Carpal Tunnel Syndrome at the Intersection of Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology, and Neurology: A Thorough Examination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PPI | Proton pump inhibitors |
| CTS | Carpal Tunnel Syndrome |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| TSH | Thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| CBC | Complete blood counts |
| MCV | Mean corpuscular volume |
| RDW | Distribution width |
| MPV | Mean platelet volume |
| PDW | Platelet distribution width |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| PLR | Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| SII | Systemic immune inflammation index |
| CAR | C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio |
| AGR | Albumin-to-globulin ratio |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| GGT | Gamma glutamyl transferase |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
References
- Osiak, K.; Elnazir, P.; Walocha, J.A.; Pasternak, A. Carpal tunnel syndrome: State-of-the-art review. Folia Morphol. 2022, 81, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, T.V.; Lusa, V.; Page, M.J.; O’Connor, D.; Massy-Westropp, N.; Peters, S.E. Splinting for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2, CD010003. [Google Scholar]
- Küçük, E.B. Temporal Changes in Electrophysiological Parameters in Untreated Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Cureus 2023, 15, e46039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Chiu, J.W.; Yang, Y.C.; Jeng, M.J. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Retrospective Population Cohort Study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 100, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitake, T.; Iwatsuki, K.; Hirata, H. Differences in characteristics of carpal tunnel syndrome between male and female patients. J. Orthop. Sci. 2020, 25, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanni, N.N.; Ahmed, S.; Anwar, S.; Kismat, S.; Halder, K.; Nesa, M.; Habib, F.B. Endoscopic and histopathological findings in adult dyspeptic patients, and their association with Helicobacter pylori infection in Dhaka, Bangladesh. IJID Reg. 2021, 2, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondim, F.A.; De Oliveira, G.R.; Teles, B.C.; Aquino, P.d.S.; Brasil, É.F.; Carvalho, A.M.; Souza, M.H.L.P.; Braga, L.L.B.C.; Rola, F.H. Clinical and Electrodiagnostic Findings in Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanık, E.A.; Erden, S. The use of the ROC curve in the evaluation of diagnostic tests. Mersin Univ. Med. J. 2003, 3, 260–264. [Google Scholar]
- Bîrsanu, L.; Vulpoi, G.A.; Cuciureanu, D.I.; Antal, C.D.; Popescu, I.R.; Turliuc, D.M. Carpal tunnel syndrome related to rheumatic disease (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2024, 28, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, Y.; Nodera, H.; Sato, R.; Haji, S.; Fujita, K.; Miyamoto, R.; Muto, K.; Yamazaki, H.; Morino, H.; Kanda, T.; et al. Peripheral nerve excitability abnormalities in Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease: Assessment with histopathological analysis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2025, 170, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilopoulou, S.; Katouni, K.; Papadopoulos, V.; Pappas, N.; Antonopoulos, I.; Giavopoulos, P.; Chrysikos, D.; Filippou, D. Variations of the Median Nerve and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Maedica 2023, 18, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojević, M.; Djuricic, N.; Parezanovic, M.; Biorac, M.; Pathak, D.; Spasic, S.; Lopcic, S.; Kovacevic, S.; Ostojic, J.N. The Impact of Chronic Magnesium Deficiency on Excitable Tissues-Translational Aspects. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025, 203, 707–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, A.; Aslani, S.; Ataollahi, M.; Mahmoudi, M. The role of magnesium in different inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padua, L.; Cuccagna, C.; Giovannini, S.; Coraci, D.; Pelosi, L.; Loreti, C.; Bernabei, R.; Hobson-Webb, L.D. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Updated evidence and new questions. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crilly, M.A.; Kumar, V.; Clark, H.J.; Williams, D.J.; Macdonald, A.G. Relationship between arterial dysfunction and extra-articular features in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjari, E.; Shahraki, H.R.; Khachatryan, L.G.; Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A. Investigating the association between diabetes and carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis approach. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneş, M.; Büyükgöl, H. Correlation of neutrophil/lymphocyte and platelet/lymphocyte ratios with the severity of idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2020, 61, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, M.; Gottsäter, A.; Dahlin, L.B. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Diabetes—A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnoli, C.; Pisani, F.; Di Mario, F.; Leandro, G.; Gaiani, F.; Angelis, G.L.D.; Fusco, C. Peripheral neuropathy and gastroenterologic disorders: An overview on an underrecognized association. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S9), 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Du, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Dai, N.; Chen, J.D.Z.; Cao, Q. Electroacupuncture Enhances Gastric Accommodation via the Autonomic and Cytokine Mechanisms in Functional Dyspepsia. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.L.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, P.H. Enteric Nervous System: The Bridge Between the Gut Microbiota and Neurological Disorders. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 810483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.A.; Lehman, P.; Ghimire, S.; Shahi, S.K.; Mangalam, A. Game of microbes: The battle within- gut microbiota and multiple sclerosis. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2387794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakootian, M.; Soveizi, M.; Gholipour, A.; Oveisee, M. Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Genetics of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Review. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 1817–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | CTS Negative (n:265) | CTS Positivity (n:265) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | % | Count | % | |||
| Gender | Female | 201 | 75.8 | 202 | 76.2 | 1.000 |
| Male | 64 | 24.2 | 63 | 23.8 | ||
| CTS Direction | Right | 0 | 0.0 | 45 | 17.0 | - |
| Left | 0 | 0.0 | 49 | 18.5 | ||
| Bilateral | 0 | 0.0 | 171 | 64.5 | ||
| CTS Severity | Mild | 0 | 0.0 | 108 | 408 | - |
| Moderate | 0 | 0.0 | 128 | 48.3 | ||
| Severe | 0 | 0.0 | 29 | 10.9 | ||
| H. pylori | Negative | 161 | 60.8 | 164 | 61.9 | 0.858 |
| Positive | 104 | 39.2 | 101 | 38.1 | ||
| Int. Metaplasia | Negative | 235 | 88.7 | 234 | 88.3 | 1.000 |
| Positive | 30 | 11.3 | 31 | 11.7 | ||
| Atrophy | Negative | 238 | 89.8 | 248 | 93.6 | 0.157 |
| Positive | 27 | 10.2 | 17 | 6.4 | ||
| Dysplasia | Negative | 261 | 98.5 | 263 | 99.2 | 0.681 |
| Positive | 4 | 1.5 | 2 | 0.8 | ||
| Mean ± S.S. Med. (Min.–Max.) | Mean ± S.S. Med. (Min.–Max.) | |||||
| Age t | 59.25 ± 11.66 60 (28–90) | 60.06 ± 10.86 60 (6–87) | 0.408 | |||
| Biochemical Findings | With CTS Negative (n:265) | With CTS Positivity (n:265) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ort. ± S.S Med. (Min.–Max.) | Ort. ± S.S Med. (Min.–Max.) | ||
| Sodium z | 140.5 ± 4.4 141 (128–180) | 140.77 ± 2.9 141 (128–150) | 0.054 |
| Potassium t | 4.41 ± 0.48 4.4 (2.8–6.2) | 4.48 ± 0.43 4.4 (3.4–5.9) | 0.073 |
| Calcium z | 9.39 ± 0.68 9.5 (4.3–11) | 9.6 ± 0.47 9.6 (7.5–11.4) | 0.000 ** |
| Magnesium z | 2.06 ± 0.57 2.01 (1.41–8.6) | 1.97 ± 0.21 1.99 (1.36–2.71) | 0.025 ** |
| Albumin z | 43.59 ± 5.24 44.7 (16.2–52) | 44.92 ± 3.06 45 (32–55) | 0.102 |
| Uric Acid t | 4.78 ± 1.37 4.6 (1.52–9.78) | 4.76 ± 1.3 4.61 (1.96–9.93) | 0.859 |
| Phosphorus t | 3.61 ± 0.59 3.6 (2.18–5.3) | 3.72 ± 0.56 3.7 (2.4–5) | 0.146 |
| CRP z | 12.69 ± 39.62 2.4 (0.06–357.46) | 10.02 ± 42.58 2.16 (0.06–389.65) | 0.151 |
| Biochemical Findings | With CTS Negative (n:265) | With CTS Positivity (n:265) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ort. ± S.S Med. (Min.-Max.) | Ort. ± S.S Med. (Min.-Max.) | ||
| Lymphocyte z | 2.09 ± 0.77 2.01 (0.24–5.18) | 2.24 ± 0.72 2.11 (0.76–6.09) | 0.016 * |
| Eos z | 0.18 ± 0.15 0.14 (0–0.95) | 0.2 ± 0.16 0.16 (0–1.11) | 0.048 * |
| Head z | 0.04 ± 0.02 0.03 (0.01–0.11) | 0.04 ± 0.02 0.04 (0.01–0.17) | 0.013 * |
| RBC z | 4.44 ± 0.63 4.5 (1.77–6.71) | 4.6 ± 0.48 4.63 (3.11–5.96) | 0.003 ** |
| HGB z | 12.4 ± 1.96 12.6 (3.72–16.8) | 13.05 ± 1.5 13 (8.3–17.2) | 0.000 ** |
| HCT z | 38.11 ± 5.46 38.6 (12.2–52.3) | 39.86 ± 4.03 39.8 (26.5–51.8) | 0.000 ** |
| RDW-CV z | 14.79 ± 5.62 14 (11.6–98.1) | 13.9 ± 1.67 13.6 (11.3–22) | 0.002 ** |
| C-PNL Index z | 627.06 ± 507.71 479.52 (22.18–4141.96) | 524.26 ± 460.56 428.55 (111–6189.07) | 0.025 * |
| NL z | 2.62 ± 2.5 1.93 (0.3–19.63) | 2.01 ± 1.52 1.7 (0.68–18.93) | 0.001 ** |
| PLR z | 137.51 ± 71.7 124.18 (5.7–654.17) | 126.01 ± 49.7 116.76 (36.94–398.78) | 0.122 |
| SII z | 339.29 ± 357.01 232.31 (4.44–3316.85) | 268.9 ± 317.58 200.87 (0–4332.35) | 0.064 |
| CAR z | 0.43 ± 1.87 0.05 (0–17.27) | 0.17 ± 0.8 0.05 (0–10.92) | 0.190 |
| AGR z | 1.72 ± 0.35 1.74 (0.23–2.92) | 1.78 ± 0.36 1.76 (0.94–4.23) | 0.244 |
| Variable | Number of Floors | CTS Positivity | Variable | Number of Floors | CTS Positivity | Variable | Number of Floors | CTS Positivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | r | 0.030 | GGT | r | 0.011 | Mono# | r | −0.033 |
| p | 0.488 | p | 0.825 | p | 0.456 | |||
| Gender | r | −0.004 | Cholesterol | r | −0.002 | Eos# | r | 0.087 * |
| p | 0.919 | p | 0.966 | p | 0.048 | |||
| H. pylori | r | −0.012 | Triglyceride | r | 0.007 | Bas# | r | 0.113 * |
| p | 0.790 | p | 0.894 | p | 0.013 | |||
| Int. Metaplasia | r | 0.010 | HDLK | r | 0.034 | RBC | r | 0.132 ** |
| p | 0.89 | p | 0.527 | p | 0.003 | |||
| Atrophy | r | −0.07 | LDLK | r | −0.029 | HGB | r | 0.165 ** |
| p | 0.116 | p | 0.637 | p | 0.000 | |||
| Dysplasia | r | −0.036 | TSH | r | 0.031 | HCT | r | 0.160 ** |
| p | 0.413 | p | 0.513 | p | 0.000 | |||
| Glucose | r | 0.004 | Ferritin | r | 0.019 | MCV | r | 0.028 |
| p | 0.930 | p | 0.707 | p | 0.529 | |||
| Urea | r | 0.052 | Folate | r | 0.049 | RDW-CV | r | −0.134 ** |
| p | 0.230 | p | 0.403 | p | 0.002 | |||
| Creatinine | r | −0.056 | Vit. B12 | r | −0.001 | PLT | r | 0.021 |
| p | 0.197 | p | 0.985 | p | 0.631 | |||
| ALT | r | 0.075 | Chloride | r | −0.063 | MPV | r | −0.058 |
| p | 0.087 | p | 0.225 | p | 0.188 | |||
| AST | r | 0.032 | LDH | r | −0.002 | PDW | r | −0.059 |
| p | 0.468 | p | 0.961 | p | 0.178 | |||
| Sodium | r | 0.086 | T.Protein | r | −0.023 | PLT–NötLenf | r | −0.100 * |
| p | 0.054 | p | 0.667 | p | 0.024 | |||
| Potassium | r | 0.078 | Albumin | r | 0.078 | NLR | r | −0.147 ** |
| p | 0.079 | p | 0.102 | p | 0.001 | |||
| Calcium | r | 0.165 ** | Uric Acid | r | −0.001 | PLR | r | −0.068 |
| p | 0.000 | p | 0.986 | p | 0.122 | |||
| Magnesium | r | −0.127 * | Phosphorus | r | 0.083 | SII | r | −0.082 |
| p | 0.025 | p | 0.208 | p | 0.064 | |||
| Total Bilirubin | r | −0.008 | CRP | r | −0.064 | CAR | r | −0.063 |
| p | 0.873 | p | 0.151 | p | 0.191 | |||
| Direct Bilirubin | r | 0.008 | WBC | r | −0.017 | AGR | r | 0.064 |
| p | 0.867 | p | 0.701 | p | 0.245 | |||
| Indirect Bilirubin | r | 0.035 | Neutrophil | r | −0.086 | |||
| p | 0.474 | p | 0.053 | |||||
| ALP | r | 0.009 | Lymphocyte | r | 0.107 * | |||
| p | 0.861 | p | 0.016 |
| Variables | CTS Direction Right (n:45) | CTS Direction Left (n:49) | CTS Direction Bilateral (n:171) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± S.S. Med. (Min.-Max.) | Mean ± S.S. Med. (Min.-Max.) | Mean ± S.S. Med. (Min.-Max.) | ||
| Age F | 56.04 ± 12.88 59 (6–76) | 61.84 ± 9.59 62 (41–82) | 60.61 ± 10.43 61 (34–87) | 0.089 |
| LDL-K F | 144.1 ± 45.53 154 (54–224) a | 117.46 ± 38.13 115.5 (46–226) b | 114.46 ± 34.44 116 (38–234) b | 0.011 * |
| Chloride H | 102.07 ± 2.69 102 (97–107.04) a | 104.11 ± 3.36 104 (99–113) b | 103.4 ± 3.31 104 (92–113) b | 0.030 * |
| Albumin H | 46.19 ± 3.24 46.3 (41.3–53) a | 43.43 ± 3.42 43.8 (33.7–52) b | 45.02 ± 2.74 45.2 (32–55) a | 0.002 ** |
| Uric acid H | 5.17 ± 1.25 4.9 (2.76–7.7) a | 4.83 ± 1.25 4.92 (2.64–7.27) a | 4.64 ± 1.31 4.5 (1.96–9.93) b | 0.045 * |
| Neutrophil H | 4.88 ± 2.55 4.23 (1.72–15.52) a | 4.01 ± 1.33 3.79 (1.45–8.19) b | 3.83 ± 1.41 3.64 (1.75–10.81) b | 0.024 * |
| MCW H | 87.37 ± 6.24 88.4 (65.2–99.1) a | 85.56 ± 4.97 86 (67.9–99.8) b | 87.18 ± 4.97 87.8 (69.8–100.5) a | 0.032 * |
| RDW-CV H | 13.98 ± 2.09 1 3.4 (11.9–21.9) a | 14.63 ± 1.92 14.15 (12.2–21) b | 13.68 ± 1.4 13.5 (11.3–22) a | 0.003 ** |
| CAR H | 0.13 ± 0.18 0.07 (0.01–0.96) | 0.39 ± 1.72 0.05 (0–10.92) | 0.12 ± 0.37 0.04 (0–3.94) | 0.053 |
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variable | B | S.E. | p | Exp(B)/ Odds Rate | Confidence Intervals 95 C.I. for EXP(B) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alt | Üst | R2 | ||||||
| CTS Positivity | Calcium | 0.70 | 0.18 | 0.000 ** | 2.00 | 1.40 | 2.88 | 4.5 |
| CTS Positivity | Magnesium | −1.09 | 0.59 | 0.064 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 1.06 | 2.1 |
| CTS Positivity | Lymphocyte | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.022 * | 1.32 | 1.04 | 1.67 | 1.4 |
| CTS Positivity | Eosinophil | 0.91 | 0.58 | 0.115 | 2.48 | 0.80 | 7.67 | 0.7 |
| CTS Positivity | RBC | 0.51 | 0.16 | 0.002 ** | 1.67 | 1.21 | 2.29 | 2.6 |
| CTS Positivity | HGB | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.000 ** | 1.24 | 1.12 | 1.38 | 4.5 |
| CTS Positivity | HCT | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.000 ** | 1.08 | 1.04 | 1.12 | 4.4 |
| CTS Positivity | RDWCV | −0.16 | 0.05 | 0.001 ** | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.94 | 3.2 |
| CTS Positivity | CompositePlt–NötLenfİndeksi | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.022 * | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.6 |
| CTS Positivity | NLR | −0.19 | 0.06 | 0.003 ** | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.94 | 3.2 |
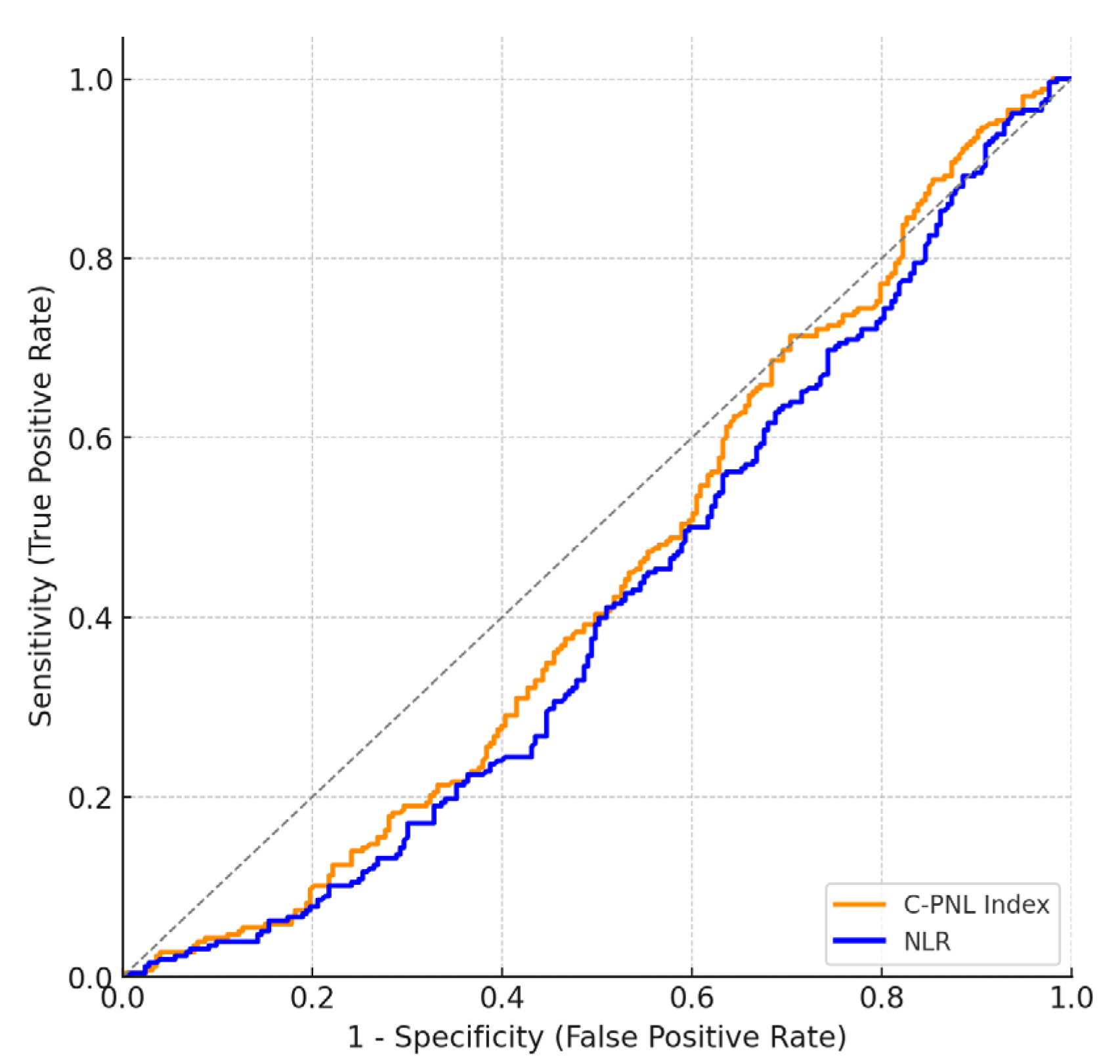
| Test Variables | AUC | Std. Error | p | Cutoff Value | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Confidence Interval (95) Lowest Highest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite PLT–Neut Lymph Index | 0.56 | 0.03 | 0.025 * | 425.8 | 60 | 50 | 0.51 | 0.61 |
| NLR | 0.59 | 0.03 | 0.001 ** | 1.69 | 62 | 50 | 0.54 | 0.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aslan, S.; Dikbaş, H.A.; Muhtaroğlu, A.; Kuloğlu, E.; Aydın, G.; Dülger, A.C. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome at the Intersection of Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology, and Neurology: A Thorough Examination. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14197022
Aslan S, Dikbaş HA, Muhtaroğlu A, Kuloğlu E, Aydın G, Dülger AC. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome at the Intersection of Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology, and Neurology: A Thorough Examination. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):7022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14197022
Chicago/Turabian StyleAslan, Sefer, Hüsniye Aylin Dikbaş, Ali Muhtaroğlu, Ersin Kuloğlu, Gökhan Aydın, and Ahmet Cumhur Dülger. 2025. "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome at the Intersection of Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology, and Neurology: A Thorough Examination" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 7022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14197022
APA StyleAslan, S., Dikbaş, H. A., Muhtaroğlu, A., Kuloğlu, E., Aydın, G., & Dülger, A. C. (2025). Carpal Tunnel Syndrome at the Intersection of Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology, and Neurology: A Thorough Examination. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 7022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14197022






