Lupus Anticoagulant Testing for Diagnosis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Perspective Informed by Local Practice
Abstract
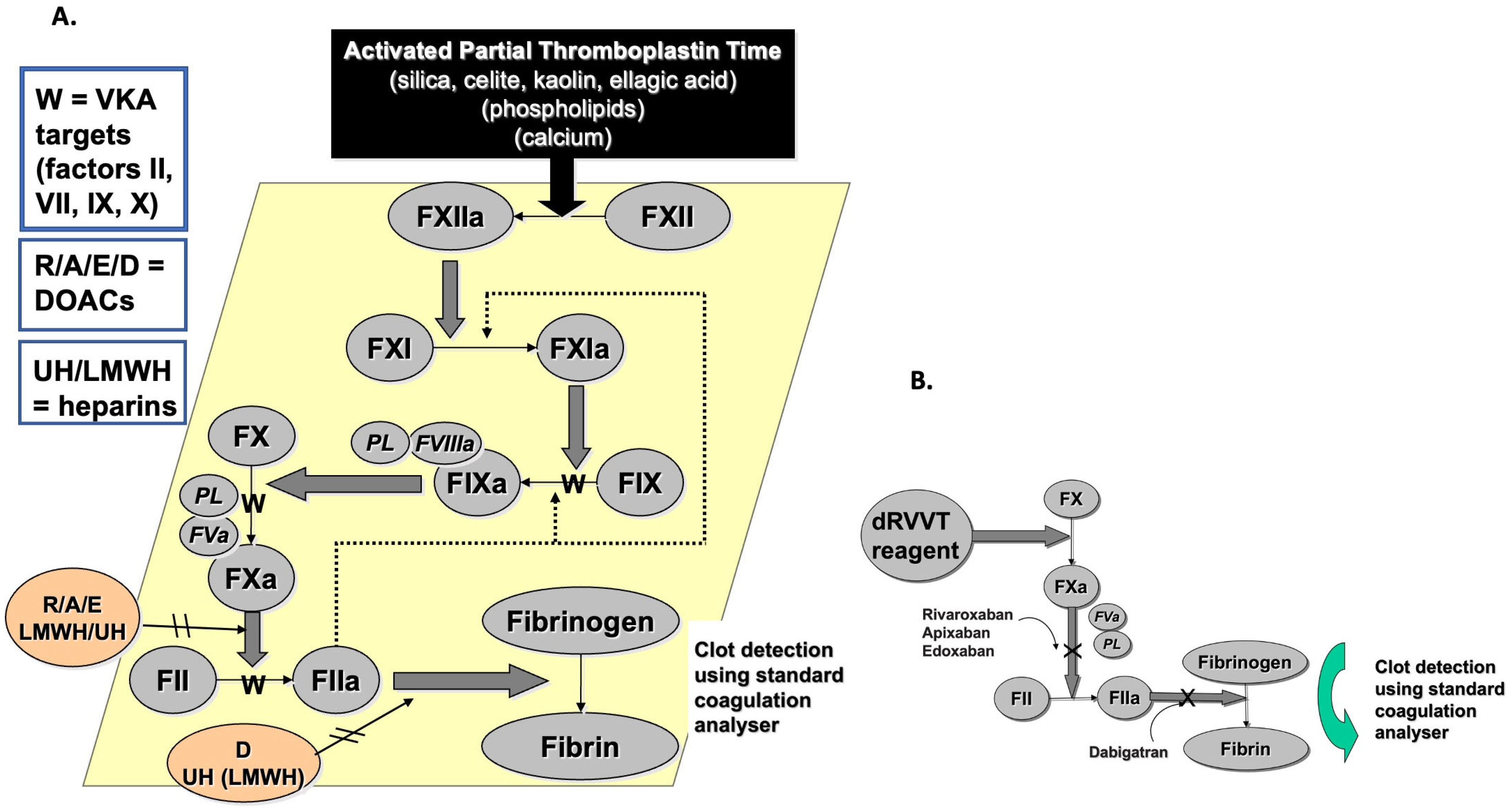
1. Introduction
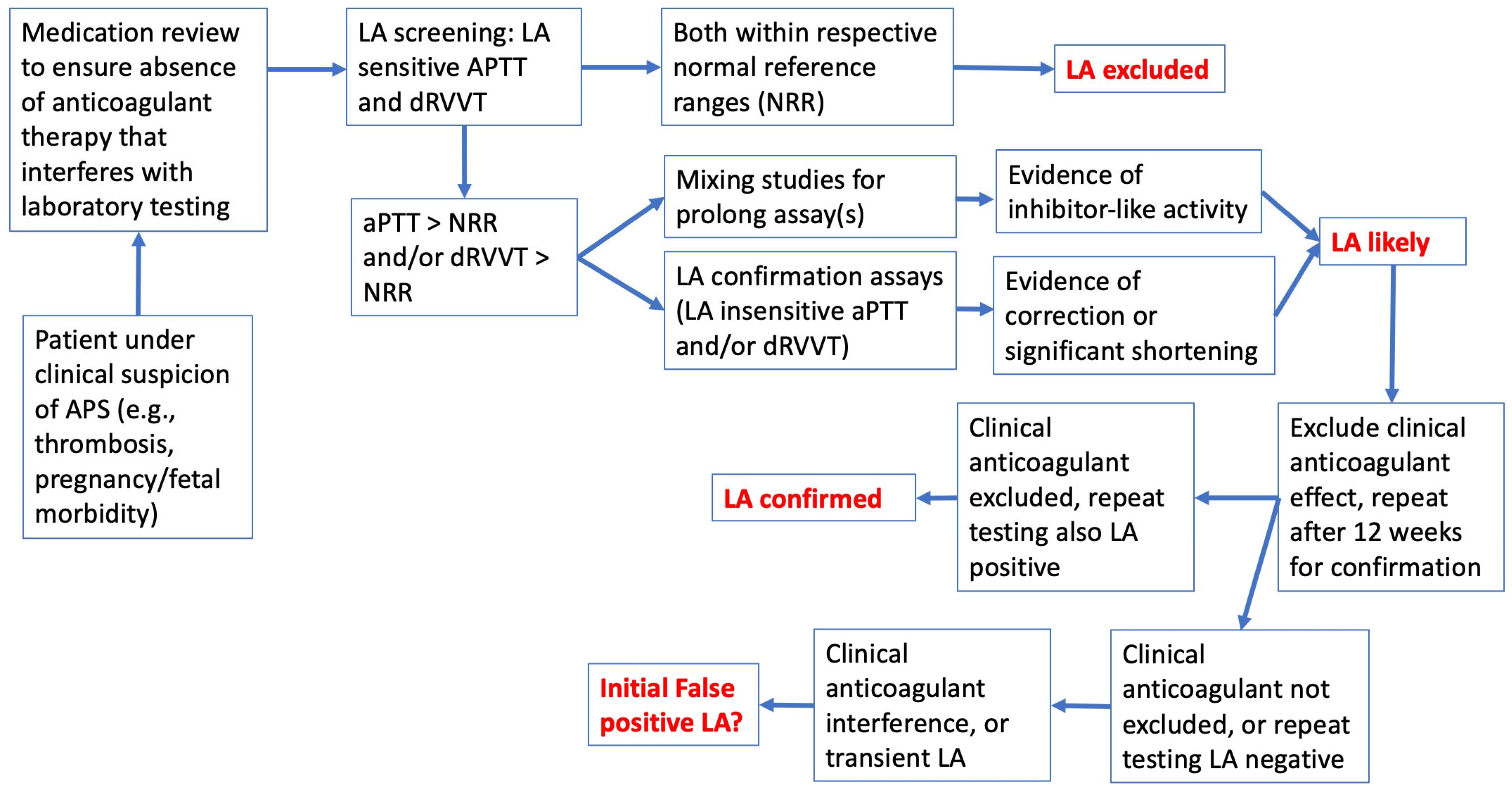
2. The Basic LA Diagnosis/Exclusion Process
3. True Positive LA vs. False-Positive LA vs. Anticoagulant Interference
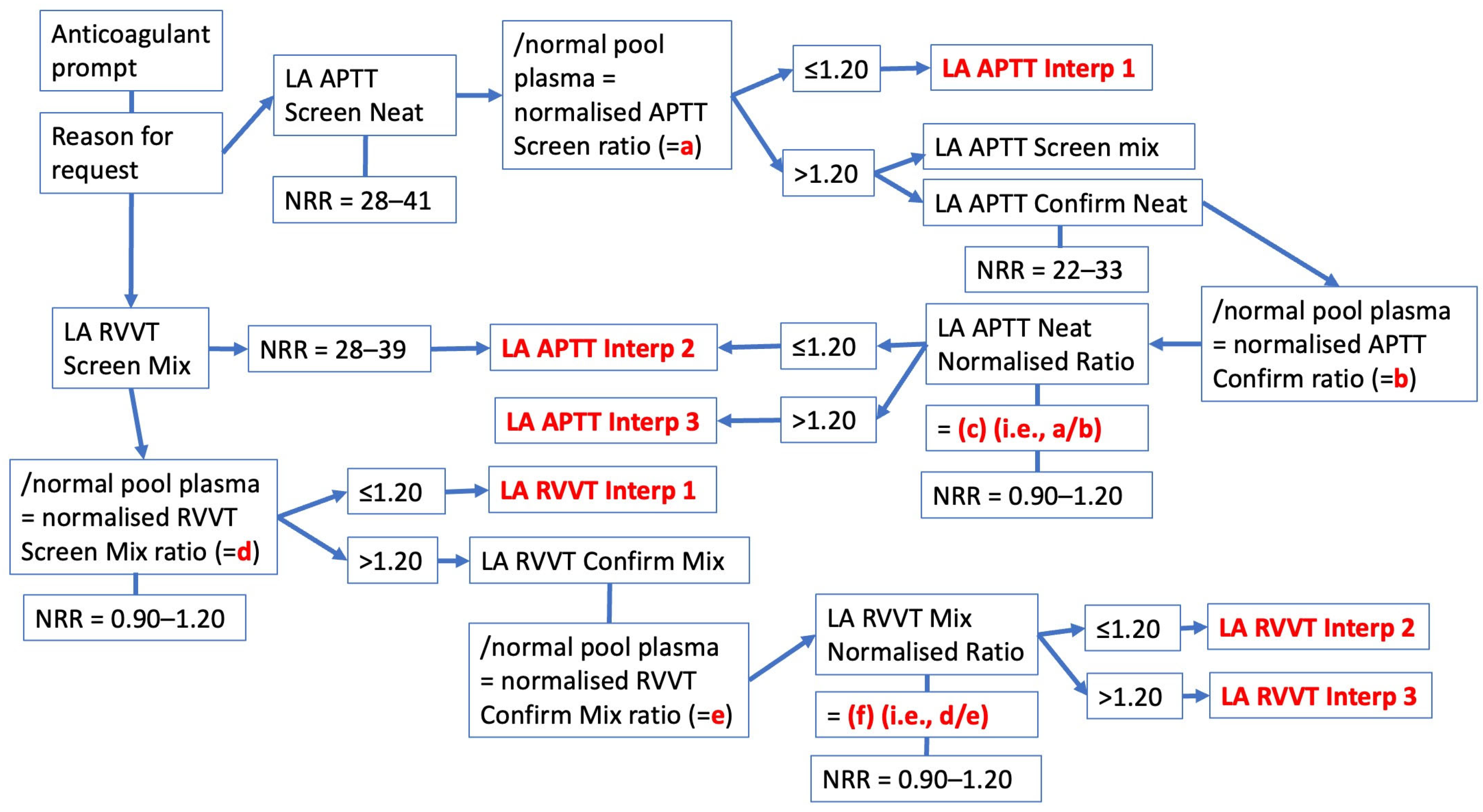
4. Interpretation and Reporting of Test Results—The Westmead Approach
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbhaiya, M.; Zuily, S.; Naden, R.; Hendry, A.; Manneville, F.; Amigo, M.C.; Amoura, Z.; Andrade, D.; Andreoli, L.; Artim-Esen, B.; et al. 2023 ACR/EULAR antiphospholipid syndrome classification criteria. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.; Derksen, R.H.; DEGroot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.A.; Gharavi, A.E.; Koike, T.; Lockshin, M.D.; Branch, D.W.; Piette, J.C.; Brey, R.; Derksen, R.; Harris, E.N.; Hughes, G.R.; et al. International consensus statement on preliminary classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome: Report of an international workshop. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 1309–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Pasalic, L.; Lippi, G. Classification Criteria for the Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Not the Same as Diagnostic Criteria for Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2024, 50, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devreese, K.M.J.; Bertolaccini, M.L.; Branch, D.W.; de Laat, B.; Erkan, D.; Favaloro, E.J.; Pengo, V.; Ortel, T.L.; Wahl, D.; Cohen, H. An update on laboratory detection and interpretation of antiphospholipid antibodies for diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome: Guidance from the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis Scientific and Standardization Committee (ISTH-SSC) Subcommittee on Lupus Anticoagulant/Antiphospholipid Antibodies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2025, 23, 731–744. [Google Scholar]
- Devreese, K.M.J. 2023 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology classification criteria for antiphospholipid syndrome: Good for patients or good for papers? Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2025, 9, 102735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devreese, K.M.J.; de Groot, P.G.; de Laat, B.; Erkan, D.; Favaloro, E.J.; Mackie, I.; Martinuzzo, M.; Ortel, T.L.; Pengo, V.; Rand, J.H.; et al. Guidance from the Scientific and Standardization Committee for lupus anticoagulant/antiphospholipid antibodies of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis: Update of the guidelines for lupus anticoagulant detection and interpretation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2828–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, L.; Wang, Z.; Qian, J.; Bai, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; et al. Impact of antiphospholipid antibodies on heart valve involvements in systemic lupus erythematosus: Based on CSTAR cohort. Lupus Sci. Med. 2025, 12, e001674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, E.; Düsing, C.; Keymel, S.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Bracaglia, C.; Canuet, M.; Cavazzana, I.; Chehab, G.; Codullo, V.; Fischer, R.; et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus: Identification of risk factors and haemodynamics characteristics in a multicentre retrospective cohort. Lupus Sci. Med. 2025, 12, e001471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; You, Y.; Cai, S.; Ye, C.; Dong, L. Effects of telitacicept in SLE patients with antiphospholipid antibody positivity: A retrospective self-controlled case series. Clin. Rheumatol. 2025, 44, 2287–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramot, B.; Singer, K. An unusual circulating anticoagulant in systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Haematol. 1956, 16, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, S. A serum anticoagulant factor in systemic lupus erythematosus. AMA Arch. Derm. 1956, 74, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, V.; Tripodi, A.; Reber, G.; Rand, J.H.; Ortel, T.L.; Galli, M.; De Groot, P.G.; Subcommittee on Lupus Anticoagulant/Antiphospholipid Antibody of the Scientific and Standardisation Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Update of the guidelines for lupus anticoagulant detection. Subcommittee on Lupus Anticoagulant/Antiphospholipid Antibody of the Scientific and Standardisation Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J.T.; Triplett, D.A.; Alving, B.; Scharrer, I. Criteria for the diagnosis of lupus anticoagulants: An update. On behalf of the Subcommittee on Lupus Anticoagulant/Antiphospholipid Antibody of the Scientific and Standardisation Committee of the ISTH. Thromb. Haemost. 1995, 74, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodi, A. Additional laboratory tests to improve on the diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 3117–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradacova, P.; Slavik, L.; Ulehlova, J.; Skoumalova, A.; Ullrychova, J.; Prochazkova, J.; Hlusi, A.; Manukyan, G.; Kriegova, E. Current Promising Biomarkers and Methods in the Diagnostics of Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Review. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W.; Platton, S.; Yartey, N.; Foxton, E.; White, D.; MacDonald, S.G. Taipan snake venom time has high sensitivity for lupus anticoagulants in non-anticoagulated, triple positive antiphospholipid syndrome patients. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2024, 46, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W. Lupus Anticoagulant Testing: Taipan Snake Venom Time with Ecarin Time as Confirmatory Test. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2663, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Dean, E.; Arunachalam, S. Variable Performance of Lupus Anticoagulant Testing: The Australasian/Asia-Pacific Experience. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2024, 50, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodi, A. Diagnostic Challenges on the Laboratory Detection of Lupus Anticoagulant. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devreese, K.M.J. Testing for antiphospholipid antibodies: Advances and best practices. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2020, 42 (Suppl. S1), 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Sun, Q.; Liu, M.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, D. Clinical Features of Antiphospholipid Syndrome with Intracardiac Mass. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murvai, V.R.; Galiș, R.; Panaitescu, A.; Radu, C.M.; Ghitea, T.C.; Trif, P.; Onița-Avram, M.; Vesa, A.A.; Huniadi, A. Antiphospholipid syndrome in pregnancy: A comprehensive literature review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devreese, K.M.J. Thrombosis in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Current Perspectives and Challenges in Laboratory Testing for Antiphospholipid Antibodies. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, V.; Sarti, L.; Antonucci, E.; Bison, E.; Pontara, E.; Cattini, M.G.; Denas, G.; Poli, D.; Palareti, G. Patients with antiphospholipid syndrome and a first venous or arterial thrombotic event: Clinical characteristics, antibody profiles and estimate of the risk of recurrence. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2024, 62, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch, D.W.; Lim, M.Y. How I diagnose and treat antiphospholipid syndrome in pregnancy. Blood 2024, 143, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, M.; Spadafora, L.; Andaloro, S.; Piscitelli, A.; Fornaci, G.; Intonti, C.; Fratta, A.E.; Hsu, C.E.; Kaziròd-Wolski, K.; Metsovitis, T.; et al. Management of Cardiovascular Complications in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Narrative Review with a Focus on Older Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Bailly, J.; Opie, J. Key Issues at the Forefront of Diagnosis and Testing for Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2024, 30, 10760296241306751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Pasalic, L. Lupus anticoagulant testing during anticoagulation, including direct oral anticoagulants. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 6, e12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodi, A.; Scalambrino, E.; Clerici, M.; Peyvandi, F. Laboratory Diagnosis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome in Anticoagulated Patients. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriez, R.; Dogné, J.M.; Gosselin, R.; Laloy, J.; Mullier, F.; Douxfils, J. Comprehensive review of the impact of direct oral anticoagulants on thrombophilia diagnostic tests: Practical recommendations for the laboratory. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021, 43, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Mohammed, S.; Curnow, J.; Pasalic, L. Laboratory testing for lupus anticoagulant (LA) in patients taking direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs): Potential for false positives and false negatives. Pathology 2019, 51, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Henry, B.M.; Lippi, G. Is Lupus Anticoagulant a Significant Feature of COVID-19? A Critical Appraisal of the Literature. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2022, 48, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kesel, P.M.; Devreese, K.M.J. Direct oral anticoagulant adsorption: Impact on lupus anticoagulant testing-Review of the literature and evaluation on spiked and patient samples. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Kershaw, G.; Mohammed, S.; Lippi, G. How to Optimize Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT) Testing: Solutions to Establishing and Verifying Normal Reference Intervals and Assessing APTT Reagents for Sensitivity to Heparin, Lupus Anticoagulant, and Clotting Factors. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 45, 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tripodi, A.; Cohen, H.; Devreese, K.M.J. Lupus anticoagulant detection in anticoagulated patients. Guidance from the Scientific and Standardization Committee for lupus anticoagulant/antiphospholipid antibodies of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Pasalic, L.; Selby, R. Testing for the lupus anticoagulant: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 8, 102385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Pasalic, L.; Lippi, G. Oral Anticoagulation Therapy: An Update on Usage and Costs in the Endemic COVID-19 Era. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Gilmore, G.; Arunachalam, S.; Mohammed, S.; Baker, R. Neutralising rivaroxaban induced interference in laboratory testing for lupus anticoagulant (LA): A comparative study using DOAC Stop and andexanet alfa. Thromb. Res. 2019, 180, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exner, T.; Dangol, M.; Favaloro, E.J. Simplified method for removing DOAC interference in mechanical coagulation test systems—A proof of concept. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Mohammed, S.; Vong, R.; Chapman, K.; Swanepoel, P.; Kershaw, G.; Cai, N.; Just, S.; Connelly, L.; Brighton, T.; et al. A multi-laboratory assessment of lupus anticoagulant assays performed on the ACL TOP 50 family for harmonized testing in a large laboratory network. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2022, 44, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchillage, D.R.J.; Laffan, M. What is the appropriate anticoagulation strategy for thrombotic antiphospholipid syndrome? Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaloro, E.J. Evolution of hemostasis testing: A personal reflection covering over 40 years of history. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2024, 50, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, G.W. Alternative assays to dRVVT and aPTT for lupus anticoagulant detection. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletto, M.; Ferrannini, G.; Galli, E.; Grosso, A.; Camerlo, S.; Bulai, F.; Marchisio, A.; Pomero, F. Direct oral anticoagulants versus vitamin-K antagonists in patients with single or double-positive antiphospholipid syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2025, 135, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchillage, D.J.; Laffan, M. Unresolved issues in the diagnosis and management of thrombotic antiphospholipid syndrome. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2025, 9, 102724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Laboratory Testing for the Lupus Anticoagulant; approved guideline; CLSI document H60-A; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Arachchillage, D.J.; Platton, S.; Hickey, K.; Chu, J.; Pickering, M.; Sommerville, P.; MacCallum, P.; Breen, K.; BSH Committee. Guidelines on the investigation and management of antiphospholipid syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 205, 855–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, T.; Santoro, R.C.; Banov, L.; Ierardi, A.; Leotta, M.; Strangio, A.; Svahn, J.; Molinari, A.C. Prolongated Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) in Pediatric Patients before Surgery-Crying Wolf: Lupus (Anticoagulant) Does Not Always Threaten Children. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W. Testing for Lupus Anticoagulant. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2022, 48, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Rico, A. Update on the Laboratory Diagnosis of Lupus Anticoagulant: Current Challenges and Clinical Involvement. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinari, A.C.; Martini, T.; Banov, L.; Ierardi, A.; Leotta, M.; Strangio, A.; Santoro, R.C. Lupus Anticoagulant Detection under the Magnifying Glass. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandevelde, A.; Devreese, K.M.J. Laboratory Diagnosis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Insights and Hindrances. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohidi-Esfahani, I.; Mittal, P.; Isenberg, D.; Cohen, H.; Efthymiou, M. Platelets and Thrombotic Antiphospholipid Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Mohammed, S.; Vong, R.; Pasalic, L. Antiphospholipid Antibody Testing for Anti-cardiolipin and Anti-β2 Glycoprotein I Antibodies Using Chemiluminescence-Based Panels. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2663, 297–314. [Google Scholar]
- Sciascia, S.; Radin, M.; Ramirez, C.; Seaman, A.; Bentow, C.; Casas, S.; Cecchi, I.; Rubini, E.; Foddai, S.G.; Baldovino, S.; et al. Evaluation of novel assays for the detection of autoantibodies in antiphospholipid syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredenburgh, J.C.; Weitz, J.I. New anticoagulants: Moving beyond the direct oral anticoagulants. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Anticoagulant | APTT | dRVVT | SCT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unfractionated heparin | ↑–↑↑↑ (concentration-dependent; most reagents do not contain neutralizer) | ⟷ (up to ~1 U/mL heparin neutralized if reagent contains heparin neutralizer) ↑ (if exceeds neutralizer capacity) | ⟷ (up to ~1 U/mL heparin neutralized if reagent contains heparin neutralizer) ↑ (if exceeds neutralizer capacity) |
| LMWH | ↑ | ⟷ (if contains heparin neutralizer) | ⟷ (if contains heparin neutralizer) ↑ (if no neutralizer) |
| VKAs | ↑ | ↑↑ | ↑ |
| dabigatran | ↑↑ | ↑↑↑ | ↑ |
| rivaroxaban | ↑ | ↑↑↑ | ↑↑ |
| edoxaban | ↑ | ↑↑ | ↑↑ |
| apixaban | ⟷–↑ (assay-dependent) | ↑ (but LA ratio may fall, since effect greater on confirm reagents) | ↑ |
| Individual Test Interp | Interpretive Comment |
|---|---|
| LA APTT Interp 1 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) not detected by APTT method |
| LA APTT Interp 2 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) test performed by APTT method, with result not detected. However, screening test suggests potential presence of other inhibitor type |
| LA APTT Interp 3 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) test performed by APTT method, with positive detected (LA APTT ratio > 1.2) |
| LA RVVT Interp 1 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) not detected by dRVVT method |
| LA RVVT Interp 2 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) test performed by dRVVT method, with result not detected. However, screening test suggests potential presence of other inhibitor type |
| LA RVVT Interp 3 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) test performed by dRVVT method, with positive detected (LA dRVVT ratio > 1.2) |
| LA APTT | LA dRVVT | Final LA Interpretive Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Interp 1 | Interp 1 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) not detected by APTT & dRVVT methods. |
| Interp 1 | Interp 2 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) not detected by APTT & dRVVT methods. However, dRVVT screening test suggests potential presence of other inhibitor type. If patient on anticoagulant therapy (vitamin K antagonist, heparin, or a direct oral anticoagulant [dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban]), please repeat testing when therapy ceased. Otherwise, please discuss with laboratory as further testing may be required. |
| Interp 1 | Interp 3 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) test detected by dRVVT method, but not APTT method. If patient on anticoagulant therapy (vitamin K antagonist, heparin, or a direct oral anticoagulant [dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban]), please repeat test when therapy ceased, as test result may not be reliable and may reflect a false-positive. Otherwise, suggest repeat testing after at least 12 weeks for confirmation. |
| Interp 2 | Interp 1 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) not detected by APTT & dRVVT methods. |
| Interp 2 | Interp 2 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) not detected by APTT & dRVVT methods. However, APTT and dRVVT screening tests suggest potential presence of other inhibitor type. If patient on anticoagulant therapy (vitamin K antagonist, heparin, or a direct oral anticoagulant [dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban]), please repeat testing when therapy ceased. Otherwise, please discuss with laboratory as further testing may be required. |
| Interp 2 | Interp 3 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) test detected by dRVVT method, but not APTT method. APTT screening test suggests potential presence of other inhibitor type. If patient on anticoagulant therapy (vitamin K antagonist, heparin, or a direct oral anticoagulant [dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban]), please repeat test when therapy ceased, as test result may not be reliable and may reflect a false-positive. Also assess test results with solid phase antiphospholipid antibody tests aCL and aβ2GPI to identify possible double or triple positivity. Otherwise, suggest repeat testing after at least 12 weeks for confirmation. |
| Interp 3 | Interp 1 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) test detected by APTT method, but not dRVVT method. If patient on anticoagulant therapy (vitamin K antagonist, heparin, or a direct oral anticoagulant [dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban]), please repeat test when therapy ceased, as test result may not be reliable and may reflect a false-positive. Also assess test results with solid phase antiphospholipid antibody tests aCL and aβ2GPI to identify possible double or triple positivity. Otherwise, suggest repeat testing after at least 12 weeks for confirmation. |
| Interp 3 | Interp 2 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) test detected by APTT method, but not dRVVT method. dRVVT screening test suggests potential presence of other inhibitor type. If patient on anticoagulant therapy (vitamin K antagonist, heparin, or a direct oral anticoagulant [dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban]), please repeat test when therapy ceased, as test result may not be reliable and may reflect a false-positive. Also assess test results with solid phase antiphospholipid antibody tests aCL and aβ2GPI to identify possible double or triple positivity. Otherwise, suggest repeat testing after at least 12 weeks for confirmation. |
| Interp 3 | Interp 3 | Lupus anticoagulant (lupus inhibitor) test detected by both APTT and dRVVT methods. If patient on anticoagulant therapy (vitamin K antagonist, heparin, or a direct oral anticoagulant [dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban]), please repeat test when therapy ceased, as test result may not be reliable and may reflect a false-positive. Also assess test results with solid phase antiphospholipid antibody tests aCL and aβ2GPI to identify possible double or triple positivity. Otherwise, suggest repeat testing after at least 12 weeks for confirmation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Favaloro, E.J.; Pasalic, L. Lupus Anticoagulant Testing for Diagnosis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Perspective Informed by Local Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4812. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144812
Favaloro EJ, Pasalic L. Lupus Anticoagulant Testing for Diagnosis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Perspective Informed by Local Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(14):4812. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144812
Chicago/Turabian StyleFavaloro, Emmanuel J., and Leonardo Pasalic. 2025. "Lupus Anticoagulant Testing for Diagnosis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Perspective Informed by Local Practice" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 14: 4812. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144812
APA StyleFavaloro, E. J., & Pasalic, L. (2025). Lupus Anticoagulant Testing for Diagnosis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Perspective Informed by Local Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(14), 4812. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144812







