Predictive Value of C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio (CAR) for Malnutrition and Sarcopenia in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Statistical Analysis
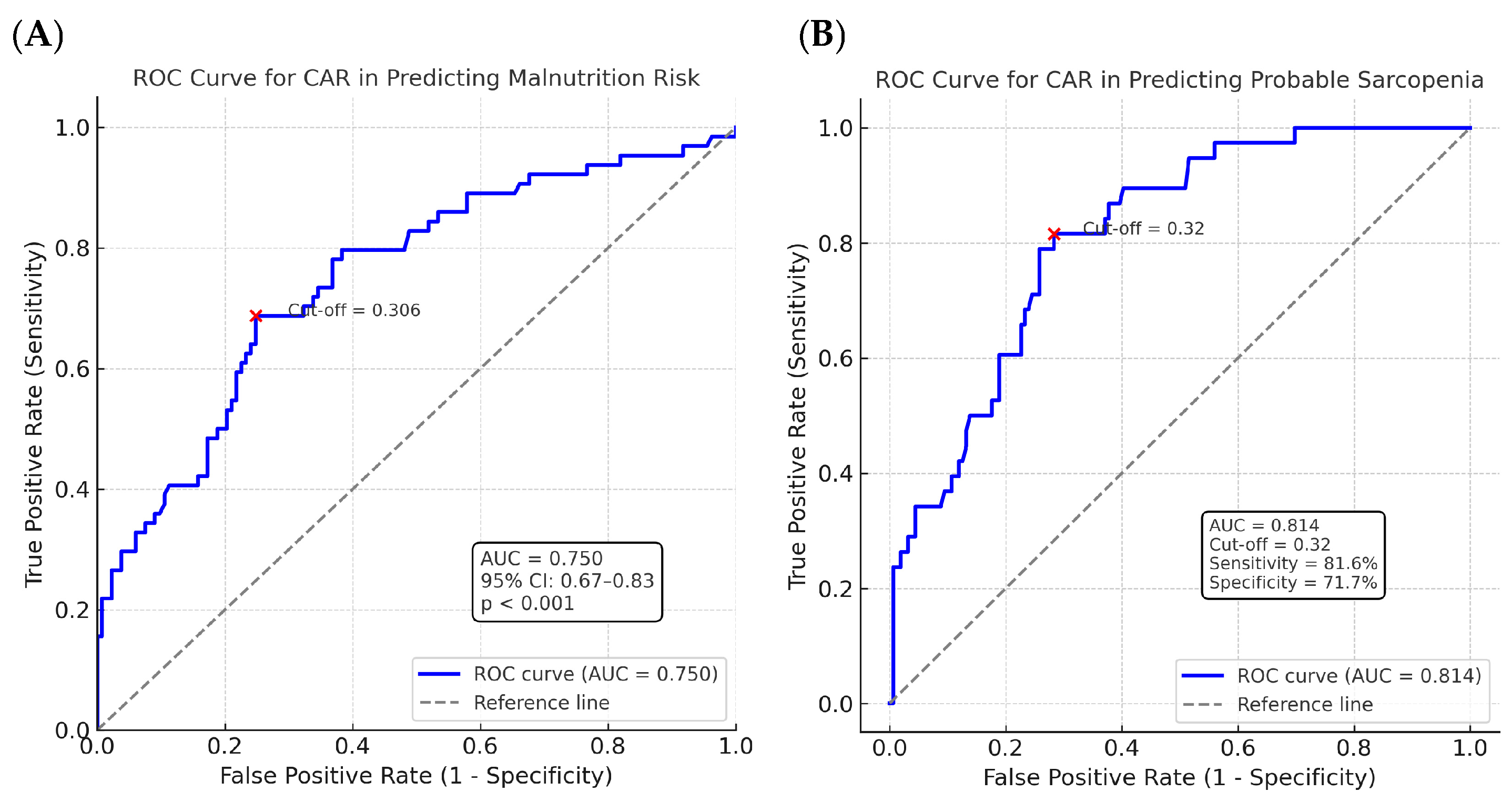
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Shi, H.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Shi, C.; Wang, Y.; Xia, C.; Xie, W. Projections of the Stroke Burden at the Global, Regional, and National Levels up to 2050 Based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e036142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.O.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P.; Grupper, M.F.; Rautalin, I. World Stroke Organization: Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2025. Int. J. Stroke 2025, 20, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosselman, M.J.; Kruitwagen, C.L.J.J.; Schuurmans, M.J.; Hafsteinsdóttir, T.B. Malnutrition and risk of malnutrition in patients with stroke: Prevalence during hospital stay. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2013, 45, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crary, M.A.; Carnaby-Mann, G.D.; Miller, L.; Antonios, N.; Silliman, S. Dysphagia and Nutritional Status at the Time of Hospital Admission for Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2006, 15, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crary, M.A.; Humphrey, J.L.; Carnaby-Mann, G.; Sambandam, R.; Miller, L.; Silliman, S. Dysphagia, nutrition, and hydration in ischemic stroke patients at admission and discharge from acute care. Dysphagia 2013, 28, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.P.; Wong, A.A.; Schluter, P.J.; Henderson, R.D.; O’Sullivan, J.D.; Read, S.J. Impact of premorbid undernutrition on outcome in stroke patients. Stroke 2004, 35, 1930–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, M.F.; González, J.; Frontera, W.R. Stroke and sarcopenia. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2020, 8, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbouh, T.; Torbey, M.T. Malnutrition in Stroke Patients: Risk Factors, Assessment, and Management. Neurocrit. Care 2018, 29, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Cho, W.S.; Park, C.B.; Kim, B.G. Effect of Sarcopenia on Functional Recovery in Acute Stroke Patients Admitted for Standard Rehabilitation Program. Medicina 2024, 60, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertsen, K.L.; Finsen, B.; Clausen, B.H. Post-stroke inflammation—Target or tool for therapy? Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeters, P.B.; Wolfe, R.R.; Shenkin, A. Hypoalbuminemia: Pathogenesis and Clinical Significance. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 43, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuemmler, R.J.; Pana, T.A.; Carter, B.; Mahmood, R.; Bettencourt-Silva, J.H.; Metcalf, A.K.; Mamas, M.A.; Potter, J.F.; Myint, P.K. Serum Albumin and Post-Stroke Outcomes: Analysis of UK Regional Registry Data, Systematic Review, and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Hertog, H.M.; Van Rossum, J.A.; Van Der Worp, H.B.; Van Gemert, H.M.A.; De Jonge, R.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Dippel, D.W.; PAIS investigators. C-reactive protein in the very early phase of acute ischemic stroke: Association with poor outcome and death. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 2003–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, J.; Guo, S.; Huang, T.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Chu, Z.; Li, Z. CRP as a potential predictor of outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Biomed. Rep. 2023, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, R.B.; Oktafia, P.; Saputra, P.B.T.; Purwati, D.D.; Saputra, M.E.; Maghfirah, I.; Faizah, N.N.; Oktaviono, Y.H.; Alkaff, F.F. The roles of C-reactive protein-albumin ratio as a novel prognostic biomarker in heart failure patients: A systematic review. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Chung, K.S.; Song, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, E.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Kang, Y.A.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Chang, J.; et al. The C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio as a Predictor of Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-K.; Yu, Y.-L.; Lin, Y.-C.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Chern, Y.-J.; Chiang, J.-M.; You, J.-F. Prognostic value of the C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in colorectal cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Tang, J.N.; Cheng, M.D.; Jiang, L.Z.; Guo, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, Z.L.; Song, F.H.; Wang, K.; Fan, L.; et al. C-reactive protein-To-serum albumin ratio as a novel predictor of long-Term outcomes in coronary artery disease patients who have undergone percutaneous coronary intervention: Analysis of a real-world retrospective cohort study. Coron. Artery Dis. 2021, 32, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonet, E.; Campana, R.; Caglioni, S.; Gibiino, F.; Fiorio, A.; Chiaranda, G.; Zagnoni, S.; Casella, G.; Campo, G. Tools for the Assessment of the Malnutrition Status and Possible Interventions in Elderly with Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Yu, H.; Ma, Y.; Kang, L.; Fu, L.; Jia, L.; Chen, X.; Yu, X.; Hou, L.; Wang, L.; et al. The increased risk of sarcopenia in patients with cardiovascular risk factors in Suburb-Dwelling older Chinese using the AWGS definition. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrup, J.; Allison, S.P.; Elia, M.; Vellas, B.; Plauth, M.; Educational and Clinical Practice Committee, European Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ESPEN). ESPEN guidelines for nutrition screening 2002. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstrom, T.K.; Miller, D.K.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Morley, J.E. SARC-F: A symptom score to predict persons with sarcopenia at risk for poor functional outcomes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, R.; Bretón, I.; Cereda, E.; Desport, J.C.; Dziewas, R.; Genton, L.; Gomes, F.; Jésus, P.; Leischker, A.; Muscaritoli, M.; et al. ESPEN guideline clinical nutrition in neurology. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 354–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.; Emery, P.W.; Weekes, C.E. Risk of Malnutrition Is an Independent Predictor of Mortality, Length of Hospital Stay, and Hospitalization Costs in Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, N.C.; Salter, K.L.; Robertson, J.; Teasell, R.W.; Woodbury, M.G. Progress Review Which Reported Estimate of the Prevalence of Malnutrition After Stroke Is Valid? Stroke 2009, 40, e66–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoban, E.; Soysal, A. The Profile of a Neurology Clinic and Malnutrition Awareness. Turk. J. Neurol. 2021, 27, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shi, K.; Wang, Y.; Shi, F.D. Neurovascular Inflammation and Complications of Thrombolysis Therapy in Stroke. Stroke 2023, 54, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluk, H.; Woźniak, A.; Tafelska-Kaczmarek, A.; Kosinska, A.; Pawluk, M.; Sergot, K.; Grochowalska, R.; Kołodziejska, R. The Role of IL-6 in Ischemic Stroke. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, M.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Hou, B. The role of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein serum levels in the prognosis for patients with stroke: A meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1199814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wan, J.; Li, F.; Yang, X.; Shen, B.; Li, N.; Didi, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y. Prognostic value of the C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in patients with stroke: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhassan, M.; Cederholm, T.; Donini, L.M.; Poggiogalle, E.; Schwab, U.; Nielsen, R.L.; Andersen, A.L.; Małgorzewicz, S.; Volkert, D.; Wirth, R. Severity of Inflammation Is Associated with Food Intake in Hospitalized Geriatric Patients-A Merged Data Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chon, J.; Soh, Y.; Shim, G.Y. Stroke-Related Sarcopenia: Pathophysiology and Diagnostic Tools. Brain Neurorehabil. 2024, 17, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Liyis, B.G.; Ardhaputra, G.Y.B.; Liyis, S.; Wihandani, D.M.; Siahaan, Y.M.T.; Pinatih, K.J.P. High C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio Predicts Mortality and Hemorrhage in Stroke Patients Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2024, 188, 211–219.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Xia, L.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, C.; Fu, F.; Cao, Y.; Han, Z. High ratio of C-reactive protein to albumin is associated with hemorrhagic transformation and poor functional outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients after thrombolysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1109144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Ueshima, J.; Kawase, F.; Kobayashi, H.; Nagano, A.; Murotani, K.; Saino, Y.; Maeda, K. Trajectories of the Prevalence of Sarcopenia in the Pre- and Post-Stroke Periods: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, G.; Trevisan, C.; Carraro, S.; Solmi, M.; Luchini, C.; Stubbs, B.; Manzato, E.; Sergi, G.; Veronese, N. Inflammation and sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas 2017, 96, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.-C.; Su, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Wu, P.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, T.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Yang, S.-H. Ratio of C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Predicts Muscle Mass in Adult Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, T.; Ulaş, S.B.; Nalbant, A.; Yıldırım, I.; İşSever, K.; Karacaer, C.; Bilgin, C.; Vatan, A.; Acar, T.; Acar, B.A.; et al. C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as a novel predictor for nutritional status of geriatric patients. Brain Behav. 2024, 14, e70017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldemir, R.; Öztürk, A.; Eraslan Doganay, G.; Cirik, M.O.; Alagoz, A. Evaluation of Nutritional Status in Hospitalized Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients and Can C-reactive Protein-to-Albumin Ratio Be Used in the Nutritional Risk Assessment in These Patients. Cureus 2022, 14, e21833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocellin, M.C.; Pastore E Silva, J.D.A.; Camargo, C.D.Q.; Fabre, M.E.D.S.; Gevaerd, S.; Naliwaiko, K.; Moreno, Y.M.; Nunes, E.A.; Trindade, E.B. Fish oil decreases C-reactive protein/albumin ratio improving nutritional prognosis and plasma fatty acid profile in colorectal cancer patients. Lipids 2013, 48, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tur, K.; Güçlü, A. Independent Association Between Malnutrition Inflammation Score and C Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 9325–9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Not at Risk of Malnutrition (n = 133) | At Risk of Malnutrition (n = 64) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 66.63 ± 12.67 | 74.33 ± 11.04 | <0.001 |
| Sex (M/F) | 74/59 | 37/27 | 0.893 |
| NIHSS (mean ± SD) | 3.97 ± 3.35 | 6.00 ± 4.27 | 0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2, mean ± SD) | 29.21 ± 5.09 | 26.33 ± 3.99 | <0.001 |
| DM, n (%) | 80 (60.2%) | 33 (51.6%) | 0.323 |
| HT, n (%) | 108 (81.2%) | 49 (76.6%) | 0.569 |
| CAD, n (%) | 60 (45.1%) | 33 (51.6%) | 0.485 |
| HL, n (%) | 105 (78.9%) | 47 (73.4%) | 0.495 |
| AF, n (%) | 32 (24.1%) | 30 (46.9%) | 0.002 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 33 (24.8%) | 10 (15.6%) | 0.201 |
| CAR (mean ± SD) | 0.364 ± 0.552 | 1.486 ± 1.935 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 1.06 | 1.03–1.09 | <0.001 | 1.05 | 1.02–1.09 | 0.003 |
| Sex (Male) | 0.91 | 0.50–1.67 | 0.773 | 1.55 | 0.57–4.25 | 0.390 |
| NIHSS | 1.15 | 1.06–1.25 | <0.001 | 1.11 | 1.01–1.23 | 0.026 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 0.70 | 0.38–1.28 | 0.254 | – | – | – |
| Hypertension | 0.75 | 0.37–1.56 | 0.449 | – | – | – |
| Coronary Artery Disease | 1.29 | 0.71–2.35 | 0.396 | – | – | – |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.73 | 0.36–1.48 | 0.389 | – | – | – |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 2.78 | 1.48–5.24 | 0.001 | 1.49 | 0.68–3.24 | 0.314 |
| Smoking | 0.56 | 0.25–1.22 | 0.147 | – | – | – |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.86 | 0.80–0.94 | <0.001 | 0.89 | 0.82–0.97 | 0.010 |
| CAR (CRP/Albumin ratio) | 2.47 | 1.64–3.70 | <0.001 | 2.13 | 1.39–3.26 | <0.001 |
| Variable | No Probable Sarcopenia (n = 159) | Probable Sarcopenia (n = 38) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 66.90 ± 12.35 | 78.47 ± 9.33 | <0.001 |
| Sex (Male/Female), n | 91/68 | 20/18 | 0.607 |
| NIHSS at admission (mean ± SD) | 4.28 ± 3.63 | 6.08 ± 4.10 | 0.007 |
| Diabetes Mellitus, n/total | 94/159 | 19/38 | 0.362 |
| Hypertension, n/total | 124/159 | 33/38 | 0.268 |
| Coronary Artery Disease, n/total | 72/159 | 21/38 | 0.284 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n/total | 125/159 | 27/38 | 0.389 |
| Atrial Fibrillation, n/total | 45/159 | 17/38 | 0.055 |
| Smoking, n/total | 40/159 | 3/38 | 0.027 |
| BMI (kg/m2, mean ± SD) | 28.64 ± 4.93 | 26.72 ± 4.75 | 0.004 |
| CAR (CRP/Albumin ratio, mean ± SD) | 0.47 ± 0.89 | 1.81 ± 2.01 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 1.13 | 1.07–1.18 | <0.001 | 1.12 | 1.05–1.18 | <0.001 |
| Sex (Male) | 0.83 | 0.41–1.69 | 0.608 | 1.68 | 0.62–4.53 | 0.308 |
| NIHSS | 1.12 | 1.03–1.23 | 0.010 | 1.16 | 1.04–1.31 | 0.011 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 0.69 | 0.34–1.41 | 0.309 | - | - | - |
| Hypertension | 1.86 | 0.68–5.13 | 0.229 | - | - | - |
| Coronary Artery Disease | 1.49 | 0.73–3.04 | 0.270 | - | - | - |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.67 | 0.30–1.48 | 0.320 | - | - | - |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 2.05 | 0.99–4.24 | 0.053 | - | - | - |
| Smoking | 0.25 | 0.07–0.87 | 0.030 | 0.60 | 0.11–3.33 | 0.563 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.92 | 0.85–0.99 | 0.035 | 0.98 | 0.89–1.08 | 0.676 |
| CAR (CRP/Albumin ratio) | 1.96 | 1.45–2.64 | <0.001 | 1.76 | 1.22–2.53 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dogan, H.; Simsek, S.; Bayram, A.H.; Topal, A.; Pamuk, M.B.; Ozmuk, O.; Ongun, N.; Akpinar, C.K. Predictive Value of C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio (CAR) for Malnutrition and Sarcopenia in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6804. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196804
Dogan H, Simsek S, Bayram AH, Topal A, Pamuk MB, Ozmuk O, Ongun N, Akpinar CK. Predictive Value of C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio (CAR) for Malnutrition and Sarcopenia in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6804. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196804
Chicago/Turabian StyleDogan, Hasan, Sugra Simsek, Ahmet Hakan Bayram, Aydan Topal, Mehlika Berra Pamuk, Ozkan Ozmuk, Nedim Ongun, and Cetin Kursad Akpinar. 2025. "Predictive Value of C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio (CAR) for Malnutrition and Sarcopenia in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6804. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196804
APA StyleDogan, H., Simsek, S., Bayram, A. H., Topal, A., Pamuk, M. B., Ozmuk, O., Ongun, N., & Akpinar, C. K. (2025). Predictive Value of C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio (CAR) for Malnutrition and Sarcopenia in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6804. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196804





