillo, G.; Amar, J.; Schwartz, G.W.; Fawzi, A.A. Reversed Neurovascular Coupling on Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Is the Earliest Detectable Abnormality before Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palochak, C.M.A.; Lee, H.E.; Song, J.; Geng, A.; Linsenmeier, R.A.; Burns, S.A.; Fawzi, A.A. Retinal Blood Velocity and Flow in Early Diabetes and Diabetic Retinopathy Using Adaptive Optics Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Li, Z. Is Preclinical Diabetic Retinopathy in Diabetic Nephropathy Individuals More Severe? Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1144257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, T.; Hoshino, M.; Hoshino, S.; Mori, A.; Sakamoto, K.; Ishii, K. Structural and Functional Changes in Retinal Vasculature Induced by Retinal Ischemia-Reperfusion in Rats. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 135, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nippert, A.R.; Newman, E.A. Regulation of Blood Flow in Diabetic Retinopathy. Vis. Neurosci. 2020, 37, E004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozolewska-Piotrowska, K.; Nowacka, M.; Masiuk, M.; Świder, M.; Babiak, K.; Safranow, K.; Machalińska, A. Flicker-Induced Retinal Vessels Dilatation in Diabetic Patients without Clinically Detectable Diabetic Retinopathy. Klin. Oczna 2019, 2019, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.S.; Ling, L.H.; Ong, P.G.; Foulds, W.; Tai, E.S.; Wong, T.Y. Dynamic Responses in Retinal Vessel Caliber with Flicker Light Stimulation and Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy and Its Progression. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Tang, F.; Wong, R.; Lok, J.; Szeto, S.K.H.; Chan, J.C.K.; Chan, C.K.M.; Tham, C.C.; Ng, D.S.; Cheung, C.Y. OCT Angiography Metrics Predict Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy and Development of Diabetic Macular Edema. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, D.M. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Study at 30 Years: Overview. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, J.; Karst, S.; Sacu, S.; Scholda, C.; Pablik, E.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Correlation between Corneal and Retinal Neurodegenerative Changes and Their Association with Microvascular Perfusion in Type II Diabetes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, e545–e550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oram, R.A.; Jones, A.G.; Besser, R.E.J.; Knight, B.A.; Shields, B.M.; Brown, R.J.; Hattersley, A.T.; McDonald, T.J. The Majority of Patients with Long-Duration Type 1 Diabetes Are Insulin Microsecretors and Have Functioning Beta Cells. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.K.; Menghini, M.; Hansen, A.; Mackey, D.A.; Constable, I.J.; Sampson, D.M. Intrasession Repeatability and Interocular Symmetry of Foveal Avascular Zone and Retinal Vessel Density in OCT Angiography. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, C.; Paulus, Y.M. Advances in Structural and Functional Retinal Imaging and Biomarkers for Early Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type 1 Diabetes Group | Mean ± SD 2018 | Mean ± SD 2022 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic Values | |||
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 17.96 ± 13.43 | - | |
| Duration of diabetes (years) | 25.68 ± 8.33 | 28.88 ± 8.04 | - |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.34 ± 0.94 | 7.60 ± 0.99 | 0.032 |
| Glycaemia (mg/dL) | 186.60 ± 113.61 | 160.40 ± 71.21 | 0.738 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 194.08 ± 34.95 | 189.80 ± 35.79 | 0.204 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 57.24 ± 13.78 | 62.24 ± 12.75 | 0.003 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 119.84 ± 27.13 | 115.00 ± 29.28 | 0.180 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 35.00 ± 7.67 | 35.89 ± 11.02 | 0.831 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.80 ± 0.12 | 0.81 ± 0.10 | 0.474 |
| Albumin/creatinine ratio (mg/g Cr) | 7.31 ± 7.83 | 8.46 ± 12.66 | 0.475 |
| Ophthalmic Evaluation | |||
| BCVA (LogMAR) | −0.19 ± 0.11 | 0.04 ± 0.07 | <0.001 |
| SE (D) | −1.16 ± 1.86 | −1.03 ± 1.71 | 0.302 |
| AL (mm) | 23.71 ± 1.12 | 23.89 ± 1.18 | 0.954 |
| IOP (mmHg) | 16.59 ± 3.00 | 16.85 ± 2.47 | 0.635 |
| Mean ± SD 2018 | Mean ± SD 2022 | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCP | C | 19.63 ± 2.66 | 22.27 ± 3.41 | <0.001 |
| S | 46.14 ± 3.61 | 48.14 ± 3.32 | 0.005 | |
| T | 44.62 ± 3.38 | 48.10 ± 2.52 | <0.001 | |
| N | 43.54 ± 2.84 | 46.68 ± 2.72 | <0.001 | |
| I | 46.81 ± 3.07 | 47.80 ± 3.08 | 0.114 | |
| FAZ area | 289.00 ± 104.30 | 288.37 ± 92.84 | 0.977 | |
| FAZ horizontal Ø | 622.16 ± 121.56 | 609.40 ± 104.03 | 0.236 | |
| FAZ vertical Ø | 576.92 ± 145.57 | 589.20 ± 136.59 | 0.206 | |
| DCP | C | 20.02 ± 4.05 | 20.30 ± 5.93 | 0.757 |
| S | 49.29 ± 2.99 | 48.41 ± 3.18 | 0.300 | |
| T | 45.84 ± 2.75 | 47.84 ± 3.66 | 0.021 | |
| N | 48.06 ± 3.46 | 47.66 ± 3.68 | 0.451 | |
| I | 51.39 ± 3.19 | 49.17 ± 3.30 | 0.020 | |
| FAZ area | 304.75 ± 86.36 | 319.36 ± 92.80 | 0.619 | |
| FAZ horizontal Ø | 704.00 ± 135.62 | 648.32 ± 95.76 | 0.007 | |
| FAZ vertical Ø | 572.04 ± 119.38 | 605.20 ± 116.91 | 0.146 | |
| CC | C | 53.85 ± 2.64 | 54.48 ± 2.23 | 0.367 |
| S | 51.48 ± 1.96 | 52.16 ± 2.35 | 0.313 | |
| T | 54.00 ± 1.86 | 54.28 ± 1.56 | 0.600 | |
| N | 52.74 ± 1.81 | 53.69 ± 1.50 | 0.045 | |
| I | 52.97 ± 2.45 | 53.17 ± 2.09 | 0.657 |
| SCP | DCP | CC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAZ abnormalities | 92% | 88% | |
| Marked ischaemia | 4% | 4% | 0% |
| Capillary dropout | 96% | 96% | 76% |
| MA | 8% | 20% | |
| Normal | 4% | 4% | 24% |
| DM1 2018 | DM1 2022 | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||
| Total retina thickness (µm) | C | 251.28 | 23.41 | 250.16 | 23.10 | 0.320 |
| IS | 322.16 | 15.18 | 321.60 | 16.36 | 0.676 | |
| IT | 291.48 | 62.32 | 307.12 | 17.96 | 0.658 | |
| IN | 323.04 | 14.31 | 321.92 | 14.78 | 0.114 | |
| II | 319.72 | 15.57 | 318.96 | 17.01 | 0.715 | |
| OS | 282.08 | 14.49 | 282.88 | 14.92 | 0.241 | |
| OT | 264.44 | 14.16 | 264.16 | 14.01 | 0.796 | |
| ON | 298.84 | 13.77 | 297.68 | 14.65 | 0.133 | |
| OI | 269.28 | 11.79 | 271.96 | 18.81 | 0.563 | |
| GCL+ protocol thickness (µm) | C | 47.72 | 7.57 | 48.44 | 6.70 | 0.234 |
| IS | 95.40 | 5.18 | 95.24 | 8.39 | 0.078 | |
| IT | 90.92 | 6.51 | 92.16 | 9.08 | 0.311 | |
| IN | 94.72 | 6.98 | 94.52 | 10.75 | 0.218 | |
| II | 94.16 | 7.34 | 94.04 | 11.30 | 0.042 | |
| OS | 67.56 | 3.97 | 67.84 | 7.80 | 0.336 | |
| OT | 71.80 | 3.58 | 72.36 | 6.01 | 0.857 | |
| ON | 73.56 | 4.87 | 74.28 | 10.29 | 0.133 | |
| OI | 63.76 | 3.90 | 64.96 | 9.22 | 0.534 | |
| GCL++ protocol thickness (µm) | C | 52.52 | 9.95 | 52.76 | 9.08 | 0.678 |
| IS | 123.76 | 6.29 | 123.28 | 10.28 | 0.777 | |
| IT | 111.36 | 7.93 | 111.44 | 9.75 | 0.415 | |
| IN | 120.48 | 6.95 | 119.64 | 9.03 | 0.977 | |
| II | 124.24 | 7.22 | 124.04 | 10.82 | 0.304 | |
| OS | 108.92 | 7.27 | 109.32 | 11.75 | 0.113 | |
| OT | 94.44 | 4.86 | 94.36 | 7.69 | 0.699 | |
| ON | 127.24 | 6.35 | 125.24 | 12.75 | 0.920 | |
| OI | 107.20 | 5.95 | 106.56 | 11.33 | 0.329 | |
| Correlations | Duration of Diabetes (Years) | HbA1c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman’s Rho | 1st Assessment | 2nd Assessment | 2nd Assessment | |
| SCP C | C. coefficient | 0.062 | −0.114 | −0.240 |
| p | 0.769 | 0.586 | 0.248 | |
| SCP S | C. coefficient | −0.294 | −0.170 | −0.471 |
| p | 0.153 | 0.416 | 0.017 | |
| SCP T | C. coefficient | −0.679 | −0.410 | −0.313 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.042 | 0.128 | |
| SCP N | C. coefficient | −0.257 | −0.338 | −0.174 |
| p | 0.215 | 0.098 | 0.406 | |
| SCP I | C. coefficient | −0.248 | −0.352 | 0.096 |
| p | 0.231 | 0.085 | 0.650 | |
| SCP FAZ AREA | C. coefficient | 0.237 | 0.271 | 0.272 |
| p | 0.254 | 0.189 | 0.188 | |
| SCP FAZ HOR Ø | C. coefficient | 0.234 | 0.312 | 0.008 |
| p | 0.261 | 0.129 | 0.969 | |
| SCP FAZ VERT Ø | C. coefficient | 0.019 | 0.155 | 0.235 |
| p | 0.927 | 0.458 | 0.258 | |
| DCP C | C. coefficient | 0.497 | −0.007 | 0.087 |
| p | 0.012 | 0.976 | 0.678 | |
| DCP S | C. coefficient | −0.180 | −0.086 | −0.567 |
| p | 0.389 | 0.682 | 0.003 | |
| DCP T | C. coefficient | −0.167 | 0.030 | −0.077 |
| p | 0.426 | 0.888 | 0.713 | |
| DCP N | C. coefficient | −0.104 | −0.043 | −0.351 |
| p | 0.620 | 0.840 | 0.085 | |
| DCP I | C. coefficient | 0.063 | −0.230 | 0.036 |
| p | 0.764 | 0.269 | 0.864 | |
| DCP FAZ AREA | C. coefficient | −0.078 | −0.190 | 0.031 |
| p | 0.710 | 0.363 | 0.882 | |
| DCP FAZ HOR Ø | C. coefficient | −0.318 | −0.042 | −0.128 |
| p | 0.122 | 0.843 | 0.541 | |
| DCP FAZ VERT Ø | C. coefficient | −0.065 | −0.267 | 0.183 |
| p | 0.757 | 0.197 | 0.381 | |
| CC C | C. coefficient | 0.035 | 0.071 | −0.517 |
| p | 0.866 | 0.735 | 0.008 | |
| CC S | C. coefficient | −0.070 | −0.106 | 0.055 |
| p | 0.739 | 0.613 | 0.794 | |
| CC T | C. coefficient | −0.127 | 0.261 | −0.123 |
| p | 0.547 | 0.208 | 0.559 | |
| CC N | C. coefficient | −0.205 | 0.361 | −0.313 |
| p | 0.325 | 0.076 | 0.128 | |
| CC I | C. coefficient | −0.077 | 0.222 | 0.290 |
| p | 0.714 | 0.286 | 0.160 | |
| Correlations | Duration of Diabetes (Years) | HbA1c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman’s Rho | 1st Assessment | 2nd Assessment | 2nd Assessment | |
| TOTAL RETINAL C | C. coefficient | −0.041 | −0.151 | 0.173 |
| p | 0.846 | 0.471 | 0.410 | |
| TOTAL RETINAL IS | C. coefficient | −0.310 | −0.255 | −0.029 |
| p | 0.131 | 0.218 | 0.889 | |
| TOTAL RETINAL IT | C. coefficient | −0.114 | −0.341 | 0.123 |
| p | 0.588 | 0.096 | 0.559 | |
| TOTAL RETINAL IN | C. coefficient | −0.425 | −0.376 | 0.091 |
| p | 0.034 | 0.064 | 0.664 | |
| TOTAL RETINAL II | C. coefficient | −0.433 | −0.445 | 0.037 |
| p | 0.031 | 0.026 | 0.862 | |
| TOTAL RETINAL OS | C. coefficient | 0.059 | −0.041 | 0.035 |
| p | 0.788 | 0.844 | 0.869 | |
| TOTAL RETINAL OT | C. coefficient | −0.044 | −0.208 | −0.096 |
| p | 0.834 | 0.319 | 0.647 | |
| TOTAL RETINAL ON | C. coefficient | −0.289 | −0.319 | −0.069 |
| p | 0.161 | 0.120 | 0.745 | |
| TOTAL RETINAL OI | C. coefficient | −0.205 | −0.178 | 0.037 |
| p | 0.325 | 0.394 | 0.087 | |
| GCL+ C | C. coefficient | −0.051 | −0.207 | −0.349 |
| p | 0.807 | 0.321 | 0.087 | |
| GCL+ IS | C. coefficient | −0.433 | −0.473 | −0.220 |
| p | 0.026 | 0.017 | 0.291 | |
| GCL+ IT | C. coefficient | −0.570 | −0.558 | −0.199 |
| p | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.340 | |
| GCL+ IN | C. coefficient | −0.428 | −0.444 | −0.263 |
| p | 0.033 | 0.026 | 0.203 | |
| GCL+ II | C. coefficient | −0.504 | −0.439 | −0.131 |
| p | 0.010 | 0.028 | 0.532 | |
| GCL+ OS | C. coefficient | 0.192 | −0.052 | 0.342 |
| p | 0.359 | 0.804 | 0.095 | |
| GCL+ OT | C. coefficient | 0.080 | −0.341 | −0.217 |
| p | 0.702 | 0.095 | 0.297 | |
| GCL+ ON | C. coefficient | −0.058 | −0.184 | 0.219 |
| p | 0.784 | 0.380 | 0.293 | |
| GCL+ OI | C. coefficient | −0.014 | −0.075 | 0.011 |
| p | 0.945 | 0.721 | 0.960 | |
| GCL++ C | C. coefficient | 0.001 | −0.222 | −0.401 |
| p | 0.996 | 0.286 | 0.047 | |
| GCL++ IS | C. coefficient | −0.374 | −0.373 | −0.707 |
| p | 0.065 | 0.066 | <0.001 | |
| GCL++ IT | C. coefficient | −0.586 | −0.340 | −0.399 |
| p | 0.004 | 0.096 | 0.048 | |
| GCL++ IN | C. coefficient | −0.287 | −0.231 | −0.619 |
| p | 0.164 | 0.266 | 0.001 | |
| GCL++ II | C. coefficient | −0.469 | −0.297 | −0.427 |
| p | 0.018 | 0.149 | 0.033 | |
| GCL++ OS | C. coefficient | 0.379 | 0.018 | −0.322 |
| p | 0.062 | 0.933 | 0.117 | |
| GCL++ OT | C. coefficient | 0.132 | −0.309 | −0.493 |
| p | 0.528 | 0.133 | 0.012 | |
| GCL++ ON | C. coefficient | 0.022 | −0.045 | −0.478 |
| p | 0.917 | 0.832 | 0.016 | |
| GCL++ OI | C. coefficient | 0.029 | 0.058 | −0.435 |
| p | 0.890 | 0.782 | 0.030 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sopeña-Pinilla, M.; Arias-Alvarez, M.; Lopez-Galvez, M.I.; Orduna-Hospital, E.; Fernandez-Espinosa, G.; Boned-Murillo, A.; Díaz-Barreda, M.D.; Tomas-Grasa, C.; Pinilla, I. Retinal Vascular Density and Thickness in Long-Term Type 1 Diabetes Without Visible Vascular Signs of Retinopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041082
Sopeña-Pinilla M, Arias-Alvarez M, Lopez-Galvez MI, Orduna-Hospital E, Fernandez-Espinosa G, Boned-Murillo A, Díaz-Barreda MD, Tomas-Grasa C, Pinilla I. Retinal Vascular Density and Thickness in Long-Term Type 1 Diabetes Without Visible Vascular Signs of Retinopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(4):1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041082
Chicago/Turabian StyleSopeña-Pinilla, Maria, Marta Arias-Alvarez, Maria Isabel Lopez-Galvez, Elvira Orduna-Hospital, Guisela Fernandez-Espinosa, Ana Boned-Murillo, María Dolores Díaz-Barreda, Cristina Tomas-Grasa, and Isabel Pinilla. 2025. "Retinal Vascular Density and Thickness in Long-Term Type 1 Diabetes Without Visible Vascular Signs of Retinopathy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 4: 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041082
APA StyleSopeña-Pinilla, M., Arias-Alvarez, M., Lopez-Galvez, M. I., Orduna-Hospital, E., Fernandez-Espinosa, G., Boned-Murillo, A., Díaz-Barreda, M. D., Tomas-Grasa, C., & Pinilla, I. (2025). Retinal Vascular Density and Thickness in Long-Term Type 1 Diabetes Without Visible Vascular Signs of Retinopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041082







